#paleognath
Text

Brown kiwi
By: Unknown photographer
From: Wildlife Fact-File
1990s
458 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Proapteryx demonstrating a hunting tactic unique to apterygiformes. Kiwi have been observed shooting powerful lasers from their eyes, directing it at the forest floor in order to kill any invertebrates before eating them. They can also use these beams in self defense. It is unknown whether or not earlier relatives like Proapteryx had this ability. I am definitely not lying about any of this (<- lying).
#art#my art#digital art#paleoart#paleontology#palaeoblr#archosaurs#dinosaurs#theropods#coleurosaurs#maniraptorans#paravians#birds#paleognaths#proapteryx#kiwi#unreality#unreality tw#queue
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
Uncharismatic Fact of the Day
If you have poor eyesight, you have something in common with the kiwi! This species of bird is nocturnal, and they rely on other senses light smell and hearing to find their prey. As a result, most kiwis have extremely poor vision, and there's even small but healthy population of completely blind individuals. The best part? Scientists believe the gene responsible for the reduction in vision is the Sonic hedgehog gene.

(Image: A North Island brown kiwi (Apteryx mantelli) by Tui de Roy)
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
113 notes
·
View notes
Text
rip to plateosaurids and pengornithids but things had to be cut
#dinosaurs#birds#animals#poll#palaeoblr#birblr#pachycephalosaurs#parasaurolophins#parankylosaurs#paleognaths#pheasants#pigeons#puffins#penguins#parrots#passerines
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
0 notes
Text
Ancient Birds
You probably have never heard of Janavis finalidens. It was a bird with webbed feet and a body vaguely reminiscent of a wild hen. It would have been the size approximating to a grey heron and had a mass estimated to be 1.5 kg. I use the past tense because it lived in the late Cretaceous, so birds had evolved away from the therapods well before the extinction. This bird was, in shape, very similar…
View On WordPress
1 note
·
View note
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: emperor penguin
This is the last Wet Beast Wednesday before Christmas and Christmas is associated with the north pole thanks to Santa. So to celebrate the season, I'm going about as far away from the north pole as it is possible to go and talking about the emperor penguin. This also happens to be the first dinosaur I've showcased on this series.

(image id: an emperor penguin lying belly-down on ice, seen from the side. Its back, wings, and head are black while its belly and neck are white. It has a patch of orange feathers near the ears. Another penguin is standing up in the background. end id)
Aptenodytes forsteri is the largest of all penguins and the sixth largest (by weight) bird in the world, only surpassed by the emu and two species each of the cassowary and ostrich. Those are all paleognaths, one of two living groups of birds, making the emperor penguin the largest of the other group: the neognaths. There are some discrepancies on their size due to the standards of bird measurement, but recent measurements list their standing height as reaching 120 cm (3.9 ft) with a weight of 22.7 to 45.4 kg (50 to 100 lbs). Their weight varies a lot during their lives, with both males and females losing a lot of weight during breeding season. Males generally weigh more than females. Genomic and anatomical analysis indicates that the emperor penguin, along with the closely-related king penguin and an extinct species, are part of a group of penguins that branched off of the family tree before the other living penguin species. As with other penguin species, they are heavily adapted for life in the water. All penguins are flightless, with their wings having adapted into flippers used for swimming. Penguins stand differently than other birds. Most birds have long legs and hold their bodies horizontally to the ground or at an angle, but penguins have short legs and hold their bodies vertically, like humans do. This, plus other adaptations, helps streamline the birds, letting them swim more efficiently. Like other seabirds, their feathers are very dense and coated with oil that repels water. This keeps the feathers from becoming waterlogged, reducing drag and helping keep the bird warm. During molting season, the feathers emerge from the skin mostly formed and push out the old feathers, preventing the penguin from developing bald or thin patched that would compromise insulation. While the feathers are responsible for most of the insulation, a layer of fat also helps. Like other birds, penguins are endothermic, commonly known as warm-blooded. Penguin tongues have backward-pointing barbs that help prevent food from escaping their mouths.

(image id: an emperor penguin jumping out of the water and onto ice. It is pictured in midair with its body roughly parallel to the ground and wings extended. Multiple other penguins are in the background. end id)
Emperor penguin's divide their year between the breeding season and the rest of their lives. During most of the year, they spend their time searching for food. Most of this food consists of fish, krill, and squid. Emperor penguins are social animals that often coordinate with each other to hunt in groups. While hunting, they will dive up to 535 meters (1,755 ft) and spend up to 21 minutes underwater before surfacing to breathe. During dives, the pressure can increase up to 40 times and the emperor penguin has some special adaptations to cope. Unlike most birds, emperor penguin bones are solid, reducing the chance of one breaking under pressure. During dives, the heartbeat slows dramatically and non-essential organs cease functioning to conserve oxygen in the blood. In addition, the hemoglobin in the red blood cells is modified to carry more oxygen in high pressure and low temperature. While on land, emperor penguins gather in colonies along the shoreline. Members of the colonies spend a lot of them time huddled against each other to keep warm. The penguins live all around Antarctica between 66 and 77 degrees southern latitude.

