#her name's Inanna
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

A couple of quick designs to practice
#star wars#star wars oc#sw#sw oc#twi'lek#twi'lek oc#mirialan#mirialan oc#i like the twi'lek a lot? make draw her more#may*#her name's Inanna#no idea who the mirialan is#name suggestions welcome#man i've been drawing so much lately#proud of myself#jano dibuja#my art
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me: Yeah Isis (goddess, thanks for that needing to be clarified ya douchebags) is really dangerous.
My mom (after I just gushed about how strong Isis is): Why? Cause she’s a woman?
Me: No, because she literally has complete control over the creator deity, is the mother of the pharaoh god and wife to the god of the dead. And without that, goddess of Egypt which could have been interpreted as the entire world or universe, magic, only one god is possibly smarter than her but she’s much more clever and literally will not stop at anything in her myths until she literally is incapable of doing anything else. It’s great that she’s a good deity because if she were like her brother everything would be dead or worse.
#isis#aset#Egyptian mythology#I think her other name’s Aset but I might be second guessing cause of Inanna and Ishtar#so many A’s#but seriously that is an objectively broken power set and that’s not even all of it
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
I would like to give everyone this photo of my dog Inanna

Give puppy forehead some kisses
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
If any trans peeps are looking for tatto suggestions, this is the Cunaiform for Inanna.


#Inanna also know as Ishtar#she was the goddess of love; war and sex#is often read as an early inspiration for Aphrodite#Queen of Heaven#but we have to fogive this monarch for how badass she is#she wasn’t the biggest bitch in the Sumarian pantheon but the Assyrians who absorbed the former absolutely loved her#she was known for taking other gods powers/domains probably because the Assyrians put her abover their own high god as favoured#also some possible links to the orphic myth as she went to the underworld and was brought back by her “attendant”#this ended up with her husband being taken in her place which caused the changing seasons#also mentions of her seem and specifically the way her name is written mean she might be older than the sumarians#i.e. older than our first known written language#re tattos I'm sticking with the symbol of Lillith; the first woman who was cast aside for refusing to be subservient to Adam.#mythology
45K notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello, I'm requesting the mini HC nightmare scenario again, of the M6 having a nightmare of MC dying, please and thank you! 🫶🏽
The Arcana Mini-HCs: M6 have a nightmare of MC dying
Julian: wakes up hoarsely crying your name in a cold sweat, freezes when he sees you, then melts in relief when he does. instantly holding trembling fingers against your wrist to feel your pulse when you brush the hair out of his eyes, hesitates to ask you to hold him for comfort but will turn into a grateful, exhausted puddle when you do
Asra: oh. oh no. wakes up with a jolt and refuses to talk about it, instead asking shakily if they can hold you before burrowing with you under the covers and clinging to your chest. doesn't say much beyond "I forgot how bad it was" as he glues his ear to your heartbeat and tangles himself up with you. tells you the dream later if you ask
Nadia: startles upright with a small scream, needs a moment or two to register that you're in front of her and okay before she snaps out of the horror-induced daze. hesitant to fall asleep again, extends a no-pressure invite to you to join her for some tea and a midnight snack. either way, she's staying where she can see you breathing and happy
Muriel: already in a full-blown panic attack by the time he wakes up and the only thing to do at that point is help him ride it out. Inanna's quick to fetch a pouch of myrrh and lean against his back, but what helps him most is when you crawl into his lap and breathe with him, each grounding, mirrored breath a reminder that you're here and ok
Portia: almost flings herself out of bed with a gasp, immediately collapses into relieved tears when she sees you still next to her. tells you between sobs about her nightmare and only really starts to calm down when she can feel you holding her just as tightly. falls back asleep fairly quickly, but spends that time gently tracing your face
Lucio: if you weren't already awake from his sleep-shouting, he's shaking you awake with tears streaming down his cheeks just in case you really are dead, please wake up, please please please - oh good you're up, hold him until he feels better and listen to him while he tells you about his dream. keeps watch the rest of the night, just in case
#ask arcana brainrot#the arcana#the arcana headcanons#the arcana hc#the arcana game#asra the arcana#julian the arcana#nadia the arcana#muriel the arcana#portia the arcana#lucio the arcana#asra alnazar#julian devorak#nadia satrinava#muriel of the kokhuri#portia devorak#lucio morgasson
478 notes
·
View notes
Text
More evidence of FTM people in history!!!
"In fact, individuals living outside of the gender binary were heavily involved and associated with the cult of Inanna, and her cult members and priests were known for their androgyny and blurring or destroying the gender binary. The gender-blurring members of her cult have often been included in poems and dedications written for her, often with Inanna personally transforming the gender of her devotees. One such example is the pilipili, a group of cultic performers in Inanna’s Sumerian festivals. The name pilipili is referenced within Passionate Inanna (80-90) in relation to an individual named pilipili who is transformed by Inanna. They are raised as a woman, the Sumerian for young woman (ki-sikil) being used to describe them, and Inanna blesses them, handing them a spear ‘as if she were a man’ and renames them ‘pilipili’. From this point forward they are referred to as ‘the transformed pilipili’. We cannot know for sure what the word ‘transformation’ means in this context, and especially since Sumerian did not use gendered pronouns it is difficult to reconstruct the exact meaning, but one interpretation is that through the blessings of Inanna, the pilipili transitioned into a man. Even if Sumerian did not use gendered pronouns, the possible phallic connotations of the word ‘spear’ add more weight to this theory.
I've only ever heard people talk about the gala when it comes to Inanna's trans worshippers, so I am delighted to hear there's evidence of some kind of FTM equivalent! (& if anyone's interested in this subject, there's also this quote which makes mention of FTM devotees of Aphrodite/us on Cyrpus as well)
Transmasculinity is divine too. Transmasculinity had its place in history too.
636 notes
·
View notes
Text
Howdy folks. I’ve said I’d make a rant about this for a while. It’s time.
Let’s start with the basics. Mesopomatia is the earliest known human civilization. Humans existed before them, but this was the first “city”. They also made the first writing. This rant also kinda covers Sumerian tuff, because the two groups had a bit of a merging.
You know what transgenderism is. You’re on tumblr dot com. Chances are you are a transgenderist yourself
Transphobes often say that transgenderism is a “new concept” and that “nobody was trans 20 years ago”. For the record, you don’t have to go as far back as Mesopotamia. There’s Greece, Egypt, Hawaii, and tons of others I fail to remember. But yeah, we date back to The First City.
The First People believed in many gods, one of which you’ve likely heard of. Today’s subject: Inanna/Ishtar, The Queen of Heaven (I’ll be calling her Inanna, as it’s her original name). She was the goddess of Sex, War, and Justice. The most notable things she was believed to do were changing people’s genders and being an absolute queen. Like fr she slayed-
Anyways, the “transgender power” as I’m gonna call it because it's funny, is well documented in poetry fragments, with the direct quote “To turn a man into a woman and a woman into a man are yours, Inanna.” This was written by Enheduanna, Inanna’s High Priestess from Ur (Ur is a city).
Speaking of Inanna’s Priests and Priestesses, they were actually known for their androgyny. Poems and Dedications to Inanna often included them, with the direct depiction of the goddess transfer-ify-ing them. It’s unknown if these and the Gala are the same priests, so I’ll add a little space and talk about them for a bit.
The Gala were priestesses for Inanna created by the god Enki (who is really fuckign cool for non-trans reasons (might talk about him sometime)) to sing for her. Mourning Rites previously sung by women got taken over by the Gala, and as men joined, they adopted ALL societal roles and expectations of women, switching to female names and singing in the Sumerian eme-sal dialect, which was reserved for women trying to render the speech of female gods. The Gala looked after the sick and poor, and were highly respected by the rest of the Mesopotamian peoples.
Time to talk about the Pilipili! They were a group of cultic performers who worshiped Inanna, with the name coming from a person named Pilipili. They were raised as a woman (according to Mesopotamia’s gender roles), and were blessed by Inanna and given the name Pilipili. Inanna gave them a spear, an item associated very heavily with masculinity “as if she were a man” and they are only referred to as “The Transformed Pilipili” from that point on. “Spear'' is also thought to have phallic meaning here, which is even more directly saying that Inanna trans’ed Pilipili’s gender.
How about we move beyond the cult on Inanna now? A statue (or technically statuette but honestly whatever) found in the city of Mari depicts a singing woman. But wait! The name of the depicted person is “Ur-Nanshe”, a masculine name! This might mean nothing, but honestly, you’d assume transgenderism too if you met a woman named Steven. The statue has a soft face with traces of makeup, and it’s got tiddies!
A statue in the British museum (which for the record should not be in there. give it back) has a label translated as “Hermaphrodite of Inanna”. Hermaphrodite has a different meaning now, which a different translator, Cheryl Morgan, recognized, stating that “person-man-woman” would be more accurate. We don’t know specifics about their gender, but clearly this was a person outside of the gender binary who was not only significant enough to have a statue of them made, but also assumedly well-liked!
So, to summarize, Ancient Mesopotamia viewed genderqueer individuals as:
often blessed by the Queen of Heaven
transgender-ify-ed by said Queen of Heaven
well respected enough to be priests
said cult of trans priests was also said to be made by another god in devotion to Inanna
significant and well-liked enough to have statues of them
sounds like we should take some notes from our ancestors, huh?
#transgender#nonbinary#genderqueer#transphobes can suck it!!!!!!#mesopotamia#history#queer history#lgbt history#trans history#reblogs appreciated
835 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey there, would you mind telling me a bit about Lilith and your practice with her? I’ve been trying to do some research on her modern worship, offerings, and signs, but it can be really difficult to find anything that’s serious when there are so many references to her in pop culture :/
Okay so Lilith is extremely, and I mean extremely complicated.
Contrary to popular belief, “Lucifer” isn’t actually a name, but a title. The name Lucifer means “light bringer” in reference to Venus as she appears in the morning, but any “light bringer” can be considered a Lucifer. Prometheus for example, the man who stole fire from the Gods to give light to humanity, is a Lucifer. And so, there are actually many different entities that have taken the role of a Lucifer throughout history and in various different retellings. Eosphorus is the name of the deity that was revered by the Greeks as Venus, but Lucifer is a title that many different figures have taken on depending on the context.
Why do I bring up Lucifer? Because he and Lilith are very similar in that regard. Our earliest mentions of Lilith throughout history paint her not as an individual but as a species of night demon that frequently takes the form of an owl, she was known to bring crib death and miscarriage.
In the myth, Inanna and the Huluppu tree, a huluppu tree (a type of willow) is planted by the banks of the Euphrates River. The tree is tended and nurtured by the goddess Inanna, who plans to use its wood to craft a throne and a bed for herself. However, as the tree grows, it becomes infested with three troublesome creatures:
A serpent that makes its home at the roots of the tree. (What troublesome serpents have been portrayed in another mythology having to do with magical trees? HMM!)
The Anzu bird (sometimes described as a mythical lion-headed eagle) that builds its nest in the branches.
The Lilitu (a female demon or spirit) that makes her lair in the trunk.
Inanna, distressed by these creatures occupying her tree, calls for help from her brother, the sun god Utu (or Shamash). When Utu does not assist her, she turns to the hero Gilgamesh. Gilgamesh comes to her aid and, with his great strength, drives away the serpent, the Anzu bird, and the Lilitu. He uproots the huluppu tree and uses its wood to craft a throne and a bed for Inanna, fulfilling her original intention. Consider that it is a human, not the God of the sun, who helps Inanna with this problem. Interesting.
The inclusion of these three very specific creatures occupying this important tree tended to by the Goddess of love, to her dismay, are very important. Especially when he consider how Inanna’s visual depictions have been syncretized with Lilith. The idea of a serpent (perhaps a Lucifer) , an Anzu bird (described quite similarly to some depictions of abrahamic angels, specifically those like the cherubim) and a Lilith being “driven away” from this mythical tree are notable, especially because these are all symbols associated with Inanna herself.
Inanna, one of the most complex deities in Mesopotamian mythology, embodies aspects of fertility, love, war, and the underworld. Inanna's association with snakes can be seen in her connection to the underworld and her transformative journeys. In her descent into the underworld, Inanna removes one magical garment as she continues into the deathly realm. Just as the snake sheds its skin, Inanna sheds her power and identity as she descends, only to be reborn and restored.
Inanna is frequently depicted with wings, highlighting her divine nature and authority. The Anzu bird in the Huluppu Tree myth, while initially a source of trouble, also connects to the theme of overcoming chaos, which aligns with Inanna's role as a powerful deity who brings order.
Lilith, often depicted as a demoness, represents untamed feminine power, independence, and sometimes chaos. In later Jewish mythology, she is considered a night demon, but her roots trace back to earlier Mesopotamian beliefs. Her inclusion in Jewish mythology is summed up in the verse Isaiah 34:14: "Wildcats shall meet with hyenas, goat-demons shall call to each other; there too Lilith shall repose, and find a place to rest." (Hm… I wonder WHERE she will find a place to rest? Perhaps in a… magical tree?)
In Jewish mysticism, the feminine side of the tree of life is what creates the potential for evil. Even though it is the lightest, brightest, goodest form of feminine energy, for some reason, every time, disobedience pops up no matter what we do. It is an aspect of the feminine itself.
In the Huluppu Tree myth, Lilith (or a Lilitu) makes her home in the tree that Inanna nurtures. This connection reflects Inanna's association with both nurturing and taming wild, untamed aspects of the feminine. Lilith's presence in the tree also highlights the tension between order and chaos, which Inanna must navigate and control.
So what does this all mean?
Each creature in the tree draw direct parallels to the Goddess of Love herself. These can be interpreted as perversions of her divine nature, that she herself cannot be-rid of on her own. Inanna the Goddess of WAR couldn’t get an owl, a big bird, and a snake out of a tree??? Why? Likewise, why did the divinities refuse to help her? Why did she have to seek out a human specifically, to get those unwelcome guests out of her tree? And if it is so that Inanna just doesn’t really like owls and snakes, why is she represented with them (and generally just hanging out with them) so often?
Lilith, the serpent, and the Anzu bird reflect aspects of the divine mother that she herself cannot even tame. Lilith as the night owl also reflects an aspect of knowledge and wisdom, as owls can see in the dark and hunt strategically. Even though she is portrayed as an enemy of Inanna, Inanna never once can or even tries to harm her. Inanna being the Goddess of fertility, and Lilith being the demon that causes miscarriage, show that they are natural opposites, yet still derived from the same divine source, and never combative towards each other.
Similarly, Lucifer’s first ever depiction was as his role as Venus, the same astrological planet as what is associated with Inanna. In Christianity, Lucifer played the role of the serpent who convinced Eve, another archetype of divine femininity, to eat the forbidden fruit of knowledge. Interestingly enough, Lilith is never actually portrayed eating the fruit. Does she posses a divine knowledge that is inherent to her qualities as a night owl, to the point where she didn’t need to eat the fruit to have the wisdom to disobey Adam? Does she possess a knowledge that is inherent to the divine feminine force from which she was created? Is this because she was created from the divine forces of femininity itself and not derived from man, as Eve was? If this is the case, that even though Eve ate the apple, she did not become a Lilith, that stands to imply that there is an inherent quality about being derived from a human man, that repels or deflects that inherent feminine rebellious quality. Instead, being replaced with the the ability to submit.
Knowledge applied with the associations of night and mystery, create a feminine energy that cannot submit, and this is likely Inanna’s fault herself, as she very notably has a big issue with respecting any authority higher than herself, even death herself (as her big sister)
From a symbolic standpoint this tells us a couple things about Venusian energy in general.
1.) Regardless of how hard it tries to behave, it is inherently chaotic
2.) It has many faces, some of which do not jive with eachother, but even so, they continue to coexist, even if not in the same places
3.) It is a creator and a destroyer.
4.) It has a very rough time with the concept of submission.
Okay YAP fest, what’s the point?
Lilith is a great example of how the dark feminine exists within the light feminine as an inevitability. Lilith is not so much associated with war, the strategic enactment of violence., but rather the inherent unpredictability of femininity. Women both create life and snuff it, women can decide to procreate or to have an abortion. Lamashtu and Lilith respectively were invoked for abortive purposes.
And of course, Lilith’s adoption by feminist spaces as a self actualized protector of individuality and feminine rage also invoke heavy associations with Inanna as the Goddess of war. So in my interpretation, Lilith is that part of Inanna that went a little unchecked for a little too long. That combined with the themes of Lucifer’s liberation, paint a very interesting narrative about how femininity as a divine force shows up in obscure ways, perhaps even negative ways, whilst still being just as divine and inherent. To recognize Lilith as the antithesis of all of these things, is to see her as the unwavering aspect of femininity that cannot be tamed, even by femininity herself. The snake, the reborn, will always cause chaos at the root of the feminine energy. The Anzu bird, the angels, are susceptible to that same corruption. And the Lilith herself will always find a home within that feminine energy, unless of course, she is snuffed by the will of a man who doesn’t respect her. Still, she does not die, just searches for another place to rest.
Wow this was really long. SO. Lilith is the entity that embodies our biggest fears about femininity and the inherent knowledge that women posses. Women know how to create life, and women have the ultimate authority in ending it. To honour Lilith as a Goddess rather than a troublesome demon, is to recognize that even the parts of femininity that femininity herself can’t control are divine in nature. The knowledge that she possesses makes women incapable of submission. And the Gods themselves are aware of this, and do not interfere with her, because she is a Goddess herself carrying out an important function, even if it doesn’t adhere to what they might like. Basically, rebellion is an inevitability to any feminine creature that possesses knowledge. It is unavoidable.
It’s incredibly difficult to find anything about the worship of Lilith because for a long time she wasn’t given her flowers as a divinity. Even Inanna herself tried to get her to fuck off. You can honour her quite similarly to the way Artemis and Athena were worshipped, alongside Inanna or Aphrodite of course. As the dark, mysterious, yet inexplicably wise mother of demons, she is the creative force behind destruction. She’s the aspect that exists in all of these Goddesses, that most of us would rather not think about. She is a woman who cannot be held in captivity, if you tell her to procreate, she will cause miscarriage. If you tell her to obey, she will become even more rebellious. The more you repress her, the stronger she becomes. No matter how oppressed women become, no matter how subservient, so long as they have any connection to the divine feminine, they will have a Lilith inside of them.
Lilith’s representation of a succubus expands upon her associations as a woman who does what women do, (men thought women were sex objects for a long time) but not for the sake of cooperation, but for her own means. Lilith is very much a woman, capable of doing what all women and feminine goddesses can do. She simply chooses not to, similarly to how Artemis simply chooses not to procreate. The element of choice, (hello again, Lucifer) always being an option to women is, from a patriarchal standpoint, really scary for men.
So how do you worship her? Worshipping Lilith, like Lucifer, is technically paradoxical. Lucifer wants us to worship ourselves. If he accepts worship it’s because you’re using him as a metaphor for yourself. Lucifer believes in no man submitting to no God, so he won’t take on the role of the usual “authority”. Lilith is quite similar, to worship her is to worship the wise and rebellious spirit that exists in the feminine- yourself. Self honouring acts honour Lilith, just as they honour Lucifer. It’s important to remember that Lilith isn’t just rebellion for the sake of arguing, she isn’t a contrarian. She is self actualization that just happens to not go with the status quo. She does what she wants, if that pisses you off: cope. She’s not inherently against men or procreation, or even women who are submissive. She is the constant exception. The random variable that always pops up whenever we deal with feminine deities. So for me, I honour her as an extension. of every existing goddess. Within Inanna, there is a Lilith, as there is within Aphrodite, Hera, Artemis, Athena, etc etc.
Wow this was long as fuck but I hope it provided a little bit of insight as to why Lilith is so fucking confusing. Regardless of which contexts you feel are the most true, Lilith, like all deities will continue to evolve with time. Just as the narrative around Medusa has gradually changed into her being a victim instead of a monster, Lilith has shifted from being a demon that just kills babies to the ultimate personification of feminine independence. All of these interpretations are correct in the right context, you just have to figure out which context best applies to you.
OKAY if you actually read this far here’s a flower 🌹
#lilith#lilith deity#witchcraft#magick#paganism#pagan#occultism#witch community#witch aesthetic#witchblr#demonology#grimoire#lucifer#inanna#luciferian#goetic demons#goetia#mythology#syncretism
182 notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the things I hear a lot from Gentile witches and neo-pagans who want to work with Lilith or claim to work with Lilith, is that she is actually a Mesopotamian goddess, usually either Ishtar/Inanna or Erishkigal, and that it was the Jews, with their horrible patriarchy juice, who slandered her and cast her down, and so the Jews do not deserve to say what happens to her and it isn't antisemitism to work with her, or to completely ignore what the Jews say about what she is in a Jewish context.
Lilith is not Ishtar or Erishkigal. However, there is a Mesopotamian figure that is pretty stinking analogous to Lilith, and is probably her folkloric ancestor, by which I mean the idea of Lilith probably comes from this Mesopotamian figure. In fact, Lilith almost certainly is either a Jewish version of this figure, or, they are both descended from the same Near Eastern and Mediterranean basin folkloric figure. That figure is Lamashtu.
Lamashtu is, much like Lilith, the supernatural embodiment of maternal and infant mortality, a figure of power and terror, who functions as a way to embody and cope with the profound dangers that are pregnancy, childbirth, and infancy without effective medical care. the Mesopotamians never worshiped Lamashtu, but they did seek to appease her, including making symbolic gifts to her, to keep her from visiting them, and killing them or their children.
An interesting side note is that there is also a Mesopotamian figure who specifically opposes Lamashtu and functions as the protector of pregnant women and infants, and that figure is Pazuzu, a wind spirit, who ruled over other wind spirits, including ones called the Iilu in the Akkadian language. Akkadian is a Semitic language, related to Hebrew, and this word is probably a cognate of Lilith, but the Iilu probably have no relationship to the figure of Lilith except her name. You might know Pazuzu as the demon featured in the movie, The Exorcist, and ironic fate for a mythological protector of women and children.
Anyway, if you'll remember, I implied above that the Lamashtu/Lilith figure, was present in various guises throughout the Mediterranean basin and the Near East, so there are of course figures analogous to both of them throughout the region, such as Lamia of Greece, and the Strix of Rome.
So if you really really want to work with a figure who functions as the supernatural embodiment of maternal and infant mortality, Lamashtu, Lamia, or the strix would all be excellent options that don't come from an extant closed religious practice. All the baby killing, none of the antisemitism and cultural appropriation.
While all three figures are almost certainly descended from the same folkloric root, they're all subtly different, because as stories and characters travel, they change. as such, they all have particular good points about them as figures of veneration.
Lanashtu is the OG bad bitch, who commanded fear, respect, and offerings, like a mythological mafiosa, collecting protection money.
Lamia has attached to her the story that she was one of Zeus's dubiously willing lovers, who was screwed over first by Zeus, the embodiment of patriarchical rule, then by a jealous Hera, the embodiment of patriarchal marriage, so if what attracted you to Lilith was the story from the Alphabet of Ben Sira, about a victim of the patriarchy getting her own back through violent vengeance, Lamia might be the girl for you. With her however, the emphasis is less on her murder of children, then on her seducing and eating men, though she does also get strongly associated with killing children, especially boys.
And the strix is particularly interesting, because the word comes down to us in the modern Italian word for witch, striga. Indeed, one of the theories as to where the witch figure came from in Early Medieval, and then Early Modern Christianity, was as the strix demon made human. This might explain the close association between Early Modern Witchcraft and infant mortality, including Italian stories of witches causing infants to die seemingly natural deaths, so that they could dig them up and eat them after their funerals, something that ties these human supposed witches very closely to demonic folkloric antecedents. If you are looking for a figure of unfairly maligned female power, the strix and her close association with later human witches, might be the one for you.
All three of these figures, much like Lilith herself, are reflections, both of the power women wielded even within patriarchal societies, over the process of pregnancy, birth, and childrearing, and also the powers of death and loss that everyone was subject to. There is something powerful, transgressive, and even healthy in acknowledging the fears and dangers presented by this death and loss,and for some people, that might take the form in venerating the underlying powers. If this is something that would be spiritually meaning for you, and you wish to work with such a figure, and you are not Jewish, please respect the fact that Lilith is part of a closed religious practice, and remember that Lilith has sisters, in other parts of the Mediterranean basin and the Near East, who are not from extant closed cultures, and who might serve your needs better anyway.
742 notes
·
View notes
Text
The most important deity you've never heard of: the 3000 years long history of Nanaya

