#loan distribution program
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
since we now know that all those "my blog is safe for Jewish people" posts are bullshit, here are some Jewish organizations you can donate to if you actually want to prove you support Jews. put up or shut up
FIGHTING HUNGER
Masbia - Kosher soup kitchens in New York
MAZON - Practices and promotes a multifaceted approach to hunger relief, recognizing the importance of responding to hungry peoples' immediate need for nutrition and sustenance while also working to advance long-term solutions
Tomchei Shabbos - Provides food and other supplies so that poor Jews can celebrate the Sabbath and the Jewish holidays
FINANCIAL AID
Ahavas Yisrael - Providing aid for low-income Jews in Baltimore
Hebrew Free Loan Society - Provides interest-free loans to low-income Jews in New York and more
GLOBAL AID
American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee - Offers aid to Jewish populations in Central and Eastern Europe as well as in the Middle East through a network of social and community assistance programs. In addition, the JDC contributes millions of dollars in disaster relief and development assistance to non-Jewish communities
American Jewish World Service - Fighting poverty and advancing human rights around the world
Hebrew Immigrant Aid Society - Providing aid to immigrants and refugees around the world
Jewish World Watch - Dedicated to fighting genocides around the world
MEDICAL AID
Sharsheret - Support for cancer patients, especially breast cancer
SOCIAL SERVICES
The Aleph Institute - Provides support and supplies for Jews in prison and their families, and helps Jewish convicts reintegrate into society
Bet Tzedek - Free legal services in LA
Bikur Cholim - Providing support including kosher food for Jews who have been hospitalized in the US, Australia, Canada, Brazil, and Israel
Blue Card Fund - Critical aid for holocaust survivors
Chai Lifeline - An org that's very close to my heart. They help families with members with disabilities in Baltimore
Chana - Support network for Jews in Baltimore facing domestic violence, sexual abuse, and elder abuse
Community Alliance for Jewish-Affiliated Cemetaries - Care of abandoned and at-risk Jewish cemetaries
Crown Heights Central Jewish Community Council - Provides services to community residents including assistance to the elderly, housing, employment and job training, youth services, and a food bank
Hands On Tzedakah - Supports essential safety-net programs addressing hunger, poverty, health care and disaster relief, as well as scholarship support to students in need
Hebrew Free Burial Association
Jewish Board of Family and Children's Services - Programs include early childhood and learning, children and adolescent services, mental health outpatient clinics for teenagers, people living with developmental disabilities, adults living with mental illness, domestic violence and preventive services, housing, Jewish community services, counseling, volunteering, and professional and leadership development
Jewish Caring Network - Providing aid for families facing serious illnesses
Jewish Family Service - Food security, housing stability, mental health counseling, aging care, employment support, refugee resettlement, chaplaincy, and disability services
Jewish Relief Agency - Serving low-income families in Philadelphia
Jewish Social Services Agency - Supporting people’s mental health, helping people with disabilities find meaningful jobs, caring for older adults so they can safely age at home, and offering dignity and comfort to hospice patients
Jewish Women's Foundation Metropolitan Chicago - Aiding Jewish women in Chicago
Metropolitan Council on Jewish Poverty - Crisis intervention and family violence services, housing development funds, food programs, career services, and home services
Misaskim - Jewish death and burial services
Our Place - Mentoring troubled Jewish adolescents and to bring awareness of substance abuse to teens and children
Tiferes Golda - Special education for Jewish girls in Baltimore
Yachad - Support for Jews with disabilities
#atlas entry#please add any more you know of an especially add fundraisers for you or people you know#if there are any fundraisers for synagogues please add those as well#jew#jewish#judaism#jumblr#punch nazis
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #14
April 12-19 2024
The Department of Commerce announced a deal with Samsung to help bring advanced semiconductor manufacturing and research and development to Texas. The deal will bring 45 billion dollars of investment to Texas to help build a research center in Taylor Texas and expand Samsung's Austin, Texas, semiconductor facility. The Biden Administration estimates this will create 21,000 new jobs. Since 1990 America has fallen from making nearly 40% of the world's semiconductor to just over 10% in 2020.
The Department of Energy announced it granted New York State $158 million to help support people making their homes more energy efficient. This is the first payment out of a $8.8 billion dollar program with 11 other states having already applied. The program will rebate Americans for improvements on their homes to lower energy usage. Americans could get as much as $8,000 off for installing a heat pump, as well as for improvements in insulation, wiring, and electrical panel. The program is expected to help save Americans $1 billion in electoral costs, and help create 50,000 new jobs.
The Department of Education began the formal process to make President Biden's new Student Loan Debt relief plan a reality. The Department published the first set of draft rules for the program. The rules will face 30 days of public comment before a second draft can be released. The Administration hopes the process can be finished by the Fall to bring debt relief to 30 million Americans, and totally eliminate the debt of 4 million former students. The Administration has already wiped out the debt of 4.3 million borrowers so far.
The Department of Agriculture announced a $1 billion dollar collaboration with USAID to buy American grown foods combat global hunger. Most of the money will go to traditional shelf stable goods distributed by USAID, like wheat, rice, sorghum, lentils, chickpeas, dry peas, vegetable oil, cornmeal, navy beans, pinto beans and kidney beans, while $50 million will go to a pilot program to see if USAID can expand what it normally gives to new products. The food aid will help feed people in Bangladesh, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Haiti, Kenya, Madagascar, Mali, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Yemen.
The Department of the Interior announced it's expanding four national wildlife refuges to protect 1.13 million wildlife habitat. The refuges are in New Mexico, North Carolina, and two in Texas. The Department also signed an order protecting parts of the Placitas area. The land is considered sacred by the Pueblos peoples of the area who have long lobbied for his protection. Security Deb Haaland the first Native American to serve as Interior Secretary and a Pueblo herself signed the order in her native New Mexico.
The Department of Labor announced new work place safety regulations about the safe amount of silica dust mine workers can be exposed to. The dust is known to cause scaring in the lungs often called black lung. It's estimated that the new regulations will save over 1,000 lives a year. The United Mine Workers have long fought for these changes and applauded the Biden Administration's actions.
The Biden Administration announced its progress in closing the racial wealth gap in America. Under President Biden the level of Black Unemployment is the lowest its ever been since it started being tracked in the 1970s, and the gap between white and black unemployment is the smallest its ever been as well. Black wealth is up 60% over where it was in 2019. The share of black owned businesses doubled between 2019 and 2022. New black businesses are being created at the fastest rate in 30 years. The Administration in 2021 Interagency Task Force to combat unfair house appraisals. Black homeowners regularly have their homes undervalued compared to whites who own comparable property. Since the Taskforce started the likelihood of such a gap has dropped by 40% and even disappeared in some states. 2023 represented a record breaking $76.2 billion in federal contracts going to small business owned by members of minority communities. This was 12% of federal contracts and the President aims to make it 15% for 2025.
The EPA announced (just now as I write this) that it plans to add PFAS, known as forever chemicals, to the Superfund law. This would require manufacturers to pay to clean up two PFAS, perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. This move to force manufacturers to cover the costs of PFAS clean up comes after last week's new rule on drinking water which will remove PFAS from the nation's drinking water.
