#lee jeong beom
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

The Man from Nowhere (2010) dir. Lee Jeong Beom. 아저씨 (2010) dir. 이정범. 7.9/10
I would recommend this movie to my friends. I would rewatch this movie.
Kim Sung Oh's characters are always kinda vile to me. This whole childhood kidnapping and slavery business makes me vomit. Oh Sang Man disgusts me.
Wonbin and the Thai man are both hot. I love their dynamic together. This movie is just to show that Wonbin is hot. That window breakthrough? We love vigilante savior behavior. Cutie doggies. This hair cut scene is just legendary.
The car accident like stopped my heart. The let me hug you once kills me. I'm crying.
The wrist slices are brutal.
#the man from nowhere#man from nowhere#아저씨#2010#이정범#Lee Jeong Beom#movie#korean#kmovie#film#review#commentary#rye-views#7.9
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

diversity loss! the worst people you know are in a QPR.
#karma spoilers#the witness#kim beom jun#kim beomjun#lee yu jeong#lee yujeong#악연#karma netflix#kdrama#cleave.txt
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today’s post: Our handsome gentleman in glasses 🤓
Which one’s your favourite?





#kim bum#kim beom#so yi jeong#lee ro joon#lee rang#monty navarro#boys over flowers#mrs cop 2#tale of the nine tailed#a gentleman's guide to love and murder#sexy men in glasses
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Study Group

TV Shows/Dramas watched in 2025
Study Group (2025, South Korea)
Directors: Lee Jang Hun & Yoo Beom Sang
Writers: Um Sun Ho & Oh Bo Hyun (based on the webtoon by Shin Hyung Wook)
Mini-review:
I've been watching this as it aired and it's been the breather I needed every week. Some people might be thrown off by the over the top, cartoonish style of the show, but that's exactly what makes it so unabashedly fun. It's basically like watching a shonen manga come to life (or in this case, an action webtoon). The fight scenes, especially those in the first and last episodes, showcase stunning choreography and effects, the likes you don't usually see in K-dramas. And the cast more than lives up to the demands of the show, in terms of both acting and physicality. It feels like Study Group leaves the door pretty open for more seasons, so if that ends up happening, they can count me right in.
#study group#lee jang hun#yoo beom sang#um sun ho#oh bo hyun#shin hyung wook#hwang minhyun#han ji eun#cha woo min#lee jong hyun#shin su hyun#yoon sang jeong#gong do yu#hong min gi#baek seo hoo#park yoon ho#lee kwang hee#joo yeon woo#seo dong gyu#kwok hyung seok#lim ji sub#shim woo sung#mo geon hu#kim young ah#lee jong hyuk#kim jung young#action comedy#dramedy#kdrama#2025 tv shows and dramas
10 notes
·
View notes
Photo

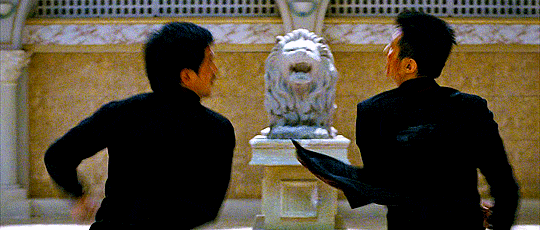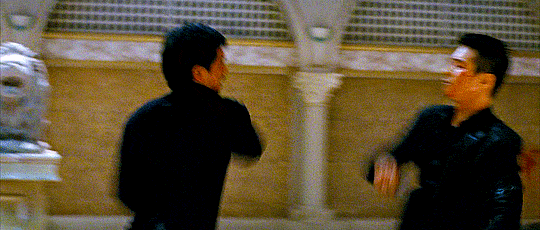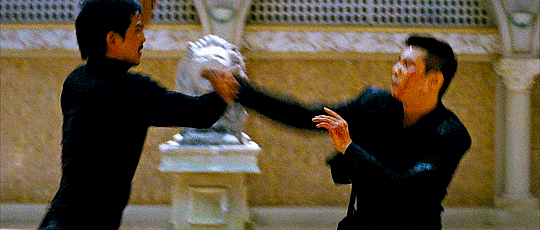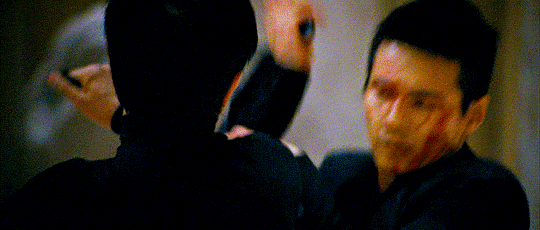
The Man from Nowhere (2010) Lee Jeong-beom
88 notes
·
View notes
Text

