#hectares of forests
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HoW Africa drylands can stabilize the Global climate?

Regreening Africa aims to reverse land degradation on 1 million hectares across 8 countries in Africa. So far, the project has improved the #livelihoods, food security, and climate resilience of 500,000 households by restoring ecosystem services.
#Regreening#land degradation#hectares of forests#projects#tree planting#drylands#climate change#sdg15#evergreen agriculture#agroforestry#reforestation
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
"With “green corridors” that mimic the natural forest, the Colombian city is driving down temperatures — and could become five degrees cooler over the next few decades.
In the face of a rapidly heating planet, the City of Eternal Spring — nicknamed so thanks to its year-round temperate climate — has found a way to keep its cool.
Previously, Medellín had undergone years of rapid urban expansion, which led to a severe urban heat island effect — raising temperatures in the city to significantly higher than in the surrounding suburban and rural areas. Roads and other concrete infrastructure absorb and maintain the sun’s heat for much longer than green infrastructure.
“Medellín grew at the expense of green spaces and vegetation,” says Pilar Vargas, a forest engineer working for City Hall. “We built and built and built. There wasn’t a lot of thought about the impact on the climate. It became obvious that had to change.”
Efforts began in 2016 under Medellín’s then mayor, Federico Gutiérrez (who, after completing one term in 2019, was re-elected at the end of 2023). The city launched a new approach to its urban development — one that focused on people and plants.
The $16.3 million initiative led to the creation of 30 Green Corridors along the city’s roads and waterways, improving or producing more than 70 hectares of green space, which includes 20 kilometers of shaded routes with cycle lanes and pedestrian paths.
These plant and tree-filled spaces — which connect all sorts of green areas such as the curb strips, squares, parks, vertical gardens, sidewalks, and even some of the seven hills that surround the city — produce fresh, cooling air in the face of urban heat. The corridors are also designed to mimic a natural forest with levels of low, medium and high plants, including native and tropical plants, bamboo grasses and palm trees.
Heat-trapping infrastructure like metro stations and bridges has also been greened as part of the project and government buildings have been adorned with green roofs and vertical gardens to beat the heat. The first of those was installed at Medellín’s City Hall, where nearly 100,000 plants and 12 species span the 1,810 square meter surface.
“It’s like urban acupuncture,” says Paula Zapata, advisor for Medellín at C40 Cities, a global network of about 100 of the world’s leading mayors. “The city is making these small interventions that together act to make a big impact.”
At the launch of the project, 120,000 individual plants and 12,500 trees were added to roads and parks across the city. By 2021, the figure had reached 2.5 million plants and 880,000 trees. Each has been carefully chosen to maximize their impact.
“The technical team thought a lot about the species used. They selected endemic ones that have a functional use,” explains Zapata.
The 72 species of plants and trees selected provide food for wildlife, help biodiversity to spread and fight air pollution. A study, for example, identified Mangifera indica as the best among six plant species found in Medellín at absorbing PM2.5 pollution — particulate matter that can cause asthma, bronchitis and heart disease — and surviving in polluted areas due to its “biochemical and biological mechanisms.”
And the urban planting continues to this day.
The groundwork is carried out by 150 citizen-gardeners like Pineda, who come from disadvantaged and minority backgrounds, with the support of 15 specialized forest engineers. Pineda is now the leader of a team of seven other gardeners who attend to corridors all across the city, shifting depending on the current priorities...
“I’m completely in favor of the corridors,” says [Victoria Perez, another citizen-gardener], who grew up in a poor suburb in the city of 2.5 million people. “It really improves the quality of life here.”
Wilmar Jesus, a 48-year-old Afro-Colombian farmer on his first day of the job, is pleased about the project’s possibilities for his own future. “I want to learn more and become better,” he says. “This gives me the opportunity to advance myself.”
The project’s wider impacts are like a breath of fresh air. Medellín’s temperatures fell by 2°C in the first three years of the program, and officials expect a further decrease of 4 to 5C over the next few decades, even taking into account climate change. In turn, City Hall says this will minimize the need for energy-intensive air conditioning...
In addition, the project has had a significant impact on air pollution. Between 2016 and 2019, the level of PM2.5 fell significantly, and in turn the city’s morbidity rate from acute respiratory infections decreased from 159.8 to 95.3 per 1,000 people [Note: That means the city's rate of people getting sick with lung/throat/respiratory infections.]
There’s also been a 34.6 percent rise in cycling in the city, likely due to the new bike paths built for the project, and biodiversity studies show that wildlife is coming back — one sample of five Green Corridors identified 30 different species of butterfly.
Other cities are already taking note. Bogotá and Barranquilla have adopted similar plans, among other Colombian cities, and last year São Paulo, Brazil, the largest city in South America, began expanding its corridors after launching them in 2022.
“For sure, Green Corridors could work in many other places,” says Zapata."
-via Reasons to Be Cheerful, March 4, 2024
#colombia#brazil#urban#urban landscape#urban planning#cities#civil engineering#green architecture#green spaces#urban heat#urban heat island effect#weather#meteorology#global warming#climate change#climate hope#climate optimism#climate emergency#climate action#environment#environmental news#city architecture#bicycling#native plants#biodiversity#good news#hope#solarpunk#ecopunk#hopepunk
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi! Just wanna raise some awareness here because South America is on fucking fire and I need to see more people talking about this.

Source: RSOE EDIS x
Im just going to talk about the ones i'm closest to, but if you know about these fires, feel free to add in the reblogs!
Chile
In Chile there's (up to Feb 5) 160 wild fires, of which 40 are still trying to be controlled by authorities. The president, Gabriel Boric, has declared State of Emergency in the whole country, and theres a Red Alert Code in most part of the country.
Isla de Chiloé, Southern Chile (900 km away from Santiago de Chile)
This is a (recently controlled) fire that lasted a week, but many neighborhoods were burnt to the ground.


The whole South is in red alert for constant sudden fires that spread quickly due to the lack of rain and the elevated temperatues in the zone. Just today, two fires had to be controlled in the main land next to this island, and more are being reported in the Los Lagos region. This is added to the "controlled" intentional fires that farmers make to clean their fields of old crops along the Central-South parts of the country, mostly surrunding the main route, Ruta 5, that connects the whole country, thus making it hard to see and breathe because of the smoke. (flashnews, most of them get out of control quickly.)
Valparaiso/Viña del Mar, Central Chile (100 km away from Santiago de Chile)

A fire that started on Friday 2nd and grew exponentially because of the wind and the dry, hot climate. More than 100 people are dead, with 70 unrecognized bodies and other 400 that have dissapeared. At least 30000 people that have lost everything to the fire.
There's massive evacuations from this and the neighboring city, Viña Del Mar.
This is said to be the second most deadly fire in the century, surpased by Australia in 2009.
45000+ hectares that include land and neighborhoods have been burnt down.
I could go on about this one, so more info here and here



Argentina
Parque Los Alerces (Esquel), Chubut
The fire strarted on the 25th January, and the climate has made it hard to contain. 3000 hectares of native forest have been burnt to teh ground. It is now growing in the direction of the nearest city, Esquel. Theres been evacuations between yesterday and today (4 and 5th Febuary)



Parque Nahuel Huapi (Bariloche), Río Negro
The reason why im writing this. The city woke up today covered in smoke after a wildfire developed yesterday during the night. The reason? A fireplace that was not turned off in a place where people cannot disembark and can only be reached via boats.