Bonus:
President Biden met a Senior named Bob in Pennsylvania who is personally benefiting from The President's capping the price of insulin for Seniors at $35, and Biden let Bob know about a cap on prosecution drug payments for seniors that will cut Bob's drug bills by more than half.
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#jobs#Economy#student loan debt#Environment#PFAS#politics#US politics#health care
764 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump Gears Up for Change on Wokeness With Education Overhaul
The president-elect has laid out big changes for America’s classrooms, including expanding school choice—and shutting down the Department of Ed
By Matt Barnum and Douglas Belkin -- Wall Street Journal
President-elect Donald Trump has vowed to remake education in the U.S., pledging to exert more control over funding and classroom lessons, to curb what he views as left-leaning tendencies at universities and even to dismantle the Department of Education.
If his White House delivers on those promises, more families could get money to send kids to private school. Schools would face pressure to limit accommodations for transgender students and to end some initiatives aimed at addressing racial disparities.
The goals are at once ambitious and controversial.
“There are a lot of very smart people who are very excited to get into positions where we can actually start making change happen,��� said Tiffany Justice, a Trump ally and the co-founder of the conservative parents group Moms for Liberty.
Eliminating the Department of Education
Trump has promised to close the Education Department and has criticized U.S. school spending.
In his first term, he proposed merging the education and labor departments, but Congress didn’t proceed. It isn’t clear whether lawmakers would go for the idea in a second term, nor how the department’s functions—such as protecting students’ civil rights, providing funding for students with disabilities and distributing student loans—would be handled if it were closed.
Some Republicans have been reluctant to eliminate the department or cut federal funding that flows to schools in their constituencies. An Associated Press poll last year found that nearly two-thirds of Americans said the federal government spends too little on education.
“I don’t think you’ll see enormous cuts because that’s super unpopular,” said Michael Petrilli, president of the Thomas B. Fordham Institute, a conservative education think tank.
Trump will have to fill the education secretary role for now. Cabinet positions often go to prominent politicians and political allies.
Presidents sometimes look to state education chiefs. High-profile leaders in Republican states include Oklahoma’s Ryan Walters, who has fought culture-war battles in schools; Louisiana’s Cade Brumley, who has supported private-school choice and tougher school disciplinary measures; and Florida’s Manny Diaz Jr., who has overseen many conservative policy changes.
In an interview, Walters said he is focused on implementing Trump’s agenda in Oklahoma. Through a spokesperson, Brumley said “my focus is on continuing the historic educational progress we are making in Louisiana.” Diaz, through a spokesperson, said if asked to serve, “Of course you listen.” Justice of Moms for Liberty said that she would be open to the position, though hasn’t spoken to the Trump team about it.
A Trump transition spokeswoman didn’t comment on specific candidates.
Waging war on ‘woke’
Trump has said he would use the power of the purse to limit left-wing ideology in schools and universities.
Although a president can’t immediately cut off money to any school, he could use various laws to pressure schools to address antisemitism on campus, disband programs that focus on nonwhite student groups or reduce accommodations for transgender students.
Trump has said that he believes that Title IX, which bars sex discrimination in education, should prevent transgender girls from playing on female sports teams. This would be a stark reversal from the Biden administration, which has interpreted Title IX to prohibit discrimination based on gender identity.
During the campaign, Trump attacked Kamala Harris for being too supportive of transgender rights, an issue that resonated with some voters.
Trump has also indicated that he would use civil-rights law to challenge critical race theory, a term used by conservatives to describe some efforts to teach about racism and racial disparities. This could include targeting university diversity, equity and inclusion offices, legal analysts have said.
“On issues that I worry about…this is at the top,” said Rachel Perera, a fellow at the Brookings Institution, a center-left think tank.
Another tool Trump has at his disposal is the accreditation system, which gives universities access to federal money. He has called it a “secret weapon.”
Colleges and universities need to meet standards set by independent accreditors to be eligible for federal funds.
Trump could weaken the influence of accreditors—which he considers too left-leaning—by reassigning some of their responsibilities to the Education Department, said Judith Eaton, past president of the Council for Higher Education Accreditation. Alternatively, the administration could replace current accreditors with ones more closely aligned with Trump’s vision, she added.
Members of Trump’s inner circle “regard the higher-ed cartel as fundamentally out of order,” said Frederick Hess, director of education policy studies at the right-leaning American Enterprise Institute.
‘Universal school choice’
Trump wants “universal school choice for every American family,” according to his platform. That likely means providing a public subsidy for private-school tuition or other educational expenses outside the public school system.
Trump has indicated he would support the Educational Choice for Children Act, already proposed in Congress. The law would provide $10 billion in federal tax credits to go toward private-school tuition, home schooling or other educational costs.
Backers say the bill would provide money for up to two million children, and help parents direct and customize their children’s education. School-choice critics say that these programs drain resources from public schools.
Prior efforts by Republican presidents to subsidize private schools—including those supported by Ronald Reagan, and Trump in his first term—have failed to garner congressional support. And while many Republican-controlled state legislatures have adopted such programs in recent years, voters in Colorado, Kentucky and Nebraska rejected school-choice ballot measures on Nov. 5.
Some Republicans “are not fully on board yet,” said Jim Blew, who served as an education official during Trump’s first term. “I think they will be in the new administration.”
#Department of Education#Woke#trump#president trump#Democrats#love#trump 2024#art#repost#nature#america first#fashion#americans first#landscape#america#food#donald trump#lol#gif#diy#ivanka#instagram
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
A few lessons so far, since my dad's death (it's only been a week):
"Denial", as a stage, doesn't necessarily mean "refusing to believe" so much as denying permission, and demanding the thing be undone.
It hasn't been things to do with his death so much that set me off when I see them in shows, but things from his life — phrases he used or words he would want to look up.
Three hour meeting at the funeral home.
If you're single, there are likely to be many fewer formal or semi-formal photos of you with significant family, and they won't be distributed as widely in family photo collections (e.g., everyone else has family or wedding photos with my dad but I'm just in the sisters group shots; no-one seems to have a photo of me with him when I was admitted).
There's a big photo gap between stopping printing film photos (this was before stopping taking them) and there being a regularly updated photo program (or FB) that stores and tags them all. Some DEEP dives into 2006 external harddrives. But a lot of photos were last seen in old emails and people have changed their accounts.
The bowl of snack-size trail mix boxes and mini-chocolates has been a good thing.
The first week is relentless — so much to do, and so little time before it has to be done.
Crying gives me a headache at the best of times, so I just committed to taking paracetemol regularly for the short term.
Newspaper obituaries aren't really a (useful) thing anymore, at least where we are. It's social media and half-remembered contact details and you vs the algorithms. And you have to ask people to spread the word to people they might be in touch with.
I ended up calling a number of my dad's closest carers so I could give them the details on what happened and check on them, without my mother having to tell the story every time she sees someone. It was really lovely talking to them, actually. But that calling and telling people who have a legitimate interest is a thing.
It's difficult to know what to offer when someone dies, and harder to know what to ask for! But in our case logistics — cash on hand for immediate expenses, loans of cars (especially given visiting family), cleaning and other services that stop on death, being available to run errands — have been the most useful. Not something that's always possible, but genuinely very helpful.
Group project, under stress, with siblings.
