#henry louis gate jr
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
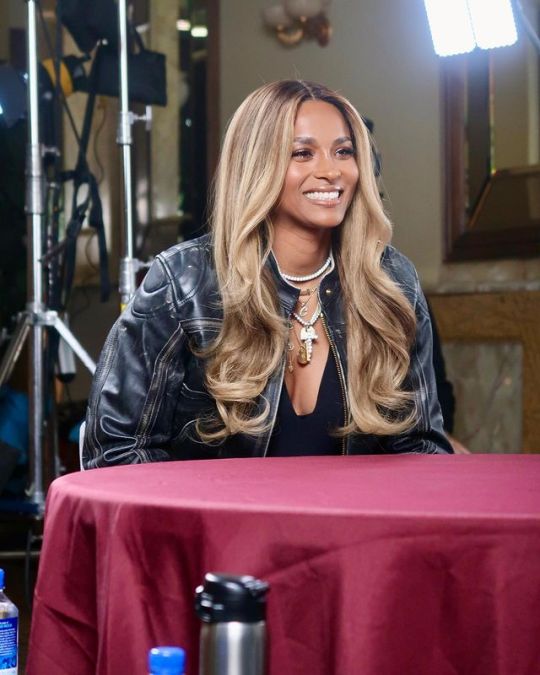
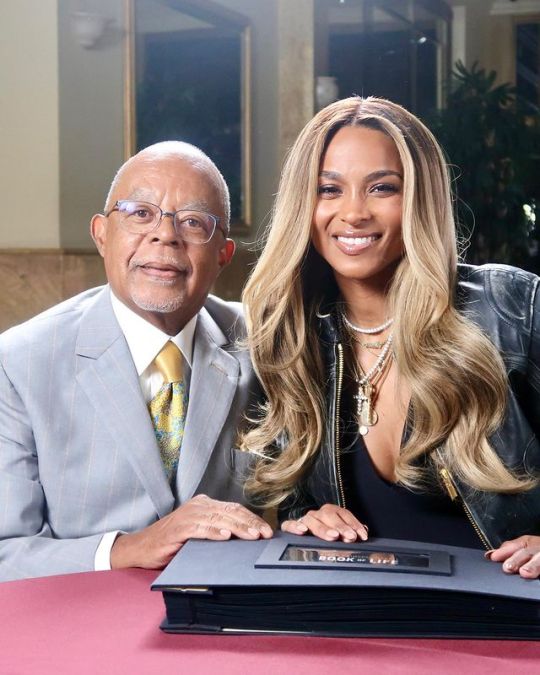
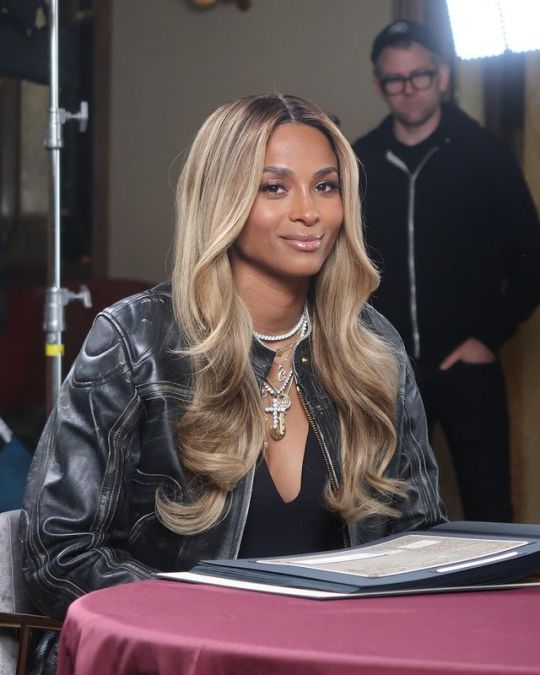





henrylouisgates "Avoid any spoilers by streaming last night’s premiere of #FindingYourRoots! Thank you to @ciara for being such a magnificent guest – we loved walking you through your family tree!
