#richard hanover
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

George IV (1762-1830) when Prince of Wales. By Richard Cosway.
21 notes
·
View notes
Text








Paintings from Buckingham Palace: part I
A retexture by La Comtesse Zouboff — Original Mesh by @thejim07
100 followers gift!
First of all, I would like to thank you all for this amazing year! It's been a pleasure meeting you all and I'm beyond thankful for your support.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the Royal Collection Trust. The British monarch owns some of the collection in right of the Crown and some as a private individual. It is made up of over one million objects, including 7,000 paintings, over 150,000 works on paper, this including 30,000 watercolours and drawings, and about 450,000 photographs, as well as around 700,000 works of art, including tapestries, furniture, ceramics, textiles, carriages, weapons, armour, jewellery, clocks, musical instruments, tableware, plants, manuscripts, books, and sculptures.
Some of the buildings which house the collection, such as Hampton Court Palace, are open to the public and not lived in by the Royal Family, whilst others, such as Windsor Castle, Kensington Palace and the most remarkable of them, Buckingham Palace are both residences and open to the public.
About 3,000 objects are on loan to museums throughout the world, and many others are lent on a temporary basis to exhibitions.
-------------------------------------------------------
This first part includes the paintings displayed in the White Drawing Room, the Green Drawing Room, the Silk Tapestry Room, the Guard Chamber, the Grand Staircase, the State Dining Room, the Queen's Audience Room and the Blue Drawing Room,
This set contains 37 paintings and tapestries with the original frame swatches, fully recolourable. They are:
White Drawing Room (WDR):
Portrait of François Salignan de la Mothe-Fénelon, Archbishop of Cambrai (Joseph Vivien)
Portrait of a Lady (Sir Peter Lely)
Portrait of a Man in Armour with a red scarf (Anthony van Dyck)
Portrait of Alexandra of Denmark, Queen Consort of the United Kingdom and Empress of India (François Flameng)
Green Drawing Room (GDR):
Portrait of Prince James Stuart, Duke of Cambridge (John Michael Wright)
Portrait of Frederick Henry, Charles Louis and Elizabeth: Children of Frederick V and Elizabeth of Bohemia (unknown)
Portrait of Infanta Isabel Clara Eugenia of Autria and her Sister, Infanta Catalina Micaela of Austria (Alonso Sanchez Coello)
Portrait of Princess Louisa and Princess Caroline of the United Kingdom (Francis Cotes)
Portrait of Queen Charlotte with her Two Eldest Sons, Frederick, Later Duke of York and Prince George of Wales (Allan Ramsay)
Portrait of Richard Colley Wellesley, Marquess of Wellesley (Martin Archer Shee)
Portrait of the Three Youngest Daughters of George III, Princesses Mary, Amelia and Sophia (John Singleton Copley)
Silk Tapestry Room (STR):
Portrait of Caroline of Brunswick, Princess of Wales, Playing the Harp with Princess Charlotte (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Portrait of Augusta, Duchess of Brunswick With her Son, Charles George Augustus (Angelica Kauffmann)
Guard Chamber (GC):
Les Portières des Dieux: Bacchus (Manufacture Royale des Gobelins)
Les Portières des Dieux: Venus (Manufacture Royale des Gobelins)
Les Portières des Dieux (Manufacture Royale des Gobelins)
Grand Staircarse (GS):
Portrait of Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen, Queen Consort of Great Britain (Martin Archer Shee)
Portrait of Augustus, Duke of Sussex (Sir David Wilkie)
Portrait of Edward, Duke of Kent (George Dawe)
Portrait of King George III of Great Britain (Sir William Beechey)
Portrait of King William IV of Great Britain when Duke of Clarence (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Portrait of Leopold I, King of the Belgians (William Corden the Younger)
Portrait of Prince George of Cumberland, Later King George V of Hanover When a Boy (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Portrait of Princess Charlotte Augusta of Wales (George Dawe)
Portrait of Queen Charlotte at Frogmore House (Sir William Beechey)
Portrait of Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saafeld, Duchess of Kent (Sir George Hayter)
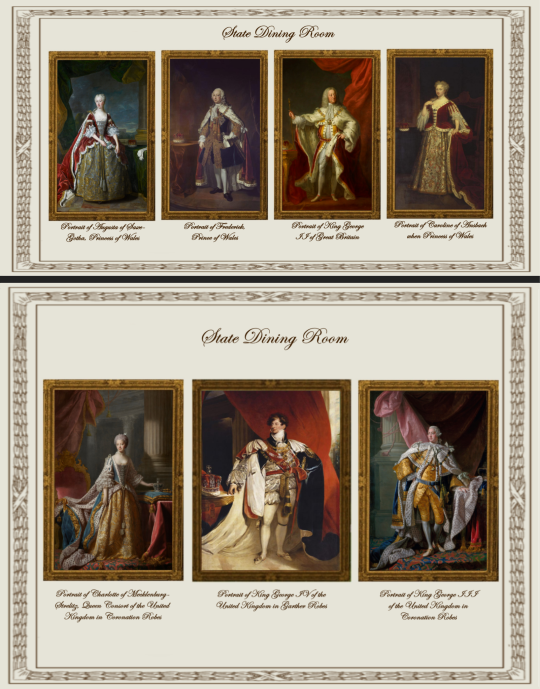
State Dining Room (SDR):
Portrait of Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Consort of the United Kingdom in Coronation Robes (Allan Ramsay)
Portrait of King George III of the United Kingdom in Coronation Robes (Allan Ramsay)
Portrait of Augusta of Saxe-Gotha, Princess of Wales (Jean-Baptiste Van Loo)
Portrait of Caroline of Ansbach when Princess of Wales (Sir Godfrey Kneller)
Portrait of Frederick, Princes of Wales (Jean-Baptiste Van Loo)
Portrait of King George II of Great Britain (John Shackleton)
Portrait of King George IV of the United Kingdom in Garther Robes (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Queen's Audience Room (QAR):
Portrait of Anne, Duchess of Cumberland and Strathearn (née Anne Luttrel) in Peeress Robes (Sir Thomas Gainsborough)
Portrait of Prince Henry, Duke of Cumberland and Strathearn in Peer Robes (Sir Thomas Gainsborough)
London: The Thames from Somerset House Terrace towards the City (Giovanni Antonio Canal "Canaletto")
View of Piazza San Marco Looking East Towards the Basilica and the Campanile (Giovanni Antonio Canal "Canaletto")
Blue Drawing Room (BDR)
Portrait of King George V in Coronation Robes (Sir Samuel Luke Fildes)
Portrait of Queen Mary of Teck in Coronation Robes (Sir William Samuel Henry Llewellyn)
-------------------------------------------------------
Found under decor > paintings for:
500§ (WDR: 1,2 & 3)
1850§ (GDR: 1)
1960§ (GDR: 2 & 3 |QAR 3 & 4)
3040§ (STR, 1 |GC: 1 & 2|SDR: 1 & 2)
3050§ (GC:1 |GS: all 10|WDR: 4 |SDR: 3,4,5 & 6)
3560§ (QAR: 1 & 2|STR: 2)
3900§ (SDR: 7| BDR: 1 & 2|GDR: 4,5,6 & 7)
Retextured from:
"Saint Mary Magdalene" (WDR: 1,2 & 3) found here .
"The virgin of the Rosary" (GDR: 1) found here .
"The Four Cardinal Virtues" (GDR: 2&3|QAR 3 & 4) found here.
"Mariana of Austria in Prayer" (STR, 1, GC: 1 & 2|SDR: 1 & 2) found here.
"Portrait of Philip IV with a lion at his feet" (GC:1 |GS: all 10|WDR: 4 |SDR: 3,4,5 & 6) found here
"Length Portrait of Mrs.D" (QAR: 1 & 2|STR: 2) found here
"Portrait of Maria Theresa of Austria and her Son, le Grand Dauphin" (SDR: 7| BDR: 1 & 2|GDR: 4,5,6 & 7) found here
(you can just search for "Buckingham Palace" using the catalog search mod to find the entire set much easier!)

Drive
(Sims3pack | Package)
(Useful tags below)
@joojconverts @ts3history @ts3historicalccfinds @deniisu-sims @katsujiiccfinds @gifappels-stuff
-------------------------------------------------------
#the sims 3#ts3#s3cc#sims 3#sims 3 cc#sims 3 download#sims 3 decor#edwardian#rococo#baroque#renaissance#buckingham#buckingham palace#royal collection trust#wall decor
129 notes
·
View notes
Text



HI HI HI THIS IS AN INTRO POST
Hi, I’m Celery/Gnome
Minor!!!
I mostly post drawings of historical characters here, used to be super into French history but not so much anymore… the people I draw the most would have to be King Charles II (Stuart), Richard III (Plantagenet), and George IV (Hanover).
Favorite kings list (AKA the ‘Pookie List’)


40 notes
·
View notes
Text
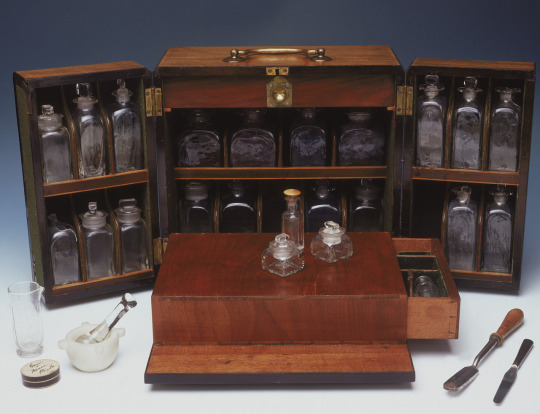

Naval Surgeon's medicine chest, belonging to surgeon Sir Benjamin F. Outram (1774-1856) and reputedly used at the battle of Copenhagen 1801
Outram was first employed in the naval medical service in 1794, and was promoted to the rank of surgeon in 1796. He served in HMS Harpy, HMS La Nymphe, and HMS Boadicea. He was surgeon in HMS Superb in the second battle of Algeciras, where Sir James Saumarez obtained a victory over the French and Spanish fleets on 12 July 1801. He received war medals and clasps for his services under Sir Richard Goodwin Keats. Then for a period he was surgeon to the royal yacht, HMS Royal Sovereign.
In 1806, with a view to private practice, Outram went to Edinburgh, and there graduated doctor of medicine on 24 June 1809. He was admitted a licentiate of the Royal College of Physicians of London on 16 April 1810, and then began as a physician at Hanover Square in London, where he lived more than 40 years. He acted as physician to the Welbeck Street Dispensary. On 3 May 1838 he was elected a fellow of the Royal Society; he also became an early member of the Royal Geographical Society.
In 1841 Outram became medical inspector of her Majesty's fleets and hospitals. He was appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath (KCB) on 17 September 1850, and was admitted a fellow of the Royal College of Physicians on 9 July 1852. He died at Brighton on 16 February 1856, and was buried at Clifton, Bristol.
#naval history#naval artifacts#medicine chest#sir benjamin outram#battle of copenhagen#naval surgeon#early 19th century#age of sail#history
114 notes
·
View notes
Text









