#liberty or death
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

End the Fed the Libertarian way.
Less Government, Less Taxes, no more wars.
333 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gordon Parks. Born Black. Harlem, New York, 1963
#Gordon Parks#Harlem#New York#1960s#1963#protest#words#Steidl#Born Black#liberty or death#liberty#60s
260 notes
·
View notes
Text

Happy Fourth, Americans
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't care if my tits ever hang below my belt and my pussy lips flap like a window shade, I will NEVER be desperate enough to fuck with a conservative.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The revolution was over. So too was a decade of fear: of privation, violence and insecurity. Instead of the 'man of virtue' as the embodiment of the highest ideals of the Revolution - civic integrity, personal sacrifice, modesty - Napoleon would offer the 'man of glory'. The strong man also promised peace, freedom and stability but his dreams of Imperial grandeur would cost French people far more than had the securing of their Revolution."
-P. McPhee, "Liberty or Death, the French Revolution"
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
“No man thinks more highly than I do of the patriotism, as well as abilities, of the very worthy gentlemen who have just addressed the House. But different men often see the same subject in different lights; and, therefore, I hope it will not be thought disrespectful to those gentlemen if, entertaining as I do opinions of a character very opposite to theirs, I shall speak forth my sentiments freely and without reserve. This is no time for ceremony. The questing before the House is one of awful moment to this country. For my own part, I consider it as nothing less than a question of freedom or slavery; and in proportion to the magnitude of the subject ought to be the freedom of the debate. It is only in this way that we can hope to arrive at truth, and fulfill the great responsibility which we hold to God and our country. Should I keep back my opinions at such a time, through fear of giving offense, I should consider myself as guilty of treason towards my country, and of an act of disloyalty toward the Majesty of Heaven, which I revere above all earthly kings.
“Mr. President, it is natural to man to indulge in the illusions of hope. We are apt to shut our eyes against a painful truth, and listen to the song of that siren till she transforms us into beasts. Is this the part of wise men, engaged in a great and arduous struggle for liberty? Are we disposed to be of the number of those who, having eyes, see not, and, having ears, hear not, the things which so nearly concern their temporal salvation? For my part, whatever anguish of spirit it may cost, I am willing to know the whole truth; to know the worst, and to provide for it. I have but one lamp by which my feet are guided, and that is the lamp of experience. I know of no way of judging the future but by the past. And judging by the past, I wish to know what there has been in the conduct of the British ministry for the last ten years to justify those hopes with which gentlemen have been pleased to solace themselves and the House. Is it that insidious smile with which our petition has been lately received? Trust it not, sir; it will prove a snare to your feet. Suffer not yourselves to be betrayed with a kiss. Ask yourselves how this gracious reception of our petition comports with those warlike preparations which cover our waters and darken our land. Are fleets and armies necessary to a work of love and reconciliation? Have we shown ourselves so unwilling to be reconciled that force must be called in to win back our love? Let us not deceive ourselves, sir. These are the implements of war and subjugation; the last arguments to which kings resort. I ask gentlemen, sir, what means this martial array, if its purpose be not to force us to submission? Can gentlemen assign any other possible motive for it? Has Great Britain any enemy, in this quarter of the world, to call for all this accumulation of navies and armies? No, sir, she has none. They are meant for us: they can be meant for no other. They are sent over to bind and rivet upon us those chains which the British ministry have been so long forging. And what have we to oppose to them? Shall we try argument? Sir, we have been trying that for the last ten years. Have we anything new to offer upon the subject? Nothing. We have held the subject up in every light of which it is capable; but it has been all in vain. Shall we resort to entreaty and humble supplication? What terms shall we find which have not been already exhausted? Let us not, I beseech you, sir, deceive ourselves. Sir, we have done everything that could be done to avert the storm which is now coming on. We have petitioned; we have remonstrated; we have supplicated; we have prostrated ourselves before the throne, and have implored its interposition to arrest the tyrannical hands of the ministry and Parliament. Our petitions have been slighted; our remonstrances have produced additional violence and insult; our supplications have been disregarded; and we have been spurned, with contempt, from the foot of the throne! In vain, after these things, may we indulge the fond hope of peace and reconciliation. There is no longer any room for hope. If we wish to be free– if we mean to preserve inviolate those inestimable privileges for which we have been so long contending–if we mean not basely to abandon the noble struggle in which we have been so long engaged, and which we have pledged ourselves never to abandon until the glorious object of our contest shall be obtained–we must fight! I repeat it, sir, we must fight! An appeal to arms and to the God of hosts is all that is left us!