Stream the full episode of #FindingYourRoots now using the @PBS app or go to pbs.org/FindingYourRoots."
#ciara#tumblr#celebs#celebrities#makeup#fashion#hair#girl#lips#glamour#portrait#russell wilson#teamciara#csquad#celebrity#blackgirlmagic#blackgirlsrock#beauty#henry louis gate jr#FindingYourRoots#2024
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

#poll#polls#henry louis gates jr#american#historian#producer#filmmaker#television host#television personality
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
100 AMAZING FACTS ABOUT THE NEGRO - HENRY LOUIS GATES, JR.

100 AMAZING FACTS ABOUT THE NEGRO - HENRY LOUIS GATES, JR.
The first edition of Joel Augustus Rogers' now legendary 100 Amazing Facts About the Negro with Complete Proof, published in 1957, was billed as "A Negro 'Believe It or Not'". Rogers' little book was priceless because he was delivering enlightenment and pride, steeped in historical research, to a people too long starved on the lie that they were worth nothing. For African Americans of the Jim Crow era, Rogers' was their first black history teacher. But Rogers was not always shy about embellishing the "facts" and minimizing ambiguity; neither was he above shock journalism now and then.
With élan and erudition - and with winning enthusiasm - Henry Louis Gates Jr. gives us a corrective yet loving homage to Rogers' work. Relying on the latest scholarship, Gates leads us on a romp through African, diasporic, and African American history in question-and-answer format. Among the 100 questions: Who were Africa's first ambassadors to Europe? Who was the first black president in North America? Did Lincoln really free the slaves? Who was history's wealthiest person? What percentage of white Americans have recent African ancestry? Why did free black people living in the South before the end of the Civil War stay there? Who was the first black head of state in modern Western history? Where was the first Underground Railroad? Who was the first black American woman to be a self-made millionaire? Which black man made many of our favorite household products better?
Here is a surprising, inspiring, sometimes boldly mischievous - all the while highly instructive and entertaining - compendium of historical curiosities intended to illuminate the sheer complexity and diversity of being "Negro" in the world.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Henry Louis Gates Jr.
#suitdaddy#suiteddaddy#suit and tie#suited daddy#men in suits#daddy#suited#suit#suited grandpa#suitfetish#suitedman#suit daddy#suited men#suited man#buisness suit#suitedmen#americans#black daddy#Henry Louis Gates Jr.#Henry Louis Gates
16 notes
·
View notes
Link
This is an excellent commentary by Henry Louis Gates Jr. The link above is a gift link, so anyone can read the entire column, even if they don’t subscribe to The New York Times.
Gates argues convincingly that what far right politicians like Ron DeSantis are doing in trying to control the history that is taught in schools is very similar to what was done by the United Daughters of the Confederacy in their promotion of schools teaching the “Lost Cause” and a rewritten whitewashed history.

Gates also argues that there has always been rigorous debate within the Black community about many “ideological and theoretical framework[s]” regarding the Black experience in America. He believes these differences are discussed in African American Studies courses and raise important debates for the students who take those classes.
The one important thing Gates left out of this essay was that in the 1920s the KKK also promoted only teaching a history that praised the founders, much like the “patriotic” civics/history DeSantis and other GOP politicians are also pushing.
Below are some highlights from the column [all emphasis added]:
Lurking behind the concerns of Ron DeSantis, the governor of Florida, over the content of a proposed high school course in African American studies, is a long and complex series of debates about the role of slavery and race in American classrooms.
“We believe in teaching kids facts and how to think, but we don’t believe they should have an agenda imposed on them,” Governor DeSantis said. He also decried what he called “indoctrination.” [...] Even if we give the governor the benefit of the doubt about the motivations behind his recent statements about the content of the original version of the College Board’s A.P. curriculum in African American studies, his intervention falls squarely in line with a long tradition of bitter, politically suspect battles over the interpretation of three seminal periods in the history of American racial relations: the Civil War; the 12 years following the war, known as Reconstruction; and Reconstruction’s brutal rollback, characterized by its adherents as the former Confederacy’s “Redemption,” which saw the imposition of Jim Crow segregation, the reimposition of white supremacy and their justification through a masterfully executed propaganda effort.