As of now, there's not much information about the fire but hopefully the firefighters will be able to contain it before it reaches Tronador Mountain, where an ancient glaciar is.
...which leads me to the other point i wanted to talk about.
Firefighters
They volunteer to do this job.
In Argentina and Chile, firefighting is not rewarded with a salary, and most of the times they dont even have full firehouses to stay in. These people are at their houses, ready to jump into action and run to the station the second the alarm goes off.
They are neighbors, people that risk their lives and run into danger willingly, just because they want to help the community.
I felt the need to give a shout-out to these people and say:
Don't be a fucking dick, don't start fires in the woods unless it's an approved place, and if you do, TURN IT OFF.
Pour abundant water on it, and do not stop when you don't see any more flames.
Keep pouring water until the ashes don't burn/feel like room temperature in your hand if you put it 10 cm away from it, and even then, pour some more just to be sure.
No heat and no smoke mean a safely extinguished fire.
Save lives and forests.
#dont even get me started on the denial of climate change from my president#didnt wanna get political here#argentina#chile#argieposting#argieblr#soff speaks#wildfires
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - June 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $Kaybarr1735! And if you tip me and give me a way to contact you, at the end of the month I'll send you a link to all of the articles I found but didn't use each week!
1. Victory for Same-Sex Marriage in Thailand
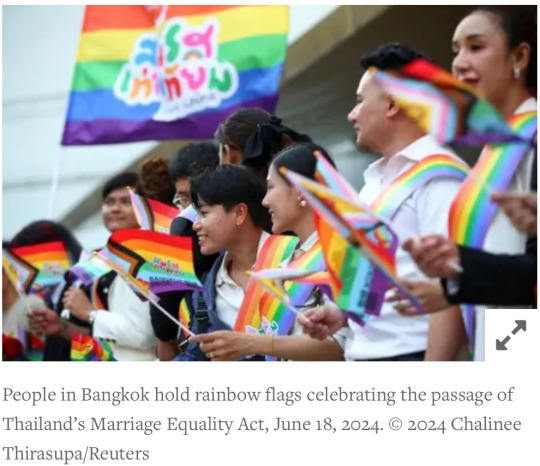
“Thailand’s Senate voted 130-4 today to pass a same-sex marriage bill that the lower house had approved by an overwhelming majority in March. This makes Thailand the first country in Southeast Asia, and the second in Asia, to recognize same-sex relationships. […] The Thai Marriage Equality Act […] will come into force 120 days after publication in the Royal Gazette. It will stand as an example of LGBT rights progress across the Asia-Pacific region and the world.”
2. One of world’s rarest cats no longer endangered

“[The Iberian lynx’s] population grew from 62 mature individuals in 2001 to 648 in 2022. While young and mature lynx combined now have an estimated population of more than 2,000, the IUCN reports. The increase is largely thanks to conservation efforts that have focused on increasing the abundance of its main food source - the also endangered wild rabbit, known as European rabbit. Programmes to free hundreds of captive lynxes and restoring scrublands and forests have also played an important role in ensuring the lynx is no longer endangered.”
3. Planning parenthood for incarcerated men
“[M]any incarcerated young men missed [sex-ed] classroom lessons due to truancy or incarceration. Their lack of knowledge about sexual health puts them at a lifelong disadvantage. De La Cruz [a health educator] will guide [incarcerated youths] in lessons about anatomy and pregnancy, birth control and sexually transmitted infections. He also explores healthy relationships and the pitfalls of toxic masculinity. […] Workshops cover healthy relationships, gender and sexuality, and sex trafficking.”
4. Peru puts endemic fog oasis under protection

“Lomas are unique ecosystems relying on marine fog that host rare and endemic plants and animal species. […] The Peruvian government has formally granted conservation status to the 6,449-hectare (16,000-acre) desert oasis site[….] The site, the first of its kind to become protected after more than 15 years of scientific and advocacy efforts, will help scientists understand climatic and marine cycles in the area[, … and] will be protected for future research and exploration for at least three decades.”
5. Religious groups are protecting Pride events — upending the LGBTQ+ vs. faith narrative

“In some cases, de-escalation teams stand as a physical barrier between protesters and event attendees. In other instances, they try to talk with protesters. The goal is generally to keep everyone safe. Leigh was learning that sometimes this didn’t mean acting as security, but doing actual outreach. That might mean making time and space to listen to hate speech. It might mean offering food or water. […] After undergoing Zoom trainings this spring, the members of some 120 faith organizations will fan out across more than 50 Pride events in 16 states to de-escalate the actions of extremist anti-LGBTQ+ hate groups.”
6. 25 years of research shows how to restore damaged rainforest
“For the first time, results from 25 years of work to rehabilitate fire-damaged and heavily logged rainforest are now being presented. The study fills a knowledge gap about the long-term effects of restoration and may become an important guide for future efforts to restore damaged ecosystems.”
7. Audubon and Grassroots Carbon Announce First-of-its-Kind Partnership to Reward Landowners for Improving Habitats for Birds while Building Healthy Soils
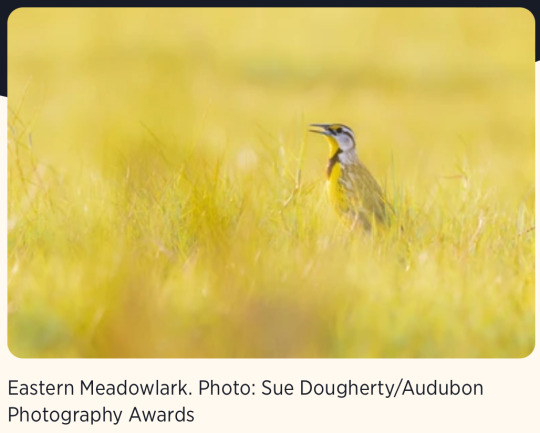

