#rigged economy
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Thousands in Los Angeles to see Bernie Sanders right now. There’s something happening. Crowd estimated at 35,000.
+
Sanders: Our good friend Elon Musk sent out a tweet and in essence, he said, you know, Bernie Sanders has been talking about the growth of oligarchy year after year after year. Well, Elon, you're damn right. That's what I've been talking about . The difference is I'm no longer talking about how we're moving to oligarchy. I'm talking about how we are living today in an oligarchic form of society
[..]
Sanders: You know why we have all these great musicians here today? We're going to make our revolution with joy. We're going to sing and dance our way to victory against hatred and divisiveness.
[..]
Sanders: Thank you Los Angeles for our biggest rally ever. 36,000 people came out today to say NO to Trumpism, NO to oligarchy, NO to authoritarianism, and NO to a rigged economy.
226 notes
·
View notes
Text
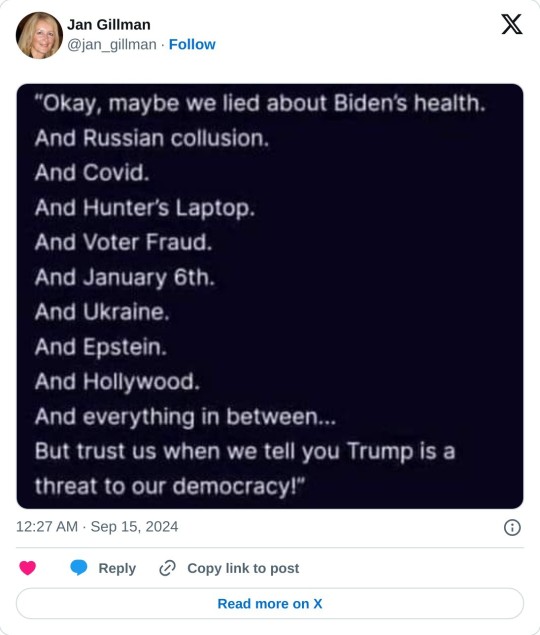
#politics#us politics#democrats are corrupt#democrats will destroy america#wake up democrats!!#democrat corruption#democrat coup#democrat lies#fbi are corrupt#department of justice#criminal left#criminal investigation association#secret service#truth justice and the american way#american constitution#american economy#america for the americans#too big to rig#too big to steal#too big to fail#illegal voting#illegal crime rate#illegal invasion#voting machines#president trump#i'm more maga than ever!#maga 2024#maga#media manipulation#media corruption
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

It was probably the news of the magical "$81 million" she pretends to have raised already. If they're cheating already, what are the odds for an honest election?
#The economy#Stock market#MAGA#kamala harris#Trump Vance 2024#god is a republican#make america great again#too big to rig#Banana Republic#kyle rittenhouse#suck my freedom#too big to steal#donald trump#congress#trump
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
*Willy showing up unscathed after almost getting blown up and then almost drowning in chocolate*
Slugworth:

#can we talk about how the chocolate cartel actually went ahead and paid for the premium economy boat ticket just to rig the ship to explode#they said insult to injury#wonka 2023#wonka#willy wonka#arthur slugworth#aladdin#aladdin 1992#jafar
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
kind of insane that colleges all charge like $50 fees just to apply, like can you imagine if jobs did that too? it totally limits ambition, especially for people in hard financial situations (ik there’s often waivers, but you have to apply for those, in which case you’re basically working to pay for the fee)
2 notes
·
View notes
Text






Dammit. I kinda liked Tim walz. But, none of these candidates got my vote in Nevada.

