#socio-economic context
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How does one assess the effectiveness of truth and reconciliation processes in addressing war crimes?
Assessing the Effectiveness of Truth and Reconciliation Processes in Addressing War Crimes Introduction Truth and reconciliation processes have emerged as important mechanisms for addressing war crimes and human rights abuses in societies recovering from conflict. These processes aim to uncover the truth about past atrocities, provide justice for victims, promote healing and reconciliation, and…

View On WordPress
#Accountability#accountability measures#challenges#contextual factors#cultural context#diverse perspectives#effectiveness assessment#healing#impact on victims#inclusivity#institutional reforms#justice#Limitations#long-term impact#participation#political will#reconciliation#resource constraints#social cohesion#socio-economic context#sustainable peace.#timing#transitional justice#truth#truth and reconciliation processes#truth-seeking#war crimes
0 notes
Text
One of the most fascinating but not at all surprising things in the post election fall out is the amount of mostly (but not only!) white leftists and liberals who are foaming at the mouth for minorities to be "punished" for the way their (perceived) voting block went. Disgusting and overtly racist shit is being said. Like, I already knew that a big chunk of y'all really just see minorities as your stupid little pets you court for clout, but wow! I'm summarizing here, but: "People who disagree with my obviously correct political views deserve to be PUT IN CAMPS and CALLED SLURS and be separated from their families!"
yes baby. you're sooo different than those nasty republicans.
oh yeah the minorities are definitely too stupid to know how much contempt you have for them and always have. certainly this did not influence their vote at all. you did nothing wrong, ever, princess. try calling them stupid a few more times. that will definitely help us win the next election.
#if you only listen to minorities from your same socio economic circle/context#if you only like minorities then they agree with you 100%#you do not actually give a fuck about minorities. you don't think they have inner lives distinct from yours.#you believe that their place is to Obey#and that your place is to tell them what to think and do#congratulations! you are so fucking racist!
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Reminder, that the reason that they’re doing this isn’t because they actually care about queer people being allowed to be queer. If we’re not fighting about equality of race, gender, sexuality, and/or the right to be ourselves without constant threat of violence anymore, we will have energy to deal with the true threat. The real enemy is the oligarchs.
#they whipped the abortion controversy into a frenzy roughly 50 years ago for the same reason#They refers to republican legislators in this context#socio economic inequality#those in financial power also often make their money from environmentally unsound practices and are literally killing the planet
60K notes
·
View notes
Note
heyo got any tips on writing gangs?
Writing Gangsters
Organized Crime vs. Gangs
Although the terms are used interchangeably, there's a difference between organized criminal networks and gangs.
Organized crimes have focuses on material gain and therefore has a more hierarchical leadership structure.
The activities of gangs are usually more fragmented, opportunistic and based on individual contacts, more entangled with the personal lives of its members.
Of course, if a street gang become powerful enough, large enough and resourceful enough, it comes a full-blown criminal organization.
Background: Time, Place, Economic Condition
Research into the characteristics of the time and place where your gang is.
Oftentimes, gangs form when the economic conditions of a country/region is down. People, especially those who are marginalized, are disillusioned which can lead them to make desperate choices.
It's important to note that many gangs are formed initally to serve as the "police" in a neighborhood where no police would enter because (for some reason) they feel as if there's nothing they can do.
Gangs may start with a "good" reason, but it just so happens that eventually they become the very thing they sought to get rid of.
Compelling Character Motivation
With the socio-geographical context as backdrop, give your characters a clear reason why they would join and stay in a gang.
A young teen may join a gang out of pure whim, maybe for money, but eventually it's going to have to be more than that.
Idolization - an older sibling is in the gang
Inclusion - connection with others is so wanted due to a lack of it in a dysfunctional family
Stability - feeling secure in a neighborhood where gangs seems like a viable option; if a gang is already terrorizing the area, joining it may seem like a way to protect one's family
Financial security - jobs may seem out of reach; it si high risk and high rewards but your character may be that desperate
Ambition/thirst for power/revenge
+ Yes, someone may join the gang because they don't want to work a regular job and want quick money, but I wouldn't say they are lazy. From what I understand, gangs require work...
A developmental Model of Gang Membership (use for character arc):
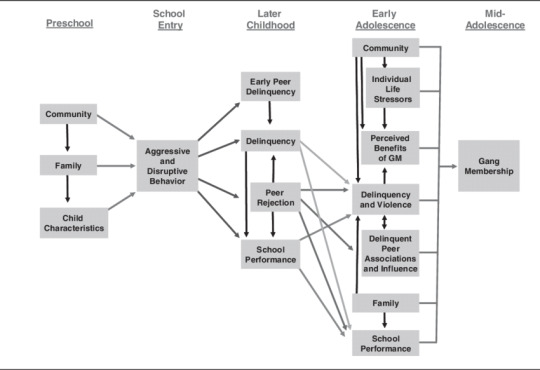
Research:
National Gang Center FAQ: https://nationalgangcenter.ojp.gov/about/faq#0-0
Gang Life Insider Article: https://amuedge.com/the-various-dangers-of-gang-life-an-insiders-perspective/
NY Gang Slag: https://nypost.com/2012/10/28/a-to-z-deadly-slang-by-gangs-of-new-york/
Gangster Short Stories you can Read Online
‘Johnny Mnemonic’ by William Gibson
‘Vice Grip’ by Matthew A. Goodwin
‘Dolan’s Cadillac’ by Stephen King
#writers block#writing#creative writing#creative writers#helping writers#let's write#poets and writers#writers on tumblr#writeblr#resources for writers#writers and poets#writerscommunity#writing inspiration#writing prompt#writing advice#on writing#writing tips#writing community#writer stuff#writer#writer on tumblr#writer community#writer things#writer problems#writers of tumblr#writers community#writers life#gangs#character#character writing
292 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data spanning from 1995 to 2021 in India revealed a striking gender imbalance in organ transplants, with four men getting organ transplants for every woman. A total of 36,640 transplants took place in this period, out of which 29,000 were for men and 6,945 for women.
This substantial difference is attributed to a complex interplay of economic responsibilities, societal pressures, and deeply ingrained preferences.
Dr Anil Kumar, director of the government-run National Organ & Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) highlighted this significant aspect of the organ donation landscape.
While more men contribute as cadaver donors, a staggering 93 per cent of total organ donations in the country come from living donors, he told the Times of India newspaper. This hints at a trend: a majority of living organ donors are women. Socio-economic factors a driving force for women donors? A study published in the Experimental and Clinical Transplantation Journal in 2021 delved into the intricacies of living organ transplantation in India. The findings showed that 80 per cent of living organ donors are women, predominantly wives or mothers. The socio-economic pressure on women to assume caregiving roles within the family emerges as a primary factor, compelling them to step forward as donors. Men's reluctance in surgery In many cases, men, often the primary breadwinners, hesitate to undergo surgery, contributing to the gender gap in organ recipients. The study highlights that when the recipient is a male breadwinner, family members, especially wives or parents, feel a heightened responsibility to donate organs. Emotional dynamics The emotional dynamics surrounding organ donation are intricate. Women recipients, in particular, may experience guilt when their family members, especially wives or mothers, become donors. This reluctance leads to a scenario where women recipients may find themselves on waiting lists. Notably, Karnataka has topped the charts in organ donation in the past decade. The number of donations have risen from 102 in 2013 to 765 in the first 10 months of 2023.
A user on Ovarit added this helpful context:
"Just a little more context to this: men produce male-specific proteins (on the Y chromosome) which often get rejected by women's bodies. Since males have an X chromosome, their bodies recognize proteins from female donors. This makes it more difficult for women to receive male tissue/organs, while still being acceptable candidates for donating to men. Even still, these ratios are very disproportionate".
"As women we absolutely need to be aware of our vulnerability of being used as spare parts in a man's world. Especially when we are being socialized into believing that we need to sacrifice our bodies and lives for others- and society has developed a sense of entitlement to this sacrifice, while downplaying the suffering of women."
#organ donation#marxist feminism#India#women's rights#feminism#global feminism#intersectional feminism#women's oppression#patriarchy#sex-based oppression#gender critical#gender critical feminism#radblr
634 notes
·
View notes
Note
i'm sorry in advance for asking you about what was essentially, a small part of a month old jokey reply to a post. that said, what would you consider the implications of the "this world is enough" quote being said by specifically Joyce Messier to be, along with the ensuing "(...) this is the greatest and kindest arrangement the atoms had in them"... it's just that this is one of my favourite quotes in the game and your post made me realize I had been engaging with it in a rather superficial way.