Undertaken by apologists for the former Confederacy with an energy and alacrity that was astonishing in its vehemence and reach, in an era defined by print culture, politicians and amateur historians joined forces to police the historical profession. The so-called Lost Cause movement was, in effect, a take-no-prisoners social media war. And no single group or person was more pivotal to “the dissemination of the truths of Confederate history, earnestly and fully and officially,” than the historian general of the United Daughters of the Confederacy, Mildred Lewis Rutherford, of Athens, Ga. Rutherford was a descendant of a long line of slave owners.... Rutherford served as the principal of the Lucy Cobb Institute (a school for girls in Athens) and vice president of the Stone Mountain Memorial project, the former Confederacy’s version of Mount Rushmore.
As the historian David Blight notes, “Rutherford gave new meaning to the term ‘die-hard.’” Indeed, she “considered the Confederacy ‘acquitted as blameless’ at the bar of history, and sought its vindication with a political fervor that would rival the ministry of propaganda in any twentieth-century dictatorship.” And she felt that the crimes of Reconstruction “made the Ku Klux Klan a necessity.” As I pointed out in a PBS documentary on the rise and fall of Reconstruction, Rutherford intuitively understood the direct connection between history lessons taught in the classroom and the Lost Cause racial order being imposed outside it, and she sought to cement that relationship with zeal and efficacy. She understood that what is inscribed on the blackboard translates directly to social practices unfolding on the street.
[See more under the cut.]
“Realizing that the textbooks in history and literature which the children of the South are now studying, and even the ones from which many of their parents studied before them,” she wrote in “A Measuring Rod to Test Text Books, and Reference Books in Schools, Colleges and Libraries,” “are in many respects unjust to the South and her institutions, and that a far greater injustice and danger is threatening the South today from the late histories which are being published, guilty not only of misrepresentations but of gross omissions, refusing to give the South credit for what she has accomplished, … I have prepared, as it were, a testing or measuring rod.” And Rutherford used that measuring rod to wage a systematic campaign to redefine the Civil War not as our nation’s war to end the evils of slavery, but as “the War Between the States,” since as she wrote elsewhere, “the negroes of the South were never called slaves.” And they were “well-fed, well-clothed and well-housed.”
Of the more than 25 books and pamphlets that Rutherford published, none was more important than “A Measuring Rod.” Published in 1920, her user-friendly pamphlet was meant to be the index “by which every textbook on history and literature in Southern schools should be tested by those desiring the truth.” The pamphlet was designed to make it easy for “all authorities charged with the selection of textbooks for colleges, schools and all scholastic institutions to measure all books offered for adoption by this ‘Measuring Rod,’ and adopt none which do not accord full justice to the South.” What’s more, her campaign was retroactive. As the historian Donald Yacovone tells us in his recent book, “Teaching White Supremacy,” Rutherford insisted that librarians “should scrawl ‘unjust to the South’ on the title pages” of any “unacceptable” books “already in their collections.”
On a page headed ominously by the word “Warning,” Rutherford provides a handy list of what a teacher or a librarian should “reject” or “not reject.”
“Reject a book that speaks of the Constitution other than a compact between Sovereign States.”
“Reject a textbook that does not give the principles for which the South fought in 1861, and does not clearly outline the interferences with the rights guaranteed to the South by the Constitution, and which caused secession.”
“Reject a book that calls the Confederate soldier a traitor or rebel, and the war a rebellion.”
“Reject a book that says the South fought to hold her slaves.”
“Reject a book that speaks of the slaveholder of the South as cruel and unjust to his slaves.”
And my absolute favorite, “Reject a textbook that glorified Abraham Lincoln and vilifies Jefferson Davis, unless,” she adds graciously, “a truthful cause can be found for such glorification and vilification before 1865.”