#incumbents#vote all incumbents out 2024#the economy#democrats rig elections#fun facts#Bernie would’ve won#Nevada progressives#none of these candidates nevada#political memes#mistaken con man#mystery sovcit theater memes#mst memes#tumblr memes#pathetic3#dankest memes#garth nader memes
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"capitalism breeds innovation"
actually capitalism breeds a dystopian nightmare you all pretend is normal
#when i say eat the rich i mean eat at their confidence until thwy have anxiety like the rest of us#when i say eat the rich i mean consune their gold in giant mouthfuls until the economys nonexistant#when i say eat the rich i mean the punishment for bigtime tax evasion shouldbe being fed to the poor as recompense#when i say eat the rich i mean cannibalism as a solution to world hunger and overpopulation#when i ay eat the rich i mean i wanna tear em limb from limb while aggresively monologuing about poverty#when i say eat the rich i mean im fucking tiredof being trapped in a system rigged to fight against me every step of the way#when i say eat the rich i mean i want everyone to have a chance at living a life they dont have to fight tooth and nail for#:p
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

#capitalism#donald trump#economy#government#democracy#democrats#republicans#the bitch and moan show#TheBitchAndMoanShow#maga#trump 2024#trump#trump derangement syndrome#president trump#biden crime family#Rigged#Witch Hunt#corruption
2 notes
·
View notes
Text










#Trump#100 days#trump’s 100 days#america#economy#gdp#deficit#how do you milk sheep#Tell them the election was rigged#Greenland#deport trump’s family#birthright citizenship#denaturalization#elon musk#the onion#once in a generation economic crisis#us federal deficit#dementia#divine
1 note
·
View note
Text
instagram
#politics#us politics#democrats are corrupt#democrats will destroy america#wake up democrats!!#illegal voting#voter fraud#too big to rig#too big to fail#too big to steal#president donald trump#true patriot#maga 2024#american constitution#american economy#american flag#america first#2020 election#2024 presidential election#Instagram
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Putting Trump in office is like hiring an 8 year old to be a brain surgeon because they played doctor at recess once
stop talking about the USA. I have heard enough about that wretched place
#absolutely no one that lives here is proud of this shithole#we don’t have control over the politicians#they just divert everyone with bullshit and do whatever they want#the numbers are clearly all rigged for entertainment#cause if it was 90/10% no one would pay attention to all these stupid fucking debates or new stories for stock market boosts#we’d know who is obviously supposed to win for a month and they’d make no money without the media drama…#yall are fucking disgusting. just kill yourselves. you’re not even leaders you don’t lead anything or do your jobs in the first place#or the economy would be fine right now… stop hiring people that don’t have the job experience#it’s not fucking complicated. stop pretending it is
41K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ripple Effect of Fuel Costs
Fuel pricing is one of those unpredictable forces that every trucker wishes they could control but can’t. It’s like trying to plan a picnic while watching storm clouds roll in—you know something’s coming, but you can’t be sure how bad it will get. For truckers, this unpredictability doesn’t just dampen the day; it can completely throw off budgets, schedules, and sometimes even livelihoods. When…

View On WordPress
#business#cash flow#cash flow management#diesel prices#Freight#freight challenges#freight industry#freight rates#Freight Revenue Consultants#fuel cards#fuel costs#fuel costs impact#fuel economy#fuel pricing#fuel surcharges#fuel-efficient rigs#logistics#owner-operators#small carriers#supply chain#supply chain delays#Transportation#transportation costs#truck driver expenses#truck driver survival#trucker budgeting#Truckers#Trucking#Trucking cash flow#trucking challenges
1 note
·
View note
Text
Billionaires destroy more than they create
In a land often championed for its economic opportunity and equality, the American Dream promises that anyone who works hard can rise to prosperity. But for many in today’s middle and lower economic classes, that dream is fading, shadowed by a reality that feels increasingly rigged. At the heart of this issue lies a stark and glaring imbalance: billionaires, a minuscule fraction of the population, wield a staggering concentration of wealth and influence. This is not just an issue of economics but one that touches the foundations of democracy and fairness.
Imagine the economy as a massive machine, built to churn wealth throughout society. In an ideal world, this wealth would cycle effectively, where each part contributes and benefits in turn. But as billionaires amass wealth at unprecedented levels, this machine has come to function more like a funnel, siphoning resources from the broader society and concentrating them at the very top. This dynamic, driven by complex financial structures and tax strategies, isn’t merely an accumulation of personal fortunes but a systematic extraction from the economic potential of others. The capital that could have flowed through wages, education, and public infrastructure is often diverted into private bank accounts and shell companies, rarely benefiting the people who drive and build the economy day by day.