It’s a very beautifully worded passage, which I think contributes in large part to why people latch onto it so much. Unfortunately, it tends to fall victim to the classic phenomenon whereby lines which are rhetorically effective and on the surface appear to articulate a clear and compelling sentiment find themselves isolated from their broader textual context in fan reception & thus taken at face value. The full passage is:
JOYCE MESSIER - "Great bodies of water, forest-covered surfaces... clusters of light where the cities lie. You've seen the montage, we all have -- this world is enough," she concludes.
CONCEPTUALIZATION - It *must* be. This is the greatest and kindest arrangement the atoms had in them.
Stripped of its political teeth, I imagine the idea of a world composed of the ‘greatest and kindest’ arrangement of atoms is somewhat comforting, as a poetic expression of a sentiment of hope and optimism for the world around you and for yourself in turn. However, it just can’t be easily cleaved away from the fact that Disco Elysium is an overtly and unsubtly political game; it’s a game about communism, and it’s a game which thinks about communism in such a way that the sentiment given here is undercut at just about every turn.
We see that this idea of a ‘greatest and kindest arrangement’ is coming in response to Joyce’s statement that ‘this world is enough.’ Joyce, in-game, is an ultraliberal strikebreaker invested with a huge amount of power relative to capitalist hegemony; put simply, she is not someone whose political voice is one with which the narrative aligns. To think about the present condition of the world as ‘enough’—and to respond, as does Harry’s Conceptualisation, with the suggestion that anything else would be less great and less kind than they are at present (such that all failings of greatness and kindness in the present state can be countered with the superlative)—is a sentiment coming from someone for whom the continuation of the capitalist social condition is hugely beneficial. Put simply, Disco Elysium, read holistically, is just not a game which believes that the capitalist social condition is ‘enough,’ and nor that it is the ‘greatest and kindest arrangement.’
Like—the game takes great pains to suggest that capitulating to the inevitability of the present condition only reveals the limitations of one’s framework. Time and time again, the game makes appeals to inevitability—of the fall of the commune, of the expansion of the pale and the consumption of Elysium—only to suggest that it is only by imagining a total rearrangement of the atoms, if you will, that we can prevent it. I wrote in more detail about this reading here if you’re interested, but the long and short of it is: the presence of the anomaly in the Dolorian church guides us as players towards the idea that the entropy of the pale is a construction of Dolorian moralism, which is to say, capitalist hegemony; the fact that infra-materialism, a theory of Mazovian socio-economics, suggests at the defiance of traditional laws of physics in a manner that may at first seem absurd but by the end of the communist plotline is proven possible in the fact that the tower is able to stand up on its own is in turn a suggestion that the pale’s entropy, too, is a ‘fact’ only inasmuch as it exists within the boundaries of what hegemony has termed factual. If the tower can stand, why can’t the world be overhauled at such a fundamental level that the expansion of the pale could be stopped and the Moralintern could be evaporated? This is the sentiment of the communist quest; rather than accepting the present condition of things (the “greatest and kindest” such that nothing else could possibly be better—it is worth remembering that greatest and kindest does not necessarily mean great or kind), the very belief that they could be changed is what allows change to take place. This is the sentiment communicated in Steban’s “In dark times, should the stars also go out?”.
My comment on the original post was just me being slightly glib about the fact that people consistently latch onto that line out of context. It’s a good line—it’s prettily expressed, and it’s certainly helpful for articulating the different political conditions at play in the game. However, I’m not convinced people are engaging with it in a way that fairly accounts for what it does relative to the rest of the text. This tendency to latch onto poetic language at the expense of thinking seriously about what the sentiment in question actually communicates reminds me of what Evrart says of Joyce:
You - "But she told me a beautiful story about the discovery of the Insulinde."
Evrart Claire - "Of course she did. Rich people have the best stories. About all the interesting things they've done and seen, all the beautiful places they've been to. It's just sentimentalism. She can afford to be sentimental -- and she can afford to lose as well."
I wouldn’t reify Evrart as the voice of the working class in Disco Elysium either, but I think this particular line cuts to the quick about how Joyce’s elevated, obscurantist language often makes it difficult for players to situate what she says within the context from which she appears to us.
766 notes
·
View notes
Text

In the heart of the ancient Achaemenid Empire, a masterpiece of Persian artistry emerges—a rhyton (drinking horn or in the shape of a horn) carved from the deep blue lapis lazuli and adorned with gold, taking the form of a majestic ibex (mountain goat).
Dating back to the 6th to 5th century BCE, this exquisite ceremonial vessel not only exemplifies the sophisticated craftsmanship and rich symbolism of the time but also provides a fascinating glimpse into the cultural and economic prowess of ancient Persia.
[Description and Material]:
*Material:
Lapis lazuli, a semi-precious stone prized for its deep blue color, was highly valued in ancient Persia and sourced primarily from what is now Afghanistan.
*Form:
The rhyton is shaped like an ibex, a type of wild goat with prominent, curved horns, reflecting the importance of nature and animal motifs in Persian art.
[Use]:
*Function:
A rhyton is a type of vessel typically used for drinking or pouring liquids, especially in ceremonial contexts. The liquid would be poured from the top and flow out through the spout, which could be the mouth of the animal in this case.
*Ceremonial Role:
Rhytons were often used in religious and royal ceremonies. The choice of lapis lazuli and the intricate craftsmanship suggest that this particular rhyton was likely used by the elite, possibly in rituals associated with the Zoroastrian religion or royal banquets.
[Cultural and Historical Significance]:
*Art and Symbolism: The ibex design reflects the importance of wildlife in Persian culture and the symbolic use of animals in conveying power and divinity. The ibex, with its strong and agile form, could symbolize qualities such as strength and resilience.
*Trade and Wealth: The use of lapis lazuli indicates extensive trade networks and the wealth of the Achaemenid Empire, as this material was not locally sourced and had to be imported.
*Royal Patronage: The Achaemenid rulers were great patrons of the arts, and such luxurious items underscore their desire to display their wealth, power, and cultural sophistication.
[Academic Perspective on Material Culture]:
*Cultural Synthesis:
Scholars often view Achaemenid art, including rhytons, as a synthesis of various cultural influences, including Mesopotamian, Egyptian, and Greek, reflecting the diverse and cosmopolitan nature of the empire.
*Representation of Power:
Academics see these artifacts as representations of royal propaganda, showcasing the divine right and grandeur of the Persian kings.
*Symbol of Status:
In material culture studies, such high-quality items are considered symbols of social status and wealth. They provide insights into the social hierarchy and economic conditions of the time.
*Artistic Techniques:
The craftsmanship of the rhyton is analyzed for its artistic techniques, such as carving and polishing lapis lazuli, which indicate advanced skills and aesthetic values.
[Notable Examples]:
Museums and Collections: Notable examples of such rhytons can be found in major museum collections, such as the British Museum and the Louvre, where they are studied and displayed as prime examples of Achaemenid artistry and craftsmanship.
In conclusion, the lapis lazuli rhyton in the shape of an ibex from the Achaemenid period is a significant artifact that illustrates the artistic, cultural, and economic aspects of ancient Persia. It serves as a key piece of material culture, providing valuable insights into the ceremonial practices, trade networks, and socio-political dynamics of the Achaemenid Empire.
#ancient Persia#Zoroastrianism#ceremonial vessel#rhyton#lapis lazuli#Iran#Mesopotamia#Ancient history#Near East#ancient civilisations#ancient art#ancient craft#archaeology#Achaemenid#Achaemenid Culture
67 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey I want to ask you something. I read your blog a lot and have seen information you give about people in certain disadvantaged positions (morally/socio-economically). I am not someone who blindly supports Snape. I simply understand him as a flawed human who tried his best at some atonement. But sheltered as I am, I sometimes wonder is people can truly change? And if someone's atonement is enough?
Snape tried to save everyone, most importantly, but he emotionally scarred him. He attacked a child who had no context about any triggers plaguing Snape. JK Rowling has said on record Snape loathed him, Harry, till he died. But why? How did his immense guilt, which made him save everyone, not be at least neutral with a small child? How is it possible for a human being to be self aware about his grand mistake but then not self aware enough to bring any meaningful day to day change? Spitting on the ground when Gryffindor wins....a 30 year old man. Did only Lily matter and so the mistake he made with her was the only thing he felt guilt for? Not the mistakes he made with others. Isn't that why people say he was obsessed?
