#instead of explaining the actual story and introducing the audience to a historical figure they may not know as much about
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

my dad's one sentence review of A Complete Unknown
#brief explanation for those of you not as insane as we are:#Brian Epstein is the person who suggested they start wearing matching suits#but Astrid Kirchherr (a photographer the Beatles met while touring Hamburg) was the originator of the Beatles haircut.#claiming Brian invented it would be giving credit for a key moment in their early career to the more well-known person in their history#instead of explaining the actual story and introducing the audience to a historical figure they may not know as much about#which is exactly what A Complete Unknown does by giving the roles of Dave Van Ronk and Phil Ochs to Pete Seeger#and ignoring Peter Paul and Mary's role in popularizing his music in order to focus on Joan Baez instead#these people did obviously have great impacts on his career but so did many other people who aren't even mentioned in the film#and it would have been better in my opinion to focus on the lesser known parts of history#instead of the ones most everyone worth their salt already knows about.
8 notes
·
View notes
Note
I have a question! Thank you for existing I deeply appreciate it. I was wondering if it is possible for a blind person to be able to read by learning the shape of raised letters, rather than braille. I ask because I have a situation in which it is reasonable that the blind character would know this, if possible, and the person they are travelling with is completely illiterate.I thought it might be interesting if the seeing character could describe the letters, or find a way to texture them so the blind character could tell them what something says. I have done a great deal of research for this character, but this is the one part I can't find a clear answer for. Thank you very much.
Good question, nonnie.
The short answer is, maybe? It would depend on the time period and location of your characters.
Since you want both characters to read, I’ll assume this culture has a formal writing system in place and values written communication.
A Brief History
In order to address this, allow me to offer a brief history of Braille. Because what you’re describing is exactly what happened in France before Braille was invented. This informative video summarizes it pretty well. Here is the text version of the video. The video mentions the embossed letter or raised type method of reading that was used at the time. It was difficult to read and the letters had to be very large in order to be understood, making it harder to read words and sentences. Reading must have been very slow.
According to this page on the National Braille Press website, reading this way required slowly tracing raised print letters. To write, one had to memorize the shapes and try to create them on paper, although they could not read the results.
Creating books was even more difficult. According to this page, [quote] “teacher Valentin Haüy made books with raised letters by soaking paper in water, pressing it into a form and allowing it to dry. Books made using this method were enormous and heavy, and the process was so time-consuming that l'Institution Royale des Jeunes Aveugles, or the Royal Institution for Blind Youth, had fewer than 100 of them when Louis Braille was a student there.” [End quote]
Braille books are already notorious for taking up several volumes. Large print books are only a little better. Textbooks used in schools take up several shelves to translate one print textbook.
Individual use and traveling with these things must have been impossible for the everyday person, even if you were a student.
Also, in this video by blind YouTuber Molly Burke, at the 9:05 time-stamp she answers the question: why don’t we raise print letters for blind people? She explains that it took too long to read and is not as efficient as Braille.
In the interest of time, I’ll try to keep this brief. The transition from the raised print letters to Braille was not a smooth one.
In 1826, first embossed letters published in English was James Gall’s triangular alphabet. Read about it and other systems here.
Another source says Gall’s writing system was introduced in 1831. The system did not gain much popularity outside of Endinburgh.
According to this page: [quote] “In 1832 The Society of Arts for Scotland held a competition for the best embossed type. There were 15 entries but Edmund Fry’s alphabetical system of roman capitals triumphed. Shortly afterwards John Alston began printing at the Glasgow Asylum for the Blind using a slightly modified version of Fry’s design. “Alston type” proved popular and inspired similar forms across Europe and North America.” [end quote]
None of these really caught on outside of certain areas.
In 1821, Charles Barbier was invited to the Royal National Institute For Blind Youth in Paris to demonstrate his Night Writing invention, which was developed for soldiers to read in the dark. It was too difficult to read and so was not used by soldiers, nor did it end up being used by the blind schools. However, a young Louis Braille was in the audience and was inspired.
In 1825, Braille thought he had figured out a good system of writing.
In 1829, he published the first Braille alphabet.
1834 - Braille is invited to Exposition of Industry in Paris, which extended the popularity of the Braille system.
1846- a school for the blind in Amsterdam starts using Braille’s system.
In 1852, Louis Braille dies.
1854- Royal National Institute For Blind Youth officially adopt Braille as official system after fighting it for years.
Because Braille didn’t take hold as quickly in Britain, the British and Foreign Blind Association, all of whom were blind, voted in 1870. They decided Braille was the best system. Braille quickly fell into use all over the world with the exception of the United States. By 1882, the embossed letter system was over.
In the U.S, from 1868-1918, the New York Point system was used. American Braille (developed by a blind teacher named Joel W. Smith) was also used from 1878 to 1918, when the U.S switched the standardized English Braille.
Would Your Character Know Raised Type?
Remember how I said you might be able to do this depending on the time period and place?
If you have French characters, you can used the raised type method as you described in your ask if the story takes place before, probably, 1825. It would be reasonable for your character to know the raised type method if they had attended a blind school before the Braille method was adopted in 1854. Between roughly 1829 and 1854, the French blind character attending school would know about the Braille system and probably complain about their school not teaching it despite Braille himself teaching there.
Similarly, they could used raised type depending on where the story is set, when the character attended school, and what system was in place at the time. If the story is a fantasy, you could make up a history similar to what I described above, although it would be important to have schools for the blind and have Braille or the equivalent be created by a blind character.
Remember that your blind character needs to learn the raised type method if you want them to use it.
If Braille would be available in real life (such as a more modern setting), I would prefer a blind character use Braille instead. Which is why I tried to offer alternatives that were historically justified.
I don’t feel very comfortable with a blind character having to use a raised type method rather than another system, because Braille literacy is declining nowadays and something about learning a raised type method over Braille (or other system, depending on where you set the story and what they were using at the time) doesn’t sit right with me. Your character doesn’t have to use Braille specifically, but I would rather they use the system that is available to blind people at that time. For example, if your story is set in the United States, it would be fine to use American Braille or the New York Point, depending on the time period.
If your story is modern, blind people can usually read raised print letters on signs, such as for the bathroom. In fact, a lot of people who can’t read Braille get by this way. However, keep in mind that we have screen-readers and audiobooks now. People aren’t reading entire texts or even many words with this method.
As for other countries, I tried my best to research what places, such as Japan, used before Braille. For several reasons, including the European-centric search results that keep coming up over and over again, finding the correct information is proving difficult. In some cases, previous methods may have unfortunately been lost due to colonization. It is important that we acknowledge that.
I feel that it would be easier to leave the research up to you since you know where you want to set your story and your own personal background, historical knowledge, etc.
Keep in mind that not all blind people in the world had access to formal education, depending on the place, time, their social class, etc. If you want your blind character to know how to read, you’ll need to find or create a setting that allows for it.
Generally, I would prefer blind characters use methods designed for blind people, whatever that happens to be in that time or culture. Prioritizing the other characters’ needs and having a blind character learn raised type over Braille when Braille actually exists in the story doesn’t work for me.
Like always, I suggest having more than one blind character in the story to avoid tokenism. Also, since your character is going to teach another character, be sure to show your blind character’s needs and goals as well.
I hope this helps. Feel free to message me or send another ask. I am not a historian and so if anyone wants to correct anything, such as dates, or provide any relevant knowledge, please feel free. I tried my best with this question. I would be grateful for help if anyone has more information!
-BlindBeta
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
One Brain Cell Theories: Chapter 17 & 18
There are a few things that may confirm my suspicions and the new chapters have reinforced it.
SPOILERS AHEAD, please click at your own risk and any input/more theories are welcome! I’m going to try and make this a series.
This is also a relatively long read so grab some snacks! We diving in boys!!
(This is one of my many theories. One day, I’ll be able to write down what’s happening in my head.)
TLDR; HUNNY we have to talk about the other human
A few things to remember before I dive in:
Solomon has a pact with Barbatos. Solomon has a ring of wisdom and is known to make a pact with larger and more powerful demons. We all know he lowkey wants a pact with Lucifer.
Lucifer told us not to trust Solomon in Chapter 2
There’s a possibility Barbatos has tried to poison us with tea, a Mandragora blend. Mandragora has the potential to be fatal, one of the most notable symptoms are hyperactivity and hallucinations.
When Barbatos sent us back in time, we found out he is extremely OP. He even has the power to look into the past and future.
Okay now onwards to the only viable explanation I can think of: Barbatos and Solomon are scheming a takeover. (or this really is a messed up “prove yourself” challenge from Diavolo)
Let’s begin to when shit started to get real.
A sorta shortened (?) recap of everything that has happened thus far, please feel free to skip if you don’t need it:
After almost confessing your love to Lucifer and dying in the process Belphie comes down the stairs and its the big reveal, everyone essentially gasps in shock. Beel, Belph, and MC run away to Luke’s joint only to get busted by Dia & Barbatos and they drag away Belphie to throw him in jail for treason (and its implied he gon’ die). Lost and afraid, Beel and MC run back to the House of Lamentation. There we have a really heartfelt scene with all the demon boys and we are determined to storm into Dia’s castle and solve the situation.
Arriving at Dia’s castle, the pair say they were expecting us. Lucifer stood up to Diavolo & he says please, LOUD AUDIENCE GASP. No matter how much we try to reason, the only way Belphie will be released is if MC goes back into the past alone and figure out who actually opening Belphie’s door. No reason is truly given to this. Diavolo explains that Barbatos has multiple abilities, some of this includes viewing the past & future and, most importantly, time travel.
As we continue to Barbatos’ room, he is super happy (and creepy) but gives us a very dire warning - do not interact with the past in any way or it will alternate the current timeline. This includes speaking to anyone or being involved in any type of action. If we want to come back to the present, we have to go through the same door that we end up entering through. Then off we go and we land in the middle of Mammon’s room with ALL OF THE BROTHERS sans Lucifer and Belphie. And things go haywire.
As we are running to go up to the attic, we are forced to hide in Lilith’s room, where we have a flashback (or hallucination) of playing hide and seek. Flashback Levi reminds us to go find Belphie. During this time, it is revealed that MC may have been the one to open Belphie’s door and tldr; Belphie kills MC.
As we lay dying, we are somehow saved by Lilith (our long lost aunt twice removed apparently) and we are outside of our own body...in another one. Dia and Barbatos stroll in saying they knew this would happen & Barbatos did us a favor and revived us using an alternate timeline MC (what). Everyone is pumped we have like 1/10,000,000 genes related to human Lillith and this is their closure.
Everything seems to be looking up and MC patches things up between Belphie and the other brothers. They throw her a joint party with Diavolo’s birthday party & give her the sweetest gifts. At the end of Chapter 18, Belphie creates a pact with MC.
This is all fine and dandy but...is it really?
A few things really popped out during these two recent chapters:
Belphie is by our side the entire two chapters. Whether this is supposed to signify a new start or something else, it isn’t entirely clear.
Beel and Belph are the only ones that text us during this time. Belphie texts us after every chapter moment.
Solomon runs into Belph and MC while shopping, randomly asking Belph if he plans on making a pact with MC. Then brazenly offers to make a pact with him instead. Belph refuses vehemently but looks at MC for a reaction. Solomon notices this.
As Belph gives us a gift of himself (lol same), he mentions how he’s doing this for us and not because of Lilith.
In the game itself, there’s a completely different game style. MC has more options to speak and the dialogue options have become more brazen. Almost as if...this is a different personality (or could signify MC is more comfortable with them in general). It felt off playing the last two chapters though, for me at least.
Now onwards to the theory: Solomon is our main antagonist.

In Chapter 2, we are formally introduced to Solomon, the other exchange student. Although the interaction is rushed, we can sense out two things: he’s insanely smart and he’s already comfortable around demons. As he runs off to class, MC runs into Lucifer and we learn a bit more about this mystery boy.
Apparently, Solomon is a wizard and has a ring of wisdom, which makes him incredibly dangerous. He has pacts with more than 70 demons (I think the exact number was 78 but I might be wrong). Among these demons are Asmodeus and Barbatos. At the end of Lucifer’s explanation, he adds that MC shouldn’t trust Solomon.
Historically and culturally, Solomon is most known as the “Wise King.” He is also regarded as a fantastical figure, someone who is known to have powers over both angels and demons.
“According to the Rabbinical literature, on account of his modest request for wisdom only, Solomon was rewarded with riches and an unprecedented glorious realm, which extended over the upper world inhabited by the angels and over the whole of the terrestrial globe with all its inhabitants, including all the beasts, fowl, and reptiles, as well as the demons and spirits. His control over the demons, spirits, and animals augmented his splendor, the demons bringing him precious stones, besides water from distant countries to irrigate his exotic plants. The beasts and fowl of their own accord entered the kitchen of Solomon's palace, so that they might be used as food for him, and extravagant meals for him were prepared daily by each of his 700 wives and 300 concubines, with the thought that perhaps the king would feast that day in her house.”
Additionally, he was given a ring, known as the “Seal of Solomon,” which gave him the ability to trap demons under his control.
A magic ring called the "Seal of Solomon" was supposedly given to Solomon and gave him power over demons or Jinn. The magical symbol said to have been on the Seal of Solomon which made it efficacious is often considered to be the Star of David. Asmodeus, king of demons, was one day, according to the classical Rabbis, captured by Benaiah (my note: Benaiah is a human, he was a soldier that helped Solomon rise to power) using the ring, and was forced to remain in Solomon's service. The Seal of Solomon, in some legends known as the Ring of Aandaleeb, was a highly sought after symbol of power. In several legends, different groups or individuals attempted to steal it or attain it in some manner.
And this is a potential plot in our story.
MC is, of course, the main protagonist of the story. We typically are. But there was never a clear antagonist. Or maybe he was playing along with our situation, a wolf in sheep's clothing?
We all know Levi’s strangely long anime names are a strange foreshadowing of the future. We have:


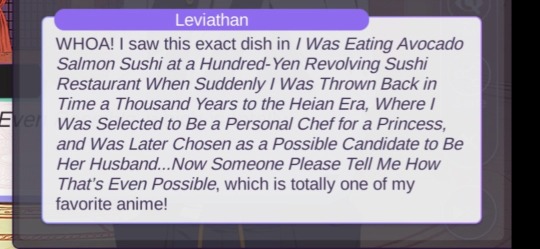
Though all titles seem to have a connection with our current plot, I’m going to focus on the first one, which seems to have the most implications regarding our current situation. I also have a sneaking suspicion that the second image with the two titles might be a backstory for Barbatos but that’s another story that I cannot fully prove yet. The third title also refers to a legend regarding Asmo and Solomon.
The first title seems...has quite obvious implications when recounting the events of chapters 15 - 18. Halfway through our journey, here we are, thrust into an alternate timeline, alone and scared but we end up making a pact with...our sixth demon? And this isn’t just a regular demon, this is one of the deadly sins. So now we have 6/7 demon brothers under our power, some of the most powerful demons in Devildom. It’s alarming how quickly MC is able to gain the trust of these demons, effectively creating pacts in the course of...maybe a few months?
What alarms me the most is how fast Belphie turned from, quite literally, killing us to making a pact with us in a course of 3 chapters. This brings me to my first suspicion in SoloBarb’s plot: This timeline is the only timeline where MC is able to make a pact with Belphie. All other timelines do not reflect this. This placement was 100% intentional from the start.
It is a known fact that Barbatos is able to view time and its events. It’s revealed this extends to alternate timelines when saving MC. If he is this powerful, wouldn’t he be able to simply look back in the past and find out who opened Belph’s door without the need for MC? This would be the easiest and most direct solution.




SIDENOTE: Keep in mind, part of the reason Barbatos could not stop the Belphie situation from happening is due to Diavolo’s restriction. Barbatos states that “Diavolo has forbidden him from using his powers freely.” HOWEVER, it then leads to the question: who really has the most control over Barbatos, Diavolo or Solomon? Traditionally, when pacts are made, it means that the demon is completely under the control of the individual but does it outweigh an authority figure? In my opinion, Solomon technically has the most power fo Barbatos. Solomon’s pact with Barbatos = a magically restrictive bond while Diavolo’s rule over Barbatos = a matter of respect of authority. There is no physically restrictive bond Diavolo has on Barbatos.
Also considering how cunning Solomon is, he could have easily manipulated Diavolo into this entire plan as well.
In addition, Solomon’s strangely direct question, asking Belphie if he was going to make a pact with MC, was alarming. It was as if he was proving his own theory: the demon brothers will make a pact with MC and never him. He seemed almost satisfied with this answer and didn’t seem to protest against it too much. Couple this with Solomon’s constant approval when MC makes pacts with the demon brothers during her stay, its...disconcerting.