(image: an emperor penguin swimming underwater. Its head is pointed up, making its body very streamlines. Its wings are extended and are used for propulsion and steering. end id)
The thing emperor penguins are most famous for is their breeding behavior. Breeding season starts at the beginning of winter in Antarctica, between March and April, and is triggered by the decrease in day length. Penguin colonies travel inland en masse moving between 50 and 120 km (31 to 75 miles) to find a spot to raise their chicks. These spots are usually large, flat patches of sea or lake ice with a barrier such as a cliff or iceberg used to block the wind. Males perform sexual displays wherein they make loud courtship calls while wandering around the colony. When a female is interested, she will face they male and they will both hold their heads up for a few minutes. Once a pair os formed, they will walk around the colony together. When ready to mate, The pair will bow to each other. Emperor penguins are serially monogamous. They will only mate with one other penguin each season, but rarely pick the same mate more than once. The pair say together until the egg is laid in late May or early June. The female then transfers the egg (only one is laid every year) to the male, a tricky process. They have to use their feet to transfer the egg without dropping it. If the egg breaks or is exposed to the ice for more than a minute or so, it will die. It is not uncommon for an egg to be lost, especially in first-time parents. If this happens, both parents will leave the colony and return to the sea, not mating again until next year. The male balances the egg on his feet and covers it with a loose flap of skin. The bottom of this skin is a featherless patch called the brood patch that only forms during this season. By keeping the egg between his feet and the brood patch, the male incubates it. Once the egg is transferred, the female returns to the sea, leaving the male responsible for the next few months. In every other penguin species, the mother and father take turns incubating their egg. for the next 65-75 days, the male will incubate the egg in the middle of the Antarctic winter, where storms are frequent and temperatures can can reach into the -60s C (-70s F). He will not eat at all during this period, which, including travel and mating time, can last for 120 days. Males can lose up to half of their body mass during this fast. If the egg is dropped even once, it has a very high chance of dying. Walking without dropping the egg is tricky, but the males will form tight bunches to conserve body heat. These bunches are mobile, with members to the outside gradually moving inward and vice-versa. The egg usually hatches after around 60 days and it can take a few days to break out of its shell, which is thicker than in most bird species. The chicks are born featherless and will freeze to death if they leave the male's brood pouch. The male produces a substance called crop milk with a gland in his esophagus. Crop milk is unique to pigeons, flamingos, and male emperor penguins and is used to feed the chick. The crop milk does not provide full nourishment to the chick, but will keep it alive for about a week.
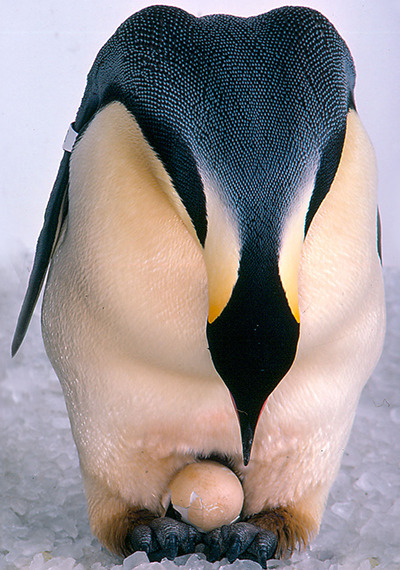

(image id: a male emperor penguin standing on ice with its egg balanced on its feet. The skin flap thet normally covers the egg is pulled back and the male is bending over to examine the egg. This egg is broken, possibly the result of being dropped, and is non-viable. end id)

(image id: a newly-hatched emperor penguin sitting on it's father's feet. It is very small and featherless, with grey skin and a black head. end id)
About this time, the female will return from her time at sea. She spent this time feeding and fattening herself up for the next leg of the parenting journey. She returns to the colony usually between 5 and 10 days after the hatching. If she arrives too late, the chick will starve. Once she arrives, she will locate her mate through the sound of his calls. The male then transfers the chick to the female's brood pouch and returns to the sea to feed and put weight on for another 3-4 weeks. The female will feed the chick by regurgitating half-digested food into its mouth. After this, the mother and father will take turns brooding the chick and feeding at sea. If either parent is delayed or dies, the chick will die as the remaining parent will eventually abandon it and return to sea. Orphaned chicks will try to seek food and shelter from other adults and mothers who have lost a chick may try to adopt an abandoned one, but as a single parent cannot raise a chick alone, it will eventually be abandoned as the adult goes to feed. Sometimes, a mother who lost her chick will attempt to steal a chick from another mother. This leads to fights over chicks that may leave chick trampled to death.
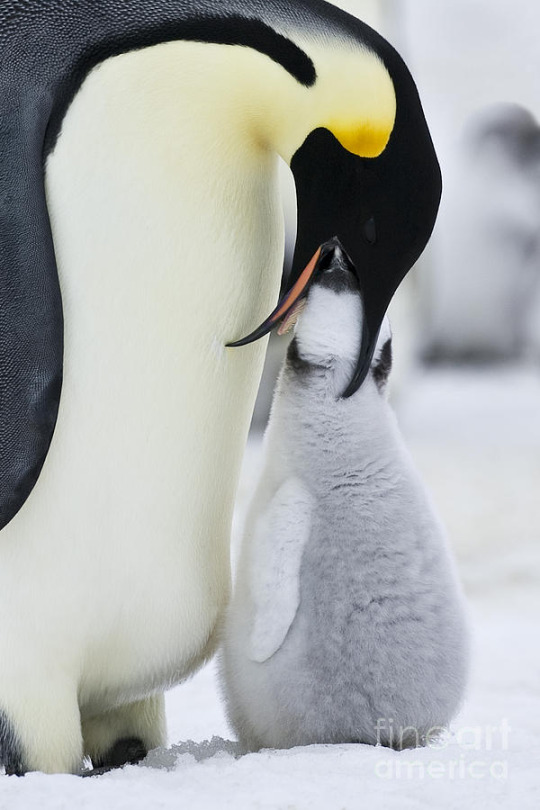