38 notes
·
View notes
Text

Excerpt from this story from Canary Media:
The Grain Belt Express, a $7 billion transmission line project that’s been more than a decade in development, has won conditional approval for a $4.9 billion federal loan guarantee.
The Grain Belt Express could enable 5 gigawatts’ worth of affordable, clean power to be developed on the windswept and sun-soaked Kansas plains and then delivered to customers in Missouri, Illinois, and broader eastern U.S. power markets. If finalized, the federal backing would help push the sorely needed transmission project over the finish line.
The proposed loan guarantee is the latest in a string of Biden administration actions aimed at bolstering the U.S. power grid. The country needs to rapidly build high-voltage transmission lines in order to accommodate new solar and wind power, reduce grid congestion that’s driving up electricity rates, and improve power system reliability in the face of extreme weather events.
Whether the Grain Belt Express will be able to make use of this financial support is unclear, however. Last week’s conditional commitment from the Department of Energy’s Loan Programs Office (LPO) may ultimately depend on whether the Trump administration decides to follow through with it.
The LPO has played a major role in the Biden administration’s clean energy agenda, announcing about $37 billion in loans and loan guarantees over the past four years. Recipients include electric vehicle and battery factories; battery mineral mining, processing, and recycling facilities; distributed solar and battery deployments; EV charging projects; makers of alternative aviation fuels; clean-hydrogen production plants;and the owner of a shuttered nuclear power plant in Michigan that hopes to restart it.
Roughly $25 billion of those commitments have yet to be finalized and contracted by the DOE, according to a late November tally from Politico. The LPO has been sprinting to complete these contracts in case the incoming Trump administration opts to freeze any in-progress loan agreements.
Many of the projects backed by the LPO are in Republican congressional districts, Politico reported. That includes the Grain Belt Express, which plans to use its conditional loan guarantee to finance the first phase of its 5-gigawatt high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission line — a 578-mile stretch from southwestern Kansas to Missouri.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - October 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles on Patreon!
1. EV owners volunteer to drive voters to the polls in 11 states (and you can too)

“ChargeTheVote.org is a nonpartisan voter education and engagement initiative to enhance voter turnout in the 2024 election by providing zero-emission transportation in electric vehicles (EVs) to local polling locations. ChargeTheVote will also host a webinar for those who are interested in participating this coming Tuesday, October 22 at 7pm Eastern time.”
2. Kenya moves 50 elephants to a larger park, says it’s a sign poaching is low

“The elephant population in the […”Mwea National Reserve”…] has flourished from its capacity of 50 to a whopping 156 […] requiring the relocation of about 100 of [them…. The] overpopulation in Mwea highlighted the success of conservation efforts over the last three decades.”
3. Australian start-up secures $9m for mine-based gravity energy storage technology

““We expect to configure the gravitational storage technology [which the company “hopes to deploy in disused mines”] for mid-duration storage applications of 4 to 24 hours, deliver 80% energy efficiency and to enable reuse of critical grid infrastructure.“”
4. Africa’s little-known golden cat gets a conservation boost, with community help

“[H]unting households were given a pregnant sow [… so that they] had access to meat without needing to trap it in the wild. […] To address income needs, Embaka started […] a savings and loan co-op[… and an] incentive for the locals to give up hunting in exchange for regular dental care.”
5. 4.8M borrowers — including 1M in public service — have had student debt forgiven

“That brings the total amount of student debt relief under the administration to $175 billion[….] The Education Department said that before Biden's presidency, only 7,000 public servants had ever received student debt relief through the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program. […] "That’s an increase of more than 14,000% in less than four years.””
6. Puerto Rico closes $861M DOE loan guarantee for huge solar, battery project

“The solar plants combined will have 200 megawatts of solar capacity — enough to power 43,000 homes — while the battery systems are expected to provide up to 285 megawatts of storage capacity. [… O]ver the next 10 years, more than 90 percent of solar capacity in Puerto Rico will come from distributed resources like rooftop solar.”
7. Tim Walz Defends Queer And Trans Youth At Length In Interview With Glennon Doyle
“Walz discussed positive legislative actions, such as codifying hate crime laws and increasing education[.… “We] need to appoint judges who uphold the right to marriage, uphold the right to be who you are [… and] to get the medical care that you need.””
8. Next-Generation Geothermal Development Important Tool for Clean Energy Economy

““The newest forms of geothermal energy hold the promise of generating electricity 24 hours a day using an endlessly renewable, pollution-free resource[… that] causes less disturbance to public lands and wildlife habitat […] than many other forms of energy development[….]”
9. Sarah McBride hopes bid to be first transgender congresswoman encourages ’empathy’ for trans people

““Folks know I am personally invested in equality as an LGBTQ person. But my priorities are going to be affordable child care, paid family and medical leave, housing, health care, reproductive freedom. […] We know throughout history that the power of proximity has opened even the most-closed of hearts and minds.”“
10. At Mexico’s school for jaguars, big cats learn skills to return to the wild
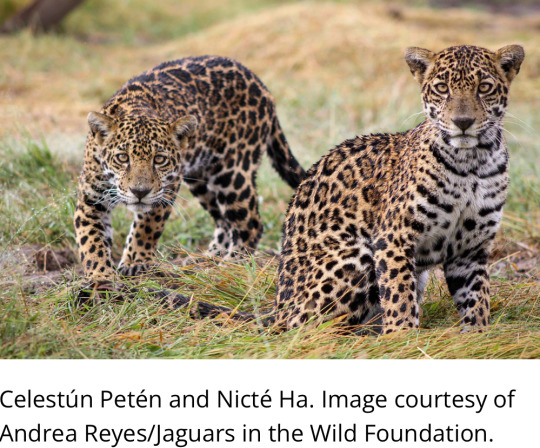

“[A team of scientists] have successfully released two jaguars, and are currently working to reintroduce two other jaguars and three pumas (Puma concolor). [… “Wildlife simulation”] “keeps the jaguars active and reduces the impact of captivity and a sedentary lifestyle[….]””
October 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#good news#hopepunk#electric vehicles#voting#elephant#kenya#conservation#australia#battery#energy storage#africa#cats#hunting#tw animal death#student loans#student debt#debt relief#education#puerto rico#solar#solar panels#solar energy#solar power#tim walz#lgbt#lgbtq#geothermal#renewableenergy#trans rights#transgender
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Musk’s dangerous bullying
ROBERT REICH
DEC 2
Friends,
No one better illustrates the sinister consequences of great wealth turned into unaccountable power than Elon Musk.
Musk, the richest person in the world, is not only claiming presidential authority to fire federal workers, but he’s posting the identities of those whose jobs he wants to eliminate — with the clear intention that his followers harass and threaten them so they quit.
Musk is utterly unaccountable. He has never been elected to anything, but he spent $120 million helping Trump become the president-elect and is now acting as if he’s Trump’s co-president, calling himself Trump’s “First Buddy.”
After buying Twitter for $44 billion, Musk turned it into a cesspool of disinformation and conspiracy theories and manipulated its algorithm to give himself 205 million followers, to whom he is now distributing treacherous lies.
In recent days, Musk boosted posts on his website singling out the names and job titles of four federal employees working in climate policy and regulation who have done nothing other than hold titles Musk dislikes. All four targets are women.