As wealth accumulates at the top, so too does political influence. Billionaires, with vast financial resources, can fund political campaigns, lobbyists, and entire networks of think tanks dedicated to shaping policy. Through these channels, they push for tax policies, regulations, and trade agreements that benefit the ultra-wealthy at the expense of middle- and lower-income families. Politicians, indebted to these donors, increasingly look to billionaire interests rather than to constituents’ needs. This creates a disturbing feedback loop: billionaires influence politics to further policies that reinforce their own wealth and power, leaving the broader populace with dwindling opportunities to influence their own government.
This concentrated power extends far beyond campaign finance and lobbying. With ownership over significant segments of media networks, billionaires control the narratives that millions consume daily. Through these media outlets, they shape public opinion, diverting attention from policies that would challenge wealth accumulation and pushing narratives that frame the ultra-wealthy as essential “job creators” or “innovators” rather than acknowledging their role in widening economic divides. Issues that might threaten their economic stranglehold are often buried, while others, that create division and distract, are amplified.
For the middle and lower classes, this confluence of wealth, media, and political power has a real impact. Stagnant wages, diminishing job security, and rising costs of living aren’t natural outcomes of a complex economy—they’re symptoms of a system shaped to benefit those at the top. Policies that could lift working-class Americans, like raising the minimum wage, universal healthcare, or better labor protections, are often stifled in legislative deadlock, thanks in part to the political influence of the ultra-wealthy who stand to lose from them.
So, as this cycle continues, the gap between billionaires and everyone else widens. The billions accumulated at the top no longer signify mere success but a barrier to mobility for everyone else. The middle and lower classes find themselves carrying the economic burdens, often working harder for less. Meanwhile, billionaires remain insulated, living in a different economic reality, one far removed from the struggles of the average American. This isn’t just an economic imbalance but a distortion of democracy itself, as the machinery of power and influence is pulled further from the reach of ordinary citizens and held more tightly by those whose interests rarely align with theirs.
Without addressing this imbalance, the promise of opportunity, the cornerstone of the American Dream, becomes less attainable with each passing year, not just for the lower and middle classes but for the nation’s future as a whole.
Addressing their manipulation
Billionaires and their advocates often employ a familiar set of narratives to justify their wealth and the structures that enable it. These arguments, framed in terms of the free market, capitalism, or fear of socialism, are not only misleading but often serve to distract from the deeper systemic issues at play. Below is a breakdown of these claims and the counterarguments that expose their flaws:
1. “It’s Just the Free Market at Work”
The myth of the “free market” implies that billionaires achieve their wealth purely through talent, innovation, and competition in a market where everyone has equal opportunity. But in reality, the U.S. economy is far from a genuinely “free” market.
Counterpoints:
• Government Subsidies and Tax Breaks: Many billionaires’ businesses rely heavily on taxpayer-funded subsidies, special tax breaks, and other forms of government assistance. Large corporations frequently lobby for policies that grant them tax advantages, including offshore loopholes and capital gains tax breaks. This creates an environment where they aren’t competing on equal ground but rather with significant state support, distorting the market in their favor.
• Anti-Competitive Practices: Many large corporations, especially in tech and finance, engage in monopolistic behavior, buying out competitors or using aggressive tactics to drive them out of the market. This concentration of power stifles competition, contradicting the notion of a “free” market where anyone can succeed if they work hard.
• Inherited Wealth and Privilege: A significant portion of billionaire wealth is inherited rather than self-made. Generational wealth compounds, giving the ultra-wealthy an enormous head start over those without similar family resources. This challenges the idea that wealth accumulation is simply the product of individual merit or a fair market.
2. “This Is What Capitalism Is Supposed to Look Like”
The argument here suggests that capitalism is an inherently competitive system, where the most successful rise to the top, benefiting everyone through innovation and job creation. This narrative hinges on the idea of “trickle-down economics,” where the wealth of the richest eventually spreads throughout society.
Counterpoints:
• Trickle-Down Economics Doesn’t Work: Decades of evidence show that wealth rarely “trickles down” to the rest of society in any meaningful way. Income inequality has only widened, with wages stagnating for most workers while billionaire wealth has soared. Billionaires tend to reinvest wealth in ways that concentrate their holdings, like in stocks, rather than in ways that benefit the broader economy.
• Wealth Extraction, Not Wealth Creation: Many billionaires achieve and maintain their fortunes through rent-seeking behavior—extracting wealth from existing resources rather than creating new value. Hedge funds, private equity, and real estate empires often profit by cutting costs (like labor) rather than by innovating or producing new goods and services. This dynamic benefits investors but hurts workers and consumers.
