#klezmer music
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
So I was just supposed to find out about klezmer punk music all on my own? This absolute hellsite wasn't going to tell me that there were queer Jewish protesters on the east coast making sick as fuck bouncy progressive punk music like ten years ago??
It's the magical overlap between ska, the mountain goats, folk punk, and genderqueer Jews. What's not to like? Why did nobody tell me about this?
Di Nigunim protested at both the DNC and the RNC in 2008, calling it a Duocracy Tour, among so much other activist work.
Schmekel was an all trans all Jewish folk punk band
Chabad Religion exists!
Wake up people!
0 notes
Text
youtube
A Jewish dance tune from Maramures, Romania, played on a tsimbl (cymbalom, a type of wooden dulcimer).
Originating from sixteenth century Hungary, the instrument became all over Eastern Europe an essential component of the klezmer band. The (singular) Hungarian word cimbalom and the Yiddish tsimbl became the plural forms cymbaly in Polish, tsymbaly in Ukrainian and Belorussian, and tambal in Romanian. The old Romanian word tambelar for a performer derives directly from Yiddish. Likewise, the appearance of the tambal mic (little cymbal) in Roma tarafs (ensembles) was a reflection of a Jewish klezmer presence in the early to mid-nineteenth century. The tsimbl is still regarded as a Jewish instrument in Poland, and as a Jewish-derived home instrument among the former Polish gentry of Belarus. The association of Jews with the instrument is found even as far west as Holland and Ireland.
159 notes
·
View notes
Text

47 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Tumbalalaika - Baklava Klezmer Soul
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
An important reminder
This is a reminder that I headcanon Medic as being culturally Jewish, autistic/ OCD and Demisexual. If any of you fucking creeps who thinks it's sexy to headcanon him as a N*Zi (or even just joke about it. It's not funny!) interact with me at all, I will block you and report your account. And that goes for anyone who parrots Antisemitism on their blog.
Antisemitism is not cute, it's not a "uwu darkfic I'm so naughty" fandom trope, it's dangerous and it is responsible for thousands of years of oppression and misery. There's been a huge rise in antisemitic hate crime in the past year, and I don't want to scroll through the website I use to have fun and get hit in the face with people who think it's OK to treat violent racists like they're some kind of naughty fandom bad boy, or parrot racist bullshit that gets people killed IRL.
It goes much deeper than just people in fandom spaces being dicks, but I'm a fandom blog, so I'm focusing on the fandom side in this post. If you want to educate yourself on Antisemitism and how to combat it, please do serious research, and read things written by Jewish people.
I am not Jewish, I have never experienced antisemitism or any other form of hatred for my race, but I have friends who have in the past year and it sickens me.
I hate talking about real-life problems or even just silly fandom discourse on this blog, because I want it to be escapism and happiness for people who want a break, but I'm putting my foot down on this one. The TF2 fandom (and Tumblr as a whole) should not be a safe place for antisemites to fester. Valve themselves said he wasn't a Nazi. So why must you insist he is?!
Take this as a warning. Antisemites are not welcome here. If you have a problem with Jews, you can FUCK OFF.
#Roberta rants#tw antisemitism#serious post#fandom antisemitism#ranting#That goes for fic writers too. The shite I've seen on Ao3 is disgusting#block button save me#TF2#team fortress two#tf2 fandom#Archimedes is KLEZMER music ffs
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
updated klezmer playlist
thought to post other playlists of mine. have this klezmer (and similiar) compilation, which i listen to in a continuous loop 🎻🎵
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Music theory notes (for science bitches) - part 2: pentatonics and friends
or, the West ain't all that.
Hello again everyone! I'm grateful for the warm reception to the first music theory notes post (aka 'what is music? from first principles'). If you haven't read it, take a look~
In that stab at a first step towards 'what is music', I tried to distinguish between what's a relatively universal mathematical structure (nearly all musical systems have the octave) and what's an arbitrary convention. But in the end I did consciously limit myself, and make a beeline for the widely used 12TET tuning system and the diatonic scales used in Western music. I wanted to avoid overwhelming myself, and... 👻 it's all around us...👻
But! But but but. This is a series on music theory. Not just one music theory. The whole damn thing. I think I'm doing a huge disservice to everyone, not least me, if that's where we stop.
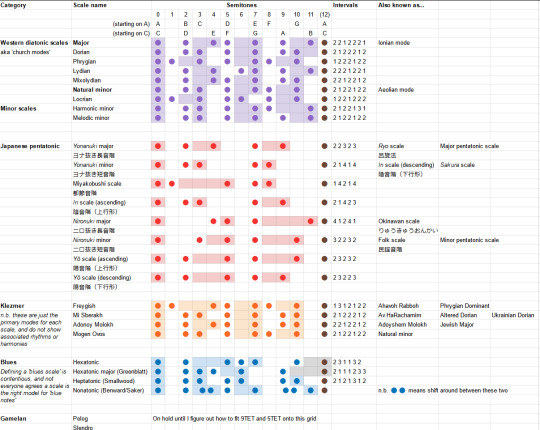
Today, then! For our second installation: 'Music theory notes (for science bitches)' will take a quick look through some examples that diverge from the diatonic scale: the erhu, Japanese pentatonic scales, gamelan, klezmer, and blues.
Also since the first part was quite abstract, we'll also having a go at using the tools we've built so far on a specific piece, the Edo-period folk song Sakura, Sakura.
Sound fun? Let's fucking gooooo
The story so far
To recap: in the first post we started by saying we're gonna be looking at tonal music, which isn't the only type of music. We introduced the idea of notes and frequencies by invoking the magic name of Fourier.