“Participating landowners can profit from additional soil carbon storage created through their regenerative land management practices. These practices restore grasslands, improve bird habits, build soil health and drive nature-based soil organic carbon drawdown through the healthy soils of farms and ranches. […] Additionally, regenerative land management practices improve habitats for birds. […] This partnership exemplifies how sustainable practices can drive positive environmental change while providing tangible economic benefits for landowners.”
8. Circular food systems found to dramatically reduce greenhouse gas emissions, require much less agricultural land
“Redesigning the European food system will reduce agricultural land by 44% while dramatically reducing greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture by 70%. This reduction is possible with the current consumption of animal protein. “Moreover, animals are recyclers in the system. They can recycle nutrients from human-inedible parts of the organic waste and by-products in the food system and convert them to valuable animal products," Simon says.”
9. Could Treating Injured Raptors Help Lift a Population? Researchers found the work of rehabbers can have long-lasting benefits
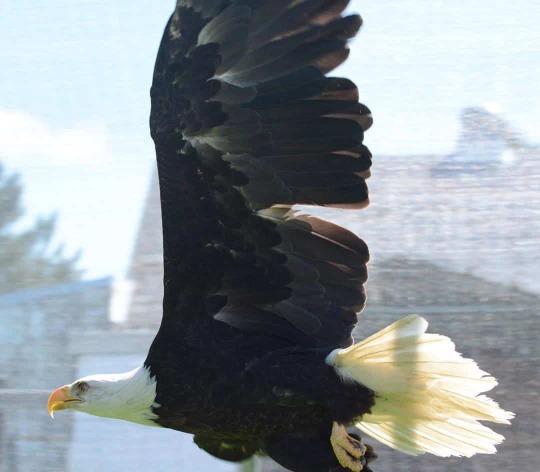

“[“Wildlife professionals”] tend to have a dismissive attitude toward addressing individual animal welfare,” [… but f]or most raptor species, they found, birds released after rehabilitation were about as likely to survive as wild birds. Those released birds can have even broader impacts on the population. Back in the wild, the birds mate and breed, raising hatchlings that grow up to mate and breed, too. When the researchers modeled the effects, they found most species would see at least some population-level benefits from returning raptors to the wild.”
10. Indigenous people in the Amazon are helping to build bridges & save primates

“Working together, the Reconecta Project and the Waimiri-Atroari Indigenous people build bridges that connect the forest canopy over the BR-174 road[….] In the first 10 months of monitoring, eight different species were documented — not only monkeys such as the golden-handed tamarin and the common squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus), but also kinkajous (Potos flavus), mouse opossums (Marmosops sp.), and opossums (Didelphis sp.).”
Bonus: A rare maneless zebra was born in the UK
June 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#lgbtq#gay rights#gay marriage#same sex marriage#thailand#lynx#big cats#cats#endangered species#endangered#sex education#prison#peru#conservation#habitat#religion#pride#faith#pride month#lgbt pride#compassion#rainforest#birds#nature#climate change#wildlife rehab#wildlife#indigenous
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
I work in a suburban community about 30-45 minutes north of Manhattan and 15-20 minutes from the nearest urban centers. People here were cautious but unsurprised when a mother bear and cub turned up in the nearby woods.
A BEAR ATE MY BEST HUMMINGBIRD FEEDER.
Rude.
#it probably doesn't help that our wilderness areas and large parks are usually NOT fenced off#I live within three blocks of a forested urban park that is over 450 hectares you can just walk into
54K notes
·
View notes
Text
One acre of hemp produces 25 % more oxygen than one acre of forest and guarantees a cellulose supply that is approximately twice as high. One acre of hemp grows within 6 months, while a forest grows for decades before it is harvested. By making hemp paper, we could save millions of hectares of forest every year. Hemp can be used in textile production, construction and even as biofuel.
David Attenborough

553 notes
·
View notes
Text
IT'S TIME TO APPRECIATE THE BLACK AND RUFOUS ELEPHANT SHREW

ON THIS WEBSITE WE LOVE WEIRD ANIMALS AND THIS LITTLE BEAUTY IS CERTAINLY ONE OF THEM. APPRECIATE THE BLACK AND RUFOUS ELEPHANT SHREW TODAY.

NATIVE TO DENSE MONTANE FORESTS OF KENYA AND TASMANIA, THEY BOUNCED BACK FROM 'THREATENED STATUS' BUT STILL FACE HABITAT LOSS DUE TO FOREST FRAGMENTATION.

THESE BEAUTIFUL VACUUM CLEANERS EAT BUGS OUT OF THE LEAF LITTER WITH THEIR NOODLY SNOOT, CAPABLY UNCOVERING BEETLES, CENTIPEDES, AND TERMITES.

MALES ATTRACT AND DEFEND A SINGLE MATE AND CONTROL UP TO A HECTARE OF TERRITORY, WHICH IS A LOT FOR A LITTLE SCOOP OF SPITE AND SNOOTING.

THESE EFFICIENT LITTLE BUSYBODIES BUILD MANY NESTS OUT OF DRY LEAVES TO SLEEP IN ALL ACROSS THE AREA, AS MANY AS A DOZEN, AND USE THEM EACH IN TURN.

DESPITE THEIR COMMITTED MONOGAMY THE BLACK AND RUFOUS ELEPHANT SHREWS DO NOT ACTUALLY LIKE EACH OTHER, MUCH LIKE TIRED BOOMER COMEDIANS: MATED PAIRS SPEND NO TIME TOGETHER OUTSIDE OF MATING.

MOTHERS DON'T EVEN LIKE THEIR KIDS. THEY VISIT THEIR YOUNG AS INFREQUENTLY AS ONCE A DAY TO NURSE. THEY GOT OTHER SHIT TO DO, APPARENTLY.

THE YOUNG ARE LESS PRECOCIAL THAN MOST ELEPHANT SHREWS, SPENDING SEVERAL WEEKS IN THEIR NESTS BEFORE GAINING INDEPENDENCE IN ONLY ANOTHER FEW WEEKS AND NEVER WRITING HOME AGAIN, NOT THAT THEIR PARENTS CARE.
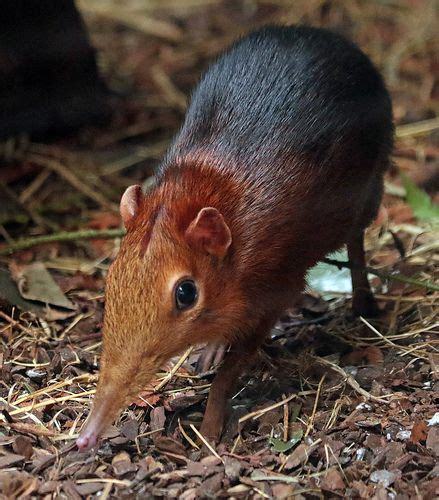

THIS HEFTY AND BEAUTIFUL DEDICATED INTROVERT AVERAGES ABOUT 28 CM / 11 IN IN LENGTH AND 450-700 G / 16-25 OZ IN WEIGHT, IMPRESSIVELY LARGE EVEN FOR AN ELEPHANT SHREW.

