#pablo carlos budassi
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

How can you visualize the entire observable universe in a relatively small rectangular area?
Using the logarithmic scale, as Pablo Carlos Budassi did, locating the most notable astronomical objects as far away as the edge of time. 🌌
Source (zoomable): buff.ly/3Av83hn
—
This vertically oriented logarithmic map spans nearly 20 orders of magnitude, taking us from planet Earth to the edge of the Observable Universe.
The scheme locates notable astronomical objects of various scales: spacecraft, moons, planets, star systems, nearby galaxies, and notable large-scale structures are some of the objects indicated.
The graphic aims to provide a concise yet comprehensive representation of a diverse range of astronomical knowledge, incorporating visual clarity and intuitive organization.
Source: pablocarlosbudassi.com
—
Pablo Carlos Budassi (born 1980) is an Argentinian artist, musician and writer, known for his passion for exploring the mysteries of the cosmos and expressing his fascination through graphic art, music, and poetry.
#observable universe#universe#Pablo Carlos Budassi#logarithmic scale#astronomy#cosmos#logarithmic map#Earth#spacecraft#moons#planets#star systems#galaxies#astrography
0 notes
Text
Ilustración logarítmica del universo observable

Pablo Carlos Budassi









#universe#logarithms#study space#science#computer scientist#scientific illustration#ilustration#scientist#planets#planet#planet earth#earth#solar system#solar#stars#star#pablo carlos budassi
1 note
·
View note
Note
Illustrations by Pablo Carlos Budassi and Fred the Oyster respectively.
tell me a strange fact about a thing you like
the dwarf planet haumea spins so quickly that its shape has become distorted and oblong. it also has rings, two moons and a red spot (although probably a smaller spot than is shown in this artist’s rendition)

the star known as achernar also possesses this property, and is the least spherical star in the milky way galaxy.

19 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rectangular log map-scheme of the Observable Universe by Pablo Carlos Budassi
#space#outer space#observable universe#planets#galaxy#galaxies#stars#void#aesthetic#grunge#indie#universe#vintage#aesthetics#alternative#universo
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Entire Observable Universe so far. Credits: Pablo Carlos Budassi
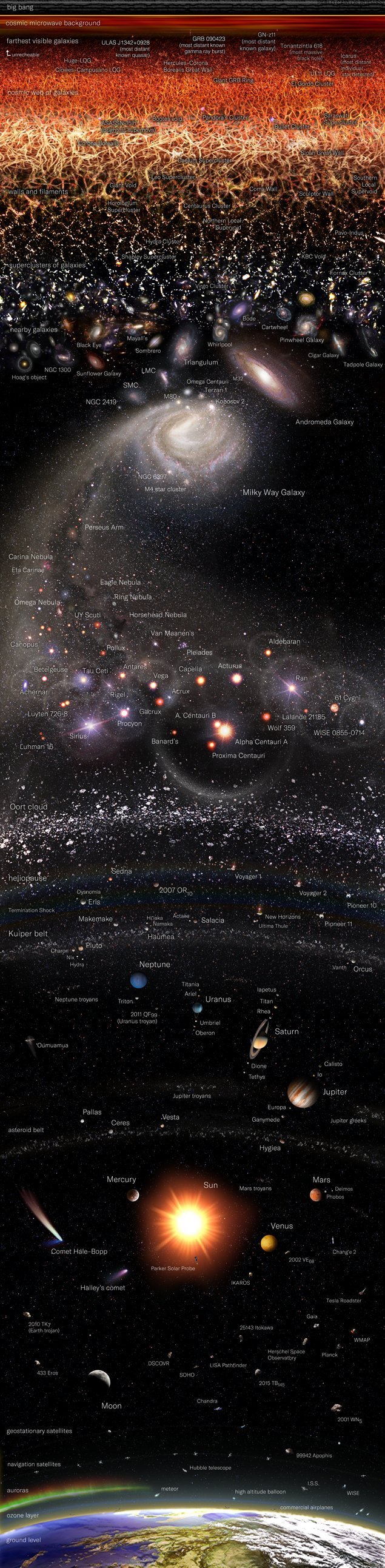

#astronomy#space#astrophotography#universe#nasa#astro#galaxy#astronout#galaxies#astro notes#outer space#planets#astro community#astro observations#planet#solar system#nasa photos#nasa picture of the day
785 notes
·
View notes
Photo




The Observable Universe Logarithmic Map
The farthest object in this map is HD1, a galaxy, at 33.2 billion light years away which was just discovered in 2022 BUT it has been beaten by CEERS-93316 at 34.6 billion light years away, discovered just 4 months after HD1.
by Pablo Carlos Budassi
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Rectangular log map-scheme of the Observable Universe
Credit to Pablo Carlos Budassi