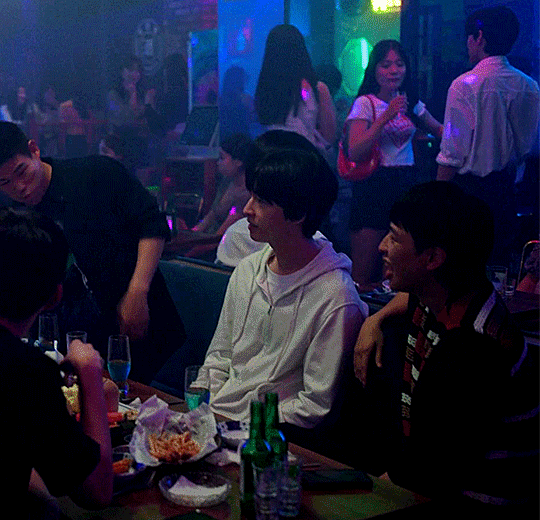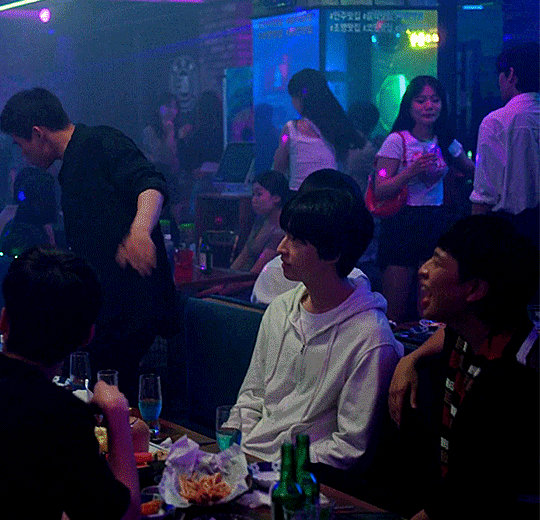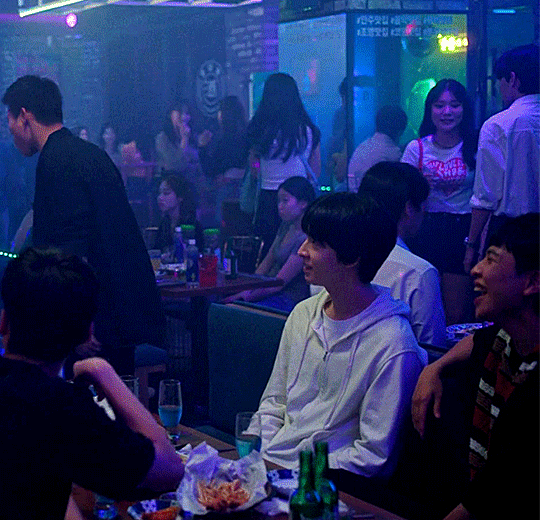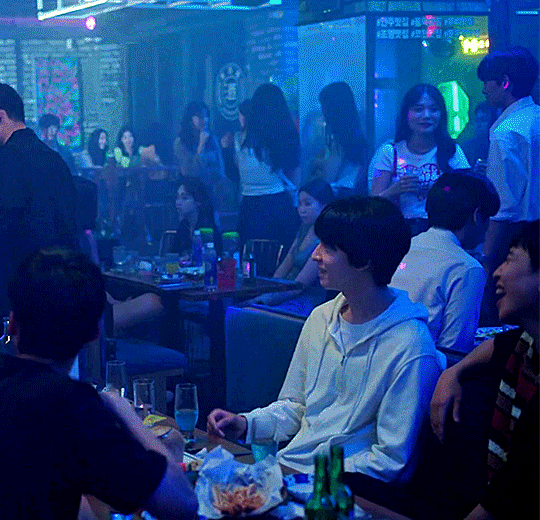
#Weak Hero Class 1#kdrama#약한영웅 class 1#weak hero class 1 kdrama#Yeon Jeong-hoon#Lee Jeong-chan#Hwang Seong-bin#Han Tae-hoon#Hong Kyung#Oh Beom-seok
6 notes
·
View notes
Text


Watching THE MAN FROM NOWHERE [아저씨] Lee Jeong-beom Korea, 2010
#watching#Lee Jeong-beom#Korean films#Won Bin#Kim Sae-ron#Kim Hee-won#Kim Sung-oh#Kim Tae-hoon#Thanayong Wongtrakunl#2010
0 notes
Text

Welcome to my blog!
I currently write for:
Squid Game
Seong Gi-Hun
The Salesman
Park Gyeong-Seok
Kang Dae-Ho
Hwang In-Ho
Hwang Jung-Ho
Choi Su-Bong (Thanos)
Park Min-Su
Gyeong-Su
Cho Hyun-Ju
Nam-Gyu
The Guest
Father Choi Yoon
The Gangster, The Cop, The Devil
Jang Dong-Soo
The Trauma Code: Heroes on Call
Baek Jang-Hyuk
Park Gyeong-Won
Yang Jae-Won
Han Yu-Rim
Bad and Crazy
Ryu Su-Yeol / K
Do In-Beom
Oh Kyeong-Tae
Andrei Kang
Jeong Yun-Ho
Bloodhounds
Kim Gun-Woo
Hong Woo-Jin
Hwang Yang-Jung
Lee Du-Yeong
Hong Min-Beom
The Player
Kang Ha-Ri
Do Jin-Woong
The Killing Vote
Kwon Seok-Joo
Kim Mu-Chan
Park Min-Chul
Train to Busan
Suh Seok-Woo
Deliver Us From Evil
Ray the Butcher
Newtopia
Arron Park
Sung Tae-Sik (Alex)
Please note that I only take requests in the form of short prompts, like the ones listed below. If you would like to submit a lyric or quote that isn't listed below, please send it in and I'll see what I can do. I do not write fics based on detailed storylines given to me by others. This is because I already have my storylines fleshed out, along with characters, worlds, plot lines etc.
Fic prompts and lyrics
Sabrina Carpenter Lyrics 💅🏻
Fluffy Prompt List✨
Sexy Time Lyric Prompt List 🚫 18+ only!
NSFW Prompt List 🚫 18+ only!
Angsty Lyric Prompts 💔
Smut Prompt List 🚫 18+ only!
Masterlists