(image id: an adult emperor penguin feeding its chick. The chick is larger and covered in fluffy, grey, downy feathers. It no longer needs to stay on its parent's feet. The adult is looking down at the chick with its mouth open. The chick has its head inside the adult's mouth. end id)
Starting 45-50 days after hatching, the chicks now have a thick enough coat of down to survive outside of the brood pouch. Starting around this time, both parents will return to the sea and occasionally return to bring food, using the sound of their chick's vocalizations to track them down. When the parents are gone, the chick huddle together for warmth. Starting in early November, the chicks will start gaining their adult plumage and the adults will stop returning to feed them. Once they get hungry enough, the chicks will make the trip to the sea (which is shorter now as it is summer in the Antarctic and the sea ice has receded) and will be independent from now on. Only 15% of chicks survive their first year, but after that the survival rate is 95%, meaning most living emperor penguins are adults. Emperor penguins reach sexual maturity at 3 years, but most do not mate until they are 4-6 years old. The average lifespan of those who live long enough to reach adulthood is 20 years, but may live up to 50 years. The high survival rate of adults is in part due to a lack of predators. Adult emperor penguins are only hunted by leopard seals and orcas, though the former prefer juveniles. Juveniles are preyed upon by seals when they reach the water and by southern great petrels when on the ice. Adult emperor penguins lack any land predators, which has resulted in them having no prey response when on land. Scientists and antarctic explorers have reported that adults will approach them without fear.
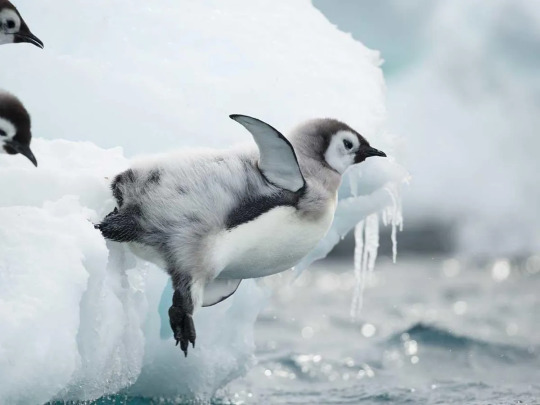

(image id: a newly-independent chick entering the water for the first time. It has not yet fully developed its adult plumage and has a mix of the chick's fluffy down and an adult's smoother coat. It is jumping off a ledge of ice into the water. Two other chicks watch from the side of the image. end id)
Emperor penguins are classified as near threatened by the IUCN, meaning they are losing population and may slip down into threatened status if conservation measures are not taken. The largest threat to emperor penguins is global warming reducing their habitat. Because they need sea ice to lay eggs and brood, the loss of sea ice every year has reduced the ability of the penguins to reproduce. in 2022, loss of sea ice led to a catastrophic failure to reproduce among nearly all known colonies. It is now estimated that 90% of colonies are at risk of dying out due to the loss of sea ice. If these trends are not reverted by reduction of global warming, the penguins could face extinction.

(Image id: two emperor penguins with their chick. The adults are standing behind the chick, which has its downy juvenile plumage. The chick stands about half the height of the parents. end id)
#wet beast wednesday#emperor penguin#penguin#marine biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#marine life#good parenting#cute#image description
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fossil Novembirb: Day 16 - Among The Giants

During the Oligocene epoch, 33-23 million years ago, the landscape of Mongolia was as endlessly vast and wild as today. Forests were rare in this part of the world, instead there were shrublands, savannahs and deserts there. This landscape was the realm of giants, like the Paraceratherium of Walking With Beasts fame. Birds were also living in this land of giants, and some were already adapting to it.
Heterostrix: A small early owl, roughly the size of modern pygmy owls. But despite its small size, it was a capable predator of large insects, lizards and mammals, even birds as large as itself.
Agnopterus: One of the earliest known true flamingoes. Little is known of this bird, but it likely fed on tiny crustaceans filtered from the water, as do modern flamingoes.
Sonogrus: One of the flightless paleognath birds that was closely related to ostriches. This fleet footed herbivore belonged to the group known as paragruids.
Ergilornis: Another stem-ostrich in the group known as ergilornithids. The inner toe of these birds was reduced in size to allow for more efficient running.
Caspiodontornis: One of the few pelagornithids known from Asia, this pseudotoothed giant flew above the remnants of the ancient Tethys Sea.
#Fossil Novembirb#Novembirb#Dinovember#birblr#palaeoblr#Birds#Dinosaurs#Cenozoic Birds#Heterostrix#Agnopterus#Sonogrus#Ergilornis#Caspiodontornis
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mininothura talenki Agnolín, 2022 (new genus and species)

(Type humerus [upper arm bone] of Mininothura talenki, from Agnolín, 2022)
Meaning of name: Mininothura = small [in Latin] Nothura [genus of tinamous including the white-bellied nothura]; talenki = small [in Tehuelche]
Age: Miocene (Burdigalian)
Where found: Pinturas Formation, Santa Cruz, Argentina
How much is known: Three partial humeri (upper arm bones).
Notes: Mininothura appears to have been a small tinamou, a group of ground-dwelling birds from the tropical Americas. Despite superficially resembling partridges, tinamous are a type of paleognath bird, like ostriches and emus. Tinamous are the only group of extant paleognaths that have not lost the ability to fly.
The tinamou fossil record is very sparsely known, but fossils of at least three other species distinguishable from Mininothura have been previously reported from the early–middle Miocene of Argentina, indicating that they had probably reached a fairly high level of diversity by that point.
Reference: Agnolín, F.L. 2022. New fossil birds from the Miocene of Patagonia, Argentina. Poeyana 513: 1–43.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Modern-type birds share several key traits, such as toothless beaks and fused foot bones. The almost 11,000 living bird species — the paleognaths (flightless birds such as ostriches), anseriformes (waterfowl), galliformes (land fowl) and neoaves (the remaining 95 percent of living bird species) — all share a common ancestor, Field says. “We think that ancestor lived at some time before the end of the Age of Dinosaurs,” he says. But there are very few bird fossils surviving from before the asteroid impact.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

