#its like archaeology but for artists
Text

fragment: asteroid pyramid
#art#my art#sketchbook#doodle#bootwither.art#drawing#pen drawing#been digging out scraps from old sketchbooks#its like archaeology but for artists
0 notes
Text
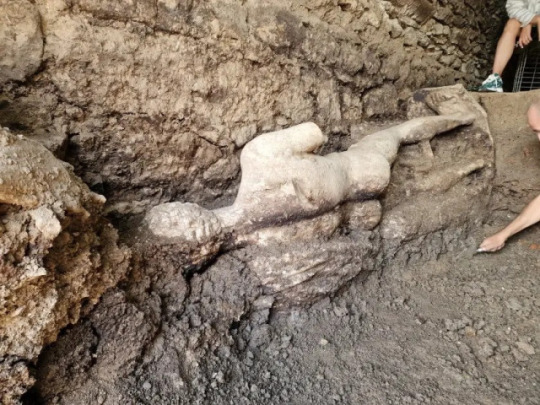

Archaeologists Unearth Remarkably Preserved Marble Statue of Hermes in Bulgaria
Archaeologists led by Prof. Dr. Ludmil Vagalinski have unearthed a remarkably well-preserved marble statue in the ancient city of Heraclea Sintika, near Petrich, Bulgaria. The discovery, announced by the municipality of Petrich, was found within the underground sewer known as "Cloaca Maxima". Efforts are underway to delicately excavate the statue without causing damage due to its exceptional state of preservation.
Standing over two meters tall, the statue is believed to depict Hermes, a prominent deity in the region during ancient times. Prof. Dr. Vagalinski, speaking to "Archaeologia Bulgarica," expressed cautious excitement about the find, noting its significance not only as the best-preserved statue discovered in Heraclea Sintika but also in all of Bulgaria. He suggests that the statue was likely buried by city inhabitants following a major earthquake in the 4th century AD, possibly to safeguard their religious heritage during the rise of Christianity.


Archaeologia Bulgarica shared updates on the excavation progress via Facebook, revealing that the statue, crafted from a single marble block in the 2nd century AD, remains partially encased in dirt. Archaeologists have noted its resemblance to other depictions of Hermes, placing it within a known iconographic type. Similar statues are rare globally, making this discovery particularly unique for Bulgaria.
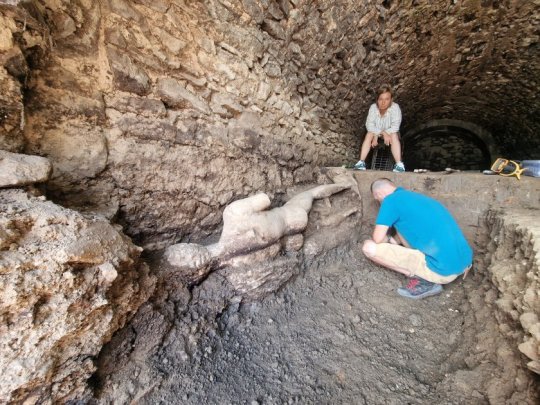
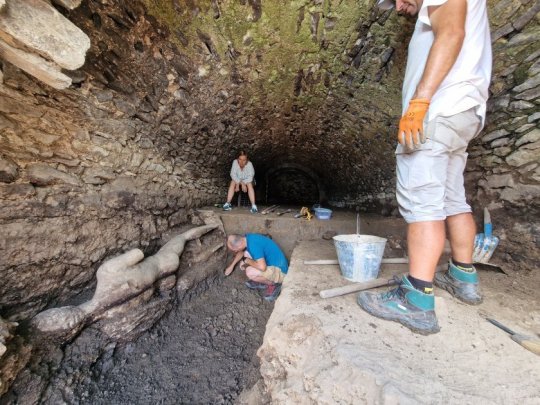



Plans are underway to carefully extract the statue from the Cloaca Maxima and transport it to the museum in Petrich, where it will undergo necessary restoration before being displayed alongside other archaeological finds. Prof. Vagalinski emphasized the challenges of preserving the ancient city's structures, especially those located on private property, where permanent conservation measures are limited. He highlighted the unexpected nature of the discovery, which came to light during routine inspections of the canal's condition.



The excavation team, which first uncovered ancient structures in the area six years ago, had placed protective barriers to secure the site. Upon closer examination, marble remnants were noticed, leading to the gradual unveiling of the statue of Hermes. Work on fully exposing and documenting the statue will continue in the coming days, offering new insights into the religious and artistic practices of ancient Heraclea Sintika.
#Archaeologists Unearth Remarkably Preserved Marble Statue of Hermes in Bulgaria#ancient city of Heraclea Sintika#Petrich Bulgaria#Cloaca Maxima#marble#marble statue#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire#roman art#ancient art
321 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Jianghu Mystery of the Middle Xi: The Tomb of Li Xiangyi
By Qiling, University of □□ (2024)

