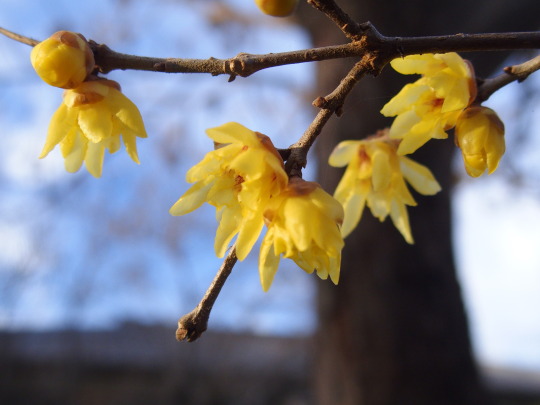
#japanese allspice
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
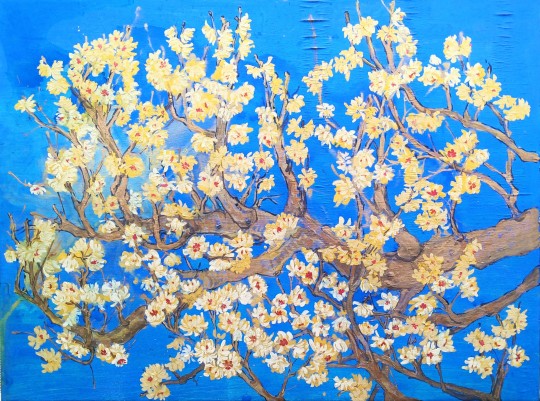

Sweet and Spice
Watercolor On Birch Panel
2022, 40"x 30"
Japanese Allspice, Wintersweet, Chimonanthus praecox
#art#nature#artists on tumblr#flowers#floral#watercolor#painting#minimalism#artwork#botany#japanese allspice#wintersweet#gold#yellow#blue#chimonaanthus#trees#flowering tree#botanical#artblr#spring#naturecore#cottagecore aesthetic#contemporary art#original art#artist#creatrs#cottagecore
442 notes
·
View notes
Text
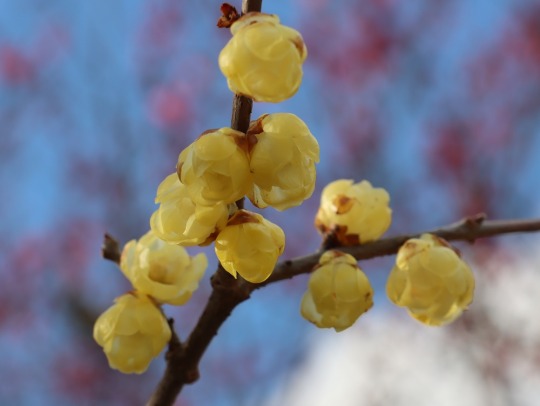

蝋梅も咲いていた(1月31日)
Zimokwiat wczesny (Chimonanthus praecox)
Wintersweet or Japanese allspice (Chimonanthus praecox)
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today's Haiku with Picture 361

Japanese allspice
Yellow blossoms bloom
In the winter sky
蝋梅の
黄色い花や
冬空に
(2023.01.05)
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo
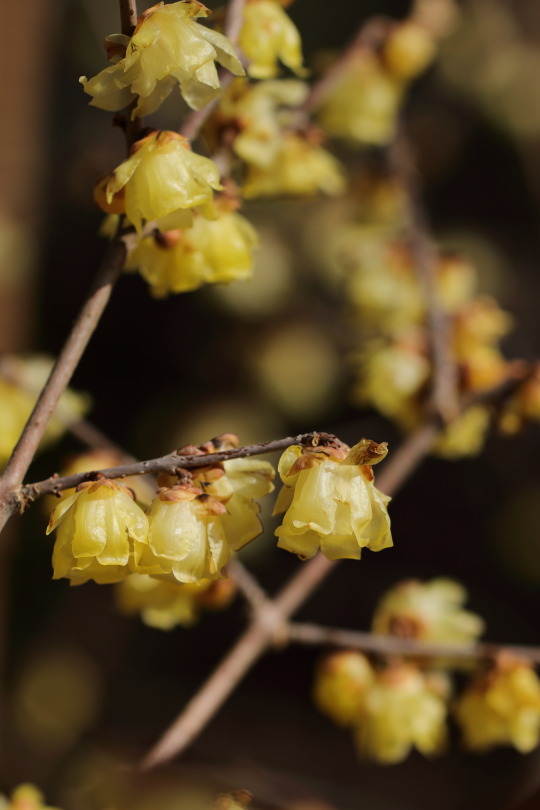

「1月といえば ~蝋梅~」 Canon EOS70D CANON EF 100mm f2.8L Macro IS USM f/4 1/2000s ISO100 -0.3step 100mm 2023/1/22 茨城県つくば市 筑波実験植物園にて
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