⋆ William, The Conqueror to William, The Prince of Wales ⋆
⤜ The Prince of Wales is William I's 24th Great-Grandson via his paternal grandmother's line.
William I of England
Henry I of England
Empress Matilda
Henry II of England
John of England
Henry III of England
Edward I of England
Edward II of England
Edward III of England
Lionel of Antwerp, Ist Duke of Clarence
Philippa Plantagenet, Vth Countess of Ulster
Roger Mortimer, IVth Earl of March
Anne Mortimer
Richard Plantagenet, IIIrd Duke of York
Edward IV of England
Elizabeth of York
Margaret Tudor
James V of Scotland
Mary Stewart, Queen of Scotland
James I of England
Elizabeth Stuart, Queen of Bohemia
Sophia, Electress of Hanover
George I of Great Britain
George II of Great Britain
Frederick, Prince of Wales
George III of the United Kingdom
Prince Edward Augustus, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
Victoria of the United Kingdom
Edward VII of the United Kingdom
George V of the United Kingdom
George VI of the United Kingdom
Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom
Charles III of the United Kingdom
William, The Prince of Wales
#royal line from william i#the british royal line#british royal family#british royals#royalty#royals#british royalty#brf#royal#royalty edit#mine.#historical royals#prince william#prince of wales#the prince of wales#william the conqueror#king edward iv#the plantagenets#house of york#house of plantagenet#house of tudor#house of stewart#house of stuart#king charles#king charles iii#queen elizabeth ii#queen victoria#house of normandy#mary queen of scots
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
List of attendees to the service of Thanksgiving to the late King Constantine of Greece on 27th February 2024.
🇬🇧 Queen Camilla
🇬🇧 Princess Anne
🇬🇧 Sir Tim Laurence
🇬🇧 Princess Beatrice
🇬🇧 Edoardo Mapelli Mozzi
🇬🇧 Zara Tindall
🇬🇧 Mike Tindall
🇬🇧 Lady Sarah Chatto
🇬🇧 Daniel Chatto
🇬🇧 Prince Richard, The Duke of Gloucester
🇬🇧 Birgitte, The Duchess of Gloucester
🇬🇧 Prince Edward, The Duke of Kent
🇬🇧 George, The Earl of St. Andrews
🇬🇧 Sylvana, The Countess of St. Andrews
🇬🇧 Lady Helen Taylor
🇬🇧 Prince Michael of Kent
🇬🇧 Princess Michael of Kent
🇬🇧 Princess Alexandra of Kent
🇬🇧 James Ogilvy
🇬🇧 Julia Ogilvy
🇬🇧 Marina Ogilvy
🇬🇧 George, The Marquess of Milford Haven
🇬🇧 Clare, The Marchioness of Milford Haven
🇬🇧 Penny, The Countess Mountbatten of Burma
🇬🇧 Lady Alexandra Hooper
🇬🇧 Thomas Hooper
🇬🇧 India Hicks
🇬🇧 David Flint Wood
🇬🇧 Amory Wood-Hicks
🇬🇧 Prince Andrew, The Duke of York
🇬🇧 Sarah Ferguson
🇬🇷 Queen Anne-Marie
🇬🇷 Crown Prince Pavlos
🇬🇷 Crown Princess Marie-Chantal
🇬🇷 Prince Achileas-Andreas
🇬🇷 Prince Odysseas-Kimon
🇬🇷 Prince Aristides-Stavros
🇬🇷 Princess Maria-Olympia
🇬🇷 Prince Nikolaos
🇬🇷 Princess Tatiana
🇬🇷 Prince Philippos
🇬🇷 Princess Nina
🇬🇷 Princess Theodora
🇬🇷 Matthew Kumar
🇬🇷 Princess Alexia
🇬🇷 Carlos Morales
🇬🇷 Princess Irene
🇪🇸 King Juan Carlos
🇪🇸 Queen Sofia
🇪🇸 King Felipe
🇪🇸 Queen Letizia
🇪🇸 Infanta Elena
🇪🇸 Infanta Cristina
🇪🇸 Juan Urdangarian
🇩🇰 Princess Benedikte
🇩🇰 Prince Gustav
🇩🇰 Princess Carina of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg
🇩🇰 Princess Alexandra of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg, Countess Ahlefeldt-Laurvig-Bille
🇩🇰 Count Michael Ahlefeldt-Laurvig-Bille
🇯🇴 Queen Noor of Jordan
🇯🇴 Prince Hassan
🇯🇴 Princess Sarvath of Jordan
🇧🇬 Prince Kyril of Bulgaria
🇷🇸 Crown Prince Alexander of Serbia
🇷🇸 Crown Princess Katherine of Serbia
🇩🇪 Bernhard, Margrave of Baden
🇩🇪 Stephanie, Margravine of Baden
🇩🇪 Landgrave Donatus of Hesse
🇩🇪 Hereditary Prince Ernst August of Hanover
🇩🇪 Princess Saskia of Hohenlohe-Langeburg
Other notable attendees
Nicholas Soames (Conservative politician)
Rocco Forte (British Hotelier)
Hugh Cavendish, Baron Cavendish of Furness (Former member of the House of Lords)
Grania Mary Caulfield (wife of Baron Cavendish of Furness)
John Kerry (United States Special Presidential Envoy for Climate
Lady Susan Hussey (Lady-in-Waiting)
Sir Jackie Stewart (Racecar Driver and good family friend)
Alexandra von Fürstenberg (American Socialite)
Dax Miller (Alexandra von Fürstenbergs husband)
#i did this for the coronation so i thought i’d do this again#there will be more people who attended so if i missed anyone significant plz dm me#king constantine ii thanksgiving service#british royal family#greek royal family#danish royal family#spanish royal family
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

We can’t let Marshal Davout get all the love today—it’s Lasalle’s birthday too (10 May 1775). And I like him more than Davout anyway. Ahem. Here’s a little tribute to him I translated from an old French book.
The name of Lasalle has remained legendary in the French cavalry. His military life, so short and full of glory, his extraordinary acts of vigor and bravery during the Egyptian campaign recalling the prowess of a Richard the Lionheart, his audacity always crowned with success in Italy, Prussia, Spain, the surrender of the fort of Stettin immortalized by a portrait by Gros in which we see Lasalle awaiting, with a proud attitude, the Prussian governor who brought him the keys of the town, his death in full triumph at the age of thirty-four years while leading the final charges which would decide the victory of Wagram, have surrounded his memory with an unequalled prestige. He died on time. He did not know the reverses in the face of which so many characters have weakened.
Count of the Empire in 1808, provided with rich dotations in Hanover and Westphalia, he rejected the selfish thoughts to which the dignitaries of the First Empire had too often yielded. His compatriot Roederer, having met him in Spain, recounted a conversation he had had with him on 28 April 1809, several weeks before his death. Roederer had told him: “One must take care of his life when it can be useful.” – “Me,” replied Lasalle, “I have lived enough by now. What does one want to live for? To bring himself honor, to make his way, his fortune; ah well! I’m thirty-three years old, I am a general of division. –Do you know that the Emperor gave me a pension of fifty thousand livres last year? That is immense!” –And as Roederer observed to him that in order to enjoy all of this he should avoid useless and inglorious dangers: “No! Not at all,” he cried; “one rejoices in welcoming all of that, one rejoices in waging war. It is already a great enough pleasure to wage war; one is in the noise, in the smoke, in the movement; and then, when one has made his name, he has enjoyed the pleasure of making it; when one has made his fortune, one is sure that his wife, his children will want for nothing. All of this, is enough: me, I could die tomorrow.”
Source: D'Essling à Wagram. Lasalle: correspondence recueillie par Robinet de Clery. 1891. Pages 1-2.
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