Left: A photograph of the inscribed text at Li Xiangyi's tomb, reading, "The grave of the Sigu Sect's departed Sect Leader, Li Xiangyi". Right: Artist's sketch renditions from eye-level frontal and aerial side views, recreating how the tomb may have appeared during the Xi dynasty.
Among the numerous important archaeological finds from the Xi Dynasty, the tomb of Li Xiangyi is not the most well-known, nor has it yielded any artifacts of particular intrigue, yet it has raised questions about certain points in history since its discovery. The tomb constitutes a small site, near a mountainous overlook which should have received little common traffic at the time of construction. Its structure is in line with some other aristocratic burials of the Middle Xi period: aboveground, with a chamber at the center of a raised rectangular dais several meters wide, large enough to bear only a single individual. A stone marker, which has survived in legible condition until today, declares it the tomb of Li Xiangyi, leader of the Sigu jianghu sect.
Records about Li Xiangyi are found at other archaeological sites contemporary with this tomb, and so his name is not an obscure one. The Sigu Sect complex has already undergone excavation for nearly two decades, with evidence that Li Xiangyi spent several years there as its first sect leader and founder. His tomb is within two hours' walking distance of the Sigu site, though isolated in its location, compared to the Sigu Sect's grand mountain entrance. (The complex itself was inhabited well after his death; bamboo slips cite Qiao Wanmian as the Sigu Sect's next major leader some years after, who oversaw it for several more decades into the later Xi). In addition, the Baichuan-Pudu site, closer to the eastern coast and historically the headquarters for the Baichuan Court, is affiliated with Li Xiangyi. Its origins apparently lay in an offshoot of the Sigu Sect, which grew into its own independent legal organization after his death.
Legends surrounding Li Xiangyi's life have been well-documented, both at Sigu and Baichuan-Pudu, but also in books and transcriptions of oral stories at sites around the country. These are dated to both the Middle and Late Xi periods, as well as a few scattered mentions in writings from the following dynasty. As a jianghu sect leader and swordsman, Li Xiangyi's reputation truly preceded him. Some tales speak of his early accomplishments, ridding towns of villainous tyrants and defeating criminals. Others talk about the founding of the Sigu Sect when Li Xiangyi was seventeen, and his subsequent missions leading his fellow swordsmen to protect the borders of the country. Not all of these narratives can be verified with surviving historical proof, and given Li Xiangyi's status in the shifting canon of folklore, the percentage that are hyperbole or fiction is likely significant. However, one that should be true, and is the most frequently told story throughout these sources, is that of Li Xiangyi's death.
All texts place Li Xiangyi as having died relatively young, with some providing a specified age, generally around twenty. He perished in a duel with Di Feisheng, leader of the Jinyuan Alliance, a rival jianghu organization and presumed threat to the Sigu Sect. As the sources say, the Jinyuan Alliance killed Li Xiangyi's sect brother, Shan Gudao, and in retaliation he used the Sigu Sect to launch a war against the Jinyuan Alliance. His final battle was the last in this war, dying in the East Sea on Di Feisheng's ship. The Jinyuan Alliance in return was badly defeated by the Sigu Sect; excavations at its first compound in the last five years have shown evidence of siege, with fire having destroyed large parts of the buildings. Afterward, the Sigu Sect disbanded without Li Xiangyi, with only the Baichuan Court continuing to function, before being resurrected one decade later.
Given this knowledge we have about Li Xiangyi, the matter of his burial should be straightforward. He had a tremendous impact on the jianghu in the few short years that he stood at its peak. He died heroically, if tragically, to obtain justice for a brother. He was honoured with a tomb, standing guard over the sect he dedicated his youth to. Why, then, is said tomb regarded as somewhat of a mystery?
This tomb was first stumbled upon during extended surveys of the Sigu site territory, with excavation taking place within the last two years. Parts of the stone chamber and foundation of the dais have withstood time, as have most things left inside. The tomb bears no signs of looting. However, there are some details which, alongside discoveries from other archaeological sites, contribute to a shadow of uncertainty on the existing narrative of Li Xiangyi's life.
Firstly, is that the austerity of the tomb does not line up with what we know of Li Xiangyi. Although overall sufficient enough for someone of his great reputation, the tomb is rather plainly embellished. There are an unexpectedly small number of burial objects inside, with those present being neither rare nor expensive. For all his contributions to the jianghu, less money and resources were poured into remembrance of Li Xiangyi than seems proper for his time.
Secondly, and far more significantly, is that the tomb holds no human remains. Whether the fact of Li Xiangyi having no recovered body to bury was made public is unknown; if it was, we do not have record of it. Certainly those who arranged for the tomb to be built and sealed would have carried this with them the rest of their lives, but no one else may be accounted for. Granted, it is not impossible for a disappeared body to have been common knowledge or presumption, as Li Xiangyi was killed at sea with no guarantee of being found. Yet this, combined with the ordinary appearance of the tomb, causes the entire site to appear... a nominal thing. Constructed to maintain acknowledgement of Li Xiangyi's absence, though his death was only marked by words, rather than a physical state.
He was given a tomb, but was Li Xiangyi truly dead before it was built?
In terms of the aforementioned other archaeological site findings, there is one that potentially implicates Li Xiangyi's death at an interesting political junction, within the context of the dynasty. The Xi Dynasty was unstable and relatively short-lived, established after taking back the Central Plains and adjacent territories from the southern conquering state of Nanyin. It endured for just under two centuries, the first of which was fraught with pockets of conflict, with many jianghu skirmishes such as that between the Sigu Sect and the Jinyuan Alliance. The greatest threat to the Xi Dynasty (until its fall) came one hundred years after its founding. Recovered archival records from the Xi capital excavation report that remaining Nanyin loyalists attempted a coup, supported by jianghu organizations, including a restored Jinyuan Alliance (although whether Di Feisheng was still its leader at this time is unclear). This attack was ultimately unsuccessful, but important to note is that the leader of this renewed Nanyin force is described as being Shan Gudao, Li Xiangyi's former sect brother.
Although Li Xiangyi brought the Sigu Sect into a war upon news of Shan Gudao's death, that demise seems to have been faked, with Shan Gudao disappearing underground only to reappear as part of a later rebellion. Could Li Xiangyi have been aware of this? Was his reaction to Shan Gudao's apparent death genuine? Or part of a coordinated plan, using him as a reason to destroy the Jinyuan Alliance, to eradicate any future resistance? Did Li Xiangyi, too, fake his death alongside Shan Gudao, in service of a shared cause? Were remnants of the Sigu Sect instructed to build an empty tomb, cementing Li Xiangyi as a dead hero so he could work in the shadows of the jianghu instead?
This is merely speculation, contradicted by the fact that if Li Xiangyi had indeed done as such, unlike Shan Gudao, after his duel with Di Feisheng he has no reappearance in any surviving records or at any archaeological site. As well, Li Xiangyi should have had no motivation for committing to such a scheme, with even loyalty to Shan Gudao a stretch for putting all the lives of the Sigu Sect on the line. That being said, history has a way of surprising the present, and this theory may not be entirely ruled out. At any rate, Shan Gudao's survival is a baffling accompaniment to Li Xiangyi's (lack of a) burial, one which will hopefully receive clarifying answers in future archaeological developments.
Perhaps the strangest piece of the puzzle concerning the end of Li Xiangyi's life, however, is Di Feisheng. After the Jinyuan Alliance was scattered by the Sigu Sect, stories regarding Li Xiangyi declared him dead and disappeared. Yet not unlike Shan Gudao, he became known in the jianghu once more about ten years later, witnessing the Nanyin's attempted coup and living long after. His tomb remained untouched, and was excavated eight years ago as part of the greater Tianji Mountain site project. The location of Di Feisheng's tomb is surprising, not only because it directly links him to the powerful and wealthy He clan of Tianji Manor, but also because he was buried next to their sole young master during the Xi Dynasty, Fang Duobing.
The son of financial minister Fang Zeshi and engineering master He Xiaohui, Fang Duobing became a notable youxia travelling the jianghu in the emperor's name, assigned in the wake of the attempted Nanyin coup. According to palace records, he was also betrothed to Princess Zhaoling, although the marriage agreement was eventually formally dissolved. What is otherwise known of Fang Duobing was his admiration of Li Xiangyi, having styled himself as a follower and disciple of him during his youth. As well, one eye-catching artifact among Fang Duobing's burial goods was a preserved wooden replica of a blade, with Li Xiangyi's name carved near the hilt. Likely a children's toy, prized and kept safe throughout Fang Duobing's life.
The exact nature of the relationship between Di Feisheng and Fang Duobing is not entirely certain, but it must have been a very close one, for Di Feisheng to have the privilege of burial on the Tianji estate. This topic justifies future study for our understanding of the Tianji He clan, already known in prior generations for its socially subversive relationships, but pertinent to Li Xiangyi is that the man whose most infamous act was to kill him, was laid to rest beside one who revered him. Why was there such a bond between these two figures, if the stories of Li Xiangyi's death have any truth to them? Did Li Xiangyi really die by Di Feisheng's blade? Did Li Xiangyi's empty tomb, plausibly signifying Di Feisheng's innocence, alter his relationship with Fang Duobing? Or indeed, did Li Xiangyi, the man himself, have a part to play in this?
No traces of him from this time remain in the archaeological record, true. But this should not be taken to mean without doubt that he was not alive then at all.
The discovery of Li Xiangyi's tomb has been an exciting development for studying this era of the Xi Dynasty, but it has also outlined doubt in areas of one man's life that were previously taken as likely facts. Li Xiangyi's tomb is scarcely fitting for his name as a founding sect leader, built more for the sake of its existence than anything else, and there was no body sealed inside to begin with. In addition, Shan Gudao— someone dear to Li Xiangyi— established a precedent of faking his death. Di Feisheng, known across the jianghu for killing the man, held a close bond with someone later in life who had personally looked up to Li Xiangyi, and so he may not have been fully responsible for Li Xiangyi's death to begin with.
What truly happened to Li Xiangyi, resulting in a tomb such as this? The past holds the answer, knowing things that we do not. Hopefully the future of archaeology will continue leading to new discoveries, and allow us to more completely understand the legend that was Li Xiangyi.
#this is probably a better archaeological research paper than the one i wrote on sanxingdui a few days ago#anyways hi yes. i just impulse wrote a fake archaeological paper for fun. enrichment. whatever#also i tried not to sound too pop culture archaeology in this#to any other anthropology or archaeology majors. if it comes off that way i am sorry </3 it's past 4am rn#mysterious lotus casebook#li xiangyi#di feisheng#fang duobing#ashton writes fic#difang#<- to any difang shippers just sit with me for a bit and think about these two being buried together
160 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Alexandria: The City that Changed the World
"Alexandria: The City That Changed the World" by Islam Issa is a biography of a city. It explores the history of Alexandria, Egypt, and its place in our collective memory. It is in part history book, essay, and travel guide, suitable for casual readers. Issa covers up to the 1952 Egyptian Revolution through the lens of his family history. Along the way, he describes the physical city, from the waterfront Qaitbay Citadel where the Lighthouse of Alexandria once stood to the congested downtown.
The book begins with Alexandria's founding by Alexander the Great after he conquered the Persian Empire. Like its legendary namesake, the city was destined for fame. Its strategic and symbolic value made it a coveted prize of world conquerors like Augustus, Napoleon Bonaparte, and Admiral Nelson. The city witnessed the death of Cleopatra, Christianity's triumph over paganism, the rise of the Islamic Caliphates, and the Industrial Age. Even today, Alexandria is an important center of trade, culture, and industry.
The Ptolemaic dynasty, who ruled Egypt in the interim between Alexander and the Roman Empire, transformed it into their crown jewel. Through institutions like the Library of Alexandria, the city became a capital of knowledge and scholarly collaboration. The combined civilizational heritage of East and West birthed a unique urban culture and architectural marvels. This wealth and cosmopolitanism attracted the artistic and scholarly communities that shaped the city's image.
Issa is a professor of literature and history at Birmingham City University, and his family lived in Alexandria for generations. The result of his experience is a powerful monograph on the city’s cultural significance. It is firmly rooted in historical fact, and it is easy to pick up on Alexandria's personal importance to the author. In the prologue, he recalls his father's old stories about Alexandria's former glory, and how they took on new significance for him as he confronted the legacy of Alexandria as an adult. The memory of the ancient city lives on as part of Egypt’s national mythology, inspiring modern-day monuments and legends.
Rather than repeating myths, Issa seeks to critically examine them in light of factual evidence, allowing both the real and imaginary Alexandria to exist side-by-side. At the beginning of the book, there is a series of maps depicting the city at different points in time, from its foundation to the 21st century. It also contains a collection of photographs, some capturing the city today and others portraying its historical sites and artifacts. While intended for casual readers, the book has endnotes and a bibliography to point readers in the direction of further study.
The author concludes the book with an examination of Alexandria's identity and Egyptian national identity in the present day. In contemporary Egypt, there is broad support for historical preservation, but politics determine which histories are deemed worthy of preservation and which are censored. Environmental changes and the rapid construction of an ever-growing modern metropolis on top of the ancient city threaten archaeological efforts. As has been true since the city’s foundation, what is believed about Alexandria’s past – and what it means to be Alexandrian – is constantly changing.
Continue reading...
96 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rose Valland !
She was a French Resistance fighter who rescued and recovered more than 60,000 works of art and cultural property stolen by the Nazis from public institutions and Jewish families during the German occupation!!! For that, she was nicknamed "Capitaine Beaux-Arts"
Rose was born in 1898 and died in 1980. Although she never spoke publicly about her private life and sexual orientation, she never married, and the only relationship she ever had was with a woman.
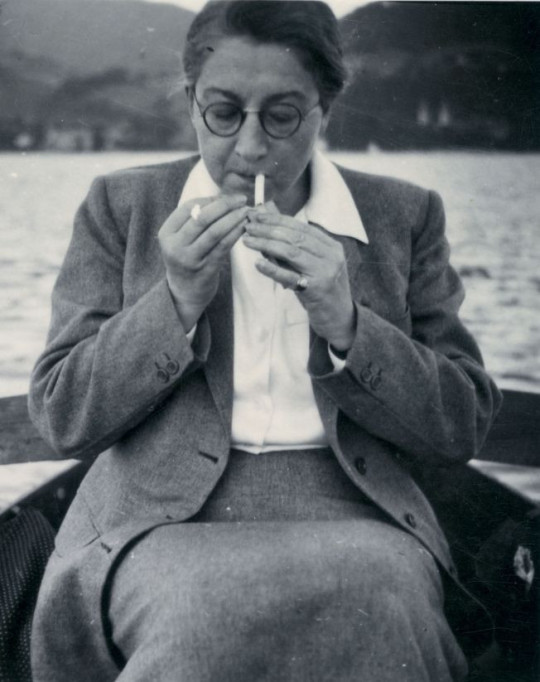

She was able to study thanks to her mother, who applied for grants for her daughter. In 1914, she entered the École normale d'institutrices in Grenoble, graduating in 1918. Gifted for drawing and encouraged by her teachers, she left to study at the École nationale des beaux-arts in Lyon.
She gained a good reputation there, because she was talented and serious, and won a lot of prizes! In 1922, she entered the École nationale supérieure des beaux-arts in Paris. She then passed the competitive examination for teaching drawing, coming 6th out of more than 300 candidates.
During the 1920s, she studied art history at the École Pratique des Hautes Études, the École du Louvre and the Institut d'Art et d'Archéologie. In 1931, she obtained her diploma from the École du Louvre on the evolution of the Italian art movement up to Giotto. At the Institute of Art and Archaeology at the University of Paris, she obtained three postgraduate certificates in modern art history, medieval archaeology and Greek archaeology. She was so intelligent and cultured, with so many diplomas, it's impressive! She published some studies and articles too, and she even learned to speak some languages like German without even studying it.

From October 1940, at the request of Jacques Jaujard, Director of the Musées Nationaux, she remained at the Musée du Jeu de Paume, officially as a curatorial attaché, unofficially instructed by Jacques Jaujard to report to him on the actions of the Germans, who had just requisitioned the museum to store works of art extorted from private collectors.
During the Occupation, the Germans began systematically looting works from museums and private collections across France, mainly those belonging to Jews who had been deported or had fled. They used the Jeu de Paume museum as a central depot before sorting and directing the works to various destinations in Germany, Austria and Eastern Europe. During the Nazi looting, Rose Valland discreetly recorded, as accurately as possible, the movements of the works passing through the Musée du Jeu de Paume, the names of the looted victims, the number of works, their destinations, the names of the agents in charge of the transfers, the names of the transporters, the marks and writing on the crates, the numbers and dates of the convoys, not forgetting the name of the artist, the work and its dimensions.
For over four years, she kept track of all the works' movements, origins and destinations. She scrupulously drew up dozens of index cards, deciphered German carbon paper discarded in the museum's garbage cans, and discreetly listened in on the conversations of Nazi officials. She provided the Resistance with essential, detailed information on the trains transporting the works, so that these convoys could be spared by the Resistance. In autumn 1944, she gave the Allies the names of German and Austrian depots (Altaussee, Buxheim, Neuschwanstein, Füssen, Nikolsburg, etc.) to avoid bombing, secure them and facilitate the recovery of stored works.
After the liberation of Paris by Allied troops, and until May 1, 1945, she worked with SHAEF (Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force), providing the Americans with vital information on storage sites for works transferred to Germany and Austria.
From May 1945, she was seconded from the Ministry of National Education to the Ministry of War, then from 1946 to 1952, seconded as a 3rd class administrator to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, occupying the Secretariat of State and then the General Commissariat for German and Austrian Affairs. Nicknamed "Captain Beaux-arts", she was appointed Captain in the 1st French Army, while also serving as Head of the Service de remise en place des œuvres d'art (SROA) within the Public Education Division of the French Group of the Board of Control.
She was sent to the various Allied occupation zones, British, American and Soviet, from where she repatriated a large number of works. She cooperated with American agents to conduct investigations and interrogate the Nazi officers and merchants responsible for the looting.
She played a decisive role in the February 1946 Nuremberg hearings on the plundering of art by Nazi leaders.
Between 1945 and 1954, she took part in the repatriation of over 60,000 items of French cultural property taken from public institutions and persecuted Jewish families.
Her courageous and heroic actions during the war and post-war years earned her numerous French and foreign decorations. In fact, Rose Valland was one of the most highly decorated women in French history.
She was :
-> made an Officer of the Legion of Honor
-> made a Commander of the Order of Arts and Letters
-> awarded the French Resistance Medal
-> awarded the Medal of Freedom, the highest civilian decoration in the USA
-> made an Officer of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany
-> awarded the Latvian medal of the Order of the Three Stars in recognition of her involvement in the Latvian Art Exhibition (painting, sculpture and folk art), held at the Jeu de Paume from January 27 to February 28, 1939.
Unfortunately, as is often the case with women in history, the role she played in the Resistance, protecting French works of art and the property of deported Jewish people, was quickly forgotten, and her name is hardly ever mentioned today when this part of history is evoked. Insane, when you know everything she's done and how many decorations she got...