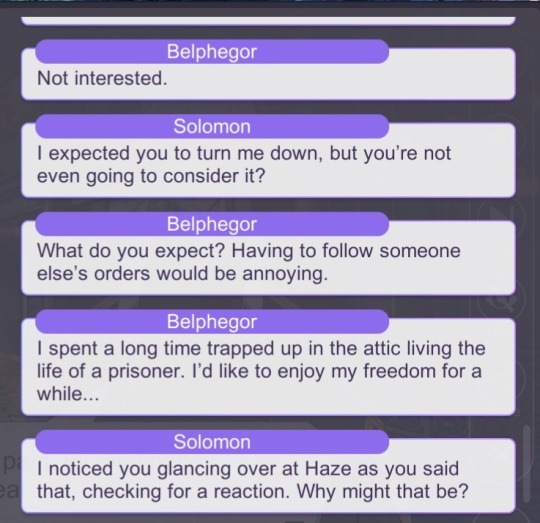

Omg he even says “If you change your mind” what kind of creepy
If we consider all of this, it truly does seem as if Solomon is our potential antagonist. It seems to me that everything is pointing at him. He’s quiet enough for us to overlook and disregard as a side character, though he seems to have a certain unnerving edge to him. My god, the demons are even wary of him. If that wasn’t the biggest tip-off, idk what is.
Also physically, we have yet to hear his entire backstory in the game or have a chapter dedicated to him. So far, in terms of side characters, we have ample interaction with Diavolo and Luke (still waiting on Simeon) but no deep dives into Solomon and Barbatos. (Which means >.> we’ll get them in later chapters)
This brings me to the next question: so how is MC a chess piece in his plot?
Hey, remember that RANDOM moment Solomon lent out his power during Diavolo’s house party. AND NO ONE QUESTIONED IT. Honestly, what the hell was that all about?
In regards to this, why did he do this? Some answers include: he did it for shits and giggles, he wanted to test out the theory of us having powerful magic in our bloodline, or he wanted a test run. Yeah. You heard me. A test run.
Prior to this, MC was unable to truly summon a demon on their own. The most she could do was give out a pretty strong verbal command and the demon (Mammon lol) must carry it out. However, MC cannot fully utilize the pact’s potential due to her lack of innate magic ability.
This is both an affirmation and leverage for Solomon’s situation. On one end, it’s confirmed that MC has huge magic potential and can properly use it when needed. On the other end, this can be a bargaining tool for the future...
Which could lead to a large plot development: Once MC gains all seven pacts (c’mon, it is going to be impossible to not make a pact with Lucifer), what will they use it for?
MY PREDICTION: Solomon will attempt to manipulate MC into his control. Magic is powerful in this game but so are humans. A human was the reason Lilith was going to be punished by God. Solomon, a human, has power and control over 70+ demons. Belphegor was set on destroying only the human world. MC has pacts with the, arguably, the strongest demons in Devildom who are also formerly fallen angels.
From what I’ve seen so far, nothing is more powerful than a pact. And nothing is more powerful than human manipulation.
What will he use MC’s powers for? ...I have a sneaking feeling it might be to overthrow Diavolo based on Solomon’s cultural legend. Solomon famously has power over Asmo, the king of demons. Of course, we know the Asmo in our game is not the king but Diavolo is. Obey me! has a funny way of interpreting these legends in a unique way. Who knows if they split up Asmo into two different entities.
but who tf really knows what’s going on
BUT
I guess we’ll have to see what happens in later chapters. Of course, this is all really a far fetch theory but there seem to be so many underlying connections to Solomon in the game. I mean ffs, he’s the only other human here and he’s SOLOMON. The very character itself is so suspicious.
THIS ENTIRE THING COULD ALSO BE A MESSED UP CHALLENGE FROM DIAVOLO
OR SOME CRAZY HALLUCINATION CAUSED BY BARBATOS GIVING US THAT SUS TEA BLEND
But tbh who really knows what’s happening. The only confirmed thing is that we’re still on this alternate timeline (that MC totally messed up) and we haven’t returned to our OG timeline. lucifer please pick me up I’m scared
If you made it this far, you are SUCH A TROOP. I hope this actually has a consistent flow and it makes sense. If you have any questions or observations I didn’t include please feel free to message me! I’m open to discussion!
A big s/o to wikipedia for the quick info on Solomon (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solomon#Seal_of_Solomon) and a thank you to @the-orizon for the screenshots & amazing info! Love you!
#i need to sleep#i did this instead of work#lol#obey me shall we date#obey me#obey me! shall we date?#obey me theories#obey me! theory#Solomon is sus#obey me solomon#obey me! solomon#obey me belphegor#obey me belphie#obey me lucifer#obey me lucy#obey me diavolo#obey me barbatos#its always the butler#obey me leviathan#obey me levi#one brain cell theories#obey me spoilers#long post
636 notes
·
View notes
Text
Optical Illusions: A Study of Aesthetics in Activism in Two Accounts
There’s been a particular thing bothering me about social media for a while. I should probably get a cool editing app, write it in a few bullet points and post it on Instagram. You know what I’m talking about, right? The goddamn infographics. If I have to sit through another slideshow explaining to me another military conflict, another societal issue, another existential unfairness on a baby pink background in a cheery font, I might combust. But the cognitive dissonance of aesthetics in activism has been a problem for a while, hasn’t it? So today, I want to examine the effect of focusing on aesthetics over content, or, on the flipside, not considering the optics of your activism enough, and what it does to the consumer of your content by picking apart two local activist-adjacent media projects, Tetraedras and Giljožinios.
Firstly, I want to make my own bias abundantly clear. I am personally acquainted with the teams of both projects, so obviously there will be innate personal bias involved. I highly encourage anyone reading to check both projects out themselves (@t3traedras and @giljozinios on Instagram, as well as Giljožinios’ YouTube channel) and make their own conclusions on the matter. I believe that while my familiarity breeds deeper knowledge of my subjects, it also makes me more vulnerable to assumptions about individuals involved. My insights come from the perspective of an observer, not an expert. Welcome to the circus.
The use of the word “optics” in a metaphorical political sense sprung up in the 1970s to describe the way major political decisions would not necessarily affect an average citizen, but how it would appear to them, e.g. 'U.S. President Barack Obama temporized for weeks, worrying about the optics of waging war in another Arab state after the Iraq fiasco' (Toronto Star, 19th March 2011). However, it’s become increasingly relevant in our age of social media, an age of perceptions over substance, of shortening attention spans and increased barrage of information one has to stomach daily. Social media is the great equalizer - a random person off the street can theoretically hold as much influence as a politician - thus it is becoming increasingly crucial for the average Joe posting on the countless apps owned by Facebook to be as familiar with PR terms as a firm with a six figure salary. Or at least that would be nice, seeing that more and more average Joes are becoming actively involved in politics and education, seeking to influence their newfound audience.
So, let’s see how successful average people with no media or politics degrees are at balancing their image. Both Tetraedras and Giljožinios lean into their 2010’s social media project optics: millennial pink themes, bold names, young teams. But that’s where the similarities end. Tetraedras’ brand is safety. The shades of color on the profile are calming, the illustrations are youthful and playful, their more serious posts are interspersed with more relaxing content (poetry, photoshoots, etc.). Giljožinios is confrontational. The colors electric, posts loud and to the point, they’re what it says on the box - a leftist project - and unapologetic about it. This might help to explain why audiences react as differently as they do to these two, on the surface, similar accounts. Because while you might’ve stumbled on Tetraedras organically while browsing, them having almost two thousand followers, Giljožinios crashed into the educational/political social media scene by being featured on the goddamn national news, that’s how controversial the project is. And obviously I am oversimplifying the issue, Tetraedras slowly built up to posting more opinionated content, while Giljožinios came in guns blazing accusing USA of imperialism, but you’ll have to let me explain. Tetraedras, in its essence, is a welcoming environment. They explain complicated problems in short bullet points with accompanying comforting visuals, their mascot is a inoffensive geometrical figure and their face is a beautiful girl, make-up matching the theme of the post. Giljožinios is named after a revolutionary device, their profile picture is a monarch being beheaded, their host quite infamously sat in front of Che Guevara memorabilia in their first and (as of writing) only video. It’s a lightning rod for angry comments by baby boomers, no matter what comes out of their mouth. In fact, I would argue that, if presented accordingly, the idea that the US is conducting a kind of modern imperialism is just a simple fact and personally can’t wait until Tetraedras posts that with a quirky illustration of Joe Biden to introduce the concept to the wider public.
This leads me to my next point, because despite what’s been previously suggested, I’m not here to solely sing Giljožinios’ praise. There is a cognitive dissonance in both of these flavors of social media activism, but while I can understand Tetraedras’ on a PR level, I’m kind of personally insulted by Giljožinios’. While purely personally I find aspects of Giljožinios’ radicalism distasteful, I appreciate the honesty in the youthful maximalism, of coming in strong and not backing down, but from the guys that made a communist Christmas tree once I almost expected something more stirring than “military industrial complex bad”. This leads me to ask: who is your content for? Your average breadtube-savvy twenty-something already heard this a thousand times, because they consume similar english-speaking content and I doubt any minds of the vatniks that came by to fume in the comment section are being changed. I’m obviously harking on a newborn project here, the team of which has already been bitten by authorities censoring their content, but so far there has been a lot of optical bark, but no substantial bite, especially considering the team seems to be in a safer place now. And the inverse is true for Tetraedras, while I can understand wanting to be visually interesting yet inoffensive, their visuals are sometimes laughably, morbidly light for the topics they discuss Sexily posing in Britney Spears-inspired outfits while discussing the horrors of her conservatorship springs to mind (funny how Britney’s conservatorship leads her to have next to none bodily autonomy, including her public costume choices). And, once again, your target audience is teenagers. They understand English, they’ve seen the news, they don’t need you to translate infographics filled with statistics and information that’s locally completely irrelevant. There needs to be some kind of middle ground between aesthetic cohesion and common sense, because this all signals to the viewer that the content is meant to be mindlessly consumed first and to educate second.
Which leads me to ponder what kind of consumption accounts like these encourage, which will surely lead me to an early grave as I drink away the existential dread of how social media rots all of our brains. Because yes, actually, producing funky visuals to convey an idea way too complicated for an Instagram post is fun. I myself got distracted multiple times during writing to make the first slide for my own post. Meta, I know. This is obviously more of a problem for Tetraedras, who seem to fervently resist injecting their content with a few more paragraphs and a tad more nuance, but even with Giljožinios choosing a more appropriate long-form format to educate, I still pray everyday they don’t get lost in the revolutionary reputation their group built up and forget to make a point, not just talking points.
Because what all this all inevitably leads to is misinforming the public. Again, this seems to be less of a problem for Giljožinios, as the amount of critical eyeballs they have on them leads to them being corrected on every incorrect numerical figure and grammatical mistake, I just hope all this harassment, once again, doesn’t get them all caught up in the optics of a revolution against all the Facebook boomers and forgetting to do their due diligence to the truth. As far as I know, the only factual mistake is miscalculating how much Lituania invests in NATO and there’s still a historical debate in their comment section about the existence of a CIA prison in Lithuania, if anyone’s concerned. Tetraedras, however, is safe. And safe content goes down just like a sugar-coated pill, you don’t even feel the need to fact-check it. And fact-checking is what it sorely requires, or else you’re left with implying that boxing causes men to become rapists and citing statistics of every country except the one in which, you know, me, the team and the absolute majority of their followers live in.
So what’s my goddamn point? Burn your phone and go live in the woods, always. But in the context of this essay, if you are a content creator that aims to educate, inform, incite, whatever, you need to put aesthetics on the backburner. And, more importantly, we as consumers need to stop tolerating content that puts being either pretty or inflammatory first instead of whatever message it’s trying to send, because the supply follows where the demand goes. Read books, watch long-form content made by experts, not teenagers on the internet chasing followers out of not even malicious intent, but almost a knee-jerk reaction. Because while the story of those two accounts cuts especially deep, expectations for local-, even friend-made content being much higher than that for some corporate accounts shooting their shot at activism, the problem is entrenched deep, thousands of accounts exhibiting the same problems racking up millions upon millions of followers. Having said that, my attention span is barely long enough to read the essays I write myself, so maybe do burn your phone and go live in the woods.
Also, pink is actually my brand so both of these accounts are being contacted by my lawyers and the rest of you don’t try any shit.
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

September Book Roundup, back-to-school edition aka The Season Of Red apparently?
Here is a selection of the books I’ve read this month. Summer is over, so the little bit of brain power I had managed to scrape together is quickly disintegrating, so enjoying the hodge podge of stories.
Binti

This was probably my favourite book that I read this month. It’s a novella I first heard about hear on tumblr and went to find a copy in my library. I have since bought the collected trilogy so I can read book two and three at my leisure because it was honestly just that friggin cool. This is exactly my flavour of scifi and I tend to be very very picky about the scifi I consume. It’s about a girl named Binti, a member of the Himba people (a real group of indigenous people from Namibia). They are a people well known for their mathematical and technical prowess, but due to their strong connection to their homeland and the earth they choose not to travel through space like so many other humans do. However, when Binti secures a position at Oomza University, the greatest university in the galaxy, she chooses to go against her family’s wishes and traditions in order to set out into space to attend. Everything is ruined though when her spaceship is attacked by a hostile alien race and everyone is killed but Binti, who must rely on all her intellect and abilities if she wants any chance at survival.
A seriously cool book with great world building – it really successfully introduces readers not only to the fictional scifi world and races of the novel but also to the culture and traditions of the Himba people. It’s a quick read, and feels like a cross between Dead Space and Tamora Pierce. Would totally recommend a read.
Fake Blood

A Canadian graphic novel. It was a goofy cute read. It’s about an awkward group of friends in middle school, and one boy with a crush on one of the girls in his class. Knowing her love for vampire stories, AJ decides, like any self-respecting middle schooler, to try to pretend he’s a vampire. Naturally nothing goes right and some things go wrong in unexpected ways. It’s funny and cute. Nothing amazing but it was a cozy evening read.
The Last Book On The Left

I’ve been listening to this podcast a lot since my friend recommended it to me and finally decided to read their book. For those that don’t know, The Last Podcast On The Left is a immaculately researched comedy podcast that’s hosted by Ben Kissel, Marcus Parks, and Henry Zebrowski, and explores the darker realms of human nature. Ghosts, paranormal, aliens, cults, and of course serial killers. In this book they collected several of their biggest name serial killer series, did some renewed research, and put together a book that is both informative, irreverent, gross, and very funny, complete with some really amazing illustrations by Tom Neely. A very cool read (and listen, if you decide to check out the podcast instead), I really love how they tell these stories without idolizing or romanticizing the people they talk about. Their humour always makes sure you know exactly how much of a pathetic loser these people are. Fantastic true crime, from someone who has never really felt the need to read about true crime before.
Midnight Sun

I won’t harp on this one, everyone is already going to firmly have their opinions here. I grew up on Twilight, I was reading them as they came out, and I still love them. Were they dumb? Oh my god yes. Did they have problems? Sure, they came out in 2005 it was part and parcel. Were they also a really fun for a thirteen year old to read? Absolutely, I don’t regret it. Sometimes teenage girls should just to get like things without being mocked.
Anyway, I am off my soapbox now (can you tell this is still a raw spot for me?) I unironically loved this book! Getting to see Edward’s perspective was really cool, and since he can read minds it essentially let you get the perspective of everyone else around him too. The Cullens family is a great set of characters so it was really cool to see more of them, and I was very impressed by how Stephenie Meyers took a YA romance she wrote in 2005 and was able to make it feel updated and more appropriate for a 2020 audience even though she couldn’t actually change any of the events themselves. So fans of Twilight, don’t be ashamed, go read Midnight Sun and have the shameless fun you deserve. Is there anymore appropriate book for the bizarre ass year that was 2020 than a return to this goofy nonsense?
The Paperbag Princess

(and Up, Up, Down, and Robert Munsch in general)
I’m back in schools so I’m back to reading children’s book! And honestly, and of you that don’t occasionally sit down and read a kids book out loud don’t know what you’re missing. Anyway, Robert Munsch is a Canadian author, and one of my all-time favourite children’s authors. It surprised me to learn he isn’t as well known in the States apparently? I don’t know if that’s changed or not, but he is a Canadian staple for a good reason, his books have ridiculous premises, are specifically written to be fun to read out loud, and have beautiful, involved, and hilarious illustrations. The Paperbag Princess is one of my absolute favourites, and as a kid it was one of the first stories I had ever read where a princess is the one saving the prince… and then telling the prince to piss off when it turns out he’s a jerk. Up, Up, Down is another favourite I reread this month, because it’s just hilarious funny and makes a fantastic read aloud with kids. Some other Robert Munsch I reread this month include: Mmm, Cookies, More Pies, Ribbon Rescue, Just One Goal, and Andrew’s Loose Tooth. You just cannot go wrong, for kids or adults.
Pit Pony

Another Canadian staple while I was growing up. If you’re a young adult know who went through the Canadian elementary school system, you probably had your entire heart ripped out and stepped on by this chapter book. It’s a historical fiction that looks at the economic hardship, debt slavery, child labour, and animal abuse that was tied to coal mining in the Maritimes. Finding a copy was harder than I would have expected give how pervasive it was a decade or so back, but reading it again was a pure shot of nostalgia.
Seeking Refuge

A graphic novel written by a German-born Canadian about a Jewish girl who flees Nazi-occupied Austria by way of Kindertransport to become a child refuge in England. It follows her as she is moved from host family to host family as the war continues to pick up and gradually makes it’s way to the United Kingdom as well. It’s very poignant and the pencil-sketch illustrations are an interesting change to a lot of the graphic novels that are out right now. This story is still aimed at a younger audience, so it never gets too brutal but it still is a hard hitting story, especially with everything else going on right now.
Silver Spoon #9/10

I know I’ve talked about these books before, but my library got some more since I last read them, so I’m continuing my way through the series. It’s about a teenaged boy who, after having a breakdown from the pressure he was feeling to study and succeeded, decided not to attend an academic, urban high school, but rather to apply for an agricultural high school so he could live in the dorms, far away from his parents. The series just gets more and more heartwarming as it continues. It’s all about failure and overcoming and how worth can be measured in different ways, and about family and understanding each other and coming together… but also about the realities of farming which aren’t always very nice, especially when it comes to finances and survival. It’s written by the mangaka behind Fullmetal Alchemist but I’ll be honest… I think I like this series more. It is honestly one of my all time favourite manga series, it just has so much heart.
Ruby Finds A Worry

aka Ruby’s Worry apparently? I can’t figure out why this has more than one title. I actually read it in French not English, so for me it was Le Souci de Calie. Regardless, this was a nice little picture book for talking about worries and anxieties with children… especially with the amount of Covid stress a lot of kids are dealing with. It explains in a really nice way how talking about anxieties are often the best way to make them more manageable, and how pretending nothing is wrong can just let it grow bigger and bigger. A good explanation for kids and possible a good reminder for adults.
War of the Realms: Journey Into Mystery

I read this because the Mcelroy family wrote it so I figured Hey! Why not give it a go! And I’m glad I did. Their brand of humour was all over it, and it made the story a delight to read. I don’t follow all of Marvel’s weirdness, so I didn’t actually know most of the characters (Miles and Kate were actually the only two I was familiar with) but they do a great job of introducing the characters and making them all feel distinct and interesting. I absolutely adore the Dog of Gods (God of Dogs) who is a very very good boy. And Miles is absolutely always a delight so you can’t really lose. It’s a single book that I think is a part of a larger plotline that I have zero interest in. This book is a fine one to read though if you don’t mind jumping into the middle of the action and just getting swept along for the ride. Also Mcelroys!
Witcher Omnibus

Bleh. Absolutely not worth it. All the misogyny and Dumb Bullshit that I hate in the original books and from video games in general. Honestly, Witcher III did way better by its characters than most of these short stories. The only one worth reading in it is Curse Of Crows – that one was actually really enjoyable, probably because it was about Ciri and had an actual fucking woman on the writing team. (Seriously guys what were you thinking with Fox Children that’s literally just a story from Season of Storms but done worse. Fuck off.) If you like The Witcher, go read Curse of Crows and skip every other story in this book.
Billy Stuart: Les Zintrépides #1