“They tell us, sir, that we are weak; unable to cope with so formidable an adversary. But when shall we be stronger? Will it be the next week, or the next year? Will it be when we are totally disarmed, and when a British guard shall be stationed in every house? Shall we gather strength by irresolution and inaction? Shall we acquire the means of effectual resistance by lying supinely on our backs and hugging the delusive phantom of hope, until our enemies shall have bound us hand and foot? Sir, we are not weak if we make a proper use of those means which the God of nature hath placed in our power. The millions of people, armed in the holy cause of liberty, and in such a country as that which we possess, are invincible by any force which our enemy can send against us. Besides, sir, we shall not fight our battles alone. There is a just God who presides over the destinies of nations, and who will raise up friends to fight our battles for us. The battle, sir, is not to the strong alone; it is to the vigilant, the active, the brave. Besides, sir, we have no election. If we were base enough to desire it, it is now too late to retire from the contest. There is no retreat but in submission and slavery! Our chains are forged! Their clanking may be heard on the plains of Boston! The war is inevitable–and let it come! I repeat it, sir, let it come.
“It is in vain, sir, to extenuate the matter. Gentlemen may cry, Peace, Peace– but there is no peace. The war is actually begun! The next gale that sweeps from the north will bring to our ears the clash of resounding arms! Our brethren are already in the field! Why stand we here idle? What is it that gentlemen wish? What would they have? Is life so dear, or peace so sweet, as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery? Forbid it, Almighty God! I know not what course others may take; but as for me, give me liberty or give me death!”
* William Wirt (1772-1834) reconstructed this accepted text of Patrick Henry’s “Liberty or Death” speech for his biography of Patrick Henry. Wirt’s Sketches of the Life and Character of Patrick Henry was published in 1817 and reprinted about two dozen times in the nineteenth-century. Historians and biographers have often debated the merits and limits of William Wirt’s reconstruction of the text.
#liberty or death#Patrick Henry#speech#U.S. history#history#give me Liberty or give me Death speech#independence
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
REBELLION RISING ON THE RISE: 2009-2018
THE FRANCE AND IRISH LINK TO THE REBELLION:
THE PARANORMAL HOTSPOT IN ROUSE HILL REGIONAL PARK
THE REAL CENTER OF THE CIVIL WAR OF THE REBELLION OF VINEGAR HILL PART 1:
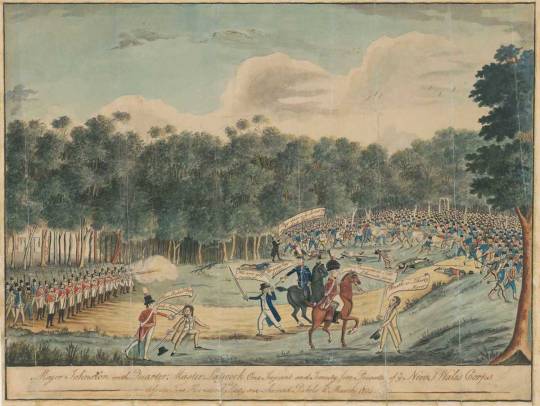

My hypothesis is there is a link to the slave revolts in Haiti and the Battle of Vinegar ill where the Irish slaves attempted to overthrow their English captors.
This is founded by my initiation into haitian voodoo, 21 divisions creole spiritism which combines with my cereominal magician tradition starting HARDCORE at the same site (the battle site of vinegar hill) back in 2009.
All events were extreme paranormal and unexplained anomalous events, experienced by a friend and I who were yet to be formally initiated into ceremonial magick or vodou.
A magical portal was opened which took me until 2018 to close
many ufo and other supernatural events took place at this site
which can be ascribed to the closest site to the only civil war in Australia has ever witnessed.

My notes on the historical context from 2022
1789
After 1789, some Volunteer units showed their sympathy with the French Revolution by holding parades on 14 July to commemorate the fall of the Bastille. In 1792, Grattan succeeded in carrying an Act conferring the franchise on the Roman Catholics; in 1794, he introduced a reform bill that was even less democratic than Flood’s bill of 1783.