Squid Game Masterlists

The Guest Masterlists

The Gangster, The Cop, The Devil Masterlists

The Trauma Code: Heroes on Call Masterlist

Bad and Crazy Masterlists

Bloodhound Masterlists - Awaiting Upload
#squid game 2#squid game#squid game x reader#squid game x you#seong gi hun#the salesman x reader#the salesman#pyeon sangwook#kang dae ho#all of us are dead x reader#all of us are dead#park min su#the guest kdrama#the guest#choi yoon x reader#the gangster the cop the devil#jang dong soo#jang dong soo x reader#bad and crazy#bloodhounds netflix#bloodhounds
170 notes
·
View notes
Text
Korean Master List:
All the posts presented below are my original contributions, with the exception of those in which I reference the work of others. In such cases, I provide original links to the sources where I found the material, thereby acknowledging the respective creators and authors.
Old Movies:
Emergency Act 19 (긴급조치 19호) - (08/08/2024)
Let's meet at Walker Hill (워커힐에서 만납시다) - Put On Hold!
Crossroads of Youth (청춘의 십자로) - (09/12/2024)
A Taxi Driver (택시운전사) (2017) - Put On Hold!
The Housemaid (하녀) (1960) - Put On Hold!
A Flower in Hell (지옥화) - Put On Hold!
Journey to the West (西游记) - Episode 1 - (03/04/2025)
The Story of Yanagawa's Canals (柳川堀割物語) - Almost Done (Translating and spell check) - Published Date (Unknown)
The Aimed School / School in the Crosshairs (ねらわれた学園) - Put on Hold!
The History of Korean Acts - 1900s-Now:
History of Korean music over the past century. (Korean Music Generations)
The History of Korean Male Groups (Rewrite):
Part 1 (Background) - (13/08/2024)
Part 2 - (21/08/2024)
Part 3 - (29/08/2024)
Part 4 - (29/08/2024)
Part 5 - (15/09/2024)
Part 6 (Background) - (08/12/2024)
Part 6.5 (Background) - (09/12/2024)
Part 7 (Background) - (10/01/2025)
Part 8 - In the Works!
The History of Korean Girl Groups (Rewrite):
A preview on what groups will be mentioned down below. This series will be coming out in the later part of next year.
Coming Soon!
Korean Soloists from the 20th Centaury:
Enjoy the history of some famous Korean performers that lived in the 20th centaury that have been lost with time.
Female:
Yun Sim-deok (Rewrite 1, 2) - (29/04/2024)
Lee Ari-su (Rewrite - Coming Soon!) - (05/03/2024)
Kim So-hee - (05/10/2024)
Jeon Hae-nam - (13/10/2024)
Kim Nan-ok - (22/01/2025)
Kim Chae-woon - (23/01/2025)
Kim Ok-jin - (26/01/2025)
Kim Wol-seon - (27/01/2025)
Kim Yeon Wol - (27/01/2025)
Lim Chun-hong - (08/02/2025)
Lee Hwa-seon - (11/02/2025)
Lee So-hee - (14/02/2025)
Park Nok-ju - Coming Soon!
Kim Ok-sim - Coming Soon!
Lee Hwa Jung Seon - Coming Soon!
Male:
Kim In Sik - (21/09/2024)
Lee Eun-sang - (27/09/2024)
Kim Saeng Ryeo (Pt. 1, 2) - (11,16/11/2024)
Lee In Beom - Coming Soon!
Kim Seong Tae - Coming Soon!
Jeong Jeong Ryeol - Coming Soon!
Im Bang Ul - Coming Soon!
Han Seong Jun - Coming Soon!
Kim Min Ik - Coming Soon!
Baek Seol Hee - Coming Soon!
Choi Nam Seon - Coming Soon!
Hyun Je Myeong - Coming Soon!
Lim Dong Hyeok - Coming Soon!
Photo Collection of Gisaeng's:
All photos below have been AI enhanced for a more clear viewing (there may be some errors in the pictures).
Part 1 - (17/07/2024)
Part 2 - (17/07/2024)
Part 3 - (17/07/2024)
Part 4 - (21/07/2024)
Part 5 - (21/07/2024)
Part 6 Finale - (24/07/2024)
Women considered to be the most beautiful in Korean History:
More than a century ago, a remarkable group of women known as Kisaengs captivated the elite with their captivating performances without ever compromising their dignity.
These extraordinary women, often referred to as the celebrities of their era, were renowned for their beauty and talent, as evidenced by historical records that ranked the most enchanting kisaengs of that time!
Part 1 Oh San-wol (오산월) - (11/07/2024)
Part 2 Jang Yeon Hong (장연홍) (1) - (14/07/2024)
Part 3 Jang Yeon Hong (장연홍) (2) - (16/07/2024)
Part 4 - Put On Hold!
The Birth of Korean Girl Groups Preview:
A preview on what girl groups I'll be posting in my series on 'The History of Korean girl groups'.
Part 1 - 1900s-1945 - (28/04/2024)
Part 2 - 1950s - 1960s - (28/04/2024)
Part 3 - 1960s - 1962 - (28/04/2024)
Part 4 - 1963 - 1965 - (28/04/2024)
Part 5 - 1965- 1966 - (28/04/2024)
Part 6 - 1967-1960s - (28/04/2024)
Part 7 - 1970-1972 - (02/05/2024)
Part 8 - 1974 - 1981 - (09/05/2024)
Part 9 - 1983 - 1987 - (09/05/2024)
Part 10 - 1989 - 1997 - (09/05/2024)
Part 11 - 1997 - (09/05/2024)
Part 12 Final - 1998 - 2000s - (09/05/2024)
H.O.T:
Stuff about H.O.T.
Michael Jackson & Friends Korea, Seoul:
S.E.S: Part 1 and Part 2
H.O.T: Put On Hold!
Discography Discussion:
These discography discussion posts are all made by @high-five-of-teenager-trashblog. All the albums are in released order from there debut to there final album.
We Hate All Kinds of Violence - (13/12/2020)
Wolf & Sheep - (23/11/2020)
Resurrection - (13/02/2019)
I Yah! - (29/08/2018)
Age of Peace (+ Album Cover) - (26/11/2020)
Outside Castle - (24/09/2018)
'Solving the H.O.T. Syndrome':
These 3 posts are all made by @1004sface.
TV Guide 1997.01.23 - (Pt. 1) (Pt. 2) (Pt. 3)
Kangta - Atlantis: The Lost Empire 2001:
H.O.T Kangta - Dreams and Faith - (27/07/2024)
Ensign O'Toole - TV Series 1962-1963:
Summary & Ep 1-12 - (26/10/2024)
Ep 13-32 - (09/12/2024)
Korean Albums:
Season 1 focuses on the 1980s, a personal favourite music decade. I will discuss 35 diverse Korean groups, duos, bands, and solo artists who released albums or made their debuts during this period.
Season 2 will explore the 1960s and 1970s through 30 episodes, highlighting a diverse range of Korean groups, duos, bands, and solo artists. I invite recommendations for Korean artists that you would like me to research and discuss.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The History of Korean Male Soloists from the 20th Century: Episode 3/?
The third episode of 'The History of Korean Male Soloists from the 20th Century' highlights prominent Korean musicians who achieved fame in the early 20th century, during the period of Japanese occupation.
The historical documentation related to these artists is frequently unreliable, largely due to the fact that their contributions occurred almost a century ago, before the Korean War, leading to the loss or unavailability of essential records.
Kim Saeng Ryeo (김생려; 金生麗)
Kim Saeng-ryeo is linked to the Yonhui Professional Orchestra (연희전문사중창단), founded in 1929, as discussed in Part 3. The Yonhui College Orchestra/Quartet, led by Hyun Je-myeong (현제명), held biannual concerts from 1930 for nearly a decade, showcasing emerging talent and reflecting the changing musical tastes of the colonial era. This orchestra was instrumental in the development of musicians such as Kim Seong-tae (김성태), Lee In-beom (이인범), Kim Saeng-ryeo (김생려), and Lim Dong-hyeok (임동혁).
Numerous types of orchestras exist, and I discovered a resource that provides a comprehensive overview of each, including philharmonic, symphony, chamber, opera, string, and wind orchestras, among others. This resource will cover a variety of orchestral forms.