Another French (Quebecois) book I read, though I believe you can get it in English as well (Billy Stuart and the Zintrepids). It’s a chapter book / graphic novel hybrid, and was honestly a fairly fun little read. It’s in a similar vein to Geronimo Stilton but done much better in my opinion. The humour was funnier, the characters felt less like caricatures, and while it still used stylized fonts it was also less intrusive and eye-strainy than the Stilton books. Also when the story suddenly pivots into the main adventure and mystery of the series? Fantastic. Was not expecting a hell-beast to appear part way through the story. Very interested in reading more.
Over all, it was cute and funny, and I can see it being a good next step when children have read their fill of the Stilton series and want something similar but possibly a bit more involved and coherent.
#chatter#book review#book reviews#midnight sun#twilight#stephenie meyer#last book on the left#last podcast on the left#lpotl#binti#robert munsch#paperbag princess#marvel#war of the realms#journey into mystery#mcelroys#mbmbam#silver spoon#fma#the witcher#billy stuart#zintrepids#geronimo stilton#spiderman#canadian literature#canlit#cancon#manga#graphic novels#comics
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of the things that stood out to me about buffy when i revisited it as an adult was how much time each episode spent on set-up. like hush is known as “the silent episode,” but the silence doesn’t even start until like 14 minutes in. or i think of something blue as “the will-be-done episode”, but that spell doesn’t start until again...14 minutes in. and the comedy antics don’t start until a few minutes later. or fool for love is the “spike backstory episode” but we don’t hit the first flashback until 12 minutes in. and although some episodes do get to the point right away, they pretty much never use in media res unless they’re picking up at the end of the previous episode.
on some level, this is just how tv is structured. you’ve got your acts, and teaser + act one, which adds up to 10-15 minutes, is responsible for first part of the story--which means introducing the problem and why the characters care about the problem. ie, doing set-up. so i was trying to figure out why it felt like buffy episodes took so long to “get to the point.” why this structure made them feel slower or somehow more old-fashioned than i remembered. not necessarily in a bad way, although sometimes that. and i realized what it was is that the time buffy spent on set-up was not spent on plot set-up, but on idea set-up. the buffy teaser + first act is always about setting up the ideas that the episode is going to be exploring via its supernatural metaphor of the day. those first fourteen minutes of hush pretty much hit you over the head with the fact that the episode is about communication (walsh: “it’s about communication”). or halloween spends all of act one and half of act two making sure we know that the episode is about duality and the parts of ourselves that we feel allowed to indulge or not, before the characters finally turn into their costumes.
i don’t know how common this was. i’m not very up on my tv history. (though i do remember trying to watch the musical episode of xena and being baffled by how long it took to get to the actual musical part). but realizing this did clarify why it is that on an intuitive level, buffy just plain never felt like a plot show to me, why it rarely bothered me when the plot didn’t make perfect sense, or characters got shuffled around in the interests of metaphor. because the structure of the episodes was based on the rise and fall of idea rather than plot. it also made me wonder if the show tended to linger on the set-up phase because it didn’t expect people to pick up on the fact that that was what it was doing, otherwise. like i watch hush now and i get sort of impatient--we know! it’s about communication!--but perhaps it felt necessary to do that in case people mistook the episode as a gimmick. i notice that the episodes that have this structure but don’t feel slow usually feel that way because the set-up is written in a fun way. in doppelgangland, vampire-willow doesn’t show up until the very end of first act, but i don’t notice because because all of the set-up is tight and pretty focused on willow as a character.
(the main other show i could think of that did this is mad men. it spends a very long time on idea set-up, and each episode has an advertisement or historical event that serves as a metaphor or cipher for whatever the show feels like exploring that week. that concept-heaviness probably explains why it’s also a show that i like a lot.)
i’m also noticing that the later seasons make an increasing number of breaks with that structure, even though they continue to center idea. especially in season six, the episodic stories tend to get to the point very quickly. like life serial is a classic metaphor episode, but the nerds start messing with buffy right away in the first act. it’s really only the teaser that handles the set-up (actually what i love about life serial is that it’s really four metaphor episodes in one). once more with feeling obviously gets to its gimmick right away too--the opening number involves buffy revealing her private feelings, which is the whole point of the episode. or in normal again buffy starts hallucinating at the end of only the teaser. and episodes like dead things don’t even really have an obvious metaphor. i mean, you could see everything up until katrina’s death as set-up, and guilt over that death as the metaphor, but the episode is more structured as a stew of feeling. the only episodes in season six with a truly old-school buffy structure are probably after life and older and far away.
and then season seven takes this even further by going more in the direction of serialization. it doesn’t totally lose the structure (the killer in me comes to mind), but i do wonder if maybe one of the reasons that season feels off to people is that the structure of the episodes makes you think that show has gotten plot-centered, but it actually hasn’t. it’s still doing idea. at its best, the “mature” episode structure in season seven allows it to do episodes like conversations with dead people, selfless and storyteller, which waste no time in telling you what they’re about, and instead let those ideas reveal themselves naturally, but at its worst leaves the audience confused, because there was no guiding introductory section to frame the events of the episode. but regardless the structure is less classically “buffy-like.”
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ideas for a Rewrite of Pixar’s Onward
So I finally watched Onward, unfortunately not in theatres because of [REDACTED] but what can you do? Gotta be honest, it didn’t wow me. :/ The world seemed flat and boring, and a lot of the tropes and story beats felt really played out and done before, even within other Pixar movies. That said, fantasy themed worlds and the potential creativity therein is a topic that is super close to my heart, and even when the trailer dropped for this movie I wasn’t super impressed with what it had to offer. From the setup of the plot itself, I’ll admit that I was skeptical of it from the outset, perhaps a bit more than usual.
I have my issues with the world building of this film from a visual design standpoint as well, but I’ll save that for another time. For now I want to discuss how I would approach rewriting this film to make it an overall stronger product in terms of story and character development. Obviously there will be spoilers for the actual plot of the movie in addition to my thoughts, so fair warning there.
Okay so when it comes to building a new world for your characters, regardless of its themes or genre, it is important to establish how much of that world pertains to the story you want to tell. As in, are you telling a story about the world itself via your characters, or are you telling a story about the characters with this world as a backdrop? It might seem like a small distinction, but a world’s rules (or lack thereof) can easily divert an audience’s focus within a story. I believe the current version of Onward is an example of the latter, but with a few complications of the former that muddles the direction of the plot a bit. The sense of scope for this film seems to go half-and-half instead, but we’ll get to that later. At the beginning of the movie, we are told about how the world of Onward followed more closely with what we would call a fantasy world; wizards, mythical creatures, knights, a magical staff, the works. But in a pretty rapid-fire scene, we are shown how modern technologies began to usurp the use of magic, thus leading to the modern day fantasy world that is the setting for the rest of the film. Despite how quickly this plays out as a sort of prologue for the movie, I do believe this is a fine set up for a movie like this...
If the movie was about the world.
But as we know, it’s about Ian and Barley’s quest to bring their father back, and almost exclusively focuses on their family. This too is a perfectly good setup, but the movie somehow ends up with both, and it leads to a lot more questions than answers as a result. The prologue setup generates a lot of questions about the world itself, such as the use and discovery of magic, that do have an effect later on in the story, but the implementation of magic itself does not have clearly defined rules about who can use it and why. Modern day law enforcement seems to govern this world, yet any use of magic does not seem to have any bearing on that. Magic clearly still exists in this world, but the audience does not know when or how it appears. Where does magic come from? What is the scarcity of it? Can you get arrested for using magic? Do people who use or own magical items get special treatment? Are magical items more valuable and therefore need to be regulated? How common are they? All creatures in this world appear to be inherently magical, or at least possess abilities from their magic-based ancestors, but seem to have “forgotten” those abilities over time. Both the pixies and the manticore have wings, but it seems that only the pixies need magic to use them. Why? Historical landmarks like the one Barley tries to protect in the film are viewed as passive history, no longer holding much significance. And even the manticore’s map is reduced to a placemat at a children’s restaurant, so the preservation of this history does not appear to be a priority for this society. Moreover, these questions also directly correlate to the main protagonists, namely, why can Ian wield magic and Barley cannot? If Wilden (the dad) could or used to wield magic, could Laurel (the mom) do it too? Are their different kinds of magic? Is there a hierarchy to how powerful one’s magic can be? Ian becomes better at using his father’s staff over time in the film, but how he is able to do so via the staff or Barley’s instruction is pretty unclear. Now, all of these are questions are actually ones that wouldn’t need to be answered necessarily, but only if the film reeled itself in a bit and its scope was a lot clearer. Many other fantasy or alternate world stories have a much smaller scope that doesn’t need to ask these questions of the audience when it doesn’t pertain to the story they’re telling. An excess of world building does not matter if it has no bearing on the current story being told. A good example is in Who Framed Roger Rabbit?, where the establishment of toons existing in the real world is the entire crux of the story, but how toons became a part of the real world is not explained, and doesn’t need to be for the direction of the plot and characters. You are introduced to the world with only the information you need, and you are taken through the story with that specific set of information. The progression of the plot does not rely on answering the question of why toons exist in this world, so it does not address it. Onward could have achieved this too, if the film didn’t explicitly ask these unanswered questions within its own plot. If the film focused solely on the Lightfoot family without the prologue, all of these questions about the world wouldn’t need to be answered. This is not a “magic was usurped by technology” story. This is a “how do I get my Dad back?” story. Which honestly begs the question:
Why does this have a fantasy setting?
With how much this film goes half-and-half on the relevance of the world to its characters, the more it seems like a coat of fantasy paint slapped on top of a story that could be told with real humans, or any other kind of creature for that matter. The fact that these characters are elves, pixies, trolls, etc. is inconsequential to the storytelling. Magic aside, if you replaced all of the fantasy races and locations with real-life equivalents, what would change about the story or its progression? In fact, if you removed the idea of magic entirely and replaced it with a series of non-magical challenges that Ian faces on his quest, you would have the same movie, just without the fantasy filter. All of the locations in the movie are not inherently fantastical, the school, the gas station, the tavern, even the vehicles and animals in the film, all have really obvious real-world equivalents, which diminishes the fantasy theme even further. Nothing separates them from these parallels. Even the main magic system is an equivalent to DnD and other tabletop roleplaying games in this world, and isn’t viewed as anything more despite becoming a prominent source of power for the protagonists. Again, having the world take a backseat to the characters is not inherently a bad thing, but if you’re going to take the time to establish how this world began and changed over time, then that has to be relevant to the story at hand in some way, otherwise you’re just establishing something that ultimately doesn’t go anywhere. So how would I fix this? Well, at this point I feel like you’d have to pick one of the two halves that this story tries to weave together: either open up the world and the relevance of magic within it, or focus exclusively on the Lightfoot family and their relationships. If it were me, I’d pick the latter, because to me the best parts of the film were the parts that focused on the family, especially the relationship between Ian and Barley. The world of Onward really isn’t that interesting as it stands, so putting more focus on that without a complete overhaul probably isn’t a good idea.
To start, I would keep the part about Ian wanting to learn more about his Dad, as well as Barley’s memories and misgivings about not saying goodbye to him. This, like most Pixar movies, is the strongest part and serves as the emotional core of the film. Both of them have their individual reasons for wanting to see their father again, and those motivations can move and change over the course of the narrative. But, have Ian tie his own identity to finding his father, as if his father is the one person who can tell him who he needs to be. A missing piece of him that only his father can fill, and this desire becomes more and more desperate as the film progresses and they run closer to that 24 hour time frame. Those earlier scenes about others who knew and admired his father could help corroborate these feelings, where Ian wishes to carry on the legacy of his father. Perhaps Barley could have similar feelings, as if being called a “screw up” throughout his life made him question the legacy of his father and his relationship with him. A “I don’t know who I am + believe in yourself” message has been done to death, but the execution could still make the ending of this film that much stronger. When the climax happens and Ian is unable to see his father before the sunset, THAT is when you want him to have the Act 3 Pixar realization about the overall message of the film, and how he had a father figure through Barley the whole time. Maybe there’s a point where Barley is hanging onto Ian in the rubble and time is running out, and he tells Barley to go see their father while he still has the chance. Have the internal realization be that Ian doesn’t need to see his father to know who he is anymore, as the journey he went on throughout the movie already gave him that answer, thus allowing him to let go and let Barley get his closure instead. Some of these points do exist in the current version of the film, but I feel that this slight reframe could strengthen it enough so that it is a common theme throughout the movie.
The subplot with the mother and Officer Colt is a strange one, further complicated by the inclusion of Corey the manticore as a secondary character, but I think it could have rounded out the story even more with a bit of work. If there really needed to be a stepparent role for this movie, I feel like Corey could have filled that role while also providing the map for Ian and Barley’s quest (I know getting a Disney Gay is like pulling teeth at this point but hear me out). There is a fairly decent amount of time spent in the movie regarding Laurel’s role in protecting her sons, especially when she recruits Corey into finding them. And with the scene at the tavern, Corey already has a decent idea of what the boys are like, which could make for good chances to bond with Laurel. There’s a good line in the movie that I feel really goes under-utilized, where Corey describes the boys’s assertiveness at the tavern. Laurel assumes she’s talking about Barley, but she’s really talking about Ian, and this surprises her. This is a really good way of showing that another’s perception of one’s character is not the whole picture. With the climax reframed to better focus on Ian’s sense of identity, this could have been an excellent line as a lead up to that climax, and for thematic coherence overall. Ian struggles with his identity while relying on others to make it for him, and that extends to his own mother’s perception of him, which changes as the story progresses. Despite that, there doesn’t seem to be a lot of conflict between Laurel and her sons, even when discussing their late father. They’re sad, yes, but ultimately they’re dealing with it okay. They love each other, and despite their differences they have a good sense of solidarity. There doesn’t have to be conflict in that way in every story like this, but her quest to rescue them could have been a good way to bridge that, bringing in a one-two punch of parental resolution at the end.
With this you could cut Officer Colt’s character entirely, in fact I don’t know why both him and Corey are in the film when they seem to fight for the same purpose in the story. His inclusion doesn’t seem to create a rift in any of their relationships outside of mild disdain when he’s first introduced. I genuinely did not know that Colt was officially in the Lightfoot family until the word “stepdad” was used over halfway through the movie. Otherwise I just assumed he was someone who was involved with the family via arresting Barley and had at least a mild romantic interest in his mother. And given the relevance of Wilden and the strength of their prior relationship, that doesn’t paint him in a very positive light at the start. But if you really wanted to keep him, there needed to be a scene that truly solidified that he cared for Ian and Barley. There is very little to suggest what kind of relationship the brothers have with him, other than Colt’s disapproval of Barley’s delinquency, but by the end of the film they’re suddenly on good terms, as if some resolution was made. He doesn’t seem to do much more other than pursue them like a cop would a criminal, and even when Laurel is worried for them, his search still seems to be nothing more than a part of his job, like it was at the start.
Perhaps he could save them from something while they’re on the quest, like when Barley sacrifices his van to make the rocks fall. Maybe it goes wrong and the rocks falling still puts the brothers in danger, forcing Colt to abandon the other officers to save them. The brothers may be surprised at this, but it would have come from a genuine desire to protect them on Colt’s part. If you really wanted to establish even a bit of a connection with the brothers, he could’ve accompanied them on part of the quest, doing things that only he could do to help them, and perhaps having a chance to hash out their relationship with him along the way. I realize that Colt having difficulties connecting with the brothers is a common stepdad trope, but if he was to have any relevance at all, he needed a reason to be there. Ironically, Corey ends up having more interactions with the boys at the tavern than Colt does for the entire film. Overall I feel like there was a lot of missed potential with Onward, and while the emotional core was there like it always is in Pixar movies, I feel like it got skewed a bit along the way, thus diminishing the final emotional punch at the end. There are some genuinely great parts of this movie, especially Ian’s final character resolution with Barley, but the whole is not greater than the sum of those parts, and that saddens me greatly. I’m not sure how much of this was Disney mandated versus Pixar implemented, but I hope they can get their groove back eventually.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revelation, Coronavirus, and the Mark of the Beast: How Should Christians Read the Bible’s Most Fascinating Book? Part 1