At an undetermined time, perhaps in the post-war years, Rose Valland met the British woman Joyce Heer, secretary-interpreter at the U.S. Embassy, who became her lover until her death. The two women shared an apartment on rue de Navarre in Paris. Rose Valland reserved a place for her beside her in the family vault.
Rose Valland died in 1980 at the age of 81 in a nursing home in Ris-Orangis, outside Paris. She is buried with her lover in the family vault in her native village of Saint-Étienne-de-Saint-Geoirs, where the secondary school and a square bear her name.
She truly was a hero, and I wish we talked about her more !
#rose valland#history#ww2#ww2 history#nazi occupation#second world war#women's history#female history#herstory#lesbian#lesbian pride#pride#pride month#lesbian history#female homosexual#female homosexuality
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sirens of Greek Myth Were Bird-Women, Not Mermaids
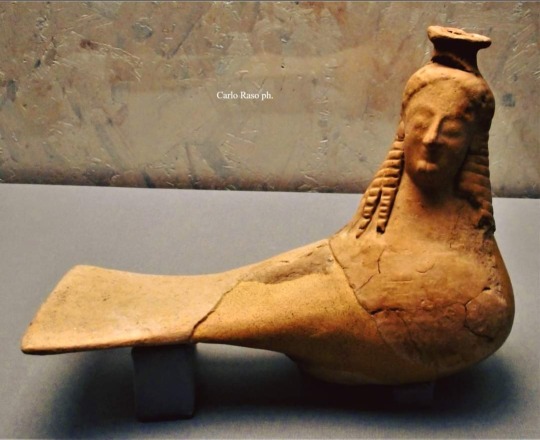

Bottle-askos in the shape of a siren (2nd half 6th century BC) from Locri / Southern Italy's Calabria. National Museum of Magna Graecia (Reggio Calabria, Italy).
In the wine-dark expanse of the Mediterranean Sea, far from the halls of civilization, there was once a small island—or so Homer, the famed poet of Ancient Greece, wrote in his epic The Odyssey. No buildings occupied its flowery meadows; no fisherman worked its shores. Those who passed in their black ships heard only voices, twining over the windless waves, singing a song that promised knowledge of all things. Once they heard it, they were enchanted; they had no choice but to land and seek out the singers. Those who did never left the island; their bodies remained, rotting amid the flowers, for none who heard the Sirens' song could escape it.
The story of the Sirens has inspired writers, poets, and artists for millennia. But somewhere along the way their form was confused. Today, Sirens are almost always represented as voluptuous mermaids, whose beauty and sexuality lure men to their deaths. But the Classical Greeks understood the Sirens differently: as bird-women, creatures that Mediterranean cultures traditionally associated with hidden knowledge.

Sirens first appear in the literary record with the Odyssey (written around 750 BCE) in a segment that’s much briefer than you’d think considering the cultural impact of these mystical, singing creatures. It goes like this: Odysseus, warned by the enchantress Circe of the danger posed by the Sirens’ song, orders his crew to stuff their ears with wax. But, curious to a fault, he has himself bound to the ship’s mast so he can listen without flinging himself into the sea. The Sirens promise him tales of all that had occurred during the war at Troy, and everywhere else besides; enchanted, he begs his crew to release him. He rants, raves, and threatens, but to no avail. His crew sails on until the song fades in the distance, and so saves his life.
Homer doesn’t describe the Sirens’ physical appearance in his epic poem, Wilson says. But in ceramic paintings and tomb sculptures from the time of writing, and centuries after, Sirens were usually depicted with taloned feet, feathered wings, and a beautiful human face. The bird-body of the Siren is significant to Wilson: In the eyes of traditional peoples all across Europe, birds were often graced with an otherworldliness associated with gods, spirits, and omens.

They inhabit the water, the air, and the earth. They’re also associated with song; they have voices that are not human voices, and kinds of movement that are not the same as human kinds of movement.
The Sirens’ role in tomb art is particularly telling. In ancient Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cultures—as far back as 7,000 years ago—birds were often depicted carrying spirits to the underworld. In Southern Italy's Calabria, archaeologists unearthed several Greek askos (unguentary vessel) in shape of sirens, most commonly found in tombs.
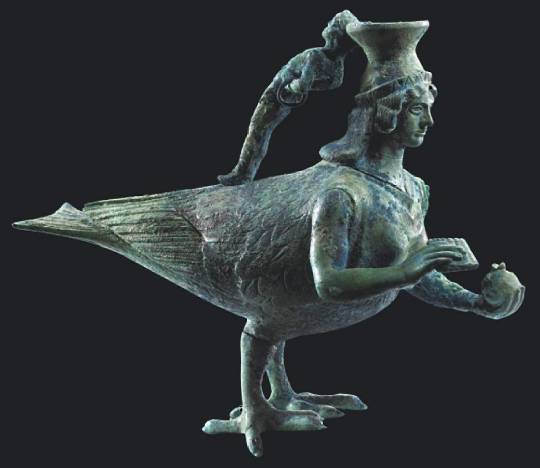

Bronze askos in the shape of a siren (5th century BC) from Crotone, Calabria, Italy - Archaeological Museum of Crotone.
Jump ahead a few millennia to 1,550 BCE, by which time Ba-birds, depictions of departing souls as human-faced birds, began appearing in Egypt. That connection between birds and dead souls seems to have then hopped over to Greece: Writing in the 5th century BCE, the playwright Euripides described the Sirens as at the beck and call of Persephone, one of the rulers of the underworld, while other writers identified the Sirens as rivals and dark echoes of the Muses, those goddesses of creativity.
These are the Sirens the Ancient Greeks would have recognized: bird creatures of the underworld, bridging the human world and what lies beyond. The Sirens—and their fateful songs—then offered a glimpse behind the veil, a chance to hear how earthly glories would echo in eternity. The question of what song the Sirens sing, what is this forbidden knowledge, what's wrong with it, what's the temptation—the text leaves a lot of open space there. Therein lies the seduction.
Yet today, mermaids or beautiful sea nymphs replace the dark, winged Sirens of ancient times.

It is during the Middle Ages that the image of the siren began its shift from bird-woman to mermaid . With the transformation of the siren's image, the attributes associated with female monsters shifted. This suggests a change in the traits that were considered monstrous in women. The siren's movement from a frightening bird-woman to a beautiful mermaid represents female beauty becoming monstrous. Throughout the Middle Ages sirens increasingly represented a male fear of female seduction, suggesting a growing fear of female sexuality.
For medieval Christians, sirens were heavily associated with female sin.
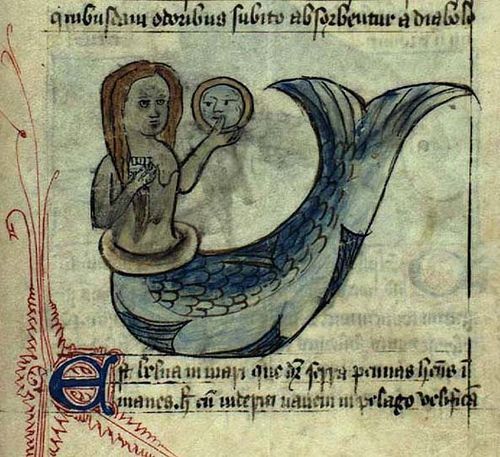

However it happened, the identification of Sirens with mermaids seems to have affected later translations of the Odyssey, and ultimately common knowledge of Sirens. Translators in the 19th and 20th centuries cast the Sirens in a sexualized light. In one prose translation, the Sirens speak of “the sweet voice from our lips,” despite the word στομάτων directly translating to the less sensual “mouths.” Another adds flowery descriptors of “each purling note/like honey twining/from our lips.” But unlike the Odyssey’s other island temptresses, Circe and Calypso, the Sirens get no admiring description of their faces or hair. Only their voice is described, and their field of bones and flowers.

That’s a pretty strong indicator that the Sirens are not meant to be read as offering a sexual temptation. You can kiss lips; mouths devour.
Folklore and mythology move on, given enough time. Today, the Siren is just another word for mermaid, and is likely to remain so. But there’s something richly thematic about the Sirens of Classical Greece that deserves to be remembered: in-between creatures on a lonely island, floating between the boundaries of life and death, and offering an irresistible song of both. Water-temptresses are a dime a dozen; the Sirens offer wisdom.
Follow us on Instagram, @calabria_mediterranea

#sirens#calabria#homer#italy#italia#south italy#southern italy#mediterranean#mediterranean sea#the odyssey#ancient greece#greek#greek art#art#terracotta#greek mythology#greek myth#underworld#mermaids#mythological creature#magna graecia#magna grecia#locri#folklore#mythology#siren#mermaid#crotone
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kente comes from the word kenten, which means "basket" in the Asante dialect of the Akan language, referencing its basket-like pattern. In Ghana, the Akan ethnic group also refers to kente as nwentoma, meaning "woven cloth". Ashanti folklore includes a story where weavers invented kente by seeking to replicate the patterns of Anansi the spider.
West African cultures have been weaving textiles for thousands of years. Archaeological evidence for the oldest form of handloom weaving in Southern Ghana has been discovered at Begho and Bono Manso. Spindle whorls and dye holes discovered in these sites have been dated to the 14th–18th centuries. At Wenchi, spindle whorls have been dated to the 16th–17th centuries.

Asante oral tradition give the origins of Kente to an individual from Bonwire who introduced a loom among the Asante from Gyaman during the reign of Nana Oti Akenten in the 17th century. Another oral source states that it was developed indigenously by individuals from Bonwire during the reign of Osei Kofi Tutu I, who were inspired by the web designs of a spider. In the 18th century, Asantehene Opoku Ware I was documented by Danish agents Nog and L.F. Rømer, to have encouraged expansion in craft work. The Asantehene set up a factory during his reign to innovate weaving in the Ashanti Empire. This was the early stages of Kente production. The Danish agents described the operations of the factory as;
Some of his subjects were able to spin cotton, and they wove bands of it, three fingers wide. When twelve long strips were sewn together it became a “Pantjes” or sash. One strip might be white, the other one blue or sometimes the was a red among them...[Asantehene] Opoke [Ware] bought silk taffeta and materials of all colours. The artists unravelled them.

— Nog.
#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#brownskin#brown skin#afrakans#african culture#afrakan spirituality#kente#kente cloth#epic video#ashanti#Ghana
72 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi, does a Dark Academia setting have to be centered around school or a learning institution? Can it use some of its qualities like clothing, Victorian mansions, dark themes etc? And still call it a Dark Academia aesthetic in my writing?
Dark Academia Setting
"Academia" means "the life, community, or world of teachers, schools, and education," so while it's somewhat important for Dark Academia settings to be rooted somewhere in that (education, intellectualism, quests for knowledge, etc.) you're not at all limited to a school or university as the primary setting.
Other options would include things like:
-- museums and research institutions
-- libraries and archives
-- research or exploratory expeditions
-- halls of cultural or literary gatherings
-- historical, cultural, or scientific societies
-- monasteries and religious institutions
-- ancient ruins and archaeological sites
-- literary or artistic retreats
-- gardens or botanical conservatories
-- opera houses or theaters
-- institutions of art or music
-- political institutions
-- secret societies
-- medical institutions and laboratories
-- gothic mansions involving any of the above
I'm sure there are a million other options I'm not thinking of, but hopefully this gives you some idea of the types of settings that work!
•••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
I’ve been writing seriously for over 30 years and love to share what I’ve learned. Have a writing question? My inbox is always open!
♦ Questions that violate my ask policies will be deleted!
♦ Please see my master list of top posts before asking
♦ Learn more about WQA here
50 notes
·
View notes
Text


