#great briton
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
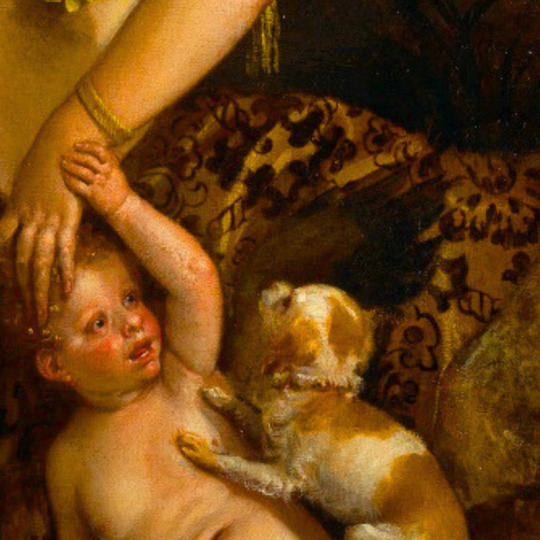
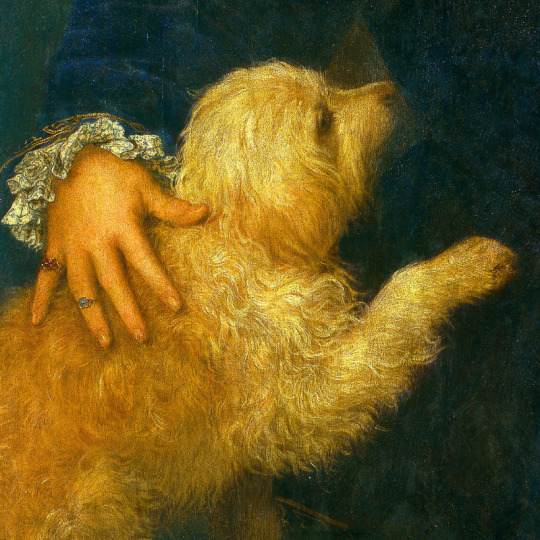
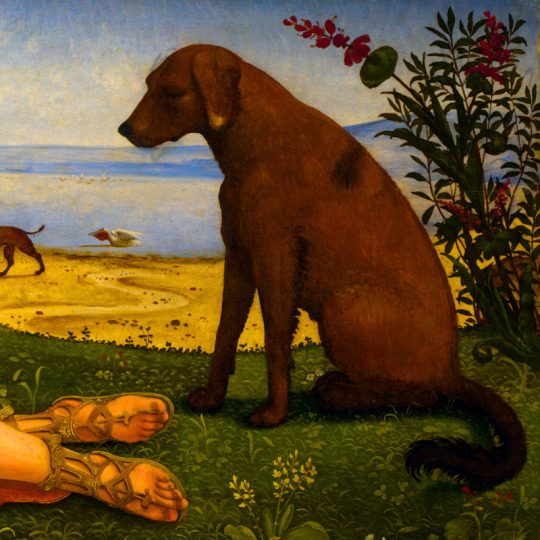
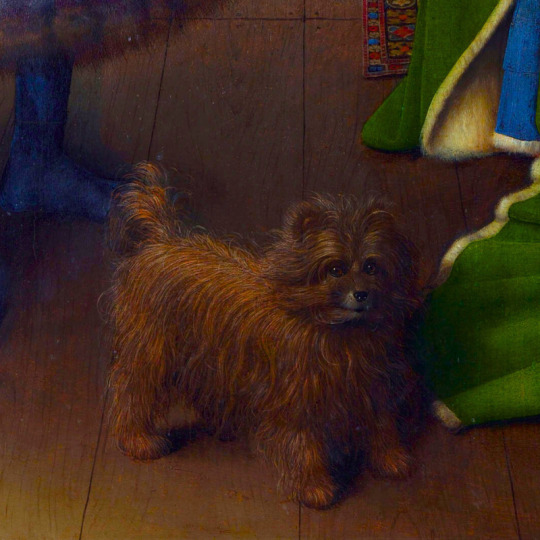
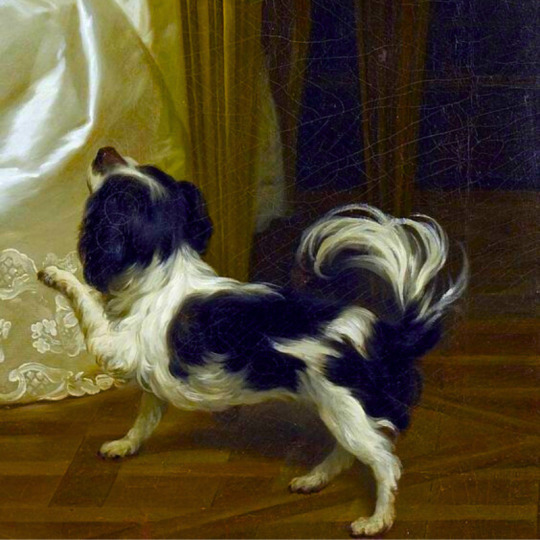
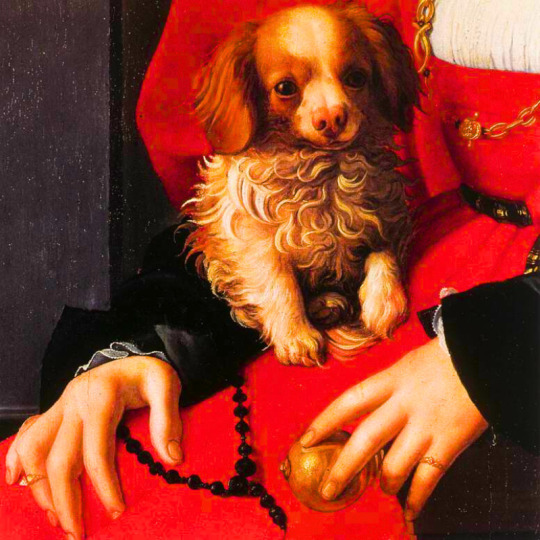
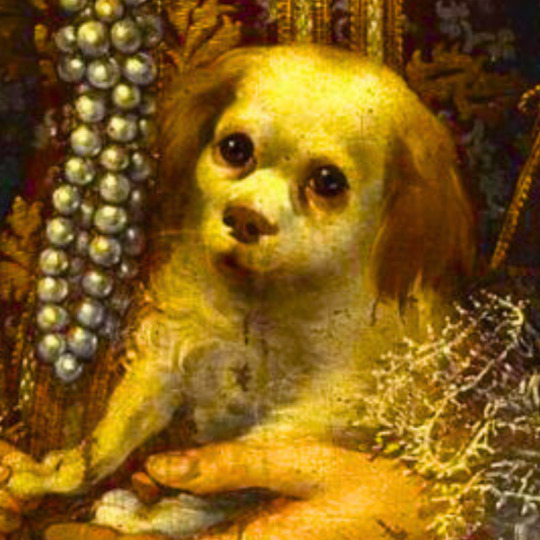
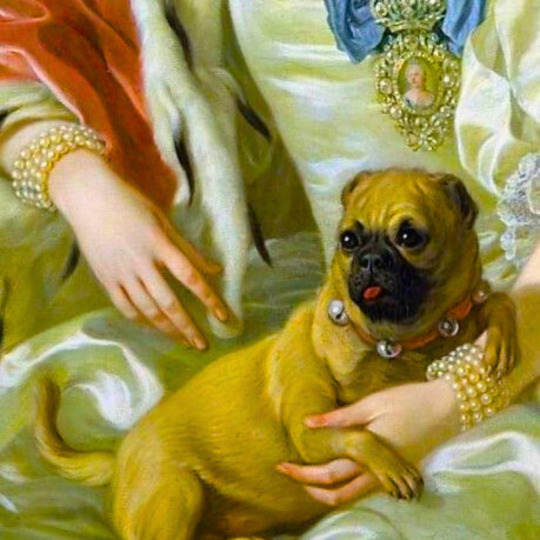
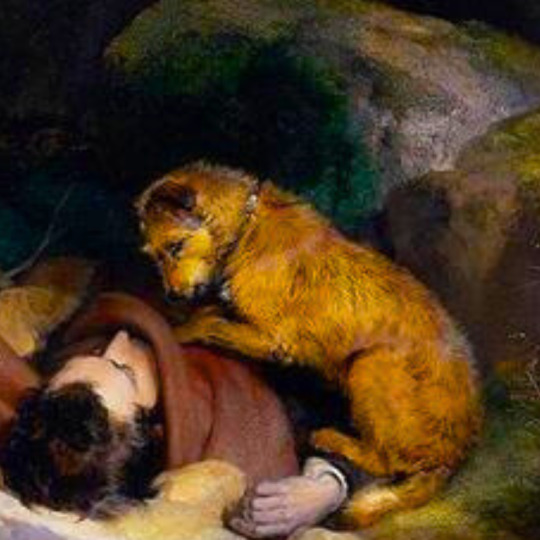
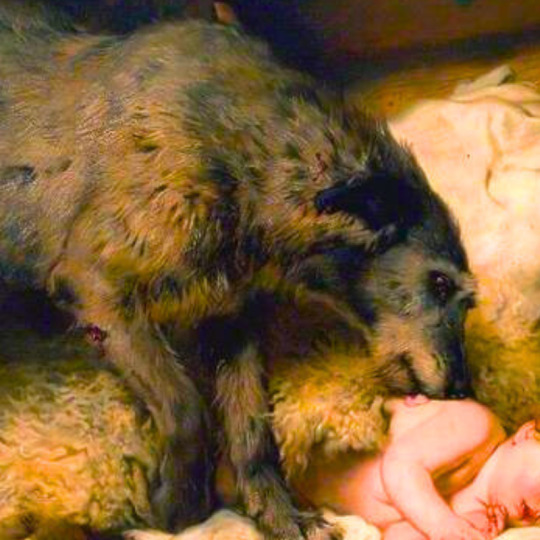
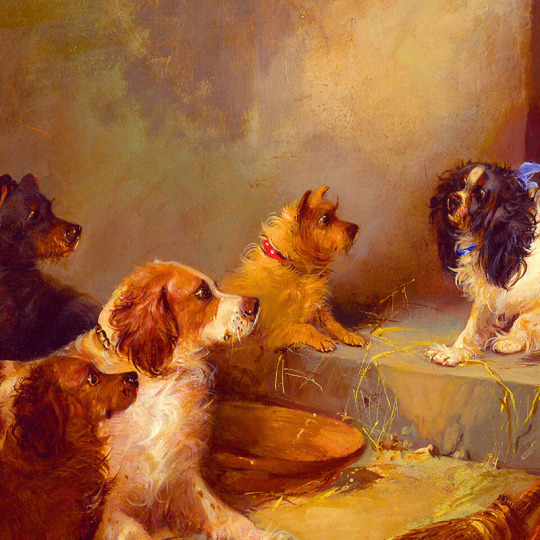
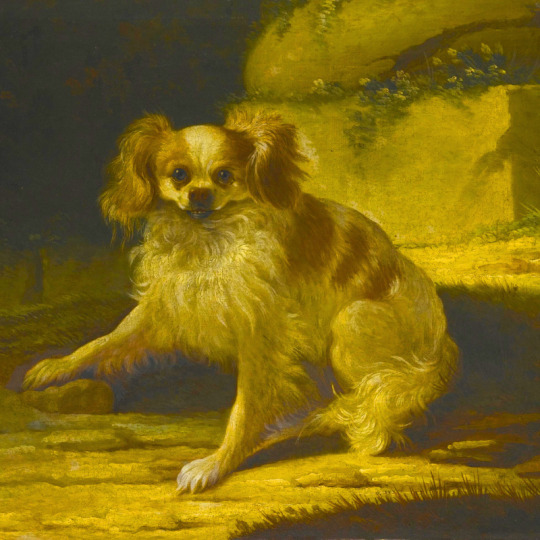
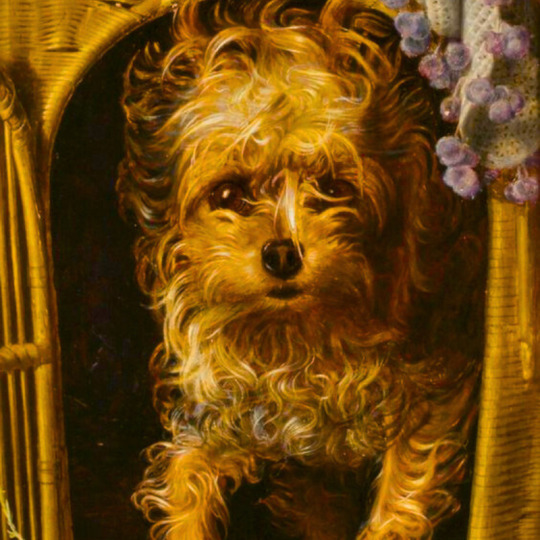
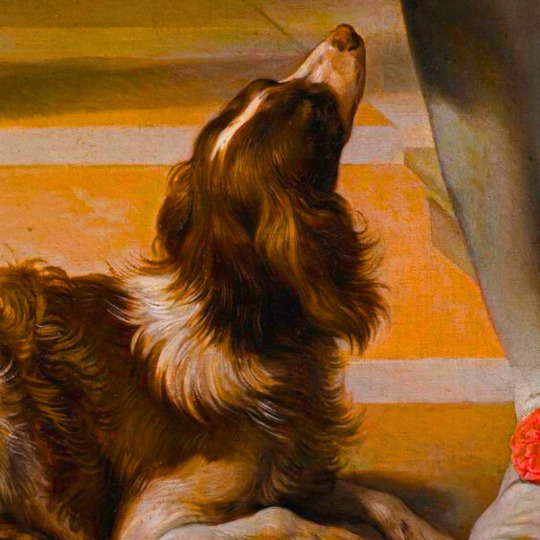
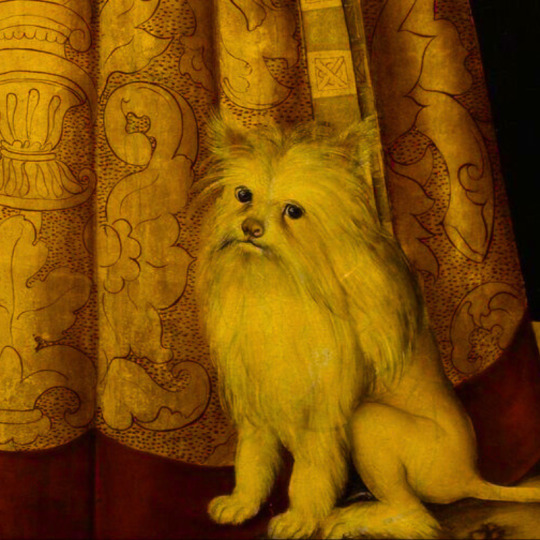
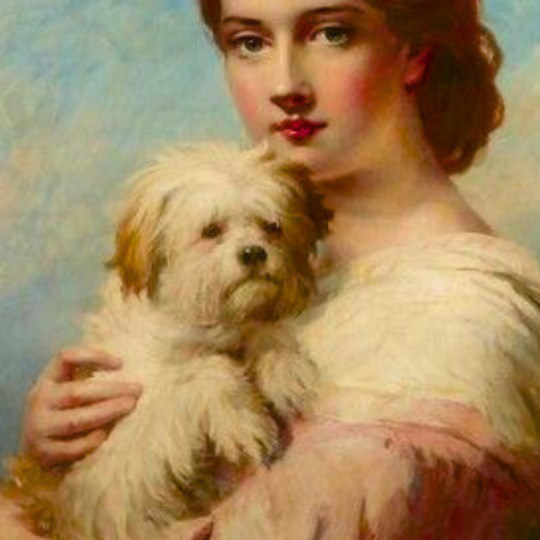
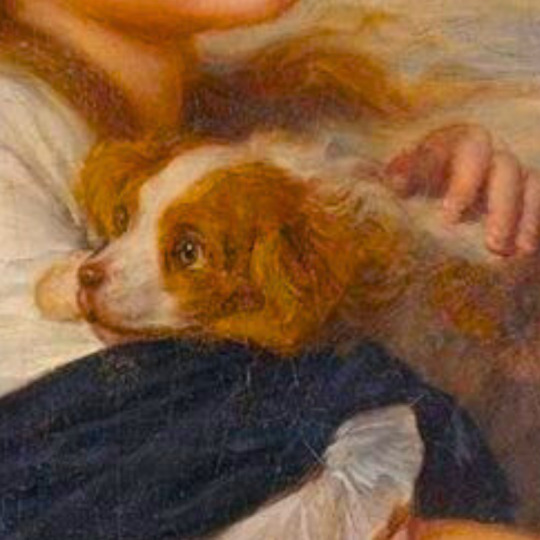
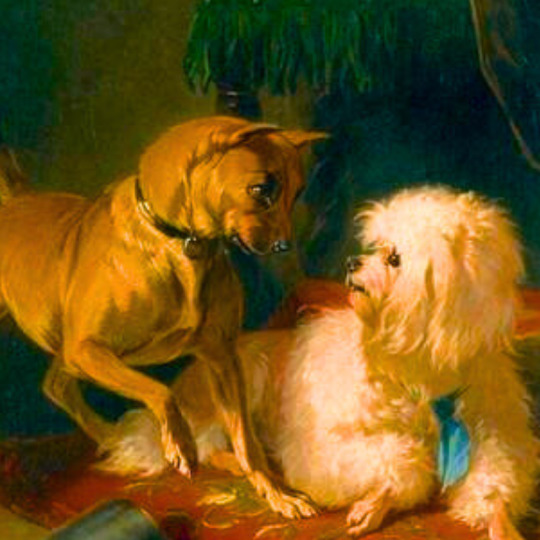
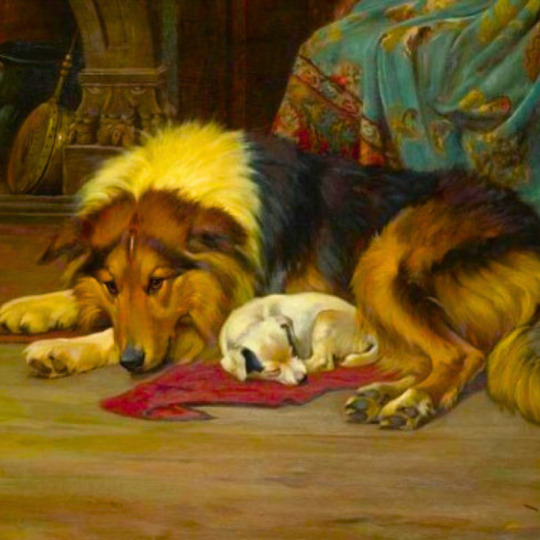
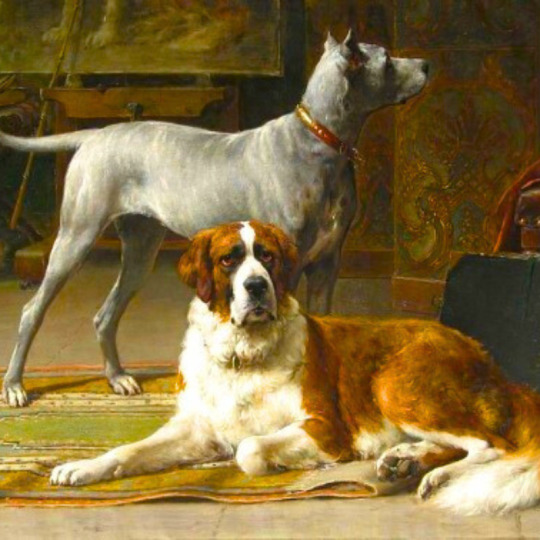
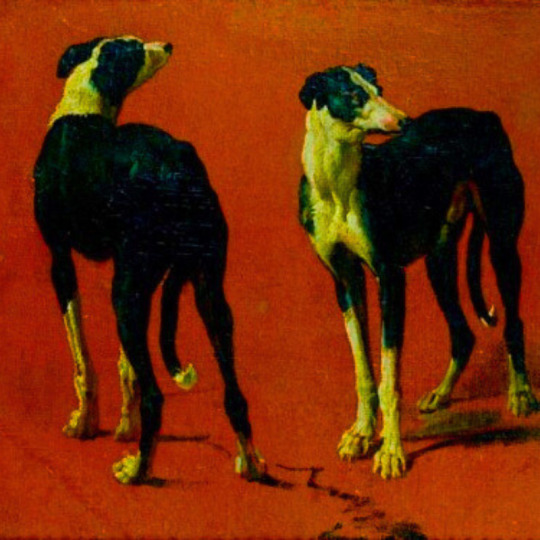
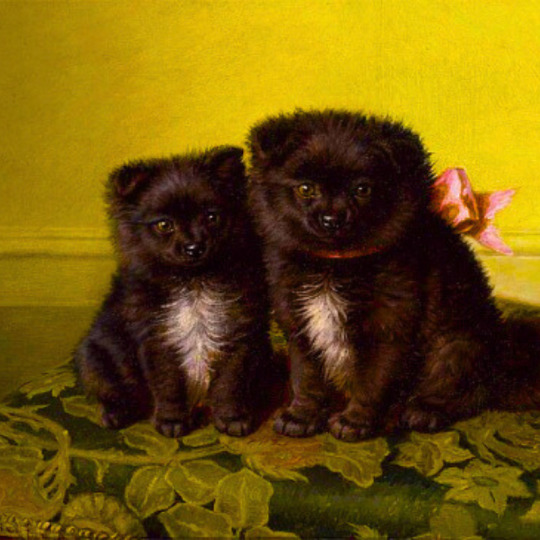






