2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Observable Universe
Credits: Licence, Wikipedia, Pablo Carlos Budassi
242 notes
·
View notes
Text
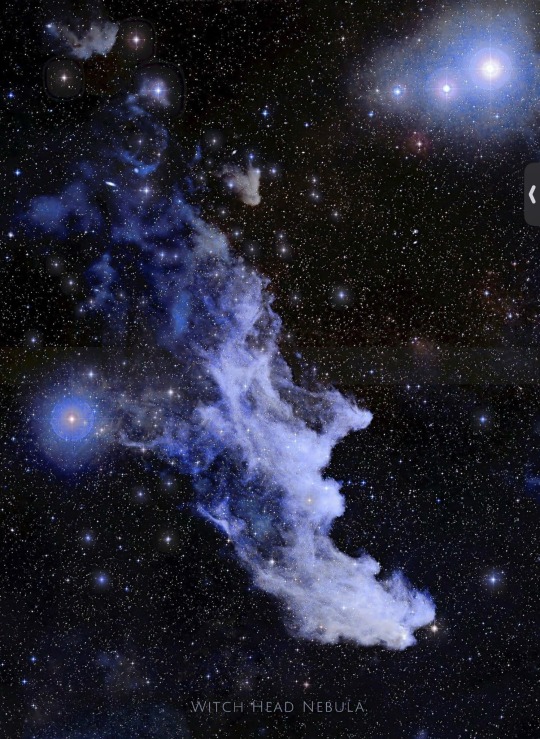
WITCH HEAD NEBULA * IC 2118 (also known as Witch Head Nebula due to its shape) is an extremely faint reflection nebula believed to be an ancient supernova remnant or gas cloud illuminated by nearby supergiant star Rigel in the constellation of Orion. It lies in the Orion constellation, about 900 light-years from Earth. The nature of the dust particles, reflecting blue light better than red, is a factor in giving the Witch Head its blue color. Radio observations show substantial carbon monoxide emission throughout parts of IC 2118, an indicator of the presence of molecular clouds and star formation in the nebula. In fact candidates for pre-main sequence stars and some classic T-Tauri stars have been found deep within the nebula. The molecular clouds of IC 2118 are probably juxtaposed to the outer boundaries of the vast Orion-Eridanus bubble, a giant supershell of molecular hydrogen blown by the high mass stars of the Orion OB1 association. As the supershell expands into the interstellar medium, favorable circumstances for star formation occur. IC 2118 is located in one such area. The wind blown appearance and cometary shape of the bright reflection nebula is highly suggestive of a strong association with the high mass luminous stars of Orion OB1. The fact that the heads of the cometary clouds of IC2118 point northeast towards the association is strong support of that relationship.. Credit to Pablo Carlos Budassi.

#nebula and quasar#dark nebula#nebulosa#neutron stars#planetary nebula#nebula#astronomy#astronomers#nasa#universe#nasa photos#astrophotography#astrophysics#outer space#nasawebb#hubble space telescope#space exploration#space#science#james webb space telescope#space shuttle#science facts#nasa science#planetary science#planet earth#i love astronomy#astronomy facts#cosmos#the universe#nasaastronaut
113 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2024 July 1
Time Spiral Illustration Credit: Pablo Carlos Budassi via Wikipedia
Explanation: What's happened since the universe started? The time spiral shown here features a few notable highlights. At the spiral's center is the Big Bang, the place where time, as we know it, began about 13.8 billion years ago. Within a few billion years atoms formed, then stars formed from atoms, galaxies formed from stars and gas, our Sun formed, soon followed by our Earth, about 4.6 billion years ago. Life on Earth begins about 3.8 billion years ago, followed by cells, then photosynthesis within a billion years. About 1.7 billion years ago, multicellular life on Earth began to flourish. Fish began to swim about 500 million years ago, and mammals began walking on land about 200 million years ago. Humans first appeared only about 6 million years ago, and made the first cities only about 10,000 years ago. The time spiral illustrated stops there, but human spaceflight might be added, which started only 75 years ago, and useful artificial intelligence began to take hold within only the past few years.
∞ Source: apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap240701.html
147 notes
·
View notes
Photo
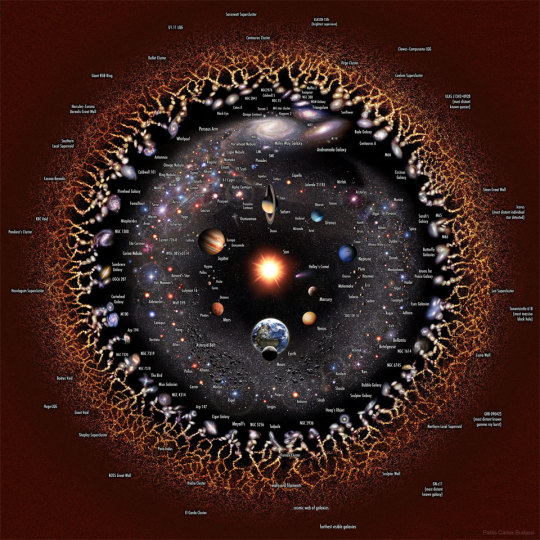
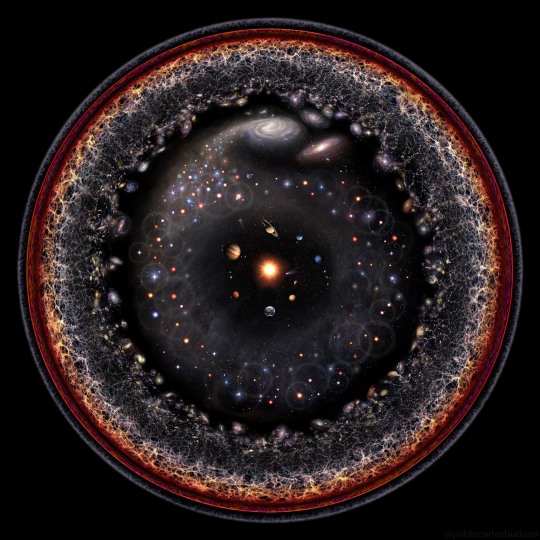