He was as anxious as Flood had been to retain the legislative power in the hands of men of property, for he had a strong conviction that while Ireland could best be governed by Irish hands, democracy in Ireland would inevitably turn to plunder and anarchy. The defeat of Grattan’s mild proposals helped to promote more extreme opinions. However, as soon as the Jacobin regime assumed power in France, radical Patriots became more reluctant to refer to France as a prime example of Catholic political action for the causes of liberty and justice. Nevertheless, one of the main inconsistencies on the Patriot political agenda by calling for increasing powers of the Irish parliament while maintaining the selective as opposed to universal suffrage seemed to have been dissolved.
However, the French Revolution also had a second, contrasting, effect. Conservative loyalists such as John Foster, John Fitzgibbon and John Beresford, however, remained opposed to further concessions to Catholics and, led by the ‘Junta’, argued that the ‘Protestant Interest’ could only be secured by maintaining the connection with Britain. In reactionary circles, it was used to emphasise the point that an open political debate without censorship as well as parliamentary reform could entail a severe blow to their special interests, and could be tantamount to inviting Radicals to overturn the political structure of the country, rather than just appeasing them. In particular, the French Revolution prompted relentless action against the radical wing of the Patriot movement, the United Irishmen that included many former Whigs. It also prevented more moderate Patriots from supporting some radical Patriot activities without reservation, depriving the Patriot movement of solidarity and unity.
1688-91
WILLIAMITE WAR
William of Orange - dutch born
William of Orange, the Dutch prince who became King of England, Scotland, and Ireland in the Glorious Revolution of 1688
Defeated catholic "james 2nd" in wiliamite-jacobite war.
Protestant ascendancy
THE DECLATORY ACT OF 1719
Loss of Independence due to the House of British Lords being able to pass laws in Ireland
Restrictions of commerce at the expense of ireland that favoured Britain were tipping this rise to the protestant ascendancy for GREATER freedoms from great britain.
ORANGE ORDER:
The basis of the modern Orange Order is the promotion and propagation of "biblical Protestantism" and the principles of the Reformation. As such the Order only accepts those who confess a belief in a Protestant religion.
As well as Catholics, non-creedal and non-Trinitarian Christians are also banned.
This includes members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints(Mormons), Jehovah's Witnesses, Unitarians, and some branches of Quakers.
Previous rules specifically forbade Roman Catholics and their close relatives from joining
but the current rules use the wording "non-reformed faith" instead. Converts to Protestantism can join by appealing to Grand Lodge.
James Wilson and James Sloan, who issued the warrants for the first Lodges of the Orange Order along with 'Diamond' Dan Winter, were Freemasons,[26] and in the 19th century many Irish Republicans regarded the Orange Order as a front groupestablished by Unionist Masons as a more violent and jingoist vehicle for the promotion of Unionism.[71] Some anti-Masonic evangelical Christian groups have claimed that the Orange Order is still influenced by freemasonry.[72] Many Masonic traditions survive, such as the organisation of the Order into lodges. The Order has a similar system of degrees through which new members advance. These degrees are interactive plays with references to the Bible. There is particular concern over the ritualism of higher degrees such as the Royal Arch Purple and the Royal Black Institutions
1795: the battle of richmond hill
Darug natives defend the land from british invaders
North richmond - pitt town wetlands.
1798
The first battle of vinegar hill
County wicklow
The catholics invasion and claim to the irish land and protestant ascendancy
Act of union 1800- rise to catholic invasion that allowed the mobilisation of the catholic poplation
Uniteed the british parliament and irish parliement in unity, to form a united front
Catholic resentment in leinster
1789
THE AFRO-CARIBBEAN LINK
UNITED IRISH PRISONER
JAMAICA
WEST INDIES
NEW FOUNDLAND
NEW SOUTH WALES
"United Irish" mutinies in Jamaica, Newfoundland and New South Wales
In October 1799 Castlereagh received reports from Jamaica that many (of the 3,200)
United Irish prisoners, "incautiously drafted" into regiments for service in the West Indies, had taken to the hills to fight alongside the Maroons and with the French: "as soon as they got arms into their hands they deserted".
