#iot embedded system
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What is the difference between IoT and embedded systems?
The rapid advancement of technology has led to a merging of boundaries between different sectors. This convergence is particularly noticeable in the realm of IoT (Internet of Things) embedded systems, where the terms "IoT" and "embedded system" are often used interchangeably. However, it's important to recognize that embedded systems and IoT are distinct concepts, even though they share some similarities.
Embedded systems have been in existence since as early as 1965 when Autonetics, a company, created a small computer for use in a missile guidance system. These embedded systems are essentially standalone devices designed with a specific, dedicated function in mind. On the other hand, an IoT embedded system is an embedded system that possesses the added capability of connecting to the internet, enabling communication with other IoT embedded systems.
In our daily lives, we are surrounded by IoT embedded systems, including devices such as set-top boxes, Point-of-Sale (POS) terminals, various medical devices, "smart" appliances like refrigerators, bicycles, fitness trackers, and even parking meters.
In the following discussion, we will delve into the intricacies of embedded systems designed for IoT devices. We will explore what defines an embedded system for IoT, its capabilities, and practical applications of embedding IoT functionality into these systems.
The key distinction between IoT (Internet of Things) and embedded systems boils down to one crucial factor: connectivity. Even an embedded system, like a pacemaker, can be transformed into an IoT embedded system when it gains the ability to communicate with the external world, such as sending heart-rate data to a central database.
Another distinguishing feature is that IoT encompasses a broader category of devices representing the interconnected world, whereas an embedded system pertains specifically to the hardware within these devices.
The fundamental difference between an embedded operating system and an IoT operating system lies in the necessity for IoT systems to support connectivity. The capability of IoT devices to network and communicate sets apart plain embedded systems from their IoT counterparts.
In every IoT scenario, there's an embedded system at its core, which is why the term "IoT embedded system" is used. Initially, there exists an embedded system, and then additional features are integrated to transform it into an IoT device.
Embedded systems can be remarkably sophisticated, such as robotic systems used in manufacturing or data warehouses. However, their function as pure embedded systems remains limited to their specific purpose until they acquire the ability to communicate and establish connectivity with other IoT embedded systems.
Therefore, the primary distinction between an embedded system and an IoT embedded system hinges on the latter's capacity for communication and connectivity.
0 notes
Text
https://electronicsbuzz.in/altium-and-aws-collaborate-to-equip-indias-next-generation-of-engineers/
#Altium#nextgeneration#cloudcomputing#digitaltransformation#embedded systems#IoT#ElectronicsDesign#CloudComputing#FutureEngineers#EdTech#powerelectronics#powermanagement#powersemiconductor
0 notes
Text
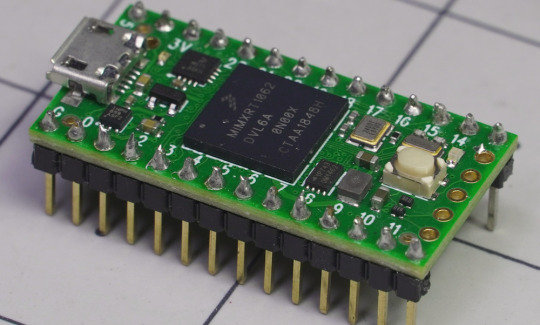
The Teensy Series of Processor Modules: A Versatile Platform for Embedded Systems
The Teensy series of processor modules is a family of compact, high-performance microcontroller boards developed by PJRC. These boards are widely recognized for their small form factor, powerful processing capabilities, and extensive I/O support, making them an ideal choice for a variety of embedded systems applications, including robotics, audio processing, and IoT (Internet of Things) projects.
#ARM Cortex#Audio Processing#CAN FD#Classical CAN#Embedded Systems#Ethernet#internet of things#IoT#Microcontroller#Robotics#Teensy
0 notes
Text
Embedded Systems: Driving Innovation in Technology
Embedded systems are specialized computing systems designed to perform dedicated functions within larger devices or applications. These systems integrate hardware and software components to execute tasks with precision, reliability, and efficiency. They are embedded in devices ranging from household appliances like washing machines and microwaves to complex industrial machines, medical equipment, and automotive systems.