In one instance, Musk quote-tweeted a post highlighting the role of 37-year-old Ashley Thomas, a little-known director of climate diversification at the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation.
Musk’s repost — “So many fake jobs” — garnered 32 million views, triggering a tsunami of taunts against Thomas, such as, “Sorry Ashley Thomas Gravy Train is Over” and “A tough way for Ashley Thomas to find out she’s losing her job.”
Musk apparently took the word “diversification” in Thomas’s title to mean the “D” in “DEI,” which Musk considers “woke.”
Thomas (who holds degrees in engineering, business, and water science from Oxford and MIT) is focused on climate diversification to protect agriculture and infrastructure from extreme weather events.
Following Musk’s tweet, Thomas shut down several of her social media accounts.
In another repost, Musk mocked Alexis Pelosi, a relative of former House Speaker Nancy Pelosi, who works as a senior adviser to climate change at the Department of Housing and Urban Development.
“Nancy Pelosi’s niece should not be paid $181,648.00 by the U.S. Taxpayer to be the ‘Climate Advisor’ at HUD,” the original account wrote. “But maybe her advice is amazing 🤣🤣” Musk snarked.
Musk also singled out the chief climate officer in the Department of Energy’s loan programs office and shared the name of an employee serving as senior adviser on environmental justice and climate change at the Department of Health and Human Services.
IMHO, Musk’s targets should sue him for defamation.
This is hardly the first time Musk has targeted specific people, and he obviously knows how dangerous such targeting can be.
After taking over Twitter in 2022, Musk targeted Yoel Roth, the platform’s former head of trust and safety, who had recently left the company. Musk tweeted, incorrectly, that it looked like Roth had argued “in favor of children being able to access adult Internet services.” Some platform users interpreted this as Musk calling Roth a pedophile, and they posted calls for Roth’s death.
Roth moved out of his house because of the threats.
Musk has also singled out specific civil servants. In 2021, he targeted Missy Cummings, a former fighter pilot and senior adviser at the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, whom Musk claimed was “extremely biased against Tesla” because she questioned the safety of Tesla’s advanced driver-assistance system.
Cummings said she received death threats and was forced to leave her home as a result of Musk’s posts.
Musk’s current targeting is even more dangerous because he has the apparent authority of the president-elect. Although the so-called “Department of Government Efficiency” that Musk is co-heading (with Vivek Ramaswamy) isn’t a real department and has not been authorized by Congress, Musk is acting as if it’s real.
Cummings says Musk’s personal intimidation is already leading some longtime federal employees to leave their jobs: “He intended for them, for people just like this, to be intimidated and just go ahead and quit so he didn’t have to fire them. So his plan, to some extent, is working.”
**
I worked in the federal government between 1974 and 1980, first at the Federal Trade Commission and then at the Justice Department, and from 1993 to 1997 I served as secretary of labor.
Most of the federal employees I came to know cared deeply about the common good. The vast majority did their work carefully and thoughtfully. We owe them a huge debt of gratitude.
But ever since Richard Nixon attacked “unelected bureaucrats” as America’s enemy and Ronald Reagan blamed “liberal bureaucrats” for government’s failings, government employees have been scapegoated. And now Trump is preparing to attack the so-called “deep state.”
In fact, America spends less each year on the federal government’s civilian workforce (roughly $200 billion) than we spend annually on federal contractors ($750 billion).
Much of the “fat” is found in these private, for-profit contractors, who aren’t accountable to anyone except the office that draws up the contracts.
The biggest waste is in the Defense Department, where many contractors have avoided competitive bidding because they have a monopoly over critical technologies.
Which brings me back to Musk, whose businesses are fast becoming among the government’s largest contract monopolists. According to USASpending.gov (the government database that tracks federal spending), Musk’s SpaceX and his Starlink satellite division have signed contracts totaling nearly $20 billion.
I don’t know how much waste and inefficiency are to be found in Musk’s government contracts because I haven’t been able to find any reports on them — which is precisely the problem.
While Musk seeks to intimidate federal civil servants whose job titles he dislikes, forcing some to leave government because his postings have elicited threats to their lives, Musk is distracting attention from himself and his own profitable dips into the taxpayer trough.
I invite any of you with an inclination to root out waste and inefficiency to find out what you can about any likely abuses in Musk’s government contracts, and let us know what you come up with.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

About the Campaign
The Aim:
We are seeking 30 acres of land with healthy soil, ideally with a previous history of agricultural use. The land should be within 20 miles of Denver, CO and grant us both water and mineral rights. The land should be valued equally to all members of the ecosystem that occupy it. We intend to use this land to grow food for our communities throughout Denver and as a place of education and healing. The land would be owned by the organization, FrontLine Farming, but would also be open to collective use in our BIPOC community.
Now is the Time:
Black, Brown and Indigenous Farmers across the United States have been systemically excluded from access to land whether through outright intimidation and theft, loan discrimination or laws such as Heirs Property Rights. Land in the United States was stolen from Indigenous Communities and while BIPOC communities represent a quarter of the US population, they own less than 5% of farmland and cultivate on less than 1% of the land. Yet those who have historically cultivated the land and comprise the over 2.4 million farmworkers in the United States are people of color from diverse communities and foodways. They are descendants of Africans brought here, immigrants, refugees and people who have continuously brought their agricultural knowledge and skills to feed nations.
We have used our radical imaginations for our vision of coming back to the land and are ready to bring this vision to life. To acquire our own soil and land will fortify our efforts to honor our ancestors, to educate our community, to generate independent economic systems, to manifest equitable policies and systems change, to lead by example, to understand history and to create our future. It is a way to co-create generational wealth for our communities, and more importantly, shared power.
Acquiring the land that we envision requires moving money and resources. We are seeking support from philanthropy, local and national networks, and donors. The funds raised from this project will aid our vision and goal.
Frontline Farming
We are a BIPOC-led farmer advocacy and food justice organization that strives to create greater equity across our food system on the Front Range of Colorado. We support and create greater leadership and access for Black, Indigenous, People of Color and Womxn in our food systems. We achieve these goals through growing food, listening, educating, honoring land and ancestors, generating policy initiatives and engaging in direct action.
In 2021, we distributed 26,000 lbs of farmed produce through various programs such as our CSA, Healing Foods and SNAP/WIC recipients. We also advocate for farmers and farm workers alike to ensure that the people who grow our country’s food have access to basic rights and protections that are already afforded to other workers in the state.
#bipoc#farming#indigenous#agriculture#food sovereignty#land back#native american#environmentalism#science#environment#nature#colorado#denver#usa
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In a swift decision, a three-judge panel of the Second Circuit Court of Appeals has unanimously affirmed a March 2023 lower court decision finding the Internet Archive's program to scan and lend print library books is copyright infringement. In an emphatic 64-page decision, released on September 4, the court rejected the Internet Archive’s fair use defense, as well as the novel protocol known as “controlled digital lending” on which the Archive’s scanning and lending is based. “This appeal presents the following question: Is it ‘fair use’ for a nonprofit organization to scan copyright-protected print books in their entirety, and distribute those digital copies online, in full, for free, subject to a one-to-one owned-to-loaned ratio between its print copies and the digital copies it makes available at any given time, all without authorization from the copyright-holding publishers or authors? Applying the relevant provisions of the Copyright Act as well as binding Supreme Court and Second Circuit precedent, we conclude the answer is no,” the decision states."