Being a major deity is not necessarily a guarantee of being remembered. Nanaya survived for longer than any other Mesopotamian deity, spread further away from her original home than any of her peers, and even briefly competed with both Buddha and Jesus for relevance. At the same time, even in scholarship she is often treated as unworthy of study. She has no popculture presence save for an atrocious, ill-informed SCP story which can’t get the most basic details right. Her claims to fame include starring in fairly explicit love poetry and appearing where nobody would expect her. Therefore, she is the ideal topic to discuss on this blog. This is actually the longest article I published here, the culmination of over two years of research. By now, the overwhelming majority of Nanaya-related articles on wikipedia are my work, and what you can find under the cut is essentially a synthesis of what I have learned while getting there. I hope you will enjoy reading it as much as I enjoyed working on it. Under the cut, you will learn everything there is to know about Nanaya: her origin, character, connections with other Mesopotamian deities, her role in literature, her cult centers… Since her history does not end with cuneiform, naturally the later text corpora - Aramaic, Bactrian, Sogdian and even Chinese - are discussed too. The article concludes with a short explanation why I see the study of Nanaya as crucial.
Dubious origins and scribal wordplays: from na-na to Nanaya Long ago Samuel Noah Kramer said that “history begins in Sumer”. While the core sentiment was not wrong in many regards, in this case it might actually begin in Akkad, specifically in Gasur, close to modern Kirkuk. The oldest possible attestation of Nanaya are personal names from this city with the element na-na, dated roughly to the reign of Naram-Sin of Akkad, so to around 2250 BCE. It’s not marked in the way names of deities in personal names would usually be, but this would not be an isolated case.
The evidence is ultimately mixed. On one hand, reduplicated names like Nana are not unusual in early Akkadian sources, and -ya can plausibly be explained as a hypocoristic suffix. On the other hand, there is not much evidence for Nanaya being worshiped specifically in the far northeast of Mesopotamia in other periods. Yet another issue is that there is seemingly no root nan- in Akkadian, at least in any attested words.
The main competing proposal is that Nanaya originally arose as a hypostasis of Inanna but eventually split off through metaphorical mitosis, like a few other goddesses did, for example Annunitum. This is not entirely implausible either, but ultimately direct evidence is lacking, and when Nanaya pops up for the first time in history she is clearly a distinct goddess.
There are a few other proposals regarding Nanaya’s origin, but they are considerably weaker. Elamite has the promising term nan, “day” or “morning”, but Nanaya is entirely absent from the Old Elamite sources you’d expect to find her in if Mesopotamians imported her from the east. Therefore, very few authors adhere to this view. The hypothesis that she was an Aramaic goddess in origin does not really work chronologically, since Aramaic is not attested in the third millennium BCE at all. The less said about attempts to connect her to anything “Proto-Indo-European”, the better.
Like many other names of deities, Nanaya’s was already a subject of etymological speculation in antiquity. A late annotated version of the Weidner god list, tablet BM 62741, preserves a scribe’s speculative attempt at deriving it from the basic meaning of the sign NA, “to call”, furnished with a feminine suffix, A. Needless to say, like other such examples of scribal speculation, some of which are closer to playful word play than linguistics, it is unlikely to reflect the actual origin of the name.
Early history: Shulgi-simti, Nanaya’s earliest recorded #1 fan

