#it is an ancient language which originates in the Middle East!
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

lo thaalan il nessyoono
#fyodor dostoevsky#bsd#bungou stray dogs#bsd fanart#my art#IM BACK BABY#fun fact! Fyodor’s last words were spoken in ‘Aramaic’ which is generally agreed upon by scholars to be a language Jesus spoke!#it is an ancient language which originates in the Middle East!
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Danny ends up a doctor like his parents, just not the type of doctor they were expecting.
Danny becomes an archeologist.
He couldn't help it! Most of his friends were dead people, some from as far back as ancient Mesopotamia! He automatically knew every dead language by virtue of being a ghost! The way his friends talked, he wanted to know more about their lives. So he goes looking and makes a name for himself.
He becomes a well known archeologist. As a grad student, he works for the Drakes, even babysitting their son, Tim. He goes to Janet's, and later Jack's, funeral, offering to take Tim in, which the boy is grateful for but declines in favor of a bio-uncle. Eventually, Danny discovers the remains of an ancient cult in the Middle East.
Ra's learns that the remains of the original League of Shadows has been uncovered by a group of archeologists. Originally visiting the dig site to ensure the group doesn't discover any traces of the modern-day League, he finds himself intrigued by the young Dr. Fenton leading the dig. He's smart and bright and the first person in 400 years that can speak Ra's birth language. He becomes fond of the good doctor, even more so when he discovers that Danny's a conservationist and is skilled with a Xiphos (all Pandora's doing). How strange that their spars often end up with them retreating to Danny's tent to be alone...
And then Danny invites Tim Drake to visit, worried about the boy being a teen CEO with no breaks. Tim agrees.
#dc x dp#dpxdc#dp x dc#dcxdp#adult danny fenton#doctored halves#but i don't like that name so i'm tagging#deadly decisions#c: danny fenton#c: ra's al ghul#c: tim drake#Tim: Oh Boy i can't wait to visit with a friend of my parents and enjoy a relaxing vacat--YOU!!#Ra's: Oh hello Timothy.#Danny frantically hiding hickies: y-yes hello tim! so good to see you!
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
I wonder how the batboys would be with a reader with a MAJOR interest in foreign languages. I'm not just talking about knowing several languages, I'm talking about a reader who's also capable of using the basics of so many languages that people don't really tend to learn or even know exist (can you imagine casually speaking Burmese or Catalan in front of the boys??), and they know how to read numerous writing systems. Imagine if the Reader's room is just full of language textbooks and their phone is full of language apps
They'd be incredibly impressed, of course. They all know their fair share of languages, considering their job/hobby/personal exercise routine, but the level of effort and care you put in is astounding.
Tim, despite himself, immediately gets competitive about it. He needs to be on the same level as you, and understand you in all ways. And if you love something as much as you love languages, he needs to love it the same way too. So, get ready for quizzes and competitions galore. He probably adds you on Duolingo, even if you didn't give him your contact details, the little stalker. He wants to win (you).
Dick's absolutely over the moon if you decide to research his family's preferred dialect of Romani. He'll happily teach you and you'll have many quiet, whispered conversations together. The language is quite romantic (it is actually a romance language), just like he is, and he probably starts flirting with you all the time in Romani. Just, constantly hitting on you, but in a way only you can understand, so he doesn't get too embarrassed. Flirt back using his mother tongue, and you'll have a swooning Dick Grayson on your hands.
Damian sees this as a grand opportunity to invite you closer into his space. His family has connections in all of the Middle East and further, and he's got access to thousands of ancient documents in hundreds of languages. Is very smug every time you ask him for his help or a book you think he might have. Which, of course, he does. Even if he doesn't he'll have it soon, so don't go asking the others, alright?
Jason 'number one Shakespeare fan' Todd suggests you start learning some old English with him. And like actual old English, not early modern English like Shakespeare actually used. Enjoys reading classic Russian novels like Dostoevsky in the original text to you. Will also quiz you, but in a chill, uncompetitive way.
#sophie speaks#sophie answers#dick grayson x reader#nightwing x reader#jason todd x reader#red hood x reader#tim drake x reader#red robin x reader#damian wayne x reader#robin x reader#headcanons#batfam x reader#yandere batfam#yandere dc#yandere batfamily#yandere x reader#but sort of yandere only for tim#because honestly i think even canon tim is a yandere like look at the time he tried to clone konner and also like#the blackmailing batman thing you really cant forget that despite how much he wants you too
881 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bharani : the birth of Venus.
Part 1

Let's talk about ancient godesses of love and Bharani nakshatra.
I will base my research on the legend of the dead and resurrected god present in many religious myths coming from the middle east (ps : i'm sorry in advance for the grammar, syntax or spelling mistakes that you may find in this post, english is not my first language)
Bharani, situated in the heart of the rashi of aries is governed by Shukr: Venus but also by Yami and Yama in vedic mythology who are twins and gods respectfully of life and death.

Yama, the main deity of Bharani is said to be one of "8 celestial gatekeepers, who guards eight directional doorways or exits through which souls travel from an earthly plane to other planes of existence" making him the lord of Dharma since at one's death, he decides basing on his actions in what plane should one reincarnate.

Since Yama is responsible for directing the flow of life on Earth the association between bharani and the yoni becomes evident: the female reproducting system serves as a portal for souls to take on a physical form. So bharani as Claire Nakti perfectly described it relates to the feminine ability to receive, hold, nurture and ultimately transform through the womb.
Because Bharani aligns itself with all the feminine qualities by excellence it makes sense as to why Venus is it's ruler.
Venus is the roman name for the goddess Aphrodite: in greek mythology. She is said to be the goddess of love and beauty at large but also the goddess of war and sexuality. First because the ancient greeks saw the duality that links love to war and how they seem to come together through sex.
Also, Aphrodite is said to be born from the sperm of Ouranos when his testicules got cut by his son Saturn as he was always feconding Gaia, the Earth and causing her distress: he was acting cruel regarding their children. The sperm of Ouranus got mixed up with the foam of the Ocean creating Aphrodite which means "risen from the foam". So it was interesting to see that as Shukr also means sperm in sanskrit and it shows the origin of Venus as a fertility goddess too.

This conception of Aphrodite directly links her to ancient goddesses of love such as Ishtar or Inana in Mesopotamian/summerian mythology or Isis in egyptian mythology. Most of the time, these goddesses are the female counterpart of a god that was once mortal, got cursed, died and then came back to life for them to form an immortal couple.
In the case of Ishtar, her consort is Dumuzi or Tammuz and Osiris is the consort of Isis.
In Mesopotamian mythology :
Ishtar or Inana in sumerian is the goddess of love and sexuality, beauty, fertility as well as war because of her status as a " bloody goddess" mostly refering to her character in plenty of myths.

For example: in one story, she became infatuated with the king Gilgamesh, but the latter knowing her fierce reputation, refused her advances. As a result she got furious and unleashed the celestial Bull on Earth which resulted in 7 years of plagues. This celestial bull was later defeated by Gilgamesh and Endiku, and its corpse was throwed in front of Inana. Blinded by rage, she decided that as a punition Enkidu must die and sad at the death of his bestfriend Gilgamesh began his journey to find a cure to Death.
Bharani is a fierce or Ugra nakshatra meaning that its nature is agressive, bold and assertive in pursuing their goals. They are ruthless in the process of accompling what they desire the most and are inclined to extreme mood swings that can result in them to be "blinded" by their extreme emotions perfectly expressing the passionate character of Venus and her other equivalents in differents pantheons of antiquity.
Inana/ Ishtar's story with Dumuzi/Tammur begins as she was convinced to chose him by her brother Utu. Then she got married with the shepphard Dumuzi instead of whom she prefered the farmer: Enkinmdou. During the courtship, Inana prefered the fine textile of the farmer and his beer rather than the thick wool and milk of Dumuzi. The preference for the shepphard illustrates that at the time the Mesopotamian civilisation was known for their proliferent agriculture with the egyptians in the region, so this myth encapsulate the opposition between nomads and sendatary people at this specifific time period.

By the way, another symbol of Bharani is the cave and traditionnaly, the cave was used as a storage room for food. Also Bharani's purpose is Artha so these individuals are motivated to accumalate resources and provide safety and security, so Bharani can be linked to the exploitation of natural ressources like the soil illustrating the preference of Ishtar for the farmer. This is reinforced also by its Earth element.
So coming back to the myth, in a mesopotamian text called Inana's Descent to the Underworld, the goddess goes to Kur (hell) with the intent of conquering it, and her sister Ereshkigal who rules the Underworld, kills her. She learns that she can escape if she finds a sacrifice to replace her, in her search, she encounters servants who were mourning her death however she finds Dumuzi relaxing on a throne being entertained by enslaved girls. Enraged by his disloyalty she selects him as a sacrifice and he is dragged to the Underworld by demons.
He is eventually resurrected by Inana and they become an "immortal couple" as he may only come back to life for half of the year, being replaced by his son (?) who is also his reincarnation for the other half of the same years, so describing the cycle of regeneration of life.
Other mythologycal stories of goddesses in the near east describe a similar patterns:
The goddess Asherah is described as being the mother and the lover of her son Adonis.

The goddess Cybele in the phrygian pantheon takes the form of an old woman as she described as the mother of everything and of all. And at the same time she is the consort of Attis who his her own son (wtf ?)

Also, Yama and Yami are implicated in a incestuous entanglement where his sister Yama wanted to lay with him however he refused establishing himself as a god with an infaillible moral campus.
All of these representations illustrate the relation between the masculine and the feminine, life and regenration which are all topics related to Bharani nakshatra. Women by their capacity to give life are seen as the source of life and therefore are eternal as they are able to regenarate themselves through daughters which are identical to them whereas man who is unable to reproduce by himself, is therefore mortal feels the need to associate with her to resurrect through a son who is identical to him. Bharani exiting as the embodiment of the link between "the father and the offspring" which is the feminine vessel.

So this is certainly part 1, I think that these ancient myths are where Claire Nakti found her inspiration for her series on Bharani.
#vedic astrology#cinema#coquette#astrology#vintage movies#aesthetic#coquette dollete#fashion#vintage#movies#greek mythology#roman mythology#ancient egypt#bharani#chitra nakshatra#purva bhadrapada#purva phalguni#cowboy carter#venus#adonis
236 notes
·
View notes
Text