Shirdal 'Lion-Eagle'
Talon Abraxas
Ancient origins of the griffin
A legendary creature with the body, tail, and back legs of a lion, the head and wings of an eagle, and, sometimes, an eagle's talons as its front feet first appears in ancient Iranian and Egyptian art dating back to before 3000 BCE. In Egypt, a griffin-like animal can be seen on a cosmetic palette from Hierakonpolis, known as the "Two Dog Palette", dated to 3300–3100 BCE. The divine storm-bird, Anzu, half man and half bird, associated with the chief sky god Enlil was revered by the ancient Sumerians and Akkadians. The Lamassu, a similar hybrid deity depicted with the body of a bull or lion, eagle's wings, and a human head, was a common guardian figure in Assyrian palaces.
In Iranian mythology, the griffin is called Shirdal, which means "Lion-Eagle." Shirdals appeared on cylinder seals from Susa as early as 3000 BCE. Shirdals also are common motifs in the art of Luristan, the North and North West region of Iran in the Iron Age, and Achaemenid art. The 15th century BCE frescoes in the Throne Room of the Bronze Age Palace of Knossos are among the earliest depictions of the mythical creatures in ancient Greek art. In Central Asia, the griffin image was later included in Scythian "animal style" artifacts of the 6th–4th centuries BCE.
In his Histories, Herodotus relates travelers' reports of a land in the northeast where griffins guard gold and where the North Wind issues from a mountain cave. Scholars have speculated that this location may be referring to the Dzungarian Gate, a mountain pass between China and Central Asia. Some modern scholars including Adrienne Mayor have theorized that the legend of the griffin was derived from numerous fossilized remains of Protoceratops found in conjunction with gold mining in the mountains of Scythia, present day eastern Kazakhstan. Recent linguistic and archaeological studies confirm that Greek and Roman trade with Saka-Scythian nomads flourished in that region from the 7th century BCE, when the semi-legendary Greek poet Aristeas wrote of his travels in the far north, to about 300 CE when Aelian reported details about the griffin - exactly the period during which griffins were most prominently featured in Greco-Roman art and literature. Mayor argues that over-repeated retelling and drawing or recopying its bony neck frill (which is rather fragile and may have been frequently broken or entirely weathered away) may have been thought to be large mammal-type external ears, and its beak treated as evidence of a part-bird nature that lead to bird-type wings being added. Others argue fragments of the neck frill may have been mistook for remnants of wings.
Lucius Flavius Philostratus (170 – 247/250 CE), a Greek sophist who lived during the reign of the Roman emperor Philip the Arab, in his "Life of Apollonius of Tyana" also writes about griffins that quarried gold because of the strength of their beak. He describes them as having the strength to overcome lions, elephants, and even dragons, although he notes they had no great power of flying long distances because their wings were not attached the same way as birds. He also described their feet webbed with red membranes. Philostratus says the creatures were found in India and venerated there as sacred to the sun. He observed that griffins were often drawn by Indian artists as yoked four abreast to represent the sun.
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Attention American Viewers:

Lost Painting:
This lithograph was published in The Ulster Journal of Archaeology in 1856. It is based off a portrait of Owen Roe O’ Neill (Eoghan Ruadh Ó Néill) which is believed to have been painted before his death in 1649. The original painting was sold to an unrecorded buyer in America in about 1884, and its current location is unknown. The portrait is of great value to the cultural history of Ireland. In it, O' Neill wears a bairéad (Irish flat cap) and brat (shaggy Irish mantle), making it a rare, detailed portrayal 17th c. Irish dress.
Dr. Hiram Morgan of University College Cork is looking for the original painting. If anyone knows where it is, please email him at [email protected]. (More info) (Also, please send me a photo of it.)
The original portrait is an oil painting on wood and is approximately 12 in x 16 in (30 cm x 40 cm). According to the 1856 description of the painting, "The colour of the hair [. . .] is not decidedly red, but only approaching to it. The tinge of redness, however, is quite sufficient to have distinguished him amongst a number of dark-haired men; and the complexion is clear and ruddy." A partially illegible text on the back of the painting reads, "Owen Roe O’Neill at the Court of [. . .] by the celebrated Dutch artist, Van Brugens".
The Ulster Journal states that the lithograph was "faithfully copied" from the painting, but if it really is an early 17th c. Dutch painting, I doubt the lithograph is an exact copy of it. 17th c. Dutch paintings tend to fill the whole canvas. They don't fade out at the edges.

A 1645 portrait by Dutch artist Bartholomeus van der Helst. Notice how the lace on her sleeves continues all the way to the bottom edge of the canvas.
If we had the original painting, it might show us more details of the garment O' Neill is wearing under his brat.
There is also a color print of this portrait by John D. Reigh. It was originally published in 1888 and was probably made after the original painting left Ireland.

I would guess the Reigh version is less accurate to the original than the Ulster Journal version. In the Ulster Journal version, O' Neill's face looks more like a distinct individual, whereas, in Reigh's version, O' Neill looks more like a generic manly man. 17th c. Dutch portrait painters tended to excel at capturing distinct individual detail, as seen in the van der Helst example above. I'm not an art expert though.
Keep an eye out, people in America. Owen Roe O’ Neill might be hiding in an attic or antique shop somewhere in the US.
#gaelic ireland#art#historical men's fashion#irish mantle#headwear#irish history#irish dress#bairéad#17th century#lost art
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Minoan Civilization: A Surprisingly Modern Society
The Minoan civilization, which flourished on the island of Crete, is renowned for its advanced and, for its time, unusually liberal society. Although our knowledge of the Minoans is incomplete due to limited written sources and primarily based on archaeological finds, a picture emerges of a culture that, from around 2700 to 1450 BC, exhibited remarkable openness, equality, and joie de vivre.
Equality and Tolerance
Current archaeological and anthropological studies often highlight the Minoans' liberal attitude. Researchers like Nanno Marinatos have examined the religious and social structures of the Minoans and found that this society exhibited an unusually high level of gender equality for its time. Women actively participated in public life, possibly held leadership positions such as priestesses, and enjoyed similar rights to men in the private sphere.
Regarding sexuality, the Minoans also appear to have adopted a tolerant attitude. Artistic depictions of intimate relationships between same-sex individuals suggest that such relationships were accepted in Minoan society. Although the interpretation of these depictions is debated among scholars, there are numerous indications that the Minoans had a more open stance towards various forms of love and romance, including same-sex relationships. The portrayal of homoerotic scenes in art and a relaxed attitude towards sexuality indicate that such relationships were accepted and respected in Minoan society.
Katherine A. Schwab: Her work on Minoan frescoes and the analysis of the scenes depicted provide insights into the social dynamics and possible homoerotic aspects of Minoan culture. Current archaeological and anthropological studies often emphasize the Minoans' liberal attitude. Researchers like Nanno Marinatos have examined the religious and social structures of the Minoans and found that this society exhibited remarkable openness and tolerance towards various lifestyles.
Cultural and Social Freedom
Minoan culture was characterized by its artistic flourishing and a preference for the beautiful and pleasurable. The Minoans were masters in the art of fresco painting, ceramics, and architecture. Their palaces, such as the famous Palace of Knossos, were not only political and economic centers but also places of art and culture.
The Minoans lived in close contact with nature, as reflected in their frescoes, which often depicted dolphins, lilies, and other natural motifs. This deep connection with the natural environment is also evident in their appreciation of water, which likely played a significant role in ritual purification and bathing practices.
Festivals, dances, and athletic competitions were integral parts of social life. These events provided not only entertainment but also strengthened the Minoan community and identity through shared experiences.
Religion and Spirituality
Religion played a central role in the lives of the Minoans, and their spiritual practices reflected their liberal values. The Minoan religion was matriarchal, with goddesses such as the Snake Goddess being central figures. The worship of goddesses is often associated with the high status of women in society, as they symbolized aspects such as female fertility and the power of nature.
Rituals and religious ceremonies were opportunities for the community to gather, celebrate, and express their connection with nature and the divine. These rituals, often accompanied by music and dance, emphasized harmony and unity with the environment.
The Minoan civilization was, in many ways, a fascinating and progressive culture, whose societal structure differed from many other ancient cultures. Their values of equality, cultural freedom, and spiritual connectedness remain relevant and inspiring today. The Minoans show us that progressive societal forms were not only a phenomenon of modernity but also existed in antiquity.
Text supported by GPT-4o, Gemini AI
Base images generated with DALL-E, overworked with SD-1.5/SDXL inpainting and composing.
#MinoanCivilization#AncientCrete#Archaeology#HistoricalSociety#LiberalCivilizations#ArtHistory#AncientEconomics#culturaldevelopment#gayart#queer#manlovesman#LGBT#gaylove
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more …
September 13



c.1350 BC – Pharoah Akhenaten, husband of Queen Nefertiti, may also have had a male lover - his younger general, Smenkhare, who later became pharoah himself.
After the discovery in 1922 of the tomb of Tutankhamen (a child of unknown relationship to Akhenaten), Percy Newberry noted that objects had been taken from Smenkhkare's burial chamber to increase the treasure in Tutankhamen's tomb; and among these was a box inscribed on its knobs with "Smenkhkare beloved of Akhenaten" and "Akhenaten beloved of Smenkhkare."
Newberry in his article (1928) also drew attention to a small private stele (upright stone slab) in the Berlin Museum, originally made for a military officer, which showed two kings (identified by their crowns, one the double crown of Upper and Lower Egypt and the other a war crown), nude and sitting side by side. Although the piece is unfinished, with its cartouches blank (ovals which usually contained names), the figures seemed easily identified as Akhenaten and Smenkhkare, the former caressing the youth's chin while Smenkhkare rests his arm around the older king's shoulder.
Two other pieces then also came to mind, a relief of a similar youth pouring wine into Akhenaten's cup (Berlin Museum) and a sculptor's trial piece of Akhenaten kissing a child seated on his lap (Egyptian Museum, Cairo) - and some scholars pondered whether these pairs might also include Smenkhkare. (Actually the former conveys no sexual meaning, and the child in the latter seems very young.)
Subsequently, Egyptologists battled over Akhenaten's sexual biology and orientation. For example, Donald Redford, a Canadian archaeologist, wrote (1984) that he personally disliked "this effete monarch, who could never hunt or do battle," while Cyril Aldred, Keeper of Art and Archaeology at the Royal Scottish Museum in Edinburgh, saw (1968) "homosexual relations between the elder and the younger monarch" pictured on the Berlin stele, taking into account also the same-sex "beloved" titles, and the disappearance of Nefertiti's name from all records near the end of Akhenaten's reign.


c.570 BC – Anacreon, born in Teos, Ionia was one of the nine Lyric Poets of the golden age of Greek poetry. And being the good and manly Greek he was, Anacreon's poems and odes were largely about the beautiful boys he loved or longed for or held in his arms as he cooed lyrical poetry to them. He kisses and tells; he names names: Smerdis, Leukapsis, Smialus, Eurylus and Bathylus, are among the youths he sings to. From his erotic verse there survive striking images of his beloved young men: the peaceful character of Megistes, the eyes of Cleobulus, the blond locks of the Thracian Smerdis.
Anacreon's poetic sentiments and style were widely imitated by Hellenistic and Byzantine Greek writers, though they tended to exaggerate the strain of drunken eroticism and frivolity present in his work.
The structure of his poesy was so popular in its own time that others imitated the eponymously named "Anacreontics." Anacreon was rediscovered by English poets int he 19th century and they swooned for him like a well-oiled boy in the gymnasium. The vogue for Anacreontics in English culminated in the popular song "To Anacreon in Heaven." In 1814, Francis Scott Key wrote "The Star Spangled Banner" on this day, based on the then popular "To Anacreon in Heaven."