A typical Ur III administrative tablet listing offerings to various deities (wikimedia commons)
The first absolutely certain attestations of Nanaya, now firmly under her full name, have been identified in texts from the famous archive from Puzrish-Dagan, modern Drehem, dated to around 2100 BCE. Much can be written about this site, but here it will suffice to say that it was a center of the royal administration of the Third Dynasty of Ur ("Ur III") responsible for the distribution of sacrificial animals. Nanaya appears there in a rather unique context - she was one of the deities whose cults were patronized by queen Shulgi-simti, one of the wives of Shulgi, the successor of the dynasty’s founder Ur-Namma. We do not know much about Shulgi-simti as a person - she did not write any official inscriptions announcing her preferred foreign policy or letters to relatives or poetry or anything else that typically can be used to gain a glimpse into the personal lives of Mesopotamian royalty. We’re not really sure where she came from, though Eshnunna is often suggested as her hometown. We actually do not even know what her original name was, as it is assumed she only came to be known as Shulgi-simti after becoming a member of the royal family. Tonia Sharlach suggested that the absence of information about her personal life might indicate that she was a commoner, and that her marriage to Shulgi was not politically motivated The one sphere of Shulgi-simti’s life which we are incredibly familiar with are her religious ventures. She evidently had an eye for minor, foreign or otherwise unusual goddesses, such as Belet-Terraban or Nanaya. She apparently ran what Sharlach in her “biography” of her has characterized as a foundation. It was tasked with sponsoring various religious celebrations. Since Shulgi-simti seemingly had no estate to speak of, most of the relevant documents indicate she procured offerings from a variety of unexpected sources, including courtiers and other members of the royal family. The scale of her operations was tiny: while the more official religious organizations dealt with hundreds or thousands of sacrificial animals, up to fifty or even seventy thousand sheep and goats in the case of royal administration, the highest recorded number at her disposal seems to be eight oxen and fifty nine sheep. A further peculiarity of the “foundation” is that apparently there was a huge turnover rate among the officials tasked with maintaining it. It seems nobody really lasted there for much more than four years. There are two possible explanations: either Shulgi-simti was unusually difficult to work with, or the position was not considered particularly prestigious and was, at the absolute best, viewed as a stepping stone. While the Shulgi-simti texts are the earliest evidence for worship of Nanaya in the Ur III court, they are actually not isolated. When all the evidence from the reigns of Shulgi and his successors is summarized, it turns out that she quickly attained a prominent role, as she is among the twelve deities who received the most offerings. However, her worship was seemingly limited to Uruk (in her own sanctuary), Nippur (in the temple of Enlil, Ekur) and Ur. Granted, these were coincidentally three of the most important cities in the entire empire, so that’s a pretty solid early section of a divine resume. She chiefly appears in two types of ceremonies: these tied to the royal court, or these mostly performed by or for women. Notably, a festival involving lamentations (girrānum) was held in her honor in Uruk. To understand Nanaya’s presence in the two aforementioned contexts, and by extension her persistence in Mesopotamian religion in later periods, we need to first look into her character.
The character of Nanaya: eroticism, kingship, and disputed astral ventures

Corona Borealis (wikimedia commons)
Nanaya’s character is reasonably well defined in primary sources, but surprisingly she was almost entirely ignored in scholarship quite recently. The first study of her which holds up to scrutiny is probably Joan Goodnick Westenholz’s article Nanaya, Lady of Mystery from 1997. The core issue is the alleged interchangeability of goddesses. From the early days of Assyriology basically up to the 1980s, Nanaya was held to be basically fully interchangeable with Inanna. This obviously put her in a tough spot. Still, over the course of the past three decades the overwhelming majority of studies came to recognize Nanaya as a distinct goddess worthy of study in her own right. You will still stumble upon the occasional “Nanaya is basically Inanna”, but now this is a minority position. Tragically it’s not extinct yet, most recently I’ve seen it in a monograph published earlier this year. With these methodological and ideological issues out of the way, let’s actually look into Nanaya’s character, as promised by the title of this section. Her original role was that of a goddess of love. It is already attested for her at the dawn of her history, in the Ur III period. Her primary quality was described with a term rendered as ḫili in Sumerian and kuzbu in Akkadian. It can be variously translated as “charm”, “luxuriance”, “voluptuousness”, “sensuality” or “sexual attractiveness”. This characteristic was highlighted by her epithet bēlet kuzbi (“lady of kuzbu”) and by the name of her cella in the Eanna, Eḫilianna. The connection was so strong that this term appears basically in every single royal inscription praising her. She was also called bēlet râmi, “lady of love”. Nanaya’s role as a love goddess is often paired with describing her as a “joyful” or “charming” deity. It needs to be stressed that Nanaya was by no metric the goddess of some abstract, cosmic love or anything like that. Love incantations and prayers related to love are quite common, and give us a solid glimpse into this matter. Nanaya’s range of activity in them is defined pretty directly: she deals with relationships (and by extension also with matters like one-sided crushes or arguments between spouses), romance and with strictly sexual matters. For an example of a hymn highlighting her qualifications when it comes to the last category, see here. The text is explicit, obviously. We can go deeper, though. There is also an incantation whose incipit at first glance leaves little to imagination:

However, the translator, Giole Zisa, notes there is some debate over whether it’s actually about having sex with Nanaya or merely about invoking her (and other deities) while having sex with someone else. A distinct third possibility is that she’s not even properly invoked but that “oh, Nanaya” is simply an exclamation of excitement meant to fit the atmosphere, like a specialized version of the mainstay of modern erotica dialogue, “oh god”.
While this romantic and sexual aspect of Nanaya’s character is obviously impossible to overlook, this is not all there was to her. She was also associated with kingship, as already documented in the Ur III period. She was invoked during coronations and mourning of deceased kings. In the Old Babylonian period she was linked to investiture by rulers of newly independent Uruk. A topic which has stirred some controversy in scholarship is Nanaya’s supposed astral role. Modern authors who try to present Nanaya as a Venus deity fall back on rather faulty reasoning, namely asserting that if Nanaya was associated with Inanna and Inanna personified Venus, clearly Nanaya did too. Of course, being associated with Inanna does not guarantee the same traits. Shaushka was associated with her so closely her name was written with the logogram representing her counterpart quite often, and lacked astral aspects altogether. No primary sources which discuss Nanaya as a distinct, actively worshiped deity actually link her with Venus. If you stretch it you will find some tidbits like an entry in a dictionary prepared by the 10th century bishop Hasan bar Bahlul, who inexplicably asserted Nanaya was the Arabic name of the planet Venus. As you will see soon, there isn’t even a possibility that this reflected a relic of interpretatio graeca. The early Mandaean sources, many of which were written when at least remnants of ancient Mesopotamian religion were still extant, also do not link Nanaya with Venus. Despite at best ambivalent attitude towards Mesopotamian deities, they show remarkable attention to detail when it comes to listing their cult centers, and on top of that Mesopotamian astronomy had a considerable impact on Mandaeism, so there is no reason not to prioritize them, as far as I am concerned. As far as the ancient Mesopotamian sources themselves go, the only astral object with a direct connection to Nanaya was Corona Borealis (BAL.TÉŠ.A, “Dignity”), as attested in the astronomical compendium MUL.APIN. Note that this is a work which assigns astral counterparts to virtually any deity possible, though, and there is no indication this was a major part of Nanaya’s character. Save for this single instance, she is entirely absent from astronomical texts. A further astral possibility is that Nanaya was associated with the moon. The earliest evidence is highly ambiguous: in the Ur III period festivals held in her honor might have been tied to phases of the moon, while in the Old Babylonian period a sanctuary dedicated to her located in Larsa was known under the ceremonial name Eitida, “house of the month”. A poem in which looking at her is compared to looking at the moon is also known. That’s not all, though. Starting with the Old Babylonian period, she could also be compared with the sun. Possibly such comparisons were meant to present her as an astral deity, without necessarily identifying her with a specific astral body. Michael P. Streck and Nathan Wasserman suggest that it might be optimal to simply refer to her as a “luminous” deity in this context. However, as you will see later it nonetheless does seem she eventually came to be firmly associated both with the sun and the moon. Last but not least, Nanaya occasionally displayed warlike traits. It’s hardly major in her case, and if you tried hard enough you could turn any deity into a war deity depending on your political goals, though. I’d also place the incantation which casts her as one of the deities responsible for keeping the demon Lamashtu at bay here.
Nanaya in art
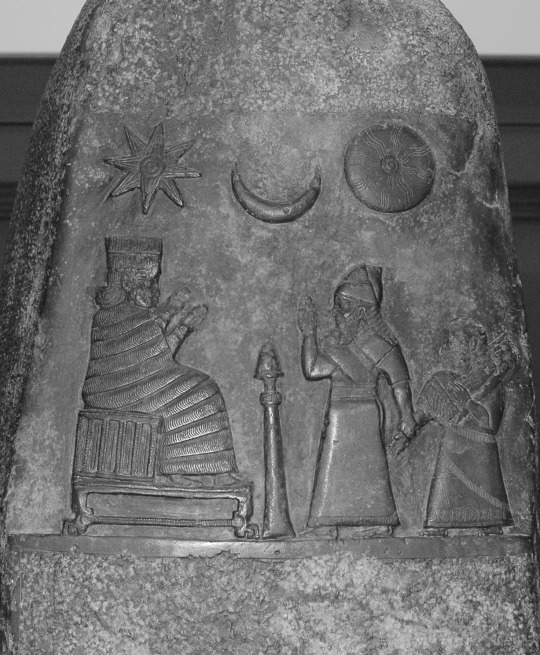

The oldest known depiction of Nanaya (wikimedia commons)
While Nanaya’s roles are pretty well defined, there surprisingly isn’t much to say about her iconography in Mesopotamian art.The oldest certain surviving depiction of her is rather indistinct: she’s wearing a tall headdress and a flounced robe. It dates to the late Kassite period (so roughly to 1200 BCE), and shows her alongside king Meli-Shipak (or maybe Meli-Shihu, reading remains uncertain) and his daughter Hunnubat-Nanaya. Nanaya is apparently invoked to guarantee that the prebend granted to the princess will be under divine protection. This is not really some unique prerogative of hers, perhaps she was just the most appropriate choice because Hunnubat-Nanaya’s name obviously reflects devotion to her. The relief discussed above is actually the only depiction of Nanaya identified with certainty from before the Hellenistic period, surprisingly. We know that statues representing her existed, and it is hard to imagine that a popular, commonly worshiped deity was not depicted on objects like terracotta decorations and cylinder seals, but even if some of these were discovered, there’s no way to identify them with certainty. This is not unusual though, and ultimately there aren’t many Mesopotamian deities who can be identified in art without any ambiguity.
Nanaya in literature
As I highlighted in the section dealing with Nanaya’s character, she is reasonably well attested in love poetry. However, this is not the only genre in which she played a role. A true testament to Nanaya’s prominence is a bilingual (Sumero-Akkadian) hymn composed in her honor in the first millennium BCE. It is written in the first person, and presents various other goddesses as her alternate identities. It is hardly unique, and similar compositions dedicated to Ishtar (Inanna), Gula, Ninurta and Marduk are also known. Each strophe describes a different deity and location, but ends with Nanaya reasserting her actual identity with the words “still I am Nanaya”. Among the claimed identities included are both major goddesses in their own right (Inanna plus closely associated Annunitum and Ishara, Gula, Bau, Ninlil), goddesses relevant due to their spousal roles first and foremost (Damkina, Shala, Mammitum etc) and some truly unexpected, picks, the notoriously elusive personified rainbow Manzat being the prime example. Most of them had very little in common with Nanaya, so this might be less an attempt at syncretism, and more an elevation of her position through comparisons to those of other goddesses. An additional possible literary curiosity is a poorly preserved myth which Wilfred G. Lambert referred to as “The murder of Anshar”. He argues that Nanaya is one of the two deities responsible for the eponymous act. I don't quite follow the logic, though: the goddess is actually named Ninamakalamma (“Lady mother of the land”), and her sole connection with Nanaya is that they occur in sequence in the unique god list from Sultantepe. Lambert saw this as a possible indication they are identical. There are no other attestations of this name, but ama kalamma does occur as an epithet of various goddesses, most notably Ninshubur. Given her juxtaposition with Nanaya in the Weidner god list - more on that later - wouldn’t it make more sense to assume it’s her? Due to obscurity of the text as far as I am aware nobody has questioned Lambert’s tentative proposal yet, though.
There isn’t much to say about the plot: Anshar, literally “whole heaven”, the father of Anu, presumably gets overthrown and might be subsequently killed. Something that needs to be stressed here to avoid misinterpretation: primordial deities such as Anshar were borderline irrelevant, and weren't really worshiped. They exist to fade away in myths and to be speculated about in elaborate lexical texts. There was no deposed cult of Anshar. Same goes for all the Tiamats and Enmesharras and so on.
Inanna and beyond: Nanaya and friends in Mesopotamian sources
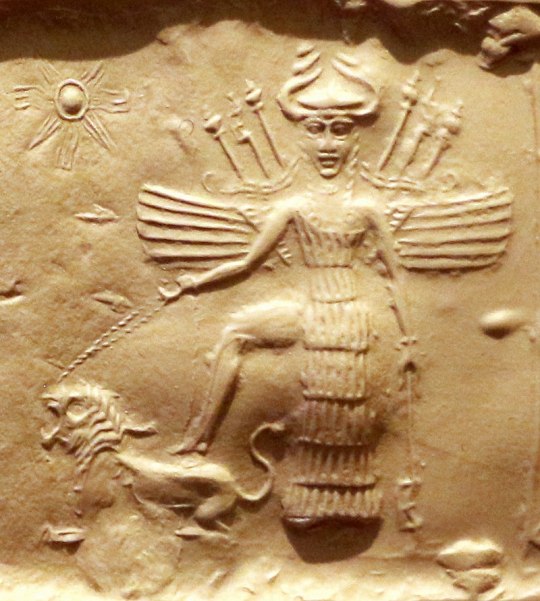