twitter thread by Mouin Rabbani
March 14, 2024
Who was there first? The short answer is that the question is irrelevant. Claims of ancient title (“This land is ours because we were here several thousand years ago”) have no standing or validity under international law.
For good reason, because such claims also defy elementary common sense. Neither I nor anyone reading this post can convincingly substantiate the geographical location of their direct ancestors ten or five or even two thousand years ago.
If we could, the successful completion of the exercise would confer exactly zero property, territorial, or sovereign rights.
As a thought experiment, let’s go back only a few centuries rather than multiple millennia. Do South Africa’s Afrikaners have the right to claim The Netherlands as their homeland, or even qualify for Dutch citizenship, on the basis of their lineage?
Do the descendants of African-Americans who were forcibly removed from West Africa have the right to board a flight in Atlanta, Port-au-Prince, or São Paolo and reclaim their ancestral villages from the current inhabitants, who in all probability arrived only after – perhaps long after – the previous inhabitants were abducted and sold into slavery half a world away?
Do Australians who can trace their roots to convicts who were involuntarily transported Down Under by the British government have a right to return to Britain or Ireland and repossess homes from the present inhabitants even if, with the help of court records, they can identify the exact address inhabited by their forebears? Of course not.
In sharp contrast to, for example, Native Americans or the Maori of New Zealand, none of the above can demonstrate a living connection with the lands to which they would lay claim.
To put it crudely, neither nostalgic attachment nor ancestry, in and of themselves, confer rights of any sort, particularly where such rights have not been asserted over the course of hundreds or thousands of years.
If they did, American English would be the predominant language in large parts of Europe, and Spain would once again be speaking Arabic.
Nevertheless, the claim of ancient title has been and remains central to Zionist assertions of not only Jewish rights in Palestine, but of an exclusive Jewish right to Palestine.
For the sake of argument, let’s examine it. If we put aside religious mythology, the origin of the ancient Israelites is indeed local.
In ancient times it was not unusual for those in conflict with authority or marginalized by it to take to the more secure environment of surrounding hills or mountains, conquer existing settlements or establish new ones, and in the ultimate sign of independence adopt distinct religious practices and generate their own rulers. That the Israelites originated as indigenous Canaanite tribes rather than as fully-fledged monotheistic immigrants or conquerors is more or less the scholarly consensus, buttressed by archeological and other evidence. And buttressed by the absence of evidence for the origin stories more familiar to us.
It is also the scholarly consensus that the Israelites established two kingdoms, Judah and Israel, the former landlocked and covering Jerusalem and regions to the south, the latter (also known as the Northern Kingdom or Samaria) encompassing points north, the Galilee, and parts of contemporary Jordan. Whether these entities were preceded by a United Kingdom that subsequently fractured remains the subject of fierce debate.
What is certain is that the ancient Israelites were never a significant regional power, let alone the superpower of the modern imagination.
There is a reason the great empires of the Middle East emerged in Egypt, Mesopotamia, Persia, and Anatolia – or from outside the region altogether – but never in Palestine.
It simply lacked the population and resource base for power projection. Jerusalem may be the holiest of cities on earth, but for almost the entirety of its existence, including the period in question, it existed as a village, provincial town or small city rather than metropolis.
Judah and Israel, like the neighboring Canaanite and Philistine entities during this period, were for most of their existence vassal states, their fealty and tribute fought over by rival empires – Egyptians, Assyrians, Babylonians, etc. – rather than extracted from others.
Indeed, Israel was destroyed during the eighth century BCE by the Assyrians, who for good measured subordinated Judah to their authority, until it was in the sixth century BCE eliminated by the Babylonians, who had earlier overtaken the Assyrians in a regional power struggle.
The Babylonian Exile was not a wholesale deportation, but rather affected primarily Judah’s elites and their kin. Nor was there a collective return to the homeland when the opportunity arose several decades later after Cyrus the Great defeated Babylon and re-established a smaller Judah as a province of the Persian Achaemenid empire. Indeed, Mesopotamia would remain a key center of Jewish religion and culture for centuries afterwards.
Zionist claims of ancient title conveniently erase the reality that the ancient Israelites were hardly the only inhabitants of ancient Palestine, but rather shared it with Canaanites, Philistines, and others.
The second part of the claim, that the Jewish population was forcibly expelled by the Romans and has for 2,000 years been consumed with the desire to return, is equally problematic.
By the time the Romans conquered Jerusalem during the first century BCE, established Jewish communities were already to be found throughout the Mediterranean world and Middle East – to the extent that a number of scholars have concluded that a majority of Jews already lived in the diaspora by the time the first Roman soldier set foot in Jerusalem.
These communities held a deep attachment to Jerusalem, its Temple, and the lands recounted in the Bible. They identified as diasporic communities, and in many cases may additionally have been able to trace their origins to this or that town or village in the extinguished kingdoms of Israel and Judah. But there is no indication those born and bred in the diaspora across multiple generations considered themselves to be living in temporary exile or considered the territory of the former Israelite kingdoms rather than their lands of birth and residence their natural homeland, any more than Irish-Americans today feel they properly belong in Ireland rather than the United States.
Unlike those taken in captivity to Babylon centuries earlier, there was no impediment to their relocation to or from their ancestral lands, although economic factors appear to have played an important role in the growth of the diaspora.
By contrast, those traveling in the opposite direction appear to have done so, more often than not, for religious reasons, or to be buried in Jerusalem’s sacred soil.
Nations and nationalism did not exist 2,000 years ago.
Nor Zionist propagandists in New York, Paris, and London incessantly proclaiming that for two millennia Jews everywhere have wanted nothing more than to return their homeland, and invariably driving home rather than taking the next flight to Tel Aviv.
Nor insufferably loud Americans declaring, without a hint of irony or self-awareness, the right of the Jewish people to Palestine “because they were there first”.
Back to the Romans, about a century after their arrival a series of Jewish rebellions over the course of several decades, coupled with internecine warfare between various Jewish factions, produced devastating results.
A large proportion of the Jewish population was killed in battle, massacred, sold into slavery, or exiled. Many towns and villages were ransacked, the Temple in Jerusalem destroyed, and Jews barred from entering the city for all but one day a year.
Although a significant Jewish presence remained, primarily in the Galilee, the killings, associated deaths from disease and destitution, and expulsions during the Roman-Jewish wars exacted a calamitous toll.
With the destruction of the Temple Jerusalem became an increasingly spiritual rather than physical center of Jewish life. Jews neither formed a demographic majority in Palestine, nor were the majority of Jews to be found there.
Many of those who remained would in subsequent centuries convert to Christianity or Islam, succumb to massacres during the Crusades, or join the diaspora. On the eve of Zionist colonization locally-born Jews constituted less than five per cent of the total population.
As for the burning desire to return to Zion, there is precious little evidence to substantiate it. There is, for example, no evidence that upon their expulsion from Spain during the late fifteenth century, the Sephardic Jewish community, many of whom were given refuge by the Ottoman Empire that ruled Palestine, made concerted efforts to head for Jerusalem. Rather, most opted for Istanbul and Greece.
Similarly, during the massive migration of Jews fleeing persecution and poverty in Eastern Europe during the nineteenth century, the destinations of choice were the United States and United Kingdom.
Even after the Zionist movement began a concerted campaign to encourage Jewish emigration to Palestine, less than five per cent took up the offer. And while the British are to this day condemned for limiting Jewish immigration to Palestine during the late 1930s, the more pertinent reality is that the vast majority of those fleeing the Nazi menace once again preferred to relocate to the US and UK, but were deprived of these havens because Washington and London firmly slammed their doors shut.
Tellingly, the Jewish Agency for Israel in 2023 reported that of the world’s 15.7 million Jews, 7.2 million – less than half – reside in Israel and the occupied Palestinian territories.
According to the Agency, “The Jewish population numbers refer to persons who define themselves as Jews by religion or otherwise and who do not practice another religion”.
It further notes that if instead of religion one were to apply Israel’s Law of Return, under which any individual with one or more Jewish grandparent is entitled to Israeli citizenship, only 7.2 of 25.5 million eligible individuals (28 per cent) have opted for Zion.
In other words, “Next Year in Jerusalem” was, and largely remains, an aspirational religious incantation rather than political program. For religious Jews, furthermore, it was to result from divine rather than human intervention.
For this reason, many equated Zionism with blasphemy, and until quite recently most Orthodox Jews were either non-Zionist or rejected the ideology altogether.
Returning to the irrelevant issue of ancestry, if there is one population group that can lay a viable claim of direct descent from the ancient Israelites it would be the Samaritans, who have inhabited the area around Mount Gerizim, near the West Bank city of Nablus, without interruption since ancient times.
Palestinian Jews would be next in line, although unlike the Samaritans they interacted more regularly with both other Jewish communities and their gentile neighbors.
Claims of Israelite descent made on behalf of Jewish diaspora communities are much more difficult to sustain. Conversions to and from Judaism, intermarriage with gentiles, absorption in multiple foreign societies, and related phenomena over the course of several thousand years make it a virtual certainty that the vast majority of Jews who arrived in Palestine during the late 19th and first half of the 20th century to reclaim their ancient homeland were in fact the first of their lineage to ever set foot in it.
By way of an admittedly imperfect analogy, most Levantines, Egyptians, Sudanese, and North Africans identify as Arabs, yet the percentage of those who can trace their roots to the tribes of the Arabian Peninsula that conquered their lands during the seventh and eighth centuries is at best rather small.
Ironically, a contemporary Palestinian, particularly in the West Bank and Galilee, is likely to have more Israelite ancestry than a contemporary diaspora Jew.
The Palestinians take their name from the Philistines, one of the so-called Sea Peoples who arrived on the southern coast of Canaan from the Aegean islands, probably Crete, during the late second millennium BCE.
They formed a number of city states, including Gaza, Ashdod, and Ashkelon. Like Judah and Israel they existed primarily as vassals of regional powers, and like them were eventually destroyed by more powerful states as well.
With no record of their extermination or expulsion, the Philistines are presumed to have been absorbed by the Canaanites and thereafter disappear from the historical record.
Sitting at the crossroads between Asia, Africa, and Europe, Palestine was over the centuries repeatedly conquered by empires near and far, absorbing a constant flow of human and cultural influences throughout.
Given its religious significance, pilgrims from around the globe also contributed to making the Palestinian people what they are today.
A common myth is that the Palestinian origin story dates from the Arab-Muslim conquests of the seventh century. In point of fact, the Arabs neither exterminated nor expelled the existing population, and the new rulers never formed a majority of the population.
Rather, and over the course of several centuries, the local population was gradually Arabized, and to a large extent Islamized as well.
So the question as to who was there first can be answered in several ways: “both” and “irrelevant” are equally correct.
Indisputably, the Zionist movement had no right to establish a sovereign state in Palestine on the basis of claims of ancient title, which was and remains its primary justification for doing so.
That it established an exclusivist state that not only rejected any rights for the existing Palestinian population but was from the very outset determined to displace and replace this population was and remains a historical travesty.
That it as a matter of legislation confers automatic citizenship on millions who have no existing connection with the land but denies it to those who were born there and expelled from it, solely on the basis of their identity, would appear to be the very definition of apartheid.
The above notwithstanding, and while the Zionist claim of exclusive Israeli sovereignty in Palestine remains illegitimate, there are today several million Israelis who cannot be simply wished away.
A path to co-existence will need to be found, even as the genocidal nature of the Israeli state, and increasingly of Israeli society as well, makes the endeavor increasingly complicated.
The question, thrown into sharp relief by Israel’s genocidal onslaught on the Palestinian population of the Gaza Strip, is whether co-existence with Israeli society can be achieved without first dismantling the Israeli state and its ruling institutions.
258 notes
·
View notes
Text
Key terms necessary for understanding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict : Part 1- Ancient Israel to the founding of modern Israel, Jewish terms
A/N: Hey! The results are in, and this is the topic my followers chose🫶 Writing this felt very much like retaking my high school history finals lol. Enjoy reading.
*These terms and definitions will be organized by topics, in chronological order. **If I have made a mistake or if you feel like I forgot something important- don’t hesitate to tell me in the comments. It is very hard to summarize thousands of years. *** Be respectful, I am human.
1. Key terms in Judaism and the connection to the land of Israel :
Israel and Judea- Were the two ancient Jewish kingdoms.
Zion ציון- Is one of the 70 biblical names for the city of Jerusalem. In fact, Jerusalem is referenced by this name in the bible over 150 times.
The word Zion is very much embedded into our culture: it is used in many prayers and Jewish texts written throughout Jewish history, songs etc.
Zion and the exile from it:
It is especially used when describing longing and the wanting of return to the land of Israel:
The most famous example that uses the word Zion is the biblical prayer from the book of Psalms, 137:
1 By the rivers of Babylon, there we sat down, yea, we wept, when we remembered Zion.
תהילים פרק קלז א עַל נַהֲרוֹת, בָּבֶל--שָׁם יָשַׁבְנוּ, גַּם-בָּכִינוּ: בְּזָכְרֵנוּ, אֶת-צִיּוֹן.
This verse is an example of the longing for Israel: as it was written after the exile to Babylon.
*Yes, the funky Boney M song is based on this Psalms verse :) Coming full circle- It is also used in the official hymn of the modern state of Israel, Ha'Tikva. התקווה, written by Naftali Herz Imber. This word might sound familiar to you, as it is also the origin of the word "Zionism".
Zionism- is the notion that the Jewish people deserve to have a state of their own.
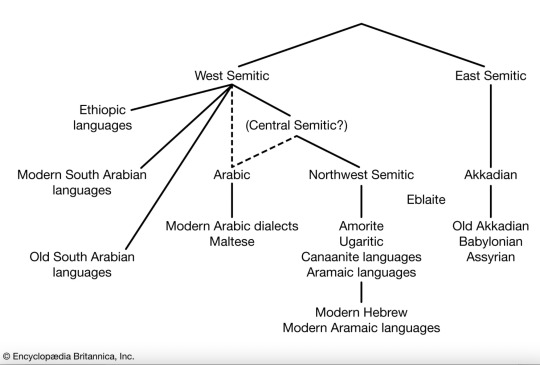
Semite- is a term for people relating to, or constituting a subfamily of the Afro-Asiatic language family:
Semite languages- are a group of ancient languages, that originated around the same time, in Africa and the Middle East- aka the neighboring countries of Israel.
The Semitic languages are: Hebrew and its other ancient dialects , Arabic, Amharic, Aramaic and more. Unfortunately , most of these are extinct and no longer spoken.
The languages that are still spoken to this very day are : Arabic, Amharic and Hebrew.
Some Hebrew Fun facts :
-While there are only estimated 8 million Hebrew speakers nowadays( most of them Israeli), Hebrew is considered a holy language in is spoken during prayer.
-Ancient Hebrew and modern Hebrew are very similar. So much so that if I were to time travel, I could have a decent conversation with my ancestors😊 (some pronunciations, grammar and words have changed, but it’s essential the same).
-Which cannot be done with Romanic languages or Celtic languages..
Antisemitism A\N: This word is getting its whole section because it simply deserves it. Nowadays, every time a Jewish person says something is antisemitic, they will usually be bombarded with mocking comments about how Jews like to call everything antisemitic. If had a nickel for every time I got those comments or an Arab person tried to troll me in the comment section by saying "I can't be antisemitic if I'm a Semite myself"... Let's make it clear (once again).
As I have explained before, the word Semite refers to a group of ethnicities. However, the word Antisemitic refers to Jewish hatred: "Antisemitism is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews.[2][3][4] This sentiment is a form of racism,[5][6] and a person who harbors it is called an antisemite. Though antisemitism is overwhelmingly perpetrated by non-Jews, it may occasionally be perpetrated by Jews in a phenomenon known as auto-antisemitism ".
TLDR: Don't be a Jerk and use antisemitic rhetoric, blood libels, and stereotypes... You don't get to choose if something is antisemitic or not, Jews do.
2. Modern Israel and its founding
The Knesset- Is the Israeli parliament consisting of 120 members, elected democratically every 4 years. Usually- there have been 5 elections in the last 5 years. It also currently has 36 ministers. Yes, that _IS_ a lot.
Kibbutz- "Kibbutz is a community where people voluntarily live and work together on a noncompetitive basis. The first kibbutzim were organized by idealistic young Zionists in the beginning of the 20th century."
As time moved on, starting in the 80s, many Kibbutzim struggled financially and closed down. Today, there are 265 Kibbutzim left, with approximately 200,000 residents. Less than 20% of them are communal.
Unfortunately today, the word Kibbutz has a different connotation:
British mandate- Yep, they colonized us too lol. After the first world war, Between 1917 and May 1948 (Israel was founded literally as soon as the mandate ended).
Fun fact- Today, there are still a few rules left from the British mandate In Israel (Most of them were updated or changed by Israeli law makers after it's founding, usually by the Knesset and the Supreme court of justice).
“Homa U’migdal” (חומה ומגדל Tower and stockade)- During the British mandate, Jewish settlements were built overnight due to a legal loophole still valid from the Ottoman rule. The loophole prevented the British from destroying the new settlement: "Homa U'Migdal is the name of an operation that the leaders of the Yishuv initiated in Palestine, during which 52 new settlements were founded. This operation was a response of the Yishuv to the 1936-1939 Arab Revolt and the restrictions the Mandatory authorities placed, both on the building of new Jewish settlements, and on the amount of Jewish immigrants allowed into Palestine. The building of each settlement began at night. First, the guard tower and the defense stockade were set up, so the operation was named “Tower and Stockade”. According to an old Ottoman law that was still valid during the Mandate period, the destroying of a building was not allowed after the roof had been erected. For this reason the British did not destroy the "Tower and Stockade" settlements which had not received building permits. "
The 2-state solution - The notion that the solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict should be two states for two people- one for Arabs and one for Jews.
Balfour's declaration- is the famous letter sent by then-British foreign secretary Lord Balfour to Lord Rothschild in 1917. In the letter, Lord Balfour stated that the British Empire would support the forming of a Jewish Zionist state in the land of Israel.
Peel Commission- was a community created in 1936 by the British rule during their Mandate over Israel. As the name suggests, the head of the Commity was Lord Peel. A suggestion for a Two-state solution was suggested to representatives of both Jews and Arabs. Unfortunately, the Arabs have refused it.
1947 Partition Plan- A partition plan suggested by the UN, that included another draft of the two-state solution, with different borders. The Arabs have refused it once more.
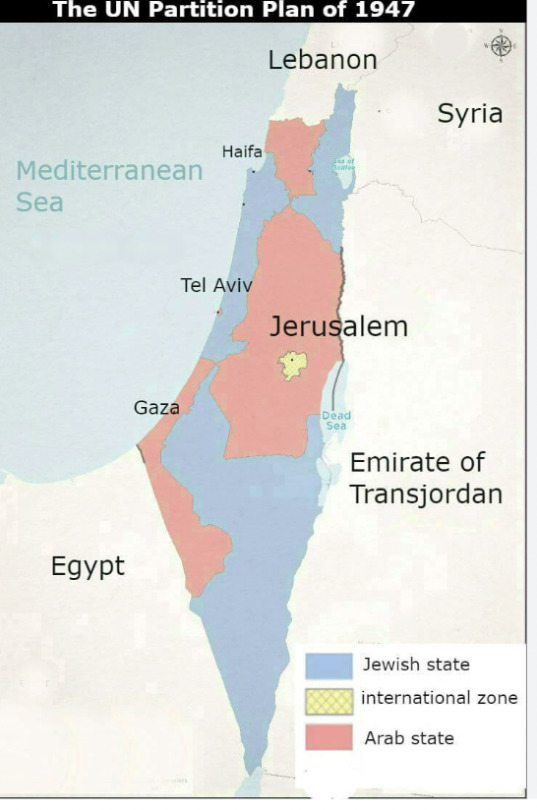
Declaration of Israel's Independence from Britain:
And so, as the British mandate ended on May 14th, 1948, the people's Council (that later served as the initial government of Israel) declared the formation of the modern state of Israel.
The day following the declaration, the Arabs in Israel revolted and with the help of 5 foreign armies that invaded Israel, tried to stop the formation of Israel: Iraq, Jordan, Egypt, Syria, and Lebanon.
They failed and Israel was formed.
You can watch David Ben Gurion, head of the council (and Israel's future first prime minister) declare its formation/independence here.
PS- this was the flag of Palestine before the current one:

Sources:
-Semite languages pic: https://www.britannica.com/topic/Semitic-languages
-Kibbutz: * https://kibbutzulpan.org/about_kibbutz/ *https://www.hamichlol.org.il/%D7%A7%D7%99%D7%91%D7%95%D7%A6%D7%99%D7%9D_%D7%91%D7%99%D7%A9%D7%A8%D7%90%D7%9C (Hebrew)
-Homa U'Migdal" : http://www.zionistarchives.org.il/en/Pages/TowerStockade.aspx
#israel#jewish history#jewish#israeli#jewblr#gaza strip#human rights#ישראל#טאמבלר ישראלי#israel palestine conflict#hamas is isis#jewish tumblr#jewish studies#jewish ≠ israel#jewish culture is#jews#jumblr#judaism#current events#middle east#Israeli#עברית#ישראלי#Gaza#israeli palestinian conflict
175 notes
·
View notes
Note
i just realized qeresî is almost identical to κεράσι/kerāsi (greek for cherry) !! it just hit me while i was replaying lol i love accidentally finding languages' and cultural similarities, especially those between greece/the middle east. it feels very at home even tho they r so different!!
also, revisiting the game after i first played it when you'd only released the first 5 chapters, i think? i'm almost up to speed and i just wanted to say it's even more beautiful than i remembered <3 hope you're good!
That's so interesting!! Apparently the origin of the word is theorized to have been derived from an Ancient Greek city in Turkey (cherry in Turkish is called kiraz, which is also quite similar). It's so fascinating seeing cultural exchange reflected in language.
So glad to have you back, and happy to hear you've enjoyed the newer chapters as well!! 💖
89 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey, question: what are your thoughts on baklava? Is it turkish or greek?
It's not a matter of opinion, it's a matter of facts and the lack of them. The answer to this is normally an one-liner but I would like to give some context because there are foreign people out there who don't understand these feuds.
The one-liner is that the origins of the baklava are unknown.
Now the context: It is funny that what you will constantly hear is the "turkish vs greek" discourse when in actuality baklava is a traditional pastry in at least a dozen more countries in the Balkans, the Middle East and South Caucasus. The reason the discourse always zooms in in these two countries is because of their historically tense relations, which makes nationalists from these places channel their frustrations even in the pettiest of topics. Another reason is that this is a region which has nurtured numerous multi-ethnic empires but Turkey and Greece are the countries which are typically the most connected to these imperial pasts.
We do not know who the cook who came up with the baklava in the Ottoman empire was or to which of the various ethnic communities of the empire they belonged. We know for a fact that baklava's name is Turkish because this was the official language of the empire. Some turkish nationalists treat the turkish name as proof but this is not a good enough reasoning in an imperial context because everything is almost always popularised via the first language of an empire. With the same reasoning, we could say that since the basis of the baklava is the phyllo (filo) dough which is a Greek word, then baklava is a turkish sweet that is half-Greek because it has a Greek basis? These things are unserious.
We also do not know whether that first cook in the Ottoman Empire created the pastry out of thin air or was heavily inspired or was copying a pastry that was already a known delicacy in these regions before the establishment of the Ottoman Empire. Actually, we know that there was a suspiciously way too similar pastry in the Byzantine Empire, named "koptoplakýs¨, a Greek name corresponding to the official language of the Byzantine Empire. We still don´t know if koptoplakys was purely a Greek recipe or it was first made by one of the other Byzantine ethnic groups or it was also inspired by something else prior to it. Several speculations place the origins of baklava and that of koptoplakys to a variety of regions, such as Ancient Greece, Armenia, the Assyrian Empire and more.
The point is that since all these regions of the Balkans, Anatolia and the Middle East were parts of empires, various ethnicities cohabitating in the same place, in the same ecosystem with the same produce, even if this coexistence was not exactly dreamy, it is natural that all these people pretty much ate similar or the same foods and such foods with "controversial" origins are genuinely part of their culinary heritage. There's no "stealing" when it comes to regular everyday things massively consumed by people living together. It's a pastry. It's not some sacred, religious or national symbol. It's a pastry, traditional and with historical presence throughout most of the Eastern Mediterranean.
Like Farya Faraji correctly says, if anything, the differences were regional and not national, since nation states are a very recent development in world history. Meaning, all these countries make the baklava but you may notice slight differentiations in each country / region's version. The standard Turkish baklava is made with pistachios. The standard Greek baklava is made with walnuts. A baklava I had in Montenegro had a lot of lemon zest in it, which definitely is not a thing in Greece. Spices can vary too.
Also, sometimes there is so much discourse about dishes with the same name when in fact the dishes are not even the same. For example, turkish and greek moussakas, another huge discourse, are literally two different dishes!
Turkish mussaka:
Greek mussaka:
(Needless to say various types of mussakas are present throughout the aforementioned regions as well, again.)
"Yes but the similarities" the similarities can be found in literally all neighbouring regions in the world, let alone in places where different ethnicities have been crammed upon each other in empires for centuries. It's inescapable and you sometimes merge so much you cannot tell who started what. (Unless in cases when we DO know thanks to documented history. Then it's a HUGE no-no to confuse or conflate different neighbouring cultures. This is often very important when it comes to actually serious things like languages, religions, historical incidents instead of... nuts and doughs.)
If you are concerned what you should define it as, simply say "I'm having an x style baklava", x being whichever nation you're getting the pastry or the recipe from. Hope that helped.
#food#history#culinary history#world cuisines#mediterranean cuisine#middle eastern cuisine#greco turkish relations#greek cuisine#anon#ask#long text#ottoman empire#byzantine empire#assyrian empire
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
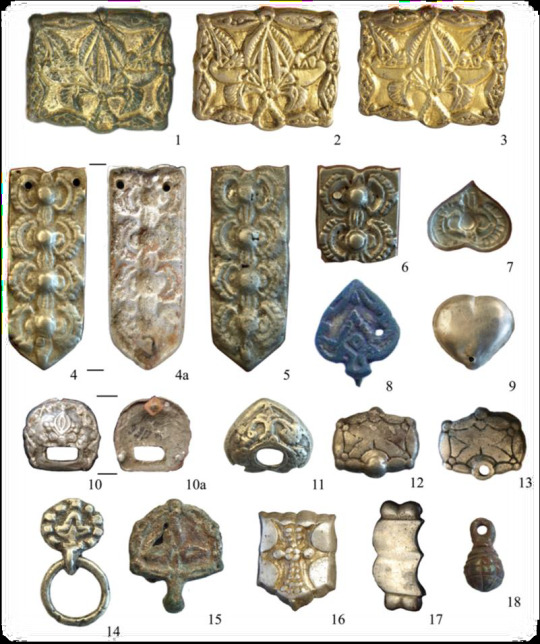
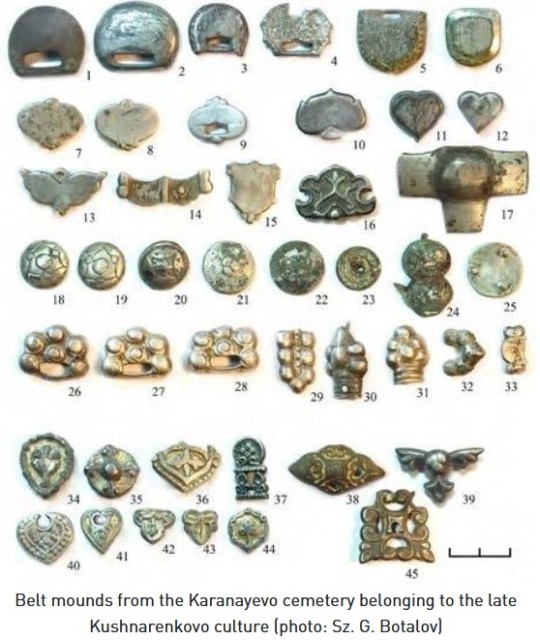
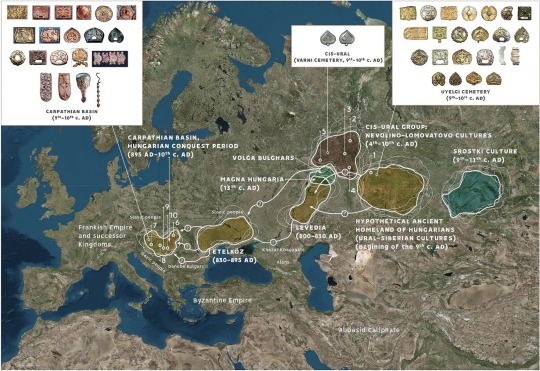


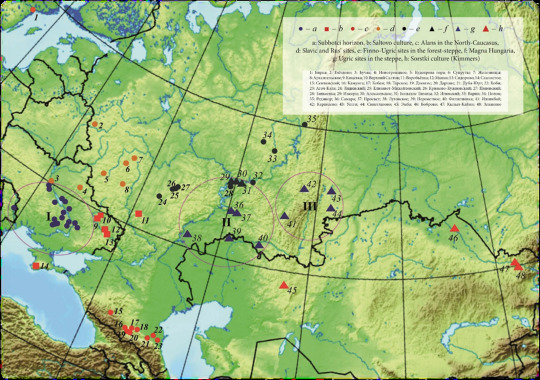




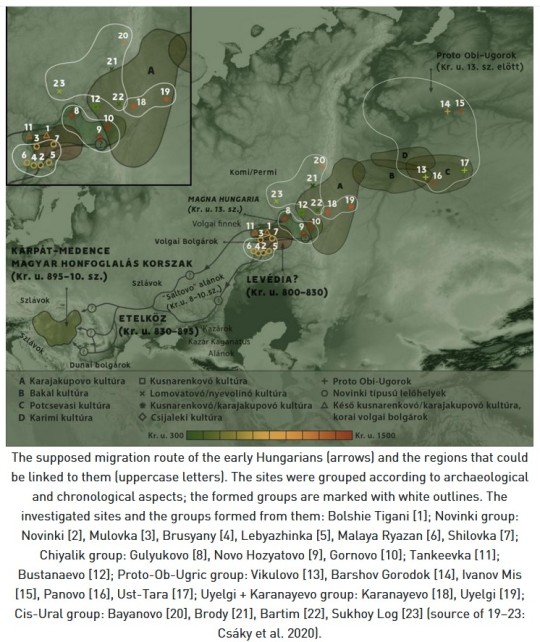
Miscellaneous Hungarian archaeological items from the migration era, from the Urals to the Carpathians 9th-10th C. CE. Sources can be found on my blog, link at bottom.
The Magyars, as a nation, seem to have originated in the region of the Urals and Volga and their original territory covered a large amount of what is European Russia today. This region was known as Magna Hungaria or Ancient Hungary in the Middle Ages. In the 13th century Christian monks tried unsuccessfully to convert the Pagan inhabitants of Ancient Hungary, who they noted spoke the same language as the Hungarians in the Carpathian Basin (will post more on this later). Now genetics show they were related too. Some of the Hungarians in the Carpathian region were found to be direct family members of these Uralic-based Hungarians according to this genetic study below. I grabbed some highlights of genetics article here and included some archaeological image finds:
"Two recent articles have investigated the Y-haplogroup variability of Hungarian conquerors describing the conqueror’s elite population as heterogenous, with significant proportion of European, Finno-Permic, Caucasian and Siberian (or East Eurasian) paternal lineages. Fóthi et al. have claimed that the Hungarian conquerors originated from three distant sources: Inner Asia (Lake Baikal – Altai Mountains), Western Siberia – Southern Urals (Finno-Ugric peoples) and the Black Sea – Northern Caucasus (Northern Caucasian Turks, Alans, and Eastern Europeans). Both studies pointed out the presence of the Y-haplogroup N-Z1936 (also known as N3a4-Z1936 under N-Tat/M46), which is frequent among Finno-Ugric speaking peoples.
...The genetic connection of Uyelgi cemetery in the Trans-Ural and 10th century Hungarian conquerors in the Carpathian Basin is supposed by close maternal relationships of the following individuals: Uyelgi3 from Kurgan 28 of the youngest horizon and three Hungarian conquerors from Karos II cemetery have identical U4d2 mitogenome haplotype (Supplementary Fig. S4p). Furthermore, the mtDNA A12a lineage of Hconq3 (30-40 years old woman from Harta cemetery dated to the first half of 10th century AD) is an ancestor of the mtDNA lineage of Uyelgi7 (from Kurgan 30 of the youngest horizon of the cemetery) based on the A12a haplogroup tree (see Supplementary Fig. S4a).
The mentioned graves from Uylegi show the characteristic of the Srostki culture, where the gilt silver mounts with plant ornaments were typical, and which was disseminated from the Siberian Minusinsk Depression and the Altai region through the Baraba Steppe and North-Kazakhstan to the Trans-Ural region (Fig. 1).
The connection of Uyelgi cemetery and Hungarian conquerors is visible on the N1a1a1a1a branch of the tree of haplogroup N1a1 too, that was prevalent among the ancient Hungarians (Fig. 5). Here seven Hungarian conqueror samples from cemeteries Kenézlő-Fazekaszug, Orosháza-Görbicstanya and Karos-Eperjesszög clustered together on one branch, while the five Uyelgi samples from the earliest and latest horizons are located together next to this branch.
Majority of Uyelgi males belonged to Y chromosome haplogroup N, and according to combined STR, SNP and Network analyses they belong to the same subclade within N-M46 (also known as N-tat and N1a1-M46 in ISOGG 14.255). N-M46 nowadays is a geographically widely distributed paternal lineage from East of Siberia to Scandinavia. One of its subclades is N-Z1936 (also known as N3a4 and N1a1a1a1a2 in ISOGG 14.255), which is prominent among Uralic speaking populations, probably originated from the Ural region as well and mainly distributed from the West of Ural Mountains to Scandinavia (Finland). Seven samples of Uyelgi site most probably belong to N-Y24365 (also known as N-B545 and N1a1a1a1a2a1c2 in ISOGG 14.255) under N-Z1936, a specific subclade that can be found almost exclusively in todays’ Tatarstan, Bashkortostan and Hungary (ISOGG, Yfull)."
-Early Medieval Genetic Data from Ural Region Evaluated in the Light of Archaeological Evidence of Ancient Hungarians
#magyar#hungarian#archaeology#genetics#hungarian art#history#art#europe#middle ages#medieval#finno ugric#pagan
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok so ... Today's absolutely fucking batshit post that I had to read with my own two eyes