11 notes
·
View notes
Text
The imposition of the largest sanctions program since the Second World War in response to Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine remains a key tool for limiting the Kremlin’s war machine. But it has inadvertently also had substantial secondary and tertiary effects, from the rewiring of European energy networks to myriad lawsuits over what insurers should have to pay for the Kremlin’s seizure of over 400 Western aircraft.
These unintended consequences have garnered far less attention than the intended ones, but the former are still multiplying and there are tens of billions of dollars already at stake in them. While sanctions rightfully continue to be tweaked to maximize their impact, policymakers have not paid due attention to the legal spats and sanctions challenges that have already arisen in their wake. Their outcome will greatly determine the effectiveness of the sanctions and the extent to which the Kremlin or the West will bear their cost.
This is not the first time the West has had to deal with such issues. At the outbreak of the war with Japan in 1941, the U.S. seized assets and businesses owned by Japanese nationals on its soil, acting under the Trading with the Enemy Act. These actions, while directed primarily at the war-time adversary, inevitably wrought a lot of collateral damage, as investors in Japanese enterprises, their creditors, or depositors in Japanese-owned banks, were often the American public.
It took years to untangle the resulting mess. And yet, when all was said and done, the U.S. Supreme Court and Congress acted to protect the interests of these investors, and ensure both the orderly liquidation and the equitable distribution of proceeds to those affected. Thus, the depositors of Yokohama Specie Bank, had their claims on the “yen certificates” preserved in a decision by the U.S. Supreme Court in 1967, allowing the certificate holders to recover at least some economic value from proceeds of the bank’s liquidation.
In short, there is a blueprint for handling the legal spats that result from waging economic war. That blueprint, in broad terms, is to act forcefully against the economic interests of the enemy, yet make full use of the institutions of law and justice for the interests of affected parties at home.
Today, as Russia and the West remain engaged in a full-scale economic war, this blueprint seems largely ignored. What we see instead, is perhaps the opposite: The adversary ruthlessly subverting the toolkit of the “rules-based international order” for its benefit with lawsuits that seem to lead Western institutions down the path of treading softly where Russian interests are concerned, while Western investors and, of course, Ukraine take the brunt of the costs and receive little or no protection.
Consider the June G-7 summit, where member states united on a plan for using the returns earned by Russia’s $300 billion in frozen sovereign assets to aid Ukraine, of which $200 billion are held as cash and securities at the Belgian financial company Euroclear. Leaders of the G7 have agreed to effectively monetize the future income flow on the frozen assets, and turn it into an immediate $50 billion in loans to Ukraine. This is as stark an acknowledgement as possible that Russia’s assets will not be returned to it any time soon, even if outright seizure is off the table for now following a chorus of complaints that doing so would not be compatible with international law.
Nevertheless, Brussels has insisted Kyiv will not receive any of the five billion euros that the frozen assets have generated thus far and continues to tread softly against Russia and its proxies. The reason: Euroclear itself is worried about lawsuits brought by Russia over this action and its freezing of other securities affected by the Western sanctions regime.
According to Euroclear, it is facing “a significant number of legal proceedings…almost exclusively in Russian courts,” where “the probability of unfavourable rulings is high since Russia does not recognize the international sanctions.”
This reveals a fundamental flaw in the arguments made by proponents of the so-called “rules-based international order.” Russia can appeal to its structures too—and, slowly but surely, make sanctions even less effective than they already are. Meanwhile in the West, the powers that be continue to dither, and ignore the blueprints for economic confrontation from the past.
Russia’s efforts here are already advancing: thus the suits against Euroclear, and the efforts of Mikhail Fridman—the sanctioned Russian oligarch—to return the nearly $16 billion of his former assets through an arbitration claim under the Soviet-Belgium-Luxembourg Bilateral Investment Treaty. As its name gives away, the pact actually even predates Russia’s establishment as an independent state and was inherited from the Soviet Union. It has not been updated since, but cannot be so easily unwound—its final clause notes that it applies to investments made before its hypothetical abrogation for 15 years thereafter.
It is also this treaty that Russia would ultimately use to try and have its domestic court rulings against Euroclear and other Western institutions enforced. We can be sure that there is more to come: Russia has already promised “endless legal challenges” if its assets or the income on these assets are seized. One of the largest such clashes is likely imminent, and will require politicians decide how to proceed. On 7 June the Permanent Court of Arbitration awarded Uniper, which was taken over after being bailed out by the German state, €13 billion in damages from Gazprom over Putin’s decision to toggle Europe’s gas taps in 2022, which forced Germany to bail out Uniper. A Russian arbitration court, on the other hand, has awarded Gazprom €14 billion from Uniper in the dispute. Berlin aims to re-IPO Uniper but will hardly be able to do so with such an albatross hanging above it.
It is therefore all the more remarkable that Western policymakers have not yet addressed how they intend to overcome such risks, nor why Russia remains permitted to take advantage of Western legal system under circumstances of a full-scale economic warfare.
Potential vulnerability to legal action by Russia and its proxies, and a lack of credible or coherent response by the West appears to have led Euroclear to take a number of actions that are clearly not in the Western interest and are often inconsistent with its past practices.
The clearing house has, for example, refused to label a number of securities as being in default in cases where the underlying entity has chosen to default rather than being forced to into default by sanctions. This has not just affected Russian corporate borrowers but even the debts of the government of neighboring Belarus. Belarus’ sovereign Eurobonds that were due to be repaid in early 2023 and are still unpaid, and thus in “default”; but Euroclear has instead designated these as “matured”. This semantic choice has significant implications, blocking the clearing and settlement of these bonds and thus impacting Western creditors – while Belarus, a key ally to Russia in its war, remains (intentionally or not) shielded from the full consequences of its default.
Good explanations for these actions are lacking, but it does appear that Euroclear has, in effect, accepted Belarus’ purported excuse: that sanctions prevent it from paying. But not all sanctions are a barrier to payment—certainly not those that have been imposed on Belarus. Notably, the Development Bank of Belarus, which faces a similar sanctions regime as the sovereign government, successfully made its coupon payment in November 2022, which was, albeit with delay, passed on to the bondholders by Euroclear. Suspension of payments, then, is simply a policy choice, and indeed, the Development Bank ultimately followed the sovereign and suspended payments as well, and this year failed to repay its Eurobonds at maturity. Euroclear took the same action with respect to the Development Bank’s bonds: they are marked as “matured” instead of “in default”.
This sort of leniency, and, seemingly, a fear of calling a “default” on a Russian ally, is without precedent, and completely at odds with the approaches by rating agencies, investors, the World Bank, the ISDA Determinations Committee (as it relates to Russia) and Euroclear’s own actions as to other sovereigns. In the recent past, the defaulted bonds of Sri Lanka, Lebanon, Zambia are all correctly marked by Euroclear as “in default” and continue to settle.
For Western creditors of Belarus, its Development Bank and the similarly placed Russian corporate borrowers, the block on trading and settlement by Euroclear is clearly harmful. For Russia and its ally, the lack of a “default” label by a key player in the Western financial infrastructure looks oddly protective. It also makes a mockery of the fact that sanctions are meant to constrain the inflow of funds to Russia and its allies instead of limiting their outflow and reducing the resources available to Russia and its allies to pursue an unjust war.