YOU HAVE NOW APPRECIATED: THE BLACK AND RUFOUS ELEPHANT SHREW. INSECTIVORE. INTROVERT. ABSENT PARENT. SNAPPY DRESSER. THIS PRINCELY POTATO HAS IT ALL, AND A DOZEN VACATION HOMES. TELL YOUR FRIENDS, UNLESS YOU TOO ARE A BLACK AND RUFOUS ELEPHANT SHREW AND DON'T HAVE ANY.
389 notes
·
View notes
Text
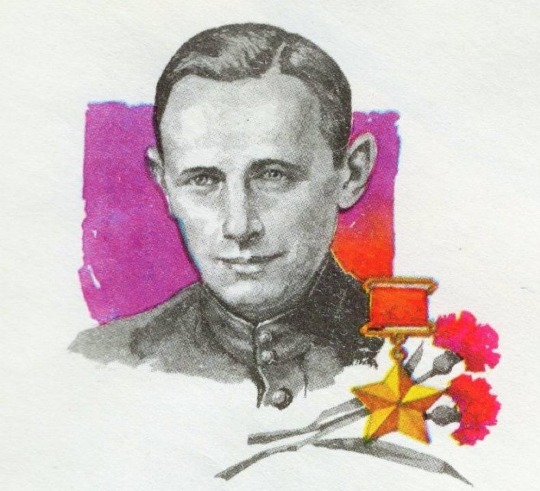