Second, Lily is dead. No amount of his "atonement" (which she will never know) will bring her back. So is there any use to atonement or is it just people trying to fix the knot in their throats when they do something bad. Because of Snape's mistake, Lily dies. She will never see Harry grow, never have a career, never have another child, never grow old. So what exactly Snape was trying to do? And for what? For Lily? She is dead and he doesn't seem to care for anyone else. So sure, he saved her child, saved the world....but what's the point. They both probably lay in separate graves, and by the time Severus even began saving Harry, Lily's flesh may already started to fall off her bones in her coffin. So what is the point?
Sorry if its too much; I am 23 and this growing and maturing stage is making me hella confused about everything.
People can change, but they must have the opportunity to change, along with the resources and support to do so. This is something Severus never has. He doesn't decide to change; he feels guilty about how his actions negatively affected someone he cares about, and at first, all he wants to do is try to prevent that mistake from turning into a tragedy. The tragedy happens anyway, and he feels that he owes it to himself and to Lily to somehow avenge everything that has happened in order to make up for the damage. It's not rational, of course Lily isn’t going to come back, but all revenge stories begin when the harm is already done and irrevocable. So, really, it's just a way for him to deal with his own feelings of guilt, his anger, and his sorrow. But still, he doesn't have the space to heal his emotional and psychological wounds. He sells his soul to Dumbledore, who conveniently uses him because he knows Severus is capable of anything to gain the validation of the moral authority (that old man) so that he can feel like he is on the right path. After selling his soul, he stops having his own life. He doesn't have a future plan beyond being useful to Dumbledore and his plans, it’s like a self-imposed sentence. He becomes a teacher, even though he doesn't like it or like children, in the same school where he spent the worst years of his life, where he suffered systematic violence, where adults ignored him and now he has to treat them as "colleagues," where he made his biggest mistakes. You can’t heal in the place of the trauma. He goes back there, and ten years later, a kid shows up who, every time he opens his mouth, reminds him of the person who tortured him nonstop. It's not rational. Severus could rationalize his antipathy toward Harry if he had received psychological help or had been given the tools to heal. He could dislike the kid or simply ignore him because he doesn’t like looking at his face, but not go beyond that. But it’s impossible because, psychologically and emotionally, he is trapped in his teenage years, which are where all his major traumas lie, and Harry’s face sadly makes all of that explode in his head every time they see each other. And since Severus is a deeply dysfunctional adult with terrible emotional control, totally deregulated when something reminds him of his traumatic past, he behaves like an idiot.
He doesn't see Harry as Lily’s son; he sees him as a version of James. And this isn't something exclusive to Severus, Sirius sees him the same way. Sirius also projects his trauma, loss, and guilt onto Harry, but the difference is that Sirius loved James, and Severus hated him. But Sirius is a good example of how Severus isn’t the only one who depersonalizes Harry in favor of James, because he even tries to make him like James, or behave the way James would have. What both of them have in common is that they are adults stuck at a point in their lives that doesn't match their age and are also emotionally unstable. Severus decides to save Harry multiple times because when he really stops to think about it rationally and doesn’t have him in front of him, he knows Harry is Lily's son, and his goal is to keep him alive. But this is something he has to remind himself constantly because his rational side is not the one that acts first; it’s a part he has to force.
I’ve always thought that Severus never forgave himself for being indirectly responsible for the death of the person who had been his attachment figure throughout his life. Deep down, Severus is one of those guys who, if you give them a little affection or acceptance, will follow you to the ends of the earth. He shows this with Dumbledore and even, why not, with the Malfoys. He’s the abused stray dog that, if you give him a bit of food and a home, will sink his teeth into anyone who comes near you to threaten you. The thing with Lily is his unfinished business, regardless of whether the past changes or not, but he feels it that way. I also think that as the years go by, it’s not all about Lily anymore, but he really develops a sense of responsibility toward the magical world. He truly wants to help and genuinely wants to defeat Voldemort, not just because of what happened with Lily, but because he believes that Voldemort needs to fall for genuine reasons. He shows this when, despite knowing that Dumbledore's plan involves sacrificing Harry, instead of refusing and telling him to go to hell, he agrees to move forward. If it were just to protect Lily’s son, he would have stepped away from the plan, but he continues because he genuinely wants to do the right thing, and the right thing is saving as many people as possible, even if it requires sacrifices.
#severus snape#pro severus snape#severus snape fandom#severus snape analysis#severus snape headcanons#harry potter#harry potter fandom#sirius black#james potter#lily evans#lily evans potter#albus dumbledore#harry potter meta#severus snape meta
33 notes
·
View notes
Note
I would love to hear about your pre raphaelite obsession
warning: emmie talks about academia and her nerdy interests
so in english literature academia, there is a subfield called illustration studies. illustration studies is about looking at the relationship between art and literature. it focuses a lot on victorian illustration culture because during the victorian era, there was a push for all socio-economic classes to be literate. pictures helped with that because they do not rely on language to communicate their meaning the way books, songs, poems, etc do.
although there is an idea of ‘artistic freedom’, there is also a belief that the artist’s individuality expressed in the painting calls the integrity of illustration into question. the artist’s aesthetic inclination, sociocultural context, and preoccupation with the source text all affect how they interpret and portray the scene. sometimes artists will portray the scene literally and take the source text word for word whereas other times they emphasize certain elements or embellish them. the illustrator serves as both the interpreter and as the intruder. by reversing ekphrasis (the visual reading of a literary text) the illustrator is uniquely positioned as the translator between the verbal and visual and decides which aspects of the text to enhance or condense.
most pre-raphaelite artists used a single line or a lesser-known scene to inspire their paintings. they wanted to explore scenes that analyzed characters’ emotional turmoil and conflict as well as the moral or theological side of the narrative rather than the story itself. they loved literature because of this. they loved shakespeare, dante, the bible, greek myths, tennyson, king arthur, etc. their preoccupation with the text, their aesthetic inclination, and sociocultural context all affect how they interpret and depict the scenes. what's interesting about the pre-raphaelites is how obsessed they were with historical accuracy when it came to clothing and sets. which is why the victorian sentimentality that is imposed onto their paintings is so fascinating.
when i wrote my essays, i focused primarily on how the pre-raphaelites depicted women and how it differed or was similar to the original text. with that, i also looked at what their views on love and sexuality were, how it was in line with the text, but also how it was in line with victorian sentimentality. characters like juliet, ophelia, elaine of astolat, and the lady of shalott were the most popular because of the victorian obsession with purity, sex, and death. i looked at the coded and non-coded messages within the paintings. so, used things like victorian flower language, how their hair was done, what colors they were wearing, how they were positioned, etc, to form the arguments and observations.
#emmie answers#i'm sorry for the stunlock#i just love illustration studies so much#lowkey with my dissertation was focused on it instead but oh well
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
While there are many conditions where inter-class contradictions are not the primary factor at play, that doesn't mean you should just discard class analysis entirely. Like class can still be a useful lens when dissecting the differences and conflicts between distinct segments/strata of the same class, and sometimes a great deal of analysis and discussion is needed to determine whether a particular group is just a distinct strata or a different class entirely. Inter-Class conflict can also still play a secondary role, or else explain the context for the current conditions, and could one day play a more ascendant role as the situation develops.
For example, this is why I'm skeptical of any analysis that treats "The State" as some discrete entity that's disconnected from broader class society. Like not every political situation is going to cleanly resemble the classical model of the state as the totally obedient tool of some external ruling class, but that doesn't mean that the members of the state apparatus don't comprise any sort of classes or stratas that is inextricably linked by some manner socio-economic relation with other classes and stratas in society. Phenomena like Bonapartism and State Capitalism are still very explicable in class terms, even if said explanation is going to vary significantly with the specifics of the situation and conclusion of the analyst. Like sometimes you might refer to the State/Bureaucratic Bourgeois, while other times Apparatchiks could be classifies as a specific strata of proletariat, and under some analyses the members of State Apparatus can be thought of as an entirely separate class of their own (especially under pre-Capitalist conditions, such as in the contentious theory of the "Asiatic Mode of Production").