There is no suggestion that this was part of any trans-Atlantic design of the United directory in Dublin or Paris.
The same is true of the "United Irish Uprising in Newfoundland" in April 1800. Two-thirds of the colony's main settlement, St. John's, were Irish, as were most of the island's locally-recruited British garrison. There were reports that upwards of 400 men had taken a United Irish oath, and that eighty were resolved to kill their officers and seize their Protestant governors at Sunday service. As in Jamaica, the mutiny (for which 8 were hanged) may have been less a United Irish plot, than an act of desperation in the face of brutal living conditions and officer tyranny.
Yet the Newfoundland Irish would have been aware of the agitation in the homeland for civil equality and political rights.
There were reports of communication with United men in Ireland from before '98 rebellion;of Thomas Paine's pamphlets circulating in St John's;and, despite the war with France, of hundreds of young Waterford men still making a seasonal migration to the island fisheries, among them defeated rebels who are said to have "added fuel to the fire" of local grievance.
In March 1804, stirred by news of Emmet's rising, several hundred United Irish convicts in New South Wales tried to seize control of the penal colony and to capture ships for a return to Ireland.[204] Poorly armed, and with their leader Philip Cunningham seized under a flag of truce,the main body of insurgents were routed in an encounter loyalists celebrated as the Second Battle of Vinegar Hill.
The 1803 Michael Dwyer, who was a captain of the irish rebellion of 1798, transported to NEW SOUTH WALES
-1807 x 2 imprisoned and x2 trials for plotting against the british penal rule in NSW
1804
The second battle of vinegar hill
LIBERTY OR DEATH!
‘Death or Liberty’
The 1804 Castle Hill convict rebellion was led by Philip Cunningham of Moyvane, north County Kerry, a government stonemason who was convicted for his involvement in the 1798 Irish rebellion; he was also involved in a mutiny on board the convict transport ship, the Anne.
He was key figure in the planning of the rebellion, along with his rebel assistants William Johnston and Samuel Humes.[
Accompanied by over 200 frustrated armed Irish convicts, their aim was to capture ships and sail to Ireland. The rebels gathered at Castle Hill, calling on other convicts to join them.
Their intention was to march from Windsor to Parramatta, and then onto Sydney, gathering recruits along the way to attain a ship to bring them back to Ireland.
The Irish rebels were betrayed by an informer Keogh, who told the authorities of the Irish convicts’ plans.
By 1804, most of the Irish leaders of the previous attempts at rebellion had been imprisoned and moved to outlying areas of the colony such as Norfolk Island. Dispersal had worked well for the authorities but with each new rebellion plan, new Irish leaders rose among the convicts more aware of what not to do next time. The leaders of rebellion on 4 March 1804 were Phillip Cunningham and William Johnston.
Cunningham was a veteran of the 1798 conflict in Ireland and the mutiny of the convict transport ship Anne. From his experiences in Ireland and NSW he understood that secrecy and a non-traceable but effective communication were essential to a successful rebellion.
Cunningham’s emphasis on secrecy was so successful that it was not until the day before the rebellion that the authorities knew of its existence.
On the evening of 3 March, one of the Irish convict overseers turned informant. On Sunday 4 March, the day of the rebellion, two more informants came forward and provided names.
John Griffen was one of the informants and had been relaying a message to the pike-maker Bryan Furey that the rebellion was on for Sunday night.
Since Furey did not get the message the areas of Sydney, Parramatta and Windsor did not rebel.
Castle Hill was the only district that rose in rebellion.
Despite this intelligence, the authorities in Parramatta and Sydney did not act immediately and on 4 March 1804, John Cavenah set fire to his hut in Castle Hill at 8.00 pm. This was the signal for the rebellion to begin.
With Cunningham leading, 200 rebels broke into the Government Farm’s buildings, taking firearms, ammunition and other weapons. Initially, there was mayhem as buildings were ransacked to cries of ‘Death or Liberty’. Two English convicts dragged the Hills District flogger, Robert Duggan from under his bed and George Harrington an English convict beat him unconscious. A constable was saved from a musket ball in the face when the musket of John Brannon misfired.
Another constable was saved in similar circumstances when Jonathon Place’s musket also misfired. Cunningham gathered the rebels and reprimanded them for their lack of disciplined behaviour.