We said music can be approximated (for now) as an idealised pressure wave, which we can divide into brief windows called 'notes', and these notes are usually made of a strong sine wave at the 'fundamental frequency', plus a stack of further sine waves at integer multiples of that frequency called 'overtones'.
Then, we started constructing a culturally specific but extremely widespread system of creating structure between notes, known as '12 Tone Equal Temperament' or 12TET. The main character of this story is the interval, which is the ratio between the fundamental frequencies of two notes; we talked about how small-integer ratios of frequencies tend to be especially 'consonant' or nice-sounding.
We introduced the idea of the 'octave', which is when two notes have a frequency ratio of 2. We established the convention treating notes an octave apart as deeply related, to the point that we give them the same name. We also brought in the 'fifth', the ratio of 1.5, and talked about the idea of constructing a scale using small-integer ratios.
But we argued that if you try and build everything with those small-integer ratios you can dig yourself into a hole where moving around the musical space is rife with complications.
As a solution to this, I pulled out 'equal temperament' as an approximation with a lot of mathematical simplicity. Using a special irrational ratio called the "semitone" as a building block, we could construct the Western system of scales and modes and chords and such, where
a 'scale' is kind of like a palette for a piece of music, defined by a set of frequency ratios relative to a 'root' or 'tonic' note. this can be abstract, as in 'the major scale', or concrete, as in 'C major'.
a 'mode' is a cyclic permutation of an abstract scale. although it may contain the same notes, moving them around can change the feeling a lot!
a 'chord' is playing multiple notes at the same time. 'Triad' chords can be constructed from scales. There are other types which add or remove stuff from the triads. We'll come back to this.
I also summarised how sheet music works and the rather arbitrary choices in its construction, and at the end, I very briefly talked about chord notation.
There's a lot of ways to do this...
I recently watched a video by jazz musician and music theory youtuber Adam Neely, in which he and Philip Ewell discuss how much "music theory" is treated as synonymous with a very specific music theory which Neely glosses as "the harmonic style of 18th-century European composers". He argues, pretty convincingly imo, that 'music theory' pedagogy is seriously weakened by not taking non-white/Western models, such as Indian classical music theories, as a foil - citing Anuja Kamat's channel on Indian classical music as a great example of how to do things differently. Here's her introductory playlist on Indian classical music concepts, which I will hopefully be able to lean on in future posts:
There's two big pitfalls I wanna avoid as I teach myself music theory. I like maths a lot, and if I can fit something into a mathematical structure it's much easier for me to remember it - but I gotta be really careful not to mathwash some very arbitrary conventions and present them as more universal than they are. Music involves a lot of mathematics, but you can't reduce it to maths. It's a language for expressing emotion, not a predicate to prove.
One of the big goals of this series is to get straight in my head what has a good answer to 'why this way?', and what is just 'idk it's the convention we use'. And if something is an arbitrary convention, we gotta ask, what other conventions exist? Humans are inventive little buggers after all.
I also don't want to limit my analytical toolbox to a single 'hammer' of Western music theory, and try and force everything else into that frame. The reasons I'm learning music theory are... 1. to make my playing and singing better, and be more comfortable improvising; 2. to learn to compose stuff, which is currently a great mystery. How do they do it? I do like Western classical music, but honestly? Most of the music I enjoy is actually not Western. I want to be able to approach that music on its own terms.
For example, the erhu... for erhuample???
The instrument family I'm learning, erhu/zhonghu, is remarkably versatile - there are no frets (or even a soundboard!) to guide you, which is both a challenge and a huge freedom. You can absolutely play 12TET music on it, and it has a very beautiful sound - here is an erhu harmonising with a 12TET-tuned piano to play a song from the Princess Mononoke soundtrack, originally composed by Joe Hisaishi as an orchestral piece for the usual Western instruments...
youtube
This performance already makes heavy use of a technique called (in English) 'vibrato', where you oscillate the pitch around as you play the note (which means the whole construction that 'a note has a fixed pitch defined by a ratio' is actually an abstraction - now a note's 'frequency' represents the middle point a small range of pitches!). Vibrato is very common in Western music too, though the way you do it on an erhu and the way you do it on a violin or flute are of course a little different. (We could do an aside on Fourier analysis of vibrato here but I think that's another day's subject).
But if you listen to Chinese compositions specifically for Erhu, they take advantage of the lack of fixed pitch to zip up and down like crazy. Take the popular song Horse Racing for example, composed in the 1960s, which seems to be the closest thing to the 'iconic' erhu piece...
youtube
This can be notated in 12TET sheet music. But it's also taking full advantage of some of the unique qualities of the erhu's long string and lack of frets, like its ability to glide up and down notes, playing the full range of 'in between' frequencies on one string. The sheet music I linked there also has a notation style called 简谱 jiǎnpǔ which assigns numbers to notes. It's not so very different from Western sheet music, since it's still based on the diatonic major scale, but it's adjusted relative to the scale you're currently playing instead of always using C major. Erhu music very often includes very fast trills and a really skilled erhu/zhonghu player can jump between octaves with a level of confidence I find hard to comprehend.
I could spend this whole post putting erhu videos but let me just put one of the zhonghu specifically, which is a slightly deeper instrument; in Western terms the zhonghu (tuned to G and D) is the viola to the erhu's violin (tuned to D and A)...
youtube
To a certain degree, Chinese music is relatively easy to map across to the Western 12-tone chromatic scale. For example, the 十二律 shí'èr lǜ system uses essentially the same frequency ratios as the Pythagorean system. However, Chinese music generally makes much heavier use of pentatonic scales than Western music, and does not by default use equal temperament, instead using its own system of rational frequency ratios. correction: with the advent of Chinese orchestras in the mid-20thC, it seems that Chinese instruments now usually are tuned in equal temperament.