We all know Mohamed Hadid is a foaming at the mouth antisemite but this is a new level.
Let's start with the caption:
1. The implication all Jews are American? Insane, untrue, erasing all Jewish history in Israel which dates back to before the Arabization of the middle east.
2. No one has a single percent of Semite in them because Semite is not a race, it's an obsolete term for a family of languages (including both Hebrew and Arabic) however I need to specify that "Antisemitism" was coined as a term specifically about Jew hate. That's what it means, it's actually nothing to do with the language Hebrew at all, it was an attempt to sciencify "judenhass" and make it sound acceptable.
Now to the post itself:
3. If you demand an end to colonialism, boy have I got something to explain about why the official language of Morocco, a country the width of a continent away from the Arabian Peninsula is Moroccan Arabic... Or to be honest, the reason that Arabs are the main demographic anywhere outside the Arabian Peninsula where they originally came from. I understand that peoples migrate but that involves moving from one place to another, not expanding our and literally colonising everything around you. The Arab conquests of the MENA region are a well documented part of history...
4. Demanding a ceasefire is all well and good but we are all aware that we will never be going back to the status quo of before - which frankly is all a ceasefire with no actual work done to rebuild and move towards peace will do. A ceasefire neccestiates thought on what happens next. This is not to say people shouldn't be advocating for an cease to the fighting, they should, this all needs to end. What people have to also do is also be discussing what happens next. The old status quo was unsustainable, and with the mounting evidence that Gazans who worked in Israel helped with the planning of Black Saturday, we will never again see the relations between the people in southern Israel and those in Gaza go "back to normal".
I would love a ceasefire but we need to talk about what happens next in the same conversation. To ignore that is at best naïve and at worst, willfully ignorant because just stopping and Israel withdrawing will do nothing to help rebuild because we all know that everyone will lose interest if that happens, as has happened over and over again.
5. It's well known that Jews are indigenous to Israel and the ancient kingdom of Judea. It's literally in the etymology of the world. Now, obviously multiple groups can be indiginous to one area, but length of time residing there is not a marker of indiginunity, it's literally a childlike playground tactic. Straight up rewriting history... We all know how bad that is.
Mohamed Hadid has over a million followers. His daughters have a total of 130 million. They can post misinformation and almost ten times the number of Jews who exist in the world will see it. This is so dangerous and frankly this level of deranged lying on the internet does not nothing to help end the war, it just puts Jews outside of Israel more at risk. We are being murdered in the streets, in our places of work and everyone is cheering it on.
The irony of people applauding the murder of Jews calling us neo-nazis is not lost on me and it's unreal that we aren't even allowed to stand up to it. Let's be very blunt here, if you are justifying the slaughter of Jews, who's the real nazi?
An additional Edit:
There will never be a ceasefire without release of the hostages and bodies kidnapped into Gaza. Like it's so stupid to think otherwise. Especially with Hamas currently refusing to give a list of who is still alive (they said they couldn't give a list until they knew the terms of a ceasefire which clearly means they COULD do it, but they are choosing not to)
#jumblr#antisemitism#i/p#cw nazi mention#this man and his daughters are a danger to jews everywhere#his daughters holiday in israel and then demonise it online. the least they could do is habe integrity and not be hypocritical#this sort of lying is so dangerous#and he knows that#he is just as dangerous as the extreme zionists who believe gaza and the west bank should become part of israel#he is an antisemite and he is applauded for it#im embarrased for everyone who has liked his post
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
I Read The Silmarillion So You Don't Have To, Part Five
Previous part: https://nyxshadowhawk.tumblr.com/post/728961431368761344/i-read-the-silmarillion-so-you-dont-have-to-part
Chapter 10: Of the Sindar Meanwhile, in Middle-earth…
Remember the Sindar? They’re the people of Elwë, the only one of the original three Elven Lords who never made it back to Valinor, and Melian, a Maia who seduced him. The Sindar are basically native to Middle-earth, and save for Elwë himself, none of them have seen the Two Trees of Valinor. That makes them “Grey Elves,” neither light nor dark. They live in Beleriand, the westernmost land mass of Middle-earth, on which most of The Silmarillion takes place, and which is completely gone by the time LotR takes place.

Elu Thingol by @bohemianweasel
The Sindar know Elwë as Thingol, which is Sindarin for “Greymantle,” and acknowledge him as king. Earlier, I assumed that Thingol and Melian were the ancestors of the Sindar, but this isn’t true; they only have one child, and her name is Lúthien. She is one of the other major players in The Silmarillion, and was based directly on Tolkien’s wife Edith, so she’s kind of a big deal. She’s born in the forest of Neldoreth, and white flowers spring up to greet her.
While Melkor was being held captive in Valinor, the Dwarves finally enter the picture in Middle-earth. They call themselves Khazâd, and the Sindar call them Naugrim, which means “stunted people.” The Elves are somewhat bewildered when the Dwarves come into Beleriand from the East, because they didn’t know that any other people existed. They assumed that they were the only living things who could speak or make things. They don’t learn the Dwarven language, but the Dwarves endeavor to learn Sindarin. When the Noldor eventually show up, the Dwarves really like them, because the Noldor share their reverence for the god Aulë and their skill at metalwork and cutting gemstones.
Because Melian is a Maia, she can see the future. She warns Thingol that the peace isn’t going to last. Thingol decides to build a fortress in case worst comes to worst, and enlists the help of the dwarves to build it. The Dwarves oblige, happy to have a new project, and Thingol pays them in pearls, which they’d never seen before. The biggest pearl is called Nimphelos, which the Dwarves particularly value. (Its name sounds a lot like Omphalos, an egg-shaped sacred stone at Delphi that the Ancient Greeks thought was the navel of the world.) The Dwarves build Thingol a mansion underground, in the style of their own. I’m guessing that, like Hobbit holes, this is a reference to Celtic fairy lore that describes fairies as living in mounds. Like the fairies of British and Irish lore, Thingol has a lavish underground palace called Menegroth, the Thousand Caves. Its pillars are carved to look like trees, with carved animals on the walls and in the “branches” of the pillars. Colorful mosaics decorate the floors, banners and tapestries chronicle the deeds of the Valar, there are silver fountains and singing nightingales, and it’s all as beautiful as anything gets outside of Valinor.
Everything’s great for a bit, but Melkor’s monsters still exist, and eventually Orcs and wolves push into Beleriand. The Elves don’t know what the Orcs are. They assume that the Orcs are Avari (Elves that refused to go to Valinor) that turned evil, which is almost right in an indirect way. Thingol needs weapons to fight Melkor’s monsters, but the Sindar don’t have any weapons and don’t know how to make them, because they’ve never needed them before. The Dwarves know how to make them, having used them to fight all the dangerous things in the East, and they teach the Sindar how to make and use them. Dwarves remain the absolute best at making things of steel, and they invented chainmail.
Remember the Nandor? They were another subgroup of Elves who split off from the Teleri while they were traveling to Valinor, and stayed in Middle-earth. They become the Wood Elves, and their descendants will be the elves of Mirkwood. But at this point in history, they come to Thingol, seeking protection from Melkor’s monsters. Thingol lets them stay in an eastern land called Ossiriand.
A Sindar Elf named Daeron invents the runic writing system, which the Elves don’t care for, but the Dwarves readily adopt.
Once again, everything’s great for a while. But then, Morgoth and Ungoliant have their struggle to the north. The Sindar hear Morgoth’s shrieking and know that something is wrong. Melian’s magic keeps Ungoliant from entering their land, but barely. The Sindar are suddenly assaulted by Morgoth’s massive army of Orcs from his northern citadel of Angband. The Orcs aren’t like anything the Sindar have ever seen, and there’s thousands of them. We get a short summary of the ensuing battle (in which Tolkien drops more place names than I can possibly keep track of).
The Elves and Dwarves win, but they lose a lot of lives in the process. The King of the Nandor, an Elf named Denethor, dies in combat. Distraught by his death, many of his people renounce open war. They are called Laiquendi, “Green Elves,” because they wear leaves. The rest of the Nandor join the Sindar, and merge with them. The Sindar fence themselves into their forest with a magic wall of “shadow and bewilderment” that Melian casts to keep the Orcs out. After that, their forest becomes known as Doriath, the “Land of the Girdle,” after the magic wall. The wall protects them, but the peace and bliss are broken.

Chapter 11: Of the Sun and Moon and the Hiding of Valinor In which the Two Trees have a last hurrah.
Back in Valinor, the Valar are very sad about the Trees, but they’re even sadder about Fëanor. Fëanor is, without a doubt, the best of the Elves. He may be a narcissist, but he’s right about how great he is: he’s the strongest, the smartest, the cleverest, the most beautiful, the most skilled, and the most capable both mentally and physically. Imagine all the good he could have done in the world, and what beautiful and useful things he might have made, if Morgoth hadn’t corrupted him! Now he’s going to waste his life on a pointless endeavor, and his entire line is cursed. It didn’t have to be like this. When a messenger tells Manwë how Fëanor responded to the prophecy of doom, Manwë cries.
However, Manwë doesn’t dispute Fëanor’s boast that people will sing of his deeds until the end of the world. After all, songs are beautiful things. If you remember, Eru Ilúvatar told Melkor that all of his evil deeds will result in more beautiful things, that no one would otherwise have conceived of. Evil always begets good, in spite of itself. Fëanor’s evil deeds will result in the creation of beautiful art in the future, thus indirectly producing good things. But that doesn’t make Fëanor’s actions any better in the present.
Yavanna, goddess of plants, and Nienna, goddess of sorrow, do their absolute best to heal the Trees. The Trees are beyond saving, but the goddesses’ lamentation does do something: With their last bit of strength, Telperion bears a single silver flower, and Laurelin bears a single golden fruit. Yavanna picks them both off the trees. After that, the Two Trees die for good, with nothing but their lifeless stems remaining in Valinor as a sad monument to what once was. Manwë blesses the flower and the fruit, and Aulë makes vessels to hold and preserve them. Then Varda hangs them in the sky as the new lamps: The flower of Telperion is the Moon, and the fruit of Laurelin is the Sun. The two lights will help the Children of Ilúvatar and hinder Morgoth.

Creation of the Two Trees by Julia Pelzer
Each group of Elves has a different name for the Moon and the Sun. The Vanyar (the Elves who got to Valinor first and stayed there) call them Isil and Anar. The Noldor call them Rána the Wayward, and Vána the Heart of Fire.
The Moon and Sun also have their own Maiar to guide them through the sky. The Maia of the Sun is called Arien, and the Maia of the Moon is called Tilion. Both Maiar had loved their respective Trees while the Trees were alive, and begged for the position of tending to the Sun and Moon. Arien is a fire goddess who doesn’t fear the heat of the sun, and Tilion is a hunter god who was one of Oromë’s companions. (This mirrors Norse Mythology, in which the Sun is driven by a goddess called Sol or Sunna, and the Moon by a god called Máni.)

Narsilion by breath-art
The Moon rises first, and brings hope to the Elves. When the Moon rises, Fingolfin and the Noldor begin their long trek into Middle-earth across the frozen north. After the Moon rises and sets seven times, the Sun is hung in the sky, and the first dawn comes. When the Sun sets, it comes to rest in Valinor, briefly reminding the Valar and remaining Elves of the light of the Two Trees and the joy they once had. But the Sun and Moon still pale in comparison to the Two Trees. The only remaining things that preserve the original light, pre-Ungoliant’s destruction, are the Silmarils.
Morgoth is obviously horrified, and immediately sends dark clouds to prevent the Sun from shining upon his land of Angband. Arien, the Maia of the Sun, is the only entity that Morgoth is really afraid of, and he no longer has the strength to attack her. But he does send evil spirits after Tilion, the Maia of the Moon. (This might explain why the moon has phases, but it’s not explicitly said.)
The Valar still remember what happened the last time they put up lamps, and they’re not about to let Morgoth destroy their paradise for a third time. They decide to almost completely cut off Valinor from the rest of the world. They make the Pélori Mountains around Valinor rise impossibly high, with sheer faces like glass. The only way in or out of Valinor is through a mountain pass called the Calacirya, which the Valar leave open to allow the Elves to see the stars. But the pass is heavily guarded. And, as an extra precaution, they fill the sea with enchanted islands that are full of illusions to confuse and trap anyone who tries to sail to Aman. The Noldor are officially, permanently cut off from Valinor — there’s no turning back now.

Telperion and Laurelin by MrSvein872
Chapter 12: Of Men In which the Men finally show up.
Having sealed themselves away, the Valar basically leave Middle-earth to the mercy of Morgoth. It’s not all bad, though; the Sun keeps Morgoth at bay, and it causes many new things to grow in Beleriand. Beleriand is a pretty nice place, for what it’s worth. Not as nice as Valinor, but, y’know… it could be worse.
When the Sun rises, the Men finally awaken. The Elves have a lot of different names for them, but the important ones are Atani (“Second People”) and Hildor (“Followers”). The Men didn’t have a Vala to invite them to Valinor. Men fear the Valar, because they don’t really know what the Valar are or why they’re there, and the Valar have stopped paying attention to Middle-earth. Ulmo watches over the Men through all the water of Middle-earth, but Men don’t know how to understand the divine messages brought to them by the water. It’s rumored that the Men befriend the Avari, the Dark Elves who never went to Valinor.
At the time, Men looked more like Elves than they do now. Men were taller, stronger, and longer-lived than they are now, but Elves were still prettier, wiser, and more skilled than Men. Elves are immortal, and do not sicken or age, but they can still be killed. Men have less robust bodies and are more prone to illness and injury. Dark Elves are better than Men, but the High Elves that saw Valinor are significantly better than both Dark Elves and Men. The only Dark Elves that come close to the greatness of the High Elves are the Sindar, and that’s only because their queen is a Maia.
The other big difference between Elves and Men is what happens after they die. When Elves die, they go to the Halls of Mandos and eventually reincarnate. The Elves don’t know what happens to Men after they die. If they go to the Halls of Mandos, they don’t go to the same part of them that the Elves go to. No one but Mandos and Manwë knows what happens to the Men after that. Only one Man ever came back from the dead (we’ll get there). It’s possible that the only entity that knows anything about what happens to Men after death is Ilúvatar himself.
The relationship between Elves and Men gets steadily worse with time, mostly because of Morgoth (again, we’ll get there). By the time of the Third Age, when LotR takes place, there are very few Elves left. They have retreated away from the sunlight, into lonely woods and caves, and “become as shadows and memories.” The Men take over from the Elves, and forget that the Elves ever existed. But the The Silmarillion is about the First Age, and back then, Elves and Men were friends. Some Men achieved greatness through learning Elven wisdom, and some Men even had children with Elves.
Chapter 13: Of the Return of the Noldor In which we return to the main plot, and a LOT of shit goes down.
Where we last left the Noldor, Fingolfin was leading them on an impossible journey across a frozen wasteland to cross into Middle-earth, because he saw Fëanor burn the boats on the opposite shore. Fëanor and his sons continued further into Middle-earth, and made a camp in the north.
Morgoth also saw Fëanor burn the boats. Even Morgoth was a little afraid of Fëanor, so he decides to preemptively attack Fëanor’s camp. Despite being taken by surprise, the Elves trounce the Orcs, because they still have the strength of Valinor in them. They’re strong and swift, with sharp and effective weapons, and the Orcs don’t stand a chance. A small handful of Elves — Fëanor, his seven sons, and their loyalists — slaughter an entire army’s worth of Orcs in only ten days. Morgoth’s plans for the conquest of Beleriand are ruined, for now.
Fëanor assumes that by chasing down the Orcs, he’ll find Morgoth. Fëanor is so impassioned, so ready to finally kick Morgoth’s ass, that he pats himself on the back for having defied the Valar. It was such a good idea to tell the Valar to go fuck themselves and come to Middle-earth! Now he gets the opportunity to personally take Morgoth down!
He spoke too soon. Fëanor promptly finds himself face-to-face with the fortress of Angband and an entire army of Balrogs. Oops.
Somehow, Fëanor manages to hold his own against multiple Balrogs, until Gothmog, the Lord of the Balrogs, nearly kills him. He only survives because his sons arrive at the last minute with reinforcements to fend off the Balrogs.