How should Western policymakers respond to these challenges? Firstly, by looking at the existing playbook for economic war, and treating as many claims as standard defaults and bankruptcies as possible. Secondly, by recognizing that the “international rules-based order” is in fact largely a set of established norms, particularly when it comes to creditor disputes, and that Russia has spent at least the last decade seeking to undermine these—beginning with its attempt to muck up Ukraine’s restructuring in 2014, something that continues to wind its way through the English courts.
That is the least that can be done to protect Western interests, free up more funds for Ukraine, and defang the Kremlin’s attempts to weaponize international law and institutions.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump & the Department of Education
Part of Trump’s Agenda47 is ten key ideas to improve schools and intention to dismantle the Department of Education and return the duties handled currently by that program to the individual states. Now, I have issues with several of Trump’s key ideas for school improvement but this post is about closing down the Department of Education.
First, Trump claims that we, the US, spend three times more money per pupil than any other nation and that we are at the bottom in education accomplishments. This is not accurate. The US is second in the amount of money we spend on our education (first is Luxembourg) and we rank 12th in the world for the development of our education system. That said, our spending is much higher than that of Japan, Canada, Korea, and Taiwan which all outperform the US in scores.
Second, let's talk about what the Department of Education does right now. The Department:
Establishes policies relating to federal financial aid for education, administers distribution of those funds, and monitors their use.
The Department distributes financial aid to eligible applicants throughout the nation for early childhood, elementary, secondary, and postsecondary education programs.
Collects data and oversees research on America’s schools and disseminates this information to Congress, educators, and the general public.
Identifies the major issues and problems in education and focuses national attention on them.
Enforces federal statutes prohibiting discrimination in programs and activities receiving federal funds and ensures equal access to education for every individual.
The Department enforces five civil rights statutes to ensure equal education opportunity for all students regardless of race, color, national origin, sex, disability, or age.
But what does that mean? Here are some highlights.
The Department funds Title I of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act which provides supplemental funding to high-poverty K-12 schools.
Head Start programs provide vital child care services for low income and rural communities across the country.
The Department administers Pell Grants which help low-income students attend college.
The Office of Special Education Programs provides resources to support students with disabilities through age 21.
The Department collects national data on schools and enforces federal civil rights laws to prohibit discrimination.
The Department serves as loan holder for most federal student loans.
Ending the Department would require much of what the Department already does to be relocated to other departments and agencies at either the federal or state level. As Trump gives no specific information as of now on how he plans to close down the Department of Education other than saying he’ll return duties to the state, I’ve turned to Project 2025 for potential clarity.
Beginning on page 319, Project 2025 outlines their vision for the dismantlement of the Department of Education. Much like Trump they state federal education policy should be limited and ultimately decisions should be left up to state and local governments. Federal funding for education should be provided as block grants without strings attached, and many of the duties involved in special programs, such as those involved with special education or education of indigenous people, would be transferred to other federal agencies. Student loan management would move to a new government agency that would work in tandem with the Treasury Department.
Project 2025 also calls to cut the Head Start program and roll back Title IX revisions that prohibit discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity. In regards to student loans, it calls to phase out Income Driven Repayment plans and remove loan forgiveness both for IDR plans and for public service.
Closing the Department of Education would require congressional action and possibly a super majority of 60 votes in the Senate which may be difficult for the Republicans to manage. Indeed, Trump isn't even the first Republican president to go after the Department of Education; many of them have long been calling for its elimination since its creation by Jimmy Carter in 1979. In short, the Trump administration will face a very uphill battle with this goal.
#democracy#democrat#democratic party#republican#republican party#donald trump#trump#us politics#politics#department of education
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Full article text so no paywall:
By Isaac Arnsdorf
and
Josh Dawsey
July 30, 2024 at 3:06 p.m. EDT
The right-wing policy operation that became a rallying cry for Democrats and a nuisance for Republican nominee Donald Trump is trying to escape the public spotlight and repair relations with Trump’s campaign.
Project 2025, a collaboration led by the Heritage Foundation among more than 110 conservative groups to develop a movement consensus blueprint for the next Republican administration, is winding down its policy operations, and its director, former Trump administration personnel official Paul Dans, is departing. The Heritage Foundation also recently distributed new talking points encouraging participants to emphasize that the project does not speak for Trump.
The former president has repeatedly distanced himself from Project 2025 after relentless attacks from Democrats using some of the 900-page playbook’s more aggressive proposals to impute Trump’s agenda since many of the proposals were written by alumni of Trump’s White House. While some participants in the project started avoiding interviews and public appearances, Trump advisers grew furious that Heritage leaders continued promoting the project and feeding critical news coverage.
Trump senior adviser Susie Wiles repeatedly called Heritage leaders instructing them to stop promoting Project 2025. She and Trump strategist Chris LaCivita repeatedly authored public statements disavowing the project, and then Trump started saying so in his own social media posts. More recently, LaCivita has started saying that people involved in the project would be barred from a second Trump administration.
“President Trump’s campaign has been very clear for over a year that Project 2025 had nothing to do with the campaign, did not speak for the campaign, and should not be associated with the campaign or the President in any way,” Wiles and LaCivita said in a joint statement Tuesday. “Reports of Project 2025’s demise would be greatly welcomed and should serve as notice to anyone or any group trying to misrepresent their influence with President Trump and his campaign — it will not end well for you.”
Some Project 2025 participants have responded by doubting a ban could be enforced when contributors include close Trump advisers such as former White House speechwriter Stephen Miller, former acting director of Immigration and Customs Enforcement Tom Homan, and former White House economic adviser Peter Navarro. Miller has denied his involvement in Project 2025, but his America First Legal group is a participating organization and his deputy, Gene Hamilton, wrote the playbook’s chapter on the Department of Justice.
Many of the plan’s proposals overlap with official pronouncements from Trump’s campaign.
Both Trump and Project 2025 have proposed eliminating the Department of Education and reversing President Biden’s student loan relief program. Both have said they want to reintroduce a policy change to weaken tenure protections for career civil servants and tighten White House supervision of the Department of Justice and other agencies. Both have proposed large-scale immigration raids and repealing temporary protections for migrants from unsafe countries. Both proposed ending affirmative action and rolling back Biden administration environmental regulations.
At least some Heritage employees are considering leaving the organization because they do not want to alienate a future Trump administration and hurt their future job prospects, according to a current employee, who spoke on the condition of anonymity to detail internal dynamics. While Heritage President Kevin Roberts has told people privately that the storm will blow over, employees have texted and messaged one another with dismay about the Trump campaign’s continued attacks on the organization.
“We are extremely grateful for [Dans’]and everyone’s work on Project 2025 and dedication to saving America," Roberts said in a statement. "Our collective efforts to build a personnel apparatus for policymakers of all levels — federal, state, and local — will continue.”
Roberts will take over direct supervision of the project. Earlier in the presidential primary, Roberts was perceived as closer to Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis. His relationship with Sen. J.D. Vance (R-Ohio) fueled new attempts by Democrats to tie Trump to the project since he chose Vance as his running mate.
Some donors have also expressed concerns about how angry the campaign seems about the project, the current employee said. Others agree that the controversy will pass.