1928 – Robert Indiana, best known as the creator of the LOVE series of paintings and sculptures, is an openly gay American artist who has incorporated autobiographical and gay themes within his work.
Indiana was born on September 13, 1928. Oil company manager Earl Clark and homemaker Carmen Watters of New Castle, Indiana, adopted the infant as their only child. Clark attended local schools before studying Russian at Syracuse University. He served in the U.S. Army Air Corps from 1946 to 1949 and then entered the Art Institute of Chicago with the assistance of the GI Bill. He won a scholarship to the University of Edinburgh. He earned an M.F.A. there in 1954 and moved to New York City. Clark rented a loft in an old warehouse on the southernmost tip of Manhattan that became an artistic center because of its cheap rents. There he became part of a group of young artists including Agnes Martin, Lenore Tawney, Jack Youngerman, and Ellsworth Kelly. For a time, he and Kelly were lovers.
Clark changed his surname to Indiana in 1958 to reflect better the American focus of his work. He first attracted notice in 1959 with unpainted assemblages, stenciled with short words and constructed from scavenged wood, pieces of iron, and wheels. Indiana is part of the pop art movement, though he deprecatingly refers to himself as a "sign painter." Like other pop artists he invests commonplace objects and familiar images with new meaning. However, his works occasionally deviate from the pop art norm by evincing intense personal and political engagement. They express concern over social issues and make pointed political statements.
His painting Yield Brother (1962), for example, focuses on the peace movement while his Confederacy series (1965-66), created during the Civil Rights movement, attacks racism in four southern states.
In addition, Indiana tends to be more autobiographical than other pop artists. For example, his EAT/DIE (1962) diptych focuses on the last word, "eat," spoken to him by his mother on her deathbed. The painting also evokes the diner his mother managed, which had the familiar "EAT" sign looming overhead. Indiana also collaborated with gay pop artist Andy Warhol on the 1962 short film Eat.
Indiana has also been influenced by the great American queer writers Walt Whitman, Herman Melville, and Hart Crane. His Melville Tryptich (1961) is considered one of his classic images, and several paintings have been inspired by Crane's poem of longing and gay affiliation, "The Bridge."
In 1964, Indiana received a commission from the Museum of Modern Art for a Christmas card design. He created a picture that emphasized the words Love is God (1964). Typical of pop artists, Indiana serialized the image. In 1966, he exhibited a series of "love" paintings, including a definitive version featuring four red block letters completely filling the canvas against a blue and green background. Each letter fills a quarter of the picture, the L and a tilted O in the top quadrants, the V and E in the bottom quadrants. The LOVE image had an immediate impact, especially among the youth culture of the 1960s. As a painting, graphic design, and a sculpture, it has become one of the most pervasive and widely disseminated images of all time.

In 1973, the U.S. Postal Service commissioned Indiana to do a LOVE postage stamp. The resulting product became the most popular stamp ever issued by the U.S. government.
In 1978, Indiana moved to Vinalhaven, Maine. Working with Vinalhaven Press, he has used the traditional printmaking media of etching and lithography to depict the solitude and isolation of his life in rural Maine. Indiana's more recent works include biographical elements of gay lives, including his own. Indiana continues to accept commissions.


1952 – Randy Jones, born in Raleigh, North Carolina, is an American disco and pop singer and best known as the cowboy from Village People.
He attended Enloe High School in Raleigh, North Carolina and graduated in 1970. While there, he was a founder of Enloe's Drama Club, which was then called "Amicus Scaena"; Latin for "friend of scene" or "friend of theatre". He then studied at North Carolina School of the Arts before moving to New York.
Jones had a marriage ceremony with his boyfriend of 20 years, Will Grega, at a New York club on May 7, 2004. Although the marriage is not legally binding, as gay marriage was still illegal in New York state, Jones commented that: "It's only a matter of time before the courts rule in favor of what's morally right and humanly decent." The pair published a book together in 1996, titled Out Sounds: The Gay and Lesbian Music Alternative.
He released in 2007 a disco and pop solo album Ticket to the World. In 2009, he appeared on Flight of the Conchords in their music video for "Too Many Dicks".


1994 – Layton Williams is an English stage actor, best known as one of the boys who played the title role in Billy Elliot the Musical at the Victoria Palace Theatre in London's West End, and as the character Kylie in the BBC TV series Beautiful People 2008 and 2009. From late 2016, he began playing Angel in the 20th anniversary tour of Rent around the UK. The production, particularly himself, received rave reviews.
After several months of training at the Billy Elliot Academy in Leeds, Williams debuted in Billy Elliot the Musical on 26 February 2007. His training was documented on The Paul O'Grady Show in which he appeared in on 25 May 2007 and then in several morning TV shows, TV interviews, and short clips related to the musical. He is the second non-Caucasian boy, the other being Matthew Koon, and the first mixed race youth to star in the show. He gave his finale performance in the musical on 29 November 2008; Williams is still the second-longest running performer as 'Billy' in the show's history. On 31 January 2009, 2 months after his final performance, Layton appeared on the programme Feelgood Factor on ITV, where he and two other 'Billy' actors, Tanner Pflueger and Tom Holland, performed a specially choreographed version of Angry Dance from Billy Elliot the Musical.
Williams has studied street dance and drama at Carol Godby's Theatre workshop in Bury, Greater Manchester. He also studied ballet at Centre Pointe, Manchester. Williams was awarded a scholarship to Sylvia Young Theatre School in Marylebone, London and stayed there until 2008. He attended Broad Oak High School in Bury, his home town, but now attends the Italia Conti Academy of Theatre Arts. During his time at the Italia Conti Academy of Theatre Arts Williams was featured in a children's documentary 'School for Stars' which was broadcast on the children's television channel CBBC.
He was offered the part as young Michael Jackson in the West End Musical Thriller Live where he did a few performances before he outgrew the role. Williams became well known to a TV audience as the character Kylie – acting, dancing, and singing – in the 2008 and 2009 BBC Two comedy Beautiful People, series 1 and 2. Since 2012 he has played Stephen Carmichael in the BBC Comedy Bad Education.
Following that he performed the part of Duane in Hairspray the Musical 2015 - 2016 tour. He has just announced that will will also be in the new 20th anniversary cast of Rent which begins touring in October 2016. Layton is a strong supporter of the charities Stonewall and Ditch the Label.
Williams is openly gay. His grandparents are from Jamaica, but his father was born in the UK.


16 notes
·
View notes
Text

900 Artifacts From Ming Dynasty Shipwrecks Found in South China Sea
The trove of objects—including pottery, porcelain, shells and coins—was found roughly a mile below the surface.
Underwater archaeologists in China have recovered more than 900 artifacts from two merchant vessels that sank to the bottom of the South China Sea during the Ming dynasty.
The ships are located roughly a mile below the surface some 93 miles southeast of the island of Hainan, reports the South China Morning Post’s Kamun Lai. They are situated about 14 miles apart from one another.


During three phases over the past year, researchers hauled up 890 objects from the first vessel, including copper coins, pottery and porcelain, according to a statement from China’s National Cultural Heritage Administration (NCHA). That’s just a small fraction of the more than 10,000 items found at the site. Archaeologists suspect the vessel was transporting porcelain from Jingdezhen, China, when it sank.
The team recovered 38 items from the second ship, including shells, deer antlers, porcelain, pottery and ebony logs that likely originated from somewhere in the Indian Ocean.
Archaeologists think the ships operated during different parts of the Ming dynasty, which lasted from 1368 to 1644.
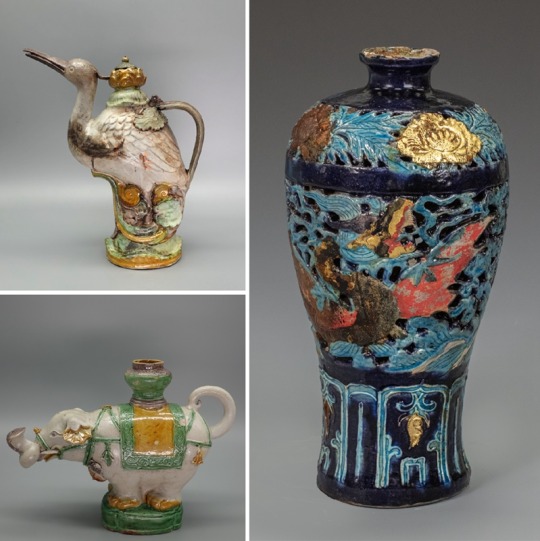
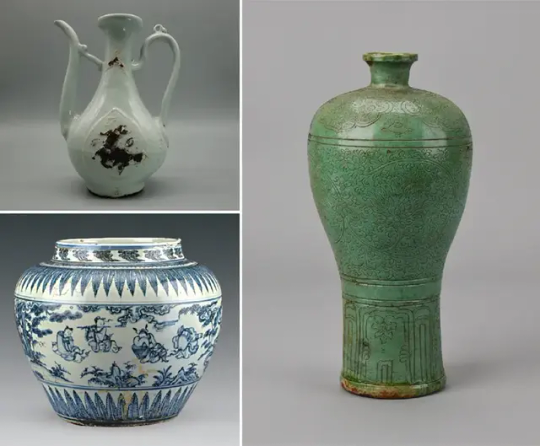
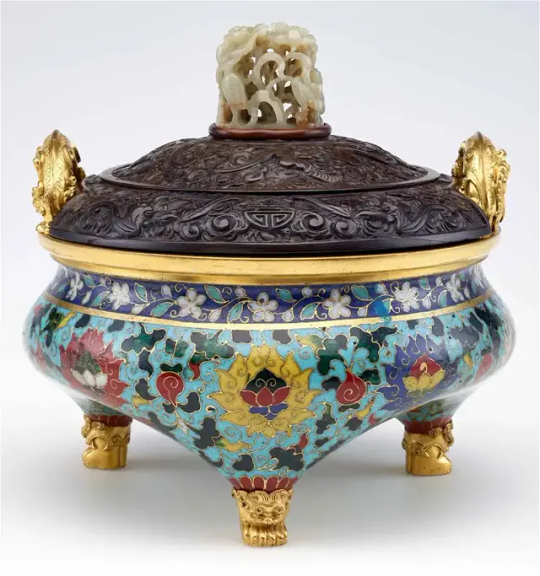



Many of the artifacts came from the Zhengde period of the Ming dynasty, which spanned 1505 to 1521. But others may be older, dating back to the time of Emperor Hongzhi, who reigned from 1487 to 1505, as Chris Oberholtz reported last year.
Archaeologists used manned and unmanned submersibles to collect the artifacts and gather sediment samples from the sea floor. They also documented the wreck sites with high-definition underwater cameras and a 3D laser scanner.
The project was a collaboration between the National Center for Archaeology, the Chinese Academy of Science and a museum in Hainan.
“The discovery provides evidence that Chinese ancestors developed, utilized and traveled to and from the South China Sea, with the two shipwrecks serving as important witnesses to trade and cultural exchanges along the ancient Maritime Silk Road,” says Guan Qiang, deputy head of the NCHA, in the agency’s statement.
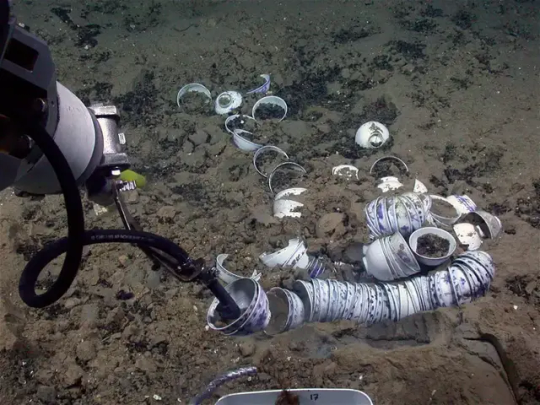



During the Ming dynasty, China’s population doubled, and the country formed vital cultural ties with the West. Ming porcelain, with its classic blue and white color scheme, became an especially popular export. China also exported silk and imported new foods, including peanuts and sweet potatoes.
The period had its own distinctive artistic aesthetic. As the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Asian Art writes, “Palace painters excelled in religious themes, moralizing narrative subjects, auspicious bird-and-flower motifs and large-scale landscape compositions.”
The shipwreck treasures aren’t the only recent discoveries in the South China Sea, according to CBS News’ Stephen Smith. Just last month, officials announced the discovery of a World War II-era American Navy submarine off the Philippine island of Luzon.
By Sarah Kuta.