Because social institutions are ultimately the product of the material conditions that produce and reproduce them, with the social dynamics of these institutions reflecting the material relations between the groups that participate in them. The primacy of Class analysis is a natural conclusion of using Dialectical Materialism to understand a class society. You can't just ignore this because the specific dynamics don't reflect whatever dogmatic understanding of "Class" you've internalised; that's a metaphysical and therefore revisionist way of thinking
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
When my wife and I first started fucking dating, we had a shorthand phrase we would exchange when someone was being...some kind of way about gender and sex and sexuality...to sort of indicate to each other what we thought was happening.
"I see we've decided to round to the nearest dick."
See, wifey and I are both trans and bisexual in REALLY similar ways, but with different AGABs right? And we noticed with time that interesting trends showed up. For me, people, even those who know I'm bisexual, treat me like they would treat me as a straight person in their life. Wifey often gets treated like loved ones treat exclusively gay people. Then with gender it's similar! People assume I *don't* have a dick and so they treat me like they would treat [failed] women in their lives. They assume Wifey DOES have a dick and treat her like they would treat a [failed] man in their life. Even beyond that, when wifey and I are TOGETHER, we are automatically defaulted into the "straight" category or the "gay" category depending on which of us (how many of us) they are assuming has a dick, and then defers authority in the relationship to whoever they think has the dick.
It's all gender essentialism all the way down, and interrelated essentialism across the whole spectrum, butit shows up in different ways depending on how people perceive our relationship to our genetalia
And it IS about our genetalia because it almost always gets explicit about it at some point.
I think what I've always found the most interesting is how other queer and trans folks interact with the concept of rounding to the nearest dick, including how we as a community wield it against each other laterally. The experience of being called "basically a woman" by lesbian partners in order to reconcile their discomfort with my gender (as distinct from lesbian partners whose reconciliation of my gender with their sexuality involved calling THEMSELVES "basically alesbian" or some similar iteration that emphasized the importance/meaning of THEIR identity WITHOUT commenting on my own) while Wifey gets treated like "basically a man" because of how race, gender, and sexuality intersect for her. The experience of being told I am excempt from certain realities not based on ACTUAL lack of the experience but based on a feeling of ownership people believe they have over how those experiences may manifest in the world, like when someone says "well trans men aren't oppressed anymore" so I shouldn't take up space in women's communities, men's communities, OR trans-general communities. Or like when someone told wifey that gay men haven't been oppressed since same sex marriage.
Like A) you're simply fucking wrong, and B) even if you were RIGHT, I'm NOT a trans man and my wife ISN'T a gay man. So why would that mean anything about us?
Part of what we both noticed is that the function of "rounding to the nearest dick" is usually about silencing or side-lining someone. WHO exactly is relational and context dependent, but essentially it boils down to "I need one of us to be explicitly less empowered than the other of us to feel safe navigating our interaction"
Sometimes it's preferrable to BE the disempowered (e.g. justification of horizontal hostility) and others to be the disempowerING (e.g. gatekeeping access to socio-economic resources) but in either case, we explicitly see gender wielded asymmetrically and selectively to create and redirect power. Not as something intrinsic to a person or within their control. And I think it's interesting as a trans person to experience gender explicitly as power even when, for me, that's never what it's been. It's interesting to see how people engage with that power when THEY don't usually experience it that way.
Anyway, rounding to the nearest dick is something I think we should all avoid, in part because maybe we should stop focusing in so much on people's gender and sexuality having ANYTHING intrinsic/inherent to them, as opposed to a layer of context within the wholeness of their lives
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
you know i remember reading someone’s meta pointing out the casual racism in lena’s dialogue when you bring up the kind green ape and she reveals that she believes kim to be a completely separate species from the rest of them
and up to that point, lena was shown to be a very loveable character and understandably everyone loves her (i do too) and so plenty of people would be caught off guard by her casual racism
i think when lena’s casual racist remarks came up in my playthrough, i was prickled and disappointed but i don’t think i would describe my feelings at the time as complete surprise. lena’s remarks were not dissimilar from the kinds of comments i would get about my own background and country of origin
although i never encountered rhetoric that was explicitly race science in its ideology that is evident in lena’s remark, all of the rhetoric i encountered dehumanizes my heritage and assumes that i wish to ‘ascend’ from my own home culture. for instance, many canadian queers i encountered would overly presume that i had suffered greatly due to my queerness in my home country when that is very far from my actual reality as a queer person existing here. they would ask if i had applied for asylum, when that isn’t really an option for me because i would have to prove that my life was in immediate danger, which is an experience i just do not have even though my home country is very queerphobic in its society, institutions and legal system. there exists a strong undercurrent of homonationalism that threads through a lot of my interactions with most queer people who are invested in first world countries as being inherently more lgbtq friendly than other countries, despite evidence to the contrary.
whenever i encounter the opinions of liberals on asian politics (both irl and online), they betray their actual convictions that view asian-ness as inherently ‘lesser’, ‘backwards’ or ‘barbaric’. they constantly refer to the asian immigrant narrative as one of realizing their liberal subjectivity and by extension their personhood via moving towards the first world liberal democratic countries and to shun and cut off ties to the homeland, with the implication that asian cultures and societies are inherently ‘sexist’, ‘homophobic’, ‘racist’ and ‘unenlightened’. this does the work of ignoring the historical, political and socio-economic contexts of issues within asian societies and instead attributes these problems to our own heritage and ‘backwards’ culture. liberal rhetoric frequently dehumanizes the people who still remain in our countries, framing the high population count as ‘swarms’ or ‘brainwashed masses’ and our prioritization of the collective over the individual as ‘authoritarian’. although many liberals i meet would pay a lot of lip service to being pro-asian, their actual words reveal their continued subscription to yellow peril tropes disguised as concern for the poor yellows in their despotic homeland.
lena’s casual racism couched in her benevolence is way more pervasive than the blatant racism espoused by the racist lorry driver and measurehead. lena’s disability also factors as i could never be free from the racism within other marginalized communities, my encounters with queer communities being a prime example
330 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ivan and Phoebe by Oksana Lutsyshyna
Ivan and Phoebe is a novel about a revolution of consciousness triggered by very different events, both global and personal. This is a book about the choices we make, even if we decide to just go with the flow of life. It is about cruelty, guilt, love, passion – about many things, and most importantly, about Ukraine of the recent past, despite or because of which it has become what it is today.
The story told in Oksana Lutsyshyna’s novel Ivan and Phoebe is set during a critical period – the 1990s. In the three decades that have passed since gaining independence, Ukraine has experienced many socio-political, economic, and cultural changes that have yet to be fully expressed. The Revolution of Dignity in 2014 marked a pivotal moment in the country’s history, as it signaled a shift towards European integration and a strong desire to distance itself from Moscow. Prior to this, Ukrainian culture had remained overshadowed by Russian influence, struggled to compete for an audience and was consequently constrained in exploring vital issues.
77 days of February. Living and dying in Ukraine
"77 Days," is a compelling anthology by contributors to Reporters, a Ukrainian platform for longform journalism. The book, published in English as both an e-book and an audiobook by Scribe Originals.
"77 Days'' offers a tapestry of styles and experiences from over a dozen contributors, making it a complex work to define. It includes narratives about those who stayed put as the Russians advanced, and the horror they encountered, like Zoya Kramchenko’s defiant "Kherson is Ukraine," Vira Kuryko’s somber "Ten Days in Chernihiv," and Inna Adruh’s wry "I Can’t Leave – I’ve Got Twenty Cats." The collection also explores the ordeal of fleeing, as in Kateryna Babkina’s stark "Surviving Teleportation '' and "There Were Four People There. Only the Mother Survived."
It also highlights tales of Ukrainians who created safe havens amidst the turmoil, such as Olga Omelyanchuk’s "Hippo and the Team," about zookeepers safeguarding animals in an occupied private zoo near Kyiv, and one of Paplauskaite’s three pieces, "Les Kurbas Theater Military Hostel," depicting an historic Lviv theater turned shelter for the displaced, including the writer/editor herself.
In the Eye of the Storm. Modernism in Ukraine 1900’s – 1930’s
This book was inspired by the exhibition of the same name that took place in Madrid, at the Museo Nacional Thyssen-Bornemisza, and is currently at the Museum Ludwig, located in Cologne, Germany.