An embedded system's core lies a microcontroller or microprocessor, which controls and processes data. Sensors, actuators, and communication interfaces are often part of the system, enabling it to interact with the physical environment. For instance, in a smart thermostat, an embedded system monitors temperature, processes user inputs, and adjusts heating or cooling accordingly.
Embedded systems are valued for their compact size, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness. They are tailored for real-time operations, ensuring quick and accurate responses to specific tasks. Industries such as automotive, healthcare, telecommunications, and consumer electronics heavily rely on these systems to innovate and improve product functionality.
As technology advances, embedded systems are becoming more sophisticated, incorporating artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, and advanced sensors. These developments are paving the way for smarter devices and systems, transforming how we live and work.
In a world increasingly driven by automation and smart technology, embedded systems play a crucial role in shaping the future of innovation.
#Embedded Systems#Microcontroller Technology#Real-Time Systems#IoT and Embedded Systems#Embedded Software Development#Embedded Hardware Design#Embedded System Applications
0 notes
Text
youtube
onsemi: Getting Started with CEM102EVB and RSL15
https://www.futureelectronics.com/resources/featured-products/onsemi-cem102-analog-front-end . Get started with CEM102 EVB, including what software you need, building your first application, and monitoring current value. https://youtu.be/-k6U8iPUmBE
#future electronics#WT#onsemi#CEM102EVB#RSL15#onsemi RSL15#Embedded Systems#Wireless Connectivity#BLE5#Evaluation Board#Development Kit#IoT Devices#Youtube
0 notes
Text
How ONVIF Cameras Are Shaping the Future of Smart Building Surveillance

As technology continues to evolve, smart buildings are becoming more advanced, with enhanced security systems being a top priority. One of the key innovations driving this transformation is the implementation of ONVIF cameras. These cameras not only provide high-definition video surveillance but also ensure interoperability across various security systems, making them a cornerstone for the future of smart building surveillance. This blog will explore how ONVIF cameras are revolutionizing the way we approach security in modern infrastructure and the long-term impact they are set to have on building management.
What Are ONVIF Cameras?
ONVIF (Open Network Video Interface Forum) is a global standardization initiative that allows IP-based security products to communicate seamlessly with each other, regardless of manufacturer. The ONVIF protocol ensures that cameras, recorders, and other surveillance equipment from different brands can work together efficiently within a unified system. ONVIF cameras are designed to meet this standard, offering a reliable and flexible solution for building surveillance.
These cameras come equipped with advanced features, such as high-definition video, motion detection, remote access, and cloud-based storage integration. As a result, ONVIF cameras are becoming an essential component in the security infrastructure of smart buildings.
The Importance of Interoperability in Smart Building Surveillance
One of the most significant advantages of ONVIF cameras is their interoperability. Unlike traditional security systems, which often require all components to come from the same manufacturer, ONVIF cameras allow building owners and security professionals to mix and match products from various brands. This opens up a wide range of options for surveillance system configurations, providing greater flexibility in system design and management.
In a smart building, multiple systems—such as lighting, HVAC, fire safety, and security—are integrated to work seamlessly together. ONVIF cameras play a pivotal role in this ecosystem by ensuring that video surveillance is not isolated but rather part of the broader building management network. For example, an ONVIF camera can work in conjunction with a building's alarm system, triggering notifications to security personnel when unusual activity is detected. This integrated approach enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the building’s security measures.
Enhancing Security with High-Quality Video Surveillance
The demand for high-quality video surveillance is increasing, especially in smart buildings that rely on video footage for security, access control, and monitoring. ONVIF cameras excel in providing high-definition video quality, which is critical for identifying faces, license plates, and other key details. This level of detail is necessary for building management teams to respond quickly to potential security threats.