Bibliography, Acknowledgements, and About the Author
Agee, James, and Walker Evans. Let Us Now Praise Famous Men. Boston: Mariner Books, 1988.
Albrecht, Gerd. Nationalsozialistische Filmpolitik: Eine soziologische Untersuchung über die Spielfilme des Dritten Reiches. Stuttgart: Ferdinand Enke, 1969.
Alter, Robert, and Frank Kermode, eds. The Literary Guide to the Bible. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press, 1987.
Arendt, Hannah. The Origins of Totalitarianism. New York: Harcourt, 1979.
Armstrong, Karen. The Battle for God. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2000.
Ault, James M., Jr. Spirit and Flesh: Life in a Fundamentalist Baptist Church. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2004.
Barton, David. A Spiritual Heritage: Tour of the United States Capitol. Aledo, TX: WallBuilder Press, 2000.
Bartov, Omer. Mirrors of Destruction: War, Genocide, and Modern Identity. New York: Oxford University Press, 2000.
Beach, George Kimmich, ed. The Essential James Luther Adams: Selected Essays and Addresses. Boston: Skinner House Books, 1998.
Beliles, Mark A., and Stephen K. McDowell. America’s Providential History. Charlottesville, VA: Providence Foundation, 1989.
Bellant, Russ. The Coors Connection: How Coors Family Philanthropy Undermines Democratic Pluralism. Boston: South End Press, 1991.
———. Old Nazis, the New Right, and the Republican Party: Domestic Fascist Networks and Their Effect on U.S. Cold War Politics. Boston: South End Press, 1991.
Belt, Don, ed. The World Of Islam. Washington, DC: National Geographic, 2001.
Biros, Florence W. Crossing Paths Treasury. Vol. 1. New Wilmington, PA: Son-Rise Publications, 1998.
Bonhoeffer, Dietrich. Life Together: The Classic Exploration of Faith in Community. Translated by John W. Doberstein. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1954.
Brinton, Crane. The Anatomy of Revolution. New York: Random House, 1965.
Brown, Karen McCarthy. “Fundamentalism and the Control of Women.” In Fundamentalism and Gender. Edited by John Stratton Hawley. New York: Oxford University Press, 1994.
Burke, Theresa, and David C. Reardon. Forbidden Grief: The Unspoken Pain of Abortion. Springfield, IL: Acorn Books, 2002.
Cantor, David. The Religious Right: The Assault on Tolerance and Pluralism in America. Edited by Alan M. Schwartz. New York: Anti-Defamation League, 1994.
Carter, Jimmy. Our Endangered Values: America’s Moral Crisis. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2005.
Chrnalogar, Mary Alice. Twisted Scriptures: Breaking Free From Churches That Abuse. Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan Publishing House, 2000.
Clarkson, Frederick. Eternal Hostility: The Struggle Between Theocracy and Democracy. Monroe, ME: Common Courage Press, 1997.
Coffin, William Sloane. The Heart Is a Little to the Left: Essays on Public Morality. Hanover, NH: University Press of New England, 1999.
Cohen, Edmund D. The Mind of the Bible Believer. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books, 1988.
Crossan, John Dominic. Jesus: A Revolutionary Biography. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1994.
Crossman, Richard H., ed. The God That Failed. Chicago, IL: Regnery Gateway, Inc., 1949.
De Vries, Hentde, and Samuel Weber, eds. Religion and Media. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2001.
Diamond, Sara. Not by Politics Alone: The Enduring Influence of the Christian Right. New York: The Guilford Press, 1998.
———. Roads to Dominion: Right-Wing Movements and Political Power in the United States. New York: The Guilford Press, 1995.
——— Spiritual Warfare: The Politics of the Christian Right. Boston: South End Press, 1989.
Dobson, James. Bringing Up Boys. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2001.
——— Dare to Discipline. New York: Bantam Books, 1970.
——— Marriage Under Fire: Why We Must Win This Battle. Sisters, OR: Multnomah, 2004.
Douglass, Frederick. “What, to the Slave, Is the Fourth of July? (1852).” In Lift Every Voice: African American Oratory, 1787–1900. Edited by Philip S. Foner and Robert James Branham. Tuscaloosa: University of Alabama Press, 1998.
——— Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself (1845). New York: Signet Books, 1968.
Ehrman, Bart D. The New Testament: A Historical Introduction to the Early Christian Writings. Third Edition. New York: Oxford University Press, 2004.
Fenn, Richard K. Dreams of Glory: The Sources of Apocalyptic Terror. Burlington, VT: Ashgate Publishing Company, 2006.
Frank, Thomas. What’s the Matter with Kansas: How Conservatives Won the Heart of America. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 2004.
Frazier, Gary. Signs of the Coming of Christ. Arlington, TX: Discovery Ministries, 1998.
Freud, Sigmund. Civilization and Its Discontents. Edited and translated by James Strachey. New York: W. W. Norton and Company, 1961.
Friedman, Richard Elliott. Who Wrote the Bible. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1989.
Gallup, George, Jr., and Jim Castelli. The People’s Religion: American Faith in the 90s. New York: Macmillan, 1989.
Ghosh, Amitav. Incendiary Circumstances: A Chronicle of the Turmoil of Our Times. New York: Houghton Mifflin Company, 2005.
Goebbels, Joseph. Signale der neuen Zeit. Munich: Eher, 1934.
Goldberg, Michelle. Kingdom Coming: The Rise of Christian Nationalism. New York: W. W. Norton and Company, 2006.
Goodrich, Chris. Faith Is a Verb: On the Home Front with Habitat for Humanity in the Campaign to Rebuild America (and the World). Brookfield, CT: Gimlet Eye Books, 2005.
Green, John C., Mark J. Rozell, and Clyde Wilcox, eds. The Christian Right in American Politics: Marching to the Millennium. Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press, 2003.
Grossman, Vasily. Life and Fate. Translated by Robert Chandler. New York: Harper and Row, 1985.
Harding, Susan Friend. The Book of Jerry Falwell: Fundamentalist Language and Politics. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2000.
Harris, Sam. The End of Faith: Religion, Terror, and the Future of Reason. New York: W. W. Norton and Company, 2004.
Hassan, Steven. Combatting Cult Mind Control. Rochester, VT: Park Street Press, 1998.
Heinemann, Larry. Black Virgin Mountain: A Return to Vietnam. New York: Doubleday, 2005.
Hitchcock, Mark. 101 Answers to the Most Asked Questions About the End Times. Sisters, OR: Multnomah Publishers, 2001.
Hoover, Stewart M., and Lynn Schofield Clark, eds. Practicing Religion in the Age of the Media: Explorations in Media, Religion, and Culture. New York: Columbia University Press, 2002.
Horton, Ronald A., ed. Christian Education: Its Mandate and Mission. Greenville, SC: Bob Jones University Press, 1992.
Hughes, Richard T. Myths America Lives By. Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press, 2004.
James, William. The Varieties of Religious Experience. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications, Inc., 2002.
Jenkins, Jerry B., Tim LaHaye, with Chris Faby. The Rise of False Messiahs: Left Behind: The Kids. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale Press, 2004.
Juergensmeyer, Mark. Terror in the Mind of God: The Global Rise of Religious Violence. Third Edition. Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2003.
Kaplan, Esther. With God on Their Side: How Christian Fundamentalists Trampled Science, Policy, and Democracy in George W. Bush’s White House. New York: New Press, 2004.
Kennedy, D. James. Evangelism Explosion. Fourth Edition. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1996.
Kennedy, D. James, and Jim Nelson Black. Character and Destiny: A Nation in Search of Its Soul. Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan Publishing, 1994.
Kennedy, D. James, with Jerry Newcombe. The Gates of Hell Shall Not Prevail. Nashville, TN: Thomas Nelson Publishers, 1996.
———. Lord of All: Developing a Christian World-and-Life View. Wheaton, IL: Crossway Books, 2005.
———. What If America Were a Christian Nation Again? Nashville, TN: Thomas Nelson Publishers, 2003.
Kepel, Gilles. The War for Muslim Minds: Islam and the West. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press, 2004.
Kintz, Linda, and Julia Lesage, eds. Media, Culture, and the Religious Right. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1998.
Klemperer, Victor. I Will Bear Witness 1933–1941: A Diary of the Nazi Years. Translated by Martin Chalmers. New York: Modern Library, 1999.
———. I Will Bear Witness 1942–1945: A Diary of the Nazi Years. Translated by Martin Chalmers. New York: The Modern Library, 1999.
Koonz, Claudia. The Nazi Conscience. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press, 2003.
Kugel, James L. The Bible As It Was. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press, 1997.
LaHaye, Tim, with Steve Halliday. The Merciful God of Prophecy: His Loving Plan for You in the End Times. New York: Warner Faith, 2002.
LaHaye, Tim, and Ed Hindson. The Popular Bible Prophecy Workbook. Eugene, OR: Harvest House Publishers, 1982.
LaHaye, Tim, and Thomas Ice. Charting the End Times. Eugene, OR: Harvest House Publishers, 2001.
LaHaye, Tim, and Jerry B. Jenkins. Apollyon: The Destroyer Is Unleashed. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1999.
———. Armageddon: The Cosmic Battle of the Ages. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2003.
———. Assassins: Assignment: Jerusalem, Target: Antichrist. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1999.
———. Desecration: Antichrist Takes the Throne. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2001.
———. Glorious Appearing: The End of Days. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2004.
———. The Indwelling: The Beast Takes Possession. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2000.
———. Left Behind: A Novel of the Earth’s Last Days. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1995.
———. The Mark: The Beast Rules the World. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2000.
———. Nicolae: The Rise of Antichrist. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1997.
———. Remnant: On the Brink of Armageddon. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 2002.
———. Soul Harvest: The World Takes Sides. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1998.
———. Tribulation Force: The Continuing Drama of Those Left Behind. Wheaton, IL: Tyndale House Publishers, 1996.