• Capitalism Can Take Other Forms: The capitalism practiced in the U.S. today, sometimes called “neoliberal capitalism,” focuses on minimal regulation, tax cuts for the wealthy, and privatization. However, other countries demonstrate that capitalism can function with stronger social safety nets, wealth redistribution policies, and tighter regulations on corporate power. Nordic countries, for example, balance capitalism with robust welfare systems, ensuring a more equitable distribution of wealth and services.
3. “Without Billionaires, There Would Be No Innovation or Job Creation”
A popular myth is that billionaires are essential “job creators” and “innovators” whose wealth ultimately benefits society by funding new businesses and creating employment. This claim positions billionaires as indispensable to economic growth.
Counterpoints:
• Public Funding Fuels Innovation: Many of the biggest technological advances, including the internet, GPS, and medical breakthroughs, were developed with public funding rather than billionaire investments. Government research grants and subsidies often lay the groundwork for major innovations that billionaires later profit from. In other words, society bears much of the financial risk, while billionaires reap the rewards.
• Small Businesses Create Most Jobs: Small businesses, not billionaires or large corporations, are responsible for most job creation in the United States. Big corporations often eliminate jobs through automation, outsourcing, or consolidation. They may employ a large workforce, but they also tend to exploit workers through low wages, precarious employment, and cost-cutting measures.
• Billionaires Accumulate Wealth Through Wealth, Not Innovation: Many billionaires maintain their wealth not by creating jobs or innovating but by using their existing capital to generate more wealth, often through financial instruments that have little to do with actual economic productivity. Stock buybacks, dividends, and passive investments grow their fortunes without necessarily contributing to broader economic prosperity.
4. “Any Alternative Is Socialism or Communism”
When calls arise for higher taxes on the wealthy, stricter regulations, or broader social programs, the response is often to invoke the fear of “socialism” or “communism.” This argument seeks to paint any attempt at wealth redistribution or regulation as a slippery slope toward total government control.
Counterpoints:
• Social Safety Nets and Regulations Are Not Socialism: Social safety nets, progressive taxation, and regulations do not equate to socialism or communism; they’re features of a balanced capitalist system that seeks to prevent extreme inequality and protect public welfare. Countries like Germany, Canada, and Denmark combine regulated capitalism with strong social programs, resulting in healthier economies and greater well-being for citizens without abandoning capitalism.
• Inequality Threatens Capitalism: Growing inequality and economic instability can undermine the foundations of capitalism. A healthy capitalist economy requires a strong middle class with buying power, which excessive wealth concentration undermines. Reforms like progressive taxation, labor protections, and universal healthcare aren’t a rejection of capitalism but rather a means of stabilizing it.
• Historical Success of Mixed Economies: Many of the most successful and prosperous countries practice a mixed economy, where capitalism coexists with social policies that promote equality. The U.S. itself has employed a mixed economy model in the past, particularly after the New Deal, which implemented social safety nets, labor protections, and financial regulations that led to a period of unprecedented growth and prosperity for the middle class.
5. “They Earned It Fair and Square”
Finally, the idea persists that billionaires deserve their wealth because they “earned” it. This argument suggests that any policy aiming to redistribute wealth is fundamentally unfair, penalizing those who worked hard to succeed.
Counterpoints:
• Systemic Advantages and Wealth Hoarding: As previously mentioned, many billionaires begin with advantages—like family wealth or elite educational opportunities—that aren’t available to most people. Additionally, billionaires often employ complex strategies to avoid taxes, lobby for favorable regulations, and capitalize on government subsidies. These factors mean they haven’t earned wealth solely through hard work or merit.
• Billionaires Didn’t Build Alone: No billionaire operates in isolation; they rely on infrastructure, public education, and the work of thousands or millions of employees. A CEO’s wealth is made possible by a web of collective contributions, yet that wealth is rarely shared equitably. While billionaires might be rewarded for their role, their fortune is far from the result of individual effort alone.
In short, these narratives around billionaires often mask a more uncomfortable truth: today’s system is structured in ways that favor the ultra-wealthy at the expense of the broader population. Economic reform, rather than a threat to capitalism, is a necessary step to ensure a more just, equitable society where wealth accumulation doesn’t depend on privilege, influence, or systemic manipulation.