Inanna on a cylinder seal from the second half of the third millennium BCE (wikimedia commons)
Of course, Nanaya’s single most important connection was that to Inanna, no matter if we are to accept the view that she was effectively a hypostasis gone rogue or not. The relationship between them could be represented in many different ways. Quite commonly she was understood as a courtier or protegee of Inanna. A hymn from the reign of Ishbi-Erra calls her the “ornament of Eanna” (Inanna’s main temple in Uruk) and states she was appointed by Inanna to her position. References to Inanna as Nanaya’s mother are also known, though they are rare, and might be metaphorical. To my best knowledge nothing changed since Olga Drewnowska-Rymarz’s monograph, in which she notes she only found three examples of texts preserving this tradition. I would personally abstain from trying to read too deep into it, given this scarcity. Other traditions regarding Nanaya’s parentage are better attested. In multiple cases, she “borrows” Inanna’s conventional genealogy, and as a result is addressed as a daughter of Sin (Nanna), the moon god. However, she was never addressed as Inanna’s sister: it seems that in cases where Sin and Nanaya are connected, she effectively “usurps” Inanna’s own status as his daughter (and as the sister of Shamash, while at it). Alternatively, she could be viewed as a daughter of Anu. Finally, there is a peculiar tradition which was the default in laments: in this case, Nanaya was described as a daughter of Urash. The name in this context does not refer to the wife of Anu, though. The deity meant is instead a small time farmer god from Dilbat. To my best knowledge no sources place Nanaya in the proximity of other members of Urash’s family, though some do specify she was his firstborn daughter. To my best knowledge Urash had at least two other children, Lagamal (“no mercy”, an underworld deity whose gender is a matter of debate) and Ipte-bitam (“he opened the house”, as you can probably guess a divine doorkeeper). Nanaya’s mother by extension would presumably be Urash’s wife Ninegal, the tutelary goddess of royal palaces. There is actually a ritual text listing these three together. In the Weidner god list Nanaya appears after Ninshubur. Sadly, I found no evidence for a direct association between these two. For what it’s worth, they did share a highly specific role, that of a deity responsible for ordering around lamma. This term referred to a class of minor deities who can be understood as analogous to “guardian angels” in contemporary Christianity, except places and even deities had their own lamma too, not just people. Lamma can also be understood at once as a class of distinct minor deities, as the given name of individual members of it, and as a title of major deities. In an inscription of Gudea the main members of the official pantheon are addressed as “lamma of all nations”, by far one of my favorite collective terms of deities in Mesopotamian literature. A second important aspect of the Weidner god list is placing Nanaya right in front of Bizilla. The two also appear side by side in some offering lists and in the astronomical compendium MUL.APIN, where they are curiously listed as members of the court of Enlil. It seems that like Nanaya, she was a goddess of love, which is presumably reflected by her name. It has been variously translated as “pleasing”, “loving” or as a derivative of the verb “to strip”. An argument can be made that Bizilla was to Nanaya what Nanaya was to Inanna. However, she also had a few roles of her own. Most notably, she was regarded as the sukkal of Ninlil. She may or may not also have had some sort of connection to Nungal, the goddess of prisons, though it remains a matter of debate if it’s really her or yet another, accidentally similarly named, goddess.
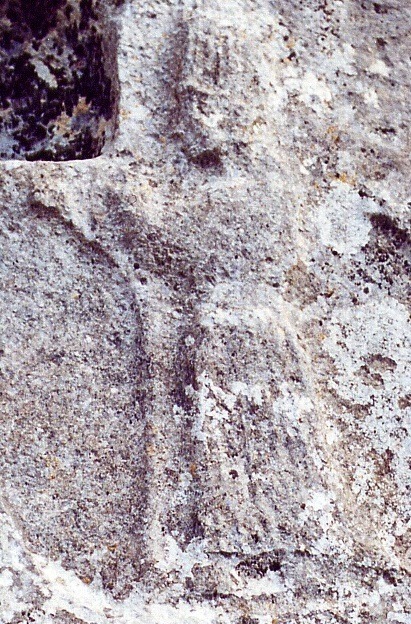

An indistinct Hurro-Hittite depiction of Ishara from the Yazilikaya sanctuary (wikimedia commons)
In love incantations, Nanaya belonged to an informal group which also included Inanna, Ishara, Kanisurra and Gazbaba. I do not think Inanna’s presence needs to be explained. Ishara had an independent connection with Inanna and was a multi-purpose deity to put it very lightly; in the realm of love she was particularly strongly connected with weddings and wedding nights. Kanisurra and Gazbaba warrant a bit more discussion, because they are arguably Nanaya’s supporting cast first and foremost. Gazbaba is, at the core, seemingly simply the personification of kuzbu. Her name had pretty inconsistent orthography, and variants such as Kazba or Gazbaya can be found in primary sources too. The last of them pretty clearly reflects an attempt at making her name resemble Nanaya’s. Not much can be said about her individual character beyond the fact she was doubtlessly related to love and/or sex. She is described as the “grinning one” in an incantation which might be a sexual allusion too, seeing as such expressions are a mainstay of Akkadian erotic poetry. Kanisurra would probably win the award for the fakest sounding Mesopotamian goddess, if such a competition existed. Her name most likely originated as a designation of the gate of the underworld, ganzer. Her default epithet was “lady of the witches” (bēlet kaššāpāti). And on top of that, like Nanaya and Gazbaba she was associated with sex. She certainly sounds more like a contemporary edgy oc of the Enoby Dimentia Raven Way variety than a bronze age goddess - and yet, she is completely genuine. It is commonly argued Kanisurra and Gazbaba were regarded as Nanaya’s daughters, but there is actually no direct evidence for this. In the only text where their relation to Nanaya is clearly defined they are described as her hairdressers, rather than children. While in some cases the love goddesses appear in love incantations in company of each other almost as if they were some sort of disastrous polycule, occasionally Nanaya is accompanied in them by an anonymous spouse. Together they occur in parallel with Inanna and Dumuzi and Ishara and Almanu, apparently a (accidental?) deification of a term referring to someone without family obligations. There is only one Old Babylonian source which actually assigns a specific identity to Nanaya’s spouse, a hymn dedicated to king Abi-eshuh of Babylon. An otherwise largely unknown god Muati (I patched up his wiki article just for the sake of this blog post) plays this role here. The text presents a curious case of reversal of gender roles: Muati is asked to intercede with Nanaya on behalf of petitioners. Usually this was the role of the wife - the best known case is Aya, the wife of Shamash, who is implored to do just that by Ninsun in the standard edition of the Epic of Gilgamesh. It’s also attested for goddesses such as Laz, Shala, Ninegal or Ninmug… and in the case of Inanna, for Ninshubur.

A Neo-Assyrian statue of Nabu on display in the Iraq Museum (wikimedia commons)
Marten Stol seems to treat Muati and Nabu as virtually the same deity, and on this basis states that Nanaya was already associated with the latter in the Old Babylonian period, but this seems to be a minority position. Other authors pretty consistently assume that Muati was a distinct deity at some point “absorbed” by Nabu. The oldest example of pairing Nanaya with Nabu I am aware of is an inscription dated to the reign of Marduk-apla-iddina I, so roughly to the first half of the twelfth century BCE. The rise of this tradition in the first millennium BCE was less theological and more political. With Babylon once again emerging as a preeminent power, local theologies were supposed to be subordinated to the one followed in the dominant city. Which, at the time, was focused on Nabu, Marduk and Zarpanit. Worth noting that Nabu also had a spouse before, Tashmetum (“reconciliation”). In the long run she was more or less ousted by Nanaya from some locations, though she retained popularity in the north, in Assyria. She is not exactly the most thrilling deity to discuss. I will confess I do not find the developments tied to Nanaya and Nabu to be particularly interesting to cover, but in the long run they might have resulted in Nanaya acquiring probably the single most interesting “supporting cast member” she did not share with Inanna, so we’ll come back to this later. Save for Bizilla, Nanaya generally was not provided with “equivalents” in god lists. I am only aware of one exception, and it’s a very recent discovery. Last year the first ever Akkadian-Amorite bilingual lists were published. This is obviously a breakthrough discovery, as before Amorite was largely known just from personal names despite being a vernacular language over much of the region in the bronze age, but only one line is ultimately of note here. In a section of one of the lists dealing with deities, Nanaya’s Amorite counterpart is said to be Pidray. This goddess is otherwise almost exclusively known from Ugarit. This of course fits very well with the new evidence: recent research generally stresses that Ugarit was quintessentially an Amorite city (the ruling house even claimed descent from mythical Ditanu, who is best known from the grandiose fictional genealogies of Shamshi-Adad I and the First Dynasty of Babylon). Sadly, we do not know how the inhabitants of Ugarit viewed Nanaya. A trilingual version of the Weidner list, with the original version furnished with columns listing Ugaritic and Hurrian counterparts of each deity, was in circulation, but the available copies are too heavily damaged to restore it fully. And to make things worse, much of it seems to boil down to scribal wordplay and there is no guarantee all of the correspondences are motivated theologically. For instance, the minor Mesopotamian goddess Imzuanna is presented as the counterpart of Ugaritic weather god Baal because her name contains a sign used as a shortened logographic writing of the latter. An even funnier case is the awkward attempt at making it clear the Ugaritic sun deity Shapash, who was female, is not a lesbian… by making Aya male. Just astonishing, really.
The worship of Nanaya

A speculative reconstruction of Ur III Uruk with the Eanna temple visible in the center (Artefacts — Scientific Illustration & Archaeological Reconstruction; reproduced here for educational purposes only, as permitted)
Rather fittingly, as a deity associated with Inanna, Nanaya was worshiped chiefly in Uruk. She is also reasonably well attested in the inscriptions of the short-lived local dynasty which regained independence near the end of the period of domination of Larsa over Lower Mesopotamia. A priest named after her, a certain Iddin-Nanaya, for a time served as the administrator of her temple, the Enmeurur, “house which gathers all the me,” me being a difficult to translate term, something like “divine powers”. The acquisition of new me is a common topic in Mesopotamian literature, and in compositions focused on Inanna in particular, so it should not be surprising to anyone that her peculiar double seemingly had similar interests. In addition to Uruk, as well as Nippur and Ur, after the Ur III period Nanaya spread to multiple other cities, including Isin, Mari, Babylon and Kish. However, she is probably by far the best attested in Larsa, where she rose to the rank of one of the main deities, next to Utu, Inanna, Ishkur and Nergal. She had her own temple, the Eshahulla, “house of a happy heart”. In local tradition Inanna got to keep her role as an “universal” major goddess and her military prerogatives, but Nanaya overtook the role of a goddess of love almost fully. Inanna’s astral aspect was also locally downplayed, since Venus was instead represented in the local pantheon by closely associated, but firmly distinct, Ninsianna. This deity warrants some more discussion in the future just due to having a solid claim to being one of the first genderfluid literary figures in history, but due to space constraints this cannot be covered in detail here. A later inscription from the same city differentiates between Nanaya and Inanna by giving them different epithets: Nanaya is the “queen of Uruk and Eanna” (effectively usurping Nanaya’s role) while Inanna is the “queen of Nippur” (that’s actually a well documented hypostasis of her, not to be confused with the unrelated “lady of Nippur”). Uruk was temporarily abandoned in the late Old Babylonian period, but that did not end Nanaya’s career. Like Inanna, she came to be temporarily relocated to Kish. It has been suggested that a reference to her residence in “Kiššina” in a Hurro-Hittite literary text, the Tale of Appu, reflects her temporary stay there. The next centuries of Nanaya are difficult to reconstruct due to scarce evidence, but it is clear she continued to be worshiped in Uruk. By the Neo-Babylonian period she was recognized as a member of an informal pentad of the main deities of the city, next to Inanna, Urkayitu, Usur-amassu and Beltu-sa-Resh. Two of them warrant no further discussion: Urkayitu was most likely a personification of the city, and Beltu-sa-Resh despite her position is still a mystery to researchers. Usur-amassu, on the contrary, is herself a fascinating topic. First attestations of this deity, who was seemingly associated with law and justice (a pretty standard concern), come back to the Old Babylonian period. At this point, Usur-amassu was clearly male, which is reflected by the name. He appears in the god list An = Anum as a son of the weather deity couple par excellence, Adad (Ishkur) and Shala. However, by the early first millennium BCE Usur-amassu instead came to be regarded as female - without losing the connection to her parents. She did however gain a connection to Inanna, Nanaya and Kanisurra, which she lacked earlier. How come remains unknown. Most curiously her name was not modified to reflect her new gender, though she could be provided with a determinative indicating it. This recalls the case of Lagamal in the kingdom of Mari some 800 years earlier.
The end of the beginning: Nanaya under Achaemenids and Seleucids