Lakoff, Mark. Moral Politics: How Liberals and Conservatives Think. Second Edition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2002.
Larson, Edward J. Summer for the Gods: The Scopes Trial and America’s Continuing Debate over Science and Religion. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1997.
Leonard, Bill J. Baptists in America. New York: Columbia University Press, 2005.
Lewis, Sinclair. It Can’t Happen Here. New York: Penguin Books, 1963.
Lifton, Robert Jay. Thought Reform and the Psychology of Totalism: A Study of Brainwashing in China. New York: W. W. Norton and Company, 1961.
Loehr, Davidson. America, Fascism and God: Sermons from a Heretical Preacher. White River Junction, VT: Chelsea Green Publishing Company, 2005.
Maharidge, Dale, with photographs by Michael Williamson. And Their Children After Them: The Legacy of Let Us Now Praise Famous Men: James Agee, Walker Evans, and the Rise and Fall of Cotton in the South. New York: Seven Stories Press, 2004.
———. Denison, Iowa: Searching for the Soul of America Through the Secrets of A Midwest Town. New York: Free Press, 2005.
———. Homeland. New York: Seven Stories Press, 2004.
———. Journey to Nowhere: The Saga of the New Underclass. New York: Hyperion, 1996.
Maimon, Solomon. Solomon Maimon: An Autobiography. Translated by J. Clark Murray. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 2001.
Manseau, Peter. Vows: The Story of a Priest, a Nun, and Their Son. New York: Free Press, 2005.
Martin, William. With God on Our Side: The Rise of the Religious Right in America. New York: Broadway Books, 1996.
Marty, Martin E., and R. Scott Appleby. The Glory and the Power: The Fundamentalist Challenge to the Modern World. Boston: Beacon Press, 1992.
———. The Fundamentalism Project. 5 vols. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1991–95.
McGirr, Lisa. Suburban Warriors: The Origins of the New American Right. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2001.
Meerloo, Joost A. M. The Rape of the Mind: The Psychology of Thought Control, Menticide, and Brainwashing. Cleveland and New York: The World Publishing Company, 1956.
Mendelssohn, Moses. Jerusalem: Or On Religious Power and Judaism. Translated by Allan Arkush. Introduction and Commentary by Alexander Altmann. Lebanon, NH: University Press of New England, 1983.
Niebuhr, Reinhold. The Irony of American History. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1952.
Niebuhr, Reinhold. Justice and Mercy. Edited by Ursula M. Niebuhr. New York: Harper & Row, 1974.
Nock, A. D. Conversion: The Old and the New in Religion from Alexander the Great to Augustine of Hippo. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1998.
O’Leary, Stephen D. Arguing the Apocalypse: A Theory of Millennial Rhetoric. New York: Oxford University Press, 1994.
Ortega y Gasset, José. The Revolt of the Masses. Translated by Anthony Kerrigan. Edited by Kenneth Moore. Notre Dame, IN: University of Notre Dame Press, 1985.
Orwell, George. 1984. New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, 1977.
Palmer, Laura. Shrapnel in the Heart: Letters and Remembrances from the Vietnam Veterans Memorial. New York: Random House, 1987.
Paxton, Robert O. The Anatomy of Fascism. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2004.
Phillips, Kevin. American Dynasty: Aristocracy, Fortune, and the Politics of Deceit in the House of Bush. New York: Penguin Group, 2004.
Popper, Karl. R. The Open Society and Its Enemies: The Spell of Plato. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1966.
Postman, Neil. Amusing Ourselves to Death: Public Discourse in the Age of Show Business. New York: Penguin Books, 1986.
Press, Bill. How the Republicans Stole Christmas: The Republican Party’s Declared Monopoly on Religion and What Democrats Can Do to Take It Back. New York: Doubleday, 2005.
Prothero, Stephen. American Jesus: How the Son of God Became a National Icon. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 1985.
Riley, Naomi Schaefer. God on the Quad: How Religious Colleges and the Missionary Generation Are Changing America. New York: St. Martin’s Press, 2005.
Robertson, Pat. The New World Order. Dallas: Word Publishing, 1991.
Rossing, Barbara R. The Rapture Exposed: The Message of Hope in the Book of Revelation. New York: Basic Books, 2004.
Rushdoony, Rousas John. The Institutes of Biblical Law. Dallas, TX: The Craig Press, 1973.
Saloma, John S., III. Ominous Politics: The New Conservative Labyrinth. New York: Hill and Wang, 1984.
Sargant, William. Battle for the Mind: A Physiology of Conversion and Brain-Washing. Cambridge, MA: ISHK, 1997.
Singer, Margaret Thaler. Cults in Our Midst: The Continuing Fight Against Their Hidden Menace. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 2003.
Smith, Christian. Christian America?: What Evangelicals Really Want. Los Angeles: University of California Press, 2000.
Smith, Chuck. Calvary Chapel Distinctives. Costa Mesa, CA: The Word for Today Publishers, 2004.
Smith, Wilfred Cantwell. What Is Scripture: A Comparative Approach. Minneapolis, MN: Fortress Press, 1993.
Spong, John Shelby. Rescuing the Bible from Fundamentalism: A Bishop Rethinks the Meaning of Scripture. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1991.
Stein, Stephen J. The Encyclopedia of Apocalypticism, Vol. 3. Apocalypticism in the Modern Period and the Contemporary Age. New York: Continuum, 1999.
Stern, Fritz. The Politics of Cultural Despair: A Study in the Rise of the Germanic Ideology. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1989.
Stern, Jessica. The Ultimate Terrorists. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1999.
Strozier, Charles B. Apocalypse: On the Psychology of Fundamentalism in America. Eugene, OR: Wipf and Stock Publishers, 2002.
Theweleit, Klaus. Male Fantasies, Vol. 1. Women, Floods, Bodies, History. Translated by Stephen Conway. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1987.
———. Male Fantasies, Vol. 2. Male Bodies: Psychoanalyzing the White Terror. Translated by Erica Carter and Chris Turner. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1989.
Tillich, Paul. The Shaking of the Foundations. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1948.
Todorov, Tzvetan. The Conquest of America. New York: HarperCollins, 1992.
———. Facing the Extreme: Moral Life in the Concentration Camps. Translated by Arthur Denner and Abigail Pollak. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1997.
———. Hope and Mercy: Lessons from the Twentieth Century. Translated by David Bellos. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2003.
Twain, Mark. The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn. New York: Charles L. Webster and Company, 1885.
Wallis, Jim. God’s Politics: Why the Right Gets It Wrong and the Left Doesn’t Get It. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 2005.
Whitcomb, John C., and Henry M. Morris. The Genesis Flood: The Biblical Record and Its Scientific Implications. Phillipsburg, NJ: P & R Publishing, 1960.
White, Mel. Stranger at the Gate: To Be Gay and Christian in America. New York: Plume, 1995.
Wills, Garry. Under God: Religion and American Politics. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1990.
Winn, Denise. The Manipulated Mind: Brainwashing, Conditioning and Indoctrination. Cambridge, MA: Malor Books, 2000.
Wolfe, Alan. The Transformation of American Religion: How We Actually Live Our Faith. New York: Free Press, 2003.
Wright, Stuart A., ed. Armageddon in Waco: Critical Perspectives of the Branch Davidian Conflict. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1995.
Acknowledgments
This book was written with the generous and unstinting support of the Nation Institute, which allowed me to work unfettered for many months on this project. I am deeply grateful for this support and encouragement, especially that of Hamilton Fish, Taya Grobow, Janine Jaquet and Jonathan Schell, as well as Peggy Suttle and Katerina vanden Heuvel at magazine. I also owe a huge debt to Princeton University, where I teach in the Program in American Studies. R. Sean Wilentz and Judith S. Ferszt, as well as C. K. “Charlie” Williams, Elaine Pagels, Sam and Liz Hynes, and many of my dedicated and brilliant students always lent encouragement and advice. I am blessed with supportive and thoughtful friends and colleagues.
Pamela Diamond, for the second time, oversaw the research and organization of a book of mine with her usual skill, patience, dedication and good humor. I cannot imagine having to go through this without her. Rebecca Beyer, a talented reporter and writer, worked extensively on the book, carrying out some interviews and attending events. She was a close and valued collaborator. Elyse Graham and Amy Paeth, two of my students at Princeton, did tremendous and important research, especially under heavy time pressure in the closing days of production. Timothy Nunan, another Princeton student, did a fine job documenting creationist attacks on Charles Darwin and evolution. I benefited greatly from his research. Lisa Winn, Lauren Brown, James Arnold, Maria Guerrero-Reyes, Linda Kane, Kate Peters, Jason Proske, Colin Maier, Moya Quinlan-Walshe and Kathryn Tippett constituted our small army of transcribers. I turned over hours of tape to them and relied on their care and dedication to produce the transcripts. I owe a tremendous debt to those few who have been among the first to investigate and explain dominionism. They include Katherine Yurica, who produces the available online; Frederick Clarkson, whose three-part series in PublicEye.org in March/June 1994 called “Christian Reconstructionism” was a groundbreaking piece of journalism and who continues to do important research into the movement; and Sarah Diamond, whose books, such as are indispensable.