I would like my understanding of music theory to have a 'first class' understanding of Chinese compositions like Horse Racing (and also to have a larger reference pool lmao). I'm going to be starting formal erhu lessons next month, with a curriculum mostly focused on Chinese music. If I have interesting things to report back I'll be sure to share them!
Anyway, in a similar spirit, this post we're gonna try and do a brief survey of various musical constructs relevant to e.g. Japanese music, Klezmer, Blues, Indian classical music... I have to emphasise I am not an expert in any of these systems, so I can't promise to have the most elegant form of presentation for them, just the handles I've been able to get. I will be using Western music theory terms quite a bit still, to try and draw out the parallels and connections. But I hope it's going to be interesting all the same.
Let's start with... pentatonic scales!
Pentatonic scales
In the previous post we focused most of our attention on the diatonic scale. Confusingly, a "diatonic" scale is actually a type of heptatonic scale, meaning there are 7 notes inside an octave. As we've seen, the diatonic scale is constructed on top of the 12-semitone system.
Strictly defined, a 'diatonic' scale has five intervals of two semitones and two intervals of one semitone, and the one-semitone intervals are spread out as much as possible. So 'diatonic scales' includes the major scale and all its cyclic permutations (aka 'modes'), including the natural minor scale, but not the other two minor scales we talked about last time!
However, whoever said we should pick exactly 7 notes in the octave? That's rather arbitrary, isn't it?
After all, in illustration, a more restricted palette can often lead to a much more visually striking image. The same is perhaps even more true in music!
A pentatonic scale is, as the name suggests, a scale which has five notes in an octave. Due to all that stuff we discussed with small-number ratios, the pentatonic scales we are about to discuss can generally be mapped quite easily onto the 12-tone system. There's some reason for this - 12TET is designed to closely approximate the appealing small-number frequency ratios, so if another system uses the same frequency ratios, we can probably find a subset of 12TET that's a good match.
Of course, fitting 12TET doesn't mean it matches the diatonic scale, necessarily. Still, once you're on the 12 tone system, there's enough diatonic scales out there that you can often define a pentatonic scale in terms of a delta relative to one of the diatonic scale modes. Like, 'shift this degree down, delete that degree'.
Final caveat: I'm not sure if it's strictly correct to use equal temperament in all these examples, but all the sources I find define these scales using Western music notation, so we'll have to go with that.
Sakura, sakura and the yonanuki scale
Let's start with Japanese music. Here's the Edo-period folk song Sakura, Sakura, which is one of the most iconic pieces of Japanese music¸ especially abroad:
youtube
This uses the in scale, also known as the sakura pentatonic scale, one of a few widely used pentatonic scales in Japanese folk music, along with the yo scale, insen scale and iwato scale... according to English-language sources.
Finding the actual Japanese was a bit difficult - so far as I can tell the Japanese wiki page for Sakura, Sakura never mentions the scale named after it! - but eventually I found a page for pentatonic scales, or 五音音階 goon onkai. So we can finally determine the kanji for this scale is 陰音階 in onkai or 陰旋法 in senpou. [Amusingly, the JP wiki article on pentatonic scales actually leads with... Scottish folk songs and gamelan before it goes into Japanese music.]
However, perhaps more pertinent is this page: ヨナ抜き音階 which introduces the terms yonanuki onkai and ニロ抜き音階 nironuki onkai. This can be glossed as 'leave out the fourth (yo) and seventh (na) scale' and 'leave out the second (ni) and sixth (ro) scale', describing two procedures to construct pentatonic scales from a diatonic scale.
Let's recap major and minor. Last time we defined them using semitone intervals from a root note (the one in brackets is the next octave):
position: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, (8) major: 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, (12) minor: 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, (12)
From here we can construct some pentatonic scales. Firstly, here are your yonanuki scales - the ones that delete the fourth and seventh:
major: 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, (12) minor: 0, 2, 3, 7, 8, (12)
Starting on C for the major and A for the minor (the ones with the blank key signature), this is how you notate that in Western sheet music. As you can see, we have just deleted a couple of steps.


The first one is the 'standard' major pentatonic scale in Western music theory; it's also called the ryo scale in traditional Japanese music (呂旋法 ryosenpou). The second one is a mode (cyclic permutation) of a scale called 都節音階 miyakobushi, which is apparently equivalent to the in scale.
In terms of gaps between successive notes, these go:
major: 2, 2, 3, 2, 3 - very even minor: 2, 1, 4, 1, 4 - whoah, huge intervals!
The miyakobushi scale, for comparison, goes...
miyakobushi (absolute): 0, 1, 5, 7, 8, (12) miyakobushi (deltas): 1, 4, 2, 1, 4
JP wikipedia lists two different versions of the 陰旋法 (in scale), for ascending and descending. Starting on C, one goes C, D, Eb, G, A; the other goes C, D, Eb, G, Ab. Let's convert that into my preferred semitone interval notation:
in scale (absolute, asc): 0, 2, 3, 7, 9, (12) in scale (relative, asc): 2, 1, 4, 2, 3 in scale (absolute, desc): 0, 2, 3, 7, 8, (12) in scale (relative, desc): 2, 1, 4, 1, 4
So we see that the 'descending form' of the in scale matches the minor yonanuki scale, and it's a mode (cyclic permutation) of the miyakobushi scale.
We've talked a great deal about the names and construction of the different type of scales, but beyond the vague gesture to the standard associations of 'major upbeat, minor sad/mysterious' I don't think we've really looked at how a scale actually affects a piece of music.