Fëanor against the Lord of the Balrogs by Evolvana
Fëanor doesn’t live for much longer, though. His sons start to carry him back to their camp, but he bleeds out on the way. He curses Morgoth and tells his sons to avenge him with his dying breath. As his spirit leaves him, his body burns to ash, because his soul is just that fiery. And that’s it — Fëanor, the mightiest Elf to ever live, is dead. His curse means that his soul is forever trapped in the Halls of Mandos, and he will never reincarnate. No one like him will ever appear in Arda again.

The Death of Curufinwe Feanaro by Gwenniel
Honestly, I’m surprised that Fëanor dies this early. I thought he was the central character, but I’m still only about a third of the way through, maybe less.
Despite having taken out Fëanor (mostly due to Fëanor’s own arrogance and impulsiveness), Morgoth still lost badly. He sends an envoy to Fëanor’s sons, acknowledging defeat and requesting a ceasefire, even offering to surrender a Silmaril. Fëanor’s eldest son, Maedhros (MY-thros, ‘th’ as in “this”) takes over from Fëanor as the leader of the Noldor. Maedhros doesn’t trust Morgoth as far as he can throw him, but decides to go to the negotiation anyway, with backup. Of course it’s an ambush, and there are Balrogs. All of Maedhros’s backup are killed, and Maedhros himself is captured and taken to Angband.
Fëanor’s other sons build themselves a mighty fortress, but Morgoth keeps Maedhros hostage until the Noldor agree to end the war and leave Beleriand. The sons of Fëanor doubt that Morgoth will keep his word on that. They also literally can’t stop fighting Morgoth, because of their oath. So, Morgoth hangs Maedhros by the wrist from the face of the Thangorodrim Mountains. The only remaining option is to try to rescue him.

Maedhros Upon Thangorodrim by Jenny Dolfen
Back with Fingolfin, the rest of the Noldor painstakingly make their way across the land bridge. It’s an agonizing journey, and many Elves die, but when the first dawn finally comes, Fingolfin unfurls his banner and blows his horn in victory. The ice starts to melt, and flowers spring up under his feet. The Sun chases Morgoth to the depths of his citadel, so he doesn’t harass Fingolfin’s group as they arrive in Middle-earth.

Helcaraxe by Stefan Meisl
Fingolfin is wiser than Fëanor, and doesn’t try to attack Angband. Instead, he tries to find the other Noldor. Most of his Fingolfin’s group really hate Fëanor and his sons, because it’s their fault that they nearly froze to death. So, they make their own camp near Lake Mithrim.
Fëanor’s group hears of their arrival. They’re astounded and impressed that Fingolfin and co. managed to survive, and that they made it to Middle-earth. They would welcome Fingolfin’s group, but they’re too ashamed to offer. Too little, too late.
Fingon, Fingolfin's son, decides to try to heal the relationship between the two groups of Noldor. He recognizes that Morgoth would be thrilled if his enemies were so divided against themselves. If they want to stand a chance against Morgoth, they have to unite. Fingon has the perfect idea for how to bring the two groups together. He was very close to Maedhros. He doesn’t know that Maedhros wanted to go back for him when Fëanor burned the ships, so, he assumes that Maedhros betrayed him. Even so, he still cares enough about Maedhros to want to try to rescue him.
He climbs the mountains of Thangorodrim by himself, hidden under the cover of the darkness that Morgoth created to shut out the sun. Then, Fingon takes out a harp and starts singing. He sings a song from Valinor, from long before the unrest took hold. His voice rings throughout the mountains, in which there had never been singing before. He sings in defiance of Morgoth like the Whos singing in defiance of the Grinch on Christmas Day.

He Sang a Song of Valinor by Jenny Dolfen
Faintly, he hears an answering voice singing the same song. Maedhros is singing, despite his suffering. Fingon climbs up to where Maedhros hangs, and cries when he sees how much pain Maedhros is in. Maedhros has long since given up hope, and begs Fingon to shoot him, to put him out of his misery. Fingon prepares to shoot an arrow, but says a prayer to Manwë, asking him to have mercy.
Fingon’s prayer is answered. Manwë sends the King of the Eagles, Thorondar, who picks up Fingon and carries him up the mountain face to where Maedhros hangs. Fingon can’t find any way to open or break the shackle that holds Maedhros, and can’t detach it from the mountain face. Maedhros again begs Fingon to kill him, but Fingon figures that it’s better to lose a hand than to die. Fingon cuts off Maedhros’ hand, and Thorondar catches him, carrying both Elves back to Lake Mithrim.

Flight from Thangorodrim by @thegreencarousel
(As you can probably guess, a lot of Silm fans ship Fingon and Maedhros. I almost did, too… and then I remembered that they’re first cousins.)
After that, the rift between the two groups of Noldor is healed. Fingon is hailed as a hero by both groups of Noldor. Maedhros steadily gets better, and recovers his strength. He pulls and Inigo Montoya and learns to wield a sword just as well with his left hand. He also waives his claim to kingship over the Noldor. He begs Fingon to forgive him for having deserted him back when Fëanor burned the boats, and tells Fingon that he’s the rightful heir of the House of Finwë. That’s a nice gesture, but it’s actually part of the curse — The House of Fëanor became known as the Dispossessed, because even though they’re the older brother’s children, they permanently lost the rulership of the Noldor.
The now-united Noldor decide to explore Beleriand a little more, and they eventually meet the Sindar. The Noldor and Sindar recognize each other as kin, but have a hard time understanding each other because they speak different languages. Eventually, they figure out a way to talk to each other. The Noldor learn about King Thingol and the magic wall around his kingdom of Doriath, and about the Sindar’s battles with the Orcs. The Sindar are delighted that these stronger, smarter elves from Valinor arrived right when they were most needed, and assume that the Valar must have sent them.
Thingol is less enthused about a bunch of hotheaded foreign princes arriving in his land. The only Noldor he trusts to let past the magic wall are Finarfin’s children: Finrod, Angrod, Aegnor, and Galadriel. This is because their mother was Eärwen, one of the Teleri Elves and Thingol’s niece. So, they’re his closest relatives among the Noldor. Angrod is the first of the Noldor to enter Thingol’s palace in Doriath. He tells Thingol all about what happened to the Noldor in the North — how they crossed over, how many of them there are, how they beat back Melkor’s forces, how Finrod saved Maedhros, etc. He leaves out the part about the kinslaying and the curse.
Thingol gives the Noldor his blessing to remain in the northern part of Beleriand, but they can’t displace the Sindar from their homes. They also aren’t allowed to come past Doriath’s magic wall, unless they’re invited, or if they desperately need an audience with Thingol. Thingol is Lord of Beleriand and the Noldor are imposing upon him, so, they’re in no position to argue.
When Angrod brings this message back to the Noldor, Maedhros straight-up laughs. “What kind of king is he? These aren’t his lands. He doesn’t have the power to grant us leave to live here, as if we were his vassals. If it weren’t for us, there’d be Orcs breaking down his door.”

Maedhros by _star热爱生活呀巴扎嘿
Caranthir, another one of Fëanor’s sons who inherited his father’s fiery temper, also doesn’t like Thingol’s conditions. “Who’s idea was it to send Finarfin’s sons as our spokesmen? I don’t trust a word they say, and I don’t trust this cave-dwelling Dark Elf. Finarfin’s sons should remember that, whoever their mother was, their father was still a Noldo — they should be loyal to the Noldor.”
Angrod is furious at this, and storms out. Maedhros chides Caranthir for going too far. The rest of the Noldor are all concerned that Fëanor’s whole family appears to be a ticking time bomb. It’s only a matter of time before one of them snaps and causes violence. Maedhros reads the room, and manages to get his brothers under control. He decides that he and his brothers should leave before things get worse. Not just leave the meeting, but leave the region — it’s better that they and the other Noldor remain friends at a distance, rather than risk another confrontation that tears them apart from within.
Maedhros and his brothers head east. Their new home is more exposed, and has less natural defense against Angband, but Maedhros doesn’t mind this. He and his brothers can be a buffer for the rest of the Noldor if Morgoth attacks again. And of course, the curse is still in effect.
Caranthir and his people are the first to find the Dwarves, who had stopped coming into Beleriand ever since the battle against Morgoth. You’d think that the Dwarves and the Noldor would have a lot in common, since both love to make things from metals and gems, and they both appreciate good craftsmanship. But nope. The Dwarves are too secretive, and Caranthir is too arrogant. He doesn’t even bother to hide that he thinks the Dwarves are ugly, and all his underlings follow suit. Despite that, the Dwarves and Caranthir’s Elves have a common enemy in Morgoth, so, they form an alliance anyway. From that alliance, Caranthir ends up learning a lot of Dwarven secrets about metalworking and masonry. It’ll really pay off for him in the future.

Caranthir by Miyota
Twenty years pass since the Sun first rose, and Fingolfin decides to throw a feast to unite all the scattered Elves. This feast is such a big deal that it has a name — Mereth Aderthad, the Feast of Reuniting. It’s a last moment of joy and happiness before everything goes to hell again. A number of Sindar attend the feast as well, alongside their leader, an Elf called Círdan (you’re gonna want to remember him). Thingol does not leave his magically-fortified palace, but he sends two diplomats to the feast — Daeron, the Elf that invented runes, and another called Mablung. There are even some Green Elves from the easternmost part of Beleriand. The main language spoken at the party is Sindarin, because the Noldor have had an easier time learning it than the other Elves have had of learning Quenya. All the Elves are on good terms with each other, and everything is great for a while. The Noldor begin to think that maybe Fëanor was right about Middle-earth being a good place for them.
Another thirty years pass. Turgon (Fingon’s brother and a son of Fingolfin) meets up with Finrod (a son of Finarfin). Together, they travel southward on the River Sirion, just to get away for awhile. They sleep on the riverbank, and Ulmo (the Vala of water) sends them a dream. Neither of them remembers the dream, only that it was troubling, and neither realizes that they had the same dream. After that, they’re both burdened with a sense of unease. Troubling dreams can only mean one thing — Morgoth is going to become a problem again. Turgon and Finrod independently decide that it’s a good idea to prepare for the worst.
Finrod and Galadriel, his sister, are briefly guests of King Thingol in Doriath (being two of the few Noldor whom Thingol would allow past the magic wall). Finrod is very impressed by the majesty of Menegroth, the king’s underground palace. He wants his own underground palace just like it, and tells Thingol as much. Thingol could have said, “no, how dare you copy me,” but instead he tells Finrod about a secret place in his realm — there’s a gorge in the River Narog, the river to the west of the Sirion, where there’s a cave complex that Finrod can use to build a palace.
Enlisting the help of some Dwarves, Finrod builds his palace, Nargothrond. He gives the Dwarves treasures from Valinor to thank them. The Dwarves are so impressed with the jewels that they make Finrod a beautiful necklace called the Nauglamír, which is said to be the finest work of the Dwarves in the First Age. It’s set with many, many gemstones from Valinor, but it’s as light as spider silk. The Dwarves are also grateful to Finrod for giving them an excuse to build another cool cave palace. They give him an epithet in their own language, Felegund, which means “Hewer of Caves.” Only a really cool Elf appreciates caves so much that he asks for his own cave palace.

Finrod by _star热爱生活呀巴扎嘿
Galadriel decided to stay in Thingol’s court, instead of following her brother to Nargothrond. She happened to meet one of Thingol’s relatives, a certain Sinda named Celeborn, and fell in love with him. Staying with Celeborn gave Galadriel the opportunity to study at the feet of Melian herself. So, if you’re wondering where Galadriel gets her wisdom and power from, it’s because she learned directly from a Maia.
Meanwhile, Turgon is feeling homesick for Valinor. He remembers the city of Tirion on its hill, with its silver tree (not the Silver Tree, one of its descendants). When he returns home, Ulmo personally appears to him, and tells him to go to the Vale of Sirion. He finds a hidden valley surrounded by mountains, in the center of which is a hill. It’s the perfect place to establish a New Tirion.
Throughout all this, Morgoth has been carefully observing the Noldor’s activities, and judging their strength. As soon as the Noldor are too distracted by city-building to prepare for war, Morgoth strikes. The Orcs are still a lot weaker than the Elves. Fingolfin and Maedhros chase the new Orc army all the way back to Angband. They kill every last one, within sight of Angband’s gates. But remember, Morgoth is a Vala, and has more up his sleeve than simply Orc armies. He causes earthquakes, fires, and volcanic eruptions. The Elves realize that there’s only one thing to do: cut the threat off at its source. They lay siege to Angband, and this siege lasts a full four hundred years.

Angband by gresetdavid
The Orcs are so afraid of the Noldor that they don’t leave Angband. Fingolfin boasts that the only way Morgoth could score a point against them is if the Noldor commit treason amongst themselves, which sounds a lot like tempting fate. Despite his confidence, the siege is a failure. Four hundred years, and the Elves don’t get any closer to capturing Angband, let alone taking back the Silmarils. Morgoth can still send spies out the back way, because the Elves can’t climb the snowy Thangorodrim Mountains. He captures Elves alive, and terrifies them so much that they do his bidding without having to be forced. He also looks for opportunities to sew dissent amongst the Noldor. It worked once, so it can work again.
A hundred years into the siege, Morgoth tries to capture Fingolfin. He knows that Maedhros isn’t about to let himself get captured again, and taking out the king would be an advantageous move. So, Morgoth sends a bunch of Orcs to sneak towards the Elves’ camp using the back way, through the same frozen mountain pass that Fingolfin used to get into Middle-earth. Morgoth should know at this point that Orcs are no problem for Elves. Fingon notices the Orcs, and slaughters them. This battle doesn’t even count as one of the “great battles,” because there aren’t enough Orcs for it to be notable. After that, there’s an interlude of peace that lasts for many years.

Fingon by _star热爱生活呀巴扎嘿
Morgoth finally gets the memo that he’s not going to beat the Elves by throwing Orcs at them. So, he tries a new tactic: A fucking dragon! If you think Smaug is bad, he’s a little baby lizard in comparison to Morgoth’s dragons. This one is called Glaurung (“gold worm” in Sindarin), and it’s a fat worm-like thing with a mouth of sharp teeth and fire breath. Glaurung is a young dragon, so, he mostly just thrashes around destroying fields and so forth. But he sufficiently terrifies the Elves.