I owe thanks for vital help and support from Bernard Rapoport and Paul Lewis, as well as Patrick Lannan, Ralph Nader, Jenny Ford, Joan Bokaer, Mariah Blake, Cristina Nehring, Ann and Walter Pincus, Lauren B. Davis, June Ballinger, Michael Goldstein, Anne Marie Macari, Robert J. Lifton, Richard Fenn, Fritz Stern, Robert O. Paxton, Charles B. Strozier, Irene Brown, Joe Sacco, Al Ross, the Reverend Mel White, the Reverend Davidson Loehr, the Reverend Ed Bacon, Bishop Krister Stendhal, the Reverend William Sloane Coffin, the Reverend Joe Hough, the Reverend Michael Granzen and the Reverend Terry Burke. The Reverend Coleman Brown, as he has done with all my books, read and critiqued each chapter. Coleman again let me rely on his profound insight and wisdom. As usual, he raised questions and offered critiques that often forced me to reconsider my position or go back to my research. Max Blumenthal, a friend and fine reporter, nursed me through much of this with sage help and advice. I would like to thank Marji Mendelsohn and Janice Weiss for guidance and research, as well as Tamar Gordon, whose advice and scholarship helped me head in the right direction. Tom Artin, as talented a jazz musician as he is a scholar and writer, went through every chapter, as did my wife, Kim Hedges, who always saves me from being too sententious and ponderous with the stroke of her red pen, her gentle smile and common sense. Barbara Moses, the gifted painter, again came to our aid with her amazing eye for detail and her iron command of grammar.
I often leaned for emotional support on my friend John “Rick” MacArthur, who keeps alive magazine, one of the great intellectual journals in America, as well as my friend the poet Gerald Stern, who appeared frequently as I was writing to drag me into the sunlight for lunch and impart needed encouragement.
My editors at Free Press, especially Dominick Anfuso and Wylie O’Sullivan, patiently edited, shaped and formed the text. I would also like to thank Michele Jacob. Lisa Bankoff of International Creative Management held my hand, for the fourth time, through this process of proposal to contract to delivery. She is a gift.
About the Author
Chris Hedges, a graduate of Harvard Divinity School, was a foreign correspondent for nearly 20 years. He was the bureau chief in the Middle East and the Balkans, and worked in other foreign posts, for The New York Times from 1990 to 2005. He worked previously for The Dallas Morning News, National Public Radio and The Christian Science Monitor in Latin America and the Middle East. He has reported from more than 50 countries. Hedges was a member of the New York Times team that won the 2002 Pulitzer Prize for Explanatory Reporting for the paper’s coverage of global terrorism, and he received the 2002 Amnesty International Global Award for Human Rights Journalism. He holds a B.A. in English Literature from Colgate University and a Master of Divinity from Harvard Divinity School. Hedges has taught at Columbia University, New York University and Princeton University, where he is currently a Visiting Lecturer in the Council of the Humanities and the Program in American Studies as well as the Anschutz Distinguished Fellow. He has written for Foreign Affairs, Granta, Harper’s, Mother Jones and The New York Review of Books. Hedges is the author of War Is a Force That Gives Us Meaning—a finalist for the National Book Critics Circle Award for Nonfiction. His other books are What Every Person Should Know About War and Losing Moses on the Freeway: The 10 Commandments in America. He lives in New Jersey.
#christianity#fascism#right-wing#us politics#xtians#United States of America#christians#anarchism#anarchy#anarchist society#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#resistance#autonomy#revolution#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#daily posts#libraries#leftism#social issues#anarchy works#anarchist library#survival#freedom
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Royal Godparents to Royal Godchildren
I did this list back in 2012, and got some great responses. I've updated and edited parts of the list. Again, any corrections and/or adds, message me! Thanks in advance!
When choosing godparents for their children, the parents often chose friends or other relatives. Often in royal circles, royals also pick other royals. Here’s a partial list. (Yes, I know some lists are incompelte as some of these royals’s godchildren are not royals themselves.) If you have any additions, please feel free to message me!
Belgium
King Baudouin I
Princess Marie-Christine of Belgium (1951)
King Leopold III
Princess Beatrix of The Netherlands (1938)
Princess Marie-Astrid of Luxembourg (1954)
King Philippe of The Belgians (1960)
Queen Astrid
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
King Albert II
Princess Marie-Esméralda of Belgium (1956)
Queen Paola
Prince Amedeo of Belgium, Archduke of Austria-Este (1986)
King Philippe
Prince Amedeo of Belgium, Archduke of Austria-Este (1986)
Princess Marie Gabrielle de Nassau (1986)
Queen Matilde
Princess Alexia of The Netherlands (2005)
Princess Isabella of Denmark (2007)
Princess Astrid, Archduchess of Austria-Este
Prince Sébastien of Luxembourg (1992)
Prince Amedeo, Archduke of Austria-Este
Princess Elisabeth of Belgium, The Duchess of Brabant (2001)
Princess Claire
Princess Eléonore of Belgium(2008)
Prince Lorentz, The Archduke of Austria-Este
Prince Carl-Johan de Nassau (1992)
Bulgaria
Queen Margarita
Prince Umberto of Bulgaria (1999)
Konstantin-Assen, Prince of Vidin, Duke of Saxony
Infanta Sofia of Spain (2007)
Princess Rosrio
Doña Irene de Todos los Santos Urdangarín y de Borbón (2005)
Denmark
Queen Ingrid
Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon (1930)
King Carl XVI of Sweden (1946)
King Christian X
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
Queen Alexandrine
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
Princess Dagmar
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
Princess Thyra
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
King Fredrick IX
King Carl XVI of Sweden (1946)
Queen Margarethe II
King Williem-Alexander of The Netherlands (1967)
Crown Prince Hakon of Norway (1973)
Prince Carl Phillip of Sweden (1979)
Crown Prince Fredrick of Denmark
Count Nikolai af Monzepat (1999)
Countess Ingrid Alexandra Irma Astrid Benedikte von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (2003)
Princess Ingrid Alexandra of Norway (2004)
Prince Oscar Carl Olof of Sweden, Duke of Skane (2016)
Crown Princess Mary
Count Henrik af Monzepat (2009)
Konstantin Gustav Heinrich Richard Johannsmann (2010)
Princess Estelle of Sweden (2012)
Prince Christian
Prince Gustav Alberct of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleberg (2023)
Princess Marie
Princess Josephine of Denmark (2011)
Princess Caroline-Mathilde
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
Princess Elisabeth
Theodor Christian Emmanuel Rosanes af Rosenborg (2009)
Princely Family of Lieiningen
Princess Alexandra
Princess Alexandra Charlotte Ulrike Maryam Virgina of Hanover (1999)
Princely Family of Hanover
Princess Sophie of Hanover
Prince Edward, The Duke of Edinburgh (1964)
Princely Family of Hesse
Prince Philipp
Count Friedrich Richard Oscar Jefferson von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (1999)
Princely Family of Waldeck and Pyrmont
Princess Elisabeth
Princess Beatrix of The Netherlands (1938)
Princely Family of Liechtenstein
Prince Constantin
Prince Georg Antonius of Liechtenstein (1999)
Princess Margaretha
Archduke Imre of Austria (1985)
Princess Louise of Belgium (2004)
Princely Family of Monaco
Prince Albert
Baron Jean-Leonard Taubert-Natta (1974)
Pierre Rainier Stefano Casiraghi (1987)
Louis Robert Paul Ducruet (1992)
Pauline Grace Maguy Ducruet (1994)
Raphaël Casiraghi Elmaleh (2013)
Princess Charlene
Raphaël Casiraghi Elmaleh (2013)
Princess Caroline of Hanover
Louis Robert Paul Ducruet (1992)
Pauline Grace Maguy Ducruet (1994)
Princess Stephanie
Andrea Albert Pierre Casiraghi (1984)
Charlotte Marie Pomeline Casiraghi
Princess Alexandra Charlotte Ulrike Maryam Virgina of Hanover (1999)
Baroness Elisabeth Anne de Massy
Princess Stephanie of Monaco, Countess of Polinac (1965)
The Netherlands
Queen Juliana
King Carl XVI of Sweden (1946)
Queen Anne-Marie of Denmark (1946)
King Williem-Alexander
Count Claus-Casmir van Orange-Nassau, Jonkheer van Amsberg (2004)
Countess Zaria of Oranje-Nassau (2006)
Princess Estelle of Sweden (2012)
Prince Constantijn
Princess Catharina-Amalia of The Netherlands, The Princess of Orange (2003)
Countess Luana of Orange-Nassau, Jonkvrouwe van Amsberg (2005)
Prince Friso
Countess Eloise van Orange-Nassau, Jonkvrouwe van Amsberg (2002)
Princess Alexia of the Netherlands (2005)
Norway
King Haakon VII
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
Queen Maud
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner(1932)
King Olav V
Princess Margriet Francisca of the Netherlands (1943)
King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden (1946)
Princess Märtha Louise of Norway (1971)
Crown Princess Martha
Crown Princess Martha
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
King Harald
Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden (1977)
Maud Angelica Behn (2003)
Princess Ingrid Alexandra of Norway (2004)
Queen Sonja
Prince Sverre Magnus of Norway (2005)
Crown Prince Hakkon
Maud Angelica Behn (2003)
Prince Christian of Denmark (2005)
Princess Estelle of Sweden(2012)
Crown Princess Mette-Mairt
Prince Christian of Denmark (2005)
Emma Tallulah Behn (2008)
Princess Märtha Louise
Count Friedrich Richard Oscar Jefferson von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (1999)
Princess Ingrid Alexandra of Norway (2004)
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen
Princess Märtha Louise of Norway (1971)
Spain
Queen Victoria Eugenia
Infante Juan, Count of Barcelona (1913)
Doña María del Rosario Cayetana Fitz-James Stuart y Silva, 18th Duchess of Alba de Tormes, Grandee of Spain (1926)
Queen Fabiola of Belgium (1928)
Prince Albert of Monaco (1957)
Felipe, Prince of Austrias (1968)
King Juan Carlos
Don Felipe Juan Froilán de Todos los Santos de Marichalar y Borbón (1998)
Leonor, The Princess of Asturias (2005
Queen Sofia
Leonor, The Princess of Asturias (2005)
King Felipe VI
Princess Sofia Vidinska of Bulgaria (1999)
Doña Victoria Federica de Todos los Santos de Marichalar y de Borbón (2000)
Prince Vincent of Denmark (2011)
Infanta Elena
Don Juan Valentín de Todos los Santos Urdangarín y de Borbón (1999)
Prince Achileas-Andreas of Greece (2000)
Infanta Christina
Don Miguel de Todos los Santos Urdangarín y de Borbón (2002)
Iñaki, the former Duke of Palma de Mallorca
Don Miguel de Todos los Santos Urdangarín y de Borbón (2002)
Infanta Maria Cristina
Princess Marie-Christine of Belgium (1951)
Infanta Cristina, Duchess of Palma de Mallorca (1965)