dogs + art
#mars and venus with cupid and a dog by paola veronese#venus of urbino by titian#portrait of federico ii gonzaga by titian#the death of procris by piero di cosimo#arnolfini portrait by jan van eyck#venus and adonis by titian#portrait of the countesse d'egmont pignatelli in spanish costume by alexander roslin#portrait of a lady in red by agnolo bronzino#maselli family portrait by lavinia fontana#children of the marquis de bethune playing with dog by francois hubert drouais#portrait of princess ekaterina dmitrievna golitsyna by louis-michel van loo#attachment by edwin landseer#gelert by charles b. barber#the poor dog the shepherd's grave by edwin landseer#requiescat by briton riviere#marie leszczinska#my lady's pets by arthur wardle#the great debate by george armfield#portrait of a brown and white toy spaniel in a landscape by jacques-charled oudry#darby in his basket kennel by anthony frederick sandys#portrait of john 3rd baron monson of burton by pompeo girolamo batoni#portrait of dutchess katharina von mecklenburg by lucas cranach the elder#young lady and her dog by james john hill#young girl with a spaniel by jean-baptise greuze#the masters chair by john henry dolph#interior with two dogs by conradijn cunaeus#no walk today by wright baker#painter's studio by otto erelman#study of greyhounds by alexandre-francois desportes#sitting pretty by horatio henry couldrey
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
Britons full of frustration over Brexit, poll shows
Britons are so disappointed with Brexit that a majority would vote to re-join the EU if the referendum was held tomorrow, a new poll has revealed.
The poll, conducted by YouGov, found that nearly six in ten Britons would vote in favour of rejoining the European Union if a referendum was held tomorrow. According to the YouGov poll, Britons would vote in favour of returning to the EU by a score of 59 per cent to 41 per cent.
It’s no surprise that the public want to return to the EU, given how much worse many feel after Brexit and how many of the Vote Leave campaign promises have failed to materialise.
Brexit has cost the UK £140bn and the country could be £311bn worse off by the middle of the next decade, according to new analysis.
The Cambridge Econometrics report, commissioned by City Hall, also showed the average Londoner became almost £3,400 worse off last year as a result of Brexit.
Following the Labour Party’s convincing victory in last month’s general election, Prime Minister Keir Starmer stressed that the new government would not return the country to the EU, the single market or the customs union and would not seek a closer relationship with Brussels while in power.
Britain’s exit from the EU, which was finalised in 2020, has been widely described as disastrous and costly for London. According to a Bloomberg report in February citing economists at Goldman Sachs, the exit reduced Britain’s real GDP by about 5 per cent compared to the performance of its economic peers and left it with an inefficient economy and a sharply rising cost of living due to reduced trade and weak business investment.
However, economists acknowledged that some of these problems could also be linked to the coronavirus pandemic.
Read more HERE

#world news#news#world politics#europe#european news#uk#uk politics#uk news#england#united kingdom#london#britain#great britain#britons#brexit#european union#eu news#eu politics
11 notes
·
View notes
Link