#900 Artifacts From Ming Dynasty Shipwrecks Found in South China Sea#island of Hainan#Ming dynasty#shipwreck#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient china#chinese history#chinese art#ancient art
225 notes
·
View notes
Text
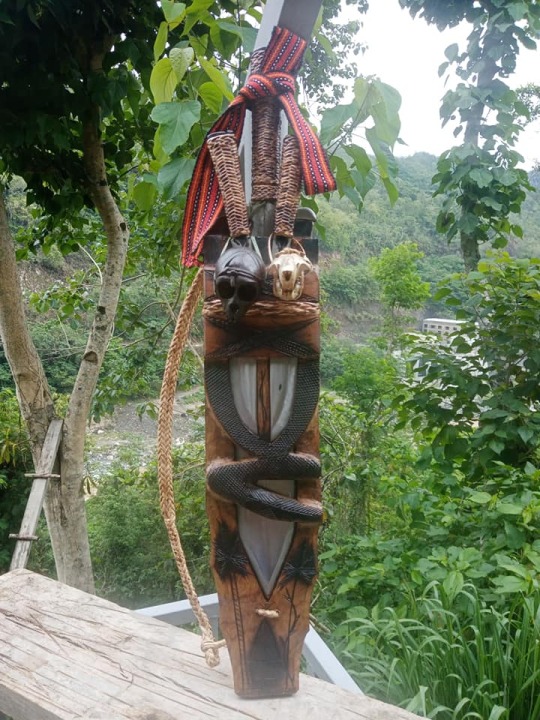
The Third Blade: Hinalung - Handheld Speartip
Five days left to go before the launch of the Gubat Banwa Kickstarter campaign!
Gubat Banwa is a TTRPG that allows you to play as warrior Kadungganan in the Sword Isles, a fantasy setting as colorful and intricate as the Southeast Asian cultures from which it draws inspiration.

I've been posting the weapons I've been drawing for the game as kind of a countdown, leading up to the launch on October 10. I was planning to do this for Swordtember, but sometimes you gotta shift the goalpost a little bit.
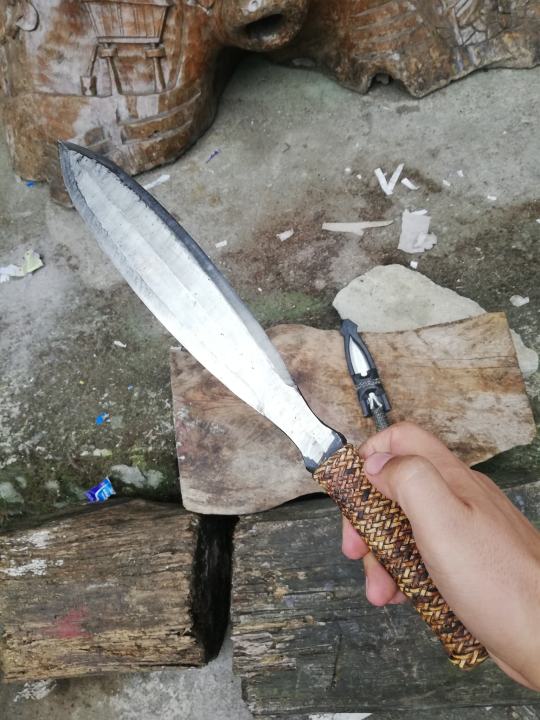
3/7 blades down, behold the HINALUNG
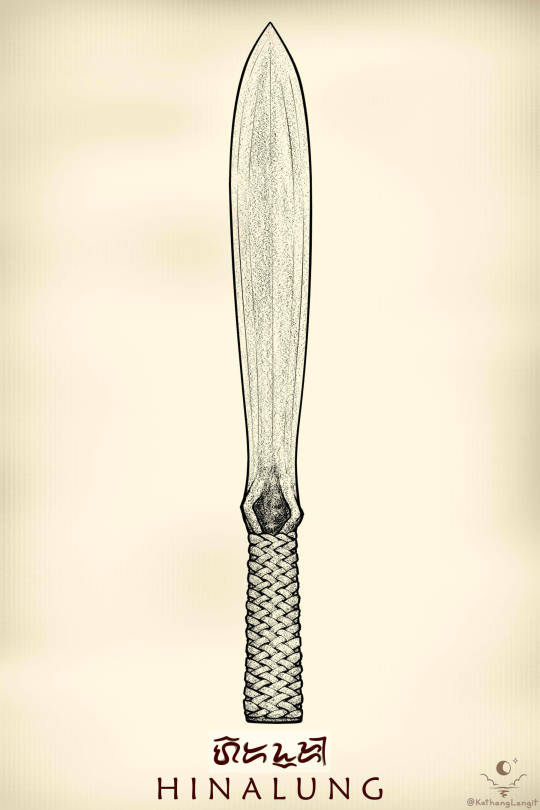
This multi-purpose blade comes in a few different shapes and sizes, but in general they are symmetrical and double-edged. They don't get much longer than one's forearm, and more often than not have handles wrapped in rattan lashings.
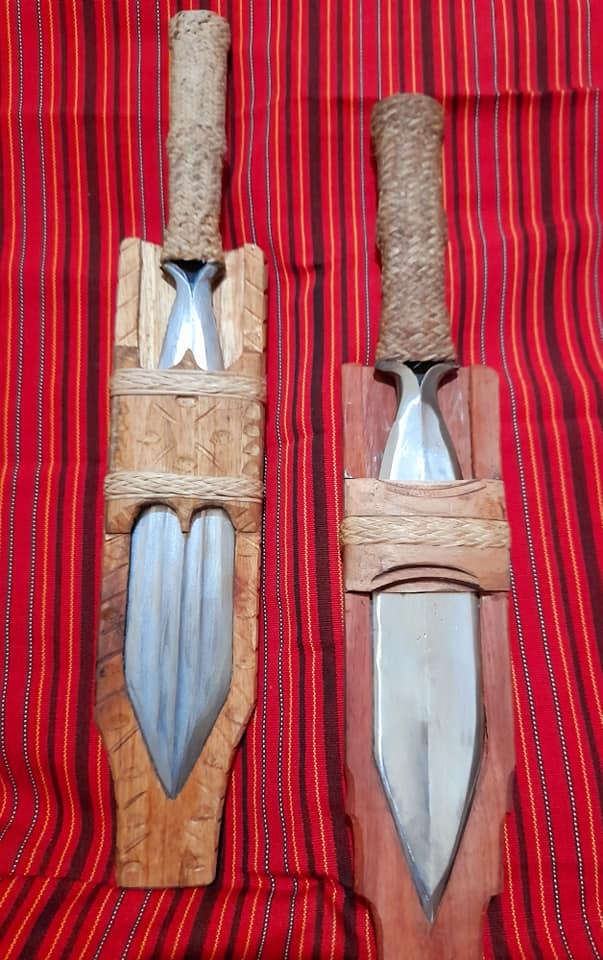

(Blades by Tatang HImanggo and one of his students- a certain Arnold; As shared by Biboy's Sharp Edges)
If I'm not mistaken, the term "hinalung" is Ifugao- referring to a certain group of indigenous peoples in the Philippine Cordilleras- though the usage of the blade itself was widespread across the mountains of north Luzon. Nowadays, it isn't just Ifugao smiths making them, and a number of contemporary smiths from across the region seem to lay claim to the blade.
In any case, the blade is of the Cordilleras, unconquered by Spain.
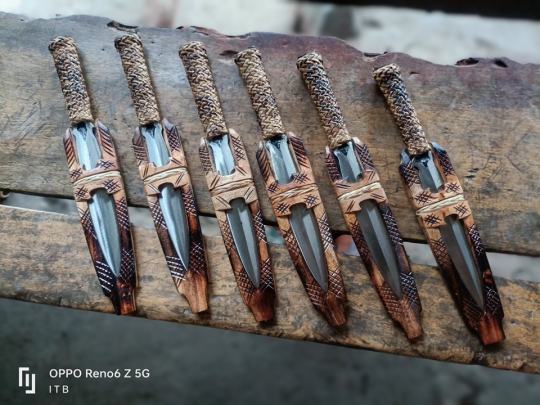

(Blades by Ifugao Traditional Blades)
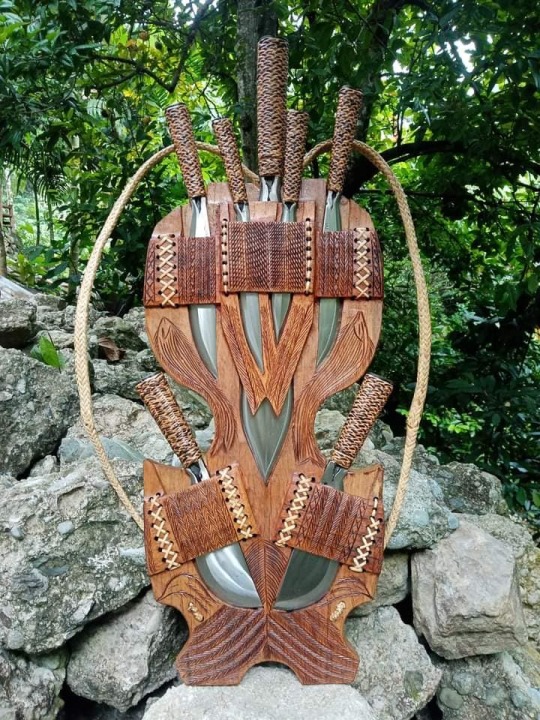
One more thing of note is the open scabbard, which seems to be common among blades in that region- not just the hinalung.
Some of them boast enough space for more than one blade to be sheathed, and are often sold as novelties. The first example below has a large hinalung in the middle, joined by a pair of pinahig.
It can very quickly get out of hand. These X-in-1 sets are usually sold as novelties.


(Blades by Orinn Mongalini/Panday Anitu Mumbaki)

(Photo from Orinn Mongalini)

(Photo from Ifugao Artistic Blade)
Now for the fun part!
You may be wondering why the handle is shaped the way it is, with that triangular opening near the base of the blade?
Or perhaps you read the title of this post and you already know where this is going?

They double as spearheads!
The handle itself is steel folded in to create a hollow socket, allowing the hinalung to be mounted on a wooden shaft, turning it into a spear. Supposedly, this spear-form was used for hunting.
You can see the hollow socket more clearly here:
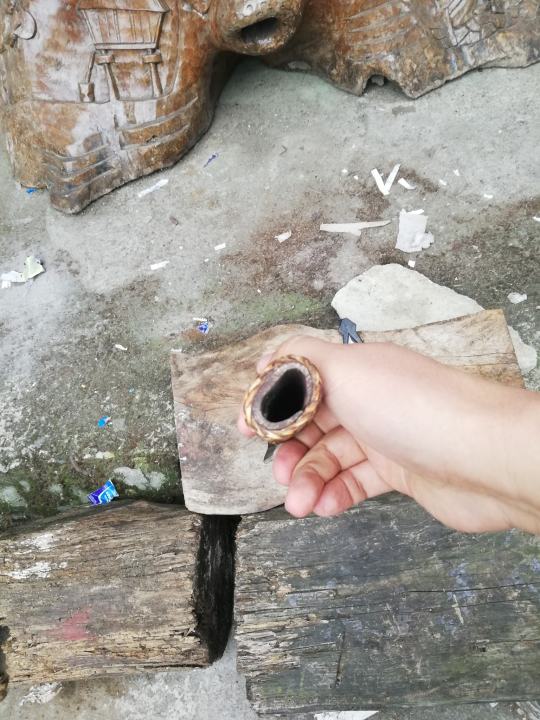


(Blade by HanYan Blades)

(Screencap from a video by AJ Blade Reviews testing the blade as a spear; Blade by Lakay Paul Dulnuan Sr.)
As mentioned previously, the Philippine Cordilleras were never conquered by Spain, and as such were able to carry their traditions with a little more ease into the present day.
It is very much apparent in the blade culture.
Present-day smiths in the Cordilleras still forge hinalung, some of them stating they do it in the traditional way, others admitting to hewing to more modern methods.