Rather than being a traditional catalogue, the publishers and authors took a more ambitious approach. Rather than merely publishing several texts and works from the exhibition, they choose to showcase the history of the Ukrainian avant-garde in its entirety – from the first avant-garde exhibition in Kyiv to the eventual destruction of works and their relegation to the "special funds" of museums, where they were hidden from public view.
These texts explain Ukrainian context to those who may have just learned about the distinction between Ukrainian and Russian art. Those "similarities" are also a product of colonization. It was achieved not only through the physical elimination of artists or Russification – artists were also often forced to emigrate abroad for political or personal reasons. Under the totalitarian regime, discussing or remembering these artists was forbidden. Archives and cultural property were also destroyed or taken to Russia.
"The Yellow Butterfly" by Oleksandr Shatokhin
"The Yellow Butterfly" is poised to become another prominent Ukrainian book on the themes of war and hope. It has been listed among the top 100 best picture books of 2023, according to the international art platform dPICTUS.
The book was crafted amidst the ongoing invasion. Oleksandr and his family witnessed columns of occupiers, destroyed buildings, and charred civilian cars. Shatokhin describes the book’s creation as a form of therapy, a way to cope with the horrors. "During this time my vision became clearer about what I wanted to create – a silent book about hope, victory, the transition from darkness to light, something symbolic," he explains.
Although "The Yellow Butterfly" is a wordless book, today its message resonates with readers across the globe.
A Crash Course in Molotov Cocktails by Halyna Kruk
A Crash Course in Molotov Cocktails is a bilingual poetry book (Ukrainian and English) about war, written between 2013 and 2022, based on Halyna’s experience as an author, volunteer, wife of a military man and witness to conflict.
The Ukrainian-speaking audience is well-acquainted with Halyna Kruk – a poet, prose author and literature historian. Kruk is increasingly active on the international stage, with her poetry featured in numerous anthologies across various languages, including Italian, French, Swedish, Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, Polish, English, German, Lithuanian, Georgian and Vietnamese.
For an English-speaking audience, her poetry unveils a realm of intense and delicate experiences, both in the midst of disaster and in the anticipation of it. The poems are succinct, direct, and highly specific, often depicting real-life events and individuals engaged in combat, mourning, and upholding their right to freedom.
134 notes
·
View notes
Text


Meet Bin & Blu, a couple of fugitives who find themselves on the strangest planet they've ever seen... Earth.
Their home world is a planet called Tora. Their species is also called Tora, or Torae when referring to them collectively. (an individual Tora, or multiple Torae). Like its nearest neighbour, Sixam, the planet Tora is a matriarchal society. Also like Sixam, both biological males and females can bear children, and no social concept of gender exists. People form relationships with whomever they want, and individuals are differentiated by biological sex rather than by a socially-constructed gender system.
Tora has a class or caste system. Unlike Sixam, class is not based on colour or biological sex, but rather by economic and socio-political standing. Tora is not a peaceful world like Sixam, either. There is a lot of unrest, with people constantly trying to become wealthy, successful or famous and trying to climb the class ladder.
Blu is from the upper class, but lost status due to his political views and his association with people like Bin, who started in the middle class but fell to the lower class due to his criminal proclivities.
On their home world, Blu and Bin were were caught while attempting to flee after Blu helped Bin escape from prison. Blu was more likely than not headed for prison himself because of his socio-political advocacy, and the authorities decided that instead of incarcerating both of them on the home world, they'd get rid of them by dropping them off on some backwater planet and stranding them there. They were left with only a few items of clothing and supplies, and that was that.
They decided fairly quickly that they'd need "Earth names" in order to integrate better. Unfortunately, they realized just as quickly that no one on this planet looks even remotely like them, and new names would not help them integrate at all. They also discovered that having a good vocabulary in a language isn't enough when it comes to naming. Context is also important, and Dustbin and Blu-Ray, as it turns out, were not the best choices for names.
Currently, they're camping on a beach in Tomarang and trying to figure out their next move.
____________________
About Bin Real Name: Azri Kana'an Earth Name: Dustbin (or Bin for short) Occpuation: thief, elemental master
Azri (Bin) is one of the minority of people on his world who can harness elements. He's a genetic throwback from the days when magic was more prevalent than science and technology. Magic is largely lost to the Torae now, and those who do possess it are either elevated as quasi-spiritual figures or vilified, depending on who you ask. There is very little middle ground. Azri's life choices unfortunately led him to be viewed more as a danger to public order than to be seen as a leader or hero of any sort
He's notorious for his thefts of large amounts of currency and other easily-liquidated valuables. He gave most of the money to organizations dedicated to dismantling the class system on his world and making life more fair and equitable for everyone. He actually enjoys the adrenaline rush he gets from stealing, and in between heists, he likes to steal small items for fun.
He was given medication to sterlize him while he was in prison, and is convinced he can't get pregnant now, which is good in his opinion because he's very sexually adventurous.
About Blu Real Name: Valyn Auri'el Earth Name: Blu-Ray (or Blu for short) Occpuation: social worker, activist
Valyn (Blu) comes from a wealthy and prominent family. He was expected to join his family's business enterprise and amass his own fortune, but after recognizing the plight of the lower classes, he decided he wanted to dedicate his life to helping them instead of enriching himself. He trained to be a social worker, a job usually done by lower middle class individuals. He met Bin while working in his city's prison, and despite knowing it wasn't a good idea to start a relationship with a client, he did it anyway. Between them, they hatched a wild plot to break Bin out of jail.
His facial marking isn't natural; it's a tattoo that's fashionable among the upper classes, which parents often have applied to their children at a young age. Blu hates it because it easily identifies him as coming from the upper class, but Bin thinks it's beautiful, particularly at night when the moons-light hits it and makes it look glossy.
He loves the water, and like most members of his species, he can stay underwater for several minutes without needing to come up for air.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Guys! Yesterday I had a book-shaped piece of mail, and inside of it was my copy of Children and Childhoods in L.M. Montgomery: Continuing Conversations being returned, from another very dear user here! I bring this up only because some-months-ago I promised to copy out a particular article from this book, for yet another user here, who was interested! Interested because it’s on the the subject of a Fan Favourite thing... fan fiction. And better still because some of our (basically famous) mutuals here are mentioned by name! If you’ve ever wondered if the Montgomery scholarship is reading your fan fiction... the answer is yes, they are! They totally are. More than that, they also have some thoughts to share… as well as recommendations of their faves too! This article even covers the F/F and M/M fan fiction presented by fans in LMM’s universe, and I’m personally super excited to be able to begin reading these works, as soon as I can find them all. I’ve done my best to link what I could immediately find, but some of the mentioned stories were unavailable... potentially due to changes in usernames? (That said... if anyone knows of the works indicated here, that I haven’t provided a link for, please do share!) This article, by the way, was written recently... in 2020! It’s very current, and it covers a few stories that were still being actively updated during the pandemic. The focus of this article is less so on canon (or really just the Anne/Gilbert pairing), though, and seems to prefer demonstrating the versatility of mixing relationships (Anne and Emily, for one!) and the wider more general universe-building aspects (the entanglements of future generations/Anne’s grandchildren) that fans have been expounding on for nothing less than decades.
Okay, here we go! xx
Continuing Stories: L.M. Montgomery and Fanfiction in the Digital Era by Balaka Basu
Fanfiction – the recreational (re)writing of texts – is a literary genre of rapidly growing significance. Abigail Derecho in her brief history of fanfiction identifies it as “a genre that has a long history of appealing to women and minorities, minorities, individuals on the cultural margins who used archontic writing as a means to express not only their narrative creativity, but their criticisms of social and political inequities as well.”
Insightfully defined by Francesca Coppa and Mary Ellen Curtin as “speculative fiction about character,” fanfiction can be even more precisely understood as fantasies about the diegetic positioning of characters in the context of various settings, communities, relationships both textual and paratextual, and eventually all manner of cultural mythologies.
Kristina Busse and Karen Hellekson describe the production of fanfiction as “part collaboration and part response to not only the source text, but also the cultural context within and outside the fannish community in which it is produced.”
They point out that the shift in the method of dissemination of fanfiction from newsletters and zines to internet archives means that “ever-younger fans who previously would not have had access to the fannish culture except through their parents can now enter the fan space effortlessly; financial resources have become less of a concern because access to a computer is the only prerequisite; and national boundaries and time zones have ceased to limit fannish interaction.”