Author
Hume, David, 1711-1776
Title The History of England in Three Volumes, Vol. I., Part A.
From the Britons of Early Times to King John
Language English
LoC Class
DA: History: General and Eastern Hemisphere: Great Britain, Ireland, Central Europe
Subject
Great Britain -- History
CategoryText
EBook-No.19211
Release Date Sep 8, 2006
Copyright Status Public domain in the USA.
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ask an older generation of white South Africans when they first felt the bite of anti-apartheid sanctions, and some point to the moment in 1968 when their prime minister, BJ Vorster, banned a tour by the England cricket team because it included a mixed-race player, Basil D’Oliveira. After that, South Africa was excluded from international cricket until Nelson Mandela walked free from prison 22 years later. The D’Oliveira affair, as it became known, proved a watershed in drumming up popular support for the sporting boycott that eventually saw the country excluded from most international competition including rugby, the great passion of the white Afrikaners who were the base of the ruling Nationalist party and who bitterly resented being cast out. For others, the moment of reckoning came years later, in 1985 when foreign banks called in South Africa’s loans. It was a clear sign that the country’s economy was going to pay an ever higher price for apartheid. Neither of those events was decisive in bringing down South Africa’s regime. Far more credit lies with the black schoolchildren who took to the streets of Soweto in 1976 and kicked off years of unrest and civil disobedience that made the country increasingly ungovernable until changing global politics, and the collapse of communism, played its part. But the rise of the popular anti-apartheid boycott over nearly 30 years made its mark on South Africans who were increasingly confronted by a repudiation of their system. Ordinary Europeans pressured supermarkets to stop selling South African products. British students forced Barclays Bank to pull out of the apartheid state. The refusal of a Dublin shop worker to ring up a Cape grapefruit led to a strike and then a total ban on South African imports by the Irish government. By the mid-1980s, one in four Britons said they were boycotting South African goods – a testament to the reach of the anti-apartheid campaign. . . . The musicians union blocked South African artists from playing on the BBC, and the cultural boycott saw most performers refusing to play in the apartheid state, although some, including Elton John and Queen, infamously put on concerts at Sun City in the Bophuthatswana homeland. The US didn’t have the same sporting or cultural ties, and imported far fewer South African products, but the mobilisation against apartheid in universities, churches and through local coalitions in the 1980s was instrumental in forcing the hand of American politicians and big business in favour of financial sanctions and divestment. By the time President FW de Klerk was ready to release Mandela and negotiate an end to apartheid, a big selling point for part of the white population was an end to boycotts and isolation. Twenty-seven years after the end of white rule, some see the boycott campaign against South Africa as a guide to mobilising popular support against what is increasingly condemned as Israel’s own brand of apartheid.
. . . continues at the guardian (21 May, 2021)
#israel#palestine#gaza#south africa#i think all of us need to seriously study the history and actions of the anti-apartheid movement#and apply these lessons to the israeli occupation
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Reasons to end the monarchy: Charles Edition
Well it's the coronation so you know what it's time for.
The entire concept of a monarchy is actively undemocratic. The head of state should not be someone who is only in that position because they were born into a certain family.
Having a monarchy upholds classism as a specific family of great wealth and power are viewed as superior to others.
They stand for a history of racism and imperialism. This country has done some truly terrible things in its history and the monarchy are a symbol of that. In order to attempt to begin to undo the harm that we have done, we need to remove this symbol of oppression.
The royal family have previously lobbied the government to hide their own personal wealth. Despite this, we are obviously aware that they have a large amount of wealth.
Prince Charles has himself lobbied the government on a number of occasions. His 'black spider memos' show that he has repeatedly pressured ministers on a wide range of topics from the Iraq war to badger culling to alternative therapies. He has used his power to lobby the government on subjects that would affect him.
The monarch does not occupy a ceremonial role as is frequently claimed. Ministers and civil servants have to consult the monarch. Civil servants have to get the consent of the royals on pieces of legislation, which can cause delays on implementation.
Even if the monarch did occupy a purely ceremonial role, as a literal billionaire he wields a ridiculously high amount of power over people.
Windsor Castle brings in less money than Windsor Legoland does. The many castles that are owned by the royal family could be used to create spaces for the public to enjoy or to be used as a shelter for the homeless. The Louvre in Paris used to be house of the French monarchy and gets over twenty times the tourists. Edinburgh castle hasn't had the monarchy live in it for centuries and yet still brings in tourism.
Prince Andrew is widely known to be connected to Jeffrey Epstein; yet he has not had to face any repercussions for his actions despite blatantly lying when being asked about his actions. The royal family have defended him and prevented him from facing the consequences of his actions.
They cost around £334 million per year. This money could be used to help the poor, given to the NHS, to repair and build infrastructure, to support small businesses that are struggling, pretty much anything.
The royal household publishes a much lower figure about the cost of the royal family, so they are actively trying to cover up their cost.
Charles has had access to confidential Cabinet papers, undermining our democracy.
He has publicly championed alternative medicine and has repeatedly promoted it. He sent at least seven letters to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, that then shortly relaxed the rules governing the labeling of herbal products, ones he as part of Charles's Duchy Originals produces.
He lobbied the health secretary regarding greater provision of alternative treatments on the NHS.
In 2018, 46% of Britons wanted him to abdicate immediately after Elizabeth died. He’s barely wanted by the country even with the sheer amount of pro-monarchy propaganda going around. Charles specifically is very unpopular.
In order to speak to him, broadcasters had to sign a 15-page contract, which includes Clarence house attending the rough and fine cut edits of films and if unhappy can remove that contribution, as well as stipulating that all questions directed at him must be pre-approved and vetted by his representative.
His personal wealth is £1.8 billion. He inherited a large amount of this from Elizabeth, with it being exempt from inheritance tax. Having an immunity from this tax when others don’t is ridiculous.
The Duchy of Cornwall was named in the Paradise papers.
The coronation is going to cost £100 million during a cost of living crisis.
People have been banned from protesting Charles with official warning letters were sent to anti-monarchists.
Protestors who block roads, airports and railways could face an entire year behind bars. Locking yourself to others, objects or buildings could go to prison for six months and face an unlimited fine. Police are allowed to head off disruption by stopping and searching protestors that they suspect.
The public were encouraged to swear allegiance to the new King when he gets sworn in, this is a deeply disturbing suggestion.
He's a billionaire who's going to use the public's money to celebrate himself.
The monarch has sweeping immunity from many laws
He owns business parks and small rented cottages, six of the ten top residential homes, 285,000 acres of mineral rich land. He’s ridiculously rich in a country where so many people are facing extreme poverty.
#uk politics#british royal family#fuck the monarchy#imperialism#royals#king charles III#may he end up like the first
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
Palantir’s NHS-stealing Big Lie

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in TUCSON (Mar 9-10), then SAN FRANCISCO (Mar 13), Anaheim, and more!

Capitalism's Big Lie in four words: "There is no alternative." Looters use this lie for cover, insisting that they're hard-nosed grownups living in the reality of human nature, incentives, and facts (which don't care about your feelings).
The point of "there is no alternative" is to extinguish the innovative imagination. "There is no alternative" is really "stop trying to think of alternatives, dammit." But there are always alternatives, and the only reason to demand that they be excluded from consideration is that these alternatives are manifestly superior to the looter's supposed inevitability.
Right now, there's an attempt underway to loot the NHS, the UK's single most beloved institution. The NHS has been under sustained assault for decades – budget cuts, overt and stealth privatisation, etc. But one of its crown jewels has been stubbournly resistant to being auctioned off: patient data. Not that HMG hasn't repeatedly tried to flog patient data – it's just that the public won't stand for it:
https://www.theguardian.com/society/2023/nov/21/nhs-data-platform-may-be-undermined-by-lack-of-public-trust-warn-campaigners
Patients – quite reasonably – do not trust the private sector to handle their sensitive medical records.
Now, this presents a real conundrum, because NHS patient data, taken as a whole, holds untold medical insights. The UK is a large and diverse country and those records in aggregate can help researchers understand the efficacy of various medicines and other interventions. Leaving that data inert and unanalysed will cost lives: in the UK, and all over the world.
For years, the stock answer to "how do we do science on NHS records without violating patient privacy?" has been "just anonymise the data." The claim is that if you replace patient names with random numbers, you can release the data to research partners without compromising patient privacy, because no one will be able to turn those numbers back into names.
It would be great if this were true, but it isn't. In theory and in practice, it is surprisingly easy to "re-identify" individuals in anonymous data-sets. To take an obvious example: we know which two dates former PM Tony Blair was given a specific treatment for a cardiac emergency, because this happened while he was in office. We also know Blair's date of birth. Check any trove of NHS data that records a person who matches those three facts and you've found Tony Blair – and all the private data contained alongside those public facts is now in the public domain, forever.
Not everyone has Tony Blair's reidentification hooks, but everyone has data in some kind of database, and those databases are continually being breached, leaked or intentionally released. A breach from a taxi service like Addison-Lee or Uber, or from Transport for London, will reveal the journeys that immediately preceded each prescription at each clinic or hospital in an "anonymous" NHS dataset, which can then be cross-referenced to databases of home addresses and workplaces. In an eyeblink, millions of Britons' records of receiving treatment for STIs or cancer can be connected with named individuals – again, forever.
Re-identification attacks are now considered inevitable; security researchers have made a sport out of seeing how little additional information they need to re-identify individuals in anonymised data-sets. A surprising number of people in any large data-set can be re-identified based on a single characteristic in the data-set.
Given all this, anonymous NHS data releases should have been ruled out years ago. Instead, NHS records are to be handed over to the US military surveillance company Palantir, a notorious human-rights abuser and supplier to the world's most disgusting authoritarian regimes. Palantir – founded by the far-right Trump bagman Peter Thiel – takes its name from the evil wizard Sauron's all-seeing orb in Lord of the Rings ("Sauron, are we the baddies?"):
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/01/the-palantir-will-see-you-now/#public-private-partnership
The argument for turning over Britons' most sensitive personal data to an offshore war-crimes company is "there is no alternative." The UK needs the medical insights in those NHS records, and this is the only way to get at them.
As with every instance of "there is no alternative," this turns out to be a lie. What's more, the alternative is vastly superior to this chumocratic sell-out, was Made in Britain, and is the envy of medical researchers the world 'round. That alternative is "trusted research environments." In a new article for the Good Law Project, I describe these nigh-miraculous tools for privacy-preserving, best-of-breed medical research:
https://goodlawproject.org/cory-doctorow-health-data-it-isnt-just-palantir-or-bust/
At the outset of the covid pandemic Oxford's Ben Goldacre and his colleagues set out to perform realtime analysis of the data flooding into NHS trusts up and down the country, in order to learn more about this new disease. To do so, they created Opensafely, an open-source database that was tied into each NHS trust's own patient record systems:
https://timharford.com/2022/07/how-to-save-more-lives-and-avoid-a-privacy-apocalypse/
Opensafely has its own database query language, built on SQL, but tailored to medical research. Researchers write programs in this language to extract aggregate data from each NHS trust's servers, posing medical questions of the data without ever directly touching it. These programs are published in advance on a git server, and are preflighted on synthetic NHS data on a test server. Once the program is approved, it is sent to the main Opensafely server, which then farms out parts of the query to each NHS trust, packages up the results, and publishes them to a public repository.
This is better than "the best of both worlds." This public scientific process, with peer review and disclosure built in, allows for frequent, complex analysis of NHS data without giving a single third party access to a a single patient record, ever. Opensafely was wildly successful: in just months, Opensafely collaborators published sixty blockbuster papers in Nature – science that shaped the world's response to the pandemic.
Opensafely was so successful that the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care commissioned a review of the programme with an eye to expanding it to serve as the nation's default way of conducting research on medical data:
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/better-broader-safer-using-health-data-for-research-and-analysis/better-broader-safer-using-health-data-for-research-and-analysis
This approach is cheaper, safer, and more effective than handing hundreds of millions of pounds to Palantir and hoping they will manage the impossible: anonymising data well enough that it is never re-identified. Trusted Research Environments have been endorsed by national associations of doctors and researchers as the superior alternative to giving the NHS's data to Peter Thiel or any other sharp operator seeking a public contract.
As a lifelong privacy campaigner, I find this approach nothing short of inspiring. I would love for there to be a way for publishers and researchers to glean privacy-preserving insights from public library checkouts (such a system would prove an important counter to Amazon's proprietary god's-eye view of reading habits); or BBC podcasts or streaming video viewership.
You see, there is an alternative. We don't have to choose between science and privacy, or the public interest and private gain. There's always an alternative – if there wasn't, the other side wouldn't have to continuously repeat the lie that no alternative is possible.