North Island brown kiwi
By: K. W. Fink
From: The Fascinating Secrets of Oceans & Islands
1972
#north island brown kiwi#kiwi#paleognath#bird#1972#1970s#K. W. Fink#The Fascinating Secrets of Oceans & Islands
182 notes
·
View notes
Text
Multituberculate Earth: Birds
(As with all animal pages so far, this only goes so far into the Oligocene… for now)
At first, the avifauna of this timeline evolved much as ours. Only the toothless crown birds survived the KT event (though outliers like Qinornis may indicate other lineages survived briefly; one study did note the similarities between pelagornithids and ichthyornithids, but it hasn’t made the plunge), several lineages quickly producing megafauna to replace non-avian dinosaurs and other great reptiles. Gastornithiforms and ratites occupied large herbivore niches on land, pelagornithids and lithornithids attained large wingspans as competing pterosaurs ceased to exist and giant penguins and plotopterids were the first vertebrates to occupy large predatory niches at sea (barring sharks of course). To say nothing of the massive variety of smaller birds like stem-tropicbirds, the passerine-like zygodactylids and carnivorous parrots.
But the absence of an Azolla Event put avian evolution in a very different track from the Eocene onwards. For starters, without a mid-Eocene cooling to alter forest biomes, lithornithids and presbyornithids didn’t decline, thus preventing an opening for several lineages like cranes, storks and pelecaniforms. Many groups that depended on the cooling temperatures, like seagulls and relatives, also did not get the opening they wished for. Some modern groups you might assume quintessential, like ducks and shorebirds, were either greatly crippled or did not get to rise.
Likewise, the evolution of flying mammals put some pressures on birds that our bats didn’t have, but for the most part both groups managed to co-exist. Niche partitioning is easy when you can fly anywhere to get resources, after all, and birds are no strangers to it given how they co-existed with pterosaurs and other Mesozoic flyers for over one hundred million years.
By far the greatest challenge faced by birds thus far was the Grand Coupure, leading to a dramatic collapse of forest habitats. For European and Balkanatolian flightless birds it was particularly hard as their isolation in Europe came to a drastic end, but several flightless lineages remained in the Oligocene.
Because there are lots of Cenozoic bird groups, some more understood than others, this is something of a work in progress. However, I will list the bird groups that I have most assuredly set in stone.
Palaeognaths
The so called “old jaws” might be something of a misnomer, as some Cretaceous birds already had a neognath palate and their own palate is much more advanced than in some other early birds, but regardless they do invoke that prehistoric mystique. In our timeline the sole survivors are the flightless ratites + tiny tinamous, animals that truly seem to come from the era of the dinosaurs.
In this timeline, ratites similarly diversified, with rheas and other poorly understood taxa in South America and Antarctica, members of the cassowary/emu line in Australia, elephant birds in Madagascar (and possibly mainland Afro-Arabia) and a variety of stem-ostriches in North America, Europe and Asia. But it is another group, the flying lithornithids, that remain the most diverse and arguably spectacular group.
In our timeline, lithornithids started the Cenozoic in style, dispersing across the northern continents as forest dwelling probers like modern woodcocks. They were far more efficient flyers than our timeline’s surviving flying paleognaths, the tinamous, there being evidence of migratory behaviour and stork-like soaring, and some species attained quite large sizes. In our timeline the mid-Eocene cooling seems to have doomed them, but in the prolonged hothouse conditions of this timeline they managed to acclimate and diversify further.
Some lineages were lost in the Grand Coupure, but those that survived were ready for the spread of open habitats. Many forms occupy niches taken in our world by cranes and storks, prowling the steppes or stalking the swamps for small animals and nutrious plant matter. Others have diversified as shorebird analogues, probing along the coastlines. Some conversely became smaller and hoopoe-like; lithornithids were already more efficient perchers than other palaeognaths, so a few managed to capitalize on arboreal niches.
Though efficient flyers, lithornithids lack tails, relying mostly on their own wings for steering (for reference, see videos on tailless kites or hawks). Like in their ratite cousins it is the male that protects the eggs and offpsring, though in some derived species the young are superprecocial and can fly soon after birth, a condition seen in many Mesozoic birds. Many species have glossy eggs and feathers like cassowaries.
Other than lithornithids, there seems to be some other flying palaeognaths about. The stem-ostrich Eogrus for example is traditionally considered capable of at least some flying abilities, while flying stem-kiwis must be around somewhere given Proapteryx. And, of course, there’s the ancestors of tinamous, which have not yet debuted in the fossil reccord for some reason (in both timelines).
Pelagornithids
The so called “pseudo-toothed” birds due to tooth-like serrations in their bills, these seabirds are a mystery. Sometimes they are grouped among albatrosses and other higher waterbirds, other times they’re considered closely related to waterfowl, with most recent studies putting them in a polytomy between both groups. As mentioned above there is a study that does note similarities between their jaws and those of aquatic toothed seabirds, and given that their serrations seem to share a true molecular origin with teeth I wouldn’t be surprised if they were surviving toothed seabirds all along.
Anyways, besides the “teeth” (which were acquired late in life, implying prolonged parental care) the most notable feature of pelagornithids is their size. These are easily the largest flying birds of all time, some reaching wingspans of over 7 meters. Because they lack the quadrupedal launching of flying mammals and pterosaurs, they compensated by become extremely lightweight like living kites, thus while they look fearsome they most hunt small, soft prey like squids. Its even possible they can’t flap their wings anymore, relying solely on thermal soaring like modern frigatebirds (and not dynamic soaring like albatrosses), to which they can be considered close analogues if much larger.
While the evolution of giant insulonycteriids might seem like a disaster for these enormous birds, in truth both groups get along just fine (most of the time). The giant flying mammals are most robust and can hunt proportionally larger prey and even dive, so if the pelagornithids are the frigatebirds the insulonycteriids are the albatrosses and gannets.
Pelagornithids in both timelines have been extrariordinarily resilient, surviving from the PETM and Grand Coupure in spite of their effects to the marine biosphere. They died out in our timeline just as humans evolved, for unclear reasons; we’ll see if they have better luck here.
Gastornithiformes
Like ratites gastornithiforms lost the ability to fly and attained large sizes, occupying the niches left by ceratopsians and other herbivorous dinosaurs. They are clearly galloanseres, though its currently debated if they are closer to waterfowl or to galliforms.
Like ratites, they attained a cosmopolitan distribution, with gastornithids in the northern continents, dromornithids in Australia and Brontornis in South America, though gastornithids disappeared from Asia and North America in the PETM. Unlike ratites they have massive, powerful beaks, apt to crush through seeds and harsh plant matter like branches. In Europe they in fact were the most common megafauna, with few large mammals, much like in our timeline. With the Grand Coupure the collapse of rainforests and the arrival of Asian predatory mammals they disappeared from the former island continent, but they continued to thrive in Australia and in South America.
Presbyornithids
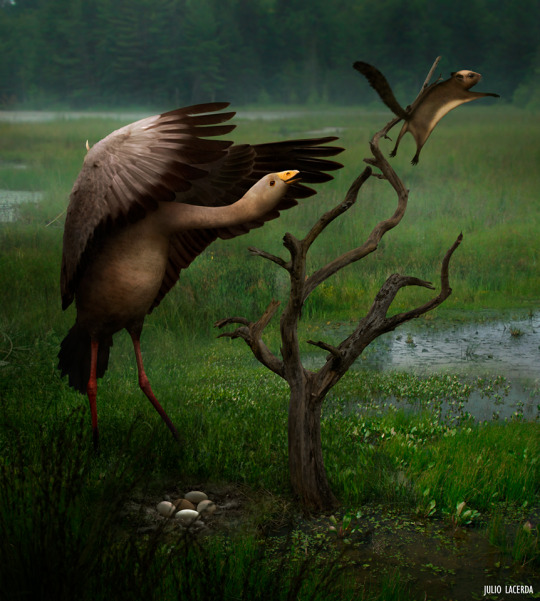