Making a change
Addressing the economic imbalance and the unchecked power of the ultra-wealthy presents a unique challenge, especially given the intense political polarization in the United States. For the middle and lower classes to push back effectively, they will need to build a coalition that transcends party lines and focuses on shared economic interests rather than divisive rhetoric.
1. Build Awareness Through Shared Issues, Not Ideology
The rhetoric around “free markets” and “socialism” often obscures real issues of economic struggle that affect both conservative and progressive working- and middle-class citizens alike. Instead of framing the issue in ideological terms, framing it in terms of tangible, shared grievances can help bridge the divide:
• Focus on Economic Inequality: Income stagnation, unaffordable healthcare, and housing insecurity are felt across the political spectrum. By shifting the narrative from “class warfare” to “economic fairness,” advocates can sidestep partisan language and emphasize the shared experience of economic struggle.
• Highlight the Impact of Corporate Power on Local Communities: Framing issues around how large corporations hurt small, local businesses can resonate strongly with both sides of the political spectrum. This approach often taps into conservative values around community and self-reliance, while also aligning with progressive critiques of corporate overreach.
2. Organize Around Labor Rights and Worker Protections
Historically, unions have been instrumental in improving working conditions and advocating for fair wages, and labor movements transcend political divisions. Many Americans—left, right, and center—share concerns about the erosion of workers’ rights, stagnant wages, and the declining influence of the average worker.
• Expand Union Participation and Labor Movements: Reinvigorating unions and expanding labor protections could give workers a stronger collective voice. New labor movements that focus on economic rights without overtly partisan language could attract support across the political spectrum, particularly when they champion issues like fair wages, workplace safety, and job security.
• Support Worker Cooperatives and Employee-Owned Businesses: Promoting models like worker cooperatives or employee-owned businesses can offer a compelling alternative to the current structure of corporate ownership without resorting to divisive rhetoric. These models prioritize local control and shared economic benefits, appealing to values of self-sufficiency and fairness.
3. Pressure Politicians on Key Economic Policies
A key to bridging the partisan gap is to focus on policies that benefit the broader populace rather than framing them as part of any ideological agenda. The majority of Americans, regardless of political affiliation, support policies like fair taxation, healthcare reform, and increased access to education when framed in terms of fairness and opportunity.
• Promote Tax Reform as “Fairness,” Not Redistribution: Instead of advocating for “redistribution,” proponents can push for tax policies that ensure everyone pays their fair share. Policies like a wealth tax or higher taxes on capital gains can be framed as holding the ultra-wealthy accountable rather than demonizing them, a stance that resonates with people who value fairness and personal responsibility.
• Advocate for Antitrust Legislation: Pushing for stronger antitrust laws to break up monopolies and prevent anti-competitive practices can appeal to both sides. For conservatives, this aligns with the values of market competition; for progressives, it aligns with corporate accountability and consumer protection.
4. Engage in Alternative Media and Independent Journalism
The ultra-wealthy often own or influence major media outlets, which can shape public opinion in ways that protect their interests. For the middle and lower classes to gain a clearer view of economic issues, alternative media sources and independent journalism that aren’t beholden to billionaire interests are crucial.
• Support Independent News Outlets: A growing number of independent news organizations are dedicated to in-depth economic reporting without catering to corporate interests. Supporting these outlets allows individuals to access a range of perspectives that help reveal the true impact of policies on ordinary people.
• Utilize Social Media Responsibly to Build Cross-Party Awareness: Social media, while often a divisive force, can also be used to spread information about economic injustice. When used responsibly to share facts, case studies, and stories of economic hardship, it can cut through the rhetoric and provide people across the political spectrum with a shared understanding of the issues.
5. Prioritize Voting Reform and Campaign Finance Reform
Money in politics is one of the core reasons why economic policies favor the wealthy. Bipartisan support for reducing corporate influence in politics is possible, especially when the focus is on fairness, transparency, and accountability in government.
• Promote Campaign Finance Reform as an Anti-Corruption Effort: Campaign finance reform, which seeks to limit the influence of wealthy donors and corporations on elections, can appeal to conservatives and liberals alike who are frustrated with the influence of money in politics. Instead of framing it as an anti-capitalist measure, framing it as an anti-corruption measure can attract broader support.