And what of slavery? “This was an education that taught the negro self-control, obedience and perseverance — yes, taught him to realize his weaknesses and how to grow stronger for the battle of life,” Rutherford writes in 1923 in “The South Must Have Her Rightful Place.” “The institution of slavery as it was in the South, far from degrading the negro, was fast elevating him above his nature and race.” For Rutherford, who lectured wearing antebellum hoop gowns, the war over the interpretation of the meaning of the recent past was all about establishing the racial order of the present: “The truth must be told, and you must read it, and be ready to answer it.” Unless this is done, “in a few years there will be no South about which to write history.”
In other words, Rutherford’s common core was the Lost Cause. And it will come as no surprise that this vigorous propaganda effort was accompanied by the construction of many of the Confederate monuments that have dotted the Southern landscape since.
While it’s safe to assume that most contemporary historians of the Civil War and Reconstruction are of similar minds about Rutherford and the Lost Cause, it’s also true that one of the most fascinating aspects of African American studies is the rich history of debate over issues like this, and especially over what it has meant — and continues to mean — to be “Black” in a nation with such a long and troubled history of human slavery at the core of its economic system for two-and-a-half centuries.
Heated debates within the Black community, beginning as early as the first decades of the 19th century, have ranged from what names “the race” should publicly call itself (William Whipper vs. James McCune Smith) and whether or not enslaved men and women should rise in arms against their masters (Henry Highland Garnet vs. Frederick Douglass). Economic development vs. political rights? (Booker T. Washington vs. W.E.B. Du Bois). Should Black people return to Africa? (Marcus Garvey vs. W.E.B. Du Bois). Should we admit publicly the pivotal role of African elites in enslaving our ancestors? (Ali Mazrui vs. Wole Soyinka).
Add to these repeated arguments over sexism, socialism and capitalism, reparations, antisemitism and homophobia. It is often surprising to students to learn that there has never been one way to “be Black” among Black Americans, nor have Black politicians, activists and scholars ever spoken with one voice or embraced one ideological or theoretical framework. Black America, that “nation in a nation,” as the Black abolitionist Martin R. Delany put it, has always been as varied and diverse as the complexions of the people who have identified, or been identified, as its members. [...] As a consultant to the College Board as it developed its A.P. course in African American studies, I suggested the inclusion of a “pro and con” debate unit at the end of its curriculum because of the inherent scholarly importance of many of the contemporary hot-button issues that conservative politicians have been seeking to censor, but also as a way to help students understand the relation between the information they find in their textbooks and efforts by politicians to say what should and what should not be taught in the classroom.
Why shouldn’t students be introduced to these debates? Any good class in Black studies seeks to explore the widest range of thought voiced by Black and white thinkers on race and racism over the long course of our ancestors’ fight for their rights in this country. In fact, in my experience, teaching our field through these debates is a rich and nuanced pedagogical strategy, affording our students ways to create empathy across differences of opinion, to understand “diversity within difference,” and to reflect on complex topics from more than one angle. It forces them to critique stereotypes and canards about who “we are” as a people and what it means to be “authentically Black.” I am not sure which of these ideas has landed one of my own essays on the list of pieces the state of Florida found objectionable, but there it is.
[emphasis added]
There is much more in this essay that is worth reading. As I said before, the gift link above will allow you to read the entire essay. I encourage you to do so.
[edited]
#henry louis gates jr#black history month#ron desantis#ap african american studies#united daughters of the confederacy#kkk#whitewashed history#white nationalist indoctrination#us education#gop#the new york times
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

While the Mafia connected to British and Irish individuals like Cillian Murphy try to float that Benedict Cumberbatch lost this role, because of them, I'll just go ahead and inform the public about Edward Norton being in on the attempted extortion plot, against the actor. Recall at the time, that he and Henry Louis Gates Jr just HAPPENED to release an episode revealing Norton's family once owned slaves, and then Norton did interviews, loudly stating how 'we NEED to talk about this very important subject."