Life and Career
Born on November 25th, 1912, in Yongbyon, North Pyongan Province, and passing away in Las Vegas on December 14th, 1995, at the age of 83, he was the only son among five siblings and married to dancer Kwon Ryeo-seong (권려성). His father, a devout Christian and elder, introduced him to the church at an early age, fostering a particular fascination with the organ. Shortly after his birth, his father established a church in Bukcheong, where Kim Saeng-ryeo spent his formative years.
He played a crucial role in the establishment of the Seoul Philharmonic Orchestra and was instrumental in founding the Seoul Symphony Orchestra after Korea's liberation, thereby leaving a significant mark on the country's symphonic music scene. His early life unfolded in Anju, South Pyongan Province, and Bukcheong, South Hamgyong Province. Like other key figures in the early development of Western music in Korea, such as Hyeon Je-yeong (현제명), Lee Heung- ryeol (이흥렬), and Gye Jeong-sik (계정식), Kim was raised in a Protestant household, which provided him with early access to Western musical traditions.
From a young age, he demonstrated exceptional skill in playing both the organ and harmonica. His journey with the violin began in elementary school, where he had already shown a unique aptitude for the organ and harmonica, often playing during his free time. His passion for music persisted even after starting school, as he would occasionally leave class to visit a church and immerse himself in musical experiences.
In the second grade, his fascination with music deepened when he encountered an amateur violinist, which inspired him to take up the violin. This pivotal moment marked a significant shift in his musical journey. After completing elementary school, he moved to Seoul to pursue further education, enrolling in the second high school, now known as Gyeongbok High School (경복고등학교; 景福高等學校), where he distinguished himself as a disciplined and diligent student.
While attending Gyeongseong Jeigo High School, he received violin lessons from Boots, the wife of a foreign doctor at Severance Hospital (세브란스병원). His serious commitment to violin studies intensified after meeting Gye Kye-sik, a returnee from Germany. He continued to practice diligently at Yonhui College (연희전문학교; 延禧專門學校) and, upon graduation, took on roles as an accompanist and conductor for the Gyeongseong Broadcasting Station Orchestra (조선방송협회(朝鮮放送協會). However, during the Gwangju Student Incident https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gwangju_Student_Independence_Movement (광주 학생 독립 운동; 光州學生獨立運動), he actively participated in protests, which led to his pursuit by the Japanese police and subsequent suspension from school. He was only reinstated after submitting a written account of his actions, but he continued to face challenges, particularly from his Japanese teachers, ultimately graduating under difficult circumstances.

Throughout his academic evolution, his commitment to music remained steadfast. After finishing elementary school, he moved to Seoul to further his education, enrolling in Jeigobo (제이고보), now recognized as Gyeongbuk High School. His association with Kim Hyung-jun (김형준; 金亨俊), a violinist and conductor, facilitated his involvement with the Gyeongseong Central Orchestra (경성중앙관현악단; 京城中央管絃樂團) as a violinist. Upon graduating from Gyeongbuk High School, he encountered Gye Jeong-sik (계정식; 桂貞植), a returnee from Germany, who helped him strengthen his foundational skills in violin, leading to his participation as a second violinist in a string quartet directed by Gye Jeong -sik.
Despite familial opposition to his musical aspirations, he persevered and, after graduating from Gyeongbuk High School, gained admission to Yonhee College through the recommendation of Hyun Je-myeong (현 종양). There, he continued to engage in musical activities and was appointed as the second violinist in a string quartet under Gye Jeong-sik's (계정식; 桂貞植) leadership. Although he attempted to follow his father's wishes by applying to Severance Medical School, he was unsuccessful and instead enrolled in the liberal arts department at Yonhee College, where he benefited from diverse musical experiences and eventually became the head of the school band.
Under the mentorship of Hyun Je-myeong, who began his role in 1929, he collaborated with notable musicians such as Kwak Jeong- seon (곽정선), Kwak Jeong-sun (곽정선), and Kim Gwan (김관). In the early 1930s, he worked with Kim Seong-tae (김성태) (violin), Lee Yu-seon (이유선) (vocal), and Hwang Jae-gyeong (황재경) (flute) within the music department at Yonhee College, further advancing his musical skills. However, following a victorious sports match against Gyeongseong Medical School, which included Japanese students, he celebrated with the band members, leading to an incident that resulted in his indefinite suspension after being held accountable for the situation.
His time in Japan represented a transitional phase, but upon his return to Korea two years later, he re-enrolled at Yonhui College. There, he secured a position with the Gyeongseong Central Broadcasting Station Orchestra and supplemented his income by working as a violin accompanist for the prestigious Victor Records orchestra. Although he graduated in 1937, two years later than his classmates due to his studies abroad, he remained actively engaged in music, including performing violin solos during chapel services at the college.
Kim Saeng-ryeo's experience at Yeonjeon coincided with the return of Hyun Je-myeong from the United States, marking a high point for the Yeonjeon Music Club. During this vibrant period, he collaborated with notable musicians such as Kim Seong-tae, Jeong Hee-seok, Lee In-beom (이익), and Hwang Jae-gyeong. After completing his studies at Yeonjeon, he continued his career as an accompanist for both the Gyeongseong Broadcasting Station Orchestra and Victor Records.
Following the return of Hong Nan-pa (홍난파; 洪蘭坡) (April 10, 1898 – August 30, 1941) from the United States, who expanded the Gyeongseong Broadcasting Orchestra, Kim Saeng-ryeo assumed the role of conductor, fostering a strong musical partnership with Hong. During this time, he also developed a close relationship with Kim Seong-tae, visiting him to study harmony and composition. When Hong Nan-pa fell ill, Kim dedicated himself to supporting him, managing the broadcasting station's responsibilities in his absence and providing care until Hong's passing.
Hong Nan-pa's counsel became a guiding principle for him: “If you aspire to be a flower, abandon music. If you wish to be a seed that flourishes for future generations, persist in music.” This philosophy provided him with resilience and served as an enduring compass during challenging times.

In the 1940s, he adopted the name Kaneyama as part of a broader national integration initiative. Following the death of Hong Nan-pa, Kim Saeng-ryeo assumed leadership of the orchestra and invited Gye Jeong -sik.to conduct. However, when the broadcasting station attempted to replace Gye-sik with a Japanese conductor, the Korean members, led by Kim Saeng-ryeo, vehemently resisted. Ultimately, when their efforts were thwarted, he chose to resign and establish a private orchestra.
He demonstrated his violin prowess at the inaugural concert of the Joseon Symphony Orchestra and at an event organized by the Joseon Music Association in 1941. That same year, he performed a solo at the "Peninsula Entire Enlistment Song Recital," which marked the introduction of the conscription system. He also participated in the "Music Patriot Weekly Music Festival" at Bumin Hall (부민관; 府民館) alongside prominent musicians. In 1942, he became the conductor of the Kyungsung/Gyeongseong Welfare Chamber Orchestra (경성후생실내악단; 京城厚生室內樂團) and joined the National Mobilization Federation of Korea/ Music Popularization Corps (國民音樂普及挺身隊) in 1943, performing at various patriotic events, including the "Battleship Donation and Patriotic Chamber Symphony Night." As the first violinist of the Kim Saeng-ryeo String Quartet and later a representative of the Hwaseong Chamber Orchestra, he continued to perform at events that celebrated the conscription system and supported pro-Japanese organizations.