Fritz Schmenkel was the only German national who became a Hero of the Soviet Union for his actions during WWII.
Fritz Schmenkel was born in Stettin (today Szczecin, Poland) in 1916. His father, Paul Krause, a brickyard worker and communist, was murdered by Stormtroopers in 1932. This caused Fritz to join the Young Communist League of Germany to fight his father's Nazi murderers.
In December 1938, he was drafted into the Wehrmacht but refused to serve citing illness and other excuses. He was imprisoned for evading conscription. In July 1941, after the beginning of Nazi Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union, Schmenkel volunteered to fight on the Eastern Front so he was released. His true intention was always deserting which he did in November 1941. But he couldn't hide in Belarusian forests forever so there was a dilemma. How not to get killed on spot by comrades because of his German uniform and communicate without knowing Russian language? The shivering and hungry Shmenkel knocked on the doors of local village residents, using a simple set of words: "Lenin, Stalin, Thälmann" - and the doors opened. In exchange for help in a simple peasant household, Fritz received food, a place to sleep, and moved on.
One day Shmenkel came across a patrol of German military police and was arrested. Fortunately for the deserter, fighters from the partisan detachment "Death to Fascism" descended on Germans some time later. After a short but stubborn battle, the garrison was routed, and the partisans learned from local residents about the strange German. Not having time for serious investigation, the fighters simply took him with them. That's how Shmenkel ended up in the partisan detachment.
Of course, at first Soviets were very wary of Fritz, they feared that he was a Nazi spy. But they still decided not to act rashly and give him a chance. And soon such an opportunity presented itself. In one of the villages, the partisans came across German detachment. A fight ensued. Shmenkel did not take part in it - he had no weapon. Since there were too many Germans, the fate of the partisans seemed to be predetermined. Fritz asked for a rifle. Realizing that they have nothing to lose and an extra fighter was now worth its weight in gold, the unit commander took a risk. And he was right. Shmenkel started successfully shooting at Germans. The partisans won that battle. Fritz was then accepted as a member of the partisans. He quickly gained the respect and affection of his unit, his comrades started nicknaming him Ivan Ivanovich jokingly adding "Why call a good person Fritz?".
Schmenkel led German military units into ambushes arranged by the partisans. This helped the partisans capture entire units of Wehrmacht soldiers, as well as ammunition and food. Schmenkel quickly rose through the ranks of the partisans. In March 1943, he traveled to Moscow at the behest of the Red Army, was awarded the Order of the Red Banner, and received further military training. He was appointed deputy commander of a special operations (sabotage and intelligence) unit that operated in a German-occupied area north of the city of Orsha.
Germans put a reward on Schmenkel's head - 8 hectares of land, a house, a cow, and two thousand German marks. Later, the reward was raised to an astronomical sum for those times - 25 thousand marks.
At the end of 1943, contact with Fritz Schmenkel was lost. Only after the war did it become known that he had been captured and tortured by the Gestapo, but Fritz had not changed his views. He was sentenced to death and executed in occupied Minsk in February 1944.
His last wish was to send a letter to his wife Erna Schäfer. He wrote: "Forgive me for the troubles I have caused you by going my way to the end. I did not renounce my views even in the last hours of my life. I am boldly going to my execution because I am dying for my convictions." He left behind three children in Germany.
By the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR of 6 October 1964, Fritz Schmenkel was posthumously awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union "for active participation in the partisan movement, exemplary fulfillment of command assignments during the Great Patriotic War and the heroism and courage displayed in doing so."
The memory of Fritz Schmenkel is immortalized in the names of streets in the cities of Nelidovo and Bely in the Tver region. And in Minsk, a memorial plaque is dedicated to him. One of the streets in East Berlin also bore the name of Shmenkel. However, it was renamed in 1992.
538 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ecuadorians voted overwhelmingly on Sunday to reject oil drilling in a section of Yasuní National Park, the most biodiverse area of the imperiled Amazon rainforest. Nearly 60% of Ecuadorian voters backed a binding referendum opposing oil exploration in Block 43 of the national park, which is home to uncontacted Indigenous tribes as well as hundreds of bird species and more than 1,000 tree species.
[...]
Sunday's vote makes Ecuador the first country to restrict fossil fuel extraction through the citizen referendum process, according to Nemonte Nenquimo, a Waorani leader. "Yasuní, an area of one million hectares, is one of the most biodiverse places on Earth," Nenquimo wrote in a recent op-ed for The Guardian. "There are more tree species in a single hectare of Yasuní than across Canada and the United States combined. Yasuní is also the home of the Tagaeri and Taromenane communities: the last two Indigenous peoples living in voluntary isolation in Ecuador." "Can you imagine the immense size of one million hectares?" Nenquimo added. "The recent fires in Quebec burned a million hectares of forest. And so the oil industry hopes to burn Yasuní. It has already begun in fact, with the Ishpingo-Tambococha-Tiputini (ITT) oil project on the eastern edge of the park."
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Despite its green image, Ireland has surprisingly little forest. [...] [M]ore than 80% of the island of Ireland was [once] covered in trees. [...] [O]f that 11% of the Republic of Ireland that is [now] forested, the vast majority (9% of the country) is planted with [non-native] spruces like the Sitka spruce [in commercial plantations], a fast growing conifer originally from Alaska which can be harvested after just 15 years. Just 2% of Ireland is covered with native broadleaf trees.
Text by: Martha O’Hagan Luff. “Ireland has lost almost all of its native forests - here’s how to bring them back.” The Conversation. 24 February 2023. [Emphasis added.]
---
[I]ndustrial [...] oil palm plantations [...] have proliferated in tropical regions in many parts of the world, often built at the expense of mangrove and humid forest lands, with the aim to transform them from 'worthless swamp' to agro-industrial complexes [...]. Another clear case [...] comes from the southernmost area in the Colombian Pacific [...]. Here, since the early 1980s, the forest has been destroyed and communities displaced to give way to oil palm plantations. Inexistent in the 1970s, by the mid-1990s they had expanded to over 30,000 hectares. The monotony of the plantation - row after row of palm as far as you can see, a green desert of sorts - replaced the diverse, heterogenous and entangled world of forest and communities.
Text by: Arturo Escobar. "Thinking-Feeling with the Earth: Territorial Struggles and the Ontological Dimension of the Epistemologies of the South." Revista de Antropologia Iberoamericana Volume 11 Issue 1. 2016. [Emphasis added.]
---
But efforts to increase global tree cover to limit climate change have skewed towards erecting plantations of fast-growing trees [...] [because] planting trees can demonstrate results a lot quicker than natural forest restoration. [...] [But] ill-advised tree planting can unleash invasive species [...]. [In India] [t]o maximize how much timber these forests yielded, British foresters planted pines from Europe and North America in extensive plantations in the Himalayan region [...] and introduced acacia trees from Australia [...]. One of these species, wattle (Acacia mearnsii) [...] was planted in [...] the Western Ghats. This area is what scientists all a biodiversity hotspot – a globally rare ecosystem replete with species. Wattle has since become invasive and taken over much of the region’s mountainous grasslands. Similarly, pine has spread over much of the Himalayas and displaced native oak trees while teak has replaced sal, a native hardwood, in central India. Both oak and sal are valued for [...] fertiliser, medicine and oil. Their loss [...] impoverished many [local and Indigenous people]. [...]
India’s national forest policy [...] aims for trees on 33% of the country’s area. Schemes under this policy include plantations consisting of a single species such as eucalyptus or bamboo which grow fast and can increase tree cover quickly, demonstrating success according to this dubious measure. Sometimes these trees are planted in grasslands and other ecosystems where tree cover is naturally low. [...] The success of forest restoration efforts cannot be measured by tree cover alone. The Indian government’s definition of “forest” still encompasses plantations of a single tree species, orchards and even bamboo, which actually belongs to the grass family. This means that biennial forest surveys cannot quantify how much natural forest has been restored, or convey the consequences of displacing native trees with competitive plantation species or identify if these exotic trees have invaded natural grasslands which have then been falsely recorded as restored forests. [...] Planting trees does not necessarily mean a forest is being restored. And reviving ecosystems in which trees are scarce is important too.
Text by: Dhanapal Govindarajulu. "India was a tree planting laboratory for 200 years - here are the results." The Conversation. 10 August 2023. [Emphasis added.]
---
Nations and companies are competing to appropriate the last piece of available “untapped” forest that can provide the most amount of “environmental services.” [...] When British Empire forestry was first established as a disciplinary practice in India, [...] it proscribed private interests and initiated a new system of forest management based on a logic of utilitarian [extraction] [...]. Rather than the actual survival of plants or animals, the goal of this forestry was focused on preventing the exhaustion of resource extraction. [...]
Text by: Daniel Fernandez and Alon Schwabe. "The Offsetted." e-flux Architecture (Positions). November 2013. [Emphasis added.]
---
At first glance, the statistics tell a hopeful story: Chile’s forests are expanding. […] On the ground, however, a different scene plays out: monocultures have replaced diverse natural forests [...]. At the crux of these [...] narratives is the definition of a single word: “forest.” [...] Pinochet’s wave of [...] [laws] included Forest Ordinance 701, passed in 1974, which subsidized the expansion of tree plantations [...] and gave the National Forestry Corporation control of Mapuche lands. This law set in motion an enormous expansion in fiber-farms, which are vast expanses of monoculture plantations Pinus radiata and Eucalyptus species grown for paper manufacturing and timber. [T]hese new plantations replaced native forests […]. According to a recent study in Landscape and Urban Planning, timber plantations expanded by a factor of ten from 1975 to 2007, and now occupy 43 percent of the South-central Chilean landscape. [...] While the confusion surrounding the definition of “forest” may appear to be an issue of semantics, Dr. Francis Putz [...] warns otherwise in a recent review published in Biotropica. […] Monoculture plantations are optimized for a single product, whereas native forests offer [...] water regulation, hosting biodiversity, and building soil fertility. [...][A]ccording to Putz, the distinction between plantations and native forests needs to be made clear. “[...] [A]nd the point that plantations are NOT forests needs to be made repeatedly [...]."
Text by: Julian Moll-Rocek. “When forests aren’t really forests: the high cost of Chile’s tree plantations.” Mongabay. 18 August 2014. [Emphasis added.]
#abolition#ecology#imperial#colonial#landscape#haunted#indigenous#multispecies#interspecies#temporality#carceral geography#plantations#ecologies#tidalectics#intimacies of four continents#archipelagic thinking#caribbean
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
In just one month, approximately 462 hectares (4.6 million m²) of woodland, "notably pines and oaks, as well as around 20 hectares of centuries-old olive groves," have been destroyed by Israeli airstrikes, said Georges Mitri, Director of the Land and Natural Resources Programme at Balamand University. Since the escalation of tensions between Hezbollah and the Israeli army on Oct. 8, the latter has used white phosphorus to set fire to forests and fields in border areas. The 1980 Geneva Convention, which Israel has not signed, prohibits the use of white phosphorous on civilians and in civilian areas due to its devastating effects on humans, animals and the environment.
[...]
Amid the ongoing economic crisis, the attacks targeting olive groves ahead of harvest season have a major negative impact on the local economy in the area. "Traditionally, people gather around the olive trees, harvest their crops, press their oil together... A big part of their lives is being lost," lamented Younes. “The olive trees being burned are centuries old," he pointed out. “If we were to replant them today, how long would it be before these fields became productive?” Giving an estimate of the economic losses attributed to the daily fires in the South, Mitri put the figure at nearly 20 million dollars. In the long term, Younes is particularly concerned about the environmental impact of the phosphorus bombs. "We have no choice but to wait until the end of hostilities before assessing the situation on the ground," he said. In Younes’ view, the greater the rate of absorption of phosphorus into the soil and water, the greater the risk of dramatic long-term consequences on Lebanon’s environment.
I'll add here that southern Lebanon has never fully recovered from 2006. There are still unexploded cluster bombs in the ground, killing and maiming people. There is still chemical contamination. The economic impact on agriculture has never been fully recouped. The cancer rates are still elevated and unaddressed. The labor structure and which crops are grown changed after 2006 and have never reverted. I remember weeping watching the bombing of Gaza in 2021 as I was in the middle of writing a paper about the long term legacies of the July War in Lebanon, with these additional long-term violences of the bombing at the forefront of my mind along with the immediate deaths and tragedies. This is a horrifying compounding of an existing injury, at a time when Lebanon is in economic free fall and (as the article also explains) in the middle of fire season, and with firefighters unable to do much because the area is. being bombed.
842 notes
·
View notes
Text
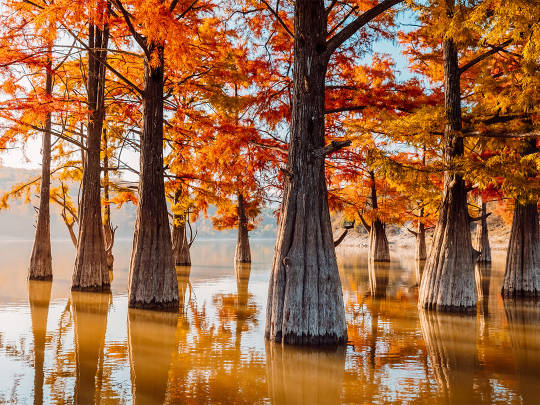
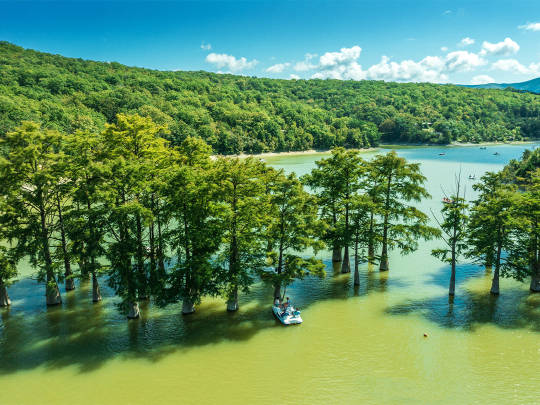
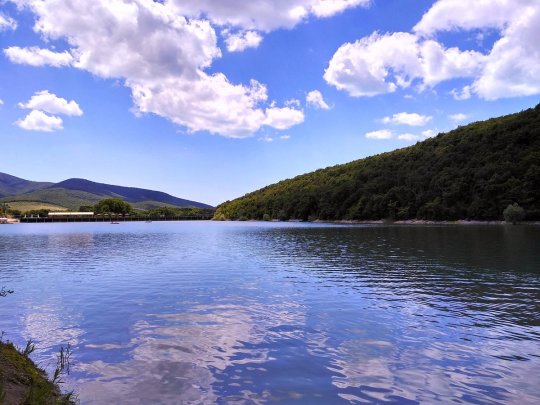
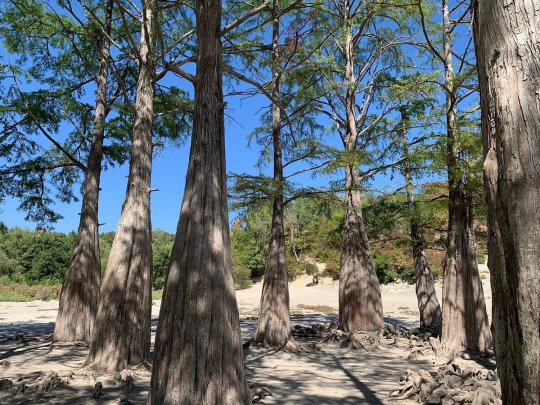
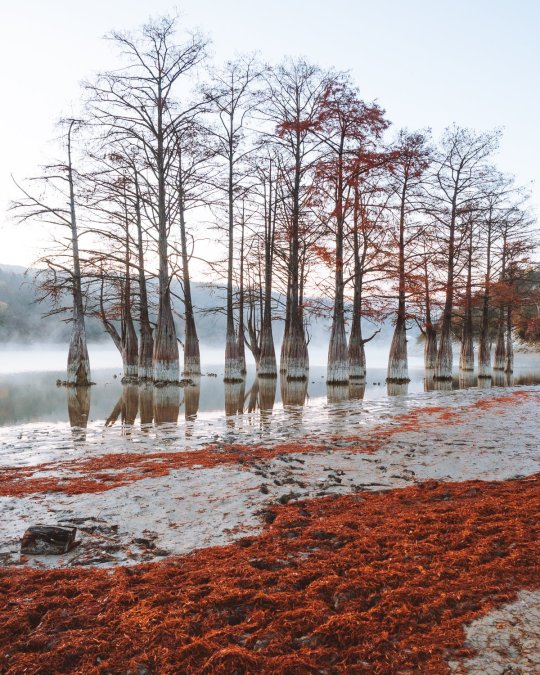
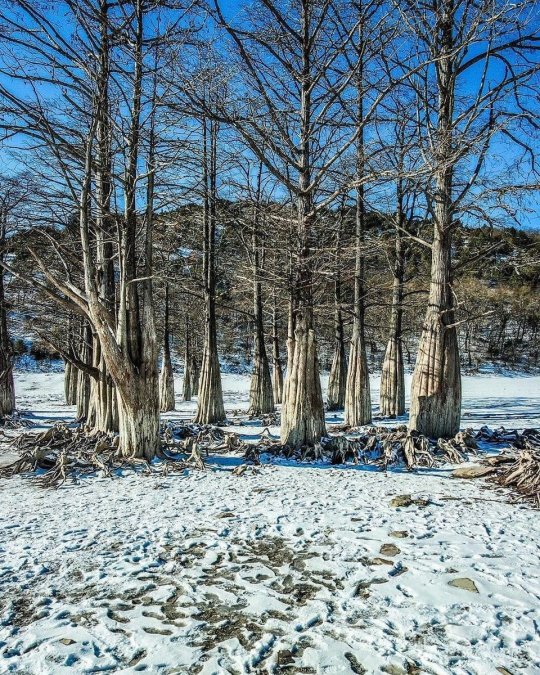
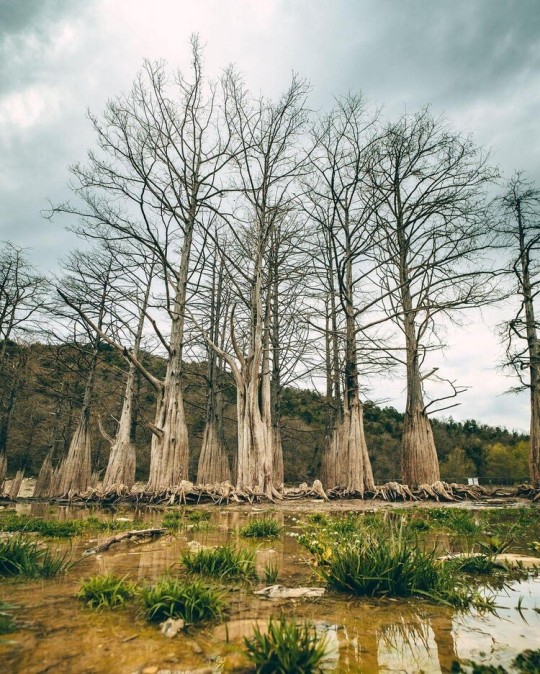



