The rebels then went from farm to farm on their way to Constitution Hill at Parramatta gathering firearms, supplies and drinking any liquor they found. The looting of farms gave the rebels over 180 swords, muskets and pistols. In 1804, this was close to one third of the colony’s entire armoury
I do therefore proclaim the Districts of Parramatta, Castle Hill, Toongabbie, Prospect, Seven and Baulkham Hills, Hawkesbury and Nepean to be in a STATE of REBELLION; and to establish Martial Law throughout those Districts…
Cunningham’s plan involved burning the MacArthur property of ‘Elizabeth Farm’ in order to draw the Parramatta garrison out of the town.
Once this was done the rebels in Parramatta would rise up and set fire to the town as a signal. The Castle Hill rebels would gather at Constitution Hill and then raid the barracks for more arms and ammunition.
From there the rebels would march to Windsor and join up with the rebels in the Hawkesbury before marching on Sydney. At dawn on 5 March, rebels were still straggling in to Constitution Hill. Phillip Cunningham and William Johnston were busy drilling the rebels on the hill while they were waiting for the signal from the uprising rebels in Parramatta. The signal never came. Cunningham’s messages to the Parramatta and Windsor rebels had not got through. Cunningham decided that the rebels would head down the Hawkesbury Road to Windsor to meet up with the rebels from the Hawkesbury. Had Cunningham effected this, King maintained it would have increased his force by a further hundred rebels.[10]
Colonial paranoia increased once evidence of planned rebellion became evident after 1800 but how real was the threat from Irish convicts?
The Defenders and United Irishmen transported between 1795 and 1806 provided leadership to those convicts, many Irish but including English transportees, who were prepared to take direct action to overthrow the colonial authorities.
Although it was the Irish convicts who were a particular concern to Hunter, King and Bligh, it is important not to over-exaggerate their significance while under-estimating the involvement of convicts of other nationalities. In addition, the Irish convict leadership had considerable experience in planning and implementing rebellious activities.
This explains why successive governors sent leaders or presumed leaders, whether there was concrete evidence of sedition or not, to the more isolated penal settlements on Norfolk Island and VDL. This had the effect of disrupting any planning for insurrection.
Finally, hatred of the British in Ireland was transposed to NSW and this meant that Irish leaders had a willing supply of convicts who were prepared to support their actions.
That support came from non-Irish convicts is a reflection of the punitive and arbitrary nature of convict life. Where they were concentrated in one area, as on the Castle Hill farm, Ireland’s cause helped bind these men together.
However, there were major problems for those seeking rebellion. First, keeping planning secret was a major difficulty and only the Castle Hill revolt in 1804 saw planning converted into action.
Convicts were always willing to ‘split upon each other’ and this allowed the authorities to intervene before matters spiralled out of control.
Secondly, the objectives of rebellion such as the rallying cry of ‘Death or Liberty’ or demands for a ship to go home were idealistic and unrealistic. Although these may have been the aims of rebel leaders, there is little evidence that they were widely held by the rank-and-file, many of whom claimed that they had been forced into rebellion
Thirdly, as in Ireland during the 1798 rebellion, when faced with even inferior military force, the rebels could not translate numerical strength into military victory.
Finally, the hoped for French aid was illusory as it was never part of French strategy and, during the critical period from 1801 to 1804 war in Europe had been suspended.
It was the British government that was constantly afraid of convict rebellion and disorder though this did not stop it from sending political prisoners to NSW despite the concerns of successive governors. For the authorities, a colony composed largely of convicts was inevitably turbulent and rebellious, something reflected in Hunter’s and King’s despatches. In his reports on NSW and VDL, Bigge considered that the best security against rebellion was the higher standard of living that convicts generally enjoyed in NSW than in Britain and the opportunities and rewards open to those with industry and skill. Some convicts ‘bolted’ but only a few rebelled.
Rouse Hill Estate
Vinegar Hill was not a formal location in 1804.
The battle between the rebels and the soldiers became commonly known as the ‘Battle of Vinegar Hill’ after the Irish battle in 1798. Common usage of the name Vinegar Hill began to appear in the 1810s and 1830s in the Rouse Hill area.
But there is no formal Vinegar Hill on a map. There have been competing thoughts for the location of Vinegar Hill.