Bumin Hall (부민관; 府民館) in the early 1940s
In 1942-1943, he established the Husung Chamber Orchestra following his resignation from the broadcasting station, which subsequently toured across the nation. Notably, soprano Kim Cheon-ae, a founding member of the orchestra, performed "Bongseonhwa" (봉선화) during the tour, providing solace to audiences mourning their country's plight, which led to her being monitored by the Japanese authorities.
In 1944, the Husung Chamber Orchestra relocated to Xingjing, Manchuria, where its members integrated into the Xingjing Symphony Orchestra. As liberation approached in 1945, he returned to Korea at the behest of Hyun Je-myeong to reestablish the Husung Orchestra, coinciding with the country's liberation. He took on the role of conductor for the newly formed Goryeo Symphony Orchestra in 1945, having previously been an active violinist during the Japanese colonial era. Following liberation, at Hyun Je-myeong's request, Kim Saeng-ryeo mobilized efforts to assemble around 50 musicians in the fall of 1945, successfully founding the Goryeo Symphony Orchestra under conductor Gye Jeong -sik., marking the inception of Korea's first orchestra post-liberation.

‘Bongsunga’ (봉선화) sheet music by Kim Hyung-jun, composed by Hong Nan-pa (100 Years of Our Western Music)
He subsequently departed from the Goryeo Symphony Orchestra. In 1946, he co-established the Seoul Music Club (서울음악동호회), recognized as the first chamber orchestra formed post-liberation of Korea, alongside Lee Jae-ok (이재옥), Jeong Hoon-mo (정훈모), Lee In-hyeong (이인형), Ahn Seong-gyo (안성교), Oh Byeong-do (오병도), and Jeon Bong-cho (전봉초). This initiative served as a foundation for the eventual formation of the Seoul Symphony Orchestra, where he assumed the role of conductor and later founded the Kim Saeng-ryeo Quartet in 1947, collaborating with Lee Yong-cheol (이용철), Choi Gyu-yeong (최규영), and Kim Jun-deok (김준덕). He was also a member of the Seoul Orchestra, alongside Jo Bong-deok (조봉덕), Lee Gyu-su, and Kim Soon-deok (김순덕). In 1947, he took the initiative to establish and manage the Seoul Symphony Orchestra, which was the precursor to the Seoul City Symphony Orchestra (서울시립교향악단; Seoul Philharmonic orchestra ,─市立交響樂團) founded in 1948, drawing from the Korea Symphony Orchestra (고려교향악단; 高麗交響樂團) and the Seoul Orchestra, and made his conducting debut at the inaugural concert held in February of the following year.

1950s picture of the Seoul Symphony Orchestra
Kim Saeng-ryeo embarked on his professional journey as a conductor through a prestigious invitation extended by the U.S. State Department. This opportunity allowed him to immerse himself in the world of classical music, where he had the privilege of studying under some of the most esteemed maestros of the time, including the legendary Leonard Bernstein and the renowned Eugene Ormandy. These formative experiences not only honed his skills but also enriched his understanding of orchestral dynamics and interpretation. As his conducting career progressed, Kim Saeng-ryeo showcased his exceptional talent by leading prominent orchestras, such as the Boston Symphony Orchestra and the Philadelphia Philharmonic. His performances on international stages garnered acclaim and recognition, establishing him as a significant figure in the global classical music scene.
Upon returning to Korea, Kim Saeng-ryeo was instrumental in founding the Seoul City Symphony Orchestra in November 1958. His vision and commitment were key in defining the orchestra's character, and he assumed the roles of permanent conductor and representative. Initially, he played as the first violinist when the orchestra commenced its activities in January of that year. The inaugural concert was conducted by Kim Seong-tae, and soon after, the orchestra began regular performances under the direction of German conductor Rolph Jacobi, who served as an advisor to the Central Broadcasting Station. However, following Jacobi's unexpected departure to Germany, Kim Saeng-ryeo took over as conductor for a concert in Daegu, marking the beginning of his conducting career.
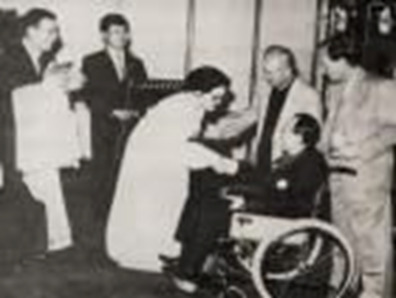
In October 1995, Kim received a distinguished invitation to conduct at the Korean Symphony Orchestra's 50th anniversary concert, he performed from a wheelchair and received enthusiastic response from the audience.
Under Kim's direction, the orchestra not only expanded its repertoire but also undertook extensive tours throughout Southeast Asia, performing in nations such as Vietnam, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. These tours highlighted the orchestra's talent and promoted cultural exchange, enhancing the appreciation of classical music in the region. Kim played a crucial role in negotiating the orchestra's establishment with the Seoul Metropolitan Government, ensuring a strong foundation for its operations and performances. His dedication to the orchestra's development established it as a significant entity in Korea's cultural scene, quickly gaining popularity among audiences, who often displayed overwhelming enthusiasm during performances. Notable works conducted by him included Kim Seong-tae's "Capriccio," Schubert's "Unfinished Symphony," and Ravel's "Bolero Dance" at various concerts.
Throughout his tenure, Kim Saeng-ryeo conducted a series of notable performances that left a lasting impact on the Korean music scene. Among these were Puccini's "Tosca," which he conducted in October 1958, and the double bill of Leoncavallo's "Pagliacci" and Mascagni's "Cavalleria Rusticana" in June 1959. These productions were significant not only for their artistic merit but also for their role in introducing Western operatic traditions to Korean audiences. In November of the same year, he conducted Bizet's "Carmen" at the National Theatre of Korea, further solidifying his reputation as a conductor capable of delivering powerful and emotive performances.