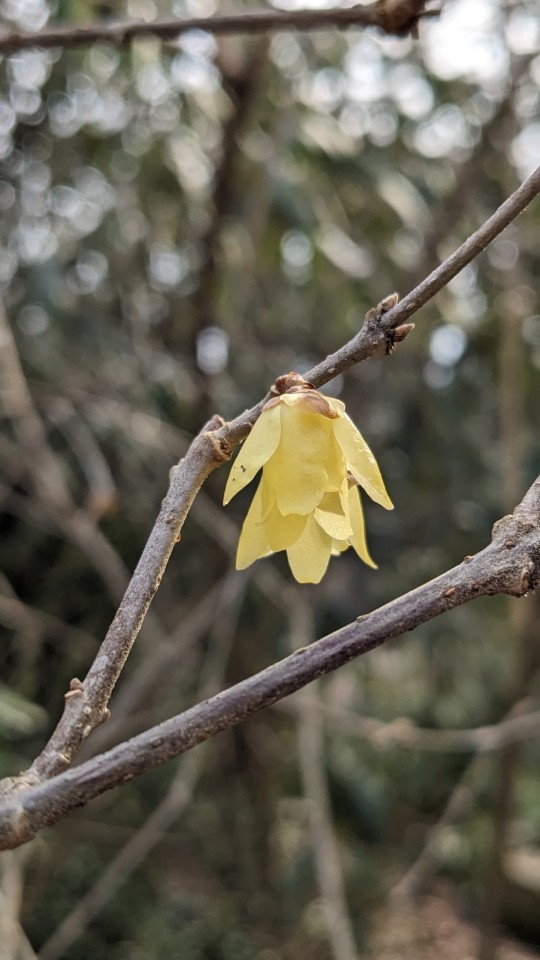

Chimonanthus praecox / Wintersweet at the Sarah P. Duke Gardens at Duke University in Durham, NC
#Chimonanthus praecox#Chimonanthus#Wintersweet#japanese allspice#Flowers#Nature photography#photographers on tumblr#Sarah P. Duke Gardens#Duke Gardens#Duke University#Durham#Durham NC#North Carolina
1 note
·
View note
Text

Vegan Birria Ramen
#vegan#lunch#dinner#japanese cuisine#mexican cuisine#soups#ramen#birria#noodles#mushrooms#jalapeño#oregano#onion#cilantro#lime#chili#cloves#cinnamon#apple cider vinegar#allspice#bay leaf#garlic#vegan mozzarella#olive oil#sea salt
42 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#tokyo #walk #chimonanthus #praecox #wintersweet #japanese #allspice #ice #flower #shape #view #美 #香 #studio_hortz #phent_quyh #東京 #日本 #studiohortz #phentquyh #japan #color #ロウバイ #蠟梅 #形 https://www.instagram.com/p/CpFdZkPPxE5/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#tokyo#walk#chimonanthus#praecox#wintersweet#japanese#allspice#ice#flower#shape#view#美#香#studio_hortz#phent_quyh#東京#日本#studiohortz#phentquyh#japan#color#ロウバイ#蠟梅#形
1 note
·
View note
Note
*pats askbox gently* there are more Thermoreceptors?