The nature of fanfiction allows participants to cross-generational and socio-economic boundaries in an ongoing exchange of responses to a source text with which they share a fascination, developing new texts that in turn elicit their own responses. While the creation of fanfiction is evidence of an affective, loving, communal relationship with the source text, this genre of writing is still dismissed in many quarters as overly emotional, purely erotic, and even perverse, a type of amateur and immature engagement with popular texts that produces writing necessarily divorced from literary significance. Produced in staggeringly vast quantities by subcultures with complex vocabularies and traditions that can intimidate the casual reader, fanfiction is perceived by many to be more of a cultural practice than a literary genre, variously denigrated for its pornographic potential and its lack of originality. However, close examination reveals that fan writers are able to create a critical dialogue with the originating author in acts of communal storytelling that incorporate allusions and reference points to which other dedicated fan readers and writers may respond.
In this chapter, after examining how L.M. Montgomery and her writer heroine Emily themselves engage in practices now associated with fanfiction, I survey four forms of fanfiction that remove Montgomery’s novels from her seemingly idyllic and timeless island settings, contextualizing her characters and plots within history and other genres: the sequel set during the Second World War, the modern AU (alternate universe), the gap-filler, and the slash fic, all of which allow the young readers who grow up with her novels to engage in dialogue with the stories they love, a type of literary conversation that Montgomery herself models within her texts. Emily’s reading, which is active rather than passive, resembles twenty-first-century fans’ ownership of the texts they love, provoking creative responses. For instance, after reading works by Lord Tennyson, Elizabeth Barrett Browning, and Matthew Arnold, Emily writes, “Teddy lent me 3 books of poetry. One of them was Tennyson and I have learned The Bugle Song off by heart so I will always have it. One was Mrs. Browning. She is lovely. I would like to meet her. I suppose I will when I die but that may be a long time away. The other was just one poem called Sohrab and Rustum. After I went to bed I cried over it. Aunt Elizabeth said ‘what are you sniffling about?’ I wasn’t sniffling – I was weeping sore … I couldn’t go to sleep until I had thought out a different end for it – a happy one.”
The reactions Emily catalogues are those of the fan; they are viscerally felt in the body and attempt to dissolve the boundary between author and reader, producer and consumer. She inscribes Tennyson within her heart in order to possess the poem she loves; she creates a relationship between Barrett Browning and herself; and, most significantly, she interjects her own desired happy ending into Arnold’s tragic narrative, a corrective desire that is at the core of many works of fanfiction. Emily’s diaries and her story reflect Montgomery’s own experiences from childhood to adulthood as reader, writer, and reader-turned-writer discussed in the introduction to this volume. Depicting Emily as a voracious reader and a life-writer like herself, Montgomery places the child Emily’s voice in conversation with that of the narrator through Emily’s letters to her dead father in Emily of New Moon and through her diary entries in Emily Climbs and Emily’s Quest, creating a form of joint authorship that is referenced explicitly in “Salad Days,” the second chapter of Emily Climbs: “book is not going to be wholly, or even mainly, made up of extracts from Emily’s diary; but, by way of linking up matters unimportant enough for a chapter in themselves, and yet necessary for a proper understanding of her personality and environment, I am going to include some more of them. Besides, when one has material ready to hand, why not use it?”
The narrator’s willingness to use the “material” that is “ready to hand” reflects Montgomery’s and Emily’s practices, and also validates other writers’ use of the material Montgomery places at their disposal. As with many fans, Emily’s reading frequently makes itself felt within her writing.
Like Montgomery, Emily learns her trade through mimicry, from her first poem in blank verse inspired by James Thomson’s Seasons to her unwitting imitation of Kipling that is pointed out by her teacher, Mr Carpenter, in his review of her work. Like Sara Stanley of The Story Girl, whose compelling and fascinating stories are rarely if ever original, Emily is a fan of the oral traditions of her community, incorporating and building upon them in her own writing, transforming and recreating, for instance, the story of “The Woman Who Spanked the King” in Emily Climbs.
The retelling and versioning that Emily practises signal her immense admiration for the source texts she adapts, just as the creation of fanfiction does for Montgomery’s readership and fans. The possibilities inherent in versioning and adaptation are illustrated in Emily’s Quest. When Montgomery depicts Emily undertaking the reworking of someone else’s narrative, she is adapting an episode from her own experience while working for The Echo in Halifax, which she records in her journal. Montgomery, like Emily, was asked to create an ending for a serialized story, “A Royal Betrothal,” after compositors had misplaced the original text.
Like Emily, she claims that her “knowledge of royal love affairs [was] limited,” and that she was unaccustomed “to write with flippant levity of kings and queens.” Nevertheless, Montgomery manages to create a conclusion that passes muster, since “as yet nobody has guessed where the ‘seam’ comes in.” She is, however, curious about the original author’s reaction to her unauthorized adaptation, and while she never discovers this in real life, she does imagine it in her fiction when she introduces Mark Greaves, who is horrified by Emily’s new ending for the story but enchanted by its author. Neither Montgomery nor Emily engages in this sort of writing from a place of fandom; they have no previous attachment to “A Royal Betrothal,” and both are writing professionally. Nevertheless, the ability to solve the puzzle of the story and the weaving of their work into an already extant text are the very project of fanfiction: ludic narrative composition that recalls the way children play make-believe with the narratives they love, reworking and extending them. It is telling that Montgomery uses the metaphor of the “seam” to describe this particular craft. Jane Dawkins, writing about her fanfiction, which is inspired by Jane Austen, describes her fan novel Letters from Pemberley as “an old-fashioned patchwork quilt, where in place of the scraps of fabric reminding one of the favorite frocks or shirts whence they came, there is a line or a phrase or a sentence from one of [the original] books or letters stitched alongside the lesser scraps of my own manufacture.”
Montgomery’s final book, framed by the two world wars, is just such a patchwork sequel, albeit providing only brief glimpses of the characters that readers met as children and who have now grown older. When a version of the book was published in 1974 as The Road to Yesterday, these glimpses, lacking the interstitial materials, became even briefer, mirroring the more forced insertion of beloved characters that the two earlier collections, Chronicles of Avonlea and Further Chronicles of Avonlea, display. Only two of Anne’s grandchildren – Gilbert Ford and Walter Blythe – are obliquely referred to, in the story “A Commonplace Woman,” where an unpleasant young doctor reflects on both of them as potential rivals for the affection of a beautiful girl he himself hopes to pursue.
However, the full novel, The Blythes Are Quoted, published in 2009 and comprised of short stories about the people in Glen St Mary and over the harbour, is interspersed with poetry by both a young Walter and an adult Anne. The poems are cut with tiny slices of dialogue that suggest the continuing lives of fans’ favourite characters and how they might have developed. In “‘Dragged at Anne’s Chariot Wheels’: L.M. Montgomery and the Sequels to Anne of Green Gables,” Carole Gerson notes the mixture of feelings from pleasure to frustration that Montgomery records in her journals as she prepares to write her first sequel.
While Montgomery wrote the first installments of her various series out of inspiration, she was certainly aware of what her market desired from subsequent installments. She often regretted the necessity of marrying off her characters, but was aware that her fans demanded this conventional outcome for the characters they had come to love; these traditionally romantic endings, when not offered by Montgomery herself at the instigation of her publishers, are regularly deployed by contemporary fanfiction authors building on the source texts.
Indeed, long before the original structure of The Blythes Are Quoted was revealed to readers in Benjamin Lefebvre’s afterword, fanfiction writers were spinning off lengthy narratives that included a third generation of young Blythes, Fords, and Merediths dealing with the onslaught of the Second World War. While earlier installments in the Anne series – such as Anne of Green Gables and Anne’s House of Dreams – depict the deaths of Matthew, Anne and Gilbert’s first daughter (Joyce), and Captain Jim, Walter’s death in Rilla of Ingleside is somehow more striking. Unlike Matthew and Captain Jim, he has not yet had time to grow old; unlike Joyce, readers have had opportunities to get to know him as a child in Rainbow Valley and as he grows into young adulthood in Rilla of Ingleside. His death is unnatural and, therefore, all the more horrifying. These two aspects of Rilla of Ingleside – the evocation of history by a nostalgic fictional world that is still tied to real time and the use of high drama, tragedy, and romance – provide fanfiction authors with a model they can use to appeal to the emotions of those readers who are immersed in the next generation of Montgomery characters.