Kevin DeYoung
Whenever there is a cataclysmic global crisis—be it war, rumors of war, or a novel coronavirus—we see a sharp uptick of interest in the book of Revelation. While paying attention to the Bible is always a good thing, Revelation is too often used (by Christians and non-Christians) in a way that does less to edify the body of Christ and more to stoke the fires of wild speculation and unfounded conspiracy theories.
It may be helpful, then, to understand what kind of book Revelation is and how to make sense of imagery like the mark of the beast. We’ll get to the mark of the beast in the third and final installment of this short series. But before we get there I want to take a couple posts to look at what Revelation is all about and how we should interpret this not-as-strange-as-it-seems book.
Big Picture
Probably no book of the Bible has been harder for Christians to understand and, as a result, produced more bizarre theology than the book of Revelation. Although it is called “revelation,” it has been anything but a revelation for many Christians. It is a closed book for many of us, not correcting, not teaching, not rebuking, not training in righteousness like all Scripture should.
I remember teaching through part of Revelation for a Sunday school class several years ago and telling my mom about it over the phone. She said something like, “Kevin, you’re not going act like you have everything figured out are you? John Calvin didn’t even write a commentary on Revelation. You don’t know more than John Calvin, do you?” It is true that Calvin did not write a commentary on Revelation (one of the few books he didn’t write on), and it’s true that I don’t have everything figured out. But most of Revelation can be understood and applied if we will take the time to study it.
In fact, the entire book of Revelation can be summed up in one word: nike. Nike is the Greek word for victory. It occurs one time in the New Testament—1 John 5:4 states, “This is the victory that has overcome the world, even our faith.” Another form of the word (nikos) appears four other times, three times in 1 Corinthians 15 (e.g., “Death has been swallowed up in victory;” “He gives us the victory through our Lord Jesus Christ”). The verb form, nikao (meaning to conquer, to overcome, to triumph), occurs more frequently—28 times. Seventeen of those occurrences, more than in the rest of the New Testament combined, are in Revelation.
Revelation is the story of the Devil trying to conquer the church, but the church overcomes the Devil and the world because she belongs to the Lord who has won for us the victory (Rev. 5:5; 17:14). The book of Revelation gives instruction for the believer on how to conquer instead of being conquered, how to triumph instead of being trampled, and how to be an overcomer instead of a succumber. That’s why each of the seven letters to the seven churches concludes with “to the one who conquers . . .” If we cave and give in to persecution and give into worldliness and give into the Devil’s temptations, we will lose. But if we overcome through trial and suffering and seeming irrelevance, we will win (Rev. 21:6-7). That’s where history is heading, and that’s the big idea of Revelation.
(Possible) Map for the (Seeming) Madness
There is no one inspired way to understand the structure of Revelation. When studying this book in-depth several years ago, I found 11 different outlines, which suggests there probably isn’t one obvious structure we’re supposed to see.
One simple approach is to see Revelation as divided into two main sections. Chapters 1-11 introduce the story of God’s triumph, and chapters 12-22 explain the story in greater detail, this time unveiling in more depth the role of evil through the beast, the false prophet, and the whore of Babylon.
Another way of approaching the book is to divide it into four main sections, each marked off by the phrase “what must soon take place” or “what must take place after this.”
Rev. 1:1 The revelation of Jesus Christ, which God gave him to show his servants the things that must soon take place.
Rev. 1:19 Write therefore the things that you have seen, those that are and those that are to take place after this.
Rev. 4:1 “Come up here, and I will show you what must take place after this.”
Rev. 22:6 “And the Lord, the God of the spirits of the prophets, has sent his angel to show his servants what must soon take place.”
The language in these four passages comes from Daniel 2 and indicates that Old Testament prophecy is already and not yet completed in Revelation.
There’s another way to outline the book into four main sections. This approach marks out the times John says he was caught up in the Spirit.
Rev. 1:10 I was in the Spirit on the Lord’s Day, and I heard behind me a loud voice like a trumpet.
Rev. 4:2 At once I was in the Spirit, and behold, a throne stood in heaven, with one seated on the throne.
Rev. 17:3 And he carried me away in the Spirit into a wilderness.
Rev. 21:10 And he carried me away in the Spirit to a great, high mountain, and showed me the holy city Jerusalem coming down out of heaven from God.
By this reckoning, Revelation consists of four main visions that John saw while he was in the Spirit on four different occasions.
Yet one more way of approaching the book—and the approaches are not mutually exclusive—is to look for sets of sevens. Everyone recognizes that seven is a crucial number in Revelation, and that there are at least four sets of sevens: seven letters, seven seals, seven trumpets, and seven bowls. This much everyone agrees on. But from here things get less clear. Since there are plainly at least four sets of sevens, many scholars have wondered if we are meant to see seven sets of sevens. I am convinced there are seven sets of sevens, but I certainly wouldn’t be dogmatic about it. My outline, which is similar to outlines I’ve seen from others, looks like this:
Prologue: 1:1-8 I. Seven letters: 1:9-3:22 II. Seven seals: 4:1-8:5 III. Seven trumpets: 8:6-11:19 IV. Seven visions: 12:1-15:4 V. Seven bowls: 15:5-16:21 VI. Seven judgments: 17:1-19:10 VII. Seven last things: 19:11-21:8 VIII. The beautiful bride: 21:9-22:21
You’ll notice there is an eighth section that is not a set of seven. An eighth section makes sense because eight is often the number of new creation in the Bible (Jesus rose on the eighth day/first day of a new week, eight people started the new humanity after the flood, sons were to be circumcised on the eighth day), and this eighth section is about the new heavens and new earth. But there is nothing inspired about the outline above. It’s just one way of making the book more manageable and putting together some possible patterns with some obvious ones.
Our Interpretive Lens
The last thing I want to do in this post is look at the various ways Christians have understood Revelation. There are four main schools of thought.
The first school of interpretation is called preterism. The preterist approach teaches that a large portion of the book of Revelation was fulfilled in the first century, specifically in the destruction of the temple in AD 70. Further, most of the prophecies in Revelation were fulfilled by the fall of the Roman Empire in the fifth century.
The strength of the preterist school is that it puts Revelation in its original context. Revelation was written to first-century Christians with first-century metaphors and imagery and referents. If we jump to the 21st century and ask, “What does this mean for me?,” we will almost surely get the wrong answer. We have to first ask, “What did this mean to them, to John’s original audience?”
Preterism is not without weaknesses. First, some preterists try to find a single, specific fulfillment to the prophecies of Revelation when it seems more likely that John’s visions often portray generalized spiritual battles and struggles that occur throughout the ages. Second, full-blown preterists argue that all of the end-time events, like the second coming and the last judgment, actually were fulfilled by AD 70. This does not seem in keeping with the cataclysmic language used at the end of each sequence.
The second school of interpretation is called historicism. The historicist reads Revelation as a straightforward, sequential roadmap of history. Revelation is seen as predicting any number of key historical figures and events from Napoleon to Hitler to the European Union to the United Nations.
The strength of historicism is that it makes Revelation relevant for all Christians. It focuses our attention not on the fall of the temple or on the Roman Empire but on the way of the church in the world.
But besides this strong point, historicism is the worst way to try to understand Revelation. It is full of weaknesses. Let me quickly mention just four.
First, historicism is often anachronistic and takes Revelation out of its original context. I am thinking of those who argued that the country out of the north (from Daniel, not Revelation) must be Russia, or that the locust swarm from Revelation 9 is foretelling a helicopter battalion. These sorts of interpretations completely ignore the imagery of ancient prophecy and the context of the first century.
Second, historicism, with its end-of-the-world predictions and identifications of the beast, has often been demonstrably wrong. During the cold war, people saw Russia in Revelation. A decade ago they saw Iraq. Now they see the coronavirus. In a few years, they will be on to something else. Historicists tend to see Revelation being fulfilled in whatever crisis is pertinent for the day. And then on another day, another group of historicists see that view was wrong and find something completely different.
Third, historicism limits the prophecies of Revelation to one exclusive location or personality instead of allowing that the imagery of Revelation may be well suited to an inclusive number of different figures and times. That is, I think historicists are right to see Revelation unfolding in history, but they are wrong to think that Revelation is uniquely unfolding in one historical moment.
Fourth, historicism is irreducibly subjective. There is simply no objective standard of interpretation. Who’s to say that Hitler was more the beast than Stalin? Or that 666 is a reference to Bill Clinton (as one website I found argues)? Or, as another article maintains, that Ronald Wilson Reagan (six letters in each of his names!) was the beast? It’s all hopelessly subjective. The text ends up saying anything we want it to.
The third school of interpretation is futurism. The futurist reads Revelation (chs. 4-22) as a prophecy solely concerned with the distant future. The events depicted refer to the time involving, or immediately preceding, the end of history. Dispensationalists are futurists (though not all futurists are dispensationalists).
The strength of futurism is that it emphasizes how Revelation speaks to the future, not just about the past. Futurism is right to see that some things in Revelation deal with the final consummation of human history. Futurists are also right to see that the future is moving somewhere, toward the triumph of the Lamb.
But futurism also has weaknesses.
First, if Revelation 4-22 is entirely and only about the distant future, then most of Revelation was barely relevant to its original readers. Sure, it would have helped them see the end of the world, but it really spoke little into their immediate context (when John says Revelation revealed “what must soon take place”).
Second, futurism often assumes a strict sequential chronology. And yet, we cannot assume that what is shown to us in chapter 12 comes in time after what we see in chapter 6. To the contrary, one of the keys to interpreting Revelation is to understand that its visions are recapitulated. So, Revelation gives us a sweep through history in the seven seals, and then does the sweep again in the seven bowls. Revelation comprises overlapping prophecies that go back and forth between the present and the future and are not strictly chronological.
Don’t think of the visions of Revelation as frames from a movie reel running through the light one after the other. Think of the visions as portraits in a gallery. You look at one portrait and get a glimpse of reality, and then you look at the next portrait, and then you walk over to the next room and look at the portraits over there. They are pictures telling the same story and pointing to the same reality, but they aren’t sequential clips from a movie.
The fourth school of interpretation is idealism. The idealist reads Revelation as a symbolic conflict between the forces of good and evil. Revelation, idealists argue, does not point to particular historical figures but depicts the timeless struggle between God and Satan. It interprets Revelation as a series of repeated symbolic pictures, focusing on the church’s triumphant struggle from the first century until the last judgment and the eternal state.
The strength of idealism is that is understands the symbolic nature of Revelation. It realizes that Revelation’s imagery is rooted first in Old Testament language and second in the known world of the first century. The other strength is that it sees behind the first-century context deeper spiritual realities that would outlive and transcend ancient Rome and remain relevant for believers throughout the ages.
The weakness of idealism is that it can at times under-emphasize the fact that all of history is moving somewhere. That is, idealism sometimes sounds vague, as if there were no end point in history as we know it, as if Revelation was just about the struggle between good and evil and not also about the ultimate triumph of Jesus Christ.
Interpret the Book
So what approach do I think helps us best understand Revelation? I think each approach offers something needed. This doesn’t mean that I think every approach is good or that one is not better than another (I’m basically an idealist with a partial preterist bent). But each school of interpretation does offer something important.
With the preterist, we must read Revelation in its immediate context.
With the idealist, we must look at Revelation as a symbolic portrayal of God’s work, most of which can be applied to any historical time.
With the futurist, we must read Revelation with end of history in mind, recognizing that the book depicts, in parts, the second coming, the final judgment, and the eternal state.
And with the historicist, we must understand that the prophecies of Revelation, though they are not limited to one particular occurrence, are fulfilled in time and space.
The best way to defend one’s interpretive grid is to actually interpret the book. But since this is a three-part blog series and not a 50-part sermon series, we will have to settle for just one more post on the subject. In the first three verses, John makes clear that this book is an apocalypse, a prophecy, and a letter. Once we know what each of the terms entail, we will be better equipped to understand the book as a whole and specific imagery like the mark of the beast.
Note: This post was first published through The Gospel Coalition website.
1 note
·
View note
Text
FoZ Notes 22
Okay, here we go, final volume of the series. Not likely to be much added value here, but I took these notes regardless, so I’m posting them.
---------------------------------
We open with a bit about Brimir and Sasha, showing he put the Lífþrasir rune on her to potentially avert catastrophe while really hoping he didn't have to do so. It seems to be implied he doesn't want to get Sasha killed, but it's ambiguous and could be taken as him not wanting to nuke the Elves or something of the sort. Looking back after reading the rest of the volume... I honestly have no idea how this is meant to be taken.
The narrative refers to Colbert as being one of the 'rare realists' of Halkegina. That's... morbidly comedic in how grossly wrong it is, but there you go: Colbert is supposed to be a realist in the pessimistic sense of 'that sounds too good to be true, so it probably isn't true'.
Vitorrio apparently already knows that the place Saito comes from is 'the holy land'. I... have far too many questions...
Vitorrio dumps on us a backstory about how Brimir being God or Jesus-analogue is a lie and actually Brimir came from Earth and all magical nobles come from Earth having fled from the technology-using humans who are our ancestors. This is dumb nonsense, but foreshadowed dumb nonsense. Much worse is Vitorrio randomly claiming commoners haven't awakened to their magical power as an inevitable consequence of 'the blood thinning', where returning to Earth is supposed to be a solution. HOW???
If magic is a genetically inherited thing where breeding with non-mages is 'diluting' magical blood and reducing the portion of the population who can do magic, going back to Earth with it's technophile non-mage population is the OPPOSITE of a solution to magic power fading. Furthermore, how did we end up with mages in a minority in the first place? Did the original mages actually run away with a massive population of non-mages? If so, why? Were they slaves? SO MANY slaves that Halkeginia is predominantly non-mages? 'cause if so I have zero sympathy for the population that became Halkeginians.
Furthermore, Halkeginia is FILLED with magical races! If Vittorio wants to make magical humans the default form of human and the narrative is going to invoke magical eugenics while making Vitorrio entirely amoral in pursuit of his goals, the correct solution is to fight to overcome human prejudice against elves and orcs and other demihumans and in fact attempt to institutionally encourage cross-species breeding between commoners and assorted magical species. It's not like this series has been shy about sexualizing eg Tabitha's dragon when she's in human form, so you can’t tell me the series is shying away from bestiality undertones!
But no, Vitorrio's True Plan For Real This Time is literally to conquer Earth in some insane, nonsensical attempt to Get Magic Back. And of course nobody calls him on this being utterly insane nonsense that cannot POSSIBLY accomplish his stated goal.
Okay, and he also wants to conquer Earth to escape the Wind Stone-based catastrophe, with eyebrow-raising logic about how surely nobles will survive it just fine and only commoners will die, but seriously the magic genetics bit is blatant, horrifying nonsense, and it’s Vittorio’s inner thoughts so there’s no room to headcanon it as a lie or something else that would excuse this awfulness.
Also Vitorrio magically gets to drain Saito's life force as a side effect of opening the door. No explanation or justification provided. Just... loldrama.
This conveniently causes Saito to go into an Expositional Flashback™ in which he meets Brimir again and Brimir conveys that he's trying to kill all elves everywhere because "we can't understand each other", with this somehow supposed to be connected to magic stone catastrophe stuff. So, you know, stuff we already knew that doesn't make any more sense than last time.
When we cut back to Louise and company, we learn they immediately screwed off to wring their hands over Saito's unconscious form, instead of fighting Vitorrio’s horrible plan. Really?
Louise is explicitly willing to DIE to prevent Earth from being invaded... but no one entertains the notion of eg killing Vitorrio to stop his nonsense. Nah, they're going to try to talk him out of his insane plan. Really?
Henrietta is now using -dono when referring to Saito. Are you kidding me?
Henrietta and Vitorrio magically recognize a relatively modern pistol as being better than Halkeginian firearms... by just looking at the pistol laying around. Not testing it and seeing it has superior performance, or even remarking on something like it being made of parts too fine for a smith to pull together so precisely. Just... magically knowing it's good on sight.
Vitorrio also reveals that Earthlings have somehow invaded Halkeginian in ages past via a never-before-established natural portal between the world's, and now claims he wants to hit Earth before Earth figures out how to harness the Void (Why he thinks non-mages will be ABLE to do so goes unexplained) and attacks Halkeginian. This is ALMOST like a sensible, coherent motivation, but requires ignoring how contradictory and insane the premise is.
Turns out Vitorrio somehow knows for a fact that Louise can cancel the Wind Stone catastrophe, but is withholding this information from everyone to try to force people into going with the Conquer Earth plan. This is dumb, but plausible human dumb. Much dumber is the narrative talking directly to the audience to reveal that Julio is being left out because he's totally unsuited to deception and is actually a naive innocent sort... in utter contravention of literally EVERY prior scene Julio was in.
The Romalian church steals a nuke from under the sea, and Julio magically surmises its principles and informs Vitorrio that it's operating on Void principles. So... Void magic is now supposed to just be atomic shenanigans? I'm pretty sure the narrative previously heavily implied they're quantum shenanigans and regular magic is somehow atomic shenanigans. Consistency!
Pegasi are apparently a thing in Halkeginia. I don't think such came up before and it feels like a poor fit, but it's been a while since I last read so I might be forgetting something is all.
It's now being retconned in that Saito being the Lífþrasir familiar means that A: ANYONE using Void magic will tap Saito's life, and B: he will die in a matter of days for no good reason even if nobody taps his life force any further. Really? That admittedly makes the earlier bit of Saito collapsing into an Expositional Flashback™ a part of this retcon instead of pure arbitrariness, but this is a blatant, stupid retcon that cannot possibly be reconciled with prior events.
Derflinger is continuing to absorb magic while 'asleep', which I'm pretty sure contradicts what happened in prior volumes.
Also, Saito is perfectly willing to attack Romalian forces in an attempt to stop them from using nukes... but people continue to completely ignore any possibility of attacking Vitorrio himself. What is this garbage?
We get introduced to the Vysendal, Tristan's royal flagship built to carry dragons for the fight with Albion... which we somehow never heard about the many volumes ago it should've cropped up in. It’s basically a fantasy aircraft carrier airship.
Three loud knocks followed by two quiet knocks is how Agnes announces herself to Henrietta, apparently, and it's apparently forbidden for anyone else in the Tristainian palace to use this knock. O...Kay?
Bizarrely, Henrietta is of the opinion Saito would never cause trouble without a good reason. Attempted-rapist Saito, you mean? The Saito who has picked fights with people over issues of ego? That Saito? Mind, she barely knows him to be honest, but that just shifts the issue elsewhere. Hell, she even describes him as 'not hot-blooded', which is just laughably wrong.
We get introduced to Château d'If, which is an Elven prison. This is a little confusing given Elves have always solved these kinds of problems with exile or murder historically, but okay. Really, I'm more baffled by the French-sounding name, given Gallia is Not-France and the Elves haven't previously had Frenchness to them. In any event, it's an island prison off the shore of Eumenes, which... seems unlikely...
Also, it's directly named after a real place. Oh, and the narrative draws attention to the French naming, saying the name means 'prison island's in Gallian... but doesn't explain WHY it's named in a language Elves sneer at.
We get explicitly told only Elves that have committed serious crimes, such as treason, get locked up here. You know, the kinds of crimes we previously got told got Elves exiled. We also get told the island has been nearly totally abandoned by the Great Will (for some reason...) so Elves can't use Ancient Magic on it... except apparently the guards can due to making contracts of some sort, in contravention of prior Ancient Magic mechanics.
... and now Guiche is joining in on the 'Saito wouldn't make trouble without a good reason' nonsense train. He actually kind of knows Saito! Not only that but he's repeatedly projected his own shitty behavior onto Saito! He's very nearly the last character I'd buy this belief from!
The 'Great Will' is supposedly a giant chunk of magic rock (I forget if this already came up or if I’m getting mixed up by having run across some spoilers in earlier note-taking), and it grounding arbitrarily accumulating spiritual energy periodically is what causes the Wind Stone disaster stuff. We get this info from Brimir, with no explanation of how he drew this conclusion.
The story also throws in a line about how even blowing up the Wind Stones with Void magic isn't a valid answer because yadda yadda exhaustion. Honestly, this looks like a Suspiciously Specific Denial, like readers raised exactly this possibility, and the author is going 'shit, that's a really good point, but I can't have my intended drama if that's a valid answer so I've gotta invent a reason why it isn't'. Because seriously, with the scale of destructiveness Void magic is capable of, particularly considering how much the story is playing it up... yeah, blowing the Wind Stones up really ought to be a valid answer.
Compounding this is that Brimir explains his plan to prevent the Wind Stone disaster was... to blew up the Great Will. And it apparently worked. So the story is just contradicting itself; which is it? Explosions aren’t helpful, or explosions are helpful? It can’t be both.
Oh, and there's drama about how Brimir tried to explain his plan to the Elves, but they refused to move their city away from the Great Will so he could nuke it without killing them, with Elven leaders saying that if the Great Will wants the world destroyed then so be it and Brimir also remarking arbitrarily that the city at the foot of the Great Will would be the only place safe from the Wind Stone disaster so the story is kind of implying the Elves are actually going 'well, we'll be fine, so we don't care if you all die'.
Anyway, Brimir was pushed over the edge into nuking the area because his home village was slaughtered by Elves while he was trying to talk the Elves into letting him nuke the Great Will. So honestly this is revenge in part. (No explanation is ever offered for why they slaughtered his village, incidentally)
We also learn Sasha killing Brimir was in response to nuking the Elven city, and that Brimir let himself be killed, at least in part to free Sasha of her Familiar runes so the arbitrary death-by-being Lífþrasir won't kick in.
A recurring thing in this final volume is that the Gandalfr boost for just holding a weapon lets Saito function in spite of being heavily weakened. As in, he literally cannot stand, and then holding a weapon let's him walk, and in fact fight athletically.
There's a surprisingly clever moment during Tabitha and Saito's escape where she summons some water to use it as a reflective surface to check around a corner. It's just a variation on using a hand mirror to check around corners, but if characters had been using magic in this kind of way the whole time I'd be a lot more willing to overlook the series' many, many flaws.
We get told the Knights of Parterre are good at casting spells undetected... no explanation for how this works... and that Tabitha has mastered this skill, too. Ambush spellcasting is a neat idea, admittedly, but the context this is being invoked in is just confusing to invoke it in.
There's a bit about Elves being helpless if they can't complete magical chants. It's been a while, but I'm pretty sure previously part of what made Elves scary-powerful was that Markey needed to chant and Elves did not. Certainly, I remember for sure that Markey were chanters the whole time, which is conspicuously failing to be mentioned in this volume...
Aaaand now the story is saying Saito being emotionally moved by his rescuers (Louise not being among them, note) is helping to power his Gandalfr abilities, trampling on that whole 'powered by love' thing. Really? Like, it’s a dumb plotpoint, but undermining it by making emotions-in-general provide power has a lot of thematic and practical problems.
Vittorio's other name is Serevare, apparently. I presume that's his personal name, though it's not actually clear. I don't think this has been alluded to before. In any event, him spending a night praying is able to make mountains rise from underwater. 'cause Void magic. The exact justification provided is that he's specifically manipulating the magic Stone with Void magic, but this just raises obvious questions about the potential to use this capability to address the Wind Stone catastrophe, since those are also magic stones of the exact same sort. Sure, Vitorrio is lying about being unable to deal with the crisis, but nobody within the story notices this. Even with how low my opinion is of the intelligence of these characters, I can't suspend disbelief over this. It's a gaping hole in the argument Vitorrio is using to coerce Louise into helping him invade Earth. The story HAS to address this, and it doesn’t, instead stacking on drama scene after drama scene even as it rips out their foundations as they’re being pushed.
We get told Gandalfr powers can't actually compensate for lost vitality (even though that's exactly what Saito has been doing for a while now), but Derflinger can do so. (Never mind that he was re-acquired only minutes before this claim) Gandalfr powers can 'only' make Saito light as a feather. Yeah, just ignore this nonsense, it's just a crappy attempt to say Saito is even closer to death than ever before without actually impairing him in combat scenes any.
You remember how Derflinger has Convenient Magical Memory Loss? Yeah, while he was 'asleep' he got rid of that. Gosh. How convenient. And no, the story isn't going to try to explain why he didn't do this sooner, or explain how he knew how to do it now. Admittedly it's completely in-character for Derflinger to create problems for no actual reason while claiming to be helping... with the qualifier that's clearly not meant to be part of his character.
This is dumb and arbitrary, is what I'm getting at.
"Wow, even swords can cry." "No I won't, because then I'd rust." Wow, that's actually a great exchange that legit got me to laugh.
Holy crap, the story also remembered about crow familiars being used as serial scouts. That last showed up, what, 15 volumes ago?
Vitorrio apparently deliberately aims the portal at a US army base. At least, that's how Saito's internal narration presents it, but I'm pretty sure this is just the writer talking directly at the audience. This is presented as a sensible and intelligent course of action, which is confusing given I'd think Vitorrio would want to get his entire army on the other side before they had to face resistance. Even considering how intrinsically dumb his entire plan is, this is just confusing.
Turns out the Gandalfr killing their master makes Void magic go away. Because Reasons. So naturally Louise has committed suicide-by-Saito, to save his life. I cannot express in words how thoroughly I hate this stupid, monstrous, lazy culmination.
Then the story doubles down on the stupid, lazy, monstrous writing by having Derflinger commit suicide to revive Louise.
Bafflingly, Louise mourns Derflinger. I honestly cannot think of a single even marginally positive interaction the two had to justify this response. Like sure fine I can buy her feeling grateful for his sacrifice -ignoring how garbage everything about the sacrifice and its leadup is- but the story has her reminiscing about how he was 'always helping' and all. Conspicuously, where Saito flashbacks to a bunch of Actual Prior Events when mourning Louise's death, Louise doesn't name even a single incident in which Derflinger was helpful. So the writer can't remember any such moment either, and just hopes readers won't notice the lack.
Also, in literally the final volume, the place Saito was originally summoned finally has a name: Austri Plaza. Uh. Sure?
Cattleya gets convenient 'secret Elf medicine's to cure her incurable condition. So never mind that bit of respect I had for the series.
Louise permanently awakens to wind magic, because of course she does.
The elemental siblings show up, and we get told they're... vampire-human hybrids??? What? Did that crop up before and I just totally forgot?...
Oh, and Louise and Saito go live Happily Ever After in Japan after a bunch of drama is wrung out of Saito intending to first stay in Halkeginia and then more drama was wrung out of him deciding to go home even though it meant being separated from Louise. The story conspicuously fails to address how this could possibly work out well; Louise has pink hair, and is unlikely to completely avoid using her magic. She’s going to end up on an MiB dissection table in no time flat, frankly, not live happily ever after. This isn’t even touching on how messed-up it is for Louise to throw away her life in Halkeginia to follow Saito back; she has responsibilities of myriad sorts in Halkeginia. Heck, so does Saito at this point! Whereas back in Japan, the story has consistently indicated Saito’s parents are literally the only people who will notice or care about him going missing.
For that matter, there was this whole thing with Siesta, Louise, and Saito working out a three-person relationship, and while I found it cringe-y and was dubious because of the likely motives, this is just throwing that out by summarily cutting out Siesta. And also trashing the creepy, stupid crap with Tabitha and Henrietta loving Saito for no actual reason.
This ending is awful and antithetical to what lead up to it on so many levels.
-----------------------------------------------
So that’s it, I’m done taking notes on this series. I have a few things I’ll be saying in the coming weeks, but the note-taking is done, finally.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Alfredo Guttero
Who: Alfredo Guttero
What: Artist and Art Promoter
Where: Argentinian (active in Argentina and throughout Western Europe)
When: May 26, 1882 - December 1, 1932