Name your price for 18 of my DRM-free ebooks and support the Electronic Frontier Foundation with the Humble Cory Doctorow Bundle.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/08/the-fire-of-orodruin/#are-we-the-baddies

Image: Gage Skidmore (modified) https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Peter_Thiel_(51876933345).jpg
CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#peter thiel#trusted research environment#opensafely#medical data#floss#privacy#reidentification#anonymization#anonymisation#nhs#ukpoli#uk#ben goldacre#goldacre report#science#evidence-based medicine#goldacre review#interoperability#transparency
530 notes
·
View notes
Text












Arthur of the Britons (1972-1973) | Under Camelot's Banner by Sarah Zettel | Excalibur (1981) | The Great Captains by Henry Treece | The Story of Sir Launcelot and His Companions by Howard Pyle | Sword of Lancelot (1963) | Exiled From Camelot by Cherith Baldry | The Adventures of Sir Galahad (1949) | Two Bits of Embroidery by Phyllis Ann Karr | The Adventures of Sir Lancelot (1956-1957) | The Sword and The Circle by Rosemary Sutcliff
#arthuriana#arthurian legend#arthurian mythology#arthurian literature#sir kay#sir kai#sir cei#arthur of the britons#sword of lancelot#excalibur 1981#the adventures of sir lancelot#the adventures of sir galahad#cherith baldry#phyllis ann karr#howard pyle#rosemary sutcliff#sarah zettel#henry treece#webweaves by L#my post
121 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (known in antiquity as the Vallum Hadriani or the Vallum Aelian) is a defensive frontier work in northern Britain which dates from 122 CE. The wall ran from coast to coast at a length of 73 statute miles (120 km). Though the wall is commonly thought to have been built to mark the boundary line between Britain and Scotland, this is not so; no one knows the actual motivation behind its construction but it does not delineate a boundary between two countries.
While the wall did simply mark the northern boundary of the Roman Empire in Britain at the time, theories regarding the purpose of such a massive building project range from limiting immigration, to controlling smuggling, to keeping the indigenous people at bay north of the wall. The wall continued in use until it was abandoned in the early 5th century CE.
Purpose
The military effectiveness of the wall has been questioned by many scholars over the years owing to its length and the positioning of the fortifications along the route. The argument goes that, had the wall actually been built as a defensive barrier, it would have been constructed differently and at another location. Regarding this, Professors Scarre and Fagan write,
Archaeologists and historians have long debated whether Hadrian's Wall was an effective military barrier…Whatever its military effectiveness, however, it was clearly a powerful symbol of Roman military might. The biographer of Hadrian remarks that the emperor built the wall to separate the Romans from the barbarians. In the same way, the Chinese emperors built the Great Wall to separate China from the barbarous steppe peoples to the north. In both cases, in addition to any military function, the physical barriers served in the eyes of their builders to reinforce the conceptual divide between civilized and noncivilized. They were part of the ideology of empire. (Ancient Civilizations, 313)
This seems to be the best explanation for the underlying motive behind the construction of Hadrian's Wall. The Romans had been dealing with uprisings in Britain since their conquest of the region. Although Rome's first contact with Britain was through Julius Caesar's expeditions there in 55/54 BCE, Rome did not begin any systematic conquest until the year 43 CE under the Emperor Claudius (r. 41-54 CE).
The revolt of Boudicca of the Iceni in 60/61 CE resulted in the massacre of many Roman citizens and the destruction of major cities (among them, Londinium, modern London) and, according to the historian Tacitus (56-117 CE), fully demonstrated the barbaric ways of the Britons to the Roman mind.
Boudicca's forces were defeated at The Battle of Watling Street by General Gaius Suetonius Paulinus in 61 CE. At the Battle of Mons Graupius, in the region which is now Scotland, the Roman General Gnaeus Julius Agricola won a decisive victory over the Caledonians under Calgacus in 83 CE. Both of these engagements, as well as the uprising in the north in 119 CE (suppressed by the Roman governor and general Quintus Pompeius Falco), substantiated that the Romans were up to the task of managing the indigenous people of Britain.
The suggestion that Hadrian's Wall, then, was built to hold back or somehow control the people of the north does not seem as likely as that it was constructed as a show of force. Hadrian's foreign policy was consistently “peace through strength” and the wall would have been an impressive illustration of that principle. In the same way that Julius Caesar built his famous bridge across the Rhine in 55 BCE simply to show that he, and therefore Rome, could go anywhere and do anything, Hadrian perhaps had his wall constructed for precisely the same purpose.
Continue reading...
213 notes
·
View notes
Text
This weird historical fiction book that I'm reading rn and also a nonfiction book which colm tóibín apparently wrote on the same topic which argue that irish ppl took anti british sentiment during the great famine too far and it's some major problem that people hated the british during the famine are so bizarre to me because obviously on one hand, you are the cruellest person ever and it astonishes me that the words "the irish should have been nicer to the british people who were starving and colonising them" have just come out of your mouth and [james joyce the dead voice] west briton! but on the other hand girl it was, how do I put this nicely, nearly two centuries ago
85 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Happy #FatTuesday! Here's a few costume designs by artist Charles Briton for the 1873 New Orleans Mardi Gras. See more great carnival designs, and learn about their creators, in our essay by @AllisonCMeier: https://publicdomainreview.org/essay/illustrating-carnival-remembering-the-overlooked-artists-behind-early-mardi-gras #MardiGras
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
Our 296 Noble and Worthy Contenders
Adhemar, Count of Anjou [Rufus Sewell], A Knight's Tale (2001)
Prince Aemond Targaryen [Ewan Mitchell], House of the Dragon (2022-)
Aguilar de Nerha [Michael Fassbender], Assassin's Creed (2016)
Ahchoo [Dave Chapelle], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Ahmad [Mahesh Jadu], Marco Polo (2014)
Ahmed Ibn Fahdlan [Antonio Banderas], The 13th Warrior (1999)
Alessandro Farnese [Diarmuid Noyes], Borgia (2011-2014)
King Alfred the Great [David Dawson], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Shah Ala ad Daula [Olivier Martinez], The Physician (2013)
Allan-A-Dale [Joe Armstrong], BBC’s Robin Hood (2006-2009)
Sultan Alauddin [Ranver Singh], Padmavaat (2018)
Amarendra Baahubali [Prabhas], Baahubali Series (2015-2017)
Amleth [Alexander Skarsgård], The Northman (2022)
Ancelyn ap Gwalchmai [Marcus Gilbert], Doctor Who: “Battlefield” (1989)
Antonius Block [Max von Sydow], The Seventh Seal (1957)
Aragorn, Son of Arathorn [Viggo Mortensen], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Arman [Matevy Lykov], I Am Dragon (2015)
Arn Magnusson [Joakim Nätterqvist], Arn: The Knight Templar (2007)
Arondir [Ismael Cruz Córdova], The Rings of Power (2022-)
Arthur Pendragon [Oliver Tobias], Arthur of the Britons (1972, 1973)
King Arthur [Richard Harris], Camelot (1967)
King Arthur [Graham Chapman], Monty Python and the Holy Grail (1975)
King Arthur [Nigel Terry], Excalibur (1981)
King Arthur [Sean Connery], First Knight (1995)
King Arthur [Alexandre Astier], Kaamelott (2004-2009)
King Arthur [Bradley James], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
King Arthur [Charlie Hunnam], King Arthur: Legend of the Sword (2017)
Asbjörn [Tom Hopper], Northmen: A Viking Saga (2014)
Ash Williams [Bruce Campbell], Army of Darkness (1992)
Asneez [Isaac Hayes], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Athelstan [George Blagden], Vikings (2013-2020)
Azeem [Morgan Freeman], Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves (1991)
Azog the Defiler [Manu Bennett], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Balian de Ibelin [Orlando Bloom], Kingdom of Heaven (2005)
Bard the Bowman [Luke Evans], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Ser Barristan Selmy [Ian McIlhinney], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Father Beocca [Ian Hart], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Beowulf [Gerard Butler], Beowulf & Grendel (2005)
Bilbo Baggins [Martin Freeman], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Bjørn Ironside [Alexander Ludwig], Vikings (2013-2020)
Bofur [James Nesbitt],The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Boromir, Son of Denethor [Sean Bean], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Sir Bowen [Dennis Quaid], Dragonheart (1996)
Sir Brian de Bois-Guilbert [Sam Neill], Ivanhoe (1982)
Sir Brian de Bois-Guilbert [Ciaran Hinds], Ivanhoe (1997)
Bronn [Jerome Flynn], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Brother Cadfael [Derek Jacobi], Cadfael (1994-1998)
Carlos I [Álvaro Cervantes], Carlos Rey Emperador (2015-2016)
Caspian X [Ben Barnes], The Chronicles of Narnia (2010)
King Caspian X [Samuel West], Prince Caspian and the Voyage of the Dawn Treader (1989)
Cesare Borgia [Mark Ryder], Borgia (2011-2014)
Cesare Borgia [Francois Arnaud], The Borgias (2011-2013)
Charles Brandon [Henry Cavill], The Tudors (2007-2010)
Prince Charmont [Hugh Dancy], Ella Enchanted (2004)
Prince Chauncley [Daniel Radcliffe], Miracle Workers: The Dark Ages (2020)
Chris Vexler [Karan Soni], Miracle Workers: The Dark Ages (2020)
Chu Hun [Peter Ho], Double World (2020)
“Cinderella’s Prince” [Chris Pine], Into the Woods (2014)
Connor MacLeod [Christopher Lambert], Highlander (1986)
Corlys Velaryon [Steve Toussaint], House of the Dragon (2022-)
Ser Criston Cole [Fabien Frankel], House of the Dragon (2022-)
Daario Naharis [Michiel Huisman], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Prince Daemon Targaryen [Matt Smith], House of the Dragon (2022)
Darkness [Tim Curry], Legend (1985)
Ser Davos Seaworth [Liam Cunningham], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Prince Dastan [Jake Gyllenhaal], Prince of Persia: The Sands of Time (2010)
Dong Yilong [Henry Lau], Double World (2020)
Khal Drogo [Jason Momoa], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Durotan [Toby Kebbell], Warcraft (2016)
Eamon Valda [Abdul Salis], The Wheel of Time (2022-)
King Ecbert Ealhmunding [Linus Roache], Vikings (2013-2020)
Lord Eddard Stark [Sean Bean], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Edgin Darvis [Chris Pine], Dungeons & Dragons: Honour Among Thieves (2023)
King Edmund the Just [Skandar Keynes, Mark Wells], The Chronicles of Narnia (2005-2010)
King Edward I Plantagenet [Stephen Dillane], Outlaw King (2018)
King Edward III Plantagenet [Blake Ritson], A World Without End (2012)
King Edward IV Platagenet [Max Irons], The White Queen (2013)
Edward, the Black Prince [James Purefoy], A Knight’s Tale (2001)
Edward Seymour, Earl of Hertford [Claude Rains], The Prince and the Pauper (1937)
Elendil [Lloyd Owen], The Rings of Power (2022-)
Elrond Half-elven [Hugo Weaving], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Elrond Half-elven [Robert Aramayo], The Rings of Power (2022-)
Sir Elyan [Adetomiwa Edun], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Éomer, Son of Éomund [Karl Urban], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Erik Thurgilson [Christian Hillborg], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Étienne de Navarre [Rutger Hauer], Ladyhawke (1985)
Faramir, Son of Denethor [David Wenham], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Fezzik [André the Giant], The Princess Bride (1987)
Fili [Dean O’Gorman], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Finan [Mark Rowley], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Fjölnir [Claes Bang], The Northman (2022)
Forge Fitzwilliam [Hugh Grant], Dungeons & Dragons: Honor Among Thieves (2023)
Francesco de Pazzi [Matteo Martari], Medici (2016-2019)
Francois Villon [Ronald Colman], If I Were King (1938)
Frodo Baggins [Elijah Wood], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Sir Galahad [Michael Palin], Monty Python and the Holy Grail (1975)
Galavant [Joshua Sasse], Galavant (2015-2016)
Galessin, Duke of Orkney [Alexis Hénon], Kaamelott (2004-2009)
Gandalf [Ian McKellan], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Gawain [Dev Patel], The Green Knight (2021)
Gendry Waters [Joe Dempsie], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Geoffrey Chaucer [Pier Paolo Pasolini], The Canterbury Tales (1972)
Geoffrey Chaucer [Paul Bettany], A Knight’s Tale (2001)
George Plantagenet, Duke of Clarence [David Oakes], The White Queen (2013)
Geralt z Rivii [Michał Żebrowski], Wiedźmin {The Witcher} (2002)
Geralt of Rivia [Henry Cavill], The Witcher (2019-)
Gest [Jakob Þór Einarsson], Hrafninn flýgur {When the Raven Flies}(1984)
Gimli, Son of Gloin [John Rhys-Davies], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Giuliano de Medici [Bradley James], Medici (2016-2019)
Glenstorm [Cornell John], The Chronicles of Narnia: Prince Caspian (2008)
Prince Graydon Hastur [Tony Revolori], Willow (2022)
Gríma Wormtongue [Brad Dourif], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Gu Tingye [Feng Shaofeng], The Story of Minglan (2018)
Guildenstern [Tim Roth], Rosencrantz and Guildenstern Are Dead (1990)
Gündoğdu Bey [Kaan Taşaner], Diriliş: Ertuğrul {Resurrection: Ertuğrul} (2014-2019)
Sir Guy of Gisbourne [Basil Rathbone], The Adventures of Robin Hood (1938)
Sir Guy of Gisburne [Robert Addie], Robin of Sherwood (1984-1986)
Sir Guy of Gisborne [Michael Wincott], Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves (1991)
Sir Guy of Gisborne [Richard Armitage], BBC’s Robin Hood (2006-2009)
Sir Gwaine [Eoin Macken], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Haldir of Lothόrien [Craig Parker], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Prince Hamlet [Laurence Olivier], Hamlet (1948)
Prince Hamlet [Christopher Plummer], Hamlet at Elsinore (1964)
Hamlet [Iain Glen], Rosencrantz and Guildenstern Are Dead (1990)
Lord Harekr [Bradley James], Vikings: Valhalla (2022-)
King Henry II Plantagenet [Peter O’Toole], Becket (1964)
King Henry II Plantagenet [Peter O’Toole], The Lion in Winter (1968)
King Henry V Plantagenet [Laurence Olivier], Henry V (1944)
King Henry V Plantagenet [Kenneth Branagh], Henry V (1989)
King Henry V Plantagenet [Tom Hiddleston], The Hollow Crown (2012-2016)
Henry VII Tudor [Luke Treadaway], The Hollow Crown (2012-2016)
King Henry VIII [Ray Winstone], Henry VIII (2003)
Prince Henry [Dougray Scott], Ever After (1998)
Hubert Hawkins [Danny Kaye], The Court Jester (1955)
Hugh Beringar [Sean Pertwee], Cadfael (1994-1998)
Prince Humperdink [Chris Sarandon], The Princess Bride (1987)
Inigo Montoya [Mandy Patinkin], The Princess Bride (1987)
Isildur, Son of Elendil [Maxim Baldry], The Rings of Power (2022-)
Ivanhoe [Anthony Andrews], Ivanhoe (1982)
Ivar the Boneless [Alex Høgh Andersen], Vikings (2013-2020)
Jacques le Gris [Adam Driver], The Last Duel (2021)
Jack [Tom Cruise], Legend (1985)
Jafar [Marwan Kenzari], Aladdin (2019)
Ser Jaime Lannister [Nikolaj Coster-Waldau], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
James Douglas [Aaron Taylor Johnson], Outlaw King (2018)
Jareth, the Goblin King [David Bowie], Labyrinth (1986)
Jaskier [Joey Batey], The Witcher (2019-)
Prince Jingim [Remy Hii], Marco Polo (2014)
Little John [Nicol Williamson], Robin and Marian (1976)
Little John [Eric Allan Kramer], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Prince John [Claude Rains], The Adventures of Robin Hood (1938)
Prince John [Richard Lewis], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Prince John [Oscar Isaac], Robin Hood (2010)
Jon Snow [Kit Harrington], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Ser Jorah Mormont [Iain Glen], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Kai [Michael Gothard], Arthur of the Britons (1972, 1973)
Kili [Aiden Turner], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
The Kurgan [Clancy Brown], Highlander (1986)
al’Lan Mandragoran [Daniel Henney], The Wheel of Time (2022)
Sir Lancelot [Luc Simon], Lancelot du Lac (1974)
Sir Lancelot [Nicholas Clay], Excalibur (1981)
Sir Lancelot [Richard Gere], First Knight (1995)
Sir Lancelot [Santiago Cabrera], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Legolas Greenleaf [Orlando Bloom], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Leofric [Adrian Bower], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Sir Leon [Rupert Young], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Lin Shu [Hu Ge], Nirvana in Fire {Lángyá Bǎng} (2015)
Loial [Hammed Animashaun], The Wheel of Time (2022-)
Lurtz [Lawrence Makoare], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Madmartigan [Val Kilmer], Willow (1988)
Le Maître d'Armes (the fencing master) [Christian Bujeau], Kaamelott (2005-2009)
“Man With Snake” [Barry John Clarke], Edward II (1991)
King Mark of Cornwall [Rufus Sewell], Tristan & Isolde (2006)
Martin [Rutger Hauer], Flesh + Blood (1985)
Massetto [Dave Franco], The Little Hours (2017)
Matrim “Mat” Cauthon [Donal Finn], The Wheel of Time (2022)
“The Mayor of Hamelin” [Claude Rains], The Pied Piper of Hamelin (1957)
Mehmed II [Cem Yiğit Üzümoğlu], Rise of Empires: Ottoman (2020-2022)
Meriadoc “Merry” Brandybuck [Dominic Monaghan], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Merlin [Nicol Williamson], Excalibur (1981)
Merlin [Sam Niell], Merlin (1998)
Merlin [Colin Morgan], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Mikoláš Kozlík [František Velecký], Marketa Lazarová (1967)
Miles Hendon [Errol Flynn], The Prince and the Pauper (1937)
Mordred [Jason Done], Merlin (1998)
Much [Sam Troughton], BBC’s Robin Hood (2006-2009)
Murtagh Morzansson [Garrett Hedlund], Eragon (2002)
The Mute [Jon Bernthal], Pilgrimage (2017)
Nasir [Mark Ryan], Robin of Sherwood (1984-1986)
Niankoro [Issiaka Kane], Yeelen (1987)
Niccoló Machiavelli [Julian Bleach], The Borgias (2011-2013)
Niccoló Machiavelli [Thibaut Evrard], Borgia (2011-2014)
Nicodemus Ravens [Jakob Oftebro], Skammerens Datter {The Shamer's Daughter} (2015)
Prince Oberyn Martell [Pedro Pascal], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Odda the Elder [Simon Kunz], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
“One-Eye” [Mads Mikkelsen], Valhalla Rising (2009)
Osferth [Ewan Mitchell], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Sir Percival [Tom Hopper], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Peregrin “Pippin” Took [Billy Boyd], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Pero Tovar [Pedro Pascal], The Great Wall (2016)
Perrin Aybara [Marcus Rutherford], The Wheel of Time (2022-)
Petyr “Littlefinger” Baelish [Aiden Gillen], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
High King Peter the Magnificent [William Moseley, Noah Huntley], The Chronicles of Narnia (2005-2010)
Philip II [Timothy Dalton], The Lion in Winter (1968)
Phillippe Gaston [Matthew Broderick], Ladyhawke (1985)
“The Player” [Richard Dreyfuss], Rosencrantz and Guildenstern are Dead (1990)
Podrick Payne [Daniel Portman], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Prince Prospero [Vincent Price], The Masque of the Red Death (1964)
Ragnar Lothbrok [Travis Fimmel], Vikings (2013-2020)
Ramsay Bolton [Iwan Rheon], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Rand al’Thor [Josha Stradowski], The Wheel of Time (2022-)
Ravenhurst [Basil Rathbone], The Court Jester (1955)
“The Red Death” [John Westbrook], The Masque of the Red Death (1964)
Renly Baratheon [Gethin Anthony], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Richard Cypher [Craig Horner], Legend of the Seeker (2008-2010)
King Richard [Timothy Omundson], Galavant (2015-2016)
Richard II Plantagenet [Ben Whishaw], The Hollow Crown (2012-2016)
Richard III Plantagenet [Aneurin Barnard], The White Queen (2013)
King Richard III Plantagenet [Benedict Cumberbatch], The Hollow Crown (2012-2016)
King Richard IV [Brian Blessed], The Black Adder (1982)
Rilk [Jesse Lee Keeter] JourneyQuest (2010)
Robert of Artois [Jean Piat], The Accursed Kings (1972)
Robert of Huntingdon [Jason Connery], Robin of Sherwood (1984)
Robert the Bruce [Chris Pine], Outlaw King (2018)
Robin Hood [Errol Flynn], The Adventures of Robin Hood (1938)
Robin Hood [Richard Todd], The Story of Robin Hood and His Merrie Men (1952)
Robin Hood [Sean Connery], Robin and Marian (1976)
Robin Hood [Michael Praed], Robin of Sherwood (1984)
Robin Hood [Kevin Costner], Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves (1991)
Robin Hood [Cary Elwes], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Robin Hood [Jonas Armstrong], BBC’s Robin Hood (2006-2009)
Robin Hood [Tom Riley], Doctor Who: “The Robot of Sherwood” (2014)
Robin Longstride [Russell Crowe], Robin Hood (2010)
Rodrigo Borgia [Jeremy Irons], The Borgias (2011-2013)
Rollo [Clive Standen], Vikings (2013-2020)
Roose Bolton [Michael McElhatton], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Rosencrantz [Gary Oldman], Rosencrantz and Guildenstern Are Dead (1990)
Count Rugen [Christopher Guest], The Princess Bride (1987)
Saburo Naotora Ichimonji [Ryu Daisuke], Ran (1985)
Saladin [Milind Soman], Arn: The Knight Templar (2007), Arn: The Kingdom at Road’s End (2008)
Samwise Gamgee [Sean Astin], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Sandor Clegane [Rory McCann], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Saruman [Christopher Lee], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Stannis Baratheon [Stephen Dillane], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Tajomaru [Toshiro Mifune], Rashomon (1950)
“The Sherriff of Nottingham” [Alan Wheatley], The Adventures of Robin Hood (1955-1959)
“The Sherriff of Nottingham” [Peter Cushing], The Sword of Sherwood Forest (1960)
“The Sherriff of Nottingham” [Alan Rickman], Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves (1991)
“The Sherriff of Rottingham” [Roger Rees], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Sid [Luke Youngblood], Galavant (2015-2016)
Sihtric Kjartansson [Arnas Fedaravicius], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Simon Aumar [Justice Smith], Dungeons & Dragons: Honor Among Thieves (2023)
Steapa [Adrian Bouchet], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Syrio Forel [Miltos Yerolemou], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
“Taunting French Guard” [John Cleese], Monty Python and the Holy Grail (1975)
Theoden, Son of Thengel [Bernard Hill], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Thierry de Janville [Jean-Claude Drouot], Thierry la Fronde (1963-1966)
Thomas Becket [Richard Burton], Becket (1964)
Thomas Cromwell [Mark Rylance], Wolf Hall (2015-2024)
Sir Thomas Gray [Nigel Terry], Covington Cross (1992)
Thorin Oakenshield [Richard Armitage], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Thranduil, The Elvenking [Lee Pace], The Hobbit Trilogy (2012-2014)
Thraxus Boorman [Amar Chadha-Patel], Willow (2022)
Tom Builder [Rufus Sewell], The Pillars of the Earth (2010)
Tormund Giantsbane [Kristofer Hivju], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Sir Tristan [Kingsley Ben-Adir], King Arthur: Legend of the Sword (2017)
Trumpkin [Peter Dinklage], The Chronicles of Narnia: Prince Caspian (2008)
Mr. Tumnus [James McAvoy], The Chronicles of Narnia: The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe (2005)
Turgut Alp [Cengiz Coşkun], Diriliş: Ertuğrul (2014-2019)
Tyrion Lannister [Peter Dinklage], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Lord Tywin Lannister [Charles Dance], Game of Thrones (2011-2019)
Ubbe [Jordan Patrick Smith], Vikings (2013-2020)
Uglúk [Nathaniel Lees], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Uhtred of Bebbanburgh [Alexander Dreymon], The Last Kingdom (2015-2022)
Ulrich von Jungingen [Stanislaw Jasiukiewicz], Knights of the Teutonic Order (1960)
“Unnamed Elf Escort” [Bret McKenzie], The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003)
Uther Pendragon [Gabriel Byrne], Excalibur (1981)
Uther Pendragon [Anthony Stewart Head], BBC’s Merlin (2008-2012)
Vaisey, Sheriff of Nottingham [Keith Allen], BBC’s Robin Hood (2006-2009)
Vlad III Dracula [Luke Evans], Dracula Untold (2014)
King Vortigen [Jude Law], King Arthur: Legend of the Sword (2017)
Wat [Alan Tudyk], A Knight’s Tale (2001)
Wen Kexing [Gong Jun], Word of Honor (2021)
Westley [Cary Elwes], The Princess Bride (1987)
Wil Ohmsford [Austin Butler], The Shannara Chronicles (2016)
William Wallace [Mel Gibson], Braveheart (1995)
Will Scarlet O’Hara [Matthew Porretta], Robin Hood: Men in Tights (1993)
Will Scarlett [Patrick Knowles], The Adventures of Robin Hood (1938)
Will Scarlett [Christian Slater], Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves (1991)
Will Scarlett [Harry Lloyd], BBC’s Robin Hood, (2006-2009)
William Thatcher [Heath Ledger], A Knight’s Tale (2001)
Willow Ufgood [Warwick Davis], Willow (2022)
Xenk Yendar [Regé-Jean Page], Dungeons & Dragons: Honor Among Thieves (2023)
Zbyszko z Bogdanca [Mieczyslaw Kalenik], Knights of the Teutonic Order (1960)
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
Britons warned to check valid passports before going on holiday
UK citizens who want to spend holiday in any of the EU destinations are advised to check the validity of their passport before travelling to the Schengen area, Schengen Visa Info reports.
Under Schengen rules, passports of third-country nationals, including UK citizens after Brexit, must be valid for at least three more months after leaving the EU. Otherwise, these citizens may face with serious consequences.
As well as passport validity requirements, British passports must be issued within ten years before entering the Schengen area, so Britons should now also check the date of issue of their passport. UK’s Foreign Office said in a statement:
“Contact the embassy of the country you are visiting if you think that your passport does not meet both of these requirements. Renew your passport if you need to.”
Britons are also reminded to check the stamps in their passports when entering or leaving the Schengen area, which are checked by border guards and indicate whether the 90-day visa-free limit for short stays has been respected.
Read more HERE