Photo 1 -> Kim Saeng-ryeo 1972 Photo 2 -> Newspaper clipping published in June 25th 1972
Despite successfully navigating numerous challenges to develop the orchestra, the onset of the Korean War compelled him to abandon his ambitions for the ensemble, leading to a three-month period of hiding under communist rule until Seoul was recaptured on September 28. Ultimately, the Seoul Symphony Orchestra was disbanded after its 23rd regular concert due to the war. At its formation, the orchestra included a wide array of musicians, featuring first and second violinists, violists, cellists, and various woodwind and brass players. Among the distinguished members were Kim Saeng-ryeo and Jo Bong-deok on first violin, alongside a diverse group of instrumentalists such as flutists, oboists, clarinettists, and trumpeters. The ensemble also incorporated percussionists and a pianist, creating a rich auditory experience that defined the orchestra's performances during its short yet significant existence.
Full List of the members at the time of its founding of Seoul Symphony Orchestra were as follows: . 1st Violin (제1 바이올린): Kim Saeng-ryeo (김생려), Jo Bong-deok (조봉덕; 趙鳳德), Lee Gyu-su (이규수; ���奎秀), Kim Soon-deok (김순덕; 金順德), Lee Gye-seong (이계성; 李桂成), Baek Hae-je (백해제; 白海帝), Lee In-hwan (이인환; 李仁煥), Heo Sang (허상; 許湘), Lee Sung-tae (이숭태; 李崇泰), Shin Sang-cheol (신상철; 申相徹), Kim Hae-ryong (김해룡; 金海龍). . 2nd Violins (제2 바이올린): Lee Jae-ok (이재옥; 李在玉), Nam Chang-hyun (남창현; 南昌鉉), Jo Gyu-won (조규원; 趙奎元), Choi Ho-won (최호원; 崔豪源), Moon In-yeon (문인연; 文麟連), Lee Dong-hee (이동희; 李東熙), Kim Seon-hwa (김선화; 金善化), Jeon Chang-jae (전창재; 全昌宰), Jeon Oh-bok (전오복; 全五福), Park Jun-hwang (박준황; 朴俊晃). . Violas (비올라): Ahn Seong-gyo (안성교; 安聖敎), Lim Chun-ok (임춘옥; 林春沃), Lee Yeong-don (이영돈; 李泳敦), Lee Jae-man (이재만; 李裁晩). . Cello (첼로): Jeon Bong-cho (전봉초; 全鳳楚), Woo Dal-hyeong (우달형; 禹達亨), Lee In-gyu (이인규; 李寅圭), Park Guk-rok (박국록; 朴國錄), Kim Jong-myeong (김종명; 金鍾明), Lee Jeong-eon (이정언; 李禎彦), Yoo Jeong-yong (유정용; 劉廷鏞). . Flute (플루트): Oh Byeong-do (오병도; 吳炳道), Lee Gi-yoon (이기윤; 李基潤), Hong Su-man (홍수만; 洪壽萬). . Oboe (오보에): Lee Byeong-woo (이병우; 李炳祐). . Clarinet (클라리넷): Hong Gwang-eun (홍광은; 洪光銀), Kim Seong-hun (김성훈; 金成勳). . Bass (파곳): Kim Yeong-gyu (김영규; 金英圭), Na Moon (나문; 羅文). . Horn (혼): Jeong Hoe-gap (정회갑; 鄭回甲), Kim Jong-sun (김종순; 金宗純), Kim Yun-seong (김윤성; 金潤成), and Hyeon Su-so (현수소; 玄壽瀟). . Trumpets (트럼펫): Kim Jong-dae (김종대; 金鍾大), Park Ju-doo (박주두; 朴柱斗), and Kim Man-bok (김만복; 金萬福). . Timpani (팀파니): Han In-hang (한인항; 韓麟恒). . Battery/ Baeteoli (배터리): Kwon Yong-jin (권용진; 權龍鎭), Han Seong-jin (한성진; 韓聖振). . Piano (피아노): Lee In-hye (이인형; 李仁亨). . Conductor/Arrangement (지휘·편곡): Jacobi (쟈코비), Kim Seong-tae (김성태; 金聖泰). . Vocalists (성악): Kim Cheon-ae (김천애; 金天愛), Kim Hye-ran (김혜란; 金惠蘭), Lee In-beom (이인범; 李仁範), Kim Hyeong-no (김형노; 金炯魯).

The Symphony Orchestra of Seoul City gave a concert in Hong Kong on April 20, 1947. (Photo by: Universal History Archive/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
Following the recapture of Seoul during the Second Battle of Seoul in 1950, the establishment of the Seoul Symphony Orchestra was initiated alongside the formation of the Naval Military Training Band, which served as the precursor to the Seoul Metropolitan Symphony Orchestra. This endeavour marked a significant cultural development in a time of conflict.
In his role as conductor, he assembled musicians and sought support from the Navy to create the Navy Military Band. Despite the ongoing war, this ensemble was unique in its provision of employment for musicians and opportunities for music enthusiasts to enjoy performances. He maintained his leadership of the band throughout the duration of the war, ensuring its continued presence in the musical landscape.
As a founding member of the Korean Musicians Association established on November 8, 1949, he played a pivotal role in the organization of the Naval Military Music Band in October 1950, where he served as captain. Following the appointment of all 120 members of the Naval Cultural Promotion Corps as civilian naval officers, the band held its inaugural concert in November 1950 at Sigong Hall, celebrating both the Navy's fifth anniversary and the recapture of Seoul. The band, which returned to Seoul in 1953, became influential in the performance scene, showcasing significant works and ultimately evolving into the Seoul Symphony Orchestra, which was later restructured into the Seoul Metropolitan Symphony Orchestra in 1960.

The main characters Patty Kim (김혜자; 金惠子) (left) and Kwak Gyu-seok (곽규석) (Right) at the premiere of the musical 'Saljjagi Obseye' (살짜기 옵세아이) by the Yegreen Orchestra in 1966. [Joongang Photo]
Kim was appointed as the first conductor of the Seoul City Symphony Orchestra, a role he maintained until 1961. Initially optimistic about fostering a vibrant symphony orchestra movement, his ambitions were thwarted by the political turmoil surrounding the April 19 Student Revolution in 1960 and the May 16 Military Coup in 1961. These events culminated in his resignation, prompted by legal disputes involving current and former orchestra members. Nevertheless, during his tenure, Kim Saeng-ryeo actively guided the orchestra, undertaking performances both domestically and internationally, including tours throughout Southeast Asia, thereby establishing a significant foundation for the orchestral movement in Korea.
In January 1962, Kim assumed the role of director for the Yegreen Orchestra, which was founded with the guiding principle of "Remembering the Past and Yesterday for Tomorrow." By September of that year, the orchestra had successfully staged five performances of the "Chuseok Play," showcasing a variety of musical selections. After the orchestra's dissolution, the exact timing of which is uncertain, Kim established the Arirang Folk Arts Troupe, which toured extensively across the United States, Canada, Europe, and other regions, playing a vital role in the dissemination of South Korean culture.
In the same year, Kim also held several significant positions, including head of the music department at Kyunghee University, representative of the Yegreen Orchestra, and artistic member and commander of the Naval Military Music Band. His diverse engagements in these organizations, along with his role in representing the Seoul Metropolitan Symphony Orchestra, highlighted his prominent influence in the South Korean music landscape during this era.