Originally it was thought to be Rouse Hill, George Mackanass challenged this in the 1950s marking the location of Vinegar Hill as the crossroads between Windsor Road and Schofields Road.
THIS WAS THE LOCATION OF ROUSE HILL REGIONAL PARK, in which my friend and I partook in rituals with an optical crystal ball resulting in FULL BLOWN MANIFESTATIONS.
-1816
Richard rouse
Built tollhouses, turnpikes, estates from Parramatta to Liverpool
On 8 October 1816 Rouse was granted 180 hectares (450 acres) near the site of the Castle Hill convict rebellion; at the suggestion of Macquarie the grant was named Rouse Hill. The actual possession of the land had taken place a few years previously, as the Sydney Gazette had first mentioned Rouse Hill on 27 November 1813, and the homestead was begun soon afterwards. It took a few years to build and was a two-storey, twenty-two room house, which has been occupied by members of the Rouse family ever since.
Old government house & THOMAS MITCHELL ROYAL PEDIGREE ANCESTRAL ASSET
& THE HIDDEN HAND OF PARRAMATTA GOVERNMENT HOUSE AND THE TIMEKEEPERS SOUTHERN HEMISPHERE
this is an actual freemasonic ancestral connection of mine... this links to the rebellion and the colonisation of the country.
The Observatory, erected in 1822 was part of Brisbane's intention to make Parramatta "the Greenwich of the Southern Hemisphere" (DPWS 1997: p. 39).
1828, when Thomas Mitchell began the first trigonometrical survey of New South Wales, his initial meridian was taken from the Parramatta transit instrument in consultation with Dunlop. That survey underpinned mapping in New South Wales until recent times (Rosen 2003: p. 80).
Surveyor Edward Ebbsworth, when conducting his 1887 survey of Parramatta Park, ensured that the exact location of the piers would be preserved by fixing a copper plug in the basal stone of the piers.
Brisbane was accompanied to Australia by two astronomers: Charles Rumker, who had already attained a good reputation as an astronomer and mathematician; and James Dunlop, whose great natural ability in mechanical appliances and instruments saw him identified as a suitable man for second assistant in the Observatory in an out of the way place like Parramatta. On arrival in New South Wales, Brisbane's instruments were immediately set up on piers in the Domain to allow the observation of the solstice on 21 December 1821. B
April 1822, the construction of the observatory had been completed in anticipation of the appearance of Encke's Comet, an event not observable in Europe or at the Cape of Good Hope (Rosen 2003: p. 80).
The observatory was privately funded by Brisbane and consisted of two buildings: an observatory equipped at Brisbane's personal expense; and a residence attached to it. Located about 91 m (100 yards) behind Government House, the observatory was a plain building, 8.5 m (28 feet) square by 3.4 m (11 feet) high, with a flat roof with two domes 3.51 m (11 feet 6 inches) in diameter projecting from it, one at the north and the other at the south.
On the north and south sides were five windows, three of which were in a semi-circular projection from the wall at the base of the domes.
Transit openings in the domes extended to one of the windows to allow observations of the horizon. A 0.41-metre (16 in) Reichenbach repeating circle was located under the north dome and a 1.2-metre (46 in) equatorial Banks telescope was under the south dome.
There was also a Troughton mural circle and a 1.7-metre (5+1⁄2 ft) Troughton transit instrument. A Hardy clock showed sidereal time and a Brequet clock showed mean time.
All instruments were mounted on solid masonry piers.
There was also a Fortin pendulum and two instruments for observing the dip and variation of the magnetic needle.
CONVICT LIES
O’Farrell estimates about 1.5% of these were unambiguously sent out as political offenders or participants in rebellion or conspiracy, with the great bulk of these coming in the aftermath of the 1798 Rebellion.
If crimes of agrarian discontent and social disaffection are included under the heading of ‘political crimes’, then the proportion of Irish political transportees rises to about 20%. The great majority of Irish convicts were, therefore, sent to Australia largely for petty crimes.