#world news#world politics#news#europe#european news#uk news#uk#uk politics#england#united kingdom#great britain#britons#passport photos#passport services#passport renewal#visit#holiday#destination#vacation#traveling#travel#travelling#schengen visa
1 note
·
View note
Text
Did the ancient Celts really paint themselves blue?
Part 2: Irish tattoos
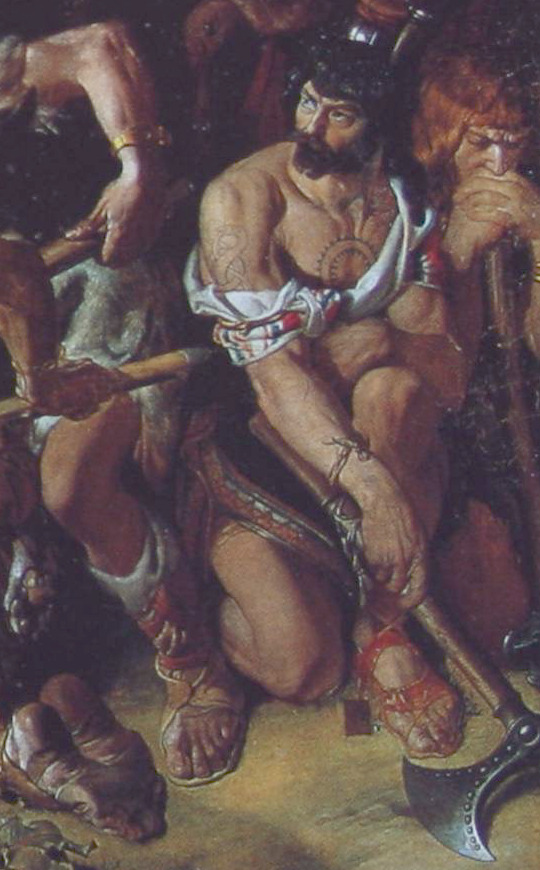
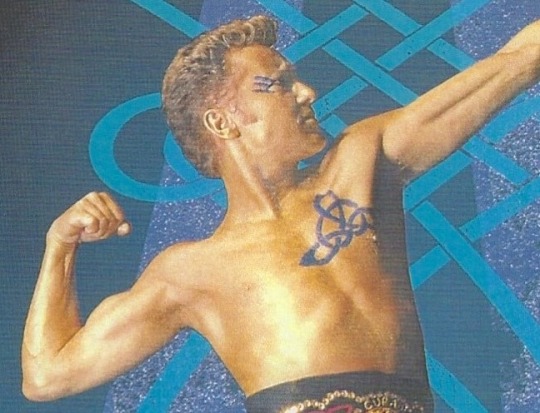
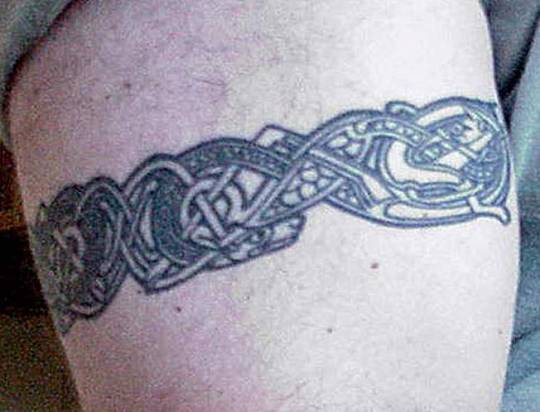