Glaurung by Vaejoun
Fingon isn’t afraid, though, and takes a band of archers to pummel Glaurung with arrows. Glaurung’s armored scales haven’t fully developed yet, so the arrows drive him crawling back into Angband. Fingon is endlessly praised by the Noldor for having defeated the dragon, and Morgoth is kicking himself for having shown his hand too soon.
After Glaurung’s defeat comes the Long Peace, which lasts two hundred years. In that time, the Elves have the opportunity to build beautiful cities and write books of lore and create other art. (This time is called the “Long Peace” because Morgoth doesn’t make any attacks, but presumably, the Siege of Angband is still going on.) The Noldor and Sindar also intermix, becoming more like one society, though the biological and cultural differences between them remain: The Noldor are still smarter and stronger, wiser, better warriors, and they like living in stone buildings. The Sindar have better singing voices, and are better musicians in general, and like living in the woods. Some Sindar are nomadic and wander around Beleriand, singing as they go.
*whew.* That’s it for this section.
Next part.
#the silmarillion#silm#the silm fandom#silmarillion#silm art#summary#the lord of the rings#lotr#feanor#fëanor#fingolfin#maedhros#fingon#finrod#thingol#the noldor#the sindar#morgoth#jrr tolkien#tolkien#middle earth#elves#tolkien elves#silm elves#beleriand#angband
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
In Israel, you’ll find a patchwork of different communities. Most Israeli Jews originate from Europe, North Africa and the Middle East, but some come from other regions, such as India.
According to the Indian Embassy in Tel Aviv, there are about 85,000 Jews of Indian origin in Israel — so Indian Jews make up just 1.2% of Israel’s Jewish population. This small community is divided into four groups: the Bene Israel from Maharashtra, the Cochin Jews from Kerala, the Baghdadi Jews from Kolkata, and the Bnei Menache from Mizoram and Manipur.
Although I grew up in the U.S., my mother’s family is from the Cochin Jewish community in Israel. I wanted to find out more about how this community is preserving our unique Jewish traditions from the South of India.
Many of these traditions are at a risk of dying out. For example, the language of the Cochin Jewish community is called Judeo-Malayalam. Today, this dialect has only a few dozen native speakers left (you can hear it spoken in this video).
According to legend, the first Jews arrived in Cochin during the time of King Solomon. The oldest physical evidence of their presence is a set of engraved copper plates dating from around 379-1000 CE, which were given to community leader Joseph Rabban by the Chera Perumal dynasty ruler of Kerala.
Jewish sailors originally arrived in Kodungallur (Cranganore), an ancient port city known as Shingly by Jews, before shifting to Cochin following a flood in 1341. These Jews became known as the Malabari Jewish community. After the expulsion of Jews from Spain in 1492, a group of Sephardic Jews also came to Cochin, and became known as the Paradesi (Foreign) Jews. The Malabari and Paradesi Jews historically lived separately and maintained their own traditions, although in modern times this division has become less important.
Today, the vast majority of Cochin Jews live in Israel. I spoke with several community members to learn about current projects in Israel to preserve Cochini Jewish culture.
Hadar Nehemya, a jazz musician and performer, runs a food delivery service sharing traditional Cochin Jewish recipes. Hadar learned the art of cooking from her mother, who learned it from her paternal grandmother.
Cooking her dishes from scratch and selling them at markets and for delivery, Hadar’s goal is to introduce Cochini cooking into the mainstream of Israeli culture. “Many Israelis don’t know much about Cochin Jewish culture. Maybe they met a Cochini person in the army,” she said. “But Indian food is popular in Israel, because Israelis love to visit India after they finish their army service.”
Cochin Jewish cuisine is similar to other types of South Indian cuisine, but also has influences from Iberian and Middle Eastern cooking. One example is pastel, pastries with a spicy filling that are similar to empanadas. Other staples include fish and egg curries, chicken stew, black-eyed pea stew, dosa (thin rice pancakes) and dishes cooked with coconut and mango.
Hadar’s favorite dishes to cook are idli and sambar, which are often eaten together. Idli is a type of savory rice cake, while sambar is a spiced lentil stew. Although Hadar says it’s difficult to maintain an Indian food business from an economic perspective, she’s passionate about cooking and enjoys creating homemade dishes with the right balance of spices.
Along with cooking, music is also important in Cochini culture. In most religious Jewish communities, women aren’t permitted to sing in front of men who aren’t their immediate relatives. However, this prohibition was not part of the Cochini tradition.
In the Cochin Jewish community, women have sung in Hebrew and Judeo-Malayalam for centuries. Piyyutim (liturgical poems) were sung in the synagogue or at people’s homes during holidays. Judeo-Malayalam folk songs were sung at weddings and special occasions, and the lyrics of these songs were recorded in notebooks to hand down to future generations. Later, many women also learned Zionist songs in preparation for moving to Israel. I have memories of my own grandmother singing these songs at home.
In recent years, audio recordings have been produced of Cochini songs, including a collection called “Mizmorim” (Psalms) featuring Hadar’s grandmother, Yekara Nehemya. Hadar then created her own version of one of the songs, “Yonati Ziv.”
Today, community leader Tova Aharon-Kastiel has organized a choir which meets once or twice a month at different locations. In the choir, Cochini and non-Cochini women, mostly aged 65-85, sing songs in Hebrew and Judeo-Malayalam. The older generation is eager for the younger generation to get involved, but since most younger Cochin Jews have a mixed background and are assimilated into mainstream Israeli culture, this is sometimes proving a challenge.
Still, many young Cochin Jews are eager to connect with their roots. The community maintains several Facebook groups, including one specifically geared towards the younger generation. The group description reads: “If you are a young Cochini, you surely know (at least partially) the wonderful heritage of our forefathers and mothers… the sad truth is that this heritage is currently on its way to pass from the world.”
Shlomo Gadot is the CEO of Inuitive, a semiconductor company, and is actively involved with Cochini community projects. His nephew, Ori, runs the Facebook group for the younger generation. Shlomo says events are regularly held at the Indian Embassy in Tel Aviv for young Cochinis. “Normally the embassy gives them their office in Tel Aviv, and they invite the young Cochini people to come there and do a trivia contest,” he said. “They do it twice a year, once at Hanukkah and once at Passover.”
According to Shlomo, the embassy also has initiatives to create connections between Indian and Israeli tech companies. “Sometimes they invite people to the ambassador’s house or office to see how they can create connections between Israeli and Indian companies,” he said. “They also have a program to bring young people to India to help them get to know India better.”
Anil Abraham is one of the few Cochin Jews with recent memories of life in India. Born in Jerusalem, his family returned to India when he was 8 years old, and he lived there until age 35 before migrating back to Israel. He says he found growing up Jewish in India difficult, but rewarding. “It was very difficult to move there from Israel and learn Malayalam,” he said. “But it was amazing to be part of the community and enjoy Cochini food prepared from scratch. We used to attend prayers in the Paradesi Synagogue, because right now there are fewer than 20 Jews in Kerala.”
Today, Anil runs tours of Kerala for the Cochin Jewish community and others. “The kids travel with their parents and grandparents to India,” he said. “That’s how our traditions are passed down.”
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ancient Semitic-Speaking Peoples

By Rafy - Own work, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=13256859
The ancient Semitic-speaking peoples lived in the MENA (Middle East and North Africa) region of the Afro-Eurasian continents. Some of these peoples include the Arabs, Arameans, Assyrians, Jews, and Samaritans. Proto-Semitic existed during the 4th millennium BCE and writing was developed by the mid-3rd millennium BCE. From there, the language developed into three identifiable language groups, East, Central, and South Semitic languages. The Eastern branch includes languages like Akkadian and Eblaite. The Central branch includes two sub branches of northwest, which includes Aramaic and Canaanite, and the southern branch, which inclues Arabic and Hebrew. Southern branch is further divided into southwestern, which includes Qatabanic and Minaic, and Southeastern, which includes Mehri and Harusi. Geographically, this language family covers from modern day Iraq through the Arabian Peninsula, and over to Ethiopia.

source: https://www.reddit.com/r/geography/comments/1ao5pfh/what_ecological_and_biological_effects_would_the/
Exactly where the Semitic-speaking peoples originated is still a question with possible locations being Mesopotamia, the Eastern Mediterranean including the Levant and/or Arabian Peninsula, Eritrea and Ethiopia, and North Africa. The most accepted theory points to the Levant around 3800 BCE where the dialects then languages spread out from there with groups like the Phoenicians, who were renown as traders and sailors along the Mediterranean coast. The dissenting theory is that since all five or more of the other Afroasiatic family languages originated in North or Nortwest Africa, that the Semitic languages originated there as well during the late Neolithic, perhaps during the Green Sahara, which made travel in the area by foot much easier.

By Msanzl - Own work, cf. Manuel Sanz Ledesma, 'Manual de lingüística semítica', ed. Bubok, Madrid 2012, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=30681320
During the Bronze Age, Semitic languages had spread over the Ancient Near East with the earliest written record found in Mesopotamia in around 2800 BCE by the Akkadian Empire, who adapted Sumerian cuneiform to their language. From there, writing moved into the Levant and Canaan and into the Sinai Peninsula and into Anatolia, dominating the area known as the Fertile Crescent. There is no currently known evidence of the Semitic languages being spoken in North Africa or in the Horn of Africa at this time. as the Akkadian Empire expanded through the Ancient Middle East. The Eblaites begin to appear in the historical record, as well. Their language is closely related to Akkadian and also used cuneiform as its writing system. Akkadian continued to appear in writing until the 1st century AD and cuneiform continued to be used about a century longer, though the still extant Assyrians still use some Akkadian grammatical features and words
West Semitic languages begin to appear in the Proto-Sinaitic alphabet that appeared around 1500 BCE, though there appears to be earlier uses of the alphabet. With Akkadian being used in the lingua franca in the area, most of the writing that remains is in Akkadian, so writing in other languages is much more sparse than those in Akkadian, but does become more available as the 2nd millennium BCE continues. There also appears to be some snobbery among those who speak Akkadian and had a higher level of technology against the Amorites, who they called the Martu with mentions in Akkadian saying 'he MAR.TU who know no grain… The MAR.TU who know no house nor town, the boors of the mountains… The MAR.TU who digs up truffles… who does not bend his knees (to cultivate the land), who eats raw meat, who has no house during his lifetime, who is not buried after death.' This difference in technology, however, has its origin with the Akkadian speaking peoples of the Old Assyrian Empire preventing those in northern Mesopotamia from participating in the activities they complain they don't do.

By Iry-Hor - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=34922151
A group of Canaanite-speaking peoples appear to have entered Egypt. They came to be known as the Hyksos by the Egyptians. They conquered Lower Egypt and became the 15th Dynasty, which ruled from approximately 1650-1550 BCE and were displaced by the Kush from Upper Egypt. They introduced technology, which included the war chariot, and intensive trade with the Canaanites. They also were recorded as having ransacked Egyptian temples and the pyramids for treasures.
The fall of the first Babylonian Empire in 1595 BCE allowed for about 300 years of other languages to develop, especially in the Levant and Canaan. Some of the people groups that developed their own language in the 14th century BCE, which were closely related to Ugaritic, a West Semitic language, included the Phoenicians, Moabites, Ammonites, and Israelites. Through the 13th to the 11th centuries BCE, multiple small states arose, including the Edomites, Hebrews (Israelites/Judeans/Samaritans), and Amalekites. These peoples spoke languages that were closely related to each other. The Philistines, who appeared in the 12th century BCE, appear to have been one of the Sea Peoples. There is little evidence of their language, but based on the pottery style they left behind, which was very similar to Mycenaen Greek pottery, their language was probably related to Indo-European rather than Proto-Sianitic.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
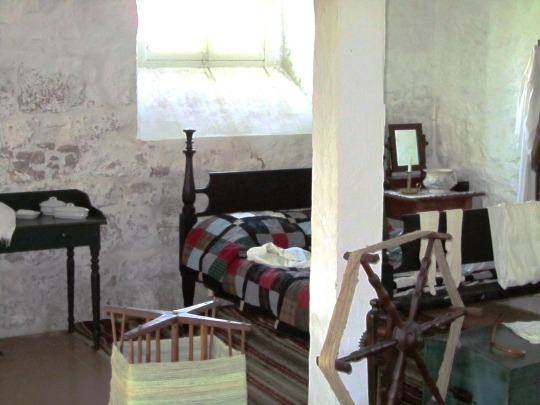