(I'm sorry ur dome was so hot; I hope its much cooler now!)
My bluff has been called! Hooray!!
I am not a neurologist, a biologist, or a scientist. If anyone with better credentials than "obsessed with emergent properties" contradicts me, listen to them instead.
Cell membranes include little portal proteins that open under certain circumstances based on the shape of the protein and let chemicals into and out of the cell. These portals are useful for all sorts of things: managing water and nutrients, sending messages to nearby cells, serving the whims of tiny intercellular cats. Science hasn't found the tiny intercellular cats yet, but we all know they're there; the existence of a door that can be opened necessarily implies an indecisive feline.
Some protein shapes open up if the temperature is within a certain range. This means that if a cell with that sort of protein in its membrane experiences a temperature in the right range, it will move some chemicals around. This is used to make nerve cells that send a message towards the brain whenever they experience a certain temperature.
Because evolution does all its best work the night before the deadline while on a Code Red Mountain Dew bender, the opened-by-temperature portal proteins are mostly copied from opened-by-a-specific-chemical portal proteins. All of them, in fact, still open for specific chemicals, which means there exist out in the world liquids you can put in a bottle that most animals will instead perceive as "a temperature between 8 and 26 degrees" So things can get a little weird.
Temperature-opening portal proteins:
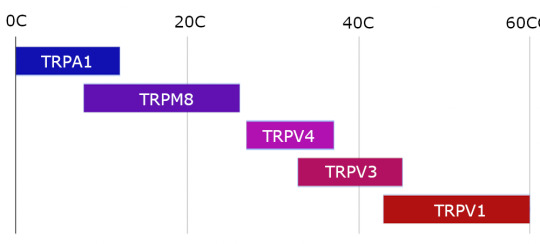
TRPA1 Opens for temperatures below 12C (not air temperature, skin or body temperature, so you might be kind of in trouble when this happens). Used by hunting snakes to detect where heat isn't so they can find prey. Feels painful in an itchy sort of way.
This one also opens for allyl isothiocyanate. Many plants have evolved to take advantage of the existence of a chemical most animals perceive as itchy pain, especially horseradish and wasabi. Allyl isothiocyanate is harmful to plants, so they keep two separate components in tiny compartments. When an animal bites the plant, the compartments break open their contents mix to create allyl isothiocyanate.
"This plant tastes like itching" is a good defense against almost all animals, but some humans have taught themselves to appreciate the taste of itching.
TRPM8 Opens for temperatures between 8 and 26 degrees. Opens for menthol (peppermint, spearmint, wintergreen) and linalool (roses, orange blossoms, basil). Feels cool or cold.
"This plant tastes like cold" is a somewhat less effective defense against being eaten than "this plant tastes like itching" but it's a more widespread defense because TRPM8-activating chemicals don't harm plants and don't need elaborate two-part storage.
TRPV4 Opens for temperatures from 27-37 C. I'm not sure what this one feels like, or if even feels like anything, since it covers normal human body temperatures. Whatever feeling we get from this one, we're feeling it nearly all the time.
Plants do make a chemical that tastes like this temperature, and it can repel nonhuman creatures with different body temperatures: allicin, the flavour of garlic. Like allyl isothiocyante, it is stored in two compartments inside the plant, and combined when the plant is bitten.
Maybe this is why vampires abhor garlic. There is a feeling that, as humans, we always have. Something we don't notice, something deeper than touch. That feel disappears forever when you become a vampire, except those unbearable moments when garlic returns to you for a fleeting moment the experience of lost humanity.