Presbyornithids are a clade of long legged waterfowl that first evolved in the Cretaceous and attained a diversity peak during the Paleocene, before declining in the Eocene of our timeline, reduced to only the terrestrial, goose-like Wilaru by the Miocene. This is often attributed to competition with anatid waterfowl, but studies show that they were incapable of filter-feeding, so they must have occupied fairly different ecological niches at the water’s edge.
In this timeline, they kept thriving thanks to the continuous hotshouse conditions, and more overtly diversified in piscivorous and crustacean eater niches akin to those of shoebills, spoonbills and even pelicans and ibises. Consequently, many of these waterbirds did not evolve in this timeline.
A partiular clade related to Wilaru kept exploring terrestrial biomes. These developed a novel way to process food: chewing it. Yes, some birds can chew (even used in the past to explain phylogenetic relationships between cuckoos and mousebirds before genetics said nah), using the cranial kinesis common to all crown birds to slide the upper jaw against the lower jaw in a pestle and mortar like way.
These birds, the Chakranatids, found thus a way to not only process plant matter more efficient while minimising fermentation, so they for the most part retained the ability to fly. Still, some have become large flightless herbivores, a distant echo of the Mesozoic hadrosaurs.
Palaelodids
The niche of ducks was instead taken by a decidedly non-waterfowl clade: the palaeolodids, relatives to flamingos and grebes. Neither divers or specialised filter-feeders (barring some species), these birds are rather generalistic, adapted to swim and catch small animals and plants with their broad beaks. They first debuted in the Oligocene in both timelines, though they might have a potentially older origin given grebes and flamingos split further back in the Cenozoic and Eocene fossil birds like Juncitarsus seem to represent the last common ancestor between these three groups.
Coliiformes
(A suggestion by Tozarkt777 on reddit)
In our timeline’s Paleocene, before passerines had evolved and spread to the northern hemisphere, the songbird niche was held by the Coliformes, an order that now only includes the mousebirds in our timeline, but back then comprised of many more species and many more niches, from generalistic grain-feeders to raptorial forms. They were most diverse in the Paleocene and Eocene before losing ground from there onwards.
Their decline likely is attributed to the PETM, and with the warm conditions of Multituberculate Earth having been maintained, so did mousebird rule. These are now the dominant small birds in the northern and African canopies, passerines now mostly restricted to small insectivores and nectivores.
Cariamiformes
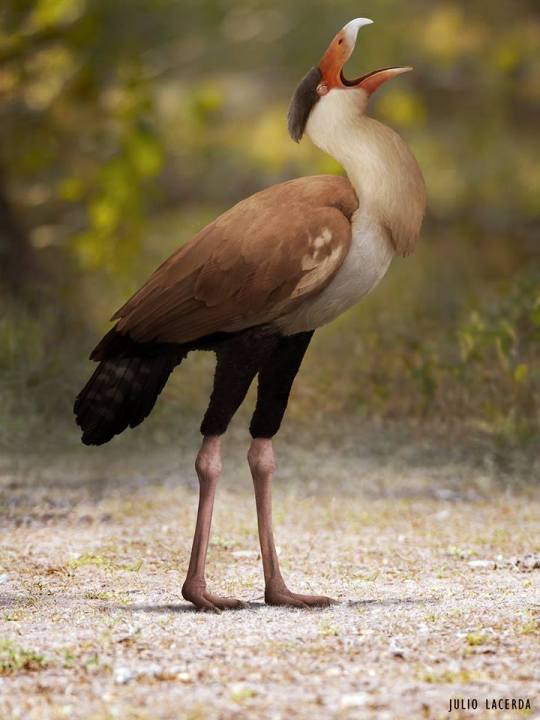