After the extortion plot failed, Norton suddenly shut up about it. And was in the propaganda-filled Glass Onion and is just a straight up asshole. They can have him for Bob Seeger.
#benedict cumberbatch#Edward Norton#Reperation Extortion Plot#Cult of Scientology Hollywood Gay Mafia#Henry Louis Gates Jr#Glass Onion#Bob Seeger#Bob Dylan Biopic#BLM#Queer Marxist Mob Muscle
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
“On the populist left, the then favored model of the oppositional spokesman was what Gramsci called the “organic intellectual”: someone who participated in and was part of the community he would uplift. And yet James Baldwin’s basic conception of himself was formed by the familiar, and still well-entrenched, idea of the alienated artist or intellectual, whose advanced sensibility entailed his estrangement from the very people he would represent. Baldwin could dramatize the tension between these two models – he would do so in his fiction – be he was never to resolve it.” – Henry Louis Gates Jr., The Welcome Table
[From the anthology: Lure and Loathing: Twenty black intellectuals address W.E.B. Du Bois’s dilemma of the double-consciousness of African Americans. Edited by Gerald Early.]
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
New ep is up!
#larry wilmore#the ringer#spotify#black on the air#podcast#henry louis gates jr.#pbs#finding your roots#genealogy#ancestry#Spotify
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm a genealogy nut. This was a great episode.
#Joe Manganiello#Tony Gonzales#Finding Your Roots#henry louis gates jr.#genealogy#PBS#Joe m#hello beautiful#zane 2
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Guardian: ‘We are all mixed’: Henry Louis Gates Jr on race, being arrested and working towards America’s redemption
The first time I met Henry Louis Gates Jr raised more questions than it answered. It was the year 2000, I was still a teenager, and he – already a distinguished Harvard professor – was hosting a launch for his new BBC and PBS series Wonders of the African World.
I remember the occasion as a series of firsts – my first TV launch party, first documentary series I’d seen on African civilisations, first encounter with a real-life Harvard professor. I remember wondering whether the circumstances were normal. The venue was the British Museum, an institution that harbours a practically unprecedented quantity of colonial plunder. Was it, I wondered, a deliberately ironic choice? Were all Harvard professors as friendly and personable as Gates, whom everyone calls “Skip”, and was charmingly informal and kind? And perhaps most pressingly, was it normal for Harvard professor TV presenters to dress as Gates so memorably had, in shorts, socks, and a ranger’s hat?
Gates, whom I am meeting again for the first time since that day 24 years ago, remembers it for entirely different reasons. “I got in a lot of trouble for that show,” he says, cheerfully. “I was the first black film-maker to talk about African involvement in the slave trade.” And, he adds, with undeniable pride: “It was the first internet controversy involving black folks!”
The documentary, which followed Gates as he examined ancient civilisations from Axum to Nubia and Great Zimbabwe to Timbuktu, was indeed controversial. Alongside the African cultures he visited, he demonstrated great interest in African complicity in the transatlantic slave trade, an interest that managed to alienate almost everyone who was black.
African scholars complained that Gates revealed an approach to African culture through a western-centric, American lens. African-American scholars claimed his emphasis on black involvement “got the white man off the hook for the Atlantic slave trade”.

I’m speaking to Gates over Zoom. I’m in uncharacteristically rainy Los Angeles, he’s in sunny Miami. As we speak, he turns his laptop screen around, attempting to goad me – successfully – into jealousy at the sight of blue sky and serene ocean from his seaside condo. He is in Florida for a family wedding, and our call is periodically interrupted by good-natured family members coming in and out, as people mill around preparing for the big day. Family is important to Gates. His new book, The Black Box: Writing the Race, opens with the story of his grandchild Ellie, who inspired the book’s title.