Trilingual (Persian, Elamite and Akkadian) inscription of the first Achamenid ruler of Mesopotamia, Cyrus (wikimedia commons)
After the fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire Mesopotamia ended up under Achaemenid control, which in turn was replaced by the Seleucids. Nanaya flourished through both of these periods. In particular, she attained considerable popularity among Arameans. While they almost definitely first encountered her in Uruk, she quickly came to be venerated by them in many distant locations, like Palmyra, Hatra and Dura Europos in Syria. She even appears in a single Achaemenid Aramaic papyrus discovered in Elephantine in Egypt. It indicates that she was worshiped there by a community which originated in Rash, an area east to the Tigris. As a curiosity it’s worth mentioning the same source is one of the only attestations of Pidray from outside Ugarit. I do not think this has anything to do with the recently discovered connection between her and Nanaya… but you may never know. Under the Seleucids, Nanaya went through a particularly puzzling process of partial syncretism. Through interpretatio graeca she was identified with… Artemis. How did this work? The key to understanding this is the fact Seleucids actually had a somewhat limited interest in local deities. All that was necessary was to find relatively major members of the local pantheon who could roughly correspond to the tutelary deities of their dynasty: Zeus, Apollo and Artemis. Zeus found an obvious counterpart in Marduk (even though Marduk was hardly a weather god). Since Nabu was Marduk’s son, he got to be Apollo. And since Nanaya was the most major goddess connected to Nabu, she got to be Artemis. It really doesn’t go deeper than that. For what it’s worth, despite the clear difference in character this newfound association did impact Nanaya in at least one way: she started to be depicted with attributes borrowed from Artemis, namely a bow and a crescent. Or perhaps these attributes were already associated with her, but came to the forefront because of the new role. The Artemis-like image of Nanaya as an archer is attested on coins, especially in Susa, yet another city where she attained considerable popularity.
Leaving Mesopotamia: Nanaya and the death of cuneiform

A Parthian statue of Nanaya with a crescent diadem (Louvre; reproduced here for educational purposes only. Identification follows Andrea Sinclair's proposal)
The Seleucid dynasty was eventually replaced by the Parthians. This period is often considered a symbolic end of ancient Mesopotamian religion in the strict sense. Traditional religious institutions were already slowly collapsing in Achaemenid and Seleucid times as the new dynasties had limited interest in royal patronage. Additionally, cuneiform fell out of use, and by the end of the first half of the first millennium CE the art of reading and writing it was entirely lost. This process did not happen equally quickly everywhere, obviously, and some deities fared better than others in the transitional period before the rise of Christianity and Islam as the dominant religions across the region. Nanaya was definitely one of them, at least for a time. In Parthian art Nanaya might have developed a distinct iconography: it has been argued she was portrayed as a nude figure wearing only some jewelry (including what appears to be a navel piercing and a diadem with a crescent. The best known example is probably this standing figure, one of my all time favorite works of Mesopotamian art:
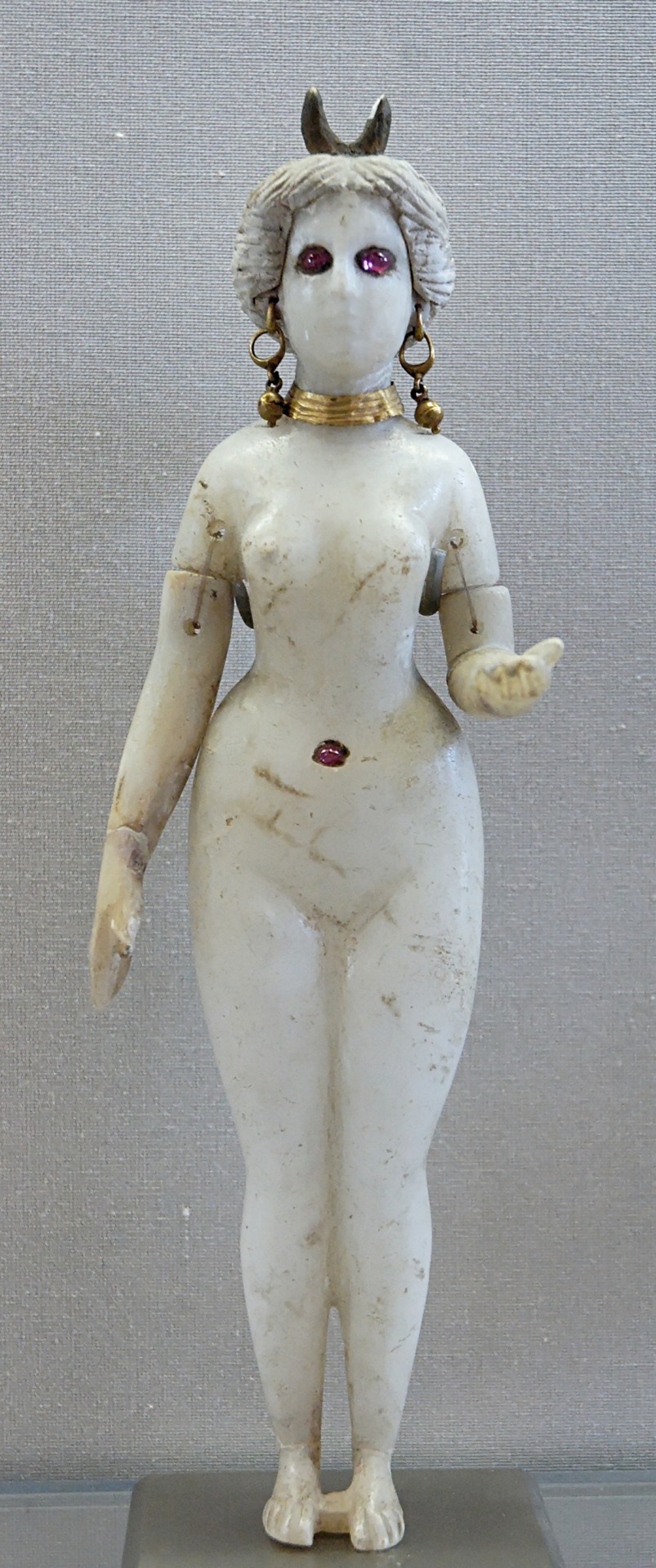

Parthian Nanaya (wikimedia commons; identification courtesy of the Louvre website and J. G. Westenholz)
For years Wikipedia had this statue mislabeled as “Astarte” which makes little sense considering it comes from a necropolis near Babylon. There was also a viral horny tweet which labeled it as “Asherah” a few months ago (I won’t link it but I will point out in addition to getting the name wrong op also severely underestimated the size). This is obviously even worse nonsense both on spatial and temporal grounds. Even if the biblical Asherah was ever an actual deity like Ugaritic Athirat and Mesopotamian Ashratum, it is highly dubious she would still be worshiped by the time this statue was made. It’s not even certain she ever was a deity, though. Cognate of a theonym is not automatically a theonym itself, and the Ugaritic texts and the Bible, even if they share some topoi, are separated by centuries and a considerable distance. This is not an Asherah post though, so if this is a topic which interests you I recommend downloading Steve A. Wiggins’ excellent monograph A Reassessment of Asherah: With Further Considerations of the Goddess.
The last evidence for the worship of Nanaya in Mesopotamia is a Mandaean spell from Nippur, dated to the fifth or sixth century CE. However, at this point Nanaya must have been a very faint memory around these parts, since the figure designated by this name is evidently male in this formula. That was not the end of her career, though. The system of beliefs she originated and thrived in was on its way out, but there were new frontiers to explore. A small disgression is in order here: be INCREDIBLY wary of claims about the survival of Mesopotamian tradition in Mesopotamia itself past the early middle ages. Most if not all of these come from the writing of Simo Parpola, who is a 19th century style hyperdiffusionist driven by personal religious beliefs based on gnostic christianity, which he believes was based on Neo-Assyrian state religion, which he misinterprets as monotheism, or rather proto-christianity specifically (I wish I was making this up). I personally do not think a person like that should be tolerated in serious academia, but for some incomprehensible reason that isn’t the case.
New frontiers: Nanaya in Bactria
The key to Nanaya’s extraordinarily long survival wasn’t the dedication to her in Mesopotamia, surprisingly. It was instead her introduction to Bactria, a historical area in Central Asia roughly corresponding to parts of modern Afghanistan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. The early history of this area is still poorly known, though it is known that it was one of the “cradles of civilization” not unlike Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley or Mesoamerica. The so-called “Oxus civilization” or “Bactria-Margiana Archaeological Complex” flourished around 2500-1950 BCE (so roughly contemporarily with the Akkadian and Ur III empires in Mesopotamia). It left behind no written records, but their art and architecture are highly distinctive and reflect great social complexity. I sadly can’t spent much time discussing them here though, as they are completely irrelevant to the history of Nanaya (there is a theory that she was already introduced to the east when BMAC was extant but it is incredibly implausible), so I will limit myself to showing you my favorite related work of art, the “Bactrian princess”:
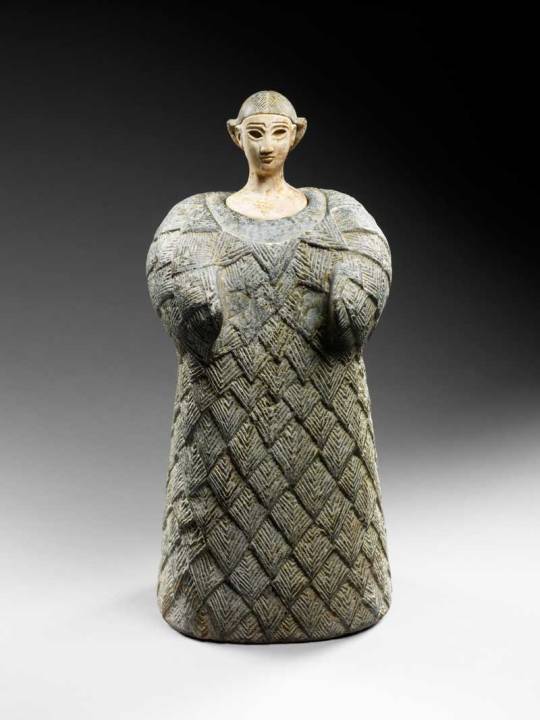

Photo courtesy of Louvre Abu Dhabi, reproduced here for educational purposes only.
By late antiquity, which is the period we are concerned with here, BMAC was long gone, and most of the inhabitants of Bactria spoke Bactrian, an extinct Iranian language. How exactly they were related to their BMAC forerunners is uncertain. Their religious beliefs can be compared to Zoroastrianism, or rather with its less formalized forerunners followed by most speakers of Iranian languages before the rise of Zoroaster. However, there were many local peculiarities. For example, the main deity was the personified river Oxus, not Ahura Mazda. Whether this was a relic of BMAC religion is impossible to tell.We do not know exactly when the eastward transfer of Nanaya to Bactria happened. The first clear evidence for her presence in central Asia comes from the late first century BCE, from the coins of local rulers, Sapadbizes and Agesiles. It is possible that her depictions on coinage of Mesopotamian and Persian rulers facilitated her spread. Of course, it’s also important to remember that the Aramaic script and language spread far to the east in the Achaemenid period already, and that many of the now extinct Central Asian scripts were derived from it (Bactrian was written with the Greek script, though). Doubtlessly many now lost Aramaic texts were transferred to the east. There’s an emerging view that for unclear reasons, under the Achaemenids Mesopotamian culture as a whole had unparalleled impact on Bactria. The key piece of evidence are Bactrian temples, which often resemble Mesopotamian ones. Therefore, perhaps we should be wondering not why Nanaya spread from Mesopotamia to Central Asia, but rather why there were no other deities who did, for the most part. That is sadly a question I cannot answer. Something about Nanaya simply made her uniquely appealing to many groups at once. While much about the early history of Nanaya in Central Asia is a mystery, it is evident that with time she ceased to be viewed as a foreign deity. For the inhabitants of Bactria she wasn’t any less “authentically Iranian” than the personified Oxus or their versions of the conventional yazatas like Sraosha. Frequently arguments are made that Nanaya’s widespread adoption and popularity could only be the result of identification between her and another deity.Anahita in particular is commonly held to be a candidate. However, as stressed by recent studies there’s actually no evidence for this. What is true is that Anahita is notably missing from the eastern Iranian sources, despite being prominent in the west from the reign of the Achaemenid emperor Artaxerxes II onward. However, it is clear that not all yazatas were equally popular in each area - pantheons will inevitably be localized in each culture. Furthermore, Anahita’s character has very little in common with Nanaya save for gender. Whether we are discussing her early not quite Zoroastrian form the Achaemenid public was familiar with or the contemporary yazata still relevant in modern Zoroastrianism, the connection to water is the most important feature of her. Nanaya didn’t have such a role in any culture. Recently some authors suggested a much more obvious explanation for Anahita’s absence from the eastern Iranian pantheon(s). As I said, eastern Iranian communities venerated the river Oxus as a deity (or as a yazata, if you will). He was the water god par excellence, and in Bactria also the king of the gods. It is therefore quite possible that Anahita, despite royal backing from the west, simply couldn’t compete with him. Their roles overlapped more than the roles of Anahita and Nanaya. I am repeating myself but the notion of interchangeability of goddesses really needs to be distrusted almost automatically, no matter how entrenched it wouldn’t be. While we’re at it, the notion of alleged interchangeability between Anahita and Ishtar is also highly dubious, but that’s a topic for another time.