Harris campaign manager Julie Chavez Rodriguez said Democrats will not stop talking about Project 2025.
“Hiding the 920-page blueprint from the American people doesn’t make it less real – in fact, it should make voters more concerned about what else Trump and his allies are hiding," she said in a statement. “Project 2025 is on the ballot because Donald Trump is on the ballot. This is his agenda, written by his allies, for Donald Trump to inflict on our country."
Project 2025 published its playbook in 2023, and it always planned to wind down the policy program and hand off recommendations to the official presidential transition when it starts this summer. Another arm of the project, a personnel database of more than 20,000 applicants for potential political appointments should Trump be reelected, will remain in operation, people familiar with the matter said.
In a departing message to staff on Monday, Dans lamented attacks on the project’s work as a “disinformation campaign" that aims to “falsely associate Former President Trump with the Project.” Dans ended by quoting Trump’s words after he survived an assassination attempt on July 13, which quickly became a MAGA movement mantra: “Fight! Fight! Fight!”
Dans did not respond to requests for comment.
Democrats routinely use Project 2025 and Trump’s plans for a second term interchangeably. Left-wing discussion of the project surged in June as the Biden campaign and surrogates started focusing on proposals in Project 2025 to portray Trump as extreme. While some project contributors took pride in being vilified by Democrats and in news coverage, they grew concerned when they started feeling the pressure coming from Trump.
Other areas of divergence have caused headaches for the Trump campaign. In particular, Project 2025 proposes restricting access to abortion medication and blocking shipments through the mail. Trump has said he opposes a federal abortion ban.
In another recent message to participants, communications adviser Mary Vought advised them to respond to questions about the project saying it is not partisan and not affiliated with any candidate. “If asked during a media interview, you can use these points to pivot,” she wrote.
The talking points included: “While President Trump and Project 2025 see eye to eye on many issues, President Trump alone sets his agenda. Project 2025 does not speak for President Trump or his campaign in any capacity.”
End article text.
I've said it before and I'll say it again: publishing their manifesto was the worst mistake the MAGAts could have made. Now we know exactly what bullshit they wanna pull off. And their plans are falling apart. I continue to be filled with hope for November. Get out and vote, people. Democracy can live another day, if we all participate in it.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finding: Lackluster Oversight Resulted in Transnational Criminal Organizations and Fraudsters Stealing U.S. Taxpayer Money from Pandemic Relief Funds
International criminal organizations and foreign government-affiliated actors exploited the urgency of relief programs and orchestrated sophisticated fraud schemes that span multiple countries.
Chinese government-linked hackers stole at least $20 million in U.S. Government COVID-19 relief funds
An USSS investigation revealed that hackers affiliated with the Chinese government, specifically identified as APT41, were implicated in theft of $20 million of U.S. Government COVID-19 relief funds
APT41 has a history of fraudulent activity in the past, specifically traditional unemployment insurance fraud against SBA across dozens of states
APT41 also has a history of espionage activities on behalf of the Chinese government, including attacks on pro-democracy politicians in Hong Kong and data breaches affecting more than 100 organizations
A Nigerian fraud ring stole $10 million in pandemic relief funds
Mr. Abemdemi Rufai, a Nigerian government official, organized a large-scale cyberfraud scheme—named Scattered Canary—targeting COVID-19 relief funds
Scattered Canary, a business email compromise operation, filed at least 174 fraudulent unemployment claims in Washington state and 17 in Massachusetts that were all accepted, all with an expected payout of $5.4 million
An Indian national stole $8 million in a COVID-19 relief fraud scheme
A federal grand jury in Newark, New Jersey indicted an Indian national for submitting fraudulent PPP loan applications totaling more than $8.2 million
The defendant submitted at least 17 applications on behalf non-existent companies, using false information about employees and payroll
He also fabricated tax filings on behalf of a non-existent business to receive more relief payments
He reportedly received $3.3 million in loan proceeds which he then laundered
Domestic and International Fraudsters that Stole from Pandemic Relief Programs were also Connected to Other Organized Crimes
Fraudsters involved with stealing millions of dollars were also involved in other federal crimes including wire fraud and drug smuggling
DOL IG has continued to connect abuse of UI relief funds to organized criminal groups
The National UI Fraud Task Force was created to combat fraud of UI perpetrated by domestic and international criminal organizations, many of which include street-level criminal organizations with ties to illegal guns and drugs
The U.S. Attorney's Office charged six individuals, including two Maryland State Department of Labor subcontractors, with participating in a conspiracy to fraudulently obtain $3.5 million in UI benefits
The lead defendant now faces separate narcotics and firearms charges, including allegations that he unlawfully possessed a machine gun in furtherance of a drug trafficking crime
Another convicted felon charged with CARES Act fraud also committed firearm offenses and possession with the intent to distribute fentanyl
The U.S. Attorney's Office for the District of Maryland targeted cases with connections between COVID-19 fraud and individuals involved with violent crime, organized criminal networks, business email compromise schemes, and narcotics distribution
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
personal/professional anecdote related to my last reblog:
I remember when I was first starting out in my masters program back in 2014 and approached my advisor with my thoughts about how to affordably approach digital preservation of records, I received the most skeptical and condescending of responses, and it took the wind right out of my sails for the next two years.
my advisor: how interesting, can you demonstrate how this would work
me: well, no, but I can show you the website of a distributed digital preservation network in my home state that spreads the costs of maintaining the network across all participating member institutions, which lowers the barriers of access to small community archives and libraries
him: cool, can you bring up the website now?
me, getting out a pen and a notepad: no, I don't have a laptop, but I can write down the URL for you--
him, cutting me off: you don't have a laptop? you've enroled in a masters program here at [prestigious canadian university] and you don't have a laptop? you are going to struggle in my courses. you'll struggle in the whole program.
me, totally thrown off-balance and humiliated but trying not to show it: um, I have a desktop computer at my apartment. the graduate studies office said we could rent laptops from the faculty for completing coursework, and I've always taken my notes by hand--
him: if you are serious about this field, you really need to get a laptop.
me, wondering what any of this has to do with my ideas: I can't afford a laptop.
him, smiling and shrugging his shoulders: (:
it really bears mentioning that this guy's background and CV were why I applied to this program, put myself nearly $70K into student loan debt, and moved myself literally a cross a continent in the first place. (don't fret about the money; I have nearly paid it all off by now, but the me of 2014 certainly had no way of knowing that was going to happen.)
I just remember sitting across from this titan in the field while he smiled at me with this expression of pleasant condescension on his face, and I remember trying desperately to understand why my inability to be able to afford a laptop as new immigrant graduate student with barely enough money in the bank to buy groceries or cat food or make that month's rent had any bearing on the value of my ideas. (ideas which were, you'll note, about how to make digital preservation work when you don't have any fucking money.) what I can't remember is how I ended the conversation; I just know that I went home and shamefully begged my dad for help buying a laptop that neither of us could really afford to spend money on at the time.
it's been nearly ten years since I had that conversation with my advisor, and I am now what just about anyone would consider 'professionally successful' in my field, but that field is not digital preservation. because I was so shamed by this conversation, and I so completely internalized my advisor's attitude that my inability to afford this one piece of technology meant I was not 'serious' about the field. which is stupid, and I have the experience and self-confidence and success to my name now to know just how stupid that is.
anyway if I bump into him at an alumni reunion sometime, I think I'll tell him exactly how much his words undermined my self-confidence and changed my professional trajectory, and politely ask him to never say that to another poor, first year graduate student ever again.