(Antique from the Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology)

(Modern build by Lakay Pabian, photo by Ramon Bathan)
Like I said before: Blade culture is alive and still developing.
One of the Five Major Mahamandalas of Gubat Banwa pays homage to and gleans inspiration from living cultures like those I mentioned here. If you want to know what the first half of that sentence means, check out the game and its Kickstarter!
The Gubat Banwa Kickstarter launches in 5 days! Check it out here:
I've watched this game be started, written, and developed by like- one guy, who just managed to drum up enough interest and meet enough people willing to help shape the dream, and make it what it is today. It could not have gotten this far without all of them.
Still, it remains a very small team of creators from the global south, with very limited resources. We would dearly appreciate any and all help in getting the word out about the game!
#gubat banwa#gamedev#ttrpg#ttrpgs#indie ttrpg#indie ttrpgs#tabletop rpgs#rpgs#rpg#southeast asia#southeastasia#dnd#kickstarter#swords#philippine blade#weapon design#dagger#philippine history#philippine culture#filipino artists#artists on tumblr#kathang langit#help us get the word out!#fantasy#fantasy worldbuilding#swordtember#bolo#itak#hinalung#igorot
97 notes
·
View notes
Note
I thought about Huebei and thought of a couple of really cute ideas.
First and foremost, I can see archeology and paleantology being a special interest of hers even going into her adulthood. Girl wants to work on archeology dig sites and stuff and loves the museum. In Soft Boiled Wukong asks MK to help him out by taking her to a trip to a museum while he and the rest of the Noodle Gang set up a surprise party for her on the island the first time her birthday comes up after the monkey family met the group.
Second... and I don't really know WHY, but I can see her being a dancer. Maybe a ribbon dancer or something, but I think of her dancing gracefully as her tall, lanky teenage self and as her buffer adult self and think,'Yeah, that fits.' I can only assume it's the bit of Macaque's dad's influence that she likes performing. Goodness knows she didn't get it from Wukong! Although he can be just as artistic too and as someone who is artistic from an artistic family, I find that if an inheritance trait, even if my style of art is completely different from my siblings' preferred media. We all joke I'm the only one who can draw even tho all the rest of them can play music, something I frankly am terrible at no matter how much I practice altho that could be the stage fright speaking
Third, I can totally see her and Red being inseparable as babies. They were born not far apart in age and basically have similar powers to each other, whenever Uwkong needed a break he'd go to DBK for babysitting and vice versa up until their falling out and Wukong being forced to seal DBK away. It's for this reason I imagine she would like to sneak out to Uncle Bull's resting place just to be near him again. She knows her dad didn't really have a choice, but she misses Uncle Bull and Red. She makes sure Red never sees her or knows she's there when the Bull Family visit.
The first thing Wukong teaches her, besides how to control her lazer eyes, is the transformations. This was a bit of a necessity since, during the journey and shortly afterwards, Wukong would find himself in a situation where demons and celestials of all walks in life would try to sneak onto the island to search him and his cub out. While most were just curious, a few beings did not mean them well, but luckily for Wukong, they only ever searched for a monkey and his baby... they never searched for a sparrow or a tiger. Fresh from the Journey, visitors were the last things Wukong wanted to deal with!
Yuebei quickly starts to see MK as a sort of big brother figure, in spite if her jealousy that he of all beings got picked to be her father's heir and not her. It didn't matter to her that she had explicitly told her father once she never wanted to follow in his footsteps, that staff is her BIRTHRIGHT! Even so, the first time MK got hurt in front of her (Calabash episode actually) she near lost her shit.
Haha! I do love having Yuebei be interested in bone-based sciences due to her literary association with bones. She was def a "dinosaur-kid" who would run up and down beaches, digging up little shell fossils to bring home and show to her baba. Wukong isn't 100% sure what a trilobite is, but his cub is super excited to explain them to him when she found a weird fossilized pillbug. Wukong just loves that his babygirl has such a passionate interest in the world.
As Yuebei gets older, she goes through phases of hyperfixating on different archaeological eras and cultures. As someone who has an ornament cabinet full of Egyptian god statues from one such phase, I can imagine a few sections of the Stone Palace treasury has been organized so Yuebei can display her interests.
I can imagine (even pre-series) Tang running into Yuebei at the museum, the little glamoured demon just fascinated by a display/diorama on Tang-era trade routes. The scholar thinks its the cutest thing ever! The two become sort of nerd buddies once Yuebei warms up to the Noodle Gang.
And ooo ribbon dancer Yuebei!!
I have watched some performances, and many of the dancers are buff af.
youtube
I can see Wukong struggling to find a creative or physical outlet his daughter would enjoy, only to turn around to find the cub dancing with a stray phoenix feather. He sighs, knowing that the theatrical spirit of Macaque has lived on in some way. Heavens know Yuebei is far more confident on stage than Wukong will ever be!
Yuebei and Red Son were def tight as cousins well up until Bull got imprisoned, and they still have an "older sibling, younger sister" relationship in the modern day. PIF and Red never held Wukong's actions against his child, and if the little rebel liked to visit her auntie and cousin without her baba's permission, then they would accommodate her.
I love the idea of Wukong training his daughter some key powers, like the transformations. Yuebei's different transformations tend to be dark furred/scaled/feathered with little red-orange flecks. Almost like a certain Macaque's... one thing she has trouble changing is the age of the animal she turns into. She's almost always a juvenile of the species no matter how hard she tries.
Yuebei, showing off: "Watch this! I can turn into a tiger!"
MK, excited: "Sweet!"
Yuebei: (*transforms into a tiger cub*)
MK, wondering if that was intentional: "Umm..."
Yuebei, furious: "Not. A. Word."
And ofc the baby girl had a problem with her lazer eyes shooting off whenever she had a tantrum - so Wukong had to devise a way to help her control those early on. Welding goggles and sunglasses help a lot on his end, but Guanyin also helped teach younger Yuebei meditation techniques so she could calm down in the moment and avoid triggering a shot.
In the end, even if Yuebei naturally developed a lot of her baba's powers, she sort of resents that MK was chosen as his successor and not her. But she also *knows* it killed her baba to give the Nüwa-made cub up to give him a "normal" life. A life that she couldn't have...
She wants MK to realise his responsibility and not waste it. But also wants to be a kid like he does. The two have to work together to make a balance.
#soft boiled stone egg au#lmk yuebei xing#yuebei xing#lmk mk#qi xiaotian#sun wukong#lmk tang#lmk#lego monkie kid#lmk aus
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
Can you make a post about the evolution of Greek art from the ancient times until now in modern age?
Because we often talk about the evolution of art but unfortunately we don't appreciate after ancient times the other art movements Greece went through the centuries.
That’s true! I am sorry for taking ages to answer this but I don't know how it could take me less anyway hahaha I made this post with summaries about all artistic eras in Greek history. I have most of it under a cut because with the addition of pictures it got super long, but if you are interested in the history of art I recommend giving it a try! I took advantage of all 30 pictures that can be possibly attached in a tumblr post and I tried to cover as many eras and art styles as possible, nearly dying in the process ngl XD I dedicated a few more pictures in modern art, a) because that was the ask and b) because there is more diversity in the styles that are used and the works that are available to us in great condition in modern times.
History of Greek Art
Greek Neolithic Art (c. 7000 - 3200 BC)
Obviously, with this term we don’t mean there were people identifying as Greeks in Neolithic times, but it defines the Neolithic art corresponding to the Greek territory. Art in this era is mostly functional, there are progressively more and more defined designs on clay pots, tools and other utility items. Clay and obsidian are the most used materials.

Clay vase with polychrome decoration, Dimini, Magnesia, Late or Final Neolithic (5300-3300 BC).
Cycladic Art (3300 - 1100 BC)
The art of the Cycladic civilisation of the Aegean Islands is characterized by the use of local marble for the creation of sculptures, idols and figurines which were often associated to womanhood and female deities. Cycladic art has a unique way of incidentally feeling very relevant, as it resembles modern minimalism.

Early Cycladic II (Keros-Syros culture, 2800–2300 BC)
Minoan Art (3000-1100 BC)
The advanced Minoan civilisation of Crete island was projecting its confidence and its vibrancy through its various arts. Minoan art was influenced by the earlier Egyptian and Near East cultures nearby and at its peak it overshadowed the rest of the contemporary cultures and their artistic movements in Greece. Colourful, with numerous scenes of everyday life and island life next to the sea, it was telling of the society’s prosperity.

The Bull-leaping fresco from Knossos, 1450 BC.
Mycenaean Art (c. 1750 - 1050 BC)
Mycenaean Art was very influenced by Minoan Art. Mycenaean art diverged and distinguished itself more in warcraft, metalwork, pottery and the use of gold. Even when similar, you can tell them apart from their themes, as Mycenaean art was significantly more war-centric.
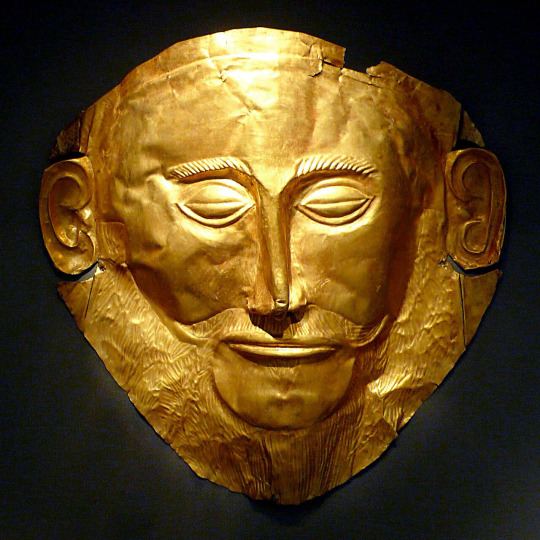

The Mask of Agamemnon in the National Archaeological Museum of Athens. The mask likely was crafted around 1550 BC so it predates the time Agamemnon perhaps lived.
Geometric Art (1100 - 700 BC)
Corresponding to a period we have comparatively too little data about, the Geometric Period or the Homeric Age or the Greek Dark Ages, geometric art was characterized by the extensive use of geometric motifs in ceramics and vessels. During the late period, the art becomes narrative and starts featuring humans, animals and scenes meant to be interpreted by the viewer.

Detail from Geometric Krater from Dipylon Cemetery, Athens c. 750 BC Height 4 feet (Metropolitan Museum, New York)
Archaic Art (c. 800 - 480 BC)
The art of the archaic period became more naturalistic and representational. With eastern influences, it diverged from the geometric patterns and started developing more the black-figure technique and later the red-figure technique. This is also the earliest era of monumental sculpture.
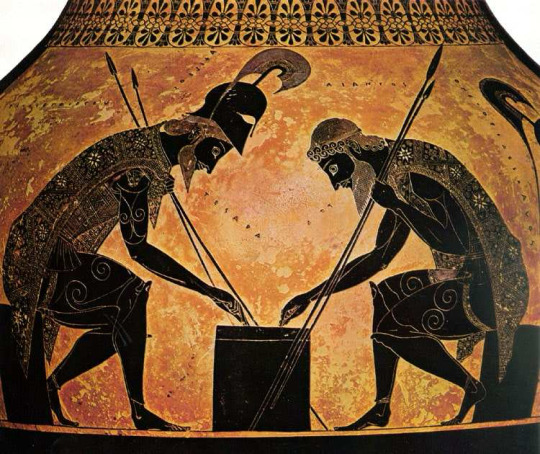

Achilles and Ajax Playing a Board Game by Exekias, black-figure, ca. 540 B.C.

Kroisos Kouros, c. 530 B.C.
Classical Art (c. 480 - 323 BC)
Art in this era obtained a vitality and a sense of harmony. There is tremendous progress in portraying the human body. Red-figure technique definitively overshadows the use of the black-figure technique. Sculptures are notable for their naturalistic design and their grandeur.
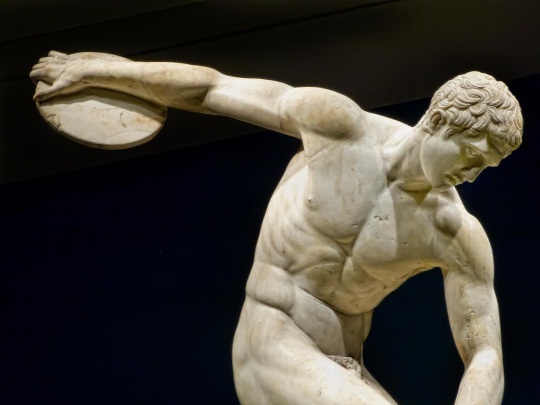

The Diskobolos or Discus Thrower, Roman copy of a 450-440 BCE Greek bronze by Myron recovered from Emperor Hadrian’s Villa in Tivoli, Italy. (British Museum, London). Photo by Mary Harrsch.