With features like remote access, ONVIF cameras enable building managers and security teams to monitor live footage from anywhere in the world via smartphones, tablets, or computers. This real-time access allows for faster decision-making, ensuring that any suspicious activity is addressed immediately. Moreover, many ONVIF cameras come with advanced analytics, such as facial recognition and motion detection, which add an extra layer of intelligence to the security system.
Cost-Efficiency and Scalability
Another key benefit of ONVIF cameras is their cost-efficiency and scalability. Traditional security systems often come with high installation and maintenance costs, particularly when expanding or upgrading the system. ONVIF cameras, by contrast, offer a more affordable and flexible solution. Since the cameras adhere to a standardized protocol, building managers can integrate them into existing security infrastructures without the need for extensive reconfigurations.
Scalability is also a significant advantage of ONVIF cameras. As the needs of a smart building evolve, additional cameras and devices can be easily integrated into the system. Whether a building is undergoing renovations or expanding to accommodate more tenants, ONVIF cameras provide the flexibility to scale the security system without the need for a complete overhaul. This makes them an ideal solution for buildings of all sizes, from small office complexes to large commercial properties.
The Role of Cloud-Based Storage in Smart Building Surveillance
Cloud-based storage is becoming increasingly important in smart building surveillance. With ONVIF cameras, video footage can be securely stored in the cloud, providing numerous benefits over traditional on-site storage solutions. Cloud storage offers scalable storage capacity, remote access, and reduced hardware costs, making it an attractive option for building managers.
Moreover, cloud-based storage allows for the easy retrieval and sharing of footage, which is especially important in case of incidents that require investigation or legal proceedings. With ONVIF cameras integrated into the cloud, security teams can store vast amounts of video data without the need for expensive on-premises servers or data centers. This not only reduces costs but also enhances the overall flexibility and accessibility of the surveillance system.
Future Trends in ONVIF Camera Technology
The future of ONVIF cameras in smart building surveillance is promising. As technology advances, ONVIF cameras are expected to become even more sophisticated, offering features like 4K video resolution, enhanced low-light performance, and improved artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. AI-powered cameras will be able to detect and analyze patterns in real-time, such as identifying unusual behavior or predicting security threats before they occur.
Additionally, the integration of ONVIF cameras with other smart building systems, such as lighting and HVAC, will create even more advanced and efficient surveillance solutions. For example, cameras may be able to adjust the lighting in a building based on motion detection, improving both security and energy efficiency.
As the demand for smart buildings continues to grow, ONVIF cameras will play a crucial role in shaping the future of building security. With their ability to deliver high-quality video, seamless integration with other systems, and scalability, ONVIF cameras are poised to be a key technology in the development of intelligent, secure, and efficient buildings.
Take Your Building Security to the Next Level
Investing in ONVIF cameras is an investment in the future of your smart building's security infrastructure. With the benefits of interoperability, high-quality video surveillance, scalability, and cloud-based storage, ONVIF cameras are a smart choice for any building manager looking to enhance security.
Ready to future-proof your building? Get in touch with our team of experts to explore how ONVIF cameras can transform your security system today.
0 notes
Text
GateFi 6 Channel Powered by ESP32: The Future of IoT Connectivity with 4G
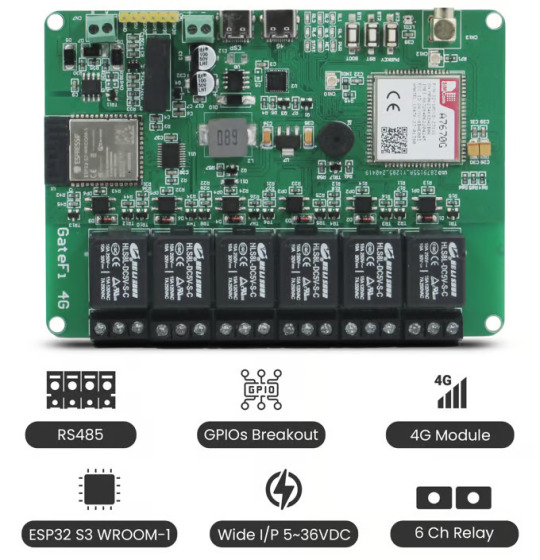
The rapidly advancing world of IoT (Internet of Things) and automation calls for devices that offer robust, flexible, and high-performance capabilities. The GateFi 6 Channel Powered by ESP32 with 4G Connectivity Microcontroller stands as a powerful solution for these needs, designed for industrial and commercial applications that demand reliable control, remote access, and seamless communication.