(Image Description: Retrato del pintor, Victorica, 1929 [a self portrait]. It shows Guttero in his apartment. Outside is a very geometric skyline of smokestacks, steep roofs, and a brown sky. His room is slate colored and he sits in a chair in the foreground. He has a jacket thrown over the back of his chair. His pose is casual and he looks as if we [the viewer] have just distracted him from painting. He sits with his legs to one side, turned almost unnaturally toward the viewer. One leg is lifted slightly and one hand is on the chair's seat as if he is in the middle of turning completely to the viewer. He is a man with a receding hairline and a high forehead. He has a dark mustache and dark hair and low eyebrows. He is wearing a white shirt and bowtie and has his sleeves rolled up to the elbow and his collar is ruffled and loosened. The whole thing hangs very loose but you can still see some of his body's lines of musculature. His tie undone and hanging around his neck. His pants are ordinary and green/brown. His expression is calm but confident and he looks directly at the viewer. The colors are bold but not really bright. The style blends geometry and flatness and realism in a way I am explaining very poorly. End ID)
Guttero is not terribly well remembered today, which is too bad. Looking through his oeuvre I quite like his work. Maybe it is because he lacked the bombastic personality of many modernist artists, maybe it is due to his diversity of styles without one that seems to define his work, or maybe it is because he was one of so many talented artists of his generation. He was well renown in his era, however, and used his popularity and skill to foster the next generation of Argentinian artists.
Guttero's life began mundanely enough. He always loved art, appreciating it and creating it, but pursued a legal career instead. But he was unhappy with his life as a lawyer, so Guttero left it to become a painter. He pursued his dream and passion, inspired and pushed by other Argentine artists. In 1904 his reputation was good enough that the Argentinian government sponsored his move to Paris, then the epicenter of the truly exciting and revolutionary art world, its influence expanding outward. He studied there for a few years under Maurice Denis before appearing in the Salon.
He remained in Paris until 1916 when he began to travel extensively across Western Europe for more than a decade, first to Spain, then Germany, Austria, and beyond. He traveled to nearly every country in the area between the years of 1916 and 1927. His work was shown in various exhibitions around the continent from being featured in the Salon in Paris to a major solo exhibition in Genoa.
After that he returned to Argentina for the first time since his initial departure in 1904. Guttero remained active in his native country including creating free art classes called, aptly enough, Cursos Libres de Arte Plástico, with other Argentine artists. During this time he focused on his work as an art promotor, perhaps even more than his own art. During this time he introduced and showed new Argentinian artists to a wider audience. Indeed he created an organization for this purpose: the Hall of Modern Painters. He was dedicated to promoting and preserving modern art in the face of a world growing increasingly dark and reactionary. He died young and without much warning.
His art is undeniably modernist but trickier to pin to a specific movement. He has many different styles he utilizes with different degrees of naturalism and curves vs geometry. His scenes are by and large mundane and human, he uses bright colors, often huge central subjects, kinetic poses and positions, modern settings, and by and large human or urban subjects. He often painted on plaster using a "cooked plaster" technique of his own devising.
(Image Description: Martigues for Charles Jacques [1909], a brightly colored painting showing a scene in a Martigues canal. It is not completely realistic nor completely geometric and abstract. He favors color over outlines. In the background is a bright blue sky interrupted by yellow buildings with tile roofs, maybe houses, lit by the unseen sun. One of the building's lower doors is open. There is a small tree to the far right. In the foreground in the sparkling water of the canal are several small work boats, probably fishing boats judging by the silvery nets lying over the hulls. On the right a boat is coming in, there is a pale skinned, dark haired man working on one of the nets. His sail is red and white. On the left is a pale man in an orange hat and yellow shirt. He is stooped and just by his pose appears older, both of the men are too far away for many identifying details. End ID)
Possible Orientation: Mspec ace, gay ace, or aroace with an aesthetic attraction to multiple genders. (I am so unsure I have changed "probable" to "possible.")
I admit this one is a stretch on my part.
I am classifying Guttero based largely on absence, i.e. the absence of a remembered/recorded spouse, sexual/romantic partner, or liasian. I have no quotes or historical documents to prove my point. I have none of his personal philosophy or writings to draw from. Just the fact that he dedicated his life to art more than human relationshipa. That this is something I have seen before: Cause and its role in the life of many aros/aces/aroaces (outlined in Weil's entry the other day) and the fact that he had no recorded romantic/sexual partners that I can find in hours of research.
This illustrates why it is so, so difficult to find aspecs in history. We are not, as aphobes believe, impossible to locate, there is externally visible evidence, but it is less obvious than most other orientations. And cishets would rather we didn't exist so we are often buried under excuses. The easiest ways to find them are 1) if they were notably "married to their job" in their lifetimes (e.g. Jeanette Rankin and Carter Woodson), they talked/wrote about it in some capacity (e.g. T.E. Lawrence or Frédéric Chopin), they were distrusted because of it (John Ruskin and James Barrie), they made it part of their persona (Nikola Tesla and Florence Nightingale), aside from that I really need to search deep into their personal lives. Information not always available.
And often even when people essentially say "I am aromantic and/or asexual" the general population will not accept that. After all Newton is often remembered as allo and gay, despite never expressing interest in men. Chopin is often listed as allo and bi. Rankin is often considered cishet but too deeply concerned with her work. Barrie gets called a pedophile despite showing no interest in children. For eccentric aspecs like Weil/Tesla/etc. their being aspec becomes part of their oddness. If they weren't Like That they would be allo. Their being aspec becomes a symptom of their weirdness and would be unacceptable in a "normal" person.
History with a capital H does not want to acknowledge aspecs and, as with other queer identities, will go to insane measures to erase them. But even other queer historians will do this to aspecs. I am shocked how many people do exactly to Newton/Lewis/and the like what cishet historians do to Alexander the Great. In the case of Alexander the cishets ignore the obvious accounts that he loved Hephestian in nearly every way possible and queer historians and history buffs call them out, then often the non-aspec ones look at Newton and Lewis who had no interest in men and say they must have been gay. And it isn't really just history, Tim Gunn is by his own admission both gay and ace and the second part of that statement is either erased or, even crazier, I have seen aphobes say that he is mistaken about his own identity.
Anyway the root cause of this lack of nuance in the discussion of sexual orientation is a long sidebar that this is not the place to explore. I have left Guttero behind paragraphs ago. I have written a lot about how aces and aros end up getting erased from history and this isn't about that.
This is about Guttero and the difficulty of finding aros and aces. The presence of something is so much easier to find than the alternative, obviously, like if Historical Figure X exclusively slept with/courted men and was a man we can say he was (most likely) gay. But if Historical Figure Y didn't sleep with anyone/court anyone it is harder to prove. This is obviously severely simplifying identity but for the purposes of this example I beg your apology.
Long Story Short: the absence of evidence of something is not proof of the absence of something. A lot of aphobes will point this out and utterly ignore the fact that sometimes it is.
So, Guttero. The only thing I can say conclusively is that he never married and he was romantically or sexually tied to anyone as far as I can find. He was, in his time, very active in the art world. If he had been involved someone would probably have taken note. Especially considering his art is often very appreciative of the human form, especially the male one, it would not be hard to believe he was allo and gay or mspec.
I am going to take his art another way putting some dusty analysis/critique/art history skills to good use. Here's the thing, those who follow me on my personal blog or even here know I find the Death of the Author extremely important but it is also extremely complicated (it was actually the topic of my senior thesis). I don't want to use an artist's work to talk about their personal lives because art is often not reflective of life, but there is always some cross contamination in one way or another. I am going to explain what I mean on a superficial level, using myself as an example so I can say this is 100% accurate. I love the found family trope, and I think those relationships are the best in the world. So whenever I write something you can be damned sure if I can get some found family goodness in there I will. What I am saying is, I don't love or even approve of everything I write about, but I do write about some things because I love them and want to explore them and experience them on some level. The same may be true for Guttero and the subjects he painted.
Guttero often pays a lot of attention to human form. Look at his work The Market (I couldn't find a large enough image to put it in this post) and you will see his appreciation for amab musculature and on the other side of the male spectrum...

(image description: Retrato de Lucien Cavarry [1911] It shows a thin, lanky, and well dressed young man reclining on a green floral patterned couch and a black pillow. He is pale with neat, dark hair. He has a shadow of 5 o'clock shadow on his super hero jaw. His suit is white, his slightly rumpled tie is black, as are his socks and polished shoes. One arm is across the back of the couch and a red and gold pillow the other is dangling. This style is very different from the other portraits I showed/referenced. Still a modern but more realistic style, more flowing, less geometric. The man is drop dead gorgeous by Western beauty standards. End ID)
As for women...he seems to find them colder, more distant, but there is still a physical appreciation there. (Linking Mujeres Indolentes so I don't get flagged for "female presenting nipples" or whatever Tumblr's BS is. [The name alone tells you a lot]). Or the somewhat judgemental gaze of the woman below:

(Image Description: Georgelina. It shows a portrait of a pretty young woman sitting in front of a field. She is pale and long and beautiful. She has red hair, sharp eyes, a long flowing white dress with a gold sash around her waist, and a white hat with a black bow that is blowing in the wind. She takes up most of the frame and her expression is challenging and she holds eye contact with the viewer. The colors are bright and she is almost porciline in color. The background is mostly flat planes of color. In style it is somewhere between the self portrait and the portrait of Cavarry. End ID.)
Not all of his portraits of women have them so sour/distant but they all have a sort of challenging look. Beauty tinged with something dangerous, while the men always seem more innocent.
So here is why I say aspec rather than allo using his work alone, none of his work is particularly sexually inviting even with the sexiness/physical European attractiveness. The men are bashful or unaware of the viewer, the women are certainly not interested.
And back to the self portrait at the top: Guttero is in a fairly sexy pose, but it is sexy without being sexual. He is rumpled but the thing he was doing was painting, there is a sexless explanation. He is looking at the viewer, but you are distracting him from working. At first glance I thought his legs were spread, but they are simply in motion so he can face his guest more comfortably. This all could mean nothing, but I found it striking that this is how he chose to depict himself, at first he appears to be inviting the viewer in for a more physical interaction, but then it seems he is doing exactly the opposite, his passionate energy has been instead put into painting.
And in reality toward the end of his life that was what he did. He dedicated himself to his own art and the art of others.
So again, this could mean nothing. But...it could mean he is aspec.
And that is how the person I am least sure about got the longest entry.