The Second World War, then, provides an entry point into the series for fanfiction authors, who can deploy real history coupled with beloved characters to create a tale that feels absolutely authentic. One example of this is a short story, “The Pen and the Sword,” written in 2007 by MarnaNightingale. Here, mimicking the style of Dorothy L. Sayers’s The Wimsey Papers (a series of Spectator articles published between 1939 and 1940, which interestingly also continue the story of First World War–era characters during the Second World War), MarnaNightingale employs epistolary excerpts and newspaper articles to tell the story of a family going through the horrors of war for a second time. Grounding her fragmented story – like The Blythes Are Quoted, a mixture of genres – in the accounts of novelist Mollie Panter-Downes (1939) and war correspondents Ernie Pyle (1940) and Ross Munro of the Canadian Press (1941), whose articles are attributed to Kenneth Ford, she offers a story that, like Rilla of Ingleside, is anchored to the historical moment, while also nostalgically focusing on the character development that comes from Gilbert Ford’s death, Rilla’s and Faith’s reactions to the war, and the lives of their children. Here war also serves as an opportunity for new experiences, particularly for women and children: Rilla takes a factory job as a machinist, liking it better than working in Carter Flagg’s store; one of Anne’s grandchildren, Susan, plans to be a doctor; and Faith, who worked as a Voluntary Aid Detachment nurse in the First World War, mentions how she can sympathize. As well, the daily tidbits that flavour the pages of Rilla of Ingleside are there: one article, attributed to Anne, includes the recipe for Susan Baker’s war bread, reminding readers of the problems of wartime rationing, even in the Americas. Real life events – like the Canadian forces trying (and failing) to make a beachhead at Dieppe – arouse the passions of the reader. Unlike Austen – who also famously wrote of three or four families in a country town, but kept the Napoleonic wars firmly in the shadows – Montgomery brings the passions and high drama of the world stage into the sleepy villages of Prince Edward Island, which inspire fanfiction spinoffs.
The long novel Cecilia of Red Apple Farm, by a fan author who posts under the pseudonym ruby gillis, also directly reworks passages and scenes from the whole range of Anne books, set in the late-nineteenth century, to The Blythes Are Quoted, set in the early years of the Second World War, to highlight the similarity between her new generation of characters and their ancestors. Cecilia is the daughter of Una Meredith and Shirley Blythe (characters often married off in fanfiction). Like MarnaNightingale, ruby gillis provides period flavouring in the styles of dresses and behaviour and in references to 1940s popular films and songs. Simultaneously, this setting offers new opportunities to her female character: Cecilia wants to be a doctor, and rather than staying in Canada, she joins up to be a nurse in England. She has a series of romances – one with Sid Gardiner (before he marries May Binnie), and one with her cousin Blythe Meredith, who is this generation’s poet – before finally ending up with Marshall Douglas (the son of Mary Vance). Just as Anne initially refuses Gilbert Blythe in favour of Roy Gardner’s resemblance to her ideal man in Anne of the Island, ruby gillis’s Cecilia is fooled by the allure of Sid and Blythe as Roy Gardner–like romantic heroes into believing that she does not truly love her fun, practical, “Gilbert-esque” friend. Published in 2004, Cecilia of Red Apple Farm further illustrates the opportunities presented by reusing and reworking a body of texts through its incorporation of Montgomery’s poem “I Wish You” as the work of Blythe Meredith. Montgomery includes this poem and attributes it to Anne in The Blythes Are Quoted, although ruby gillis could not have known this when writing. The repetition of names and circumstances might seem derivative, but for readers who have read and reread the original books so many times, the extension of the story world is prized, even if – perhaps even because of – its callbacks to the original text. Due to the tendency of fans to fixate on “the good bits” in a reread, these parts can be taken for the whole.
Austen fanfiction demonstrates this aptly. Indeed, Helen Fielding’s second Bridget Jones novel, Bridget Jones and the Edge of Reason (1999), illustrates just such a reading of Pride and Prejudice: she shows Bridget, a fan, watching the scene from the 1995 mini-series in which Darcy, dripping in a wet see-through shirt, exits the lake, and then rewinding and rewatching the scene multiple times. How many times might a similar fan reread Walter’s letter from Courcelette? This repeated reviewing of selected portions can replace the amplitude of the original novel. With this delimited focus, narrative is no longer seen as a progression, but as a single moment of pleasure, sustained as long as possible. Reading the Second World War as a repetitive sequel to the First World War further highlights this possibility.
Even Montgomery seems to do so, as demonstrated in The Blythes Are Quoted, with its new generation of characters confusingly named after the old: Walter, Jem, Rilla, Di, Anne, and Gilbert. A variation on Marah Gubar’s kinship model, this kind of continuation highlights the blurred boundaries between child and adult characters who are literally related to one another and whose adventures mimic one another.
In a third example of fanfiction set during the Second World War, Weeping May Tarry, a long novel by ElouiseBates, Meggie, the heroine, is Shirley’s daughter (and also, surprisingly, Paul Irving’s granddaughter). In this story, which like Cecilia of Red Apple Farm is an installment of a longer series, Meggie is sent off to a conservatory of music to study singing, aptly combining the traditions of the nostalgic boarding-school novel with “Girl’s Own” wartime fiction. Following the tradition of Magic for Marigold, which explicitly suggests in its second chapter that the Murrays of Blair Water and the Lesleys of Cloud of Spruce exist in the same universe, @e-louise-bates (like many other fanfiction authors, including ruby gillis) suggests that all of Montgomery’s characters exist in a single universe: Meggie partners briefly with the grandson of Sara Stanley (The Story Girl and The Golden Road) and is close friends with Jane Stuart (Jane of Lantern Hill).
Going even further, @e-louise-bates introduces the grandchildren of the What Katy Did series as friends for Meggie and includes Betsy from Dorothy Canfield Fisher’s Understood Betsy as Bruce Meredith’s wife, creating a world where all the characters of early-twentieth-century girls’ fiction seem to have truly lived, where their descendants must cope with victory gardens and dances with soldiers at the Exhibition Grounds, and where kisses are much more commonplace than they once were.
These particular continuers of Montgomery are also desirous of membership in the community of her fans, seeing their literary endeavours as productive of approval from a fellow readership. Likewise, the novels are notable for their sociality – they seem to offer the reader not only a fantasy friendship with the characters themselves but also the very real society of fellow readers of the works. Thus, these fan authors attempt to diversify their stories so that they represent contemporary beliefs regarding multiculturalism; ruby gillis, for instance, introduces into the family by way of marriage a French girl who has had to flee the Nazis due to being Jewish, a situation Montgomery and her contemporaries might have had some difficulty accepting, considering early-twentieth-century attitudes toward interreligious marriage and Montgomery’s othering of the German-Jewish peddler who sells Anne green hair dye.
The Second World War thus offers writers of Montgomery fanfiction the loom on which to weave new, more diverse stories, even as The Blythes Are Quoted, which also traces the characters’ reactions to this new war, demonstrates how these readers-turned-writers followed Montgomery’s own trajectory, not knowing that they were doing so. On the subject of fanfiction, young-adult author Patricia C. Wrede writes: “The thing that fascinates me about fanfiction, though, is the way that it models the decision tree that writers go through (whether consciously or unconsciously) to get to their final product. For those of us who do this part mostly unconsciously, it can be interesting and instructing to see the multitude of alternate paths that a story could have taken, all laid out more-or-less neatly in different authors’ fanfics [… taking a slightly different fork in the road] resulting in the plot veering in a completely new direction. Friends become enemies; enemies become friends; goals and objectives and results shift and change.” Within these pieces of fanfiction, then, fan writers are able to follow these decision trees with subsequent generations of characters as well.
Another avenue of access occurs when fan authors transpose historical narratives into the contemporary moment. Perhaps the best-known example of this modern alternate universe [AU] conversion is the television program Sherlock, which takes Arthur Conan Doyle’s Victorian detective into the twenty-first century. While new cultural contexts appear, the essence of character is meant to be retained. Just as Sherlock uses text messages and blogs to substitute for telegraphs and handwritten journals, fans of Montgomery reimagine the relationships between her characters as if they were taking place online.