So let's have a look at the semitone intervals in Sakura, Sakura in absolute terms from to the first note...
sakura, sakura, ya yoi no so ra-a wa 0, 0, 2; 0, 0, 2; 0, 2, 3, 2, 0, 2-0, -4
and in relative terms between successive notes:
sa ku ra, sa ku ra, ya yo i no so ra-a wa 0, 0, +2; -2, 0, +2; -2, +2, +1, -1, -2, +2, -2, -4
If you listen to Sakura, Sakura, pay attention to the end of the first line - that wa suddenly drops down a huge distance (a major second - for some reason I miscalculated this and thought it was a tritone) and that's where it feels like damn, OK, this song is really cooking! It catches you by surprise. We can identify these intervals as belonging to the in/yoyanuki minor scale, and even starting on its root note.
Although its subject matter is actually pretty positive (hey, check it out guys, the cherry blossoms are falling!), Sakura, Sakura sounds mournful and mysterious. What makes it sound 'minor'? The first phrase doesn't actually tell you what key we're in, that jump of 2 semitones could happen in major or minor. But the second phrase, introduces the pattern of going up 2, then up 1, from the root note - that's the minor scale pattern. What takes it beyond just 'we're in minor'? That surprise tritone move down. According to the rough working model that 'dissonant notes create tension, consonant notes resolve it', this creates a ton of tension. This analysis is bunk, there isn't a tritone. It's a big jump but it's not that big a jump.
How does it eventually wrap up? The final phrase of Sakura, Sakura goes...
i za ya, i za ya, mi ni yu - u ka nn 0, 0, 2; 0, 0, 2; -5, -4, 2, 0, -4, -5 0, 0, +2; -2, 0, +2; -5, +1, +4, -2, -4, -1
Here's my attempt to try and do a very basic tonal/interval analysis. We start out this phrase with the same notes as the opening bars, but abruptly diverge in bar 3, slowing down at the same time, which provides a hint that things are about to come to a close. The move of -5 down is a perfect fourth; in contrast to the tritone major second we had before, this is considered a very consonant interval. (A perfect fourth down is also equivalent to going up a fifth and then down an octave. So we're 'ending on the fifth'.) We move up a little and down insteps of 4, 2, and 1, which are less dramatic. Then we come back down and end on the fifth. We still have those 4-steps next to 1 steps which is the big flag that says 'whoah we're in the sakura pentatonic scale', but we're bleeding off some of the tension here.
Linguistically, the song also ends on the mora ん, the only mora that is only a consonant (rather than a vowel or consonant-vowel), and that long drawn-out voiced consonant gives a feeling of gradually trailing away. So you could call it a very 'soft' ending.
Is this 'tension + resolution' model how a Japanese music theorist would analyse this song? It seems to be a reasonably effective model when applied to Japanese music by... various music theorist youtubers, but I don't really know! That's something I want to find out more about.
Something raised on the English wiki is the idea that the miyakobushi scale is divided into two groups, spanning a fourth each, which is apparently summarised by someone called Koizumi Fumio in a book written in 1974:

Each group goes up 1 (a semitone or minor second), then 4 (major third), for a total of 5 (perfect fourth). The edges of these little blocks are considered 'nucleus' notes, and they're of special importance.
Can we see this in action if we look at Sakura, Sakura? ...ehhhh. I admit, the way I think of the song is shaped by the way I play it on the zhonghu; I think of the first two two-bar phrases as the 'upper part' and the third phrase as the 'lower part', and neither lines up neatly with these little groups. Still. I suspect Koizumi Fumio, author of Nihon no ongaku, knows a little more about this than I do, so I figure it's worth a mention.
Aside: on absorbing a song
Sakura, Sakura is kinda special to me because it's like the second piece I learned to play on zhonghu (after Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star lmao). I can't play it well, but I am proud that I have learned to play it at least recognisably.
The process of learning to play it involved writing out tabs and trying out different ways of moving my hand. I transcribed Sakura Sakura down to start on F, since that way the open G string of the zhonghu could be the lowest note of the piece, and worked out a tab for it using a tab system I cooked up with my friend. Here's what it looks like. The system counts semitones up from the open string, and it uses an underline to mark the lower string.
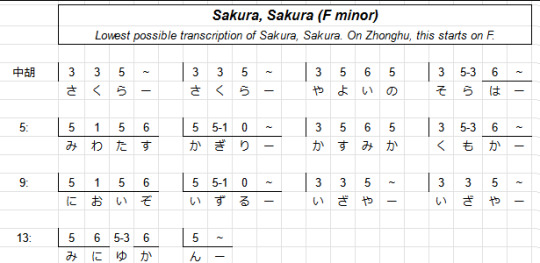
(Also, credit where it's due - I would never have made any progress learning about music if not for my friend Maki Yamazaki, a prodigiously multitalented self-taught musician who can play dozens of instruments, and also the person who sold me her old zhonghu for dirt cheap, if you're wondering why a white British girl might be learning such an unusual instrument. You can and should check our her music here! Maki has done more than absolutely anyone to make music comprehensible to me, and a lot of this post is inspired by discussing the previous post with her.)
When you want to make a song playable on an instrument, you have to perform some interpretation. Which fingers should play which notes? When should you move your hand? How do you make sure you hit the right notes? At some point this kind of movement becomes second nature, but I'm at the stage, just like a player encountering a new genre of videogame, where I still don't have the muscle memory or habituation to how things work, and each of these little details has to be worked out one by one. But this is great, because this process makes me way more intimately familiar with the contours of the song. Trying to analyse the moves it makes like the above even more so.