In this post, we will delve into the key features and capabilities that make the GateFi 6 Channel ESP32 S3 WROOM-1 an ideal choice for building smart systems with efficient relay control, fast connectivity, and advanced communication options.
What is GateFi 6 Channel Powered by ESP32 with 4G Connectivity?
The GateFi 6 Channel is a microcontroller designed to offer versatile and high-performance solutions for a wide range of IoT applications. Powered by the robust ESP32, a popular microcontroller that integrates Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, the GateFi 6 Channel is further enhanced with 4G connectivity. This combination ensures that your devices have seamless communication over the internet, even in areas where traditional Wi-Fi infrastructure might not be available or reliable.
This device can handle six independent channels simultaneously, making it ideal for tasks that require multiple communication points or data collection from various sensors, devices, or systems. The ESP32 ensures efficient processing and connectivity, while the 4G module guarantees that data can be transferred quickly and reliably over mobile networks.
Key Features
ESP32 S3 WROOM-1 Microcontroller: The ESP32 microcontroller is the heart of the GateFi 6 Channel. It provides a high processing power with dual-core capabilities, enabling fast data processing and communication. Additionally, the ESP32's Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support offer plenty of flexibility in local wireless communication.
6-Channel Relays with Optically Isolated Circuits: Comes equipped with 6 relay channels, which provide the ability to control a wide range of devices such as motors, alarms, or industrial machinery. These relays are optically isolated, offering protection against electrical surges and ensuring that high-voltage circuits are safely separated from the sensitive low-voltage control system. This isolation increases the reliability and longevity of your equipment, particularly in industrial applications where power spikes are common.
4G Connectivity with A7670G Module: The A7670G module provides 4G LTE connectivity, ensuring fast data transmission speeds even in remote areas with poor Wi-Fi coverage. This feature is perfect for applications like remote monitoring, data collection, and control over large distances. With the A7670G module, you can be confident in maintaining stable and fast communication, even in environments where traditional internet infrastructure might be lacking.
Visual and Audio Alerts: RGB WS2812 LED & Buzzer: The GateFi 6 Channel includes both RGB WS2812 LED and a buzzer for visual and audio alerts. The WS2812 LEDs can be programmed to display a variety of colors to indicate system status or trigger alerts. The buzzer, on the other hand, provides a sound notification for critical events, system errors, or triggered alarms. Together, these features ensure that operators and users are immediately informed about the state of the system.
Wide Voltage Range: 5V to 36V DC: Offers a flexible voltage range from 5V to 36V DC, making it suitable for various applications in both consumer and industrial settings. This wide input range means that the system can be integrated into a wide array of environments, from low-power consumer applications to high-voltage industrial equipment, without the need for additional power regulation.
RS485 Communication for Industrial Integration: The GateFi 6 Channel microcontroller includes RS485 communication support, enabling it to connect and communicate with other industrial equipment, sensors, or controllers over long distances. Whether it’s a smart factory, building automation system, or remote asset management, RS485 ensures reliable communication between devices even in noisy environments.
Interface Options: Dual Type C Ports: Offers two Type C ports—one for programming and one for 4G control. The Type C interface is becoming the industry standard due to its fast data transfer speed and reversible connector, making it easier to connect the system to various devices.
Connectivity: 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5 (LE): Is well-equipped with 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5 (LE) for local wireless communication. Whether you need to control the system through a mobile app, communicate with nearby devices, or connect to a cloud platform, the combination of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5 (LE) ensures a seamless and flexible communication experience.