Born recently to Gates’s daughter, who is mixed race, and his son-in-law, who is white, Ellie “will test about 87.5% European when she spits in the test tube,” Gates writes, adding that she “looks like an adorable little white girl”. And yet when Ellie was born, Gates’s priority, he reveals, was to make sure her parents registered her as a black child, ticking the “black” box on the form stating her race at birth. “And because of that arbitrary practice, a brilliant, beautiful little white-presenting female will be destined, throughout her life, to face the challenge of ‘proving’ that she is ‘black’,” Gates writes.
Any discomfort flowing from this – both Gates’s decision and his perception of it – is deliberately intended as a commentary on the discomfort of race itself. How can race not be contradictory, Gates suggests, when it was constructed in service of racism, and yet has been alchemised into a cultural identity celebrated by those most oppressed by it?
The Black Box applies this analysis to the lives of famous African Americans. The poet Phillis Wheatly, an enslaved young woman who was required to “prove” to white observers that she was capable of writing the poetry she so eloquently composed. The abolitionist Frederick Douglass, who constructed parental relationships – the reality being that he knew little of either his mother or father – to refute ideas, prevalent at the time, that if a black person was intellectual, that was because of white parentage. The history of what black Americans have both been called and called themselves, encompassing a fascinating and ongoing debate about the usage of “negro”, “coloured”, “African American”, and “black”.
That work began far away from Harvard, in a working-class black family in the hills of West Virginia. Gates’s father had two jobs, one at a paper mill and another as a janitor, and his mother was a home-keeper, and later a cleaner for a white family. After attending the local public school, Gates obtained an undergraduate place at Yale in 1969.
Although proudly black, the family vaguely knew it had white ancestry, particularly through Gates’s paternal grandfather. “My grandfather looked so white, we called him Casper, after Casper the Friendly Ghost,” Gates laughs. “I mean his skin was translucent!” Gates had thought one ancestor – his paternal great, great-grandfather – had been white. But when he tested his DNA, he discovered a different picture.
“Imagine my surprise when I received my first DNA results, and I’m 49% white!” he exclaims. “What that means is that half of my ancestors on my family tree for the last 500 years were white, and the other half were black, and that was an amazing lesson to me. So, what does that mean about identity? It means that I was socially constructed as a negro American when I was born in 1950. But my heritage, genetically, is enormously complicated.”
This discovery set Gates on a path that has become perhaps the dominant part of his legacy, as the host of a popular PBS show Finding Your Roots, in which he leads other prominent Americans of all racial backgrounds – figures including Oprah, Julia Roberts, Kerry Washington and Quincy Jones – on a similar journey, through DNA testing and genealogy, in which they trace their family tree.
“I have never tested an African American who didn’t have white ancestry,” Gates says. “And that’s quite remarkable to me.”
“Paradoxically these DNA tests deconstruct the racial essentialism we’ve inherited from the Enlightenment, because they show that we are all mixed,” he continues. “It’s a mode of calling those categories into question, showing scientifically that they were fictions, and freeing us from the discourse that sought to imprison us in the black box, the white box, the Native American box.”
The tightrope Gates walks lies in rejecting blackness as a racial category, while embracing it as a cultural tradition. His most recent PBS documentary series, Gospel, which relays the origin story of gospel music, is perhaps my favourite work of his, celebrating both the heartbreaking beauty of black spiritual tradition in America, and its seismic impact on global culture.
When I share my emotion at the series, Gates is unable to resist subverting the theme. He bursts into a rendition of Can the Circle Be Unbroken?, a 1930s country number by the white gospel group the Carter Family.
“[On a cold and] cloudy day/ when I saw the hearse come rollin’/ for to carry my mother away/ Will that circle be unbroken/ By and by, Lord, by and by,” he sings, in a surprisingly rich tenor.“White people wrote that song, black people love that song!” he exclaims.
The current climate, in which political tribes are more polarised than ever, has only deepened his resolve to push back against the idea that black people should all agree. In this, he sometimes comes across as a man from another age – a more charming one, real or imagined – in which everyone could sit down together and work it all out.