TRPV3 Opens for temperatures 33-39 degrees. Opens for eugenol, found in cinnamon, nutmeg, bay leaf, holy basil, ginger, allspice, and cloves. Feels like warmth.
Plants with high quantities of eugenol, like holy basil and Japanese star anise, are sometimes sacred to buddhists because they smell nice and bugs don't like to eat them, so you can burn them as incense without worrying about all the little crawly guys.
Humans apparently think food that tastes like "warm" is comforting.
TRPV1 Opens for temperatures over 43 degrees. (The one I was experiencing in the overheated dome, which I had never felt from air before) Opens for capsaicin, the active chemical in hot peppers. Opens for the combination of temperature and acidity of fevers and infected wounds. This one we feel as pain, as burning, as flame.
TRPV1 says: Your flesh is failing, and your doom is very near.
Humanity says: This is incredible. We are going to breed plants that cause this sensation as much as possible, and we will spend thousands of years getting it right. We are going to dry this and powder this and flake it and grill it and ferment it and eat it with everything.
And when we leave earth and go into space, we take hot peppers with us. Without gravity, fluid builds up in nasal passages, and astronauts sort of have colds the entire time they're in space and can't smell food very well. But the Nearness Of Your Doom is not a smell and is not perceived by the nose, so - with their doom always on the other side of ten centimeters of insulated aluminum - astronauts can taste hot peppers. In 2002, Peggy Whitson, commander of the ISS, jokingly refused to let a replacement crew on board until they handed over the hot sauce.
We are a strange and wonderful species.
#question#ame-kage#vampires#astronauts#intercellular cats#fun post to tag#we are growing something that affects each of these. :)#there are at least three more heat-reactive ion channels but I don't think we use them for much: TRPM3 ANO1 TRPV2
255 notes
·
View notes
Text
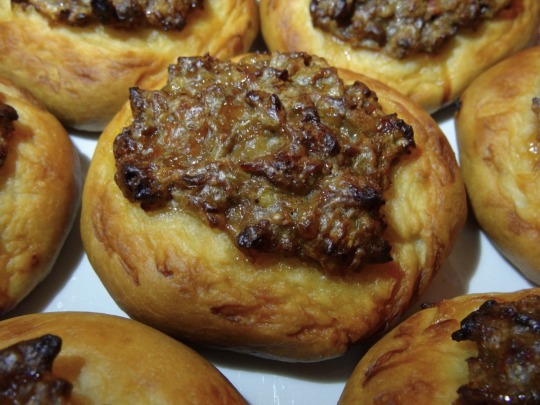
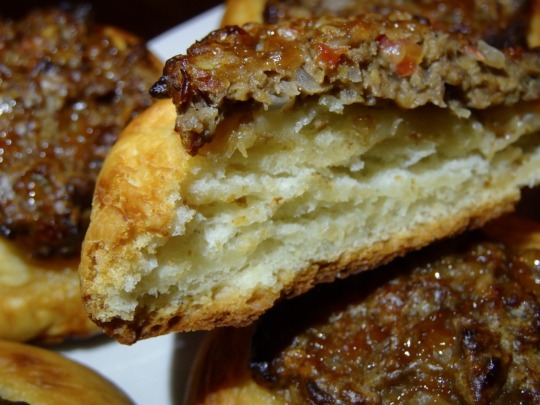


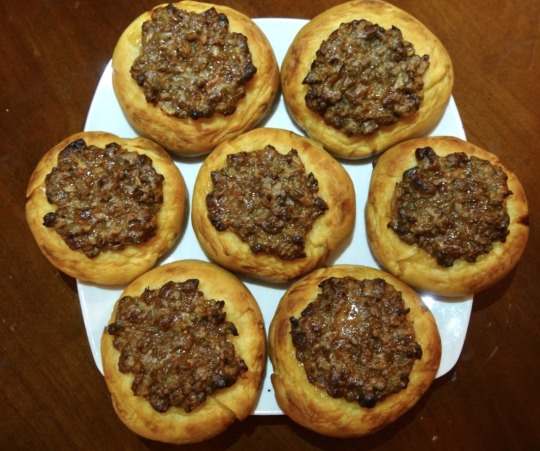
[ID: First image is a close-up on a plate of small flatbreads topped with ground ‘meat’; second is a cross-section of one of the breads. End ID]
صفيحة فلسطينية / Safiha falastinia (Palestinian topped flatbread)
Etymology and origins
صَفِيحَة (“ṣafīḥa”), also transliterated “sfiha” and “sfeeha,” is a flatbread eaten in Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria, comprising a yeasted dough topped with a filling made from ground lamb or beef, spices, and chopped aromatics and vegetables. It may also be called “اللَحْم بالعَجِين” (“al-laḥm b al-‘ajīn,” “meat with dough”)—this phrase is the source of the Turkish “lahmacun” and the Armenian “Լահմաջո” (“lahmadjo”), which describe a closely related dish.