Applications for GateFi 6 Channel Powered by ESP32
Industrial Automation
Smart Homes & Building Automation
Remote Monitoring & Control
Security Systems
Conclusion
The GateFi 6 Channel Powered by ESP32 by SB Components with 4G connectivity is a revolutionary device that brings powerful features to both industrial and residential automation. With its robust microcontroller, versatile relay channels, easy programming interface, and extensive connectivity options, the GateFi 6 Channel offers everything you need for efficient control and monitoring of various devices and systems.
Whether you’re upgrading your existing infrastructure or starting a new automation project, the GateFi 6 Channel is a solid investment for a smarter, more connected world.
#iot applications#iot#4g connectivity#gatefi6#innovation#relay board#electronics#technology#embedded systems#microcontrollers
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding Embedded Computing Systems and their Role in the Modern World
Embedded systems are specialized computer systems designed to perform dedicated functions within larger mechanical or electrical systems. Unlike general-purpose computers like laptops and desktop PCs, embedded systems are designed to operate on specific tasks and are not easily reprogrammable for other uses. Embedded System Hardware At the core of any embedded system is a microcontroller or microprocessor chip that acts as the processing brain. This chip contains the CPU along with RAM, ROM, I/O ports and other components integrated onto a single chip. Peripherals like sensors, displays, network ports etc. are connected to the microcontroller through its input/output ports. Embedded systems also contain supporting hardware like power supply circuits, timing crystal oscillators etc. Operating Systems for Embedded Devices While general purpose computers run full featured operating systems like Windows, Linux or MacOS, embedded systems commonly use specialized Real Time Operating Systems (RTOS). RTOS are lean and efficient kernels optimized for real-time processing with minimal overhead. Popular RTOS include FreeRTOS, QNX, VxWorks etc. Some simple devices run without an OS, accessing hardware directly via initialization code. Programming Embedded Systems Embedded Computing System are programmed using low level languages like C and C++ for maximum efficiency and control over hardware. Assembler language is also used in some applications. Programmers need expertise in Microcontroller architecture, peripherals, memory management etc. Tools include compilers, linkers, simulators and debuggers tailored for embedded development. Applications of Embedded Computing Embedded systems have revolutionized various industries by bringing intelligence and connectivity to everyday devices. Some key application areas include: Get more insights on Embedded Computing
Unlock More Insights—Explore the Report in the Language You Prefer
French
German
Italian
Russian
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Portuguese
Alice Mutum is a seasoned senior content editor at Coherent Market Insights, leveraging extensive expertise gained from her previous role as a content writer. With seven years in content development, Alice masterfully employs SEO best practices and cutting-edge digital marketing strategies to craft high-ranking, impactful content. As an editor, she meticulously ensures flawless grammar and punctuation, precise data accuracy, and perfect alignment with audience needs in every research report. Alice's dedication to excellence and her strategic approach to content make her an invaluable asset in the world of market insights.
(LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/alice-mutum-3b247b137 )
#Embedded Computing#Embedded Systems#Microcontrollers#Embedded Software#Iot#Embedded Hardware#Embedded Programming#Edge Computing#Embedded Applications#Industrial Automation
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Tips for Learning IoT and AI

As we navigate the evolving landscapes of IoT and AI, it’s essential we establish a strong foundation in programming languages like Python and Java. Engaging in hands-on projects not only solidifies our understanding but also bridges the gap between theory and practice. By connecting with online communities, we can share insights and resources that enhance our learning. However, staying updated on industry trends and exploring real-world case studies are equally crucial. So, what are the specific strategies we can employ to maximize our efforts in these areas?
Build a Strong Programming Foundation

While we dive into the realms of IoT and AI, it’s crucial to build a strong programming foundation. Having solid programming skills not only aids in understanding complex algorithms but also equips us to handle data effectively. We should start by mastering languages like Python and Java, as they’re widely used in both fields.