Terracotta bell-krater, Orpheus among the Thracians, ca. 440 BCE, The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
Hellenistic Art (323 - 30 BCE)
Hellenistic art perfects classical art and adds more diversity and nuance to it, something that can be explained by the rapid geographical expansion of Greek influence through Alexander’s conquests. Sculpture, painting and architecture thrived whereas there is a decrease in vase painting. The Corinthian style starts getting popular. Sculpture becomes even more naturalistic and expresses emotion, suffering, old age and various other states of the human condition. Statues become more complex and extravagant. Everyday people start getting portrayed in art and sculpture without extreme beauty standards imposed. We know there was a huge rise in wall painting, landscape art, panel painting and mosaics.

Mosaic from Thmuis, Egypt, created by the Ancient Greek artist Sophilos (signature) in about 200 BC, now in the Greco-Roman Museum in Alexandria, Egypt. The woman depicted in the mosaic is the Ptolemaic Queen Berenike II (who ruled jointly with her husband Ptolemy III) as the personification of Alexandria.

Agesander, Athenodore and Polydore: Laocoön and His Sons, 1st century BC
Greco-Roman Art (30 BC - 330 AD)
This period is characterized by the almost entire and mutually influential merging of Greek and Roman artistic expression, in light of the Roman conquest of the Hellenistic world. For this era, it is hard to find sources exclusively for Greek art, as often even art crafted by Greeks of the Roman Empire is described as Roman. In general, Greco-Roman art reinforces the new elements of Hellenistic art, however towards the end of the era, with the rise of early Christianity in the Eastern aka the Greek-influenced part of the empire, there are some gradual shifts in the art style towards modesty and spirituality that will in time lead to the Byzantine art. During this era mosaics become more loved than ever.

A mosaic from the island of Kos (the birthplace of Hippocrates) depicting Hippocrates (seated) and a fisherman greeting the god Asklepios (center) as he either arrives or disembarks from the island. Second or third century CE.
Introduction to Byzantine Art
Byzantine art originated and evolved from the now Christian Greek culture of the Eastern Roman Empire. Although the art produced in the Byzantine Empire was marked by periodic revivals of a classical aesthetic, it was above all marked by the development of a new aesthetic defined by its salient "abstract", or anti-naturalistic character. If classical art was marked by the attempt to create representations that mimicked reality as closely as possible, Byzantine art seems to have abandoned this attempt in favor of a more symbolic approach. The subject matter of monumental Byzantine art was primarily religious and imperial: the two themes are often combined.
Early Byzantine Art (330 - 842 AD)
The establishment of the Christian religion results in a new artistic movement, centered around the faith. However, ancient statuary remains appreciated. Most fundamental changes happen in monumental architecture, the illustration of manuscripts, ivory carving and silverwork. Exceptional mosaics become integral in artistic expression. The last 100 years of this period are defined by the Iconoclasm, which temporarily restricts entirely the previously thriving figural religious art.

Mosaics in the Rotunda of Thessaloniki, 4th - 6th century AD.
Macedonian Art & Komnenian Age (843 - 1204 AD)
These artistic periods correspond to the middle Byzantine period. After the end of the Iconoclasm, there is a revival in the arts. The art of this period is frequently called Macedonian art, because it occurred during the Macedonian imperial dynasty which generally brought a lot of prosperity in the empire. There was a revival of interest in the depiction of subjects from classical Greek mythology and in the use of Hellenistic styles to depict religious subjects. The Macedonian period also saw a revival of the late antique technique of ivory carving. The following Komnenian dynasty were great patrons of the arts, and with their support Byzantine artists continued to move in the direction of greater humanism and emotion. Ivory sculpture and other expensive mediums of art gradually gave way to frescoes and icons, which for the first time gained widespread popularity across the Empire. Apart from painted icons, there were other varieties - notably the mosaic and ceramic ones.

Paris Psalter, 10th century AD. Prophet Isaiah from the Old Testament in the company of the symbolisms for night (clear inspiration drawn from the ancient deity Nyx) and morning (Orthros, not to be confused with the mythological creature).
Palaeologan Renaissance (1261 - 1453)
The Palaeologan Renaissance is the final period in the development of Byzantine art. Coinciding with the reign of the Palaeologi, the last dynasty to rule the Byzantine Empire (1261–1453), it was an attempt to restore Byzantine self-confidence and cultural prestige after the empire had endured a long period of foreign occupation. The legacy of this era is observable both in Greek culture after the empire's fall and in the Italian Renaissance. Contemporary trends in church painting favored intricate narrative cycles, both in fresco and in sequences of icons. The word "icon" became increasingly associated with wooden panel painting, which became more frequent and diverse than fresco and mosaics. Small icons were also made in quantity, most often as private devotional objects.

Detail of Anástasis (Resurrection) fresco, c. 1316–1321, Chora church, Constantinople (Istanbul) (photo: byzantologist).
Cretan School (15th - 17th century)
Cretan School describes an important school of icon painting, under the umbrella of post-Byzantine art, which flourished while Crete was under Venetian rule during the Late Middle Ages, reaching its climax after the Fall of Constantinople, becoming the central force in Greek painting during the 15th, 16th and 17th centuries. By the late 15th century, Cretan artists had established a distinct icon-painting style, distinguished by "the precise outlines, the modelling of the flesh with dark brown underpaint, the bright colours in the garments, the geometrical treatment of the drapery and, finally, the balanced articulation of the composition". Contemporary documents refer to two styles in painting: the maniera greca (in line with the Byzantine idiom) and the maniera latina (in accordance with Western techniques), which artists knew and utilized according to the circumstances. Sometimes both styles could be found in the same icon. The most famous product of the school was the painter Domenikos Theotokopoulos, internationally known as El Greco, whose art evolved and diverged significantly in his later years when he moved in Spain and was involved in the Spanish Renaissance, and though it often alienated his western contemporary artists, nowadays it is viewed as an incidental early birth of Impressionism in the mid of the Renaissance’s peak.

Icon by Andreas Pavias (1440-1510), Cretan School, from Candia (Venetian Kingdom of Crete). The Latin inscription suggests the icon was meant for commercial purposes in Western Europe. National Museum, Athens. (Source: https://russianicons.wordpress.com/tag/cretan-school/)

Crucifixion (detail), El Greco (Doménikos Theotokópoulos), ca. 1604 - 1614.
Heptanesian School (17th - 19th century)
The Heptanesian school succeeded the Cretan School as the leading school of Greek post-Byzantine painting after Crete fell to the Ottomans in 1669. Like the Cretan school, it combined Byzantine traditions with an increasing Western European artistic influence and also saw the first significant depiction of secular subjects. The center of Greek art migrated urgently to the Heptanese (Ionian) islands but countless Greek artists were influenced by the school including the ones living throughout the Greek communities in the Ottoman Empire and elsewhere in the world. Greek art was no longer limited to the traditional maniera greca dominant in the Cretan School. Furthermore, the Heptanesian school was the basis for the emergence of new artistic movements such as the Greek Rocco and Greek Neoclassicism. The movement featured a mixture of brilliant artists.

Archangel Michael, Panagiotis Doxaras, 18th century.
Greek Romanticism (19th century)
Modern Greek art, after the establishment of the Greek Kingdom, began to be developed around the time of Romanticism. Greek artists absorbed many elements from their European colleagues, resulting in the culmination of the distinctive style of Greek Romantic art, inspired by revolutionary ideals as well as the country's geography and history.

Vryzakis Theodoros, The Exodus from Missolonghi, 1853. National Gallery, Athens.
The Munich School (19th century Academic Realism)
After centuries of Ottoman rule, few opportunities for an education in the arts existed in the newly independent Greece, so studying abroad was imperative for artists. The most important artistic movement of Greek art in the 19th century was academic realism, often called in Greece "the Munich School" because of the strong influence from the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of Munich where many Greek artists trained. In academic realism the imperative is the ethography, the representation of urban and/or rural life with a special attention in the depiction of architectural elements, the traditional cloth and the various objects. Munich School painters were specialized on portraiture, landscape painting and still life. The Munich school is characterized by a naturalistic style and dark chiaroscuro. Meanwhile, at the time we observe the emergence of Greek neoclassicism and naturalism in sculpture.

Nikolaos Gyzis, Learning by heart, 1883.
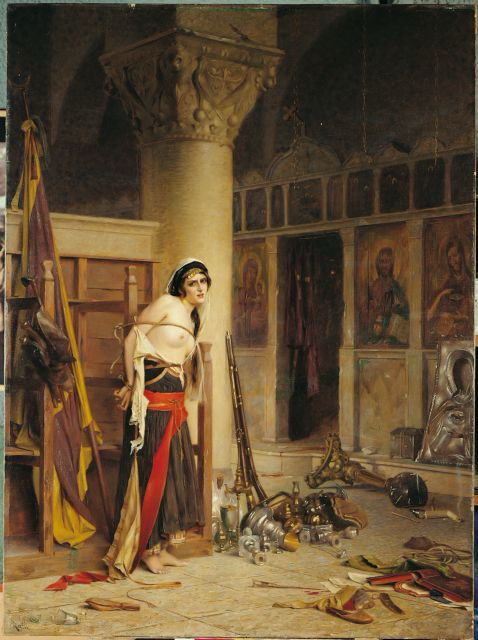

Rallis Theodoros, The Booty, before 1906.
20th Century Modern & Contemporary Greek Art
At the beginning of the 20th century the interest of painters turned toward the study of light and color. Gradually the impressionists and other modern schools increased their influence. The interest of Greek painters, artists changes from historical representations to Greek landscapes with an emphasis on light and colours so abundant in Greece. Representatives of this artistic change introduce historical, religious and mythological elements that allow the classification of Greek painting into modern art. The era of the 1930s was a landmark for the Greek painters. The second half of the 20th century has seen a range of acclaimed Greek artists too serving the movements of surrealism, metaphysical art, kinetic art, Arte Povera, abstract excessionism and kinetic sculpture.

Yiannis Moralis, Two friends, 1946.

Art by Giannis Gaitis (1923-1984), famous for his uniformed little men.

By Yorghos Stathopoulos (1944 - )

Art (detail) by Nikos Engonopoulos (1907 - 1985)
Folk, Modern Ecclesiastical and Secular Post-Byzantine Art
Ecclesiastical art, church architecture, holy painting and hymnology follow the order of Greek Byzantine tradition intact. Byzantine influence also remained pivotal in folk and secular art and it currently seems to enjoy a rise in national and international interest about it.

A modern depiction of the legendary hero Digenes Akritas depicted in the style of a Byzantine icon by Greek artist Dimitrios Skourtelis. Credit: Dimitrios Skourtelis / Reddit

Erotokritos and Aretousa by folk artist Theophilos (1870-1934)

Example of Modern Greek Orthodox murals, Church of St. Nicholas.

Ancient Greek philosophers depicted in iconographic fashion in one of Meteora’s monasteries. Each is holding a quote from his work that seems to foreshadow Christ. Shown from left to right are: Homer, Thucydides, Aristotle, Plato and Plutarch. This is not as weird as it may initially seem: it was a recurrent belief throughout the history of Christian Greek Orthodoxy that the great philosophers of the world heralded Jesus' birth in their writings - it was part of the eras of biggest reconciliation between Greek Byzantinism and Classicism.

Prophet Elijah icon with Chariot of Fire, Handmade Greek Orthodox icon, unknown iconographer. Source
If you see this, thanks very much for reading this post. Hope you enjoyed!
#greece#art#europe#history#culture#greek art#artists#greek culture#history of art#classical art#ancient greek art#byzantine greek art#christian art#orthodox art#modern art#modern greek art#anon#ask
63 notes
·
View notes