Nana (Nanaya) on a coin of Kanishka (wikimedia commons)
Nanaya experienced a period of almost unparalleled prosperity with the rise of the Kushan dynasty in Bactria. The Kushans were one of the groups which following Chinese sources are referred to as Yuezhi. They probably did not speak any Iranian language originally, and their origin is a matter of debate. However, they came to rule over a kingdom which consisted largely of areas inhabited by speakers of various Iranian languages, chiefly Bactrian. Their pantheon, documented in royal inscriptions and on coinage, was an eerie combination of mainstays of Iranian beliefs like Sraosha and Mithra and some unique figures, like Oesho, who was seemingly the reflection of Hindu Shiva. Obviously, Nanaya was there too, typically under the shortened name Nana. The most famous Kushan ruler, emperor Kanishka, in his inscription from Rabatak states that kingship was bestowed upon him by “Nana and all the gods”. However, we do not know if the rank assigned to her indicates she was the head of the dynastic pantheon, the local pantheon in the surrounding area, or if she was just the favorite deity of Kanishka. Same goes for the rank of numerous other deities mentioned in the rest of the inscription. Her apparent popularity during Kanishka’s reign and beyond indicates her role should not be downplayed, though. The coins of Kanishka and other Bactrian art indicate that a new image of Nanaya developed in Central Asia. The Artemis-like portrayals typical for Hellenistic times continue to appear, but she also started to be depicted on the back of a lion. There is only one possible example of such an image from the west, a fragmentary relief from Susa, and it’s roughly contemporary with the depictions from Bactria. While it is not impossible Nanaya originally adopted the lion association from one of her Mesopotamian peers, it is not certain how exactly this specific type of depictions originally developed, and there is a case to be made that it owed more to the Hellenistic diffusion of iconography of deities such as Cybele and Dionysus, who were often depicted riding on the back of large felines. The lunar symbols are well attested in the Kushan art of Nanaya too. Most commonly, she’s depicted wearing a diadem with a crescent. However, in a single case the symbol is placed behind her back. This is an iconographic type which was mostly associated with Selene at first, but in the east it was adopted for Mah, the Iranian personification of the moon. I’d hazard a guess that’s where Nanaya borrowed it from - more on that later. The worship of Nanaya survived the fall of the Kushan dynasty, and might have continued in Bactria as late as in the eighth century. However, the evidence is relatively scarce, especially compared with yet another area where she was introduced in the meanwhile.
Nanaya in Sogdia: new home and new friends

A Sogdian depiction of Nanaya from Bunjikat (wikimedia commons)
Presumably from Bactria, Nanaya was eventually introduced to Sogdia, its northern neighbor. I think it’s safe to say this area effectively became her new home for the rest of her history. Like Bactrians, the Sogdians also spoke an eastern Iranian language, Sogdian. It has a direct modern descendant, Yaghnobi, spoken by a small minority in Tajikistan. The religions Sogdians adhered to is often described as a form of Zoroastrianism, especially in older sources, but it would appear that Ahura Mazda was not exactly the most popular deity. Their pantheon was seemingly actually headed by Nanaya. Or, at the very least, the version of it typical for Samarkand and Panijkant, since there’s a solid case to be made for local variety in the individual city-states which made up Sogdia. It seems that much like Mesopotamians and Greeks centuries before them, Sogdians associated specific deities with specific cities, and not every settlement necessarily venerated each deity equally (or at all). Nanaya's remarkable popularity is reflected by the fact the name Nanaivandak, "servant of Nanaya", is one of the most common Sogdian names in general. It is agreed that among the Sogdians Panjikant was regarded as Nanaya’s cult center. She was referred to as “lady” of this city. At one point, her temple located there was responsible for minting the local currency. By the eighth century, coins minted there were adorned with dedications to her - something unparalleled in Sogdian culture, as the rest of coinage was firmly secular. This might have been an attempt at reasserting Sogdian religious identity in the wake of the arrival of Islam in Central Asia. Sogdians adopted the Kushan iconography of Nanaya, though only the lion-mounted version. The connection between her and this animal was incredibly strong in Sogdian art, with no other deity being portrayed on a similar mount. There were also innovations - Nanaya came to be frequently portrayed with four arms. This reflects the spread of Buddhism through central Asia, which brought new artistic conventions from India. While the crescent symbol can still be found on her headwear, she was also portrayed holding representations of the moon and the sun in two of her hands. Sometimes the solar disc and lunar orb are decorated with faces, which has been argued to be evidence that Nanaya effectively took over the domains of Mah and Mithra, who would be the expected divine identities of these two astral bodies. She might have been understood as controlling the passage of night and day. It has also been pointed out that this new iconographic type is the natural end point of the evolution of her astral role. Curiously, while no such a function is attested for Nanaya in Bactria, in Sogdia she could be sometimes regarded as a warlike deity. This is presumably reflected in a painting showing her and an unidentified charioteer fighting demons.

The "Sogdian Deities" painting from Dunhuang, a possible depiction of Nanaya and her presumed spouse Tish (wikimedia commons)
Probably the most fascinating development regarding Nanaya in Sogdia was the development of an apparent connection between her and Tish. This deity was the Sogdian counterpart of one of the best known Zoroastrian yazatas, Tishtrya, the personification of Sirius. As described in the Tištar Yašt, the latter is a rainmaking figure and a warlike protector who keeps various nefarious forces, such as Apaosha, Duzyariya and the malign “worm stars” (comets), at bay. Presumably his Sogdian counterpart had a similar role. While this is not absolutely certain, it is generally agreed that Nanaya and Tish were regarded as a couple in central Asia (there’s a minority position she was instead linked with Oesho, though). Most likely the fact that in Achaemenid Persia Tishtrya was linked with Nabu (and by extension with scribal arts) has something to do with this. There is a twist to this, though. While both Nabu and the Avestan Tishtrya are consistently male, in Bactria and Sogdia the corresponding deity’s gender actually shows a degree of ambiguity. On a unique coin of Kanishka, Tish is already portrayed as a feminine figure distinctly similar to Greek Artemis - an iconographic type which normally would be recycled for Nanaya. There’s also a possibility that a feminine, or at least crossdressing, version of Tish is portrayed alongside Nanaya on a painting from Dunhuang conventionally referred to as “Sogdian Daēnās” or “Sogdian Deities”, but this remains uncertain. If this identification is correct, it indicates outright interchange of attributes between them and Nanaya was possible.
The final frontier: Nanaya and the Sogdian diaspora in China Sogdians also brought Nanaya with them to China, where many of them settled in the Six Dynasties and Tang periods. An obviously Sinicized version of her, accompanied by two attendants of unknown identity, is portrayed on a Sogdian funerary couch presently displayed in the Miho Museum.

Nanaya (top) on a relief from the Miho funerary couch (Miho Museum; reproduced here for educational purposes only)
For the most part the evidence is limited to theophoric names, though. Due to unfamiliarity with Sogdian religious traditions and phonetic differences between the languages there was no consistent Chinese transcription of Nanaya’s name. I have no clue if Chinese contemporaries of the Sogdians were always aware of these elements in personal names referred to a deity. There is a fringe theory that Nanaya was referred to as Nantaihou (那那女主, “queen Nana”) in Chinese. However, the evidence is apparently not compelling, and as I understand the theory depends in no small part on the assertion that a hitherto unattested alternate reading of one of the signs was in use on the western frontiers of China in the early first millennium CE. The alleged Nantaihou is therefore most likely a misreading of a reference to a deceased unnamed empress dowager venerated through conventional ancestor worship, as opposed to Nanaya. Among members of the Sogdian diaspora, in terms of popularity Nanaya was going head to head with Jesus and Buddha. The presence of the latter two reflected the adoption of, respectively, Manichaeism and Buddhism. Manicheans seemingly were not fond of Nanaya, though, and fragments of a polemic against her cult have been identified. It seems ceremonies focused on lamentations were the main issue for the Manichaeans. Sadly there doesn’t seem to be any worthwhile study of possible Mesopotamian influence on that - the only one I found is old and confuses Nanaya with Inanna. We do not have much of an idea how Buddhists viewed Nanaya, though it is worth noting a number of other Sogdian deities were incorporated into the local form of Mahayana (unexpectedly, one of them was Zurvan). It has also been argued that a Buddhist figure, Vreshman (Vaisravana) was incorporated into Nanaya’s entourage. Nanaya might additionally be depicted in a painting showing Buddha’s triumph over Mara from Dunhuang. Presumably her inclusion would reflect the well attested motif of local deities converting to Buddhism. It was a part of the Buddhist repertoire from the early days of this religion and can be found in virtually every area where this religion ever spread. Nanaya is once again in elevated company here, since other figures near her have been tentatively interpreted as Shiva, Vishnu, Kartikeya and… Zoroaster.

Buddha conquering Mara (maravijaya) on a painting from Dunhuang (wikimedia commons)

zoom in on a possible depiction of Nanaya next to a demon suspiciously similar to Tove Jansson’s Fillyjonk
To my best knowledge, the last absolutely certain attestation of Nanaya as an actively worshiped deity also comes from the western frontier of China. A painting from Dandan Oilik belonging to the artistic tradition of the kingdom of Khotan shows three deities from the Sogdian pantheon: the enigmatic Āδβāγ (“highest god”; interpreted as either Indra, Ahura Mazda or a combination of them both) on the left, Weshparkar (a later version of Kushan Oesho) on the right and Nanaya in the center. It dates to the ninth or tenth century.