Data analysis is equally important, so familiarizing ourselves with libraries like Pandas and NumPy will enhance our ability to manipulate and interpret data.
Next, we need to define clear objectives for our projects. Establishing SMART goals helps us stay focused and measure our progress. Identifying relevant data sources is essential too—both internal and external—ensuring we gather high-quality data for training AI models.
As we collect data, let’s pay attention to cleaning and preprocessing techniques, as these steps significantly impact the performance of our models.
Lastly, we should engage with online communities and forums. Collaborating with peers not only enriches our learning experience but also exposes us to diverse perspectives.
Engage in Hands-On Projects

Engaging in hands-on projects is one of the most effective ways to deepen our understanding of IoT and AI. By applying theoretical knowledge, we can see how these concepts play out in real-world scenarios.
Let’s start by building small projects that incorporate IoT devices, like using sensors to track environmental conditions or automating tasks within our homes. This practical application helps us grasp the mechanics behind these technologies.
As we progress, we can explore more complex setups, such as creating smart classrooms. Imagine using IoT-enabled projectors and interactive whiteboards to enhance collaborative learning. These projects not only solidify our skills but also demonstrate the power of IoT in educational environments.
Moreover, we shouldn’t shy away from experimenting with AI algorithms. By developing simple machine learning models, we can analyze data and gain insights into how AI interprets information. This hands-on experience encourages creativity and problem-solving, essential skills in this evolving field.
Ultimately, engaging in hands-on projects empowers us to bridge the gap between theory and practice, making our journey in IoT and AI both exciting and impactful.
Let’s dive in and start building!
Join Online Communities

In today’s digital age, joining online communities can significantly enhance our learning experience in IoT and AI. These platforms provide exclusive access to structured courses and resources that cater to our specific learning needs.
We can participate in live learning sessions with top educators, allowing us to interact directly with experts and fellow learners.
Networking opportunities abound within these communities. We can connect with diverse individuals who share our interests, fostering collaboration and support.
Engaging in discussions and exclusive chat groups enriches our understanding and exposes us to different perspectives, greatly benefiting our learning journey.
Moreover, many online communities offer certification upon course completion, which we can showcase on platforms like LinkedIn. This recognition enhances our professional credibility and supports our career advancement.
Stay Updated on Trends

Staying on top of trends in IoT and AI is essential for anyone looking to thrive in these rapidly evolving fields. We need to recognize the staggering growth projections, like the IoT market reaching $650 billion by 2026 and the expected 30.9 billion active IoT devices. This rapid expansion means we must continuously educate ourselves about emerging technologies and industry shifts.
We should pay attention to key trends, such as the ongoing chip shortage impacting IoT investments, with many semiconductor executives predicting supply chain improvements. Additionally, as IoT devices proliferate, security becomes a pressing concern. Staying informed about new regulations and security measures will help us navigate this landscape effectively.
We must also explore how AI is increasingly intertwined with IoT, providing real-time insights and enhancing decision-making across various sectors. By keeping up with research, attending webinars, and reading relevant publications, we can ensure our knowledge remains current and applicable.
In this way, we can position ourselves not just as learners but as informed participants ready to seize opportunities in the dynamic fields of IoT and AI.
Explore Real-World Case Studies

Exploring real-world case studies offers us valuable insights into how IoT and AI technologies are transforming various industries. For example, the iRobot Roomba uses AI to efficiently map home layouts and optimize cleaning patterns. This innovation, first launched in 2002, paved the way for widespread consumer adoption of smart home devices.
Similarly, Nest Labs’ smart thermostat learns user preferences, adjusting energy use accordingly, and showcases AI’s impact on energy efficiency.
In the automotive sector, Tesla’s self-driving technology employs machine learning to predict driver behavior based on extensive road data, demonstrating the potential of AI in transportation.
Additionally, companies like Kairos are leveraging AI for marketing insights, serving high-profile clients like Nike and IBM.
As we delve into these applications, we also need to consider the ethical implications, especially concerning privacy and security with technologies like facial recognition.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Learn AI and Iot?