The word “صَفِيحَة” literally means “thin plate” or “sheet”; it comes from the root ص ف ح (ṣ f ḥ), which produces words related to flatness. Compare for example “صَفَّحَ” (“ṣaffaḥa”) “to flatten,” “صَفْحَة” (“ṣafḥa”) “page,” and “صَافَحَ” (“ṣāfaḥa”) “to shake hands.” This term has been borrowed into Brazilian Portuguese as "esfirra" or "esfiha," when the flatbread was brought to Brazil by Levantine immigrants—mostly Christians—beginning in the 1890s. Today, esfiha has been naturalized as a "'typical' Brazilian bar food"; it is said that the typical resident of São Paulo is a "Japanese who speaks Portuguese with an Italian accent while eating an esfiha."
In English, lahmacun (also transliterated "lahmajoun") is sometimes called "Armenian pizza." Similarly, it may be called "صفيحة الأرمنية" ("safiha al-'armaniyya"), "Armenian safiha," in Palestine, indicating that it is regarded as a borrowing from the local Armenian immigrant community. In Armenia, lahmadjo is a very thin, soft flatbread typically topped with beef or lamb, tomatoes, tomato paste, bell peppers, onion, garlic, parsley, red chili paste, and black pepper. With Palestinian safiha, lamb is the typical choice of meat; the dough may be thicker, and enriched with the addition of milk, milk powder, or yoghurt; bell peppers are ommitted; and fried pine nuts may be added. Palestinian restaurateur Nassar Odeh remembers lahmadjo being served in Jerusalem's Old City decades ago; he says that "Armenian dishes" such as this have become "part of the Palestinian culture."
Though the Arabic-derived "lahmadjo" and related terms may be heard, [1] the most common Armenian-language name for this dish is "լոշմիս" ("loshmis")—presumably from "լոշ" "losh" "lavash, thin bread" + "միս" "mis" "meat." Some Western Armenian variations on the name reverse this order (meat-dough, rather than dough-meat): "մսաշոթ" ("msashot"), from "մսա" "msa" "meat" + "շոթ" "shot" "thin bread"; and "մսալոշ" ("msalosh"), from "մսա" "msa" "meat" + "լոշ" "losh" "thin bread."
The dish
A common part of everyday Palestinian cooking, صَفَائِح ("ṣafā'iḥ"; plural of "ṣafīḥa") are often eaten as a snack or a portable lunch. They may also be served as a مَزَّة ("mazza"; "appetizer") for عِيد ("'īd"; "feast," "holiday"; often transliterated "Eid") or Christmas.
Safa'ih are shaped into pinwheels in the port city of يَافَا ("Yāfā"; often transliterated "Yaffa" or "Jaffa"), stuffed with ground meat or spinach. In the Bethlehem region the topping is often mixed with tahina, as well as vinegar or lemon juice, and perhaps pomegranate molasses. Other versions of the meat topping omit tahina and vinegar, and are more tomato-heavy instead.