Princely Family of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg
Gustav, 7th Prince of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg
Count Friedrich Richard Oscar Jefferson von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (1999)
Konstantin Gustav Heinrich Richard Johannsmann (2010)
Prince Vincent of Denmark (2011)
Carina, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleberg
Countess Athena af Monzepat
Princess Nathalie of Sayn-Witentein-Berleburg
Countess Ingrid Alexandra Irma Astrid Benedikte von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (2003)
Princess Benedikte
Prince Joachim of Denmark (1969)
Princess Madeleine of Sweden, Duchess of Hälsingland and Gästrikland (1981)
Royal Family of Italy
Prince Carlo, Duke of Castro
Princess Joesphine of Denmark (2011)
Greece
Queen Olga
Prince Phillip, Duke of Edinburgh (1921)
Prince George
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
King Constantine II
Prince Constantijn of the Netherlands (1969)
Prince William of Wales (1982)
Crown Prince Pavlos
Prince Christian of Denmark (2005)
Prince Sverre Magnus of Norway (2005)
Princess Alexia
Don Pablo Nicolás Sebastián de Todos los Santos Urdangarín y de Borbón (2000)
Countess Ingrid Alexandra Irma Astrid Benedikte von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (2003)
Princess Isabella of Denmark (2007)
Emma Tallulah Behn (2008)
Prince Nikolas
Count Friedrich Richard Oscar Jefferson von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (1999)
Grand Ducal Family of Luxembourg
Grand Duchess Charlotte
Princess Marie-Astrid of Luxembourg (1954)
Grand Duchess Josephine-Charlotte (1927-2005)
Princess Astrid of Belgium, Archduchess of Austria-Este (1962)
Prince Felix (1893-1970)
Prince Albert of Belgium (1934)
Princess Margaretha of Luxembourg (1957)
Prince Jean of Luxembourg (1957)
Princess Marie-Gabrielle (1925)
Grand Duke Henri (1955)
Prince Jean (1957-)
Prince Félix of Luxembourg (1984)
Grand Duchess Joesphine-Charlotte
Princess Marie-Esméralda of Belgium (1956)
Princess Astrid of Belgium, Archduchess of Austria-Este (1962)
Grand Duke Henri
King Albert II of Belgium (1934)
Princess Marie-Gabrielle of Luxembourg (1986)
Guillaume, Hereditary Grand Duke
Prince Sébastien of Luxembourg (1992)
Prince Paul-Louis of Luxembourg (1998)
Prince Noah of Nassu (2007)
Princess Ariane of the Netherlands (2007)
Princess Alexandra
Prince Gabriel de Nassau (2006)
Prince François Henri Louis Marie Guillaume of Luxembourg (2023)
Prince Louis
Prince Charles Jean Philippe Joseph Marie Guillaume of Luxemborug (2020)
Princely Family of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Hohenstein
Prince Georg of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Hohenstein
Countess Ingrid Alexandra Irma Astrid Benedikte von Pfeil und Klein-Ellguth (2003)
Sweden
King Gustaf V
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
King Carl XVI Gustaf of Sweden (1946)
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
Prince Carl of Sweden & Norway (1861-1951)
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
Prince Eugen of Sweden & Norway (1865-1947)
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
Princess Ingeborg of Sweden & Norway (1878-1958)
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
Princess Margaretha of Sweden & Norway
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
Princess Margaretha of Luxembourg (1957)
Princess Margaretha (1899-1977)
Prince Jean of Luxembourg(1957)
Princess Ingeborg
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
King Carl XVI Gustav
Hakon, Crown Prince of Norway (1973)
Crown Princess Victoria
Prince Constantine Alexios of Greece & Denmark (1998)
Baroness Madeleine von Dincklage (1999)
Princess Catharina-Amalia of the Netherlands (2003)
Princess Ingrid Alexandra of Norway (2004)
Prince Christian of Denmark (2005)
Princess Eléonore of Belgium (2008)
Princess Leonore Lilian Maria of Sweden, The Duchess of Gotland (2014)
Prince Alexander Erik Hubertus Bertil of Sweden, The Duke of Södermanland (2016)
Prince Carl Phillip
Princess Estelle of Sweden, The Duchess of Ostergotland (2012)
Prince Nicolas of Sweden, Duke of Ångermanland (2015)
Princess Madeleine
Prince Oscar Carl Olof of Sweden, The Duke of Skane (2016)
Prince Gabriel Carl Walter of Sweden, The Duke of Dalarna (2017)
Princess Christina
Prince Joachim of Denmark (1969)
Princess Désirée, Baroness Silfverschiöld
Crown Princess Victoria of Sweden (1977)
Prince Bertil, Duke of Halland
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
Prince Carl Phillip of Sweden (1979)
Princess Birgitta
Prince Carl Phillip of Sweden (1979)
Princess Margaretha
Princess Märtha Louise of Norway (1973)
Mr. Gustaf Magnusson
Prince Nicolas Paul Gustaf of Sweden, The Duke of Angermanland (2015)
Mr. Victor Magnusson
Prince Alexander Erik Hubertus Bertil of Sweden, Duke of Södermanland (2016)
United Kingdom
Queen Victoria
Prince Albert Edward Kamehameha of Hawaiʻi (1858–1862)
Prince Alfred Alexander William Ernest Albert of Edinburgh, later Hereditary Prince of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (1874–1899)
Princess Alice Mary Victoria Augusta Pauline of Albany (1883–1981)
Prince Edward Albert Christian George Andrew Patrick David of York, later Edward VIII (1894–1972)
Prince Albert Frederick Arthur George of York, later George VI (1895–1952)
Grand Duchess Olga Nikolaevna of Russia (1895–1918)
Princess Victoria Alexandra Alice Mary of York (1897–1965)
Prince Louis Francis of Battenberg, later 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (1900–1979)
King George V
Queen Elizabeth II (1926)
Queen Mary
Queen Elizabeth II (1926)
Princess Margriet Francisca of the Netherlands (1943)
Queen Anne-Marie of Greece (1946)
Mary, Princess Royal and Countess of Harewood
Princess Elizabeth Alexandra Mary of York, later Elizabeth II (1926)
Prince Edward George Nicholas Patrick Paul, The Duke of Kent (1935)
Prince George, The Duke of Kent
Princess Astrid, Mrs. Ferner (1932)
King Edward VIII
Princess Margaret of York (1930)
Princess Alice, Countess of Athlone
Princess Beatrix of The Netherlands (1938)
Prince Arthur, Duke of Connaught
Princess Elizabeth of York (1926)
Princess Mary, Viscountess Lascelles
Princess Elizabeth of York (1926)
The Princess Victoria
Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon (1930)
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
King George VI
Princess Ragnhild, Mrs. Lorentzen (1930)
Queen Elizabeth, The Queen Mother
Prince Alexander of Yugoslavia (1924)
Gerald David Lascelles Esq (1924–1998)
Princess Astrid of Norway (1932)
Princess Alexandra of Kent (1936)
Princess Sofia of Greece, later Queen of Spain (1938)
Princess Irene of the Netherlands (born 1940)
Prince William Henry Andrew Frederick of Gloucester (1941–1972)
Princess Benedikte of Denmark, Princess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg (1944)
Prince Richard of Gloucester, later Duke of Gloucester (1944)
Princess Anne of Edinburgh (1950)
The Hon (Robert) Jeremy Lascelles (1955)
Queen Elizabeth II
David Henry George Lascelles, 8th Earl of Harewood (1950)
Princess Fredrike of Hanover (1954)
David Albert Charles Armstrong-Jones, Viscount Linley (1961)
Edwina Victoria Louise Brudenell (1961)
James Robert Bruce Ogilvy (1964)
Princess Theodora of Greece & Denmark (1983)
Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon
King Charles III (1948)
Prince Phillip, Duke of Edinburgh
Crown Princess Margareta, Custodian of the Crown of Romania (1948)
Norton Louis Philip Knatchbull, 8th Baron Brabourne (1947)
Princess Maria Tatiana of Yugoslavia (1957)
Prince Christopher of Yugoslavia (1960)
George Windsor, Earl of St. Andrews (1962)
Prince Philippos of Greece and Denmark (1986)
King Charles III
The Hon. Nicholas Knatchbull (1964-1979)
The Hon. Timothy Knatchbull (1964)
Marina Victoria Alexandra Ogilvy (1966)
Pavlos, Crown Prince of Greece (1967)
India Amanda Caroline Hicks (1967)
Lord Nicholas Windsor (1970)
Alexander Patrick Gregers Richard Windsor, Earl of Ulster (1970)
The Hon. Edward John Hugo Tollemache (1975)
Peter Mark Andrew Phillips (1977)
The Hon. Nicholas Louis Charles Norton Knatchbull (1981)
Hugh Grosvenor, The Duke of Westminster (1991)
Lord Frederick Charles Wellesley(1992)
Princess Maria-Olympia of Greece & Denmark (1996)
Samuel David Benidict Chatto (1996)
Kumar Padmanabh Singh, Crown Prince of Jaipur (1998)
Diana, Princess of Wales
The Lady Edwina Louise Grosvenor (1981)
Alexandra Victoria Edwina Diana Knatchbull (1982)
Prince Philippos of Greece and Denmark (1986)
Jakie James Warren (1986)
The Lady Mary Luise Wellesley (1986)
Edward Edmund Maximilian George Windsor, Lord Downpatrick (1988)
Jack William Bartholomew (1989)
Benjamin Peter Marcus Samuel (1989)
Domenica Marianna Tertia Lawson (1995)
The Prince William, The Prince of Wales
Prince Constantine-Alexios of Greece & Denmark (1998)
Mia Grace Tindall (2014)
The Prince Andrew, The Duke of York
Zara Anne Elizabeth Phillips Tindall (1981)
Prince Henry, The Duke of Sussex (Prince Harry, 1984)
The Prince Edward, The Duke of Edinburgh
The Lady Rose Gilman (1980)
Lady Ella Mountbatten (1996)
Count Nikolai af Monzepat (1999)
Sophie, The Duchesss of Edinburgh, The Countess of Wessex
Lady Alexandra Mountbatten (1998)
Anne, The Princess Royal
Philip, Hereditary Prince of Hohenlohe-Langenburg (1970)
Haakon, Crown Prince of Norway (1973)
Prince Peter of Yugoslavia (1980)
Princess Eugenie, Mrs. Jack Brooksbank
Maud Daphne Marina Windsor (2013)
Zara Anne Elizabeth Tindall
Prince George Alexander Louis of Wales (2013)
David Armstrong-Jones, The 2nd Earl Snowdon
Princess Beatrice Elizabeth Mary, Mrs. Edoardo Mapelli (1988)
The Lady Sarah Chatto
The Lady Rose Gilman (1980)
Prince Henry of Wales (1984)
Lady Louise Alice Elizabeth Mary Mountbatten-Windsor (2003)
Princess Michael of Kent
Princess Maria Chiara Amalia Carola Louise Carmen of Bourbon-Two Sicilies (2005)
Katharine, Duchess of Kent
Prince Edward, The Duke of Edinburgh (1964)
Princess Alexandra of Kent, The Hon. Lady Ogilvy
George Windsor, The Earl of St Andrews (1962)
The Prince William of Wales (1982)
James Robert Bruce Ogilvy
Princess Eugenie Victoria Helena, Mrs. Jack Brooksbank (1990)
#Royal Godparents#British Royals#Belgian Royals#Spanish Royals#Danish Royals#Swedish Royals#German Royals#Greek Royals#Defunct Monarchies#Dutch Royals#monegasque princely family
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