1967 Yegreen Orchestra ‘Kkotnim, Kkotnim, Kkotnim’ (꽃님, 꽃님, 꽃님). The middle of the second row is Na Yeong-su (나영수), and next to him on the left is Hwang Ik-pyeong (황익평), Moon Hye-ran (문혜란), Lim Yeong-ung (임영웅), Park Yong-gu (박용구), Choi Chang-kwon (최창권), and Kwak Gyu-seok (곽규석) (Fry Boy). The man sitting in the middle of the front row is Hwang Un-heon (황운헌) (Chief of the Literature Department).
In 1962, he travelled to the United States to pursue studies in conducting, and by 1971, he had taken on a professorship in the Department of Music at Hanyang University. He returned to the United States in 1976, where he held the position of permanent conductor for the Southern California Philharmonic Orchestra until 1992.
In October 1995, he received a distinguished invitation to conduct at the Korean Symphony Orchestra's 50th anniversary concert, performing from a wheelchair and receiving an enthusiastic response from the audience. His impact on the Korean symphonic scene was significant; he established the Seoul Symphony Orchestra Association and the Seoul Symphony Orchestra, while also enhancing Korean music through his leadership of the Yegreen Orchestra, his role with the Arts Council, and his teaching at Kyunghee University. His achievements were acknowledged with numerous awards, including the Swedish Red Cross Medal and the Seoul City Cultural Award. Kim passed away due to diabetes-related complications at Sunrise Hospital in Las Vegas, USA, on December 14, 1995, at the age of 83.
Activities and Achievements
Kim Saeng-ryeo's career in music began in 1939 when he served as the conductor for the Seoul Central Broadcasting Station Orchestra. He played a pivotal role in establishing several orchestras, including the Seoul Welfare Chamber Orchestra in 1942, where he was a violinist, and the Goryeo Symphony Orchestra in 1945, for which he was the founding conductor. His influence continued with the founding of the Seoul City Symphony Orchestra in 1948, where he also held the position of conductor. By 1950, he became the Permanent Conductor of the Philadelphia Symphony Orchestra in the United States, while also commanding the Naval Music Band (해군정훈음악대; 海軍政訓音樂隊).

The 14th Program of the Korea Symphony Orchestra (1947)
Throughout his career, Kim received numerous accolades for his contributions to music. Notable awards include the Prime Minister's Cultural Medal in 1948, the Merit Award from the Swedish Red Cross in 1951, and the Seoul City Cultural Award in 1955. His international recognition was further solidified with the Greek Theatre Arts Medal in 1964 and the Republic of Korea National Academy of Arts Award in 1974, among others. These honours reflect his significant impact on the cultural landscape both in Korea and abroad.
In addition to his conducting roles, Kim was actively involved in various artistic initiatives. He conducted the Danwood Symphony Orchestra during the Bergsha Music Festival in 1953 and led the Arirang Folk Art Troupe on tours in the United States and worldwide in 1964. His collaboration with prominent orchestras, such as the Ormandy and Boston Symphony Orchestra in 1968, showcased his versatility. Notably, he celebrated the 500th regular concert of the Seoul City Symphony Orchestra in 1994, marking a significant milestone in his enduring legacy within the music community.
Seoul City Orchestra "Kim Saeng- ryeo's Reminiscence" Concert
Seoul City Orchestra "Kim Saeng-ryeo Reminiscence" Concert 11th Sejong Centre for the Performing Arts - Reporter Ryu Yun-jong
The "Emperor" of 44 years ago has been revived as today's "Emperor." The Seoul City Orchestra's regular concert, held at 7:30 PM on the 11th in the Sejong Center for the Performing Arts Main Hall, will be a meaningful stage with the subtitle "Kim Saeng-ryeo Reminiscence." It is a place to commemorate the first anniversary of the death of the late Kim Saeng-ryeo, the founder of the Seoul City Orchestra, and to honor his achievements and will. In this concert, Kim Won-mo (professor at Dankook University) will be the guest conductor and Baek Nak-ho (chairman of the Korea Music Association) will perform Beethoven's Piano Concerto No. 5 "Emperor."
youtube
서울시립교향악단 제 545회 정기연주회 "김생려 회상" [1996] Seoul City Symphony Orchestra 545th Regular Concert "Kim Saeng-ryeo Reminiscence" [1996]
Although it is a collaboration stage between a veteran pianist and a mid-career conductor that anyone would know by name, their meeting that day holds special meaning. In the midst of the smoke of the 1952 war, Baek Nak-ho (백낙호) performed "Emperor" with the Naval Music Band, the predecessor of the Seoul Philharmonic Orchestra, under the direction of Kim Saeng-ryeo in Busan, where he was a refugee. Professor Kim Won-mo (김원모) is Kim Saeng-ryeo's second son. He arranged Tchaikovsky's Symphony No. 6 "Pathetique," which his father enjoyed conducting, as the second half of the concert.
Baek Nak-ho (백낙호) recalled, "During the three years of my refuge in Busan, I spent my time with Kim Saeng-ryeo in the Naval Music Band, and we built a friendship as seniors and juniors."
At the concert, Lim Won-sik (임원식; 林元植) (Professor Emeritus of Chugye University for the Arts), who played a leading role in the founding of the National Symphony Orchestra (now the KBS Symphony Orchestra) in 1957 and competed with the Seoul Philharmonic Orchestra in good faith, will share his memories of the deceased in the form of reminiscences.
#south korea#history#korea#Korean Music#Korean Music History#Music History#Kim Saeng-ryeo#김생려#photography#korean history#Youtube
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
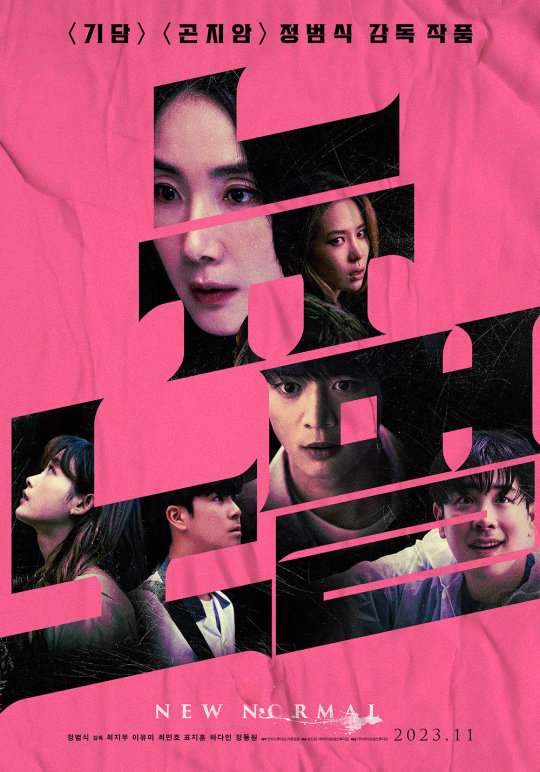