Nanaya (center) on the Dandan Oilik painting (wikimedia commons)
We will probably never know what Nanaya’s last days were like, though it is hard to imagine she retained much relevance with the gradual disappearance of Sogdian culture both in Sogdia and in China in the wake of, respectively, the rise of Islam in Central Asia and the An Lushan rebellion respectively. Her history ultimately most likely ended with a whimper rather than a bang. Conclusions and reflections Obviously, not everything about Nanaya could be covered in this article - there is enough material to warrant not one, but two wiki articles (and I don't even think they are extensive enough yet). I hope I did nonetheless manage to convey what matters: she was the single most enduring Mesopotamian deity who continued to be actually worshiped. She somehow outlived Enlil, Marduk, Nergal and even Inanna, and spread further than any of them ever did. It does not seem like her persistence was caused by some uniquely transcendent quality, and more to a mix of factors we will never really fully understand and pure luck. She is a far cry from the imaginary everlasting universal goddesses such longevity was attributed to by many highly questionable authors in the past, from Frazer to Gimbutas. Quite the opposite, once you look into the texts focused on her she comes across as sort of pathetic. After all, most of them are effectively ancient purple prose. And yet, this is precisely why I think Nanaya matters. To see how an author approaches her is basically a litmus test of trustworthiness - I wish I was kidding but this “Nanaya method” works every time. To even be able to study her history, let alone understand it properly, one has to cast away most of the dreadful trends which often hindered scholarship of ancient deities, and goddesses in particular, in the past. The interchangeability of goddesses; the Victorian mores and resulting notion that eroticism must be tied to fertility; the weird paradigms about languages neatly corresponding to religions; and many others. And if nothing else, this warrants keeping the memory of her 3000 years long history alive through scholarship (and, perhaps, some media appearances). Bibliography
Julia M. Asher-Greve & Joan Goodnick Westenholz, Goddesses in Context: On Divine Powers, Roles, Relationships and Gender in Mesopotamian Textual and Visual Sources (2013)
Paul-Alain Beaulieu, The Pantheon of Uruk During the Neo-Babylonian Period (2003)
idem, Nabû and Apollo: The Two Faces of Seleucid Religious Policy in: Orient und Okzident in Hellenistischer Zeit (2014)
Matteo Compareti, Nana and Tish in Sogdiana (2017)
idem, The So-Called "Pelliot Chinois 4518.24". Illustrated Document from Dunhuang and Sino-Sogdian Iconographical Contacts (2021)
Olga Drewnowska-Rymarz, Mesopotamian Goddess Nanāja (2008)
Benjamin R. Foster, Before the Muses: an Anthology of Akkadian Literature (2005)
Andrew R. George & Manfred Krebernik, Two Remarkable Vocabularies: Amorite-Akkadian Bilinguals! (2022)
Valerie Hansen, Kageyama Etsuko & Yutaka Yoshida, The Impact of the Silk Road Trade on a Local Community: The Turfan Oasis, 500-800 in: Les sogdiens en Chine (2005)
Wilfred G. Lambert, Babylonian Creation Myths (2013)
Enrico Marcato, An Aramaic Incantation Bowl and the Fall of Hatra (2020)
Christa Müller-Kessler & Karlheinz Kessler, Spätbabylonische Gottheiten in spätantiken mandäischen Texten (1999)
Lilla Russel-Smith, Uygur Patronage in Dunhuang. Regional Art Centres on the Northern Silk Road in the Tenth and Eleventh Centuries (2005)
idem, The 'Sogdian Deities' Twenty Years on: A Reconsideration of a Small Painting from Dunhuang in: Buddhism in Central Asia II. Practices and Rituals, Visual and Material Transfer (2022)
Tonia M. Sharlach, An Ox of One's Own. Royal Wives and Religion at the Court of the Third Dynasty of Ur (2017)
Michael Shenkar, Intangible Spirits and Graven Images: The Iconography of Deities in the Pre-Islamic Iranian World (2014)
idem, The Religion and the Pantheon of the Sogdians (5th-8th Centuries CE) in Light of their Sociopolitical Structures (2017)
idem, The So-Called "Fravašis" and the "Heaven and Hell" Paintings, and the Cult of Nana in Panjikent (2022)
Marten Stol, Nanaja in: Reallexikon der Assyriologie, vol. 9 (1998)
Michael P. Streck & Nathan Wasserman, More Light on Nanāya (2013)
Aaron Tugendhaft, Gods on Clay: Ancient Near Eastern Scholarly Practices and the History of Religions in: Canonical Texts and Scholarly Practices. A Global Comparative Approach (2016)
Joan Goodnick Westenholz, Nanaya, Lady of Mystery in: Sumerian Gods and Their Representations (1997)
idem, Trading the Symbols of the Goddess Nanaya in: Religions and Trade. Religious Formation, Transformation and Cross-Cultural Exchange between East and West (2014)
Xinjiang Rong, The Colophon of the Manuscript of the Golden Light Sutra Excavated in Turfan and the Transmission of Zoroastrianism to Gaochang in: The Silk Road and Cultural Exchanges between East and West (2022)
Gioele Zisa, The Loss of Male Sexual Desire in Ancient Mesopotamia. ›Nīš Libbi‹ Therapies (2021)
#mesopotamian mythology#sumerian mythology#mythology#bactrian mythology#sogdian mythology#sogdia#nanaya
481 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Enheduanna
The Akkadian poet Enheduanna (l. 2285-2250 BCE) is the world's first author known by name and was the daughter of Sargon of Akkad (Sargon the Great, r. 2334-2279 BCE). Whether Enheduanna was, in fact, a blood relative of Sargon's or the title was figurative is not known.
It is clear, however, that Sargon placed enormous trust in Enheduanna in elevating her to the position of high priestess of the most important temple in Sumer (in the city of Ur) and leaving to her the responsibility for melding the Sumerian gods with the Akkadian ones to create the stability his empire needed to thrive.
Further, she is credited with creating the paradigms of poetry, psalms, and prayers used throughout the ancient world which led to the development of the genres recognized in the present day. Scholar Paul Kriwaczek writes:
Her compositions, though only rediscovered in modern times, remained models of petitionary prayer for . Through the Babylonians, they influenced and inspired the prayers and psalms of the Hebrew Bible and the Homeric hymns of Greece. Through them, faint echoes of Enheduanna, the first named literary author in history, can even be heard in the hymnody of the early Christian church. (121)
Her influence during her lifetime was as impressive as her literary legacy. Entrusted by her father with great responsibility, Enheduanna not only exceeded those expectations but changed the entire culture. Through her written works, she altered the very nature of the Mesopotamian gods and the perception the people had of the divine.
Life
Enheduanna's name translates as 'High Priestess of An' (the sky god) or 'En-Priestess, wife of the god Nanna'. She came from the northern city of Akkad and, as Kriwaczek notes, "would have had a Semitic birth name on moving to Ur, the very heartland of Sumerian culture, she took a Sumerian official title: Enheduanna – 'En' (Chief Priest or Priestess); 'hedu' (ornament); 'Ana' (of heaven)" (120).
She organized and presided over the city's temple complex, the heart of the city, and held her own against an attempted coup by a Sumerian rebel named Lugal-Ane who forced her into exile. The Akkadian Empire, for all the wealth and stability it brought to the region, was constantly plagued by uprisings in the various regions under its control. One of Enheduanna's responsibilities in the region of Sumer would have been to keep the populace in check through religion.
In the case of Lugal-Ane, however, she seems to have been bested, at least initially. In her poem The Exaltation of Inanna, she tells the story of being driven from her post as high priestess and cast into exile. She writes a plea for help to the goddess Inanna requesting her to petition the god An for help:
Funeral offerings were brought, as if I had never lived there.
I approached the light, but the light scorched me.
I approached the shade, but I was covered with a storm.
My honeyed mouth became scummed. Tell An about Lugal-Ane and my fate!
May An undo it for me! As soon as you tell An about it, An will release me. (lines 67-76)
Inanna apparently heard her prayer and, through divine intercession, Enheduanna was finally restored to her rightful place in the temple. She seems to have been the first woman to hold this position in Ur and her comportment as high priestess would have served as an exemplary model for those who followed her.
Continue reading...
116 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ereshkigal is the Mesopotamian Goddess of the Underworld. Sometimes known as Irkalla, (the name of the Mesopotamian underworld itself) Ereshkigal has domain over all of the dead along with the other gods of the underworld including her husband, Nergal. In some greco-syncretism, Ereshkigal is associated with Hecate, the Greek Goddess of Magic and is known as Hecate Ereshkigal. She is also associated with her younger sister Inanna (commonly known by her Assyrian/Babylonian name, Ishtar), the Mesopotamian Goddess of Love and War.

#artists on tumblr#digital art#hades fanart#hades game#hades supergiant#hades#oc art#supergiant hades#hades 2#hades art
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lady Aphrodite/Venus deep dive

Lady Aphrodite/Venus is Amazing and beautiful in soul and looks, graceful as a swan and as kind as a mother, I adore Lady Aphrodite/Venus as a worshiper and as a researcher, she is far beyond interesting, she is a powerful and wonderful goddess and a mother
Herbs • anemone, daffodil, myrtle, lettuce , pomegranate, apple, rosemary fresh roses, vanilla, cinnamon, cypress, jasmine, the olive tree, narcissus, honeysuckle, the apple tree, the lime tree, Strawberries, Oranges, Pears, lotus
Animals• hare, turtle-dove, sparrow, goose, swan, horses, hummingbirds, cats, butterflies, bees, fish, hare.
Symbols• Hearts, Seashells, Mirror, Girdles, Dolphins, Doves, Swans, Sparrows, Bees, Sea Foam, Pomegranates, Apples, Strawberries, Oranges, Pears
Colors • pink & red, rose gold , blue, green, white, gold, baby blue, pastel colors, Seafoam green, Aqua
Appearance in astral or general • many ancient artworks of her, depicted her with traditionally male features, like beards, along with traditionally female features, she can change looks many times, but no matter her looks she is the most beautiful alive.
Crystal• rose quarts, garnet, pearls, diamond, sapphire, aquamarine, opal, sea glass, silver, emerald, rhodonite, rhodochrosite, ocean jasper, morganite
Jewelry • pearls, rose gold, promise rings, diamonds
epithets of Aphrodite• Psytiros - whispering Aphrodite, epithet also is attributed to Eros, Euploia - a marine epithet to Aphrodite of easy sailing, fair voyage, Leaina -the Lioness, an epithet given to the Goddess by Athenian orator Democha, Praxis - Aphrodite of action, a statue to whom stood in the city of Megara, Peitho - as an epithet to Aphrodite, it describes Her a persuasive, Epiodoros - Aphrodite of bountiful gifts as She was titled by Greek poet Stesichoru, Argounis - shining Aphrodite, worshiped in Boeotia and likely associated with Dawn, Philomedes - Aphrodite of a lovely smile or smiling Aphrodite, Helikoblepharos - quick-glancing, or Aphrodite with an ever-moving eye, Polychrisou - rich in gold, rich in many golden gifts, Chrisopeplos - gold-clad, Aphrodite dressed in gold, Chrisostephanos - Aphrodite wearing a golden wreath, Chrisanios - Aphrodite holding golden rein as Her chariot was often said to be fully made of gold, Nikêphoros- She is the Warlike, Areia- She is the averter of unlawful desires and actions, Apostrophia- She is one who blessed marriage and unions, Migôntis- She is the one who turns to love, Ourania- Heavenly, Divine Love, Pandêmos- Common To All, Epistrophia - She who Turns to Love, Nympthia Hêrê - Of Hera of Marriage, Symmakhia- Ally in Love, Pontia - Of the Sea, Kypria - Of Cyprus, Pothon Mater - Mother of Desire, Chrysea- Golden, Aphrodite Urania (also spelt Ourania), Aphrodite Pandemos, Venus Genatrix, Peitho, - meaning persuasion, Philommeidḗs - "smile-loving", Cypris and Cythereia - for her association of Cyprus and Cythera, Eleemon, In Athens, she was known as Aphrodite in kopois ("Aphrodite of the Gardens”, At Cape Clias, a town along the Attic coast, she was venerated as Genetyllis "Mother", Aphrodite Euploia - of the fair voyage, Anaduomenê - The Goddess Who Arose From The Sea, Ambologêra - The Ons Who Delays Old Age, Antheia - The Blooming One / Friend Of Flowers , Apotrophia - The Expeller ( Of Shameful and Sinful Desire), Areia - The Warlike, Kupria/Kuprigeneia - The One Born in The Island Of Cyprus, Despoina - The Rulling Goddess/ The Mistress , Genetullis - The Protectress Of Births , Nikêphoros - Bringer Of Victory
Cult epithets • Ourania (heavenly) , Pandémos (common to all) , areia (of ares, warlike) , hòplismené (armed) , Symmakhia (ally in love)
Poetic epithets • Kypris ( of Cyprus) , philomeidês (laughter loving) , aphrogenia (foam born) khryseé (golden) Pothón Mêtêr (mother of desire)
Names• Venus, Aphrodite, Harthor, Astare, Priyah, inanna, isis, Freaya,
Mortal or immortal • immortal
Zodiac • Libra, taruas
How to get closer • sign her hymms or dance in her honor
Number• 5
Courting• Ares, she is no longer married.
Past lovers and flings • Anchises (a mortal in the past she dated), Adonis ( handsome young man killed by a boar (Ares in disguise), Dionysus, Zues (maybe), Hermes, Phaethon, Posideon, Butes, Apollon
Devine children • Phobos, Deimos, Harmonia, Eros, Anteros, pothos, hermaphrodios, (From the mortal Anchuses), Aeneas a mythical hero of Troy and Rome, and Lyrus/Lyrnus (From Butes), eryxs, Meligounis and several more unnamed daughters, Hymenajks, lacchus, priapus, the Charites, (graces: Aglaea, Euphrosyne, Thalia) (From Dionysus) Phobos, Deimos, Harmonia, The Erotes (Eros) , Anteros, Himeros , Pothos, from Ares, Hermaphroditos, Priapus, from Hermes, Rhodos from Posideon, Beroe, Golgos, Priapus (rarely) (from Adonis), Astynous from Phaethon, Priapus (from Zeus)
Attendees • The erotes, Harmonia, Hebe, peithos, the kharites , Naiades
Regions• Cyprus; Kytherea, Corinth, Eryx in Sicly
Holiest shrine• Paphos, island of Cyprus, (her birth place & seat of her mysteria)
Other shrines • Temples throughout Greece and Asia Minor and ur moms house. Some places, most notably Sparta, Thebes, and Cyprus honored her as a goddess of war.
Parents • Ouranos Sometimes it’s said that she is the daughter of Zeus and Dione. And born from the severed genitals of the primordial god Ouranos.
Siblings • Aeacus, Angelos, Apollo, Ares, Artemis, Athena, Dionysus, Eileithyia, Enyo, Eris, Ersa, Hebe, Helen of Troy, Hephaestus, Heracles, Hermes, Minos, Pandia, Persephone, Perseus, Rhadamanthus, the Graces, the Horae, the Litae, the Muses and the Moirai.
personality• she isn’t intimidating at first, she likes not having already used products on her alter if possible, a clean, nice smelling alter.
dislikes• She does not like Medusa, she wants nothing to do with her for some reason, just what I’ve heard from people who worshiped Aphrodite and Medusa in close timelines
Diety of • Sex, libido, self-image, self-love, relationships, friendships, parent love and pet love, crushes, lust, procreation, seduction, pleasure, happiness, sadness, passion, stalking, ports, port homes
Home• Olympus and was living in the sea before Olympus
Hate• Boars, pigs.
Likes• Faries, unicorns, butterflies, lacy & frilly things, music boxes, ballet, cars.
Roots• Greek, born near Paphos, on the island of Cyprus
Offerings • pastries, cakes, , olive branches, dark chocolate, wine, apples, perfume, makeup, Pomegranate: said to be first planted by Aphrodite herself, Strawberries, Raspberries, Blackberries, Figs, Watermelon, Sea shells, handheld mirrors/ beautifully ornate mirrors, makeup products, perfumes (sweet/sensual/seductive ones), skin/body care products, fruits, apples, lettuce, pomegranates, chocolates, sugar and cream, honey, wine (rosé or sweet-scented), sweetened rose tea, rose quartz, pearls, jewelry, roses, flower bouquets, statues of her sacred animals (ex- swans) , myrtle or myrrh incense, pink/gold/white candles, seawater, the artwork of her, devotional poems, self-care routines, ritual baths, have a rose garden that you can take care of in her name if possible, be supportive of women and the LGBTQ+ community. • olive oil, fruit, honey, chocolate, dark chocolate (she loves it) , Apples/golden apples, Mermaids, Jewelry, Cherries, Dolphins imagery, Perfumes, Cologne, Makeup, Combs, Affirmations/Affirmation Cards, Beach Sand, Sea imagery, Water, Love poems, Oyster shells, Pink Salt, Driftwood, Sea glass, Amenome/Roses/Carnations, Other flowers, Valentine's Day gifts, Teddy bears, Rose water, Eros/Cupid imagery, Cakes, (Dress up) Dolls, Chapstick/lipstick, Fishnets, Honey cakes, Undergarments, Hearts, Handheld fans, Pictures of loved ones, Condoms/lube(18+), Lingerie(18+), Undergarments(18+), Sex toys(18+), NSFW magazines/books/movie(18+) (AND I MEAN IT WHEN I SAY 18+, OR ASK HER!!), roses, Myrtles, Apples, Pomegranates, Honey, Chocolates, Cookies or cakes made to look like one of Her symbols (ex- hearts), Strawberries, Oranges, Pears, Bath Salts, Bath oils, Bubble bath soap, Scented lotions or fancy soaps
Devotional• light your favorite candle, put on your favorite lotion or perfume, put on your favorite piece of jewelry, put on your favorite article of clothing, enjoy a sweet treat, Sex magic, Glamour spells, Dressing up, acts of self care and acts of self- love, Caring for mental & physical health, Take a bubble bath,Spend time at the sea, Collect sea shells, Read Sappho poetry, Donate to LBGTQ+, Support sex workers, Have safe sex and learn about it, Stand up for yourself and what you believe in, Donate to woman programs and shelters, Do stuff to make ur self feel empowered and beautiful, Honor her kids and ares, watch a romcom, watch a regular romantic movie or show or read your favorite romantic story, Make plans with loved ones and friends or your lover in her honor, Treat yourself to something you enjoy, if you have a pet and they like to snuggle, snuggle or lay with them. Talk to them and tell them how much you love them (If able take them for a walk or a ride), listen to ocean/sea soundscapes, read up on all the many kinds of love, engage in an act of self-care, listen to love songs, listen to a devotional playlist for her, make a Pinterest board or playlist, or journal all of your favorite things and things that you love, learn about the different kinds of love, do things that boost your self esteem, be gentle with yourself, take it easy, etc, watch a ballet, read love poems, Dress up and selfies, Keep menstrual products on you (even if you don't bleed), Advocate for pro-choice, Give/accept compliments, Advocate for SA victims, Go on a date, Take yourself on a date, Do something nice for your partner, get a Manicure/pedicure, Flirt, Affirmations in the mirror, Drink wine, Advocate for proper sex ed (Including queer sex ed), Experiment with your style, Mirror scrying, Listen to sleep affirmations, Love letter to self/her/partner, Take a bath/shower,Go to the ocean/water, Finally give into that one kink (You know the one, 18+), do Masturbation in her honor (only 18+, I heard she’s not comfortable with minors doing it, but that’s between y’all, just ask her beforehand.), Practice safe sex (18+), Educate yourself on the porn industry, Support sex workers (TIP THEM, 18+), Have sex (18+), Get educated on consent/safe sex, Take nude/lewds (18+)
Holiday • on March 18, goddess of fertility day
Season• spring
Status• Olympian, major goddess
Music • Harry styles, Classical music, old love songs (50s & 60s)
Day• Friday
Planet• Venus
Tarot• High priestess, the lovers, the empress, the star
Rituals • honored and invoked for love and fertility and beauty
Festivals • Aphrodisa, kinyrades ( summer festival) adonia ( mourning for Adonis, woman only)
Fact• She was most worshiped during times of politics, Many people offered her Opiates, or did Opiates in her honor. opium-burners were often found at her shrines in ancient times, please do not do opium.
Prayer•
1• sing, sing, oh i sing to aphrodite who is most beautiful! she who stirs the passionof men & god alike! o, to she — i sing! golden goddess with soft lashes, golden goddess withsoft arms, i spin and sing and delight in the bright rose that is you. may i dance with your grace, lifted up as the foam from the sea as you were — may my smile be blessed with delight. golden-haired goddess, bless my tongue to be sweet as honey, bless my fingers to be delicate and swift, bless my steps so they may bound forth in soft beauty. glory to she — praise to she! goddess of ever golden smiles, of fierce beauty, of spilling laughter and delight. o! may i love as you love — may i delight as you delight! goddess, fill me with your beauty — may i shine & rise above the wrathful waters of those around me and delight, delight, delight in the glory that you have given to me!
2•Golden Aphrodite
Lady of beauty and grace, Please give me the power to appreciate my body, Grant me confidence in my masculinity, Help me to feel your love within myself, and to express it outwardly as well, Lady Aphrodite, please hear my prayer, I sing your praises and offer you this incense
3•Aphrodite, guide me towards love. Help me discover it, receive it, embrace it, give it, celebrate it, honor it, teach it, and live it. Let love be the mark I leave, as your devotee, as a human being.
4• Antheia
Hear to me my call for spring to have sprung,Oh, sweet one scented of honey and nectar. Hear my call Aphrodite Antheia,As I harken a need for the sweet bloom. I crave the beauty of the opening flower, The sweet taste of its nectar upon my lips. Ah Aphrodite Antheia, Bring to me the joy of the fresh blooms. Let the petals cascade upon my body, Allow me the joy of the sunshine. Oh sweet one, Oh Aphrodite Antheia. Bestow upon me and mine, The gifts of the flowers fair.
5•daughter of seafoam, goddess of beauty, aphrodite please hear my cries. please listen as i describe all the parts of me that are shattered & torn, please understand as i tell my stories of pain. aphrodite accept me please. aphrodite pick me up & help me mend myself for i am yours, thank you so much & so mote it be
6• Aphrodite rivals the beauty of the sun setting over an ocean's horizon as you stand on the shore, the water tickling your feet as it pulled in and pushed back out repeatedly by the waves.
Scents/Inscene • Rose, wine, fresh roses, Frankincesne, Myrrth, vanilla, cinnamon, cypress, jasmine, cherry blossom, lavender.
Other• images of things she’s associated with, jewelry, perfume, bath salts , scented lotion, seawater, seashells, sand, makeup, feathers, self care essentials.