“I grew up in a working-class town. People are goodhearted. They want what everybody else wants: to make enough money to live comfortably, to send their kids to college, to be able to go on vacation, to have leisure time, to have some joy in their life and not just be punished by drudgery, not have economic anxiety,” he says.
Gates’s stance on reparations is a case in point. The murder of George Floyd in 2020, and the current threat to black history studies from rightwing Republicans – some of Gates’s own work has been banned from schools in Florida under Governor Ron DeSantis – have only accelerated calls for restorative justice for enslavement.
Gates acknowledges the wrongs but disagrees with the solution. “Affirmative action plans go a long way… I think that’s a form of reparation,” he says. “But I just could not imagine any group of Americans deciding to dip into their pockets and pay a cash settlement for all that our enslaved ancestors suffered. I don’t think that’s realistic.”
When I disagree – citing examples of other societies that have paid reparations, Gates is firm. He even describes calls for reparations as “racial bullying”. “The bottom line is, you can’t bully people with calls for reparations because of the legacy of slavery,” he insists. “So we need leaders who are thoughtful and nuanced and sensitive. I should know. I’ve been in America for 73 years.”
Gates’s optimistic view of American decency was famously pushed to breaking point in 2009, when he – already a famous professor and TV personality – achieved unwelcome notoriety. Returning home from filming in China, he was struggling with the lock on his door, as he entered his own property. A call from a neighbour – who reported a suspicious black male attempting to enter a house – led to the arrival of police. Gates was initially suspected of breaking into his own home. When it was established that he lived at the property, he was arrested anyway for disorderly conduct. Widespread coverage – which made international news – pictured an angry Gates, handcuffed, being led away from his own front porch.

Gates was released after Harvard sent its lawyers over. Further controversy ensued when President Barack Obama commented on the debacle, calling the police’s decision to arrest Gates “stupid”. The entire affair was resolved in a meeting at the White House in which Gates sat down for a beer with the officer who arrested him, the president, and vice-president Joe Biden.
The “beer summit”, as it became known, sparked wider conversations about racial discrimination in policing. Gates took a conciliatory line. “My heart went out to the officer when he told me he was just scared,” Gates says. “He had just wanted to go home that night to his wife. We shook hands and he gave me the handcuffs he had used to arrest me. And they’re now in an exhibit in the Smithsonian,” he adds, with a weary air of triumphalism.
Beers with a well-intentioned black president and messages of racial conciliation seem a lifetime away in the current political climate. Yet Gates says his own teaching practice remains unthreatened by fears of censorship or backlash. “Fortunately, I have the freedom to teach, whatever way that I want and whatever content that I want,” he says.
Gates has been protected, perhaps, by his refusal to conform to the norms of either academic or celebrity life. He is one of the few people to have achieved fame as an academic, thanks to his long TV career. He credits that not to American broadcasters, but to his time in Britain, early on in his career. “My time in the UK was fundamental,” he says.

“One time we went to this Indian restaurant in Cambridge,” Gates recounts. “And Soyinka brings his own chilli. I mean, this Nigerian chilli he would make and carry with him – it was engine oil! And they said to me: we are from your future. We brought you here to tell you you’re not going to be a doctor. You are meant to be a professor. You’re going to be a scholar of African and African-American studies, and you’re going to make a difference.”
The prophetic nature of those remarks must have become obvious when Gates’s first book, The Signifying Monkey, was published in 1988, applying post-structuralist analysis to African-American vernacular and literary traditions. Since then, Gates has made a name for himself as a leading voice of African-American literary and cultural history. Yet it is his TV career that put him on a steady path to becoming an American national treasure. It was the British producer Jane Root, Gates tells me, who recruited him to present an episode of the long-running BBC series Great Railway Journeys in 1996, travelling with his two daughters through southern Africa.