Clockwise from top left: Deirdre and Naoise from the Ulster Cycle by amylouioc, detail from The Marriage of Strongbow and Aoife by Daniel Maclise, a modern Celtic revival tattoo, Michael Flatley in a promotional image for the Irish step dance show 'Lord of the Dance'
This is my second post exploring the historical evidence for our modern belief that the ancient and medieval Insular Celts painted or tattooed themselves with blue pigment. In the first post, I discussed the fact that body paint seems to have been used by residents of Great Britain between approximately 50 BCE to 100 CE. In this post, I will examine the evidence for tattooing.
Once again, I am looking at sources pertaining to any ethnic group who lived in the British Isles, this time from the Roman Era to the early Middle Ages. The relevant text sources range from approximately 200 CE to 900 CE. I am including all British Isles cultures, because a) determining exactly which Insular culture various writers mean by terms like ‘Briton’, ‘Scot’, and ‘Pict’ is sometimes impossible and b) I don’t want to risk excluding any relevant evidence.
Continental Written Sources:
The earliest written source to mention tattoos in the British Isles is Herodian of Antioch’s History of the Roman Empire written circa 208 CE. In it, Herodian says of the Britons, "They tattoo their bodies with colored designs and drawings of all kinds of animals; for this reason they do not wear clothes, which would conceal the decorations on their bodies" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). Herodian is probably reporting second-hand information given to him by soldiers who fought under Septimius Severus in Britain (MacQuarrie 1997) and shouldn't be considered a true primary source.
Also in the early 3rd century, Gaius Julius Solinus says in Collectanea Rerum Memorabilium 22.12, "regionem [Brittaniae] partim tenent barbari, quibus per artifices plagarum figuras iam inde a pueris variae animalium effigies incorporantur, inscriptisque visceribus hominis incremento pigmenti notae crescunt: nec quicquam mage patientiae loco nationes ferae ducunt, quam ut per memores cicatrices plurimum fuci artus bibant."
Translation: "The area [of Britain] is partly occupied by barbarians on whose bodies, from their childhood upwards, various forms of living creatures are represented by means of cunningly wrought marks: and when the flesh of the person has been deeply branded, then the marks of the pigment get larger as the man grows, and the barbaric nations regard it as the highest pitch of endurance to allow their limbs to drink in as much of the dye as possible through the scars which record this" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
This passage, like Herodian's, is clearly a description of tattooing, not body staining or painting. That said, I have no idea of tattoos actually work like this. I would think this would result in the adult having a faded, indistinct tattoo, but if anyone knows otherwise, please tell me.
The poet Claudian, writing in the early 5th c., is the first to specifically mention the Picts having tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). In De Bello Gothico he says, "Venit & extremis legio praetenta Britannis,/ Quæ Scoto dat frena truci, ferroque notatas/ Perlegit exanimes Picto moriente figuras."
Translation: "The legion comes to make a trial of the most remote parts of Britain where it subdues the wild Scot and gazes on the iron-wrought figures on the face of the dying Pict" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
Last, and possibly least, of our Mediterranean sources is Isidore of Seville. In the early 7th c. he writes, "the Pictish race, their name derived from their body, which the efficient needle, with minute punctures, rubs in the juices squeezed from native plants so that it may bring these scars to its own fashion [. . .] The Scotti have their name from their own language by reason of [their] painted body, because they are marked by iron needles with dark coloring in the form of a marking of varying shapes." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
Isidore is the earliest writer to explicitly link the name 'Pict' to their 'painted' (Latin: pictus) i.e. tattooed bodies. Isidore probably borrowed information for his description from earlier writers like Claudian (MacQuarrie 1997).
In the 8th century, we have a source that definitely isn't Romans recycling old hearsay. In 786, a pair of papal legates visited the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria (Story 1995). In their report to Pope Hadrian, the legates condemn pagans who have "superimposed most hideous cicatrices" (i.e gotten tattoos), likening the pagan practice to coloring oneself "with dirty spots". The location of the visit indicates that these are Anglo-Saxon tattoos rather than Celtic, but some scholars have suggested that the Anglo-Saxons might have adopted the practice from the Brittonic Celts (MacQuarrie 1997).
A gloss in the margin of the late 9th c. German manuscript Fulda Aa 2 defines Stingmata [sic] as "put pictures on the bodies as the Irish (Scotti) do." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997).

Fulda Aa 2 folio 43r The gloss is on the left underlined in white.
Irish Written Sources:
Irish texts that mention tattoos date to approximately 700-900 CE, although some of them have glosses that may be slightly later, and some of them cannot be precisely dated.
The first text source is a poem known in English as "The Caldron of Poesy," written in the early 8th c. (Breatnach 1981). The poem is purportedly the work of Amairgen, ollamh of the legendary Milesian kings. In the first stanza of the poem, he introduces himself saying, "I being white-kneed, blue-shanked, grey-bearded Amairgen." (translation from Breatnach 1981)

The text of the poem with interline glosses from Trinity College Dublin MS 1337/1
The word garrglas (blue-shanked) has a Middle Irish (c. 900-1200) gloss added by a later scribe, defining garrglas as: "a tattooed shank, or who has the blue tattooed shank" (Breatnach 1981).
Although Amairgen was a mythical figure, the position ollamh was not. An ollamh was the highest rank of poet in medieval Ireland, considered worthy of the same honor-price as a king (Carey 1997, Breatnach 1981). The fact that a man of such esteemed status introduces himself with the descriptor 'blue-shanked' suggests that tattoos were a respectable thing to have in early medieval Ireland.
The leg tattoos are also mentioned c. 900 CE in Cormac’s Glossary. It defines feirenn as "a thong which is about the calf of a man whence ‘a tattooed thong is tattooed about [the] calf’" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
The Irish legal text Uraicecht Becc, dated to the 9th or early 10th c., includes the word creccoire on a list of low-status occupations (Szacillo 2012, MacNeill 1924). A gloss defines it as: crechad glass ar na roscaib, a phrase which Szacillo interprets as meaning "making grey-blue sore (tattooing) on the eyes" (2012). This sounds rather strange, but another early Irish text clarifies it.
The Vita sancti Colmani abbatis de Land Elo written around the 8th-9th centuries (Szacillo 2012) contains the following episode:
On another time, St Colmán, looking upon his brother, who was the son of Beugne, saw that the lids of his eyes had been secretly painted with the hyacinth colour, as it was in the custom; and it was a great offence at St Colmán’s. He said to his brother: ‘May your eyes not see the light in your life (any more). And from that hour he was blind, seeing nothing until (his) death. (translation from Szacillo 2012).
The original Latin phrase describing what so offended St Colmán "palpebre oculorum illius latenter iacinto colore" does not contain the verb paint (pingo). It just says his eyelids were hyacinth (blue) colored. This passage together with the gloss from the Uraicecht Becc implies that there was a custom of tattooing people's eyelids blue in early medieval Ireland. A creccoire* was therefore a professional eyelid tattooer or a tattoo artist.
A possible third reference to tattooing the area around the eye is found in a list of Old Irish kennings. The kenning for the letter 'B' translates as 'Beauty of the eyebrow.' This kenning is glossed with the word crecad/creccad (McManus 1988). Crecad could be translated as cauterizing, branding, or tattooing (eDIL). McManus suggests "adornment (by tattooing) of the eyebrow" as a plausible interpretation of how crecad relates to the beauty of the eyebrow (1988). The precise date of this text is not known (McManus 1988), but Old Irish was used c. 600-900 CE, meaning this text is of a similar date to the other Irish references to tattoos.