Озеро Сукко (Кипарисовое озеро), или Голубое озеро — одна из самых популярных и фотогеничных локаций в окрестностях Анапы. Удивительные деревья с узловатыми корнями и приятным смолистым ароматом растут здесь прямо из воды. О происхождении названия озера существует множество предположений. С адыгейского топоним можно перевести как «водоем кабанов». Существует также вариант трактовки «Сукко» как «су» — вода и «къко» – свинья или дельфин. Озеро в Сукко было создано искусственно путем строительства плотины на реке, впадающей в Черное море, что привело к затоплению долины. Этот водоем занимает площадь всего 8 гектаров. Высота Кипарисового озера - 40 м над уровнем моря. Особую известность озеру принес уникальный эксперимент, проведенный в 1934–1935 годах, когда были посажены 32 болотных кипарисов, которые успешно прижились и выросли. Изначально кипарисы были посажены на сухой земле, однако из-за значительных изменений рельефа территории они со временем оказались в воде. В периоды засухи уровень воды в озере понижается, обнажая обширную корневую систему деревьев. Кипарисы достигают внушительной высоты почти в 30 метров, а их стволы могут быть шириной до полуметра. Роща прекрасна практически в любой сезон: весной свежая листва хвойных деревьев нежно-зелёная, летом приобретает более тёмный и насыщенный оттенок, а осенью полыхает ярко-оранжевым или красным цветом. К зиме деревья полностью сбрасывают листву, обнажая ветвистые кроны — в чём тоже есть своя красота.
Из-за обилия известняковых отложений в зависимости от освещения озеро Сукко может менять цвет от нежного молочно-голубого до насыщенного бирюзового. Голубое озеро не только известно своими кипарисами и кристально чистой водой, но и окружающей его природой. Водоем находится среди лесопарка с дубами и грабами, а с северной стороны его окружают склоны горы Широкая. Рядом также расположена можжевеловая роща, создающая лечебный воздух в этой местности.
Lake Sukko (Cypress Lake), or Blue Lake, is one of the most popular and photogenic locations in the vicinity of Anapa. Amazing trees with knotty roots and a pleasant resinous aroma grow here directly from the water. There are many speculations about the origin of the name of the lake. From the Adyghe toponym can be translated as “pond of wild boars.” There is also an option to interpret “Sukko” as “su” - water and “kko” - pig or dolphin. The lake in Sukko was created artificially by building a dam on a river flowing into the Black Sea, which led to flooding of the valley. This reservoir covers an area of only 8 hectares. The height of Cypress Lake is 40 m above sea level. The lake became especially famous due to a unique experiment conducted in 1934–1935, when 32 swamp cypress trees were planted, which successfully took root and grew.Initially, the cypress trees were planted on dry land, but due to significant changes in the terrain, they eventually ended up in water. During periods of drought, the lake's water level drops, exposing the trees' extensive root systems. Cypress trees reach an impressive height of almost 30 meters, and their trunks can be up to half a meter wide. The grove is beautiful in almost any season: in the spring, the fresh foliage of coniferous trees is soft green, in the summer it acquires a darker and richer shade, and in the fall it blazes with bright orange or red. By winter, the trees completely shed their leaves, revealing branched crowns - which also has its own beauty.
Due to the abundance of limestone deposits, depending on the lighting, Lake Sukko can change color from delicate milky blue to rich turquoise. Blue Lake is not only famous for its cypress trees and crystal clear water, but also for the nature that surrounds it. The reservoir is located among a forest park with oaks and hornbeams, and on the northern side it is surrounded by the slopes of Mount Shirokaya. There is also a juniper grove nearby, which creates healing air in this area.
Источник: https://kukarta.ru/ozero-sukko,//ezhevika-travel.ru /tur/ozero-sukko-foto,/turistexpert.ru/rossiya/anapa/kiparisovoe-ozero/,//kiparisovoe-ozero.ru,/blijehotel.ru/articles/kiparisovoe-ozero/, /experience.tripster.ru/sights/kiparisovoe-ozero-sukko/, /www.tripadvisor.ru/Attraction_Review-g3226223-d2331079-Reviews-Sukko_Lake-Sukko_Krasnodar_Krai_Southern_District.html.
#Russia#Anapa#nature#nature aesthetic#landscape photography#nature photography#mountains#lake#Cypress Lake#Lake Sukko#trees and forest#cypress trees#blue sky#travel#wonderful#Россия#природа#Анапа#Пейзаж#озеро#Озеро Сукко#Кипарисовое озеро#горы#лес#небо#туризм#природнаякрасота
214 notes
·
View notes
Text
The World's Forests Are Doing Much Better Than We Think