(image description: Elevadores [1928]. A painting showing a factory complex. There is a raised platform running around it and several buildings in bright colors. There is a tree to the right side and a green hill. The building in the near-center [lightly left] is red. The sky is yellow and blue, perhaps the unseen sun is rising up behind the right-hand buildings. In style it is mostly geometric and flat color. End ID.)
#queer#lgbtq#asexual#ace#history#aromantic#aro#gay#mspec#20th century#artists#south america#Argentina#Argentinian#Alfredo Guttero
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chilling Adventures of Sabrina Season One Easter Eggs And References
I so greatly enjoyed Chilling Adventures Of Sabrina, and I’m really interested to see what they do in season two, which is almost done filming. I still maintain that this show is like if Riverdale and Supernatural had a baby. It’s definitely creepy and not for everyone, but I found it fascinating.
I’ve got Easter eggs galore, though I didn’t go through and explain who every comic book character is like I would normally do with a superhero show. And yes, the Netflix series is based on the 2014 Chilling Adventures of Sabrina comic, which in turn was named after another comic from decades earlier. Sabrina Spellman is an Archie Comics character, but it’s not clear if her show is set in the same universe as Riverdale or not.
There are spoilers here, but as usual, I’ve broken this list down episode by episode for those who want to read while they watch. Enjoy.
S1E01 “Chapter One: October Country”
Opening Credits
The opening credits feature the artwork of Robert Hack. Hack is the artist who actually illustrated The Chilling Adventures of Sabrina comic book. A lot of his art inspires the look of the show as well.
The Episode Title
October Country gets its name from a collection of stories by Ray Bradbury. They were all considered pretty dark, and the volume mostly reprinted stories included in a different anthology, only adding a few new pieces, king of like this show.
The Very 70s Aesthetic
The show kind of has a weird timewarp thing going on like sister series Riverdale. There’s a lot of cars, furniture, and even clothing that seem to be inspired by the 1970s. That’s likely because Sabrina made her comic book debut in the 70s. It’s a way to give an homage to the original books as well as the newer series the show adapts.
Cerberus Books
Cerberus was a three headed dog who guarded the gate to the underworld in Greek mythology. We’ll discuss him more in a later episode.
Dr. Saperstein
My guess is that someone on staff is a Parks and Rec fan. This is Jean-Ralphio’s surname, and his father, was, in fact, a doctor. Of course, it’s also the name of the doctor in Rosemary’s Baby, so… pick your reference.
Sabrina’s Thermos
You’ll notice some characters on Sabrina’s thermos. Those happen to be a musical group named The Archies. Yep, they’re Archie and the gang from Riverdale, which does make you wonder if the two shows are in the same universe or if one is the fictional version of the other or what.
Sabrina Makes Harvey Forget
She does it with a kiss here, but in the 90s television sitcom, she made him forget she was a witch a lot of times. This made me wonder if she might have to do it a few more times over the course of this series, or if the next time he finds out, it sticks.
Her Parents Were Flying To Italy
This is an awfully interesting destination. Why? Because what’s in Italy? That would be Rome and the Vatican, home of the Catholic Church, which is interesting in and of itself. It’s both a very romantic and a very religious destination for a witch and a mortal to be traveling to. It also happens to be where the first Sabrina The Teenage Witch movie was set, if I remember right.
The Weird Sisters
These three get their nickname from the trio of witches in Shakespeare’s MacBeth. There’s a lot of Shakespeare references throughout the show, but I think that’s really just because writers like their Shakespeare.
Salem
The show’s take on Salem is interesting. In the Chilling Adventures Of Sabrina comic, he was Sabrina’s familiar, but that’s not became he was a goblin. Instead, he was cursed by a witch in Salem to become a cat. He was a mortal man named Samuel who got her pregnant and, because he had nothing to offer her, he didn’t want her to have to marry him. She took offense, Satan ate their kid and she cursed him to become her familiar. When she died in the witch trials, Satan renamed him Salem as a nod to what happened.
The 90s sitcom had Salem as a warlock who was cursed to cat form by the witches council after committing a crime. It seems like Ambrose on house arrest is filling that role this time around.
S1E02 “Chapter Two: The Dark Baptism”
“...a movie star like cousin Montgomery.”
I like the idea that this is a nod to Elizabeth Montgomery, the star of the series Bewitched, which followed a witch named Samantha who married a mortal. Samantha’s evil cousin on the show? Her name was Sabrina.
A Riverdale Mention
So, Riverdale is likely just across the river from Greendale here since we hear the town named.
Black Narcissus
The name of the goat snagged for Sabrina’s baptism is also the name of a 1947 film. There’s actually a ton of classic movie references, posters, etc in the show, just like in Riverdale. I probably won’t point them all out because this would be a list of nothing but movie references.
S1E03 “Chapter Three: The Trial Of Sabrina Spellman
“Conserve water. Plug it up, plug it up…”
This is a sign on the bathroom door in the high school It’s a nod to the horror movie Carrie, which was based on a book by Stephen King. The movie also inspired a musical episode of Riverdale in season two.
Daniel Webster
The lawyer is named after a character in a pretty famous short story about a farmer who sells his soul to the devil and is then defended by a talented lawyer.
Archie’s Madhouse
Another comic from the Archie world of comics. One of its covers is on the wall in Harvey’s room. He’s clearly a fan of many different types of comics.
Ravens VS Bulldogs
We get another nod to the fact that Riverdale exists. About half way into the episode, there’s a kid putting up a flyer for a bowling match between the Baxter High Ravens and the Riverdale High Bulldogs.
Dr. Specter
I just thought it was funny that an eye doctor has this name. It’s not really an Easter egg, just cute.
Side note: Ambrose asks Luke if he’s a vampire. So, I’m going to go with witches aren’t the only supernatural beings the show will eventually introduce. Vampires, werewolves, there is no limit to what I expect now.
S1E04 “Chapter Four: Witch Academy”
Gehenna Station
“Gehenna” is an old biblical term that means hell-like. I kind of think it’s fitting that the school is disguised as an old train station as well since a lot of artists imagine purgatory as a train station. Hell-like purgatory seems like a good training ground for witches.
Nick Scratch
Old Scratch is a common slang, or at least it used to be, for the devil. Here, I think it’s just a nod to the fact that Nick’s a warlock. (Also, Nicholas Scratch was the name of a Marvel villain once upon a time, but that’s a whole different publisher.)
Valac
One of the names seen in a book is that of Valac. I think fans of The Conjuring franchise will recognize it as a demon there. Another movie reference in this episode? The “light as a feather, stiff as a board” chant used by the harrowed kids. That’s courtesy of The Craft.
S1E05 “Chapter Five: Dreams In A Witch House”
Batibat
Her makeup looks pretty reminiscent of The Witches (movie based on a Roald Dahl book), but that’s actually all I’ve got for this episode. Unless we count Sabrina using the children’s string game Jacob’s Ladder as her way to get the spiders’ webs going, but I think that’s just a result of that particular game being a prevalent one in the 90s, and thus, amongst the writers.
S1E06 “Chapter Six: An Exorcism In Greendale”
Harvey As Johnny Depp
Harvey with his headphones on in the #10 tee? That’s am almost exact remake of a shot of Johnny Depp in A Nightmare On Elm Street. (Side note: I kind of feel like this shot should have been in the previous episode, the one that actually focused on nightmares.)
Apophis
Apophys is a death metal group. Apophis is the name of an asteroid, but also a derivation of the name of an Egyptian ruler, as well as an Egyption entity of chaos. Apep was drawn as a giant serpent and was an enemy of “the light.”
The Exorcist Homage
Okay, this episode really just plays as a loving homage to The Exorcist. There are so many shots that echo frames from the film. I’m not going to even attempt to list them all.
The Witches That Came Before
Okay, Sabrina calls on the power of a whole lot of historical figures as she names “witches” during her exorcism. My personal favorites? The goddesses Artemis and Luna, the queen Anne Boleyn, and the mythical first wife of Adam, Lilith. She also calls on Morgan Le Fay of the famous Arthurian legend. She actually appeared in an old Archie comic involving time travel called Jughead’s Time Police. Yeah, even Archie comics got weird back in the day.
Afterlife With Archie
This is the more supernatural version of the Archie comic book universe. Luke actually has a copy of an issue in his hands while he’s in Cerberus. It’s funny because this comic book storyline was created by Sabrina trying to bring Jughead’s dog back to life… we’ll call that foreshadowing for a future episode.
S1E07 “Chapter Seven: Feast of Feasts”
Grandpa Kinkle
TV fans might recognize Grandpa Kinkle as Michael Hogan. He’s been all over genre shows for decades. Most recently though, and where Sabrina’s target audience will know him from, he played a hunter on Teen Wolf. There, he came from a long line of werewolf hunters. Here, he’s from a long line of witch hunters. Coincidence? I have a feeling it’s not.
Ben
Poor, tragic pizza delivery boy. Okay, so the most recent season of Riverdale also featured a character named Ben. Specifically, Ben Button. Ben Button was played by Moses Thiessen. Guess who this Ben is played by? That would also be Moses Thiessen. And, guess what else? They both (spoiler alert for Riverdale fans who haven’t watched yet) died in weird ways. What does this mean? I have no idea.
Side note: The only witches in the coven who don’t seem to partake in the feast are Sabrina, Zelda, Nick, and surprisingly, Prudence. (And Hilda and Ambrose, but they aren’t invited) There’s a part of me that wonders if that will be significant in season two.
S1E08 “Chapter Eight: The Burial”
1693
Above the entrance to the mine, we see that the Kinkle’s took over, or created, the South Line in 1693. I’ll admit, my first thought was, oh, that’s when the Sanderson sisters originally died in Hocus Pocus. It’s also the year that the Salem Witch Trials took place, providing a nod to the history the show pulls from. The Von Kunkles hunted down witches and stole their land while the trials were going on in Salem, which also indirectly led to the hanging of the original Greendale witches. Yikes.
American Vampire: Lord of Nightmares
A comic book published by Vertigo, this happens to land on Harvey’s bedside table. Another vampire reference, eh? I hope we see one eventually.
S1E09 “Chapter Nine: The Returned Man”
Dr. Phibes
He’s named for a Vincent Price character. If you don’t know who Vincent Price was, he was pretty much the face of horror in American cinema for a while. Do yourself a favor and look him up.
Pop Culture Nods
I have no idea why someone who claims to be as dark as Zelda chooses a song from The Sound of Music for the Church of Night’s choir. Your guess is as good as mine. Susie tries to shoplift Orlando by Virginia Woolf. I’ve never read it, but it’s certainly the type of novel Susie, or even a witch in Greendale would be interested in. It follows a poet who changes sex (male to female) and lives for hundreds of years.
S1E10 “Chapter 10: The Witching Hour”
Mr. Loomis
This is likely a nod to the Halloween franchise, but I’d be remiss if I didn’t say that it was also the last name of Sidney’s boyfriend in Scream, but that was a nod to Halloween in and of itself.
Riverdale
Again, a Riverdale nod. Harvey’s dad had the funeral home in Riverdale take care of Tommy instead of the Spellman’s. But is it in the Riverdale we know on TV? Who knows?
“Let Greendale cast a spell on you…”
This is the town motto on the sign at the edge of town. (I’d like to point out the sign is designed just like the one of CW’s Riverdale, so nice consistency in set design there.) It’s cute, but I’m also wondering how the town got this motto since everyone seems bent on rewriting the towns witchy history.
Cerberus
The owner of Cerberus books? His eyes flash yellow after getting a kiss from Hilda. I’d like to think he’s something canine to go with his name, and perhaps his store stands over an actual gate to hell. Whether he’s a real hellhound or a werewolf, or the show pays off on its vampire nods with him, remains to be seen.
Madame Satan
She reveals her real name. She also reveals she’s Lilith, first wife of Adam. I find it funny that Sabrina actually invoked her during the exorcism.
Comic Book Look
Sabrina gets her comic book accurate hair in the end here. You know, I don’t think she needed it, but it’s a nice nod that there’s been a transformation in her power level.
Bonus Motifs
These things showed up a lot, and I didn’t want to have to write about it every single time.
13
Pop culture has got 13 as being unlucky and associated with magic, so I like that the show embraced it. A witch’s pregnancy lasts 13 months, 13 minutes is just enough time for a soul to leave a body, and 13 hours is how long Sabrina has to wait to see if her resurrection spell worked.
Cain And Abel
These two brothers were the sons of Adam and Eve, for those who know their biblical stories. They represent jealousy and murder, etc. We’ve got Hilda with her Cain pit in the garden, but there’s actually a lot of more subtle references to them. Cain was a farmer (Hilda) and Abel was a shepherd (Zelda, leading the way), for example. There’s a lot of focus on sibling relationships considering the show’s main character is an only child. Harvey and Tommy, Hilda and Zelda, the Weird Sisters, etc.
Suspira
A lot of the set design (windows and ceilings, specifically) are nods to the horror film Suspira. I’ve never seen it, but it got a lot of notice from horror fans on social media, so I figured I should add that here.
Real Spells
According to interviews and set visits, the crew wanted the set to be authentic, so that had practicing witches cast protection spells on the set and used real symbols around the Spellman house. The Spellman house even has a German protection spell carved into the floor.
Jughead
Also according to set visits, one of the shelves in the Baxter High library has a shelf where you can see a crown and “Jughead was here” carved into it. I don’t think it’s actually visible while watching the show though.
So, what did you guys think about the show? Love it? Hate it? Did you spot more Easter eggs?
#chilling adventures of sabrina#sabrina on netflix#sabrina season one#chilling adventures of sabrina spoilers#easter eggs
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
BOOK REVIEW : Empress of the East: How a European Slave Girl Became Queen of the Ottoman Empire by Leslie Peirce
co-authored with @gevherhans
Haseki Hürrem Sultan (or Roxelana) was catapulted into the history books after she became Sultan Süleyman’s concubine & his favorite. She would eventually become his chief consort - his haseki, a title created for her position as chief consort, but unequal to that of the sultan. Her true name is lost to history; however, she was renamed Hürrem - a name that she used to refer to herself for the rest of her life. Captured & enslaved as a young woman, Hürrem was ultimately brought to the imperial harem, an institution Peirce thoroughly examined in The Imperial Harem: Women and Sovereignty in the Ottoman Empire. Going against the tradition of one son per concubine, Hürrem would remain in Süleyman’s bed & would give birth to six children, five of them sons; her son Selim would become sultan after Süleyman’s death.
Despite its interesting subject matter, Peirce’s Empress of the East: How a European Slave Girl Became Queen of the Ottoman Empire is a terribly written & biased piece that lacks structure, neglecting to include important information at logical junctures. More alarmingly, she distorts & exaggerates historical fact to embellish her subject’s power & influence, caters to fans of the ruthless second wave feminism trope, & ultimately tries to spin history into a fairytale rags-to-riches story. In the attempt to exonerate Hürrem & frame her as a heroine worth rooting for, Peirce presents her as far too brilliant, far too powerful, & far too perfect. Peirce’s Hürrem can do no wrong; she is intelligent, politically aware, & a keen manipulator of circumstance, but at the same time indisputably innocent of charges leveled against her - not even to ensure one of her sons would take the throne. Conversely, those who stood against Hürrem’s success like Mahidevran, Ibrahim, & Mustafa are consistently painted in a far more negative light. Their importance is watered down, their merits are downplayed, & their figures presented dismissively order to serve the narrative & make Hürrem look better.
When compared to her academic work, Empress falls flat on itself. While the prose is easy to read, Peirce’s writing falters as she attempts to write for a general audience. Rather than providing a scholarly analysis backed up by historical evidence, she favors a biased narrative that relies heavily on speculative “imagining”, value judgments, & tenuous yet sweeping claims. Her use of romantic & idyllic language drags down her writing rather than lift it up, & uncritically attempts to frame Hürrem & Süleyman’s relationship as a love story. The concluding statement of the introduction provides no better example of Peirce’s modus operandi, in which she asserts the Ottoman Sultanate’s survival was largely “bolstered by the reforms she introduced”, a process “generated along with the Ottoman empire’s greatest love story.”
This language is typical in the book. Peirce forces the reader to see the Ottoman world through her lens & adopt her wishful imagings, instead of allowing them to form their own views & imagine independently. Her “speculation” includes comparisons that make little sense, all the while implying that Hürrem “must have thought” of such things herself! Peirce notes that women forced into sexual servitude may not have viewed their status positively, yet at one point abhorrently tries to justify it because of the “compensations” - that these women “must” have known they probably wouldn’t have had easy lives or happy marriages in their homelands, & would be comforted that, even as palace slaves, they could at least live in the lap of luxury: “An emotionally & sexually fulfilling marriage had not necessarily been in store for them in their hometowns & villages. The common practice of arranged marriage could saddle them with husbands who were unattractive, considerably older, or even brutal. Mostly peasants, they were more likely than not destined for a life of daily toil - perhaps poverty - early death. The dynastic family to which they now belonged at least kept them in luxurious comfort - good health.”
Of course, no one knows what Hürrem thought during certain events; suggestions that she would have connected herself to other women in history, or compare the converted Ayasofya to her own experience, do not belong in a biography. Peirce can speculate - draw conclusions based on the facts that she has. However, she can’t lead readers to imagine that Hürrem ever thought of what architectural endeavors she might take on should she succeed with Süleyman, sympathized with Anne Boleyn, or compared herself to Gürcü Hatun (a Christian-born consort beloved by a Muslim ruler) - Byzantine royals like Eirene; that Süleyman instructed her in the art of war, tutored her as a diplomat, or gave her a say in how the design of the new palace harem, especially whilst Süleyman’s mother Hafsa was alive. There’s no evidence for any of these things. Such fanciful scenarios are better suited for a work of historical fiction - & considering how Peirce omits pertinent information she herself described in The Imperial Harem to suit the narrative, she might as well have written a novel!
Empress gives the impression that it was by marrying Süleyman that Hürrem became a “queen” & obtained the stature that she had. However, this is not the case. Although Peirce mentions that noblewomen married Ottoman sultans in prior centuries, she neglects to inform the reader that because royal wives were barred from having children, they were not as powerful as their slave counterparts who did. “Women without sons were women without households & therefore women of no status,” she summarized in Harem. Because the Ottomans granted greater prestige to women who bore a son over a childless one, limiting reproduction limited access to political power: “Royal wives were deprived of this most public mark of status [the patronage of public buildings], presumably because they lacked the qualification that appears to have entitled royal concubines to this privilege: motherhood. The suppression of the capacity of royal wives to bear children is an example of the Ottoman policy of manipulating sexuality & reproduction as a means of controlling power. To deny these women access to motherhood, the source of female power within the dynastic family, was to diminish the status of the royal houses from which they came.”
Peirce gives the example of Sittişah (Sitti) Hatun, who married Mehmed the Conqueror. She describes Sitti’s wedding to Mehmed, an event surrounded by great pomp & circumstance. However, she neglects to inform the reader that Sitti’s marriage to Mehmed bore no children. Franz Babinger writes that although she had wed to the great conqueror himself, the childless Sitti was ultimately powerless & died lonely & forsaken. As Peirce explained in 1993, unions such as that of Sitti & Mehmed were largely symbolic & strictly political in nature: “Although their careers as consorts of the sultans often began with the ceremonial of elaborate weddings, royal brides were ciphers in these events. What counted was the ceremony itself & what it symbolized: less the union of male & female than a statement of the relationship between two states. The function of the bride, particularly in view of the non role that awaited her as the sultan’s wife, was to symbolize the subordinate status of the weaker state.”
There is no question that Hürrem & Süleyman’s marriage rattled Ottoman society. Nevertheless, it is alarming that Peirce, who once authored a seminal work on the structure & politics of the harem, omits the fact that it was motherhood & not marriage that empowered a woman in the dynastic family. Such gaps in knowledge might lead those previously unfamiliar with the Ottoman harem to believe that marriage made Hürrem a “queen” & gave her political power, going so far to describe her & Süleyman as a “reigning couple” at one point. (Bizarrely, she does discuss abortion in Empress, yet avoids writing about dynastic family politics beyond mentioning “political planning”.)
Far more perturbing is Peirce’s insistence that Hürrem did more than she actually did for the empire. She claims that it was Hürrem who played a pivotal role in “moving the Ottoman Empire into modern times” & allowed the sultanate to survive through reforms she introduced. While she certainly paved the way in some regards for the women who followed her, Peirce overestimates Hürrem’s impact on the history of the Ottoman empire. There are other influential figures who helped preserve the sultanate, other forces that allowed it to flourish. Furthermore, Peirce downplays external factors that allowed for Hürrem’s ascent in the first place - namely the absence of a valide after 1534, not to mention Süleyman’s lasting infatuation for her - in favor of emphasizing her purportedly “unique” qualities of endurance, intelligence, & being a survivor.
Peirce goes on to anachronistically frame Hürrem as a feminist figure. In one passage, she describes her as a “forward-thinking equal opportunity employer” who “challenged women’s etiquette” because she wanted a female scribe for her foundation. Peirce’s language suggests that it was Hürrem alone who bolstered women’s opportunities, yet she does not present any evidence that Hürrem introduced or influenced any social or political reforms for women of the time. Yet perhaps most erroneous is Peirce’s claim that credits Hürrem with the start of “a more peaceable system of identifying the next sultan”. This couldn’t be further from the truth. Following their Hürrem’s death, her sons Selim & Bayezid became entangled in a civil war that ultimately ended with the deaths of Bayezid & his children. Even in the absence of prolonged violence, subsequent secession crises of the sixteenth century were resolved through the execution of the new sultan’s brothers, including infants. It was only with the ascent of thirteen-year-old Ahmed in 1603 that this tradition was set aside for dynastic concerns, although the practice of fratricide did not cease entirely.
When Peirce isn’t falling over to frame Hürrem as a wonder woman, she dismisses those who stood in opposition to her ascent, such as Mahidevran, Süleyman’s previous consort & mother of his firstborn son, Mustafa. Peirce takes a dim view of Mahidevran, presenting her as a jealous woman who needed to be reminded of her duties as mother of a prince. She is depicted a woman worried about losing a man’s favor, rather than a woman who, by all historical accounts, was deeply concerned for her son’s future. Early in Süleyman’s reign, the ambassador Pietro Bragadin reported that Mustafa was his mother’s “whole joy” at their residence in Istanbul. Later, the crucial role Mahidevran played in supporting her son at his provincial governorships was detailed by visiting diplomats. In 1540, Bassano noted her guidance in “[making] himself loved by the people” at his court in Diyarbakır. Mahidevran’s efforts to protect Mustafa, as well as the bond between mother & son, were observed by Bernardo Navagero in 1553: “[Mustafa] has with him his mother, who exercises great diligence to guard him from poisoning & reminds him every day that he has nothing else but this to avoid, & it is said that he had boundless respect & reverence for her.”
Ibrahim Pasha is another figure disparaged by Peirce’s negative bias. A friend from Süleyman’s youth who quickly ascended to the rank Grand Vizier, Ibrahim was not only a skilled & cultured diplomat admired by his counterparts in Europe, but a talented administrator & commander. Eric R. Dursteler writes, “During this time, by all accounts, Ibrahim ruled the day-to-day affairs of the empire effectively. Süleyman seems to have been content to give Ibrahim nearly unlimited power & autonomy in running the Ottoman state, & all matters of any significance passed directly through his hands. […] If Ibrahim’s initial ascent was due to his personal ties to Süleyman, in his years as grand vizier, he proved himself a capable diplomat & an effective political & military leader. In 1524, Süleyman sent Ibrahim to Egypt to restore order following an uprising led by a rebellious Ottoman official sent to rule the earlier conquered province. Ibrahim reorganized legal & fiscal institutions, punished mutinous officials & subjects with severity, established schools, restored mosques, &, by all accounts, restored peace & order to the region.”
Conversely, Peirce describes Ibrahim as “dispensable”, implies that he was holding Süleyman back from achieving his greatest accomplishments, & states “other minds were better suited” to administer the empire as Grand Vizier. When comparing her portrayal of Ibrahim to that of Rüstem Pasha, Mihrimah Sultan’s husband - & Hürrem’s son-in-law - Peirce’s bias becomes clear. She fawns over Rüstem while being completely dismissive of Ibrahim.
Finally, there is Mustafa: the son of Hürrem’s rival Mahidevran & Süleyman’s oldest living son. Empress paints Mustafa as a brat, calling him “a proud child whose sense of entitlement was apparently both acute & insecure.“ Peirce recounts an ambassadorial report describing the young prince’s jealousy over his father’s relationship with Ibrahim - a story she previously featured in Harem: ‘The sultan sent İbrahim the gift of a beautiful saddle for his horse with jewels & all; & Mustafa, aware of this, sent word to İbrahim to have one like it made for him ; [İbrahim] understood this & sent him the said saddle, & said to him, ‘now listen, if the sultan learns of this, he will make you send it back.”