This recipe is for Bethlehem mazza-style safa'ih, with thick crust that's crisp on the outside and light and fluffy on the inside. Vinegar and pomegranate molasses provide a bright, slightly fruity lift to the topping, while tahina grounds it with a toasty, nutty aroma. Black pepper, allspice, and a green chili pepper add complexity and heat.
[1] There is a proliferation of possible spellings for "lahmadjo" in Armenian, which would indicate that it is a loanword (probably via Turkish, ultimately from Arabic). These spellings include "լամաջո" ("lamadjo") [common]; "լահմաջո" ("lahmadjo"); "լահմաջու" ("lahmadjou"); "լահմաջոն" ("lahmadjon"); "լահմաջուն" ("lahmadjoun") [literary; uncommon]; "լահմաջին" ("lahmadjīn"); and "լահմաջի" ("lahmadjī") [rare]. The letter "ջ" is pronounced as "dj" (IPA: [d͡ʒ]) in Eastern Armenian and a "tch" (IPA: [t͡ʃʰ]) in Western Armenian (timestamp: 40:33).
Support Palestinian resistance by donating to Palestine Action’s bail fund; buying an e-sim for distribution in Gaza; or donating to help a family leave Gaza.
Ingredients:
Makes 24 small safa'ih. Serves 24 as an appetizer, or 6-7 as a main dish.
For the dough:
5 cups (600g) white flour
1 cup (230g) non-dairy yoghurt (لبن رائب) (I used soy)
1/2 cup (125 ml) olive oil
1 1/2 Tbsp (15g) dry yeast
1/2 Tbsp (4g) kosher salt
1 tsp (5g) sugar
A scant cup (220g) of water
A more "everyday" preparation of this dish might make larger, flatter safa'ih out of a dough without dairy. This holiday variant includes yoghurt and makes smaller, fluffier safa'ih; but the yoghurt may be omitted (or milk or milk powder may be added) without injury, and the flatbreads can be made any shape you like.
Leila al-Haddad writes that, in Gaza, white flour used to be eaten as a treat and for special occasions before it later came to replace whole wheat white flour in many kitchens.
For the topping:
500g ground beef substitute (as a replacement for minced lamb)
1 medium tomato, minced
1 medium onion, minced
1-2 green chili peppers, minced
2 tsp kosher salt (1 tsp table salt)
3/4 tsp black pepper
3/4 tsp allspice; or Palestinian 7-spice / mixed spices (بهار مشكل)
1/4 cup white tahina
2 Tbsp pomegranate molasses
2 Tbsp white vinegar, or lemon juice
For a tomato filling, omit the tahina and vinegar, and instead use 2 Tbsp tomato paste; or 8 diced or puréed tomatoes, cooked down.
Instructions:
For the dough:
1. Combine all dry ingredients in a large mixing bowl.
2. Make a well in the center and add in the yoghurt, olive oil, and water. Mix them together and then combine them with the rest of the dough. Add water or flour as needed to obtain a soft, slightly tacky dough.
3. Knead the dough on a clean surface for 5-10 minutes, until it bounces back when pressed. Allow to rise, covered, in an oiled bowl for 1-2 hours, until doubled in size.
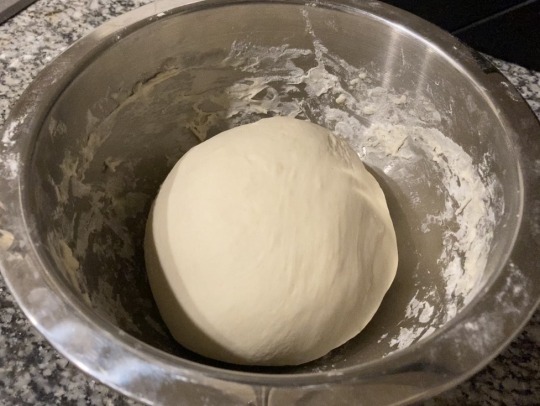

For the filling:
1. Mince vegetables, or run them through a food processor. Mix all filling ingredients together.
To assemble:
1. Divide dough in half, and then half again; roll out each quarter of the dough into a cylinder and cut it into six equal pieces.