You might be surprised to discover... that many of the world’s woodlands are in a surprisingly good condition. The destruction of tropical forests gets so much (justified) attention that we’re at risk of missing how much progress we’re making in cooler climates.
That’s a mistake. The slow recovery of temperate and polar forests won’t be enough to offset global warming, without radical reductions in carbon emissions. Even so, it’s evidence that we’re capable of reversing the damage from the oldest form of human-induced climate change — and can do the same again.
Take England. Forest coverage now is greater than at any time since the Black Death nearly 700 years ago, with some 1.33 million hectares of the country covered in woodlands. The UK as a whole has nearly three times as much forest as it did at the start of the 20th century.
That’s not by a long way the most impressive performance. China’s forests have increased by about 607,000 square kilometers since 1992, a region the size of Ukraine. The European Union has added an area equivalent to Cambodia to its woodlands, while the US and India have together planted forests that would cover Bangladesh in an unbroken canopy of leaves.
Logging in the tropics means that the world as a whole is still losing trees. Brazil alone removed enough woodland since 1992 to counteract all the growth in China, the EU and US put together. Even so, the planet’s forests as a whole may no longer be contributing to the warming of the planet. On net, they probably sucked about 200 million metric tons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere each year between 2011 and 2020, according to a 2021 study. The CO2 taken up by trees narrowly exceeded the amount released by deforestation. That’s a drop in the ocean next to the 53.8 billion tons of greenhouse gases emitted in 2022 — but it’s a sign that not every climate indicator is pointing toward doom...
More than a quarter of Japan is covered with planted forests that in many cases are so old they’re barely recognized as such. Forest cover reached its lowest extent during World War II, when trees were felled by the million to provide fuel for a resource-poor nation’s war machine. Akita prefecture in the north of Honshu island was so denuded in the early 19th century that it needed to import firewood. These days, its lush woodlands are a major draw for tourists.
It’s a similar picture in Scandinavia and Central Europe, where the spread of forests onto unproductive agricultural land, combined with the decline of wood-based industries and better management of remaining stands, has resulted in extensive regrowth since the mid-20th century. Forests cover about 15% of Denmark, compared to 2% to 3% at the start of the 19th century.
Even tropical deforestation has slowed drastically since the 1990s, possibly because the rise of plantation timber is cutting the need to clear primary forests. Still, political incentives to turn a blind eye to logging, combined with historically high prices for products grown and mined on cleared tropical woodlands such as soybeans, palm oil and nickel, mean that recent gains are fragile.
There’s no cause for complacency in any of this. The carbon benefits from forests aren’t sufficient to offset more than a sliver of our greenhouse pollution. The idea that they’ll be sufficient to cancel out gross emissions and get the world to net zero by the middle of this century depends on extraordinarily optimistic assumptions on both sides of the equation.
Still, we should celebrate our success in slowing a pattern of human deforestation that’s been going on for nearly 100,000 years. Nothing about the damage we do to our planet is inevitable. With effort, it may even be reversible.
-via Bloomburg, January 28, 2024
#deforestation#forest#woodland#tropical rainforest#trees#trees and forests#united states#china#india#denmark#eu#european union#uk#england#climate change#sustainability#logging#environment#ecology#conservation#ecosystem#greenhouse gasses#carbon emissions#climate crisis#climate action#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey- so, not a normal post for me, but if you have mutual(s) living in BC or Northern Alberta, Canada please keep them in your thoughts. Wildfire season is no joke and we’re now entering evacuation season too. Jasper, AB has already been evacuated due to severe wildfires ranging over hundreds of hectares worth of forest, and now a sect of my home town has received an evacuation alert as well from a lighting caused fire of over 133 hectares and is rapidly growing by the hour.
Knock on wood but times are getting extremely worrisome, each summer is getting hotter and more deadly than the last, and people are being displaced from their homes at an alarming rate. Not just people but their animals too.
I know in the grand scheme of things this is not the most troubling thing happening in our world but it’s scary none the less.
A gentle reminder for any one living in BC or Alberta, Canada. Be prepared, be informed, and be ready. If you haven’t already you can download the BC WILDFIRE SERVICE app to keep updated on fires in your area, updates, notices, evacuation alerts, etc.
Please don’t forget to love one another and help your neighbours. Please reblog if you can ❤️
#lemon talks#I don’t even know what to tag this#british columbia#alberta#wildfire season#forest fires#fire safety#wildfire#climate change#climate crisis
236 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - May 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Support me on Ko-fi or $Kaybarr1735! Also, if you tip me on Ko-fi or CashApp (and give me some way to contact you if it doesn’t automatically), at the end of the month I'll send you a link to all of the articles I found but didn't use each week - almost double the content!
1. Scientists Invent Healthier More Sustainable Chocolate