Peirce’s two treatments of the same story is telling. In Harem, the account illustrates “İbrahim’s kindly patience in soothing the child Mustafa’s jealousy of his father’s affection for his favorite”, with Peirce noting that the relationship “seems to have consolidated” over time - particularly with the emergence of his half-brothers as a greater threat. In Empress, on the other hand, Peirce only concludes that such incidents “may simply reflect a jealousy on Mustafa’s part of anyone close to his father” without mention of the relationship improving, nor of Mustafa recognizing his true rivals to survival.
Whenever Peirce describes Mustafa’s intelligence & his worthiness, she emphasizes that these are the opinions of his contemporaries. It’s as though she wants to disagree, but can’t because historical evidence only points to Mustafa being how he is remembered to be: an intelligent & a worthy heir to the throne. Mustafa was the clear favorite among the people & the army. In Harem, Peirce notes that “Mustafa was universally desired to follow his father to the throne” according to Venetian reports in 1550 & again in 1552. He was more popular than Selim or Bayezid, Hürrem’s living sons who were contenders to the throne. Mehmed, Hürrem’s firstborn, could have been a match for Mustafa had he lived longer, but in the absence of evidence this is mere speculation.
Mustafa’s execution did indeed stain Hürrem’s name. She & Rüstem Pasha were blamed by contemporaries for orchestrating the downfall of the beloved heir apparent. Peirce predictably sets out to clear Hürrem’s name & exonerate her of involvement in the tragedy, but instead of focusing on a lack of hard evidence, she illogically places blame on Mustafa for his own demise. Writing that previous historians studying the topic “largely failed to consider Mustafa’s part in the affair”, Peirce points out the prince’s popularity & that people were already hailing him as “sultan” - something Süleyman would undoubtedly find threatening. Perhaps Mustafa was the victim of his own success, but it would be deeply unfair to blame him for meriting praise & adoration from others, which could only be earned through excelling in his princely duties.
Had Mustafa won the throne after Süleyman died, Ottoman tradition would dictate the deaths of Hürrem’s sons - even Cihangir, said to be fond of his eldest half-brother. According to Navagero, Süleyman reminded Cihangir of this reality, warning his son that “Mustafa will become the sultan & will deprive [you & your brothers] of your lives.” Per the Ottoman practice of institutionalized fratricide, someone would have to die.
Beyond the fact that her sons would face near-certain death had he ascended the throne, a victory for Mustafa would deprive Hürrem of power, leaving her to face the fate that had befallen Mahidevran after her son’s death: destitute & cast aside. As Thys-Senocak explained in [book:Ottoman Women Builders: The Architectural Patronage of Hadice Turhan Sultan|514467]: “Unlike her European counterparts, the prestige & political legitimacy that an Ottoman valide possessed was derived from her position as the mother of the reigning sultan, rather than through her position as the widow of the deceased sultan […] Once the father of her son was dead, the valide’s sole source of power & legitimation was through her son, the reigning sultan.” If Mustafa took the throne after Süleyman’s death, Hürrem would have lost not only her sons, but also her status.
The fate of a mother was thus closely bound to the survival of her son. It was not only a mother’s duty to ensure that her son was a contender to the throne, but through his mother’s influence that he survived. A prince’s mother was his mediator, his guardian, his most steadfast ally; it was she who sought to safeguard him from potentially hostile forces, including his own father. While imperial lalas (tutors) ensured that a prince was prepared to take the throne, it was the mother who acted as “an effective agent for her son through her connections with the imperial court, her wealth, & her status as a royal consort & as the most honored person at the provincial court after her son.”
Hürrem, however, did not accompany her sons to their provincial governorships to fulfill the principal role of a prince’s mother. Once again bucking established practice, she remained in Istanbul with Süleyman during this time save for the occasional visit.
Herein lies the irony of Peirce’s Hürrem. Only remotely involved with her sons’ provincial careers, painting Hürrem as an innocent flower who never intrigued at court would mean she did nothing to protect, promote, or prepare them at one of the most crucial points of their lives. If she did not have a hand in anything, whether at sanjak or in Istanbul – not even to eliminate their biggest competition – what did Peirce’s Hürrem do to ensure her sons’ success and survival? It is only in the epilogue of Empress that she briefly notes Hürrem’s involvement in ensuring one of her sons received aid he might need. Nevertheless, in the quest to exonerate her subject, Peirce inadvertently makes it seem Hürrem neglected her chief responsibility as mother of the sultanate’s heirs. Even with multiple sons and no precedent to follow, one would think she would’ve done anything to help or protect them – and by extension, herself. Yet Peirce provides no evidence or examples of Hürrem’s involvement in educating or preparing her sons for rulership.
Ultimately, Empress of the East only does Hürrem a disservice by presenting her as a proto-feminist, empowered heroine rather than a complex, controversial historical figure. Peirce embellishes and exaggerates when it suits her narrative, just as she painstakingly aims to clear her subject of alleged wrongdoings. But this approach backfires when one considers the book as a whole: rather than a mother and a politician who understood the importance of protecting her sons and readied them for the throne, Peirce gives the impression Hürrem did little to advance their interests – despite the allegedly large clout she had as “queen”.
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
Without Remorse Ending Explained
https://ift.tt/3t8m3pU
This article contains Tom Clancy’s Without Remorse spoilers. You can find our spoiler-free review here.
For the most faithful Tom Clancy fans, it’s probably not the ending they anticipated. Amazon’s adaptation of the author’s John Clark origin story, Without Remorse, ends not with a justification for Cold War paranoia but instead with a greater fear of the enemy within. Defense Secretary Thomas Clay (Guy Pearce) swore to uphold the Constitution and American interests. But in the end, the only oath kept was the one Michael B. Jordan’s then-John Kelly made to his late wife Pam.
“Her name was Pam, and [I swore] you’re going to say it before you die.” And so Clay did in his final moments after John drove the secretary’s vehicle off a D.C. bridge and into the cold waters below, drowning the old man and making it look like a suicide.
It’s a relatively downbeat climax to a movie that’s featured high octane shootouts, fisticuffs, and one gnarly torture sequence in a burning car. Yet it’s worth considering how the movie got to this watery moment, and how it appears to be intentionally tweaking Clancy’s worldview.
Throughout much of Without Remorse, viewers think they’re watching a simple revenge movie. At the top of the film, John led his team of Navy SEALs on a mission to Syria on the pretext that they were rooting out Syrian sanctioned murderers and thugs. Who they really left dead, however, were Russian spies. Afterward, every member of Kelly’s team was murdered seemingly by Russian agents, as was John’s wife and unborn daughter, who were executed while Pam slept.
Following the assault on his wife, Kelly went into Jack Bauer mode and killed every Russian official and underling who could bring him closer to Viktor Rykov (Brett Gelman), the alleged Russian operative who led the attack on John’s home at the beginning of the movie. And to be sure, Rykov was certainly there, as both John and the audience saw him with his mask off when John was shot during the home invasion.
However, the big twist of Without Remorse is that Rykov was not a Russian asset; he was an American one. When John, Naval officer Karen Greer (Jodie Turner-Smith), and CIA agent Robert Ritter (Jamie Bell) track Rykov to a Russian apartment, they discover the whole movie has been an elaborate ruse, played at the expense of American intelligence and (soon) the public. John and his family were just collateral damage.
“There are no other ops, John,” Rykov says when the American special forces team corners him in an apartment, revealing he’s been lying in wait with a suicide vest. “You and me being here is the real op.”
As Rykov explains before pushing the button, he fancies himself a true patriot, even more so than “those behind us in Washington.” He’s been convinced that the best way he can serve his country is by dying in a fiery explosion in Russia. His goal isn’t to take John Kelly or his team with him either. It’s quite the opposite, in fact. Rykov is working for “those behind us,” and those D.C. insiders needed John, or an American soldier like him, to be in the building when the explosion went off. That way it’d look pretty damning to Russian authorities, especially since snipers working with Rykov murdered the first Russian cops to arrive at the scene.
This plan was executed on the assumption that an international incident would be created when it reached the press that American soldiers were killed on Russian soil while performing an illegal operation—which itself would be seen by the American public as retaliation for the illegal operation on American soil that killed John’s wife.
That perception is why Rykov personally executed the man who actually shot Pam in her bed. Rykov didn’t know John would take more of their men down, but the trigger man handed Rykov his gun, ready to die because it would build the narrative that Russian agents murdered an American family in their own home. If Americans then died in an even bigger clusterf*ck in Russia, the ensuing chaos would usher in a new Cold War. Hence rather than Russians being the bad guys, the villains of Without Remorse are Americans who want to pretend the 1980s never ended.
John, Ritter, and Greer figure out this much when they let John go ghost and report back to Langley he died in the explosion. John “being dead” gives him the freedom to sneak up on the Defense Secretary and test whether he actually had knowledge about Rykov’s op. The fact the Cabinet member didn’t balk when John mentions the suicide vest—a detail Greer intentionally left out of her report—is all he needs to know. Soon enough, with threats against his family, Clay plays ball and spills his guts about the whole setup.
“You know who won World War II?” Clay whines. “It wasn’t the generals or the admirals, it was the economists. War, tanks, planes, and all that spending lifted this entire nation out of poverty, freed the world from tyranny. A big country needs big enemies. The best enemy we ever had was the Soviet Union. Our fear of them unified our people, gave us purpose. The problem today, John, is half this country thinks the other half’s its enemy because they have no one else to fight.”
In other words, the shadowy conspiracy (which is still not fully unmasked) involved high ranking officials in the executive branch engineering a phantom menace out of Russia by killing a few Americans and a few Russians in both hemispheres. They only failed to anticipate how hard John Kelly would be to kill. Yeah, that’s definitely worth a dip in the drink.
What’s interesting is that this ending pretty much flies in the face of Clancy’s literary Without Remorse and his generally Cold War-attuned worldview. On the surface, this could be viewed as a naked attempt to play into the worst cynicisms of our age. While the movie was filmed before the Covid pandemic and 2020 election, it very much was written and produced after the 2016 one where Russian intelligence mounted a disinformation campaign designed to sew division in the U.S.
When a newscaster says in Without Remorse that this is the lowest moment in relations between the U.S. and Russia since the Cold War, a viewer doesn’t have to imagine what that plot point feels like. Some might therefore read Without Remorse’s ending as a subtle play on the conspiracy theories in the U.S. (some of which were propagated by a former American president) that suggest any reports of Russian election interference are exaggerated.
However, I would disagree with that reading of the Without Remorse ending. While the film certainly plays fast and loose with “ripped from the headlines” plotting, the film feels as much a subtle critique of Clancy as any sort of movie about modern realpolitik.
It is indeed worth noting how much the cinematic version of Without Remorse differs from its source material novel. As with all Clancy page-turners, the narrative of Without Remorse is arguably too dense to transfer to a two-hour film. So gone are entire subplots involving prostitution rings and the historic crime of funneling Asian drugs to the U.S. inside the corpses of dead American soldiers (the book is set in 1970 during the Vietnam War). But also gone is the fact that the bad guys really are the Russians.
On the page, the man Kelly killx turns out not to be a KGB mole, but there is indeed a Russian asset high up in the U.S. government: he’s a senator’s aide who is cooperating in Russian efforts to sabotage the Vietnam War effort. And by working for an anti-war dove politician, one can sense the disdain in Clancy’s politics, which imagines anti-war leaders at least playing into Russian interests to undermine American foreign policy. (Oh, what he might’ve thought about his political party in 2020?)
In Clancy’s novels, the villains are almost always the Russians or other foreign threats attempting to besiege Fortress America. For all their technical authenticity and understanding of late 20th century spycraft, they’re very much fantasies tailor-made for the era Clancy found his initial success in as an author: Ronald Reagan’s 1980s America. In fact, what turned his first bestseller into a bestseller was President Reagan enthusing how satisfying the plot is in The Hunt for Red October.
Read more
Movies
Why Tom Clancy’s Name Isn’t on the Patriot Games Poster
By Simon Brew
Movies
Michael B. Jordan’s Upcoming Movies: What’s Next After Without Remorse
By Nick Harley
This is not to say that Clancy’s worldview was as simplistic or jingoistic as his critics might suggest. After all, that first novel which birthed the best Clancy adaptation to date, John McTiernan’s The Hunt for Red October (1990), is about a Soviet submarine captain attempting to de-escalate the Cold War by defecting and funneling a nuclear Russian sub to the Americans. Of course, this is also because he and most of his officers secretly covet the freedoms borne from the democratic and capitalist West.
Other Clancy novels are not quite so nuanced in their view on Cold War politics, including literary Without Remorse. Yet the movie version of the film ironically brings it closer to the first novel, as well as another book/film which introduced fans to John Clark on screen: Clear and Present Danger.
That tangled narrative involves the perceived menace of South American narcotics at the height of America’s drug war and the criminal empire of Pablo Escobar. However, the greatest villain in the story, particularly the movie adaptation released in 1994, turns out not to be drug lords but a corrupt president who uses the War on Drugs as an excuse to turn American special forces into a personal hit squad out for his revenge—he then leaves those soldiers stranded to die.
The ending to Michael B. Jordan’s Without Remorse very much comes in line with the wary cynicism of Clear and Present Danger, which also feels a lot timelier after the last four years than it did in the ‘90s.
In fact, 2021’s Without Remorse leads fairly well into the Clear and Present Danger movie. At the end of Without Remorse, John Kelly drowns the Defense Secretary, making it look like a suicide. He is then saved by Karen Greer, who must’ve known about John’s plans to drive off the bridge. Remember, she helped set Clay up by omitting Rykov’s suicide vest.
She then escorts John to the airport and gives him his new CIA sanctioned identity, John Clark. Clark is of course the more famous name of Clancy’s protagonist. He is also introduced by that alias in Clear and Present Danger when Robert Ritter, now Deputy Director of the CIA, travels down to Panama City to meet Clark and enlist him in the corrupt POTUS’ secret war against Colombian cartels.
Barring the differences of actors and eras, one could even watch 1994’s Clear and Present Danger movie (also on Amazon Prime) and see a pseudo-sequel to Without Remorse. In the ‘90s movie, Willem Dafoe plays Clark as a hardened and skeptical expatriate who’s been living in South America for some time. He and Ritter have a long off-screen history, with the CIA bureaucrat eventually persuading Clark via the government’s checkbook to lead an illegal special ops team, which has eerie parallels to the Reagan administration’s own South American misadventures with the Iran-Contra Affair. In the ’94 film, Ritter is a slimy middle man for the corrupt interests of the White House, and it is not hard to imagine Jamie Bell’s 21st century Ritter from Without Remorse going along with a similarly corrupt fiasco.
Of course Clark is still a hero in the earlier movie, eventually teaming up with Harrison Ford as CIA analyst Jack Ryan. They even build trust over a mutual friendship with Rear Admiral James Greer, who is mentioned as Karen Greer’s off-screen uncle in the Without Remorse movie.So in the end, it’s all connected. Or perhaps this can just become the sequel crossover with Amazon’s Jack Ryan TV series?
cnx.cmd.push(function() { cnx({ playerId: "106e33c0-3911-473c-b599-b1426db57530", }).render("0270c398a82f44f49c23c16122516796"); });
The post Without Remorse Ending Explained appeared first on Den of Geek.
from Den of Geek https://ift.tt/2QOcGOR
1 note
·
View note
Text
Toumyu Japan Expo Interview
It appears the boys gave an interview for some French TV show. WATCH IT HERE. No subtitles from me, but I do have a translation that more or less covers what went on... (Holy shit, they were unexpectedly not-serious/fooling around here!) I wasn’t entirely certain of some bits, so please excuse any mistakes. ^^
SR: Sato Ryuji ST: Sakiyama Tsubasa KR: Kitazono Ryo OS: Ohira Shunya SD: Saeki Daichi
Please mind I barely understand any French, questions and answers were all translated from Japanese.
MC: Bonjour, Touken Ranbu! Good afternoon!
ALL: Good afternoon! Bonjour, Paris! MC: Yesterday was your first performance in Paris. How was it? How was the French audience? SR: They were incredibly excited. OS: Yes, they were. ST: It was beyond expectation. KR: Many people were already cheering during the opening video, before we even appeared on stage. It made us really happy.
MC: Could you explain to the audience the motive behind Touken Ranbu?
SR: Who will answer it? OS: Motive?
MC: In French, Touken Ranbu literally translates to "fighting and dancing swords". It's hard to picture what it is about, so could you give a simple explanation of the concept?
SR: Ah, I see. ST: We're, as you can see, human personifications of historical Japanese swords that played an important part in Japanese culture. And throughout the story we dance, sing and fight, I guess?
MC: I suppose it isn't easy to act like a sword. Could you tell us how you prepared for your roles? Like, did you play the game, or did you do any other research?
OS: Um, right now there is an Anime adaption, but during the time of the Trial performance and Atsukashiyama we only had the game and some manga to work with. And neither of those have any real movement to them. ??: Are you all right? OS: Are you all right? ...when it came to creating our characters, all of us once belonged to a historical person. For example, I'm Yoshitsune's sword. So, we looked into who they were, thought of what they stood for and based our characters off that information.
MC: If you don't mind, instead of introducing yourself, could you introduce the person left to you? Could you give us their name and explain what kind of character they are?
SR: That's new. ALL: Sounds interesting. SD: So, I should do his introduction? [looks at Shunya] ??: Yes. SD: He's really skilled. OS: At what? ST: This is perfect. SD: Good, let's do this. I am Imanotsurugi... ST: They won't understand it! OS: Hey! ST: They won't understand it... SD: I am Lord Yoshitsune's sword. ST: That's acting, not introducing. [To Shunya] Show us the real thing! OS: That's not how I act, that's... ST: Show them the real thing! OS: I'm Imanotsurugi, I'm Lord Yoshitsune's sword! SD: I'm Imanotsurugi... ??: No, that's not... SR: You're confusing the staff. They have no clue what's going on.
MC: OK, let's move on. ??: Who's next?
OS: I am? Um, this is Sato Ryuji, he plays the role of Kashu Kiyomitsu. Unlike the four of us, who are all swords made by Sanjo Munechika, he was the sword of the Shinsengumi's Okita Soji. And he's the captain of our team. SD: So serious.
SR: Sitting next to me is Sakiyama Tsubasa, who portrays Ishikirimaru. His eboshi hat and his oodachi sword that's longer than any of ours are his distinguishing features. And... [gets nearly hit in the face by Tsubasa’s sword] That's it, I'm done. ST: I’m sorry I'm sorry. SR: Good, next. KR: I'm counting on you.
ST: This is the sword Kogitsunemaru. His right hand is sticking out. KR: Yes, my right hand. My fingers are sticking out. ST: And he's rather well-muscled. KR: Are you kidding me? SD: That was pretty terrible. ST: Well, there's a demon fox and as was mentioned before, he's a sword made by Sanjo Munechika. He's the ghost sword forged by Sanjo Munchika and that demon fox.
ST: Now you introduce the girl. KR: OK, so I should introduce the girl next to me? KR: Should I introduce her? MC: Yes, please. KR: Well, I only met her today. [Looks at Daichi] He's Musashibo's Naginata. Naginata aren't swords, he's a halberd. His name is Iwatooshi, and he's played by Saeki Daichi. He usually kills people while bursting with laughter. SD: I don't kill people though. KR: Right, you don't kill people, you only kill enemies. I'm sorry. You kill enemies while bursting with laughter. Not people, my mistake. OS: He only kills the History Retrograde army. KR: I'm really sorry.
MC: We received a lot of questions from your fans, but we're out of time. Could you address a few words to the fans watching right now.
??: Ryuji, why don't you? ?? Come on, captain. SR: Shouldn't we all say something? KR: Don't worry, we leave it to you.
MC: You call all give a comment, even at the same time if you'd like.
SR: Good, let's do it at the same time. ST: At the same time? SR: [To interpreter] Please translate all of it. Okay let start…1,2! Good, one, two, three...
[Everyone talking over each other]
??: Good, let's do this one by one. KR: Yes, I'm really happy we got to perform at Japan Expo. I'll work hard in Japan, so I can visit Paris again someday and stand on the stage here again. Thank you very much.
SD: When the musicals started, I never imagined I'd one day go to Paris. It was a huge pleasure to be here. I'll work hard so the five of us, or maybe other Touken, will be able to come to Paris again. Thank you very much. Bonjour, Paris. KR: This is the end, the end.
ST: Yes, today we've mostly been messing around, but if you're interested in our actual performances and would like to see how we usually dance, sing and fight, you can probably find videos on youtube, please check it out. Thank you very much. Merci.
OS: Right, I feared we'd run in a language barrier at Japan Expo, but I was really glad we were able to communicate with our audience without problem. I think we've successfully shown everyone a bit more of Japanese culture. I really hope we'll be able to stand on a stage here again. So, everyone, please continue to support Touken Ranbu.
SR: Good, since Katsugeki Touken Ranbu started airing in France just before we came, I figured we'd be all right. But I'm extremely grateful for the overwhelmingly warm welcome by the French audience. I'd love to come again, so... we'll come again! You were amazing! ALL: Wait, wait, that hasn't...
ALL: Thank you.
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
Episode 5 Review: In Which the Horror Begins (+ A Lesson on Irony)
{ YouTube: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 }
{ Synopses: Debby Graham | Bryan Gruszka }
{ Screencaps }
We have reached the end of the first week of Strange Paradise and the real beginning of the fun. I hoped to get to this post a week or two earlier, but I kept having to postpone writing entries for this blog because life kept getting in the way. I’ve also been re-watching episodes from later in the Maljardin arc, because I actually re-watch, screencap, and write commentary on each episode twice before I review.
In the last episode, THE DEVIL JACQUES ELOI DES MONDES, while possessing his descendant Jean Paul Desmond, brought Jean Paul’s sister-in-law Dr. Alison Carr to his private island Maljardin. (I find it amusing how these soaps introduce almost everyone with their full names each episode and include so much exposition about earlier events. I know that it was necessary at the time because most soap opera episodes only aired once and DVRs weren’t invented yet, but it still sounds silly.) In this episode, Alison discovers to her horror what we the audience already know: that her sister Erica is dead and sealed in the cryonics capsule.
The first half of this episode and the way it is written is a good example of dramatic irony. Nowadays, the concept of irony is often misunderstood because of the way certain hipsters in recent years have abused the word, to the extent that few people now know what it really means. The term “irony” actually refers to several distinct devices used in fiction, rhetoric, etc. which all involve a difference between the appearance of or one’s expectations for a situation and the reality:
There’s verbal irony, when someone says the opposite of what they mean: for instance, if Raxl were to sarcastically call Jacques an angel or I were to say that this show is as subtle as a neon pink sledgehammer to the skull.
There’s situational irony, when something goes differently to what we the audience expect: say, Jacques signing his name instead of Jean Paul’s on Dan’s documents while impersonating him, or no one but Raxl and Quito knowing about the temple despite its incredibly obvious “hidden” door. (Had it ever happened, Raxl calling Jacques an angel would also qualify, because she is always so upfront about how she feels about him.)
There’s historical irony, when history turns out to be the opposite of what one predicts: take this early ad for the show that boasts, “Don’t laugh. Wait until you see the ratings.”
There’s cosmic irony, when a character’s fate turns out the opposite to their expectations. This is what happens to the protagonists in the majority of deal-with-the-Devil stories, who are manipulated into signing pacts for things like unlimited wealth or magical knowledge and who trick themselves into thinking that their good fortune will last forever, but who end up damned to Hell when the Devil comes to collect their souls.
There’s Socratic irony, which means feigning ignorance to trick an enemy. This is Jacques’ usual modus operandi when someone tries to unmask him.
There’s romantic irony or metafiction, which is not present in this show at all. Strange Paradise is not meta; it takes itself too seriously.
And then there’s dramatic irony, which applies to the plot of the first half of this episode. Dramatic irony is when we the audience know something that a character does not, but which will influence their ultimate fate.
Alison came to the island to visit Erica, to ensure that she was alive and well. Jacques disguised as Jean Paul convinced her that Erica was OK and then repeatedly changed the subject and took her on a tour of Maljardin to distract her. Thinking that she must be somewhere upstairs, Alison starts to climb the steps and says, “I’m going to see her. Where is she?”
“She’s not upstairs,” Jacques replies, making Bissits Face™ as a mike shadow passes along the wall. “She’s”--dramatic pause--”below. In the family crypt.”