2. Roll each piece of dough into a ball between your hands, and then flatten it into a disc about 1” (2 1/2 cm) high and 3” (8cm) wide. Place on a baking sheet prepared with parchment paper, leaving an inch of space between each circle.
3. Press the center of each dough circle down to create a crust around the edge. Add a few spoonfuls of filling to the center of each safiha and press flat.

4. Bake safa'ih in the middle of an oven at 450 °F (230 °F) for 25-30 minutes, until crust is golden brown.
Serve as an appetizer alongside vegetable salads, pickles, olives, &c.

438 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1678, a Chaldean priest from Baghdad reached the Imperial Villa of Potosí, the world’s richest silver-mining camp and at the time the world’s highest city at more than 4,000 metres (13,100 feet) above sea level. A regional capital in the heart of the Bolivian Andes, Potosí remains – more than three and a half centuries later – a mining city today. [...] The great red Cerro Rico or ‘Rich Hill’ towered over the city of Potosí. It had been mined since 1545 [...]. When Don Elias arrived [...], the great boom of 1575-1635 – when Potosí alone produced nearly half the world’s silver – was over, but the mines were still yielding the precious metal. [...]
On Potosí’s main market plaza, indigenous and African women served up maize beer, hot soup and yerba mate. Shops displayed the world’s finest silk and linen fabrics, Chinese porcelain, Venetian glassware, Russian leather goods, Japanese lacquerware, Flemish paintings and bestselling books in a dozen languages. [...]
Pious or otherwise, wealthy women clicked Potosí’s cobbled streets in silver-heeled platform shoes, their gold earrings, chokers and bracelets studded with Indian diamonds and Burmese rubies. Colombian emeralds and Caribbean pearls were almost too common. Peninsular Spanish ‘foodies’ could savour imported almonds, capers, olives, arborio rice, saffron, and sweet and dry Castilian wines. Black pepper arrived from Sumatra and southwest India, cinnamon from Sri Lanka, cloves from Maluku and nutmeg from the Banda Islands. Jamaica provided allspice. Overloaded galleons spent months transporting these luxuries across the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic oceans. Plodding mule and llama trains carried them up to the lofty Imperial Villa.
---
Potosi supplied the world with silver, the lifeblood of trade and sinews of war [...]. In turn, the city consumed the world’s top commodities and manufactures. [...] The city’s dozen-plus notaries worked non-stop inventorying silver bars and sacks of pesos [...]. Mule trains returning from the Pacific brought merchandise and mercury, the essential ingredient for silver refining. [...] From Buenos Aires came slavers with captive Africans from Congo and Angola, transshipped via Rio de Janeiro. Many of the enslaved were children branded with marks mirroring those, including the royal crown, inscribed on silver bars.
Soon after its 1545 discovery, Potosí gained world renown [...]. Mexico’s many mining camps [...] peaked only after 1690. [...] Even in the Andes of South America there were other silver cities [...]. But no silver deposit in the world matched the Cerro Rico, and no other mining-refining conglomeration grew so large. Potosí was unique: a mining metropolis.
Thus Don Elias, like others, made the pilgrimage to the silver mountain. It was a divine prodigy, a hierophany. In 1580, Ottoman artists depicted Potosí as a slice of earthly paradise, the Cerro Rico lush and green, the city surrounded by crenellated walls. Potosí, as Don Quixote proclaimed, was the stuff of dreams. Another alms seeker, in 1600, declared the Cerro Rico the Eighth Wonder of the World. A [...] visitor in 1615 gushed: ‘Thanks to its mines, Castile is Castile, Rome is Rome, the pope is the pope, and the king is monarch of the world.’ [...]