Stones In The Square
17th January 1964: British rock group the Rolling Stones, (from left) Charlie Watts, Mick Jagger, Keith Richards, Brian Jones and Bill Wyman, outside St George's Church, Hanover Square, London. (Photo by Terry Disney/Express/Getty Images)
#keith richards#rolling stones#mick jagger#rhythm and blues#rock and roll#charlie watts#stones sixty#bill wyman#brian jones
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

Henry Kissinger, who has died at the age of 100, was the most controversial US foreign policy practitioner of the last half-century, the architect of American detente with the Soviet Union, the orchestrator of Washington’s opening to communist China, the broker of the first peace agreement between Egypt and Israel, and the man who led the US team in the protracted talks with North Vietnam which resulted in US forces leaving Indochina after America’s longest foreign war.
Feted for these accomplishments as national security adviser and later secretary of state under Richard Nixon, Kissinger achieved global celebrity status and in 1973 was awarded the Nobel peace prize. But it later emerged via leaked documents and tapes and former officials’ memoirs that behind his diplomatic skills and tireless energy as a negotiator there lurked an inordinate love of secrecy and manipulation and a ruthless desire to protect US national and corporate interests at any price. His contempt for human rights prompted him to ask the FBI to tap his own staff’s telephones and, more seriously, to give the nod to Indonesia’s military dictator for the invasion of East Timor, to condone the actions of the apartheid regime in South Africa in invading Angola, and to use the CIA to help topple the elected government of Chile.
A formidable academic before he worked for the government, Kissinger reached greater heights of political influence than any previous immigrant to the US. His nasal German accent never left him, an eternal reminder to his adopted countrymen that he was a European by origin. To Kissinger himself, the fact that a man born outside the US, and a Jew to boot, could become its secretary of state was a never-ending source of pride.
Although Kissinger was often seen as a supreme believer in a world order based on realpolitik and a balance of power, at heart he was ultra-loyal to the individualistic American ideal. In love with his adopted country, he was infused with a missionary zeal to maintain American hegemony in a shifting world.
Heinz Alfred Kissinger was born to a comfortable, middle-class family in Fürth in Bavaria. His father, Louis, was a teacher, his mother, Paula (nee Stern), a housewife. As a boy, he was old enough to comprehend the collapse of their domestic stability when the Nazis came to power. He and his younger brother were beaten up on the way to school, and eventually expelled. His father lost his job. The family emigrated to New York in 1938.
Kissinger rarely discussed his refugee past, and once told an interviewer to reject any psychoanalytical link between his views and his childhood, but some observers argued that his personal experience of nazism led to his horror of revolutionary changes as well as to the underlying pessimism of his analysis of world affairs.
After George Washington high school in Manhattan, his accountancy course at the City College of New York was interrupted in 1943 when he was conscripted. He was with the US army in Germany for the Nazi surrender and the first months of occupation. He won a bronze star for his role in capturing Gestapo officers and saboteurs in Hanover. In 1946 he went to Harvard, where he stayed intermittently for the next quarter of a century. He received his PhD in 1954 with a study of the 19th-century European conservatives Metternich and Castlereagh, which he turned into a book entitled A World Restored: Metternich, Castlereagh and the Problems of Peace, 1812-1822 (1957).
His subsequent studies led him to become a specialist on nuclear weapons, who caught the eye of Nelson Rockefeller, the governor of New York and a bastion of east coast liberal Republicanism. Kissinger’s desire for influence on policy was already leading him to spend time in Washington, and he combined his academic work with consultancies for various government departments and agencies, including the Joint Chiefs of Staff and the National Security Council under Dwight Eisenhower.
Kissinger’s patron, Rockefeller, failed to make much headway in the presidential campaigns of 1960 and 1964, but after Nixon won the presidency for the Republicans in 1968, Kissinger was appointed national security adviser, with an office in the White House. His intellectual drive, as well as geographical closeness to the president, allowed him to turn what had previously been a backroom job into a high-profile, decision-making post.
Kissinger knew that access is power, and that the relationship goes both ways. Having the ear of the president gave him the ear of a competitive, news-hungry Washington press corps which admired his charm and brilliance and eagerly printed a generous amount of his on-the-record comments while finding ways to divulge unattributably the confidential titbits and insider gossip that he loved to drop.
A battle developed between Kissinger and the secretary of state, William Rogers, the nominal architect of US foreign policy, during Nixon’s first term. Kissinger won it easily. Rogers was excluded not only from the administration’s central concerns – Vietnam, the Soviet Union and China – but even the Middle East, the one area where he achieved some praise in 1970 with the so-called Rogers plan. The plan was a US effort to impose a settlement between Egypt and Israel with the backing of the Soviet Union. Israel rejected it while Kissinger felt that the goal of US policy in the region, as indeed throughout the developing world, should be to reduce the Kremlin’s influence rather than give Moscow equal status.
When Rogers eventually resigned a few months after the start of Nixon’s second term, Kissinger got the job he coveted most. Four years of private advice and back-channel negotiating were to be crowned by formal acceptance as Washington’s senior international representative and America’s major speechmaker on foreign affairs. Kissinger had already scored the two biggest coups of his career, proving that he was more than just an academic consultant and bureaucratic in-fighter, but a cunning negotiator. He ran the secret diplomacy which culminated in July 1971 with the stunning announcement that Nixon was to go to China to meet Mao Zedong the following year. He also led the negotiations in Paris with Hanoi for the peace treaty that sealed the departure of American troops from Vietnam. For the second of these feats, he shared the Nobel peace prize with Le Duc Tho, the North Vietnamese negotiator, though the latter refused to accept it.
The award aroused a huge controversy since it coincided with revelations that Kissinger had supported Nixon’s decisions to mount a secret campaign of bombing Cambodia in 1969. Cambodia had long been used by North Vietnamese troops for bases and supply depots, but Nixon’s predecessor, Lyndon Johnson, resisted pleas from the joint chiefs of staff to bomb them. The country was officially neutral and its leader, Prince Norodom Sihanouk, was desperately trying not to take sides.
But the Nixon administration wanted to send a strong message to North Vietnam that the new president would be tougher than Johnson. Tapes of White House conversations (the Watergate tapes) revealed that Nixon called it the “madman theory” – “I want the North Vietnamese to believe that I’ve reached the point where I might do anything to stop the war,” he told his chief of staff, Bob Haldeman. Kissinger endorsed the concept, though he preferred to put it in more academic language by arguing that US policy must always retain an element of unpredictability.
In March 1969 Nixon and Kissinger ignored the reluctance of Rogers and launched waves of B52s on carpet-bombing missions over Cambodia, as they had already done in Vietnam. The raids went on for 14 months, although officially the administration pretended the targets were all in South Vietnam. Initially, Kissinger did not even want the pilots to know they were striking Cambodia, but he was advised that they would soon find out and be more likely to leak the information unless sworn to secrecy ahead of the raids.
The bombing remained secret in Washington for an astonishing four years, becoming public only when a military whistleblower wrote to Senator William Proxmire, a prominent critic of the Vietnam war, and urged him to investigate. In Cambodia the campaign led to an estimated 700,000 deaths as well as 2 million people being forced to flee their homes. It also led a pro-US army general, Lon Nol, to seize power from Sihanouk in 1970 and align the country with the US. The bombing and the coup fuelled popular unrest, added to the strength of Cambodia’s communist guerrillas, the Khmer Rouge, and paved their way to power in 1975.
The Paris peace talks on Vietnam also coincided with an escalation of US bombing in Vietnam itself. At the height of the negotiations at the end of 1972, Nixon and Kissinger took the war to new heights with the “Christmas bombing” campaign, comprising targets across North Vietnam. It enraged the US peace movement and provoked a huge wave of new protests and draft-card burning by conscripts. Kissinger’s aim was not so much to intimidate Hanoi as to persuade Washington’s ally, South Vietnam’s president Nguyen Van Thieu, to accept the accords which the US was making with the North. The bombing was meant to assure him that if there were any North Vietnamese violations after the accords came into effect, they would be met with all-out American force.
Kissinger was aware that the Paris deal was flawed, and might well lead to Thieu’s replacement by a communist government. His goal was merely to win a “decent interval” between the pull-out of US troops and the inevitable collapse of the regime in Saigon so that the US could escape any perception of defeat. The phrase “decent interval” appeared in the briefing papers for Kissinger’s secret trip to Beijing in 1971 that were later declassified. They show he told the Chinese that this was US strategy in Vietnam. A year later he informed China’s prime minister, Zhou Enlai: “If we can live with a communist government in China, we ought to be able to accept it in Indochina.”
When the North Vietnamese army and its southern allies, the Vietcong, stormed into Saigon in April 1975, forcing the US ambassador into a humiliating helicopter escape, the image was clearly one of defeat, in spite of the two-year interval since the departure of most US troops. But Kissinger blamed Congress, claiming it had undermined the peace deal by refusing to finance new arms shipments to Thieu. This was a favourite refrain. He continually attacked Congress for interfering in foreign policy, apparently never recognising the value of democratic checks on strong executive power.
Turning his skills to the Middle East, Kissinger gave birth to the concept of shuttle diplomacy, a term first used to the press by his close aide Joe Sisco. He flew between Jerusalem and Cairo during the October 1973 war to hammer out a ceasefire after the Israelis had sent their troops across the Suez canal and come close to the Egyptian capital. He later secured Israel’s withdrawal back across the canal, and shuttled to and from Damascus to make a deal with Syria for the Israelis to withdraw from a small part of the Golan Heights.
Behind all three issues lay the Americans’ competition with the Soviet Union, then at the height of its international power. The US opening to China was designed to wrong-foot the Russians by turning what they thought was an evolving, bilateral relationship of parity and mutual respect with Washington into an unnerving triangle which seemed to ally China and the US against them. Kissinger hoped to exploit the two communist powers’ rivalry to persuade both of them to abandon the Vietnamese, thus making it easier for the US to win the peace, if not the war. So he threatened Moscow and Peking (now Beijing) with the argument that they would lose the benefits of dialogue and trade with Washington if they did not stop their arms supplies to Hanoi.
In the Middle East, Kissinger’s aim was to exclude the Russians, who had been longtime allies of Egypt and Syria. By extracting concessions from Israel and brokering a ceasefire in the 1973 war, Kissinger persuaded Cairo and Damascus that only the US could achieve movement from the Israelis, thanks to its unique influence. A year before the war, Anwar Sadat, the Egyptian president, had shown his distrust of Moscow by asking thousands of Russian advisers to leave Egypt. The move was meant as a signal to Washington that Egypt preferred good relations with the US, provided Washington put pressure on Israel. Kissinger missed the signal and did nothing until Sadat, in desperation, launched his attack on Israel in October 1973.
Kissinger’s strategy of detente with the Soviet Union was also designed to reduce Moscow’s room for manoeuvre. Although rightwing Republicans criticised it as appeasement, he argued that Washington should not just contain the Soviet Union, as previous American administrations had sought to do. The US should tame it by giving it a stake in the status quo. Instead of going for ad hoc deals with the Kremlin, Kissinger was the first senior American to try to establish a complex of agreements with a range of penalties and rewards for bad and good behaviour. This, he argued, would limit Soviet adventurism. Sometimes he called it a network, at other times a web, but in both cases the aim was to provide the Soviet Union with benefits from expanded trade, investment and political consultation with Washington.
The strategy failed to produce a new world order because Kissinger was not willing to abandon adventurism on the American side. In the developing world, in particular, Kissinger pursued policies of confrontation with Moscow, often based on faulty analysis of what the Russians were doing or exaggerated claims of the extent of their influence. The successful US effort to overthrow the elected president of Chile, Salvador Allende, in 1973 fitted into the long US history of intervening in Latin America against leftwing governments that nationalised US corporations (in this case, the big copper companies). But Kissinger also disliked Allende’s closeness to Moscow’s ally, Cuba. “I don’t see why we need to stand by and watch a country go communist due to the irresponsibility of its people,” he commented.
By 1974 Kissinger’s boss was being engulfed by the Watergate scandal. Although Kissinger was involved in secretly taping his own staff, he was not connected to Nixon’s decision to burgle the headquarters of the Democratic party at the Watergate apartment complex in 1972 and then cover up the truth – the charges that brought the president down. In spite of the scandal – or perhaps because of it – Nixon’s relationship with Kissinger remained close, in large part because the beleaguered president saw Kissinger as his best ally in foreign policy, the area where Nixon felt that he had been most successful. He wanted Kissinger to be the man to preserve his legacy.
In his memoirs, Kissinger described how Nixon virtually clung to him during his last hours in the White House in August 1974. The disgraced president asked him to pray beside him in the Lincoln bedroom for half an hour. “Nixon’s recollection is that he invited me to kneel with him and that I did so. My own recollection is less clear on whether I actually knelt. It is a trivial distinction. In whatever posture, I was filled with a deep sense of awe,” Kissinger wrote.
Although Kissinger was not charged over Watergate, his image nonetheless became tarnished. Damaged by revelations of the secret bombing of Cambodia, the favourable media bubble burst. Kissinger’s path from miracle worker to being perceived as a cynical trickster proved short. If Nixon was a serial liar on the domestic stage, Kissinger was seen as a similar villain on the international one. Nevertheless the next president, Gerald Ford, who had limited foreign experience, kept Kissinger on as secretary of state as a symbol of continuity. But Kissinger’s star was in decline. He tried to change his focus by shifting his attention to Africa, which he had ignored until then.
His results were far from positive. He may well have set back the fall of apartheid by several years by approving the involvement of the CIA in the Angolan civil war and giving the nod to South Africa’s invasion in 1975 as the Portuguese withdrew from their erstwhile colony and granted it independence. The South African intervention prompted Cuba to send hundreds of troops to support the Angolan government, thereby launching one of the bloodiest “proxy wars” between the superpowers.
When the Republicans lost the White House to the Democrats under Jimmy Carter in 1976, Kissinger’s time was up. He spent the next decades as a consultant to multinational corporations, and speaking on the international lecture circuit. In 1982 he founded his own firm, Kissinger Associates.
Although he had brief hopes of a comeback when Ronald Reagan won the 1980 election, the new president and his men did not feel comfortable with Kissinger’s image or the strength of his personality. His public persona of pragmatism did not fit their crusading ideology of anti-communism and their constant claims of Soviet expansionism. They were from the school which felt his contacts with the Soviet leader, Leonid Brezhnev, during the period of detente, had smacked of appeasement.
The charge was absurd. It reflected the difference between subtlety and simplicity, as I discovered at one of the occasional deep-background “non-lunches” which Kissinger gave for representatives of European newspapers. Europe was never a high priority for Kissinger, in large part because it was not a region of US-Soviet competition. He favoured a strong and united western Europe so as to keep Germany in check, hence his much-quoted comment: “If I want to call Europe, who do I call?”
But he seemed to like meeting European correspondents, flattering us with the sense that we asked deeper questions than our American colleagues. At one such lunch, I was staggered by Kissinger’s emotional outburst when someone delicately raised the appeasement charge that rightwing senators were making. “Do you really think a man who stopped Allende wouldn’t want to stop Brezhnev?” he retorted.
If ever there was an American super-patriot, it was Kissinger. As a European intellectual, he knew better than his adopted compatriots how to run an empire. The bedrock of his policies was fear of a resurgent, “unanchored” Germany, a firm desire to keep western Europe closely tied to the US, and a fierce determination to outwit the Soviet Union and maintain American dominance, if necessary through the use of military might. It was no surprise that in his 80s, long after the Soviet Union had collapsed, he became a close consultant of George W Bush, supporting his invasion of Iraq.
Kissinger’s private life was a tempestuous subject in the Washington gossip columns, at least in the interval between his two marriages, which happened to coincide with his years at the apex of power. His first, to Ann Fleischer, with whom he had two children, Elizabeth and David, ended in divorce in 1964. Ten years later, he married Nancy Maginnes, one of his former researchers. She and his children survive him.
🔔 Henry Alfred Kissinger, statesman, born 27 May 1923; died 29 November 2023.
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