Kenning of the letter 'b' with gloss from TCD MS 1337/1
There is a sharp contrast between the association of tattoos with a venerated figure in 'The Caldron of Poesy', and their association with low-status work and divine punishment in the Uraicecht Becc and the Vita. This indicates that there was a shift in the cultural attitude towards tattoos in Ireland during the 7th-9th centuries. The fact that a Christian saint considered getting tattoos a big enough offense to punish his own brother with blindness suggests that tattooing might have been a pagan practice which gradually got pushed out by the Catholic Church. This timeline is consistent with the 786 CE report of the papal legates condemning the pagan practice of tattooing in Great Britain (MacQuarrie 1997).
There are some mentions of tattooing in Lebor Gabála Érenn, but the information largely appears to be borrowed from Isidore of Seville (MacQuarrie 1997). The fact that the writers of LGE just regurgitated Isidore's meager descriptions of Pictish and Scottish (ie Irish) tattooing without adding any details, such as the designs used or which parts of the body were tattooed, makes me think that Insular tattooing practices had passed out of living memory by the time the book was written in the 11th century.
*There is some etymological controversy over this term. Some have suggested that the Old Irish word for eyelid-tattooer should actually be crechaire. more info Even if this hypothesis is correct, and the scribe who wrote the gloss on creccoire mistook it for crechaire, this doesn't contradict my argument. The scribe clearly believed that eyelid-tattooer belonged on a list of low-status occupations.
Discussion:
Like Julius Cesar in the last post, Herodian of Antioch c. 208 CE makes some dubious claims of Celtic barbarism, stating that the Britons were: "Strangers to clothing, the Britons wear ornaments of iron at their waists and throats; considering iron a symbol of wealth, they value this metal as other barbarians value gold" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). If the Britons wore nothing but iron jewelry, then why did they have brass torcs and 5,000 objects that look like they're meant to attach to fabric, Herodian?
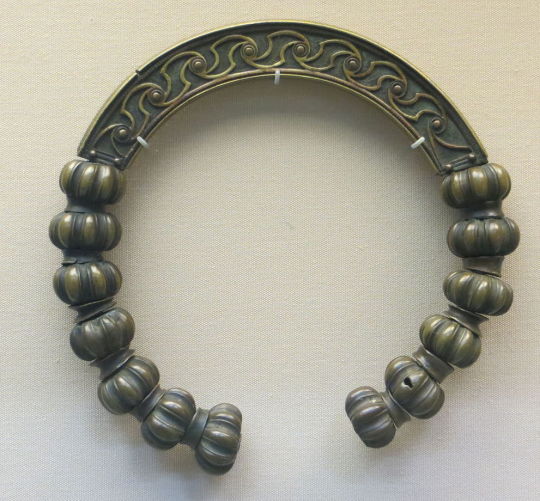
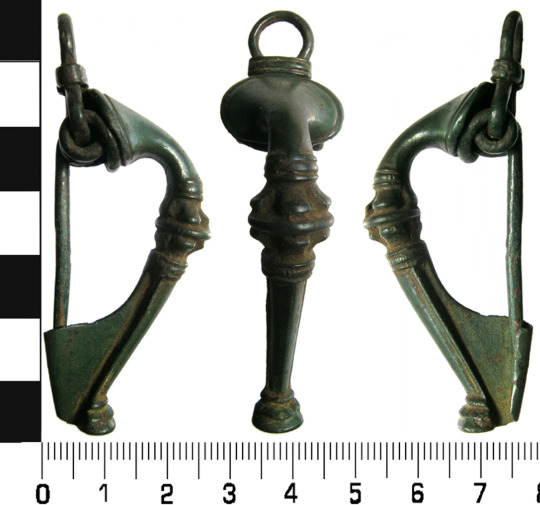


Brass torc from Lochar Moss, Scotland c. 50-200 CE. Romano-British trumpet brooch from Cumbria c. 75-175 CE. image from the Portable Antiquities Scheme.
Trumpet brooches are a Roman Era artifact invented in Britain, that were probably pinned to people's clothing. more info
Although Herodian and Solinus both make dubious claims, there are enough differences between them to indicate that they had 2 separate sources of information, and one was not just parroting the other. This combined with the fact that we have more-reliable sources from later centuries confirming the existence of tattoos in the British Isles makes it probable that there was at least a grain of truth to their claims of tattooing.
There is a common belief that the name Pict originated from the Latin pictus (painted), because the Picts had 'painted' or tattooed bodies. The Romans first used the name Pict to refer to inhabitants of Britain in 297 CE (Ware 2021), but the first mention of Pictish tattoos came in 402 CE (Carr 2005), and the first explicit statement that the name Pict was derived from the Picts' tattooed bodies came from Isidore of Seville c. 600 CE (MacQuarrie 1997). Unless someone can find an earlier source for this alleged etymology than Isidore, I am extremely skeptical of it.
Summary of the written evidence:
Some time between c. 79 CE (Pliny the Elder) and c. 208 CE (Herodian of Antioch) the practice of body art in Great Britain changed from staining or painting the skin to tattooing. Third century Celtic Briton tattoo designs depicted animals. Pictish tattoos are first mentioned in the 5th century.
The earliest mention of Irish tattoos comes from Isidore of Seville in the early 6th c., but since it seems to have been a pre-Christian practice, it likely started earlier. Irish tattoos of the 8-9th centuries were placed on the area around the eye and on the legs. They were a bluish color. The 8th c. Anglo-Saxons also had tattoos.
Tattooing in Ireland probably ended by the early 10th c., possibly because of Christian condemnation. Exactly when tattooing ended in Great Britain is unclear, but in the 12th c., William of Malmesbury describes it as a thing of the past (MacQuarrie 1997). None of these sources give much detail as to what the tattoos looked like.
The Archaeology of Insular Ink:
In spite of the fact that tattooing was a longer-lasting, more wide-spread practice in the British Isles than body painting, there is less archaeological evidence for it. This may be because the common tools used for tattooing, needles or blades for puncturing the skin, pigments to make the ink, and dishes to hold the ink, all had other common uses in the Middle Ages that could make an archaeologist overlook their use in tattooing. The same needle that was used to sew a tunic could also have been used to tattoo a leg (Carr 2005). A group of small, toothed bronze plates from a Romano-British site at Chalton, Hampshire might have been tattoo chisels (Carr 2005) or they might have been used to make stitching holes in leather (Cunliffe 1977).
Although the pigment used to make tattoos may be difficult to identify at archaeological sites, other lines of evidence might give us an idea of what it was. Although the written sources tell us that Irish tattoos were blue, the popular modern belief that woad was the source of the tattoo pigment is, in my opinion, extremely unlikely for a couple of reasons:
1) Blue pigment from woad doesn't seem to work as tattoo ink. The modern tattoo artists who have tried to use it have found that it burns out of the person's skin, leaving a scar with no trace of blue in it (Lambert 2004).
2) None of the historical sources actually mention tattooing with woad. Julius Cesar and Pliny the Elder mention something that might have been woad, but they were talking about body paint, not tattoos. (see previous post) Isidore of Seville claimed that the Picts were tattooing themselves with "juices squeezed from native plants", but even assuming that Isidore is a reliable source, you can't get blue from woad by just squeezing the juice out of it. In order to get blue out of woad, you have to first steep the leaves, then discard the leaves and add a base like ammonia to the vat (Carr 2005). The resulting dye vat is not something any knowledgeable person would describe as plant juice, so either Isidore had no idea what he was talking about, or he is talking about something other than blue pigment from woad.
In my opinion, the most likely pigment for early Irish and British tattoos is charcoal. Early tattoos found on mummies from Europe and Siberia all contain charcoal and no other colored pigment. These tattoos range in date from c. 3300 BCE (Ötzi the Iceman) to c. 300 CE (Oglakhty grave 4) (Samadelli et al 2015, Pankova 2013).
Despite the fact that charcoal is black, it tends to look blueish when used in tattoos (Pankova 2013). Even modern black ink tattoos that use carbon black pigment (which is effectively a purer form of charcoal) tend to look increasingly blue as they age.
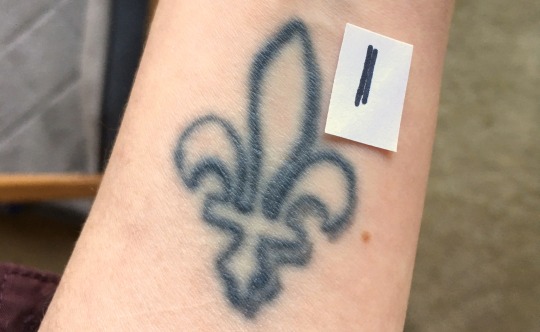
A 17-year-old tattoo in carbon black ink photographed with a swatch of black Sharpie on white printer paper.
The fact that charcoal-based tattoo inks continue to be used today, more than 5,000 years after the first charcoal tattoo was given, shows that charcoal is an effective, relatively safe tattoo pigment, unlike woad. Additionally, charcoal can be easily produced with wood fires, meaning it would have been a readily available material for tattoo artists in the early medieval British Isles. We would need more direct evidence, like a tattooed body from the British Isles, to confirm its use though.
As of June 2024, there have been at least 279 bog bodies* found in the British Isles (Ó Floinn 1995, Turner 1995, Cowie, Picken, Wallace 2011, Giles 2020, BBC 2024), a handful of which have made it into modern museum collections. Unfortunately, tattoos have not been found on any of them. (We don't have a full scientific analysis for the 2023 Bellaghy find yet though.)
*This number includes some finds from fens. It does not include the Cladh Hallan composite mummies.
Tattoos in period art?
It has been suggested that the man fight a beast on Book of Kells f. 130r may be naked and covered in tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). However, Dress in Ireland author Mairead Dunlevy interprets this illustration as a man wearing a jacket and trews (Dunlevy 1989). Looking at some of the other figures in the Book of Kells, I agree with Dunlevy. F. 97v shows the same long, fitted sleeves and round neckline. F. 292r has long, fitted leg coverings, presumably trews, and also long sleeves. The interlace and dot motifs on f. 130r's legs may be embroidery. Embroidered garments were a status symbol in early medieval Ireland (Dunlevy 1989).
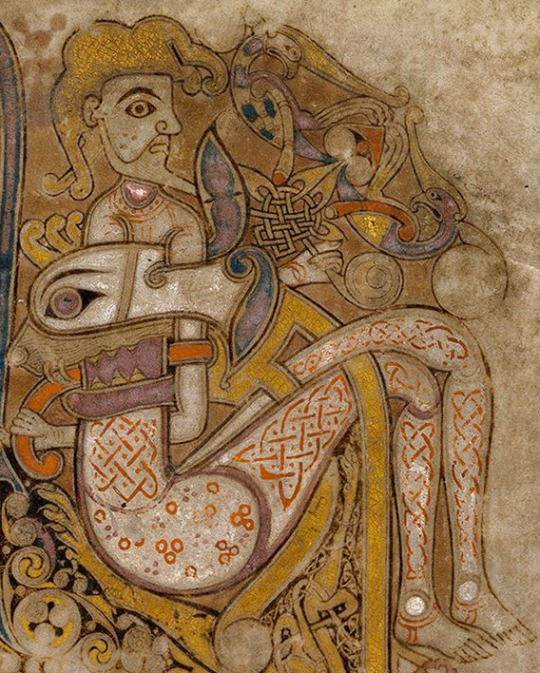

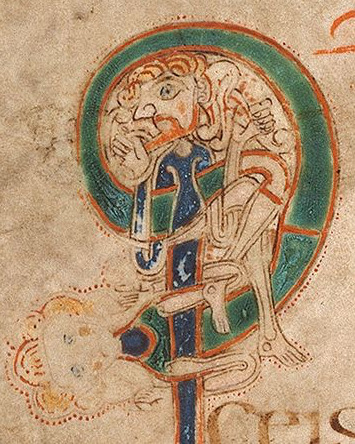

Left to right: Book of Kells folios 130r, 97v, 292r
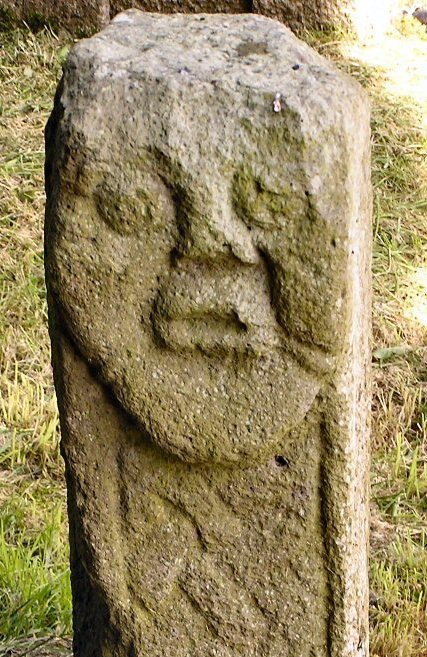
A couple of sculptures in County Fermanagh might sport depictions of Irish tattoos. The first, known as the Bishop stone, is in the Killadeas cemetery. It features a carved head with 2 marks on the left side of the face, a double line beside the mouth and a single line below the eye. These lines may represent tattoos.
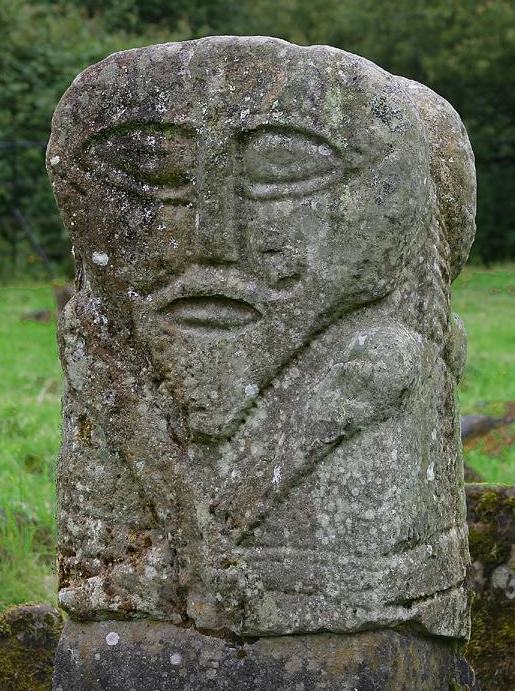