---
For all its glory, Potosí was also the stuff of nightmares [...].
Almost a century before Don Elias visited Potosí, Viceroy Francisco de Toledo revolutionised world silver production. Toledo was a hard-driving bureaucrat of the Spanish empire [...]. Toledo reached Potosí in 1572, anxious to flip it into the empire’s motor of commerce and war. By 1575, the viceroy had organised a sweeping labour draft, launched a ‘high-tech’ mill-building campaign, and overseen construction of a web of dams and canals to supply the Imperial Villa with year-round hydraulic power, all in the high Andes at the nadir of the Little Ice Age. Toledo also oversaw construction of the Potosí mint, staffed full-time with enslaved Africans. [...] Toledo’s successes came with a steep price. Thanks to the viceroy’s ‘reforms’, hundreds of thousands of Andeans became virtual refugees (those who survived) and, in the search for timber and fuel, colonists denuded hundreds of miles of fragile, high-altitude land. [...] The city’s smelteries belched lead and zinc-rich smoke [...].
The Habsburg kings of Spain cared little about Potosí’s social and environmental horrors. [...] For more than a century, the Cerro Rico fuelled the world’s first global military-industrial complex, granting Spain the means to prosecute decades-long wars on a dozen fronts – on land and at sea. No one else could do all this and still afford to lose. [...]
By [...] 1909 [...], mineral rushes had helped to produce cities such as San Francisco and Johannesburg, but nothing quite compared for sheer audacity with the Imperial Villa of Potosí, a neo-medieval mining metropolis perched in the Andes of South America.
---
Text by: Kris Lane. “Potosi: the mountain of silver that was the first global city.” Aeon. 30 July 2019. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sweet and Spice
Watercolor On Birch Panel
2022, 40"x 30"
Japanese Allspice, Wintersweet, Chimonanthus praecox
#art#nature#artists on tumblr#flowers#floral#watercolor#painting#minimalism#artwork#botany#japanese allspice#wintersweet#gold#yellow#blue#chimonaanthus#trees#flowering tree#botanical#artblr#spring#naturecore#cottagecore aesthetic#contemporary art#original art#artist#creatrs#cottagecore#plants
134 notes
·
View notes
Text






Goth Thanksgiving one was a success.
Goth Chicken had a pomegranate and orange glaze with rosemary
Regular Chicken had a honey, raspberry balsamic reduction, with thyme and oil
Roasted vegetables were purple yams, Japanese sweet potato, yam, purple , white and orange carrots and beets with brown sugar, canola, raspberry reduction, cayenne and cinnamon.
Basic ass mashed potatoes
Pies are pumpkin with white chocolate skulls and peach and blueberry with cinnamon and allspice
Used my grandmother lard pie crust recipe.
Cocktail is gin, Cointreau, pomegranate, tonic and simple syrup.
Yes, your Miss can cook.
34 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Japanese scented allspice. Text and image by Japanese photographer 雅ぴこ写真垢 @miyaby99
55 notes
·
View notes
Text

Machiko Kyo
19 January 2021, smell of wax Japanese allspice from somewhere.
今日マチコ「2021年1月19日、どこからか蝋梅の香り」
What about "Japanese allspice? "
Japanese allspice is from January to February. japanese allspice flowers start to bloom when it is still cold enough to turn the tip of the nose red. The flowers have a gentle fragrance that awakens the eyes in the middle of the cold winter months.
Japanese allspice flowers are soft, bright yellow like custard cream and have an attractive translucent texture, as if coated with wax.
Japanese allspice can also be enjoyed as cut flowers. Flowering japanese allspice branches start to be distributed in flower markets from around December. The branches are well drained and the flowers can be enjoyed for a long time. Decorate your entrance with wax plum blossoms and enjoy their entrancing fragrance when you return home.
22 notes
·
View notes