To learn AI and IoT effectively, we should focus on programming and data analysis. Let’s engage in hands-on projects, join communities, and stay updated on trends to deepen our understanding and practical skills.
Which Is Better to Learn Iot or Ai?
When deciding between IoT and AI, we should consider our interests. If we enjoy hardware and connectivity, IoT’s practical applications might excite us. If data analysis fascinates us, AI’s predictive capabilities could be more appealing.
How Can AI Be Used in Iot?
AI enhances IoT by enabling smart devices to make real-time decisions, learn patterns, and automate tasks. Together, they improve efficiency and responsiveness in various sectors, transforming how we interact with technology daily.
Which Is Better, Aith or Ai?
When we compare AI and AIth, it’s clear that AIth offers greater integration by combining AI’s capabilities with IoT. This synergy allows for smarter decision-making and enhanced efficiency in real-world applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering IoT and AI starts with a solid programming foundation and practical experience. By diving into hands-on projects, we can truly grasp these technologies. Connecting with online communities keeps us informed and inspired, while staying updated on industry trends ensures we remain relevant. Finally, exploring real-world case studies helps us understand the ethical implications of our work. Let’s embrace this journey together and unlock the potential of IoT and AI!
How Zekatix Helps You on the Journey
Zekatix is here to make your journey into IoT and AI smoother, combining all the steps essential for mastering these technologies. With courses that build your programming foundation, hands-on project resources, and insightful case studies, Zekatix equips you with everything you need to grow. Our platform connects learners to active online communities, keeping you updated on the latest trends and innovations in IoT and AI. As you explore these rapidly evolving fields, Zekatix serves as your partner in learning and innovation, helping you thrive in tech. Join today and take the next leap toward mastering the future of technology!
Sign up for free courses here. Visit Zekatix for more information.
Sign up for free courses here.
Visit Zekatix for more information.
#edtech company#courses#embedded systems#nanotechnology#artificial intelligence#embeded#academics#online courses#robotics#zekatix#AI#IOT#iotsolutions#iot applications#iot development services#innovation#embedded#iot platform#techinnovation
0 notes
Text
Leveraging Node.js for IoT: Building Connected Devices and Smart Applications
Introduction:The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how devices interact with each other and the world around them. As IoT continues to expand, the need for a scalable, efficient, and easy-to-use platform to manage these connected devices becomes increasingly important. Node.js, with its non-blocking I/O, event-driven architecture, and vast ecosystem of libraries, is well-suited for…
#automation#Embedded Systems#Internet of Things#IoT#JavaScript#MQTT#Node.js#Smart Devices#WebSockets
0 notes
Text
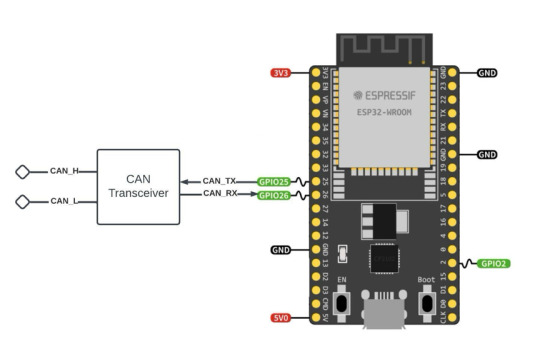
ESP32 Development Kits with Onboard CAN Bus Controller
The ESP32 includes a CAN Bus controller compatible with the NXP SJA1000, making it compliant with the CAN 2.0B (ISO 11898, also known as Classical CAN) specification.
Nevertheless, as with the SJA1000, the ESP32 CAN Bus controller only provides the data link layer and the physical layer signaling sublayer. As a result, an external transceiver module is needed to convert the ESP32's CAN-RX and CAN-TX signals into CAN_H and CAN_L bus signals.