Theory to link back to
JOHN DEE AND THE OPTICS OF THE CRYSTAL BALL USED BY THE MONARCHY OF BRITISH CROWN
BASED ON THE PROJECTION INTO THE ASTROLOGICAL, ASTRONOMICAL TRANSITS TO CONQUER VIA USING EDWARD KELLY AS "COURT MAGE" AND THE ENOCHIAN CHESS IN THE GLOBAL CONQUEST
real scrying methods take two or more people in the spiritual court for impact, as per 2009 - 2014 when K and I had adopted the original crystal ball between us resulting in full-blown manifestations, later confirmed by Kardec spiritism sources
my spirits advise me Australia is the prime spot for HAITI 2.0 FOR THE SECOND COMING OF THE SLAVE REVOLT IF THINGS CONTINUE THIS WAY ....
note the date and time and motions of movement
note the present economic, social and political happenstance
note the pestilence that has persistence against the masses who only want freedom and peace
note the objections from the overlords through clauses like agenda 2030, and sustainable development, which are just fancy names for the "new world order". which is just a modern 'human slave agenda" decked out in bureaucratic red tape.
freedom of choice, or be denied all liberty?
look at the manipulation that occurred as a result of COVID-19 and the forced COVID-19 vaccine agenda
when will the next thing that replicates occur, and when will humanity rise against the overlords to object in the most amicable and peaceful or diplomatic way, as clearly, the violence and bloodshed aren't going to work here.
PEACEFUL REBELLION.


#john dee#crystal ball#vinegar hill#1804#rebellion#the battle of vinegar hill#australian history#haunted australia#paranormal australia#parramatta#john dee and edward kelley#thomas mitchell#rouse hill regional park#supernatural australia#haunted places in australia#ley lines#the rum rebellion#haitian revolt#slave rebellion#irish rebellion#liberty or death#calling down the lwa.#rum rebellion#crystal balls#scrying#spiritism#haitian vodou#ogun#spirts#revolt
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
Lead armies, make critical decisions, and shape the fate of the nation of the United States of America 🇺🇸 in this 16-bit historical war simulation! 🦅
#Liberty or Death#SNES#Super Nintendo#Retro Gaming#Retro Games#History#Historical Simulation#War Games#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text


Javier Milei
23 notes
·
View notes
Text



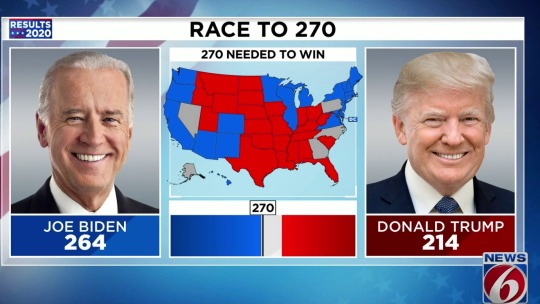



#koei#romance of the three kingdoms#liberty or death#nobunaga’s ambition#2020 pandemic#covid 19#historical simulation series#retrogaming#new horizons#harvey weinstein conviction#harry and meghan#parasite wins best picture#biden wins#pink floyd#time
0 notes
Text

Liberty or Death for the PC
#Liberty or Death#LibertyOrDeath#Founding fathers#Founding#Fathers#American Independence#PC#IBM#Pixel Crisis
0 notes
Text
Friday Night Shots - The Shelf of Shame
Friday Night Shots - The Shelf of Shame @gmtgames @Pandasaurusgame @HBuchanan2 @Volko26
Yes, I know it’s Saturday. But after a day of having a hole punched in our wall and then another day of long driving (which was great and I picked up a couple of awesome-looking games, but it was long), I wasn’t in the mood to write anything last night. The rum flowed better tonight, though this is still going to be a fairly short post compared to some of mine. So welcome back to the bar!…

View On WordPress
#A Distant Plain#Bezier Games#Brian Train#Castles of Mad King Ludwig Collector&039;s Edition#COIN Games#Dinosaur World#GMT Games#Harold Buchanan#Kenneth Tee#Liberty or Death#Minerva#Pandasaurus Games#People Power#Plantagenet: Cousins&039; War for England#The Discard Pile#The Last Hundred Yards#Volko Ruhnke
0 notes
Text

had to do it to em

the og panel
#dungeon meshi#delicious in dungeon#labru#kabru of utaya#laios touden#redrew a death note panel for this but took artistic liberties
534 notes
·
View notes