Represented by the vicious little seriemas in our timeline’s present, this group is best known for producing the infamous terror birds. However, a variety of other extinct groups also existed in the early Cenozoic, including another clade of infamous flightless killers, the bathornithids. Though known from usually more fragmentary remains, they too were incapable of flying and had deep, powerful beaks, well suited to tear flesh.
Proving that mammals still oughta fear theropods, the terror birds spread far and wide in the Eocene. Eleutherornis and relatives terrorised Europe while Lavocatavis and kin terrorised Africa; it is in fact unclear if terror birds evolved in the Old World and later raft/swam (or flew, if the last common ancestor still could fly) to South America like many mammals did or if inversely it went the other way around. We do know at least that Eleutherornis is a late comer to Europe as it arrived only in the mid-Eocene, so the group likely didn’t evolve there, though many other cariamiform groups were present, from the crow-like Salmila to the herbivorous, also flightless Strigogyps.
Meanwhile, South America was host to a larger diversity of terror birds, and across the sea North America was ruled by a large diversity of bathornithids. Both groups co-existed with predatory mammals in both timelines, and attained large sized species over two meters tall. The African and European species seem to have gone extinct in the Grand Coupure – the later doubtlessly affected by the extinction of indigenous prey and the arrival of new competitors – but the Americas saw an adaptive radiation in response to the spread of open grasslands. Predatory mammal groups may rise and fall, but these dinosaurs seem to be a constant, though for how long remains to be seen.
Besides large predatory forms, there are a variety of other poorly understood forms, like the aforementioned European species. Some, like Elaphrocnemus, appear to have been efficient flyers, less adapted to run like their terrestrial cousins but capable of soaring for long distances. while others like Qianshanornis seem to have been functionally similar to hawks and eagles. Most of these groups died out in the Grand Coupure, unable to cope with the loss of forest habitats.
#multituberculate earth#speculative zoology#spec evo#speculative biology#speculative evolution#bird#birds#dinosaur#dinosaurs#bathornis#lithornis#presbyornis
10 notes
·
View notes
Photo
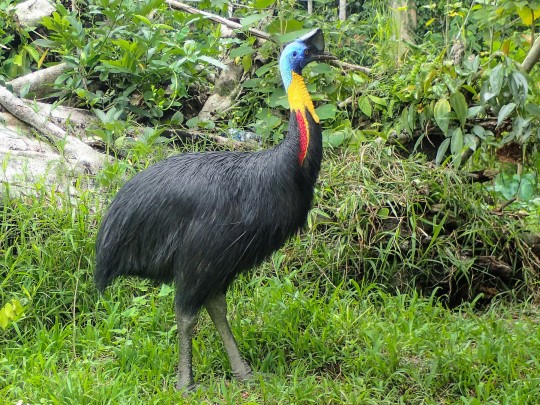
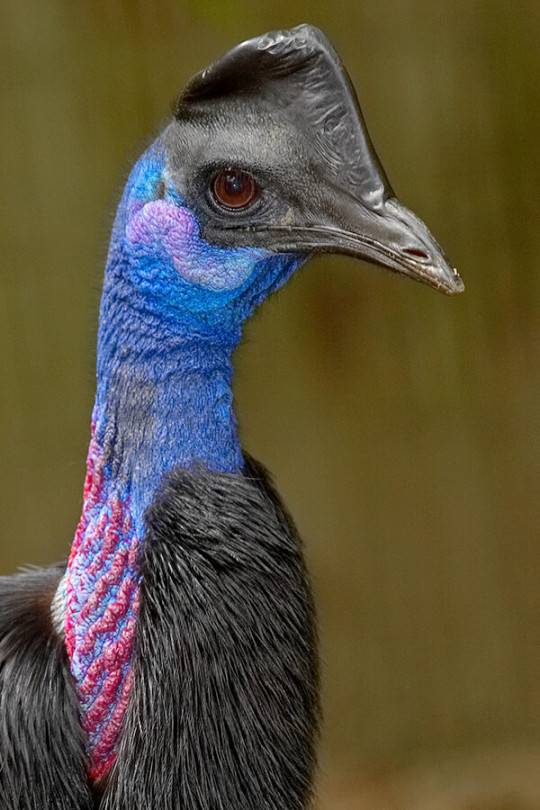