National Quilting Day
A quilt is a type of bed cover, traditionally composed of three layers of fiber, a woven cloth top, a layer of batting or wadding, and a woven back, combined using the technique of quilting. A quilt is distinguishable from other types of blankets because it is pieced together with several pieces of cloth.
National Quilting Day recognizes quiltmakers and their quilt-making abilities. The word ‘quilt’ comes from the Latin word ‘culcita,’ which means stuffed sack, it became adapted to the English language from the French word ‘cuilte.’
Quilting practices can be found in almost every area of the world and it is celebrated on the third Saturday in March every year. The National Quilting Association started National Quilting Day in 1991 and since then it has grown into a global celebration for all quilt lovers and makers.
History of National Quilting Day
Quilting refers to the technique of joining at least two fabric layers by stitches or ties. The quilting practice dates back as far as 3400 B.C. It was mainly a practical technique that provided physical protection and insulation. However, decorative elements were often also present and many quilts are now primarily art pieces.
In the United States, quiltmaking was common in the late 17th century and early years of the 18th century. In these times, only the wealthy had the time to practice quilting so it was done by only a few persons. Commercial blankets or woven coverlets were a more economical bed covering for most people unlike the colonial quilt bed covering which displayed the fine needlework of the maker, such as the Baltimore album quilts. Presently, quilting is now a popular hobby, with an estimated base of twenty-one million quilters.
The oldest example of a quilted piece is kept at the Saint Petersburg department of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Archaeology section. It is a linen carpet that was found in a Mongolian cave, between 100 B.C. and 200 A.D.
The origin of the quilting day can be traced to the Quilters Day Out, which was organized by the Kentucky Heritage Quilt Society in 1989 to celebrate the ancient tradition and its practice in the state of Kentucky. Two years later, this event became so popular that the National Quilting Association decided to declare an official holiday for quilting. From this day, the name changed from Quilters Day Out to National Quilting Day. Over the years, this event has attracted people to celebrate from all over the world and participate in helping to build and maintain the global heritage of quilting.
The first remnants of quilting were dated to 3400 B.C., showing that this art form had existed far into pre-history. They were traded extensively until sometime in the 12th century when these types of trade goods were returned from the Middle East by the Crusaders. Since then, it had become an integral part of the Colonial textile arts and one of the things they were well known for.
National Quilting Day timeline
1170 — 1800
The Birth of Pieced and Applique Quilts
During American Colonial times, quilts are known to be predominantly whole cloth quilts. Later on, pieced and applique quilts begin to appear.
1989
The Roots of Quilting Day
Quilters Day Out is first organized by the Kentucky Heritage Quilting Association in 1989, which later leads to the birth of National Quilting Day.
1991
The Dawn of National Quilting Day
In June, members of the National Quilting Association pass a resolution in Lincoln, Nebraska, for the celebration of National Quilting Day.
2001
Commemoration of the Demise
The National Quilt Museum is honored to host a collection of quilts from the 9/11 Memorial and Museum for the commemoration of the 20th anniversary of the September 11 attacks.
National Quilting Day FAQs
When do people celebrate National Quilting Day?
National Quilting Day is celebrated on the third Saturday in March annually.
What month is National Quilting Month?
National Quilting Month is celebrated during the month of March.
What are the types of quilts?
There are three types of quilts, namely patchwork quilts, applique quilts, and embroidered quilts.
How to Celebrate National Quilting Day
Hang quilts outdoors: On National Quilting Day, quilts are hung outside the homes to educate and inspire people to join in celebrating this ancient creative skill and as a sign that you recognize this event and that you are observing it.
Show your quilting skills: This holiday is a time to share your skills with others by offering to teach a simple quilt project A.M.D. showing them how it’s done. You can decide to teach this to your relatives/family members, schools, neighbors, friends, or a youth group.
Make it a service day: On this day, you can work on a quilt for your favorite cause — either national or local projects. You can also check departments and facilities like the police and fire departments, nursing facilities, or children’s services to see if they have a need for quilts.
5 Fascinating Facts About Quilting
The origin of the word: The word ‘quilt’ comes from the Latin word ‘culcita’, meaning a stuffed sack.
There is an identity behind a quilt: It would interest you to know that quiltmakers make the quilts in such a way that depicts the quality of their lives or custom. Think of it as a book of tradition where pieces of stories are sewed together.
A precious heritage: Apart from the professional quiltmakers, women of the old generation can make a traditional quilt and it is passed down from one generation to the other; from grandmother to mother and mother to daughter.
For armor protection: Medieval knights used quilted pads under their armors, to protect them from chaffing and to prevent the armor from rusting from sweat.
Interest for the husband: During the 19th century, it was customary for a woman to show her quilting skills to her new husband.
Why We Love National Quilting Day
It’s a day for fun: It is a day to share in the fun and appreciate the history of quilts; to share quilting stories, fabrics, and patterns.
It’s a time to reflect on the old times: Quilting is a practice that can be dated as far back as 3400 B.C. Quilting day allows us to appreciate this old-time art, understand the history, and value it, like a connection between the past and present, creativity and heritage.
It’s a day to understand its symbolism: Quilts often symbolize resourcefulness, as quilters use what resources are available to them to make a quilt covering. They also symbolize heritage.
#log cabin#Kings Landing Historical Settlement#New Brunswick#Canada#summer 2015#2012#original photography#tourist attraction#landmark#Lower Fort Garry National Historic Site of Canada#Manitoba#El Pueblo de Los Angeles Historical Monument#Los Angeles Plaza Historic District#Avila Adobe#National Quilting Day#NationalQuiltingDay#16 March 2024#third Saturday in March#Pennsylvania#2009#Amish Country#Lancaster County#British Columbia#travel#vacation#USA#architecture#Los Angeles
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
(Early Modern TTRPG anon)
After some search I found Soviet university textbooks about this period, so I guess it's good to have Russian as your first language sometimes. I am not sure how good they are because they were written in 1958, and like history is developing, but also Early Modern Europe is a period from which we literally had official and private archives this whole time, it's not like Ancient History where entire civilisations were uncovered less than a hundred of years ago (AFAIK the most recently discovered civilisation was found in '90s), so the foundation is probably sound.
While we are at it, I want to talk about my experience with history textbooks for Soviet Schools. I read a textbook that covered Ancient History and didn't see much difference with how I remember studying it except some Marxist speak here and there. Fool. All similarities that I saw were only because I spent tons of time studying history on my own. I tried to read modern textbook on the same time period and fucking couldn't (and I want to stress that textbooks here are obligated to follow the agenda from Ministry of Education and have to be approved for use, so like, you can't write anything that government doesn't approve of). If Soviet textbooks focused on Classical Antiquity then modern ones borderline ignore everything else. Civilisations of Middle East are described literally on 3 pages each, since its origin till the conquest of Alexander the Great. Yes, they fucking mixed all civilisations of Mesopotamia into one, both bronze and iron ones. In fact, difference between bronze age and iron age is literally not mentioned. Section on Egypt literally contains pop-cultural information about deities (they weren't literally animal-headed, and it doesn't even touch on absolute weirdness of different deities being aspects of one, though Soviet ones don't either). More space dedicated to pyramids then to Egyptian society, and honestly I get them, you need to be absolute fool to describe civilisation that lasted 3000 years as having one model of society.
And every second paragraph ends with "You can read about this in the Bible :)"
It's not only obnoxious, it's also chauvinistic because we have a Muslim minority. Not big, but textbooks for higher classes had additional sections about their history, so they had to at least pretend to care.
Fucking hell.
P.S.: I also found Braudel's Civilisation and Capitalism, it was published in USSR so it's probably at least not reactionary and you can read it in English, but I am afraid that it's too advanced for my cause.
(Also, to anyone who cares - the game is World of Dungeons. Look it up, it's ultra lite pbta game for D&D style adventures with 3 pages of rules. Don't look Advanced World of Dungeons, it's messy, better look Streets of Marienburg - that's the expanded version that I use)
Hello again, I don’t have much to add except that I love you and that this is so interesting to hear about. I’ve had my eye on a number of different fantasy pbta but never actually played one, I’ll check out Streets of Marienburg
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries that are no more: Ancient Carthage (814BC-146BC)
The state discussed in this post is one of the most famous and important in antiquity. Yet, it remains one of the most elusive and mysterious civilizations in world history because its own written records have been virtually erased with all contemporary written records coming from foreign sources that both praised and reviled its existence. However, it was influential for its model of government, its expansion of Mediterranean trade, its influence on models of economic production, naval exploration and for its military leaders whose tactical and strategic prowess influence warfare to the modern day and for its rivalry with the other emerging Mediterranean superpower of antiquity: Rome. A rivalry that is characterized as the quintessential clash of civilizations. This is Carthage.
Name: In its native language, the Phoenician dialect known in Latin as Punic, it was 𐤒𐤓𐤕𐤟𐤇𐤃𐤔𐤕, or annunciated as qrt-ḥdšt or Qart-Hardasht. This translates into English as "New City". In Latin it was known as Carthago or Karthago, the modern English pronunciation of Carthage comes by way of French.
Language: Carthage as a city-state and its empire more broadly held a cosmopolitan mixture of peoples and languages. However, the founders of Carthage and its ruling elite spoke Punic, a dialect of Phoenician associated with the city of Carthage which was founded by Phoenician colonists from the Levant. Punic was Phoenician in origin and became a distinct local dialect of Phoenician speakers in Carthage and other cities. These settlers founded colonies throughout North Africa and the Western Mediterranean. The Phoenician language and its dialects were from the Semitic language family native to the Middle East. It originated as a distinct dialect of the Canaanite peoples from who the Phoenicians and subsequently the Carthaginians descend from. The Canaanites also gave rise to the other Semitic speaking peoples such as the Israelites, Moabites and Ammonites among others. Modern Hebrew is said to be the extant language most similar to ancient Punic. In Carthage's empire there were also local varieties of Berber (Amazigh) languages spoken by the native Berbers who settled in North Africa. There were also local languages in Iberia (Spain and Portugal) from the Iberian and Celtic tribes settled there and the languages of native Sardinian and Balearic peoples as well. Additionally, ancient Greek was spoken by Greek colonists, mercenaries and traders who also settled within Carthage's empire and sphere of influence.
Territory: The city of Carthage is located in the environs of modern Tunis, capital of the modern state of Tunisia in North Africa. It was from this centrally located city founded by Phoenician colonists that their subsequent empire grew. The established contact and control with other Phoenician colonies in the area such as nearby Utica and eventually grew to control all of coastal North Africa from modern Morocco to western Libya. The modern states of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya were its core territory, with Tunisia being its heartland. It also included Malta, the western half of Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica's coastal regions, the Balearic Islands of Spain and the southeastern portions of Iberia, particularly the coastal areas with influence into parts of the interior and south of the Ebro River.
Symbols & Mottos: The symbols associated with the state of Carthage are often in reference to their pantheon of gods which were quite extensive but centered mostly around the Phoenician gods but also included Berber, Iberian and Greek influences within their pantheon as well. A military standard associated with Carthage includes a staff with a sun disc and topped with a crescent moon. Also, the sign of Tanit, a Phoenician goddess's whose symbol was found on Carthaginian ruins along with Phoenician ruins found back in the Phoenician colonists' homeland in the Levant (Lebanon, Israel and Syria). The sign of Tanit appears in many varieties but is usually found as a schematic like sketch of a person with a triangular base with a disc on top with horizontal lines then pointing upwards like raised arms.
Religion: With Phoenician settlers being the originators of Carthage its ruling elite, the primary state religion was their variety of the ancient Phoenician religion which was polytheistic and included many notable gods and goddesses from Tanit to Baal Hammon, Melqart and Astarte among others. Many of these gods found companions with the Greeks and indeed due to the interfacing with Greeks both through trade and war, some Greek gods would also be incorporated into the Carthaginian pantheon, though it remained distinctly Punic at its core. There also appears to be Berber (Libyan and Numidian) influences along with Sardinian and Iberian interfacing that both saw the spread of worship of the Punic/Phoenician deities with local influences likewise being adopted by the Carthaginians. Even some ancient Egyptian gods appear to be included in Carthaginian worship. This syncretism and tolerance reflect the cosmopolitan outlook and composition the Carthaginians had within their realm.
There were priests who maintained the temples and sanctuaries devoted to particular deities. Likewise, Carthaginians practiced everything from ritual banquets to funerary rites such as those in the Levant like disposing of the remains of the dead, feasts for the dead, ancestor worship and goods in the tombs of the dead, indicating belief in life after death. Cemeteries were often built outside the walls of Punic settlements and included stelae with inscriptions serving as grave markers. Carthaginians practiced both burial and cremation.
There does appear to be cases of animal sacrifice to appease the gods in Carthaginian society as well. This tended to follow very specific regulations and rules.
The most controversial topic of the Punic religion however appears to be the practice of child sacrifice. The sources for this we must bear in mind come from Greco-Roman writers that weren't known to actually witness the practice and from civilizations that had biases toward Carthage more broadly. Yet both Greek and Roman sources cite the Carthaginians as practicing child sacrifice in their religion. These sources sometimes do contradict one another in their specifics. Modern historians debate the extent of this practice and what are the contents found at the sites known as Tophet in urns with ashes that may come from human infants. The Greco-Roman sources state children were specifically killed for ritual purposes and killed in various manners and burned as offerings. Based on archaeological findings some historians take the position that the practice may have occurred but may have been relegated to the ritual cremation of infants who died of natural causes. Others uphold the Greco-Roman sources and other deny the practice at all, chalking it up as pure invention of biased sources from Greece and Rome. Because Carthage was destroyed by Rome in 146 BC and virtually all extant written sources on Carthage come from Roman and Greek sources, there doesn't appear to be any definitive answer to this practice's purported extent or even its existence. Modern archaeology can lend more nuance to the topic but a clear answer like much of what we know about Carthage and its society remains a mystery.
Currency: The basic coinage of Carthage was called the shekel which derived from its Phoenician antecedents. There were gold, silver and bronze coins found throughout Carthage's empire. Mints were found not only in North Africa but Sicily and Iberia. Coins depicted everything from date palm trees to famous soldiers and politicians both Carthaginian in origin like the Barcid family of Hannibal Barca and even Greek rulers such as Alexander the Great.
Population: At its peak the empire had probably 3.7-4.3 million people. The city of Carthage proper at its peak was anywhere 250,000-500,000 people.
Government: The basis of our understanding of Carthage's governance is limited and largely based on ancient Greek and Roman sources. Some of which write of it in disparaging terms and others praise it for its complexity and nuance.
The basic understand is that during the first few centuries of Carthage's existence it was probably a monarchy. However, the extent to which the kings ruled over Carthage is debated. The Phoenician city states from which Carthage descended, namely Tyre had nominal monarchs but who deferred to a council of advisors who helped craft policy and administer the law. It seems reasonable that Carthage followed this political model in its earliest stages with nominal monarchs who likewise consulted a council of advisors made up Carthaginian nobility to craft and administer policy. The degree to which kings of Carthage held power probably fluctuated.
Following the First Sicilian War against the Greek colonists on Sicily in 480 BC, the nature of Carthage's government changed gradually with a weakening of the monarchy. By the 300s BC Carthage was at its peak and best characterized as an oligarchic republic. It was noted to have numerous checks and balances on the branches of government, a vast and complex administrative state, high levels of public accountability and participation in civic duty. Aristotle the famed Greek philosopher wrote on Carthage in his treatise "Politics" as the only non-Greek polity to be represented in the work.
Carthage as a republic became ruled nominally by two simultaneously elected non-hereditary magistrates called sufetes or shophets. This position's title translates as "judges" and they are said to handle a mix of judicial and executive powers. How they were elected and who was eligible for this head of state position is not known. What is known is they were always from the oligarchic ruling class of Carthage and that they held annual terms. The Roman writer Livy states this was comparable to the Roman republican practice of electing two consuls for annual terms. They are said to have ruled jointly and likewise handled matters of state through the convening and presiding over the supreme consultative council known as Adirim (similar to the Roman Senate), submitting legislation to the popular assembly and adjudicating trials. The sufetes interestingly did not hold any military power as this was separated and reserved for military commanders with the generals reporting to the Carthaginian assembly in the Adirim.
The Adirim held about 30 members on the council and like senators in Rome were elected from the wealthy elite merchant families of Carthage. They administered the treasury, conducted foreign affairs and providing some control over military affairs. It is said matters of state required unanimous decision making to go into effect.
Carthage also had judicial assembly called the One-Hundred and Four. These judges provided oversight of the military and other politicians and bureaucrats within Carthage. As an example of Carthage's political checks and balances, the One-Hundred and Four had the power administer monetary fines or even the death penalty, sometimes by crucifixion on military or government officials found to have engaged in unbecoming behavior that went against the interest of the public. It also formed small committees to provide oversight on political matters.
Separate from these bodies also came numerous junior bureaucratic positions to held administer everything from tax collection, public works and the state treasury.
Carthage also contained at local levels trade unions, a popular assembly and town meetings. In matters where the sufetes and Adirim could not decide law in a unanimous manner a popular assembly was consulted to make a final determination. Whether this was a formal institution or ad hoc solution has never been determined.