More Japanese scales
So, to sum up what we've observed, the beautiful minor sounds of Sakura Sakura come from a pentatonic scale which can be constructed by taking the diatonic scale and blasting certain notes into the sea, namely the fourth and the seventh of the scale. But what about the nironuki scale? Well, this time we delete the second and the sixth. So we get, in absolute terms:
major nironuki (abs): 0, 4, 5, 7, 11, (12) major nironuki (rel): 4, 1, 2, 4, 1 minor nironuki (abs): 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, (12) minor nironuki (rel): 3, 2, 2, 3, 2
Hold on a minute, doesn't that look rather familiar? The major nironuki scale is a permutation, though not a cyclic permutation, of the minor yonanuki scale. And the minor nironuki scale is a cyclic permutation (mode) of the major one.
Nevertheless, these scales have names and significance of their own. The major one is known as the 琉球音階 ryūkyū onkai or Okinawan scale. The minor one is what Western music would call a 'minor pentatonic scale'. It also mentions a couple of other names for it, like the 民謡音階 minyou onkai (folk scale).
We also have the yō scale, which like the in scale, comes in ascending and descending forms. You want these too? Yeah? Ok, here we go.
yō scale (asc, abs): 0, 2, 5, 7, 10, (12) yō scale (asc, rel): 2, 3, 2, 3, 2 yō scale (desc, abs): 0, 2, 5, 7, 9, (12) yō scale (desc, rel): 2, 3, 2, 2, 3
The yō scale is what's called an anhemitonic pentatonic scale, which is just a fancy way of saying it doesn't have semitones. (The in scale in turn is hemitonic). The ascending form is also called the 律戦法 ritsusenpou. Here's the complete table of all the variants I've found so far.
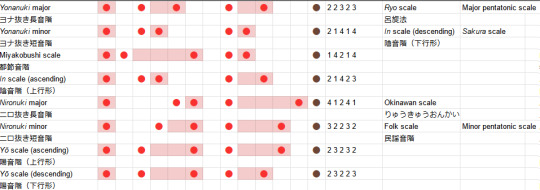
So, in summary: Japanese music uses a lot of pentatonic scales. (In a future post we can hopefully see how that applies in modern Japanese music). These pentatonic scales can be constructed by deleting two notes from the diatonic scales. In general, you land in one of two zones: the anhemitonic side, where all the intervals between successive notes, are 2 and 3, and the hemitonic side, where the intervals are spicier 1s and 4s and a lone 2. From there, you can move between other pentatonic scales by cyclic permutations and reversal.
If you analyse Japanese music from a Western lens, you might well end up interpreting it according to one of the modes of the major scale. In fact, the 8-bit music theory video I posted last time takes this approach. This isn't wrong per se, it's a viable way to getting insight into how the tune works if you want to ask the question 'how does this conjure emotions and how do I get the same effects', but it's worthwhile to know what analytical frame the composers are likely to be using.
Gamelan - when 12TET won't cut it
Gamelan is a form of Indonesian ensemble music. I do not at this time know a ton about it, but here's a performance:
youtube
However, if you're reading my blog then it's likely that if know gamelan from anywhere, it's most likely the soundtrack to Akira composed by Shōji Yamashiro.
youtube
This blends traditional gamelan instrumentation and voices with modern synths to create an incredibly bold and (for most viewers outside Indonesia!) unfamiliar sound to accompany the film's themes of psychic awakening and evolution. It was an inspired choice, adding a lot to an already great film.
'A gamelan' is the ensemble; 'gamelan' is also the style of music. There are many different types of gamelan associated with different occasions - some gamelans are only allowed to form for special ceremonies. Gamelan is also used as a soundtrack in accompaniment to other art forms, such as wayang kulit and wayang wong (respectively, shadow puppetry and dance).
Since gamelan music evidently uses quite a bit of percussion, and so far we've been focused on the type of music played on strings and wind instruments - a brief comment on the limitations of our abstractions. Many types of drums don't fit the 'tonal music' frame we've outlined so far, creating a broad frequency spectrum that's close to an enveloped burst of white noise rather than a sharply peaked fundamental + overtones. There's a ton to study in drumming, and if this series continues you bet I'll try to understand it.
But there are tonal percussion instruments, and a lot of them are to be found in gamelan, particularly in the metalophone family (e.g. the ugal or jegogan). The Western 'xylophone' and 'glockenspiel' also belong to this family. Besides metalophones, you've got bells, steel drums, tuning forks etc. Tuning a percussion instrument is a matter of adjusting the shape of the metal to adjust the resonant frequency of its normal modes. I imagine it's really fiddly.
In any case, the profile of a percussion note is quite different from the continual impulse provided by e.g. a violin bow. You get a big burst across all frequencies and then everything but the resonant mode dies out, leaving the ringing with a much simpler spectrum.
Anyway, let's get on to scales and shit. While I have the Japanese wikipedia page on pentatonic scales open, that it mentions a gamelan scale called pelog (written ᮕᮦᮜᮧᮌ᮪, ꦥꦺꦭꦺꦴꦒ꧀ or ᬧᬾᬮᭀᬕ᭄ in different languages) meaning 'beautiful'. Pelog is not strictly one scale, but a family of tunings which vary across Indonesia. Depending on who you ask, it might in some cases be reasonably close to a 9-tone equal temperament (9TET), which means a number of notes can't be represented in 12TET - you have that 4 12TET semitones would be equivalent to 3 9TET semitones. From this is drawn a heptatonic scale, but not one that can be mapped exactly to any 12TET heptatonic scale. Isn't that fun!