• Support Voting Reforms for a More Representative Democracy: Reforms like ranked-choice voting, ending gerrymandering, and preventing voter suppression can help create a political environment that more accurately represents the will of the people rather than special interests. By creating a more representative democracy, policies that reflect the economic needs of the middle and lower classes have a better chance of being enacted.
6. Create Cross-Partisan Grassroots Coalitions Focused on Economic Issues
Many grassroots organizations are focused on economic justice, but they tend to align themselves with one side of the political spectrum, often losing potential support in the process. Building cross-partisan coalitions that emphasize shared economic challenges rather than ideological differences could foster stronger, more united advocacy for middle- and working-class issues.
• Organize Around Issues, Not Parties: Groups like the Poor People’s Campaign, which focuses on poverty and economic justice, have successfully united people across political lines around issues that transcend party loyalty. This approach allows people to focus on their shared struggles, making the movement harder for politicians to ignore.
• Build Community-Level Alliances: Many economic issues are felt acutely at the local level. By focusing on community-level initiatives that address healthcare, affordable housing, and education, people can create practical, on-the-ground solutions that don’t require alignment with national politics. These local successes can serve as models for broader change.
7. Emphasize Civic Education on Economic Policies
Finally, bridging the gap will require education and awareness. Many people accept billionaire-fueled rhetoric because they lack exposure to alternative perspectives. Civic education efforts that focus on teaching economic principles, tax policy, and the influence of corporate power can empower people to understand the real impacts of current policies on their lives.
• Create Accessible Educational Resources: Podcasts, documentaries, workshops, and community discussions can all serve as tools for demystifying economic issues. When people have a clearer understanding of how things like tax policies and wage laws work, they are better equipped to make informed decisions.
• Promote Financial Literacy and Empower Individuals: Financial literacy programs that help individuals understand budgeting, credit, and investments empower people to navigate the economy more effectively. While this doesn’t directly address systemic issues, it gives individuals a greater understanding of the forces shaping their lives and can be a first step toward broader engagement.
By approaching these issues with a focus on shared struggles, fairness, and practical solutions, the middle and lower classes can work together to build a movement that transcends political divides. This movement can challenge the status quo without becoming mired in divisive ideological battles. The real strength of such an effort lies in its ability to unite ordinary people around a common vision for a fairer, more just economic system—one that serves all citizens, not just the wealthiest few.
#capitalism#reality#billionaires#middle class#trickle down economics#facts#economy#economics#wealth#ultra wealthy
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Why do so many feel like they've fallen behind? It's not because of immigrants, trans people, the “deep state,” or any other bogeyman trotted out by the GOP. It's because big corporations and billionaires have rigged markets and siphoned off most of the economy's gains.
792 notes
·
View notes
Text

#capitalism#donald trump#economy#government#democracy#democrats#republicans#the bitch and moan show#trump#trump 2024#maga#ThebitchAndMoanShow#president trump#trump derangement syndrome#trump indictment#biden#indictment#biden crime family#rigged#witch hunt
1 note
·
View note
Text
Watching Elon Musk's fall from grace in real time is so fucking funny. Like obviously I REALLY wish it didn't come at the expense of, you know, my country's government and the world economy and all that, but it's still fucking hilarious to see popular opinion turn on him more and more — precicely because it's his worst nightmare and he fucking deserves it.
Richest bitch in the world, influential enough to rig the US presidential election, but all he really wants is to be worshipped as a man-god. And for a while, he had a large, dedicated fanbase of sorry little dweebs who worshipped the ground he walked on, and everyone else was just like "k."
But it wasn't enough for him — because no one becomes a billionaire unless they have an identity-defining, endless, all-consuming gluttony — so instead of staying relatively in the shadows and just puppeteering politicians like most billionaires, he kept pushing, kept pushing — and now all of China the entire world knows that he's just a shitty little manbaby with no real skills or values developmentally arrested at age 12, pandering to whoever will give him asspats because his giant, fragile ego demands uncritical praise.
Which is to say yesterday he streamed Path of Exile 2 from his fucking private jet and was trolled relentlessly while dying repeatedly to the first tutorial boss until he blatantly faked a disconnect ON CAMERA and abruptly ended the stream. Lmao. lol
318 notes
·
View notes