Aristotle singled out the Carthaginian government as more meritocratic than its contemporary Greek counterparts. He also praised its complex balance of monarchical, aristocratic and democratic elements. Some other Greek writers went so far as to say it was the best form of government in existence at that time only equaled in the Greek world by Sparta. Meanwhile, Aristotle himself stated that Carthage had some form of constitution and found it superior to Sparta's.
The Greek historian Polybius writing for a Greco-Roman audience in his commentary on the Punic Wars between Rome and Carthage stated that Carthage had more democratic elements than Rome did and that the common people were on average given more say than Romans at the time. However, Polybius saw this as a detriment to Carthage during the Punic Wars, in his estimate too much bickering and infighting to gain a unanimous decision led to paralysis and indecision. Whereas he favored the Roman Senate's rules which were less democratic overall and therefore more decisive in determining important decisions at crucial moments such as in war.
Carthage's republican government appears to have been replicated in the colonies and territories throughout its empire with sufetes found at local colonial levels. There appears to be cooperation between Punic colonial officials and the local population under Carthaginian rule.
Carthage was primarily mercantile in its outlook. The control of trade commodities and goods throughout the Mediterranean was the basis for its economic development and always of primary concern. Hence the merchant class-oligarchy's vested interest in maintaining power.
Military: Carthage was a classic example of a maritime power. Its navy was its most important military branch in many ways. The navy was used to ensure control over the network of trade routes between the various parts of the Western and Central Mediterranean. It would win naval victories over its Greek and Roman rivals though it would ultimately face defeat by the Romans.
The navy was large in size for antiquity and benefitted from the Phoenician advent of serial production, the ancient equivalent of assembly line production which produced ships of good quality but in an efficient manner. They could maintain hundreds of ships at one time, even after their power dimmed with the rise of Rome.
The ethnic composition of the navy's sailors, oarsman, navigators and marine force was almost exclusively Phoenician. Given the Phoenicians long association with seafaring trade and navigation, the Carthaginians merely upheld this tradition including in warfare.
The army of Carthage, its land based military branch was also crucial in achieving its geopolitical goals. From the subjugation of rebellious tribes in North Africa and Iberia to battling the Greeks and Romans in foreign wars. In conjunction with the navy the ultimate goal was maintaining Carthage's control of trade routes and upholding its sphere of influence to maintain favorable conditions for said trade.
Due to the limited population of Phoenician colonists spread throughout the Carthaginian empire and given their traditional naval prowess, much of the army was not of ethnic Phoenician/Punic background. Instead, they relied on a multinational mix of auxiliaries and mercenaries to fill the armies ranks. There might be Phoenician officers and generals such as the famed Hannibal Barca and his relatives including his father Hamilcar and brothers Mago and Hasdrubal, but many other officers could be Greeks among others. The rank and file including Greek mercenaries fighting in the hoplite style, many Greek colonists from Sicily and Southern Italy, Berber infantry and cavalry, particular the light cavalry of Numidia famed for its fast-moving skirmishers armed with javelins and the Libyan infantry. Iberian infantry and cavalry of mixed Celtic and Iberian backgrounds. The famed light skirmisher infantry from the Balearic Islands who slung stones at their enemies were likewise part of the army. Also included in the army were Gallic (Celtic) infantry and cavalry from France and Italy, Sardinians (Nuragic) and Italic peoples such as Samnites, Lucanians, Etruscans and even some Latin peoples including Roman defectors could be found among Carthage's land army. The Phoenician rank and file in the army were usually colonists from other Punic settlements and not Carthage proper. The exception being the famed 3,000 strong Sacred Band of Carthage which were derived from the strongest and healthiest of Carthage's wealthiest families to fight as an elite special unit of the army. Armed and trained int the Greek hoplite style and phalanx formation.
The army also utilized African Forest elephants as a mobile force similar to a wrecking ball. These elephants provided a fearsome complement to the army and was famously used by Hannibal Barca in his crossing of the Alps to invade Roman Italy during the Second Punic War.
The major conflicts Carthage fought in its history were its colonial wars in North Africa against Berber tribes and kingdoms, Iberia and in Sicily first against the Greeks and later against its archrival Rome. The three Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome have been characterized by some historians as the ultimate and perhaps most important clash of civilizations in the ancient world and perhaps of all time. Ultimately, they would all end in Rome's favor and eventual destruction and razing of Carthage by Rome, ending Rome's biggest rival and leading to Roman supremacy over the Mediterranean basin for the next several centuries.
Economy: Economic concerns were of chief importance to the Carthaginians. Their empire was essentially a commercial one or rather an expansive and complex trade network with the state trying to aggressively uphold and expand its scope. Its origins lie with the Carthage's Phoenician roots. The Phoenicians based in the Levantine coast (mainly modern Lebanon, Israel and Syria) weren't one united people but rather a series of city states, with the most powerful being based on the coast. These included the cities of Byblos, Sidon and Tyre among the leading polities and all with an outward maritime trade orientation. The Phoenicians produced many goods and economic models that would be both enriching and influential on trade throughout the ancient world. This included purple dye for fabric, uncolored glass, wine production and Lebanese cedar for timber production and the serial production economic model.
Carthage was founded in modern Tunisia by Phoenician colonists from the city of Tyre (Lebanon) in the 9th century BC. They were not the first Phoenician colony in North Africa but they eventually rose to become the most aggressive and successful. In part this was due to its secure and strategic location. It soon became the leading trade center on the Western and Central Mediterranean. They controlled trade routes at sea and rose to prominence and domination among all the other Phoenician colonies setup in North Africa, Sicily, Malta, Sardinia and Iberia.
Mining for metals silver, lead, copper and tin were of crucial importance for the wealth of Carthage, in particular this motivated their expansion into Iberia. Additionally, the temperate and fertile climate of the Western Mediterranean lead to much wine production. They also traded in amber, timber, grains an food preservatives.
While mostly a maritime trade power, Carthage also had overland caravans to secure goods from the African interior and even the Middle East. Continual exploration for new and expanding trade routes and goods was also important for Carthage. Famed Carthaginian explorers of Punic origin included Himilco the Explorer who lived in the 6th and 5th centuries BC. He is said to have been the first Mediterranean sailor to have explored the Atlantic routes to Northwest Europe, visiting Portugal, France and the British Isles. Britain in particular was important to the ancient tin trade which was necessary in bronze production. Britain was known in the ancient world to the Carthaginians and Greeks as the Tin Isles.
Hanno the Navigator was said to have explore trade routes to western Africa. Reaching as far as modern Senegal and Cameroon,
Lifespan: Carthage was said to have been founded by Phoenician colonists from the city of Tyre circa the 9th century BC. A foundation legend raised from its founding. Namely the legend of Princess Dido from Tyre leading her fellow Phoenicians not as colonists looking for commercial benefits but political refuge from her dictator brother. According to legend Dido and her retinue arrived at Tunisia and tricked the local Berber king into grating them a sizable tract of land from which the core of what became the city of Carthage was founded.
The city was given the name by its settlers of Qart-Hadasht, which in the Phoenician language meant "New City". The year 814 BC is often cited as the approximate date of its founding.
Quickly Carthage made an association with and eventual domination of fellow Phoenician colonies in the area including Utica. Its favorable climate, arable land and strategic location were all crucial to Carthage's rapid growth and dominance of over other Phoenician colonies. It would expand to conquer lands ranging from the whole of North Africa from Morocco to Libya, the islands of Malta, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica and the Balearics and parts of the Iberian Peninsula over the coming centuries found themselves either under direct Carthaginian rule or favorable treaties incorporating the lands into its sphere of influence hence creating a trade network and empire, a classic example of a thalassocracy.
Initially, the Carthaginians paid a tribute and maintained contact to its mother city of Tyre back in Lebanon. However, this became an irregular occurrence due to Carthage's increasing independence due to its great distance from the Levant and the assertive character to its own local citizenry. Carthage began to see a mix of Phoenicians and local Berbers creating a unique Punic culture that synthesized the two cultures and ethnicities over time with the Phoenician dialect and culture remaining dominant but adaptable for its ability to incorporate other cultures. This was true as its sphere of influences expanded in the Mediterranean.
Carthage's independence was not only due to its relative distance from Tyre but due to the events back in Phoenicia. Various sieges from Babylonia and eventually later the Persian Achaemenid Empire conquered Phoenicia including Tyre circa 530-522BC. The subjugation of these lands reduced contact between the Carthaginian settlers and their Tyrian origins which had until that date sent a steady flow of colonists. While some flow of other Phoenicians would continue, the population would be buttressed by local native populaces and other Phoenician colonies rather than direct Tyrian migration.
The city of Carthage itself expanded over the centuries and created several distinct districts and architecture. At its peak in the 4th century BC, it contained a population between a quarter and half a million people. making it one of the world's largest and most prosperous cities at the time. The city had a mix of wealthy villas, apartment blocks six stories high, had warehouse and commercial districts, goods markets, a Greek style agora or public space, elaborate gardens. temples to various gods, various government buildings and a unique double harbor known as the cothon, which became the physical feature along with the Byrsa hill most associated with Carthage. The cothon featured an outer commercial harbor and military inner harbor with ship warehouses on a man-made island from which ship repairs, construction and maintenance could be addressed through its serial production. The Byrsa hill was the central district of Carthage which contained important temples, it had stair way avenues which were relatively wide for traffic, whereas most of the city's routes had narrow winding paths to navigate. The city was said to have triple walls for defenses, a shorter outer wall made of either stone or wood, followed by a ditch, a second taller stone wall 5 meters thick, a second ditch and a third stone wall 10 meters thick and with armed towers able to hold a force of over 20,000 troops.
In 509 BC it signed its first treaty with Rome, its eventual rival which at the time was the inferior power still clamoring for power on the Italian peninsula. The treaty was meant to demarcate their respective spheres of influence. From 580-265 BC, the Carthaginians found themselves in a series of wars with the Greek colonies of Sicily and Southern Italy. Namely, the city state of Syracuse which was the principal Greek settlement on Sicily.
These wars were back and forth in nature, marked by victory and defeat on land and sea for both sides. Eventually Carthage would retain control over the western half of Sicily until its loss of control in the Punic Wars with Rome. The Sicilian Wars also saw the gradual weakening of the kings of Carthage and its transition to an oligarchic republic (see government section).
The Punic Wars (264-146 BC) began almost by accident with neither Rome nor Carthage initially planning a direct confrontation with the other. The city of Messana (Messina) in Sicily found itself in the 260s BC under the control of a group of Italian mercenaries who had previously served the tyrant (king) of Syracuse who had died in 280 BC. These independent mercenaries were a threat to both Carthage and Syracuse's interests on Sicily. These mercenaries named the Mamertimes (Sons of Mars) divided into two factions, over the issue of the new Syracuse tyrant Hiero II's planned retaking of Messana. One faction advocating a Carthaginian intervention to take charge of the city's security and the other advocating for Roman intervention from the Italian peninsula. Carthage arrived first with a land garrison and naval fleet in the harbor. The Roman Senate was reluctant to assist the mercenaries but recognized the potential threat a permanent presence of Carthaginians in Messana and its location on the narrow Straits of Messina between Sicily and Italian mainland could pose on Roman trade and security. It advocated sending an expeditionary force to retake Messana to eject the Carthaginians. The attack triggered the first Punic War between the two powers. It turned into a quarter century struggle that was marked by intense fighting mostly on Sicily.
The First Punic War was ultimately a Roman victory that ended Carthage's presence on Sicily. It also saw Roman advances in naval technology such as the corvus to help board Carthaginian ships. Hitherto the Romans had little naval strength relative to Carthage but its innovations in naval warfare proved crucial in undermining Carthage's longstanding naval superiority. Meanwhile on land, despite the back-and-forth nature of the battles, the Roman army's tactical flexibility often proved superior to Carthage which after 23 exhausting years agreed to peace. It gave up control of Sicily to Rome (aside from Syracuse) and paid a tribute over the course of 10 years.
Rome also after the war used Carthage's distraction against a Libyan rebellion in the Truceless War to take control of Sardinia and Corsica in 238 BC.
To compensate for the loss of territory on Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica, the Carthaginians under Hamilcar Barca tried to expand its territory in Iberia against Celtic and Iberian tribes especially to profit from increased mining production. They also gained new manpower and agricultural production to boost their economy and military again. They also had a standing agreement with Rome to not intrude north or south of the Ebro River respectively. However, an Iberian city of Saguntum south of the Ebro had an agreement with the Romans. This upset the balance of power established with Carthage in Iberia. Hamilcar Barca's son Hannibal now in charge of the Carthaginian army in Iberia an avowed enemy of Rome, besieged Saguntum which he took in 8 months. This is turn led to Rome's declaration of war, starting the Second Punic War which lasted for the next 17 years.
In one of the most famous military campaigns of all time, Hannibal and his army complemented by Carthaginians, Numidians, Celts, Iberians crossed the Alps and invaded Italy, taking the war to Rome's home territory. Hannibal showing his tactical prowess would defeat Roman armies repeatedly on their own territory most notably at the Battle of Cannae in 216 BC. Many Italian cities that had been incorporated into Roman rule over the previous centuries rose up to join Hannibal against Rome. However, Hannibal never had sufficient strength to directly besiege Rome. Rome was constantly tested by Hannibal's victories over the next 13 years in Italy, but they refused to surrender and adopted an attritional strategy, and this wore down Hannibal by gradually retaking Italian cities allied to him if not able to defeat him directly. Likewise, they repelled Carthage's attempts to reinforce him in Italy. They also faced mixed success gradually conquering Iberia from the Carthaginians. Finally, an invasion of Tunisia forced Carthage to recall Hannibal back to North Africa to defend the capital from a Roman assault. He met the Romans in the Battle of Zama in 202 BC which resulted in a Roman victory over Hannibal himself at once.
Hannibal advocated for the government of Carthage to negotiate a treaty with Rome which it did. Its terms were harsh. A stripping of all overseas possessions of Carthage in Iberia and elsewhere including some African territories. A large punitive indemnity to paid to Rome over 50 years. A reduction of Carthage's navy ten warships, a ban on Carthage's use of war elephants. A prohibition on Carthage being able to fight war outside of Africa and any war it wages in Africa must require Rome's express permission.
Hannibal eventually became a sufete in Carthage and worked to reform the government of Carthage and stamp out corruption so as to ensure its ability to pay Rome its due from the treaty and rebuild its economy. Indeed, Hannibal was somewhat successful in his regards and Carthage's economy was somewhat rebounding but facing pressure from Rome and enemies in the local government, he went into voluntary exile in service to Greek states opposed to Roman expansion in the east. He died in exile under murky circumstances variously described as a suicide or murder.
The Third Punic War 149-146BC began will Carthage went to war in Africa with Berbers who were raiding its territory and without Rome's permission, this was used a pretext to attack Carthage itself by Rome for violating its treaty from the previous war. The third and final Punic War was characterized by a three-year siege of Carthage. Ultimately, the Romans after much pressure on both sides broke through its triple walls and assaulted Carthage in street-by-street fighting. The city was razed to the ground, much of its population killed by angered Roman troops. 50,000 Carthaginians were enslaved and sent elsewhere through the Roman Republic's empire. Carthage was no more as an independent political entity after 146 BC. A century later, Rome rebuilt the city on its ruins as part of its empire and it remained an important city within the Roman Empire until the fall of the Western half of the empire where it fell to the Germanic barbarians the Vandals who had their capital in Carthage, it was reclaimed by the Easter Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) by the forces of Belisarius in service to Justinian I. Carthage would face a final destruction as a Roman city when the Arabs of the Umayyad Caliphate destroyed the city in the year 698 AD. It never rose as a city again, instead its ruins remain part of the suburbs or the modern city of Tunis, capital of Tunisia.
Carthage despite its being steeped in legend and mystery remains worthy of study as one of the undeniably great civilizations of antiquity. A fact recognized by its contemporaries whether they wrote of it a complimentary fashion or with contempt, its power, wealth and influence was immense enough to engender scholarly study and reflection at the time. It is for these contemporary recognitions whether positive or negative and absence of surviving self-records that many continue its study into the modern age. Particularly its opposition to Rome and the perception by Rome that it was a worthy rival that needed complete annihilation, especially given Carthage's ability to stand up to Rome in a way no other power really could at its peak.
The more Carthage is analyzed both by its contemporary foreign commentators with the surviving archaeological and fragmentary historical record, the more nuance can be shed on the complexity of the civilization and influence it had on world history. Its opposition to Rome might be its most noted aspect but it shouldn't overshadow how else Carthage influenced the world. From its complex style of government and network of commercial imperialism that presaged future thalassocracies such as the Italian republics of the Middle Ages like Venice and Genoa and how it produced economic production models which influenced Rome and Greece and subsequently other areas of the world, they carried that influence on to. Likewise, another legacy of Carthage was how it helped build an ancient iteration of a globalized economy, shrinking the gap between the long distances of the ancient Mediterranean world by linking disparate geographies and peoples under a common commercial interest. In this commercial pursuit it also revealed itself to have both a distinct dominant culture but one that was not intolerant or unable to accommodate and absorb other cultural influences. In many ways ancient Carthage by way of its influence on Greece and Rome and their own influences give us glimpses into how its existence served as a precursor to the modern world we inhabit.










#history#military history#ancient history#ancient world#ancient ruins#ancient carthage#carthage#ancient rome#ancient greece#tunisia#iberia#hannibal#scipio africanus#ancient phoenicia#phoenician#punic wars#sardinia#sicily#corsica#malta#balearic
9 notes
·
View notes