#can bus#can fd#esp32#wroom-32#CAN Transceiver#Embedded System#Embedded Development#SJA1000#Classical CAN#Bluetooth#BLE#WiFi#IoT
1 note
·
View note
Text
SRI - Swarm Robotics for Indian Agriculture
INTRODUCTION Robotics is expected to play a major role in the agricultural domain, and often multi-robot systems and collaborative approaches are mentioned as potential solutions to improve efficiency and system robustness. Among the multi-robot approaches, swarm robotics stresses aspects like flexibility, scalability and robustness in solving complex tasks, and is considered very relevant for…
0 notes
Text
youtube
NXP: MCX A Series Launch Video
https://www.futureelectronics.com/resources/featured-products/nxp-mcx-n-mcx-a-microcontrollers . MCX A Series all-purpose microcontrollers (MCUs) address a wide range of applications with scalable device options, low power and intelligent peripherals. Designed to allow engineers to do more, the new MCX A series is optimized with the essential features, innovative power architecture and software compatibility required by many embedded applications. https://youtu.be/fjNG2t4TBXQ
#nxp#MCX#MCX A#all-purpose microcontrollers#MCU#MCX A series#microchip#small-footprint MCU#software compatibility#embedded applications#industrial sensors#motor control#power system#controllers#IoT devices#Youtube
0 notes
Text

Tissue Embedding System
Tissue Embedding System LTES-A10 is a compact benchtop unit crafted for smooth tissue embedding procedures. Our system comprises three key components, the main console, cryo console, and thermal console. This collectively ensures flexibility and precision. Featuring a user-frienTissue Embedding System LTES-A10 is a compact benchtop unit crafted for smooth tissue embedding procedures. Our system comprises three key components, the main console, cryo console, and thermal console. This collectively ensures flexibility and precision. Featuring a user-friendly digital LCD screen; monitoring and adjusting parameters has become effortless. Designed for efficiency, it includes built-in cassette warming trays and ample space for large moulds. T
0 notes
Text
Navigating Through the Depths of Embedded Software: Testing and Verification Strategies

In the complex realm of technology, Embedded Systems serve as the quiet foundation, driving a variety of devices from intelligent gadgets to automotive systems. At the core of these systems lies the embedded software, the unseen power coordinating smooth operation. However, ensuring the dependability and strength of this software is not a simple task. Step into the domain of Embedded Systems Testing and Verification, where BlockVerse Infotech Solutions emerges as a beacon of expertise and ingenuity.
In a time where flawless performance is a must, the importance of thorough testing and verification strategies cannot be overstressed. BlockVerse Infotech Solutions acknowledges this necessity and offers a comprehensive method tailored to tackle the distinctive challenges presented by embedded software.
Initially, understanding the complexities of the embedded environment holds great importance. BlockVerse utilizes a combination of white-box and black-box testing methods to explore deep within the software’s internal operations while replicating real-world situations. This detailed approach ensures not only functional accuracy but also deals with performance, reliability, and security concerns.
Moreover, Blockverse utilizes cutting-edge tools and techniques to simplify the testing process. From automated test frameworks to model-based testing, each tool is utilized with precision to optimize efficiency without compromising quality. By utilizing virtual platforms and emulation, BlockVerse enables thorough testing across various hardware configurations, preventing compatibility issues proactively.
However, testing alone does not guarantee the integrity of embedded software. Verification, the process of confirming that the software meets predefined requirements, is equally crucial. BlockVerse adopts a varied verification approach covering code reviews, static analysis, and formal methods. By scrutinizing every line of code and adhering to industry standards, BlockVerse guarantees compliance with strict quality benchmarks.
To wrap up, embedded software plays a crucial role in modern technology, and its reliability is crucial. With BlockVerse Infotech Solutions leading the way, navigating the intricacies of Embedded Systems Testing and Verification becomes more than just a challenge; it transforms into an opportunity to enhance performance, improve reliability, and propel innovation forward.
#embedded systems#what is embedded system#embedded software#computer hardware#embedded operating system#embedded system design#remote iot software#edge computing and iot#iot development company#Cloud computing in IOT
0 notes