To represent scales that don't exactly fit the tuning of 12TET, there's a logarithmic unit of measure called the 'cent'. Each 12TET semitone contains 100 cents, so in terms of ratios, a cent is the the 1200th root of 2. In this system, a 9TET semitone is 133 cents. Some steps in the pelog heptatonic scale would then be two 9TET semitones, and others one 9TET semitone. However, this system of 'semitones' does not seem to be how gamelan music is actually notated - it's assumed you already have an established pelog tuning and can play within that. So it's a little difficult for me to give you a decent representation of a gamelan scale that isn't approximated by 12TET.
From the 7-tone pelog scale, whatever it happens to be where you live, you can further derive pentatonic scales. These have various names, like the pelog selisir used in the gamelan gong kebyar. I'm not going to itemise them here both because I haven't actually been able to find the basic pelog tunings (at least by their 9TET approximation).
Another scale used in gamelan is called slendro, a five tone scale of 'very roughly' equal intervals. Five is coprime with 12, so there's no straightforward mapping of any part of this scale to the 12-tone system. But more than that, fully even scales are quite rare in the places we've looked so far. (Though apparently within slendro, you can play a note that's deliberately 'out of place', called 'miring'. This transforms the mood from 'light, cheerful and busy' to one appropriate to scenes of 'homesickness, love missing, sadness, death, languishing'.)
The Western musical notation system is plainly unsuited for gamelan, and naturally it has its own system - or rather several systems. In one method, the seven tones of the pelog are numbered 1 through 7, and a subset of those numbers are used to enumerate slendro tuning. You can write it on a grid similar to a musical staff.
But we could wonder with this research - is the attempt to map pélog to 'equal temperament' an external imposition? Presented with a tuning system with seven intervals that are not consistently equal temperament, averaging them to construct an equal temperament hypothesis on that basis, and finally attempting to prove that gamelan players 'prefer' equal temperament... well, they do at least bother to ask, but I'm not entirely convinced that 9TET or 5TET is the right model. Unfortunately, most of the literature I'm able to find on gamelan music theory with a cursory search is by Western researchers.
There's a fairly long history of Western composers taking inspiration from gamelan, notably Debussy and Saty. And of course, modern Indonesian composers such as I Nyoman Windha have also been finding ways to combine gamelan with Western styles. Here's a piece composed by him (unfortunately not a splendid recording):
youtube
Klezmer - layer 'em up
If you've known me for long enough you might remember the time I had a huge Daniel Kahn and the Painted Bird phase. (I still think he's great, I just did that thing where I obsessively listen to one small set of things for a period). And I'd also listen to old revolutionary songs in Yiddish all the time. Because of course I did lmao. Anyway, here's a song that combines both: Kahn's modern arrangement of Arbetlose Marsch in English and Yiddish:
youtube
That's a style of music called klezmer, developed by Ashkenazi Jews in Central/Eastern Europe starting in the late 1500s and 1600s. It's a blend of a whole bunch of different traditions, combining elements from Jewish religious music with other neighbouring folk music traditions and European music at large. When things really kicked off at the end of the 19th century, klezmer musicians were often a part of the Jewish socialist movement (and came up with some real bangers - the Tsar may have been shot by the Bolsheviks but tbh, Daloy Politsey already killed him). But equally there's a reason it sounds insanely danceable: it was very often used for dances.
The rest of the 20th century happened, but klezmer survived all the genocides and there are lots of different modern klezmer bands.
The defining characteristics of klezmer per Wikipedia are... ok, this is quite long...
Klezmer musicians apply the overall style to available specific techniques on each melodic instrument. They incorporate and elaborate the vocal melodies of Jewish religious practice, including khazones, davenen, and paraliturgical song, extending the range of human voice into the musical expression possible on instruments.[21] Among those stylistic elements that are considered typically "Jewish" in Klezmer music are those which are shared with cantorial or Hasidic vocal ornaments, including dreydlekh ("tear in the voice"; plural of dreidel)[22][23] and imitations of sighing or laughing ("laughter through tears").[24] Various Yiddish terms were used for these vocal-like ornaments such as קרעכץ (Krekhts, "groan" or "moan"), קנײטש (kneytsh, "wrinkle" or "fold"), and קװעטש (kvetsh, "pressure" or "stress").[10] Other ornaments such as trills, grace notes, appoggiaturas, glitshn (glissandos), tshoks (a kind of bent notes of cackle-like sound), flageolets (string harmonics),[22][25]pedal notes, mordents, slides and typical Klezmer cadences are also important to the style.[18]
So evidently klezmer will be relevant throughout this series, but for now, since we're trying to flesh out the picture of 'how is tuning formed', let's take a look at the notes.
So it's absolutely possible to fit klezmer into the 12TET system. But we're going to need to crack open a few new scales. Though the Wikipedia editors enumerating this list caution us: "Another problem in listing these terms as simple eight-note (octatonic) scales is that it makes it harder to see how Klezmer melodic structures can work as five-note pentachords, how parts of different modes typically interact, and what the cultural significance of a given mode might be in a traditional Klezmer context."
With that caution in mind, let's at least see what we're given. First of all we have the Freygish or Ahavoh Rabboh scale, one of the most common pieces, good friend of the Western phrygian but with an extra semitone. Then there's Mi Sbererakh or Av HaRachamim which is a mode of it, that's popular around Ukraine. Adonoy Molokh or Adoyshem Molokh is the major scale but you drop the seventh a semitone. Mogen Ovos is the same as the natural minor at least on the interval level.
Which means, without the jargon, here are the semitones (wow wouldn't it be nice if you had tables on here?):

position: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, (8) freygish: 0, 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, (12) deltas: 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2 mi sberakh: 0, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 10, (12) deltas: 2, 1, 3, 2, 2, 1, 2 adonoy m.: 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, (12) deltas: 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2 mogen o.: 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, (12) deltas: 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2
...that's a big block of numbers to make your eyes glaze over huh. Maybe this 'convert everything to semitone deltas' thing isn't all it's cracked up to be... or maybe what I need to do is actually visualise it somehow? Some kinda big old graph showing all the different scales we've worked out so far and how they relate to each other? ...hold your horses...