He looks so sincere. Not.
At first, Alison does not understand and laughs. “What on Earth is she doing in the-” she asks, but then it hits her. Then she realizes that he means that her sister is dead. “No, no, she’s not!” she cries.

“Only temporarily,” says the handsome devil.
“What kind of a man are you? Take me to her!”
He gives her directions to the crypt and then de-possesses Jean Paul, who blacked out while he was possessed and is therefore confused about what is going on. Alison calls for him and he joins her in the crypt. This is Part Two of the big reveal of the ironic twist to Alison, when she discovers the Cryonics Capsule. “You didn’t! You couldn’t!” she screams, thinking that her brother-in-law has frozen Erica alive.

"I love her too much to just allow her to die,” Jean Paul replies, but that does not reassure her. She accuses him of freezing her alive, but he denies it and reassures her that she was already dead. She starts crying and we get the first of many scenes throughout the Maljardin arc where these characters display affection for one another. And with that come even more feels.

Jean Paul/Alison is my OTP.
Jean Paul confesses that he no longer has complete control over himself. “I don't know what I believe, what I accept these strange days,” he says. “Sometimes I don't even realize what I am doing. Something drives me on, some power stronger than me. Some…evil force.” Cut to Jacques’ coffin in the crypt followed by his portrait, because this show’s directors don’t know the meaning of subtlety. “Raxl claims it’s the devil.”
Following this, we get some background information, first from Jean Paul about Erica’s death and then from Raxl about Jacques. I will probably end up referencing the former again in later posts, so I will quote it:
Erica hadn't been feeling well, so Dr. Menkin took some blood samples to the Mainland for tests. She was sitting on that couch just as you are now, when the first attack came. It was devastating. I have never known such fear. Dr. Menkin called it an eclamptic convulsion...Well, I got her up to her room and put her to bed. Dr. Menkin took over but there was very little he could do to ease her suffering...We lost [the baby]. But I couldn't care in that moment. About an hour later, when I was holding her in my arms, she cried out, "no, Jean Paul, no, don't let me go.” Her body felt like a steel spring under compression. It felt like it was almost ready to explode. When the spasm hit her, she arched. There was nothing I could do. Nothing!...All that beauty, all that life. My life, snuffed out as easily as a candle. How I loved her. How I still love her. My darling Erica, gone.
The latter is longer and contains some tangents, so I will summarize. That evening, Raxl reveals that, after Jacques’ wife gave birth to his son, he murdered her. Raxl and some unspecified others (she says “we”) avenged the death of Madame des Mondes by making the Conjure Doll and piercing its head with the silver pin, which she says “destroys all hope for salvation.” Then she tells Alison about how Jean Paul set him free and that Jacques possesses him. Alison refuses to believe her, saying that such things don’t happen “in this day and age.” That she doesn’t believe Raxl creates more dramatic irony, because, in case you haven’t already figured it out, Raxl and possibly Quito are the only good characters so far who understand what is going on. But Quito is mute and a zombie--meaning that he can’t say what he knows--and almost no one believes Raxl.

She is probably thinking something like, “Oh, Dr. Carr, you sweet summer child.”
Then they hear a scream outside and open the front door. Because this show had neither the time nor the budget to film more outdoor scenes, they stay in the Great Hall and watch as Quito carries the corpse of an old man inside.


Hmmm...I wonder who did it? Do you think there’s a slight chance it may have been that smirking man right there?
Raxl identifies the dead man immediately as Dr. Menkin, and rightly suspects Jacques. He, of course, feigns innocence, complete with more Bissits Face™ and barely disguised smirking, because apparently he thinks Raxl is stupid enough to fall for that. Here is his alibi, which is thoroughly unconvincing:


But she sees through this, because Dr. Menkin doesn’t drink, and gives him the lie. He makes her swear to keep his implied murder a secret, then orders her to leave. And then Jacques de-possesses Jean Paul, but not before plying him with booze.

I said back in my first review that this would become a common theme.
He has a fever dream that consists of Raxl shouting at him while making some seriously frightening facial expressions. Had I watched this as a kid, the faces she makes in this dream sequence would have given me nightmares.


Raxl: "Don't look! Otherwise, you may see the very man you are…the very man you might have been!"
This line--a paraphrase of one from the first episode--implies that Jean Paul and Jacques are reincarnations of the same person. If this is indeed the case, does Raxl know? Is that one of the messages she intends to communicate to her master in this bizarre sequence? That Jacques and Jean Paul are the same character is something that Ian Martin implies repeatedly but never confirms, and one of many plot points that later writers forget to explore or explain. I’m not one hundred percent certain he was planning to reveal that (I don’t have access to his notes or original outline), but it seems likely.
Anyway, Jean Paul, who does not yet know of Dr. Menkin’s death, wakes up and confronts Jacques’ portrait. He, too, has begun to see the reality and cosmic irony of his situation: that, by setting Jacques free, he may have condemned himself to eternal suffering:

Jean Paul: "You are the nightmare! Must I restore your evil life to have my darling Erica's life back? Damn you!"

“Or am I the one that’s damned? Must I be lost in Hell with you!”
This episode is the first episode of Strange Paradise to successfully invoke the feelings of terror that one expects from a horror show. Although I love this program, I have to admit that, when they try to make it scary, they often fail and end up making it unintentionally funny instead. They tried before in the pilot in the scene where Jean Paul announces “on this island...I am God,” but the drum-roll, dramatic music, and Fox and Lee’s overacting make it instead laugh-out-loud funny. Likewise, the suspense of the scene where he frees Jacques is ruined by ridiculous screechy sound effects and intersplicing with a bad cover of a jazz standard. I think that the Jacques scenes in Episodes 2 and 4 were intended to be funny and, if so, they succeeded. While Episode 3 is scary, it’s a different kind of scary than the classic horror sense, being about two powerful authority figures trying to prey on a helpless young woman: still a common theme in the Gothic genre, yes, but not what most people watch spook-shows for. No, Episode 5 is genuinely frightening and compelling in its Gothic horror, making it a good conclusion to the first week of this soap opera.

Stay tuned for a Bad Subtitles Special on Friday and join us again next week as we review Episode 6, including a detailed recap and analysis (with a side of bad costume roast) of the second flashback about the life of Jacques. I look forward to it, and I hope you do, too.
( <-- Previous: Episode 4 || Next: Episode 6, Part I --> }
#strange paradise#gothic soap opera#week 1#episode 5#maljardin arc#ian martin#review#analysis#cryonics capsule#bissits face#genuinely scary episodes#irony#jacques making jean paul drink#jean paul/alison#non flashback dream sequence#on this island i am god#raxl knows best
0 notes
Text
40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays
General explaining: 1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument.
Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point.
Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance.
Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise.
Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”.
Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making.
Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information.
Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”.
Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned.
Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”.
Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”.
Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”.
Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information.
Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time.
Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other.
Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.”
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis.
Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said.
Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion.
Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”.
Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence.
Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion.
Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”.
Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
23. Yet
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea.
Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence.
Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else.
Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing.
Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else.
Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”.
Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”.
Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”.
Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent.
Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it).
Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”.
Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview.
Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay.
Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing.
Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above.
Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”.
Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below!
source
6 notes
·
View notes