Carve Out Some Time for the Cassowary
Famous for their bright colors and short tempers, cassowaries are a group of flightless birds in the genus Casuarius. There are three species: the Northern Cassowary (C. unappendiculatus) which is found in New Guinea; the Southern Cassowary (C. casuarius), native southern New Guinea and northern Australia; and the Dwarf Cassowary (C. bennetti), endemic to New Guinea and the surrounding islands. All three species prefer tropical forests, though they are known to venture into savannahs, wetlands, and suburban areas in search of food.
Cassowaries are mainly active at dawn and dusk, and spend the time in between in their nests-- large pads of vegetation built on the ground. They opportunistic omnivores; their primary source of food is fruit and fungi, but they will also eat insects, frogs, fish, birds, small mammals, and carrion when available. Much of the fruit they eat is swallowed whole, which makes cassowaries invaluable for spreading seeds throughout their range. Additionally, due to their large size, adult cassowaries have no natural predators, and will aggressively defend their young from predators like snakes, monitor lizards, birds of prey, and wild dogs. When startled this birds can run up to 50 kph (31 mph), or lash out with their powerful legs.
Members of the Casuarius genus are solitary, save for the reproductive season. This season runs from May to September, when fruit is most abundant. Males maintain and defend territories, and call to attract mates. These calls are extremely loud, and at one of the lowest frequencies of any known bird, at about 23 Hertz. When a female approaches, the male crouches and allows the female to inspect him. She may also chase him, typically into water where the two perform a ritualistic fight before she submits. After laying her eggs, the female will move on to another male’s territory.
The eggs are extremely large and bright green, and usually laid in clutches of four. The male alone tends these eggs, incubating them and maintaining the nest for 50-52 days. The chicks that emerge stay with him for an additional 8-9 months until they become independent. Individuals take up to three years to become fully mature, and the average lifespan of wild Casuarius is anywhere from 30 to 50 years.
Southern Cassowaries are the largest of the three species, at up to 1.8 m (5ft 11 in) tall and weighing 58 kg (130 lbs) on average. Females tend to be much larger than males, and the species is considered to be the largest in Asia and the 3rd largest in the world. The Dwarf Cassowary, as the name implies, is significantly smaller at only 1.5m (4ft 11in) tall and 26 kg (57 lbs) at maximum. Northern Cassowaries lie between the two extremes. While all three species have black bodies, the coloration of their heads and necks vary significantly. Both the Northern and Southern Cassowary species have wattles-- pouches of skin that dangle from the neck-- that can be red, gold, purple, or white, which contrasts sharply with their blue necks. The Dwarf Cassowary lacks a wattle, and has a darker blue neck. In addition, it has the smallest head crest, or casque,; the Southern Cassowary’s casque is blade-shaped, and larger than the Dwarf Cassowary’s. The Northern Cassowary’s casque is more flared, and the largest of the three species.
Conservation Status: The Dwarf and Northern Cassowary species are considered Near Threatened and Least Concern respectively by the IUCN, while the Southern Cassowary is classified as endangered. All three are threatened primarily by habitat loss.
If you like what I do, consider leaving a tip or buying me a ko-fi!
Photos
Steve Parish
Kevin Schafer
San Diego Zoo
#northern cassowary#southern cassowary#dwarf cassowary#cassowary#Casuariiformes#Casuariidae#paleognaths#birds#tropical forests#tropical forest birds#tropical rainforests#tropical rainforest birds#savannahs#savannah birds#wetlands#wetland birds#asia#southeast asia#Papua New Guinea#australia#oceania
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
Danielsraptor vs Heracles
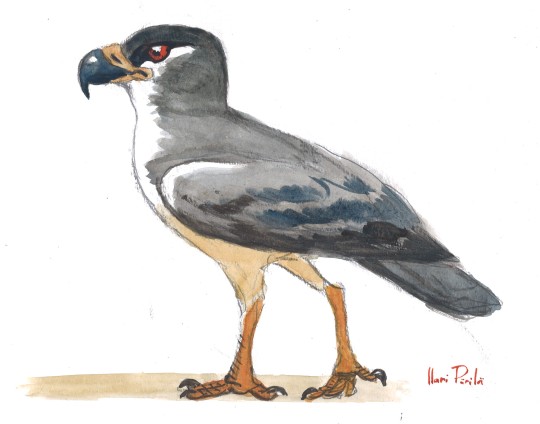


Factfiles:
Danielsraptor phorusrhacoides

Artwork by @otussketching, written by @zygodactylus
Name Meaning: Michael Daniels’ Terror Thief Bird
Time: 55 million years ago (Ypresian stage of the Eocene epoch, Paleogene period)
Location: Walton Member, London Clay Formation, England
While the Eocene fossil records of Seriemas, Passerines, and Parrots are fairly well known, the last remaining group of Australavians - the Falcons - remains something of a mystery. Danielsraptor helps to put together this puzzle a little more. Along with Masillaraptor, these birds show an early radiation of falcon-relatives from the Eocene in which they tried out a more terrestrial lifestyle! Danielsraptor had long legs, allowing it to forage and hunt on the ground like modern caracaras. It had a very large pygostyle, giving it long tail feathers - and with strong wing bones, it was able to fly in addition to hunt on the ground. It had a beak very similar to living caracaras and the extinct Terror Birds, further corroborating the idea that it was a bird of prey (and also potentially indicating a more complex evolutionary story for the early-derived Australavians). Living in the London Clay, Danielsraptor would have been one of the top predators, easily hunting the small mammals as well as the birds it shared its environment with - aided by both its terrestrial stalking abilities as well as its flying capability. Living in the London Clay, it shared its environment with the early loon Nasidytes, early owls, trogons, paleognaths, tropicbirds, duck-screamers, other diurnal raptors, the pseudotoothed bird Dasornis, and many parrot-passerine relatives. Crocodilians, snakes, turtles, fish, sharks, and a handful of mammals (including a primate) also lived in this rich post-Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum environment.
Heracles inexpectatus