The second sculpture is the Janus figure on Boa Island. (So named because it has 2 faces; it's not Roman.) It has marks under the right eye and extending from the corner of the left eye that may be tattoos.
I cannot find a definitive date for the Bishop stone head, but it bears a strong resemblance to the nearby White Island church figures. The White Island figures are stylistically dated to the 9th-10th centuries and may come from a church that was destroyed by Vikings in 837 CE (Halpin and Newman 2006, Lowry-Corry 1959). The Janus figure is believed to be Iron Age or early medieval (Halpin and Newman 2006).
Conclusions:
Despite the fact that tattooing as a custom in the British Isles lasted for more than 500 years and was practiced by at least 3 different cultures, written sources remain our only solid evidence for it. With only a dozen sources, some of which probably copied each other, to cover this time span, there are huge gaps in our knowledge. The 4th century Picts may not have had the same tattoo designs, placements or reasons for getting tattooed as the 8th c. Irish or Anglo-Saxons. These sources only give us fragments of information on who got tattooed, where the tattoos were placed, what they looked like, how the tattoos were done, and why people got tattooed. Further complicating our limited information is the fact that most of the text sources come from foreigners and/or people who were prejudiced against tattooing, which calls their accuracy into question.
'The Cauldron of Posey' is one source that provides some detail while not showing prejudice against tattoos. The author of the poem was probably Christian, but the poem appears to have been written at a time when Pagan practices were still tolerated in Ireland. I have a complete translation of the poem along with a longer discussion of religious elements here.
Leave me a tip?
Bibliography:
BBC (2024). Bellaghy bog body: Human remains are 2,000 years old https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-northern-ireland-68092307
Breatnach, L. (1981). The Cauldron of Poesy. Ériu, 32(1981), 45-93. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007454
Carey, J. (1997). The Three Things Required of a Poet. Ériu, 48(1997), 41-58. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007956
Carr, Gillian. (2005). Woad, Tattooing and Identity in Later Iron Age and Early Roman Britain. Oxford Journal of Archaeology 24(3), 273–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0092.2005.00236.x
Cowie, T., Pickin, J. and Wallace, T. (2011). Bog bodies from Scotland: old finds, new records. Journal of Wetland Archaeology 10(1): 1–45.
Cunliffe, B. (1977) The Romano-British Village at Chalton, Hants. Proceedings of the Hampshire Field Club and Archaeological Society, 33(1977), 45-67.
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
eDIL s.v. crechad https://dil.ie/12794
Giles, Melanie. (2020). Bog Bodies Face to face with the past. Manchester University Press, Manchester. https://library.oapen.org/viewer/web/viewer.html?file=/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/46717/9781526150196_fullhl.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Halpin, A., Newman, C. (2006). Ireland: An Oxford Archaeological Guide to Sites from Earliest Times to AD 1600. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://archive.org/details/irelandoxfordarc0000halp/page/n3/mode/2up
Hoecherl, M. (2016). Controlling Colours: Function and Meaning of Colour in the British Iron Age. Archaeopress Publishing LTD, Oxford. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Controlling_Colours/WRteEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
Lambert, S. K. (2004). The Problem of the Woad. Dunsgathan.net. https://dunsgathan.net/essays/woad.htm
Lowry-Corry, D. (1959). A Newly Discovered Statue at the Church on White Island, County Fermanagh. Ulster Journal of Archaeology, 22(1959), 59-66. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20567530
MacQuarrie, Charles. (1997). Insular Celtic tattooing: History, myth and metaphor. Etudes Celtiques, 33, 159-189. https://doi.org/10.3406/ecelt.1997.2117
McManus, D. (1988). Irish Letter-Names and Their Kennings. Ériu, 39(1988), 127-168. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30024135
Ó Floinn, R. (1995). Recent research into Irish bog bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 137–45). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Pankova, S. (2013). One More Culture with Ancient Tattoo Tradition in Southern Siberia: Tattoos on a Mummy from the Oglakhty Burial Ground, 3rd-4th century AD. Zurich Studies in Archaeology, 9(2013), 75-86.
Samadelli, M., Melisc, M., Miccolic, M., Vigld, E.E., Zinka, A.R. (2015). Complete mapping of the tattoos of the 5300-year-old Tyrolean Iceman. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 16(2015), 753–758.
Story, Joanna (1995). Charlemagne and Northumbria : the in
fluence of Francia on Northumbrian politics in the later eighth and early ninth centuries. [Doctoral Thesis]. Durham University. http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/1460/
Szacillo, J. (2012). Irish hagiography and its dating: a study of the O'Donohue group of Irish saints' lives. [Doctoral Thesis]. Queen's University Belfast.
Turner, R.C. (1995). Resent Research into British Bog Bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 221–34). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Ware, C. (2021). A Literary Commentary on Panegyrici Latini VI(7) An Oration Delivered Before the Emperor Constantine in Trier, ca. AD 310. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://www.google.com/books/edition/A_Literary_Commentary_on_Panegyrici_Lati/oEwMEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
#early medieval#roman era#pict#tattoos#ancient celts#apologies to people who wanted a shorter post#archaeology#art#anecdotes and observations#statutes and laws#irish history#gaelic ireland#medieval ireland#anglo saxon#insular celts#romano british
102 notes
·
View notes
Text



𝐁𝐞𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐢𝐧 𝐚 𝐩𝐨𝐥𝐲 𝐫𝐞𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬𝐡𝐢𝐩 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐔𝐛𝐛𝐞 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐅𝐢𝐧𝐚𝐧 𝐰𝐨𝐮𝐥𝐝 𝐢𝐧𝐜𝐥𝐮𝐝𝐞
⤷ gender neutral and any size reader. Requests are open, thank you for reading!
a/n: a long awaited cross over that I promised months ago.. please do not hate me! Also, Danes = vikings, but the word viking is also a verb. So, you could say 'Hey Ma I'm off to go viking!'.
Saxons = those from England
Celts are an umbrella term for Native Britons who were here before the Saxons.
ᴹᵃˢᵗᵉʳˡᶤˢᵗ | ᴹᵃˢᵗᵉʳˡᶤˢᵗ ᴵᴵ
It didn't make sense.
Ubbe's shoes walked the length of the boat and back again. Creaking wherever he put his feet, the wind was howling. Even during the day. With the sun high in the sky; not that he could see it.
None of the men or women could see more than five feet in front of them. Once he, along with two other ships left Kattegat, the mist had surrounded them.
Ubbe had the mind to turn back, but he couldn't see the shorline of Kattegat. Only the thick whirls of fog surrounding the boats.
What would have been a long journey, was shortened to mere seconds. And Ubbe was in a place he did not wish to be.
It was a place where his father had died. Where a many great Viking men had died.
But something was different. The time, Ubbe knew it; years had passed somehow. Many, many years. And when he took 4 men into a tavern to investigate, he asked and was told.
Ubbe and his men had gone through 100 years on the water.

・Life had gotten better since Uhtred and his men frequented your village - hell, everywhere had gotten better; not only were the raids less and less.
・But safety and hope were two words that Uhtred of Bebbanberg gave the people
・Well, Uhtred along with his three men - Finan, Sihtric & Osferth.
・You always had a crush on Finan. His Irish charm and humour always brightened your day.
・But he had never ventured for more than conversation and company
・You thought he must have an eye on someone else, but news never reached your ears about anyone else.
・And then something happened.
・Two ships full of Danes had washed on Englands' shores. It was not like any other raid. The Danes spoke differently, their weapons seemed old and the way they dressed was so ... incredibly different to the Danes you all knew
・Where did they come from? Why hadn't any other Dane claimed to know them? And why couldn't they point to where they were from on a map?
・These thoughts plagude you for days. You did your chores and you thought about it, you cooked and cleaned - and thought about it.
・However, curiosity won out and you snuck into the woods to get a better look at the semi-prisoners.

・One man caught your eye instantly.
・And he ...
・He was ... beautiful.
・Outlandishly so, you hadn't seen such a man and with so many unique tattoos...
・His hair was long and braided, parts shaved on the sides and you were taken aback.
・A blush creeping so bright you swore he would be able to see you in the dark - like a beacon of sorts
・But a body had bumped against your own, a hand over your mouth. You bit down - hard and Osferth hissed
"Ow!" He said, trying to keep his voice low as he flung his hand about in pain.
"Well don't do that!" You whispered incredulously.
"What are you staring at?" whispered Osferth, crouching down and following your line of sight.
"No-nothing, nothing, stop it-"
"Ooh got your eye on somethin' then?" he mocked.
・You rolled your eyes and pushed him. He caught your arm and hoisted himself up, catching you against him in the process.
・This back and forth behaviour was normal between you and Osferth. As soon as you met, it had started.
・He knows about your feelings for Finan, and has helped you to gain his attention time and time again
・The only failure in this was the fact that he didn't want to put you at risk. Finan couldn't bear to have you as some sort of target.
・But god did that change when Ubbe started talking to you.
・You decided to help around with the new Danes
・Your skills were highly renound and useful no matter who you were with
・Ubbe did everything he could to get your attention and soon Finan became a shell of his witty self.
・Grouchy and sensitive, Finan couldn't stop watching the two of you interract.
"I mean wha' does she see in 'im??"
"- Finan, please-" Uhtred interjected, trying to calm him down. He did not calm down.
"Just tell her how you feel-" Sihtric exclaimed, throwing his hands up in the air.
"I - I cannot."
"You cannot what?" You said coming up behind him, the trees and darkness hiding you easily.
・From that day on you and Finan were together, but the subject of Ubbe hung loosely in the air.
・However, your relationship was changed because of Ubbe. Who shocked both you and Finan.
"It is true, I want you. But I want both of you. The funny one as well."
・Finan gulped.
・Your relationship is very loving. It truly is.
・There's a lot of PDA
・But even more affection when people aren't around
・Like casually sitting on each other's laps
・Forehead Touches
・The union between all three of you created something. It was peace.
・Peace settled over the group, a sense of ease becoming easier and easier to grasp.
𝑹𝒆𝒍𝒂𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒔𝒉𝒊𝒑 𝑻𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒆𝒔
Shut Up” (You) x “Make Me” (Ubbe) x “Just Kiss Already.” (Finan)
Found Family
Intuitive & Attentive (Finan) x Restless & Flirty (Ubbe) x Witty & Intuitive (You)
𝑹𝒐𝒎𝒂𝒏𝒕𝒊𝒄 𝑷𝒍𝒐𝒕 𝑻𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒆
Intertwined Destinies
Love Transcending Boundaries
Legacy and Legend
𝑻𝒉𝒆𝒎𝒆 𝑺𝒐𝒏𝒈
Scotland by the BBC Scottish Symphony Orchestra
Golden Years by David Bowie
To Bring You My Love by PJ Harvey
#witchthewriter#headcanons#poly relationship#ubbe#ubbe ragnarsson#ubbe lothbrok#ubbe x reader#finan x reader#finan#seven kings must die#the last kingdom#the last kingdom headcanon#the last kingdom headcanons#uhtred#uhtred of bebbanburg#sihtric#beocca#aethelflaed#brida#the saxons#eadith#ubbe x reader x finan#ubbe x you#finan x you#ubbe x y/n#finan x y/n#skade
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
The public wants to save the planet – as long as it doesn’t personally inconvenience them
“Back in July, Just Stop Oil (JSO) experienced something unusual – they found they were the ones being protested. An alternative group called Just Stop Pissing People Off attempted to block Just Stop Oil from engaging in disruptive protests and interrupted their events, saying that the climate crisis is real but that JSO is distracting and alienating people. The counter-protests tell us a great deal about Britain’s contradictory attitude to the climate crisis.
“Broadly, Brits understand that the climate crisis climate change is a major problem. 65% of us are worried about the climate crisis (versus just 28% who aren’t) while the same proportion supports the government’s aim of reducing Britain’s net carbon emissions to zero by 2050 ... Eight in 10 back more tree planting, subsidies for energy-efficient homes and higher taxes for high-carbon companies. 62% would support a requirement for all energy production to come from renewable sources. But this enthusiasm has its limits.
“When asked if they would back policies that would impose limits on what they personally can do, Brits quickly turn against them. For instance, two-thirds oppose the idea of a limit on how much meat they can buy, and a majority oppose banning petrol and diesel cars ... Even though 62% of voters back the idea of requiring all energy to be renewable, just 39% want to ban new North Sea oil fields, and a mere 32% want to prohibit the sale of gas boilers ...
“The British public is not as supportive of action on the climate crisis as many environmentalists would hope. We favour general, uncontentious ideas – net zero, tree-planting, tax rises on high-carbon companies – but when asked for our opinion on a climate policy that would directly affect us personally, we baulk. This is partly due to worries about the cost of living, but it’s also about avoiding personal inconvenience.
“Just Stop Pissing Everyone Off perfectly encapsulates the British attitude to the climate crisis: sure, it’s a problem, but not ours. As Homer Simpson once asked: ‘Can’t someone else do it?’”
#just stop oil#climate activists#climate activism#activism#climate crisis#climate breakdown#climate change#climate#tree planting#home insulation#low emission zones#renewable energy#renewables#oil and gas#fossil fuels#motorists#public opinion#brits#uk
286 notes
·
View notes