“The new chocolate recipe from researchers at ETH Zurich uses more materials from the cocoa pod that are usually discarded, including more of the pulp as well as the inner lining of the husk, known as the endocarp. […] The resulting chocolate also [was “deliciously sweet” and] had 20% more fibre and 30 percent less saturated fat than average European dark chocolate[, and] it could enable cocoa farmers [to] earn more from their crops.”
2. Vermont Is Coming for Big Oil, Making It Pay for Decades of Climate Pollution

“Legislators in Montpelier are on the brink of enacting the "Climate Superfund Act," modeled after the federal Superfund law, that seeks to make oil, gas and coal companies pay for damages linked to historical greenhouse gas emissions. […] Companies would be held liable for the costs associated with […] floods and heat waves, along with losses to biodiversity, safety, economic development and anything else the treasurer deems reasonable[, that were caused by their emissions].”
3. Important bird habitat now protected in the Rocky Mountain Trench
“Grassland-reliant species in the Rocky Mountain Trench now have more protected habitat thanks to a new [270-hectare] conservation area near Cranbrook. […] About one-third of the Skookumchuck Prairie Conservation Area is forested[…,] Most of the site is a dry grassland[…, and] Three hectares of wetlands add to the landscape diversity and offer crucial benefits to wildlife and water systems in the area. This conservation gem also provides habitat for endangered American badger and excellent winter range for elk, mule deer and white-tailed deer.”
4. Lemur Week marked by 70th breeding success

“A wildlife park has celebrated its 70th lemur breeding success ahead of a week raising money to help save the endangered primates. […] The park's open-air Madagascar exhibit is home to 31 free-roaming lemurs and was officially opened in 2008. […] Females are only sexually receptive for just one or two days a year, leaving a small window of opportunity for males to father offspring. […] The two playful siblings, one female and one male, were born to father Bernard and mother Hira.”
5. Innovative material for sustainable building
“Researchers introduce a polymer-based material with unique properties. This material allows sunlight to enter, maintains a more comfortable indoor climate without additional energy, and cleans itself like a lotus leaf. The new development could replace glass components in walls and roofs in the future.”
6. Isle of Wight eagles don't pose threat to lambs as feared

“While there had previously been fears that the eagles would feed on livestock, such as lambs, the project has found no evidence of this. [… “W]hite-tailed eagles effectively steal meals from other predatory birds[, which is] a really important ecological role that had been lost within the landscape and is being restored.” [… The birds’] population was boosted by a chick last year – the first time the species has bred in England in 240 years.”
7. Breakthrough discovery uses engineered surfaces to shed heat
“Cheng's team has found a way to lower the starting point of the [Leidenfrost] effect by producing a surface covered with micropillars. […] The discovery has great potential in heat transfer applications such as the cooling of industrial machines and surface fouling cleaning for heat exchangers. It also could help prevent damage and even disaster to nuclear machinery.”
8. New malaria vaccine delivered for the first time
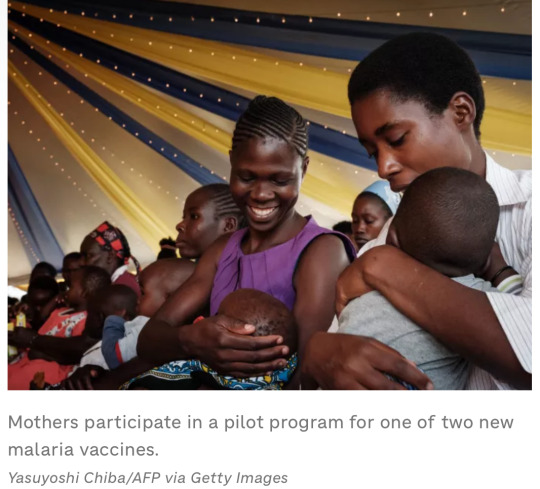
“A total of 43,000 doses arrived by air today from UNICEF, and another 120,000 are scheduled to show up in the coming days. […] They're the first vaccines designed to work against a human parasite. […] Across four African countries, these trials showed a 75% reduction in malaria cases in the year following vaccination of young children. […] The Serum Institute of India, who will be manufacturing the new vaccine, says a hundred million doses will likely be available to countries by the middle of next year.”
9. Urban gardening may improve human health: Microbial exposure boosts immune system
“"One month of urban indoor gardening boosted the diversity of bacteria on the skin of the subjects and was associated with higher levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines in the blood. The group studied used a growing medium with high microbial diversity emulating the forest soil," [… whereas] the control group used a microbially poor peat-based medium. [… N]o changes in the blood or the skin microbiota were seen. […] “This is the first time we can demonstrate that meaningful and natural human activity can increase the diversity of the microbiota of healthy adults and, at the same time, contribute to the regulation of the immune system."”
10. Cities Are Switching to Electric Vehicles Faster Than Individuals

“[M]ost large cities have adopted some kind of climate goal, and some of them are buying EVs for their municipal fleets at a faster rate than the general public. And that progress could speed up as more EVs enter the market and as cities get educated about grant funding and tax incentives that were passed over the last four years.”
May 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#chocolate#sustainability#farming#health#vermont#big oil#oil companies#climate change#cooling#technology#nuclear#malaria#vaccine#africa#unicef#eagles#livestock#england#birds#electric vehicles#glass#energy efficiency#habitat#conservation#lemur#zoo#gardening#urban gardening
334 notes
·
View notes