Artwork by @otussketching, written by @zygodactylus
Name Meaning: Unexpected Herculean Parrot
Time: 16 to 19 million years ago (Burdigalian stage of the Miocene epoch, Neogene period)
Location: St. Bathans Fauna, Bannockburn Formation, Aotearoa
Heracles was a truly alarmingly large parrot, related to modern day Kea, Kaka, and Kakapo, known from the fantastic avifauna of St Bathans. Standing more than two feet tall and weighing about fifteen pounds, this animal was much larger than any expected from the St Bathans fauna, which represented the initial colonization of Aotearoa (Zealandia) after it returned above sea level. Heracles is also the largest known species of parrot, ever. It was presumably flightless, though it is uncertain if it was nocturnal like its living relative the Kakapo. Its exact ecology is still uncertain, given the material known from Heracles is limited and its living relatives have very disparate ecologies, though it is possible it was omnivorous similar to the Kea and Kaka today. The St Bathans fauna lived in a freshwater lake system, in a subtropical emergent rainforest. Separated from land bridges, the fauna was dominated by birds, with early relatives of the Kiwi, New Zealand Wrens, Adzebills, and Wedge-Tailed eagles found in the fauna, as well as somewhat modern looking Moas. Smaller flamingos, large fruit pigeons, and a huge variety of geese and other waterfowl are known. In addition, frogs, tuataras, other lizards, crocodilians, turtles, and many different types of fish are known from this fascinating ecosystem.
DMM Round One Masterpost
#dmm#dinosaur march madness#dmm round one#dmm rising stars#palaeoblr#dinosaurs#paleontology#bracket#march madness#danielsraptor#heracles#polls
178 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anthro Allies Remastered (Part 2)





now for the first vertebrates before us mammals
Cephalochordate
Wyn (Lancelet)
Oxi (Amphioxi)
Tunicate
Hydrant (Sea Squirt)
Vagile (Larvacea)
Fen (Salps)
Sub-Flame (Pyrosome)
Fish
Lagoona (Eel/Fish Hybrid)
Josiah (Hagfish/Lamprey)
Chomps (Piranha)
Fugu (Pufferfish)
Mikayla (Mermaid hybrid)
Whirlpool (Merman hybrid)
Fossil (Coelacanth/Lungfish)
Sea Shocker (Ray Hybrid)
Ichi (Chimera fish)
Thatcher (Shark Hybrid)
Amphibians
Pads (Common frog/Bullfrog/Goliath frog)/Mutant
Zookie (Poison dart frog)
Balzo (Tree frog)
Mangrove (Horned Bullfrog)
Croaker (Toad Hybrid)
Daisy (Caecilian)
Poly (Rubber Eel)
Rigid (Newt)
Axanthic (Salamander/Axolotl)
Echo (Siren/Olm/Amphiuma)
Reptiles
Veo (Komodo Dragon/Monitor Lizard)
Ivy (Sand Lizard)
Clyde/Pygment (Chameleon)
Viridian (Skink)
Rancor (Gila Monster)
Anahera (Tuatara)
Takeo (Gecko)
Nori (Iguana/Marine iguana)
Draco (Dragon Lizard)
Chole (Softshell/Terrapin)
Beckett (Box/Pond Turtle)
Rave (Snapping Turtle)
Mechel (Big headed Turtle)
Flyta (Sea Turtle)
Bartolomeo (Tortoise)
Lu-Hyen (Caiman/Gharial)
K.Roc (Crocodilian)
Roxy (Alligator)
Herik (Viper/Cobra)
Neveah (Constrictor/Serpent)
Birds
Nimbious (Bird of Prey)
Maverick (Bird of Prey)
Felifa (Owl)
Jaxon (Sea Bird)
Valentina (Serima)
Stalks (Stork/Crane/Shoebill/Heron)
Terpsicore (Flamingo)
William (Paleognath)
Harper (Game fowl)
Martin/Frozan (Penguin)
Mallie (Water fowl)
Loco (Cuckoo)
Evelin/Evening (Corvid)
Colors (Parrot)
Rumba (Cardinal/Canary/Tanager)
Sonnet (Song Bird Hybrid)
Yashi (Woodpecker/Toucan)
Recorder (Drongo)
Tiffany (Oxpecker)
Zennon (Hummingbird)
Previous/Next
(For More Information About The Earthdemons, Neo demons, The Anthro allies , the O'Kong family and more of theses characters as well as updates please visit the @the-earthdemon-hub for more)
#my ocs#my art#elementalgod aj#aj the elementalgod#isle o#toonverse oc#The Watchful Eye#Watchful Eye#O'Kong family#Earthdemons#Neo Demons#Anthro Allies#birds#reptiles#fish#amphibians#Tunicates#Cephalochordate
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fossil Novembirb: Day 5 - It's Getting Hot in Here

It's the late Paleocene, and the climate is red hot. And it'll get hotter still. It's the start of an event called the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, or PETM. At this moment, the Earth's climate warms very rapidly, and it'll gets really warm. How warm? Warm enough for rainforests in Europe, and for towering cypress swamps to grow in the Arctic. And as for these birds living in Paleocene Wyoming, their world is a steaming hot tropical wetland.
Primoptynx: One of the earliest known owls, and was quite large. Unlike modern owls it had talons more like a hawk, and it hunted during the day.
Sandcoleus: An early relative of mousebirds, and a climbing opportunistic omnivorous forest dweller.
Anachronornis: A peculiar kind of waterfowl, related to ducks and bearing a striking resemblance to the screamers of South America.
Paragrus: Despite its name, this is bird is not related to cranes. Instead it belongs to a group of flightless birds called Geranoidids, which are related to ostritches.
Lithornis promiscuus: An early relative of Palaeognath birds like ostritches and emus. Unlike most modern paleognaths, it could fly for long distances and even soar.
Lithornis plebius: Another Lithornithid, and like all lithornithids, had a long sensitive beak for probing insects from soil and leaf litter.
#Fossil Novembirb#Novembirb#Dinovember#birblr#palaeoblr#Birds#Dinosaurs#Cenozoic Birds#Primoptynx#Sandcoleus#Anachronornis#Paragrus#Lithornis
45 notes
·
View notes