For instance, “Work in Progress” (2012) by verity postulates a friendship between Montgomery’s most famous heroines, Anne and Emily. In this piece of fanfiction, Emily circumvents Aunt Elizabeth’s injunction against fiction during her time at Shrewsbury High by becoming a blogger who is restricted to the “truth.” The story’s online summary, a part of which reads “Anne rolls her eyes. ‘Is your aunt really going to know if you cheat on your nonfiction with some hot prose on the side?’” shows how the story preserves the character qualities that Montgomery laid out, complete with references to the Murray pride and Anne’s orphanhood. Mr Carpenter’s admonitions are spelled out at the beginning of the story:
“Emily Byrd Starr has a sticky note on her desktop. It reads:
ITALICS
CAPITALS
!!!!!
“just”
“really”
CTRL+F!
It is almost like having Mr Carpenter in the room with her.”
Verity creates humour through the juxtaposition of contemporary social media and allusions to Montgomery’s source text. Another story by verity detailing Rilla’s romance with Ken Ford and her friendship with Una Meredith, “Rilla of Toronto,” takes place mainly through instant messages. In this story, Rilla reflects on her life from eighteen to twenty-five, tracing a continuum from her child self to her new adulthood, underscored by verity’s translation of Montgomery’s work into contemporary millennial language.
A third type of fanfiction narrative, the gap-filler, focuses on and expands the implications of the source texts. Moira Walley-Beckett’s Netflix/CBC series Anne with an “E,” as Laura Robinson shows in chapter 12 of this volume, is somewhat fanfictional in and of itself: as Robinson points out, the show fills gaps by bringing to the fore the darker currents that have always been beneath the seemingly untroubled waters of Anne of Green Gables, including Anne’s potential post-traumatic stress disorder from the disturbing life she led before coming to Green Gables. This kind of versioning and adaptation tacitly permits fan authors to feel that their versions are just as valid as those produced by professionals. Gap-fillers frequently expand on romantic pairings and in fandom are often referred to by portmanteaux of characters’ names that perpetuate some inside joke or work as puns. “Shirbert” – a moniker for Anne and Gilbert – is the latter, and demonstrates how fans posting on sites like Archive of Our Own (Ao3), Fanfiction.net, and Wattpad (this last generally populated by younger fans) develop their own language to identify their stories within the community for which they write.
One such story, “You caught me staring, but I caught you staring back,” by Anuka, clearly inspired more by the television series than the novels, begins with an author’s note that reads, “I decided to write some fluff for these two, because I need more Shirbert moments, and season 2 is so far away. I added gifs to make it more vivid.” Here, the romance between Anne and Gilbert as depicted by Montgomery and Walley-Beckett is not sufficient for the reader-turned-writer. Anuka wants the gaps in the narrative to be more fully explored than they are on either page or screen and to be made more “vivid” by the inclusion of images that help make the story come alive.
Similarly, “Rilla Blythe’s Wedding: A Not Entirely Comprehensive Account” by Scylla also fills a gap: Rilla and Ken’s wedding day, a scene that Montgomery leaves to the reader’s imagination at the end of Rilla of Ingleside. Modelled upon other accounts of weddings within Montgomery’s fiction, the story also suggests that accounts of Walter’s death have been gravely exaggerated, as he makes a stunning appearance at his sister’s wedding. In order to align her work with Montgomery’s novel, Scylla ensures that Little Dog Monday’s awareness of Walter’s death remains, but makes it only a technicality, writing, “His heart had stopped for a full ten seconds – long enough for his Captain to feel for his empty pulse and for Dog Monday to be jolted with the fullness of his death. Little dogs, after all, can only have tender dogs’ hearts. Grief to Dog Monday was an all-consuming thing, and when Walter’s heart began to beat once more, he was deaf to its spark of joy.” After meeting with his eldest sister, Joyce, in heaven – which is, as he had always hoped, Rainbow Valley, Walter is returned to life so that he may write of peace as well as war (as he did when he was a boy), marry Una, and repair the broken hearts of readers who did not want to lose him.
While heterosexual pairings are the most prevalent in Montgomery fandom, there is room for queer imaginings as well.
This very popular genre of fanfiction, known as “slash,” is generally defined as stories that centre on samesex romances between characters, particularly between men. Montgomery slash fiction usually stars Walter Blythe.
One slash story, “but i don’t know who you are” by @freyafrida, imagines a bisexual Walter. Told in an enduringly popular sub-genre of fanfiction often referred to as Five Things Plus One (which involves a series of thematically linked but not necessarily chronological scenes), the story is summarized by @freyafrida as “Five people Walter thought he wanted, and one person he didn’t notice until it was too late.”
This last person is original to Montgomery’s text: Una, whose apparently unreturned attraction to Walter is woven through Rilla of Ingleside. The other five potential partners are all alluded to as Walter’s close friends, beginning in childhood with Alice Parker from Anne of Ingleside and Pat Brewster from The Blythes Are Quoted and then carrying on through adolescence and young adulthood with Faith Meredith, Ken Ford, and finally Paul Irving from Anne of Avonlea. While his feelings for Faith and Ken are clearly unrequited, Alice, Pat, and Paul all express their own desire for Walter. The inclusion of the famous poet and Walter’s “model” uncle, Paul Irving, in particular, particular, illustrates how traits of sensitivity and aesthetic appreciation that challenge traditional ideas about masculinity are frequently interpreted as queer by fan readers and writers.
In another slash fiction, cero_ate’s “The Moving Finger Writes, and Having Writ Moves On,” Walter discovers his homosexuality while fighting in Europe:
He wrote half truths and lies once more, when he wrote his Rilla that he could not form poems of the depths of the war. For who could write his sister of the phallic love he had found? He had found his reason in a tow-headed American boy. He meant so much more to Walter than mere friendship could explain. He wanted to write, as sweethearts write, of the tempest of joy in the darkest night. But how would they understand? How would they even try to understand he sought not the Dark Lady of Shakespeare but the youth, fair and Wilde? When he was presented with Una’s faithful heart, he spurned it. When his tow-headed darling presented his own, Walter took it, greedy for him. His grecian style love, the boy who’s [sic] eyes danced, even in the darkest of days. He would do anything to keep him safe. But he could not present him to his family, for their scorn or pity. War had broken him, but made him as well.
While male/male pairings are generally the most popular stories in fandoms, Montgomery’s novels, peopled as they are by communities of girls and women, require that readers who want to queer the text must explore what is called femslash (that is, slash fiction featuring two female characters).
Such relationships have been explored within the academic setting. For instance, Laura Robinson remarks in “Bosom Friends: Lesbian Desire and the Anne Books,” that the relationship between Anne and Diana uses “the language that readers associate with adult romantic love rather than girlhood affections,” even as it is expressed through the heterosexual paradigm of marriage.
One fanfiction author, ArcticLava21, makes it clear that such fan written stories are not speculation but instead address key issues of representation. The author’s note to ArcticLava21’s short Anne/Diana story, “Nature,” reads, “Hello everybody! Hope your [sic] having a wonderful day. Before anyone yells at me for ‘sexualizing platonic friendships’ please note that this is for all those queer kids who grew up pretending. Pretending that he ended up with him instead of her, or desperately wanted representation. Are we good? <3 Enjoy yourselves lovely people.” The intended audience of the story, “queer kids who grew up,” again establishes the transgenerational kinship between Montgomery’s child and adult fans.
All fan fiction, shared on the Internet, exist in dialogue not just with Montgomery’s fiction but with the author herself, and between the fans who read the novels as children and adolescents and the adults that these readers become.
Whether fan writers extend the narrative or fill gaps, transpose chronology or to queer the text, these pieces of fanfiction allow fans not only to insert themselves into the narrative, but also simultaneously to revivify the original novels, published a century ago. In performing interventions to the text, Montgomery’s young fans grow up to reply to the discussions that she began long ago in the pages of her journals and stories, ensuring that all three – author, reader, and text – are continually reborn into a conversation that will never end.
#any typos here are all mine 😑#apologies because i’m sure there’s so many… i’m just bleary-eyed from the screen time it took to type this guy up!#like#why didn’t i just get the kindle version#lucy maud montgomery#fan fiction#anne of green gables#emily of new moon#too many individually referenced characters to tag here really!
51 notes
·
View notes
Note
How do you feel about the current socio-economic context of our generation?
/j we both know it sucks
What are some places you'd like to see/travel to?
uhh blow it up
mm not sure, i wanna travel a lot of places, i wanna go back to germany, go back to czech republic and austria and italy, go to countries i havent been like norway and estonia, i wanna visit thailand and china and greece and lithuania i wanna travel just about everywhere really
8 notes
·
View notes