Minho's movie 'New Normal' first poster released (HQ photos)
'Gidam' and 'Gonjiam' director Jeong Beom-sik's new film 'New Normal' has released two types of first posters with its release confirmed in November.
The first two types of posters released this time first grab attention with their intense colors and impactful titles. First, the pink poster, with its striking pop color, captured the colorful expressions of actors including Choi Ji-woo, Lee Yu-mi, 𝗖𝗵𝗼𝗶 𝗠𝗶𝗻𝗵𝗼, Pyo Ji-hoon, Ha Da-in, and Jeong Dong-won between the titles.
The black and white stills of the actors placed between the titles in the released white poster give a glimpse of their eyes and expressions, which are different from those on the pink poster.
ˢⁿⁱᵖᵖᵉᵈ---
"...to the face of actor 𝗖𝗵𝗼𝗶 𝗠𝗶𝗻𝗵𝗼, who looks at something as if filled with melancholy and stimulates curiosity..."
'New Normal’ will be available in theaters this November.
Source: link Trans ©AFlamer5299
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
⋆。‧˚ʚɞ˚‧。⋆
MASTERLIST

CONTENT GUIDE
fluff: ღ | suggestive: ✮ | smut: 𖤐 | angst: ☾ | fem: ❀ | gender neutral: ⟡ | male: ✰
ULTS + BIASES
works for: RIIZE (라이즈)
Osaki Shotaro (大崎将太郎)
— none so far
Song Eunseok (송은석)
— none so far
Jung Sungchan (정성찬)
— none so far
Park Wonbin (박원빈)
— none so far
Hong Seunghan (홍승한)
— none so far
Lee Sohee (이소희)
— best friend: your best friend sohee offers a "no strings attached" relief from the stress of your relationship but finds himself falling in too deep. 𖤐 | ❀ | ☾ (?)
Lee Chanyoung (이찬영)
— none so far
ot7 reactions + head cannons + scenarios + mtl
works for: bangtan sonyeondan 방탄소년단
Kim Seok-Jin
— none so far
Min Yoon-Gi
— none so far
Jung Ho-Seok
— none so far
Kim Nam-Joon
— none so far
Park Ji-Min
— none so far
Kim Tae-Hyung
— none so far
Jeon Jeong-Guk
— none so far
ot7 reactions + head cannons + scenarios + mtl
works for: seventeen 세븐틴
Choi Seung Cheol
— none so far
Yoon Jeong Han
— purple rose: you find out that your cranky boss at your bartending job turns out to be quite the mischievous co-host of an exclusive bdsm club. not wanting to back down, you try to ignore this new found info when at work. but once blurred lines are already crossed, can they really be forgotten? ☾ | 𖤐 | ❀
Joshua Hong
— let it happen: reader and joshua are in a confusing relationship. a constant tug of war over who can get each other more in love, and more heart broken. (based on gracie abrams “mess it up”) ☾ | ✮ | ❀
Wen Junhui (文俊辉)
— none so far
Kwon Soon Young
— none so far
Jeon Won Woo
— none so far
Lee Ji Hoon
— none so far
Lee Seok Min
— none so far
Kim Min Gyu
— none so far
Xu Ming Hao (徐明浩)
— none so far
Boo Seung Kwan
— new romantics: the “goody-two-shoes”, university athlete boo seungkwan encounters a “rebel against-all-odds”, biker!reader and truly learns what it means to have fun while living life for himself alongside new found, and utterly careless love. part 1 | ❀ | ✮
Hansol Vernon Chwe
— just wanna ease ya mind: based on jhene aiko’s “bed peace” ft childish gambino. (in other words, high sex with bf!vernon) ❀ | 𖤐
Lee Chan
— none so far
ot13 reactions + head cannons + scenarios + mtl
— if they had a black cat personality type s/o that showed affection (not so) subtly ღ | ⟡
— secret dating idol!svt — 95z line, & if you guys would get caught ⟡ | ღ
works for: t x t 투모로우바이투게더
Choi Soo Bin
— none so far
Choi Yeon Jun
— none so far
Choi Beom Gyu
— none so far
Kang Tae Hyun
— none so far
Kai Kamal Huening 정하원 休宁凯
— none so far
ot5 reactions + head cannons + scenarios + mtl
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

they both have a kink for getting money. sick fuck x crazy bitch.
#do you guys have a fun name for them because i'm blanking#karma spoilers#kim beom jun#the witness#lee yu jeong#악연#karma netflix#kdrama#suggestive#< just in case#cleave.txt
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
was watching clips from BOF, kim beom has been a heartthrob since day 1 😍😍
Nice to meet you my friend and fellow KB fan 😀😀
So… from your ask I’m assuming you’ve watched BOF many times, and like me, you reach out to youtube to for those SoEul scenes. Am I right?
I do that a lot with his shows. Most frequently watched is Lee Rang, of course, and then Law School. Every time he smiles in Law school, I just… swoon ❤️❤️
#lee rang#tale of the nine tailed#kim bum#tale of the nine tailed 1938#kim beom#so yi jeong#boys over flowers#law school#law school kdrama#han joon hwi
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo



The Man from Nowhere (2010) Lee Jeong-beom
111 notes
·
View notes
Text

Watching
NO TEARS FOR THE DEAD [우는 남자] Lee Jeong-beom Korea, 2014
#watching#Lee Jeong-beom#Korean films#Jang Dong-gun#Kim Min-hee#Brian Tee#Kim Hee-won#Jun-seong Kim#2014
0 notes