The Eye of the Universe. Pablo Carlos Budassi How far can you see? Everything you can see, and everything you could possibly see, right now, assuming your eyes could detect all types of radiations around you -- is the observable universe. In light, the farthest we can see comes from the cosmic microwave background, a time 13.8 billion years ago when the universe was opaque like thick fog. Some neutrinos and gravitational waves that surround us come from even farther out, but humanity does not yet have the technology to detect them. The featured image illustrates the observable universe on an increasingly compact scale, with the Earth and Sun at the center surrounded by our Solar System, nearby stars, nearby galaxies, distant galaxies, filaments of early matter, and the cosmic microwave background. Cosmologists typically assume that our observable universe is just the nearby part of a greater entity known as "the universe" where the same physics applies. However, there are several lines of popular but speculative reasoning that assert that even our universe is part of a greater multiverse where either different physical constants occur, different physical laws apply, higher dimensions operate, or slightly different-by-chance versions of our standard universe exist.Extended universe logarithmic illustration
192 notes
·
View notes
Text

As one of the brightest stars in the night sky, Aldebaran is also one of the most mythologized. Ancient astronomers in the Middle East, India, Greece, Mexico and Australia all had stories to explain Aldebaran's reddish glow, which is actually a product of its large size and relatively cool surface temperature.
The giant red star Aldebaran, seen in the background in this artist's conception, is 65 light-years away from the sun in the constellation Taurus. It is 44 times the sun's diameter and hosts a planet several times the mass of Jupiter.
Aldebaran comes from the Arabic phrase "al Dabarān," which translates as "the follower."
Art credit: PABLO CARLOS BUDASSI/WIKIMEDIA COMMONS
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Aldebaran: The Demon Star. Rohini Nakshatra
Red giant star 65 ly away in the constellation Taurus - 44 times the Sun's diameter - Hosts a planet several times the mass of Jupiter that was in the habitable zone when the star was at its main-sequence stage - Pablo Carlos Budassi
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
How far can you see? Everything you can see, and everything you could possibly see, right now, assuming your eyes could detect all types of radiations around you -- is the observable universe. In light, the farthest we can see comes from the cosmic microwave background, a time 13.8 billion years ago when the universe was opaque like thick fog.
Some neutrinos and gravitational waves that surround us come from even farther out, but humanity does not yet have the technology to detect them.
The featured image illustrates the observable universe on an increasingly compact scale, with the Earth and Sun at the center surrounded by our Solar System, nearby stars, nearby galaxies, distant galaxies, filaments of early matter, and the cosmic microwave background. Cosmologists typically assume that our observable universe is just the nearby part of a greater entity known as "the universe" where the same physics applies.
However, there are several lines of popular but speculative reasoning that assert that even our universe is part of a greater multiverse where either different physical constants occur, different physical laws apply, higher dimensions operate, or slightly different-by-chance versions of our standard universe exist.
📷: Wikipedia, Pablo Carlos Budassi

#nasa#astronomy#astrophotography#solar system#astrophysics#hubble#nebula#james webb space technology#physics#james webb images#observable universe#space advances#space adventures#space#space facts#science acumen#European Space Agency#amazing#amazing facts#i love universe
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
HD map of the galaxy by Pablo Carlos Budassi
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

CIRCULAR MAP OF THE UNIVERSE ALL VERSIONS - Pablo Carlos Budassi
2 notes
·
View notes