[It seems like what I've done is reinvent something called 'musical set theory', incidentally.]
OK, having enumerated these, let's return to the Wikipedian's caution. What is a pentachord? Pretty simple, it's a chord of five notes. Mind you, some people define it as five successive notes of a diatonic scale.
In klezmer, you've got a bunch of different instruments playing at once creating a really dense sound texture. Presumably one of the things you do when you play klezmer is try and get the different instruments in your ensemble to hit the different levels of that pentachord. How does that work? Well, if we consult the sources, we find this scan of a half-handwritten PDF presenting considerably more detail on the modes and how they're played. The scales above are combined with a 'motivic scheme' presenting different patterns that notes tend to follow, and a 'typical cadence'. Moreover, these modes can have 'sub-modes' which tend to follow when the main mode gets established.
To me reading this, I can kind of imagine the process of composing/improvisation within this system almost like a state machine. It's not just that you have a scale, you have a certain state you're in in the music (e.g. main mode or sub-mode), and a set of transitional moves you can potentially make for the next segment. That's probably too rigid a model though. There's also a more specific aspect discussed in the book that a klezmer musician needs to know how to move between their repertoire of klezmer pieces - what pieces can sensibly follow from what.
Ultimately, I don't want to give you a long list of stuff to memorise. (Sure, if you want to play klezmer, you probably need to get familiar with how to use these modes, but that's between you and your klezmer group). Rather I want to make sure we don't have any illusion that the Western church modes are the only correct way to compose music.
Blues - can anyone agree?
Blues is a style of music developed by Black musicians in the American south in the late 1800s, directly or indirectly massively influential on just about every genre to follow, but especially jazz. It's got a very characteristic style defined by among other elements use of 'blue notes' that don't fit the standard diatonic scale. According to various theorists, you can add the blue notes to a scale to construct something called the 'blues scale'. According to certain other theorists, this exercise is futile, and Blues techniques can't be reduced to a scale.
So for the last part of today's whirlwind tour of scales, let's take a brief look at the blues...
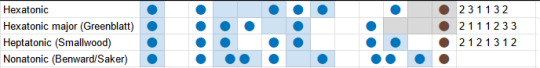
There are a few different blues scales. The most popular definition seems to be a hexatonic scale. We'll start with the minor pentatonic scale, or in Japanese, the minor nironuki scale - which is to say we take the minor diatonic scale and delete positions 2 and 6. That gives:
minor nironuki (abs): 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, (12) minor nironuki (rel): 3, 2, 2, 3, 2
Now we need to add a new note, the 'flat fifth degree' of the original scale. In other words, 6 semitones above the root - the dreaded tritone!
hexatonic blues (abs): 0, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, (12) hexatonic blues (rel): 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2
Easy enough right? Listen to that, it does sound kinda blues-y. But hold your horses! Moments after defining this scale, we read...
A major feature of the blues scale is the use of blue notes—notes that are played or sung microtonally, at a slightly higher or lower pitch than standard.[5] However, since blue notes are considered alternative inflections, a blues scale may be considered to not fit the traditional definition of a scale.
So, if you want to play blues, it's not enough to mechanically play a specific scale in 12TET. You also gotta break the palette a little bit.
There's also a 'major blues' heptatonic scale which goes 0, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, according to one guy called Dan Greenblatt.
But that's not the only attempt to enumerate the 'blues scale'. Other authors will give you slightly longer scales. For example, if you ask Smallwood:
heptatonic blues (abs): 0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, (12) heptatonic blues (rel): 2, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2
which isn't quite a mode of any of those klezmer scales we saw previously, but nearly!
If you ask Benward and Saker, meanwhile, a Blues scale could actually be nonatonic scale, where you add flattened versions of a couple of notes to the major scale.
nonatonic blues (abs): 0, 2, 3/4, 5, 7, 9, 10/11, (12)
There's also an idea that you should play notes in between the semitones, i.e. quarter tones, which would be a freq ratio of the 24th root of 2 if you're keeping score at home.
The upshot of all this is probably that going too far formalise the blues is probably not in the spirit of the blues, but if you want to go in a blues-y direction it will probably mean insert an extra, flattened version of a note to one of your scales. Muck around and see what works, I guess!
Of course, there's a lot more to Blues than just tweaking a scale. For example, 'twelve bar blues' is a specific formalised chord progression that is especially universal in Jazz. What it means for chords to 'progress' is a whole subject, and I think that's the next thing I'll try to understand for post 3. Hopefully we'll be furnished with a slightly broader model of how music works as we go there though.
To wrap up, here's the spreadsheet showing all the 12TET scales encountered so far in this series in a visual way. There's obviously plenty more out there, but this is not ultimately a series about scales. It's all well and good to have a list of what exists, but it's pointless if we don't know how to use it.
Phew
Mind you even with all this, we haven't covered at all some of the most complex systems of tonal music - I've only made the vaguest gesture towards Indian classical music, Chinese music, Jazz... That's way beyond me at the moment. But maybe not forever.
Next up: I'm going to try and finally wrap my head around chords and make sense of what it means for them to 'progress', have 'movement' etc. And maybe render a bit more concrete the vague stuff I said about 'tension' and 'resolution'.
(Also: I definitely know I have friends on here who are very widely knowledgeable about music theory. If I've made any major mistakes, please let me know! At some point I hope to republish this series with nicer formatting on canmom.art, and it would be great to fix the bugs by then!)