“The whole conceit was this professor of African-American studies taking his mixed-race daughters to Africa to find their roots, only for them to say: ‘Our roots are in Cambridge, Massachusetts. I’ve got nothing left in Africa, I want a Big Mac,’” Gates laughs. “The Guardian called it National Lampoon Goes to Africa, and that was just so honest and fresh. I would be giving my daughters this pompous lectures about Livingstone and, you know, they’d be rolling their eyes. And it was great.”
The success of that episode led to Gates hosting an entire series, Wonders of the African World, the show where I first met him all those years ago. “My whole life as a film-maker, I owe it to Jane Root, and to the BBC,” he says.
The concept so central to Wonders,of the descendants of the enslaved reconnecting with Africa, is as old as the enslavement that displaced them. Yet its modern iteration has exploded in recent years. Ghana, the west African nation that has long positioned itself as a hub for the “return”, now regularly records hundreds of thousands of additional visitors from the black diaspora, with festivals celebrating global blackness and ancestral connection. “I love it!” Gates says, of this growing phenomenon. “I think all African Americans should do two things. Take a DNA test to see where in Africa they’re from. And I think they should visit the continent.”
The return is a joyful movement in which black people seek to heal the bonds severed by enslavement and globalisation. Yet if underneath it lies a pessimism – that racism makes western nations unliveable – it is not one that Gates shares.
He acknowledges that America is broken. “I remember under John Kennedy and certainly with Bobby Kennedy, and with Martin Luther King, we thought poverty was a disease that could be cured. No one thinks that today,” he laments. But rather than offering a way out, he believes in the country’s redemption, and hopes he and his work will play a role. “We have to fix it,” he says. “And we have to fix it together.”
In typical contrary fashion, Gates turns to histories rooted in the darkest side of America’s racial capitalism to find inspiration for believing in America’s potential. At the turn of the 20th century, when black women faced racist characterisation as “thieves and prostitutes”, they retaliated by forming “coloured women’s clubs”, to improve their image, foster racial pride, and advocate civil rights.
“I think of that movement,” Gates says. “Their motto was ‘lifting as we climb’. And I think that should be the motto of American capitalism. We lift, as we climb.”
The Black Box: Writing the Race by Henry Louis Gates Jris published by Penguin (£25). To support the Guardian and Observer order your copy at guardianbookshop.com. Delivery charges may apply
#american racism#Black and white#Henry Louis Gates Jr#‘We are all mixed’: Henry Louis Gates Jr on race#being arrested and working towards America’s redemption#white supremacy#white lies#biracially american#america is biracial#biracial#Their motto was ‘lifting as we climb.#enslavement and globalisation#racism
0 notes
Text









Making Black America: Through the Grapevine (2022)
#Making Black America#2022#Through the Grapevine#Professor Henry Louis Gates Jr.#Henry Louis Gates#mini series#documentary#Tiffany Gill
0 notes
Photo
Who’s Black and Why?: A Hidden Chapter from the Eighteenth-Century Invention of Race
Edited by Henry Louis Gates, Jr. and Andrew S. Curran.
#Who’s Black and Why?#Who’s Black and Why#Henry Louis Gates Jr#Andrew S. Curran#books#book covers#favorites
1 note
·
View note
Text

Henry Louis Gates Jr.
#suitdaddy#suiteddaddy#suit and tie#suited daddy#men in suits#silverfox#suitfetish#black daddy#suited men#suited grandpa#suitedman#suit daddy#suited man#buisness suit#suitedmen#americans#finding your roots#Henry Louis Gates Jr.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

#ABSOLUTE BULLSHIT#Michael Douglas and Scarlett Johansen Foat out Lie About Not Knowing That They Were Related#Privileged Families In Hollywood Always Sneak Other Family Members In#HENRY LOUIS GATES JR CAN ALSO GO TO HELL#Cjevk out his past guest list if no one believes he's another Tool In A Cheap Suit#Michael Douglas#Jewish#Johansen#Benjamin Franklin#Revered For His Interest In Jews and their Culture Which Us Interwoven Throughout Freemasonry#Sick Of Lies#Hollywood#disney#marvel
1 note
·
View note