Links/websites/sources
@khaire-traveler
ephemeral-cryptid.tumblr.com
@mars-and-the-theoi graffitiphilosopher.tumblr.com teawiththegods.tumblr.com
@seleniangnosis
@melitheoidevotion
@seafoamsister
evilios.tumblr.com hearthcreation.tumblr.com orsialos.tumblr.com
@hisfluer

I use resources, I do not own the info, and most deep dives have UPG (that I use in my work.) And I only take some information from sources. I am 14, this is my hobby, I am learning but I spent many hours and days on this, and I am always open to criticism. I have been doing worship for 5 years. Please know you can use the info, I do not sue, but I will take action if this work is used without permission and not put as a resource if used in any work. without permisson and not put as a resource if used in any work, for the public.
#hellenic devotion#the gods#hellenic polytheism#doing the research for you#hellenic worship#aphrodite deity#aphrodite#greek pantheon#greek gods#hellenism#greek goddess#aphrodite worship#aphrodite devotee#aphrodite goddess#Aphrodite#venus#ancient rome#roman empire#roman goddess#roman mythology#info#information#greek myths#greek posts#greek tumblr#greek mythology#ancient greek#The gods#I put Venus and Aphrodite together because I personally do in my practice.
349 notes
·
View notes
Text
Worshipping Inanna / Ishtar
This is an informative post about how Inanna was worshipped, or believed to be worship, back in her time, and at the end I'll share how I worship her.
Ritual sex - her high priestess would have ritual sex (whether it was true sex or symbolic is unknown) with the new king to ensure his fortune.
Gender non-conformity - her cult was primarily composed of those outside the binary, and shows men and women adopting the opposing dialect and engaging in sex with each other.
Music and art - most of her myths are in the form of Hymns, and most of her followers were artists, musicians, or dancers. Specifically, war dances would be done in her temple.
Libations - a libation is the ritualistic act of pouring a liquid offering straight from a container onto the earth. In depictions, the person doing the offering was naked.
Unfortunately, due to the passage of time, many specific rituals have been lost. I've scoured and this is really all I can find about her ancient original worship, and a lot of it is disputed because no one knows what was a metaphorical ritual or an actual ritual.
That being said, here is how I worship her in the modern day.
Self-confidence - Inanna was not one to be meek, it is said by many experts and proven in her myths that she was headstrong and didn't care how she was perceived. To honor her, I wear whatever I want. I have a very alternative style and I used to fear people looking at me. She has helped silence my worry and in turn, helped me gain confidence.
Non-conformity - I'm nonbinary, and although my femininity is a major part of my identity, so is masculinity, and so is androgyny. Learning that she had a queer cult following was so liberating, as before learning that I felt like it was wrong of me to work with her. So every little thing I do that isn't in the social construct of the gender binary is for her.
Libations - lucky for me, this is one area of her ancient worship that can be done in a modern setting. I don't have a "proper" container, I just use a normal glass. I've done it with water, coffee, tea, lemonade, and even kool-aid.
Honey/Butter cakes - in, I believe, Inanna and The God Of Wisdom, Enki welcomes her with honey/butter cakes and alcohol. I have only made a honey cake once before and it was shit, but I plan on trying again soon to combine both into a honey bourbon cake. I know they didn't have bourbon back then, but it's a local good I can find and adds a personal touch.
Self love - my fiancé lives across an ocean, so some things we can't do together (both living with family and thin walls), so to honor and worship her, self love is a great way for those in similar situations and she enjoys it from what I've seen.
Offerings - usually dates, sometimes cherries, often lemonade or tea, and more recently honey whiskey. These offerings might not be "traditional" in style, but they work for me and her. I have a small glass from an old Costco tiramisu and an iridescent bowl I got half off at our local grocery, both have an 8pointed star on them. Usually I sit them out for days at a time, or at least over night, and then either ingest them or just toss it in the trash (any other alternative isn't doable in my current situation)
Music - I listen to a variety of music with her, songs about sex, love, anger, fighting, injustice. She loves it, and if you want more detail on this I have a post about the songs on her playlist here.
Driving with the windows down - I love driving, and I feel like doing so with the windows down is an easy multitasking way to cleanse myself and invite good vibes in. Usually I do this while playing her playlist.
Making posts - it may seem a little silly, but a way I honor her is keeping her and her family alive. They are old deities, their civilizations and worshippers lived about 6,000 years ago, and some of her family have had their names lost to time. Making posts about them helps get word out, and keep them "alive".
Digital temples - I play the sims 4 and I saw someone talk about how they wanted to make a temple to their goddess in the game, so... I'm making my own. And will probably have my sims "worship" her via a club. Some people don't see this as an act of worship, but I do. As @thrashkink-coven said in this post, the gods are as modern as they are ancient. I know she enjoys it.
I will go through and make a full post detailing specific UPGs (personal practice things not backed in historical fact) with her, for anyone interested.
#witchblr#witchcraft#deity work#eclectic witch#deity worship#deity#deity devotion#inanna devotee#goddess inanna#inanna ishtar#inanna#ishtar#deity devotee#devotee#mesopotamian mythology#mesopotamia#babylonian mythology#sumerian mythology#queer witch
66 notes
·
View notes
Text






Aphrodite and Adonis in their older Mesopotamian forms; Inanna-Ishtar, the warlike goddess of beauty, fertility, and love and Dumuzi, her husband and the shepherd king of ageless Uruk.🦁🐏

Here are the poem snippet that I used as the main inspo, written by Enhueduanna, high priestess of the moon god Nanna/Sin and daughter of King Sargon & Queen Tashlultum of Akkad. As she became a devotee of Inanna and composed various exaltation hymns to the goddess, she also composed 42 hymns addressed to many temples and sanctuaries across the land of Sumer and Akkad, the so-called Temple Hymns; which makes her become the earliest known named author in world history.
The ziggurat temple background was based on the Eanna temple (”House” of Inanna) in Uruk, which was built during the 3rd dynasty of Ur (21st cent BC) and had been mentioned throughout in the Epic of Gilgamesh; while their clothing was from later recent Assyrian & Babylonian era. All of the offerings were based on the depictions on the Warka vase from the National Museum of Iraq - an agricultural festival that seemed to be connected with the rituals involved with the goddess.
79 notes
·
View notes
Note
Could you do a mini HC for a Mc with a fox familier? ( I really like your mini headcanons for the familier’s!)
The Arcana Mini-HCs: With a fox familiar
Julian: could tell your familiar was studying him from the start, which kept throwing him off his game. now he likes having them around at night when he's staying up, as a little loving company
Asra: gets along way too well with it and has on multiple occasions teased their patron (the Magician) by calling them by your familiar's name, "on accident". likes playing and chatting idly with it
Nadia: very impressed by how intelligent and intuitive it is, and actually warmed up to it faster than it warmed up to her. it and Chandra go scavenging together which Nadia loves watching
Muriel: glad at first to see a friend for Inanna that pushed her to do more fun, exciting things - until they teamed up to get him to do fun, exciting things. will bring it foraged berries as treats
Portia: fell in love with it on the spot, and promptly scared it away due to its timid nature. almost cried. she managed to win it over with treats and continues to sneak some to it. it's getting squishy
Lucio: you know what, a fox is better than a goat. doesn't really engage with it much beyond his general love for animals. the dogs adore it, though, and the three of them wreak havoc like it's a calling
#ask arcana brainrot#the arcana#the arcana headcanons#the arcana hc#the arcana game#asra the arcana#julian the arcana#nadia the arcana#muriel the arcana#portia the arcana#lucio the arcana#asra alnazar#julian devorak#nadia satrinava#muriel of the kokhuri#portia devorak#lucio morgasson
90 notes
·
View notes