#Youtube#music theory#music notes#music#notes#japanese music#gamelan#chinese music#klezmer#blues#i took my new adhd meds and hyperfocused on this all day instead of working ><
137 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brought my viola with me to a pop-up Jewish craft fair tonight (since the event description had indicated music would be happening) and walked away having connected with a community klezmer group, gotten a reccommendation for a fiddle teacher, and with a backpack full of pages and pages of Yiddish lyrics and sheet music.
#may in fact be entering my klezmer era#but also WAUGHHH..... emotional about the transmission of music traditions tonight#jewish tag
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Update on my journey of trying to find music that hit similar to will wood/and the tapeworms because my brain is very picky and doesnt like a lot of music!!!!!
when i started looking for recs the first artists i tried were tally hall and lemon demon (though i kinda like both and know why people associate them together, theyre not similar vibes wise for me) + charlies inferno, which i love, but when i tried more that handsome devils music it didnt feel the same as this one
Then i tried ajj, rare americans and oingo boingo. Theyre also not similar but also quite enjoyable to me, especially ajj’s terrifyer and most oingo boingo songs, as theyre all alike, so if you enjoy one youll probably like more
Then i tried exploring more with the evil-antagonist-cabaret vibes. I found kabaret sybarit and a verbal equinox (yes theres also will wood …….. but listen…….) which led to the dresden dolls and amanda palmer in general
LATER I GOT ENLIGHTENED!!!!!!!! I realized the thing i enjoy the most about will woods music is the folk aspect (ESPECIALLY THE KLEZMER VIBES!!!!!!) in will woods songs theres also a saxophone that matches perfectly with it. This lend to some more artists like golem, or rokiczanka (that i already knew, but my dad said the clarinet? in wyszlabym za dziada reminds him of that saxophone in wwatt) knowing that i tried more slavic folk (which i didnt really like lmao)(besides witcher 3 soundtrack, i love it)
And after some more digging today i tried the avant garde genre. So far i think diablo swing orchestra is cool and i have to listen to some more music from them
Its still not the same and exactly what im looking for, but i feel like im getting so much closer!!!!! Now i know what will wood meant when he said he wants his music to be as original as he can. I find elements of his songs i like scattered in so many different genres, and now whats left for me is find something that combines them, like a modern klezmer and punk/rock combination, or more cabaret like songs that are more energetic.
Its a long ass rant and its so oddly specific that i dont have any hope that people would relate to my musical problems. Not complaining tho!!! The journey of finding and listening to so much unique artists helps me see what i enjoy and what dont. Also i love using tumblr as a diary. End of rant, i hope i wont find it cringe later
#will wood and the tapeworms#will wood#music genres#folk music#klezmer#polish folk#musical journey#avant garde#avant garde music
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thank you to the people who recommended music, because now you have all cemented my desire to play klezmer music (and cementing that this is a top-tier musical expression).... 🫣
#jumblr#jewish conversion#jew by choice#personal thoughts tag#bruh i LOVE how klezmer music sounds. especially when there's a healthy amount of clarinets????? WOW.#sorry but i stand firm that clarinets were *made* for this style of music and i would pick mine up solely if i could play this style forever#also thank you again for the people who helped out <3#listening to a playlist right now... there's almost too much but that's a blessing B'H
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
experiencing the horrors (antisemetic microaggressions)
#dandelion yells#wheres that reallly tired reaction image of the face looking at their phone with dark circles under their eyes#day 2 of the same conversation in the chat. with the same microaggressions#every time one of them does one i make the thing 75% more jewish#soon as soon as anyone looks at it klezmer music will start blasting in their head and theyll start compulsively dancing the hora
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
now that i can sorta type again i can put down the many benny thoughts i’ve had in the past three months and: i think benny knows the most yiddish out of any of the fnv characters because it was so common in the rat pack’s lingo and he takes it so seriously (also he was based off of bugsy siegel, who was jewish, and as far as i know spoke yiddish as a first language. or at least his parents did) which may make no nevermind to anybody else but is very important to me because i specifically made kitty’s first language yiddish because i had just started learning yiddish when i played fnv the first time so the two are inextricably linked in my mind. also i think it’d be really funny if kitty called him ongepatcheket (basically gaudy as hell) and he knew what it meant
#this has been one of your more regularly scheduled benny headcanon posts#i love yiddish and a huge part of my kitty playlist is klezmer music#in fact if you wanna hear a daniel kahn song that i put on the benny playlist look up avreml the filcher#kitty grave#benny gecko
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
I need your help! Does this sentence make sense to non-musicians?
"Bernard’s klezmer broke from a fixed tempo, allowing the clarinet to linger on its notes as if weeping."
Clarifications:
Klezmer is a musical genre (well worth checking out if you never have! 😊 ). This will be known to readers through context.
Bernard is not a musician, more like a living record player with control of the music. The clarinet is a part of the music he plays.
#writeblr#original writing#booklr#book quote#adhd writer#writers on tumblr#creative writing#writing#WritersCommunity#book quotes#music#klezmer#descriptive writing#books and reading#reading with adhd#fantasy writer#fantasy fiction#fantasy books#fantasy world#ADHD fantasy fiction
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
save me daniel kahn and the painted bird
#my beloved#ough#i love klezmorim#and i love multilingual music#and i looove daniel kahn#music#daniel kahn and the painted bird#jewish music#yiddish music#klezmer#modern klezmer#mine#text
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Mischpoke - Terk in Amerika
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
JRPG (Jewish Role-Playing Game)
#beau talks#jumblr#is this anything#insert video about the history of klezmer music influencing jrpg music
2 notes
·
View notes