#ray.txt#there's a lot I don't like about being in my 30s (all the aches and pains and not being able to turn my head all the way to the left)#but I love knowing who I am and what I'm capable of#and I will bend over backwards to help lift up other nervous young 20-something professionals#so that when they inevitably encounter a professor who has grown way too arrogant cloistered away in his ivory tower like this#they can bounce back from this bullshit
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pharma Loan License Facility in India
Pharma Loan License, also known as Loan Licensing in the pharmaceutical industry, is a practice wherein a pharmaceutical company grants permission to another company to manufacture, market, and distribute its products under the brand name. This allows the licensee to benefit from the reputation and goodwill associated with the licencor's brand.
Introducing Days H&B Pharma Loan License Facility in India is your premier gateway to expedited market entry and enhanced brand visibility in the pharmaceutical industry. Our innovative loan licensing program offers pharmaceutical companies the chance to broaden their product range and reach a wider market by collaborating with us to produce, promote, and distribute their products under our well-established brand name. Reach out to us at +919218109708 or visit our website to discover how partnering with Days H&B can elevate your presence in the Indian pharmaceutical market. Reach out to us at +919218109708 or visit our website to discover how partnering with Days H&B can elevate your presence in the Indian pharmaceutical market.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Navajo Nation has received a $55 million grant to help Navajo homeowners with mortgage payments and home repairs.
Navajo Nation President Buu Nygren said as many as 901 homeowners should qualify for the funds.
The money comes from the American Rescue Plan Act, which provides nearly $10 billion to support homeowners throughout the country who face financial hardships due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The program is open to Navajo homeowners of all income levels within the Four Corner states who live on both tribal lands and in urban areas.
The funds must be used within three years.

PHOENIX — Urban Navajos who own homes off the Navajo Nation will soon receive some unexpected help they’ll want but didn’t need to ask for.
On Sept. 11, Navajo Nation President Buu Nygren told 250 Phoenix metro area Navajo homeowners that the Nation received a $55 million federal grant to provide financial assistance to Navajo homeowners under various Homeowner Assistance Fund programs.
This includes mortgage payments and home repair assistance.
As many as 901 Navajo homeowners should qualify for the money for their homes, he said.
“Make sure we tell everybody,” Nygren told an overflow crowd in the shade outside the historic Phoenix Indian School Visitor Center, one of the remaining buildings from the 100-year-old Indian boarding school.
They were outside because a capacity crowd was already indoors awaiting the same announcement, and Nygren wanted to address those in the 105-degree F heat first.
The Homeowner Assistance Fund was authorized through the American Rescue Plan Act to provide $9.9 billion nationwide to support homeowners who face financial hardships associated with COVID-19, the Nygren said yesterday.
The funds were distributed to states, U.S. territories, and tribes. The Navajo Nation was awarded $55,420,097.
Most federally funded programs are restricted to low- and very-low-income households.
This program allows higher-income Navajo homeowners to receive financial relief from the economic effects of COVID-19, as well.
“Tell your relatives,” Nygren said. “Say the $55 million that came from our government was specifically for Navajo people who are homeowners.”
To launch the process, Nygren signed an agreement with Native Community Capital. The group is a Native-led and operated non-profit corporation that was selected as the sub-recipient to administer the Homeowner Assistance Fund Project activities on behalf of the Navajo Nation.
Native Community Capital is certified by the U.S. Department of the Treasury as a Native Community Development Financial Institution and is a licensed mortgage lender in Arizona and New Mexico.
The program is designed for both higher-income and medium-income homeowners, Native Community Capital CFO Todd Francis said.
As an example, a family of four in Maricopa County in Arizona earning as much as $132,450 a year may be eligible for the tax-free, non-repayable funds to pay their mortgage or repair their homes, he said.
The program will benefit Navajo relatives and their families who reside in both rural remote locations and those in the urban areas of Phoenix, Albuquerque, Denver, Salt Lake City, surrounding smaller cities and towns, and wherever Navajo homeowners live off-reservation, said NCC CEO Dave Castillo.
A significant lack of investment in tribal communities compared to non-Indian communities has resulted in a critical absence of homeownership on tribal lands, particularly for higher-income Native households, he said.
As a result, Navajos with higher incomes tend to purchase or build homes off the Navajo Nation where they can qualify for loans and mortgages to build equity and wealth.
The Center for Indian Country Development reports that 78% of Native people live outside of tribal trust land in counties surrounding their homelands. It is these families the HAF Project will seek to support, Castillo said.
Nygren said the Navajo HAF Project will provide financial assistance to 901 eligible Navajo homeowners to use for qualified expenses in five activities for the next 36 months.
The program will provide financial assistance to eligible Navajo homeowners in the four-state region of Arizona, New Mexico, Utah and Colorado.
Each eligible applicant could receive a maximum amount of $125,000 of combined assistance under various programs.
These include:
Monthly mortgage payment assistance to a maximum assistance level of $72,000 per participant. This is for Navajo homeowners who are delinquent in mortgage payments or at risk of foreclosure due to a loss of household income.
Mortgage reinstatement assistance would give a maximum assistance of $50,000 per participant to those who are in active forbearance, delinquency default status, or are at risk of losing a home.
Mortgage principal reduction assistance that would assist up to $100,000 for those who find the fair market value of their home is now less than the price they paid for it and now may result in a loss when it is sold.
Home repair assistance that would give $100,000 to those who need significant home repairs.
Clear title assistance of up to $30,000 for grant assistance to receive a clear title of their primary residence.
In his 2022 presidential campaign, Nygren committed to helping urban Navajos who have said for years that they felt underserved by the tribal government. He said this grant addresses that.
He said one of his administration’s next goals is to buy or construct a building owned by the Navajo Nation in the metro area to serve urban Navajo Phoenicians.
“Wouldn’t it be nice if we used the entire $55 million this year?” Nygren asked. “I know you committed to live here and to take care of your family. I see a lot of familiar faces and I understand this is where your jobs are. We want you to have access to resources.”
Castillo urged applicants to be sure their applications were complete and submitted early.
“One thing we want to emphasize is to be ready when the information is being requested on the checklist,” he said. “Make sure you have your documents prepared and you get it to our licensed professionals that will be working with you. If you do not, the application will expire in 30 days.”
He said the program has just three years to deploy the $55 million.
“It seems like we could do that quickly but we can only do it quickly if you help us, if you’re ready, and if you submit the information that’s necessary.”
Debbie Nez-Manuel, executive director of the Navajo Nation Division of Human Resources, said visits to other urban areas will be planned, scheduled, and announced by Native Community Capital.
The funds must be used within three years.
So does any of this money go to the Black Indians Tribes? @militantinremission
maybe y'all should start asking for your cut right now cause they got it
#Navajo#Navajo Nation#First Nation#Chief Buu Nygren#Nygren reveals $55 mil for Diné homeowners#HAF#The Center for Indian Country Development#Navajo Nation has received a $55 million grant to help Navajo homeowners with mortgage payments and home repair#@MilitantinRemission
19 notes
·
View notes