George Augustus Frederick FitzClarence, 1st Earl of Munster (1794–1842) by Richard Austin Artlett, after Thomas Phillips. He was the eldest illegitimate son of William IV of the United Kingdom and his long-time mistress Dorothea Jordan.
#uk#house of hanover#royal bastards#George Augustus Frederick FitzClarence#earl of munster#richard austin artlett#thomas phillips#engraving#engravings#kingdom of ireland#Peerage of Ireland#irish aristocracy
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

CAMGIRL . . . Playlist
tw: good music taste;)
──── ✰࿒࿎྇ ༃࿐ ‘CAMGIRL’ playlist



• leni. . . crystal castles • swimming pool. . . marie madeline
• gallowdance. . . lebanon hanover • oblivion. . . grimes
• crucified. . . army of lovers • bang bang bang bang. . . sohodolls
• brutus (instrumental). . . the buttress
• le monde. . . richard carter • cirque. . . sub urban
• Зеркало. . . ic3peak …and more…
#cillian murphy imagine#cillian murphy x reader#cillian x reader#cillian x y/n#imagine#soundtrack#playlist#music#cillian x fem!reader#smut#dark aesthetic#dark smut#cillian murphy#cillian murphy x oc#original series
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Enoch Powell (Bachelor of Arts in classics, Cambridge University, 1933)
Richard Nixon (Bachelor of Arts in history, Whittier College, 1934)
Antonin Scalia (Bachelor of Arts in history, Georgetown University, 1957)
Newt Gingrich (Bachelor of Arts in history, Emory University, 1965)
George W Bush (Bachelor of Arts in history, Yale University, 1968)
Mitt Romney (Bachelor of Arts in English, Brigham Young University, 1971)
Clarence Thomas (Bachelor of Arts in English literature, College of the Holy Cross, 1971)
John Roberts (Bachelor of Arts in history, Harvard University, 1976)
Mike Pence (Bachelor of Arts in history, Hanover College, 1981)
Boris Johnson (Bachelor of Arts in literae humaniores/classics, Oxford University, 1987)
Brett Kavanaugh (Bachelor of Arts in history, Yale University, 1987)
Amy Coney Barrett (Bachelor of Arts in English literature, Rhodes College, 1994)
Ron DeSantis (Bachelor of Arts in history, Yale University, 2001)
Josh Hawley (Bachelor of Arts in history, Stanford University, 2002)
Not to question the collective wisdom of Tumblr, but do you think it might be possible that studying for a humanities degree doesn't magically make you a fully rounded human being with good politics?
9 notes
·
View notes
Text








⋆ William, The Conqueror to Prince Louis of Wales ⋆
⤜ William I is Prince Louis of Wales' 25th Great-Grandfather via his paternal line through Prince Philip
William I of England
Henry I of England
Empress Matilda
Henry II of England
John of England
Henry III of England
Edward I of England
Edward II of England
Edward III of England
Lionel of Antwerp, Ist Duke of Clarence
Philippa Plantagenet, Vth Countess of Ulster
Roger Mortimer, IVth Earl of March
Anne Mortimer
Richard Plantagenet, IIIrd Duke of York
Edward IV of England
Elizabeth of York
Margaret Tudor, Queen of Scotland
James V, King of Scotland
Mary Stewart, Queen of Scotland
James I of England
Elizabeth Stuart, Queen of Bohemia
Sophia, Electress of Hanover
George I of Great Britain
George II of Great Britain
Frederick, Prince of Wales
George III of the United Kingdom
Prince Edward Augustus, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
Victoria of the United Kingdom
Princess Alice of the United Kingdom, Grand Duchess of Hesse
Princess Victoria of Hesse and by Rhine
Princess Alice of Battenberg
Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark
King Charles III of the United Kingdom
William, The Prince of Wales
Prince Louis of Wales
#royal line from william i#the british royal line#british royal family#british royals#royalty#royals#brf#british royalty#history#historical royals#house of york#house of tudor#house of plantagenet#royal#medieval ages#william the conqueror#king charles iii#prince william#the prince of wales#prince of wales#queen victoria#mary queen of scots#prince philip#duke of edinburgh#house of stuart#house of stewart#house of windsor#elizabeth of york#prince louis of wales#prince louis
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
William Boyce - David's Lamentation over Saul and Jonathan (Dublin Version, 1744) - 14. Duet: Sad Israel! thy Beauty's Pride ·
Patrick Burrowes · William Purefoy · Andrew Watts · Richard Edgar-Wilson · Michael George · Choir of New College Oxford · The Hanover Band · Caroline Brown · Pavlo Beznosiuk · Graham Lea-Cox
3 notes
·
View notes