#frederick v of denmark
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Portrait of Frederick V in Anointment Robe
Artist: Carl Gustaf Pilo (Danish, 1711–1793)
Date: c. 1750
Medium: Oil on canvas
Collection: Statens Museum for Kunst, Copenhagen, Denmark
Frederick V of Denmark
Frederick V (Danish and Norwegian: Frederik V; 31 March 1723 – 14 January 1766) was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Schleswig-Holstein from 6 August 1746 until his death in 1766. A member of the House of Oldenburg, he was the son of Christian VI of Denmark and Sophie Magdalene of Brandenburg-Kulmbach.
#portrait#oil on canvas#fine art#artwork#frederick v of denmark#danish history#danish royal family#danish culture#full length#crown#annointment robe#king of denmark#king of norway#danish art#oil painting#carl gustaf pilo#danish painter#european art#18th century painting#statens museum for kurnst
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
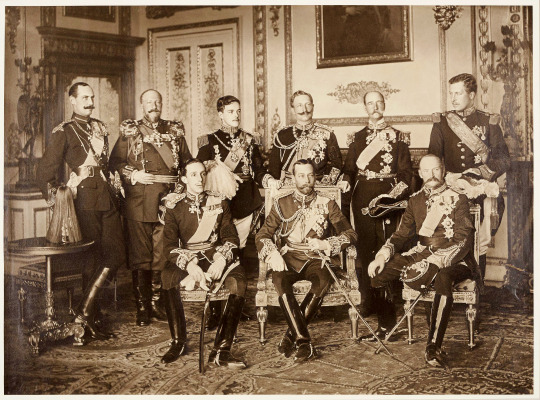

Nine European Sovereigns at Windsor Castle for the funeral of King Edward VII of the United Kingdom (Photo courtesy of Royal Collection Trust) | May 20, 1910
Standing (left to right): King Haakon VII of Norway, King Ferdinand of Bulgaria, King Manuel of Portugal, Emperor William II of Germany, King George I of the Hellenes, King Albert of the Belgians Seated (left to right): King Alfonso XIII of Spain, King George V, King Frederick VIII of Denmark
#royaltyedit#theroyalsandi#george v#king george v#king george v of the united kingdom#haakon vii of norway#king ferdinand of bulgaria#king manuel of portugal#king william ii of germany#king george of hellenes#king albert of the belgians#king alfonso xiii of sapin#king frederick viii of denmark#british royal family#my edit
80 notes
·
View notes
Text

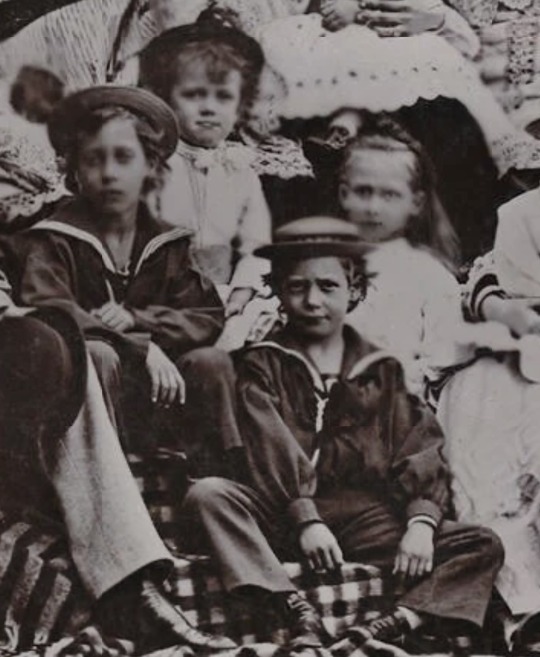
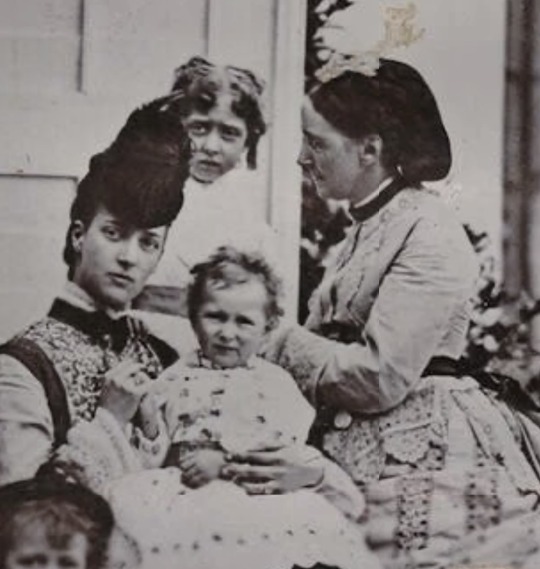
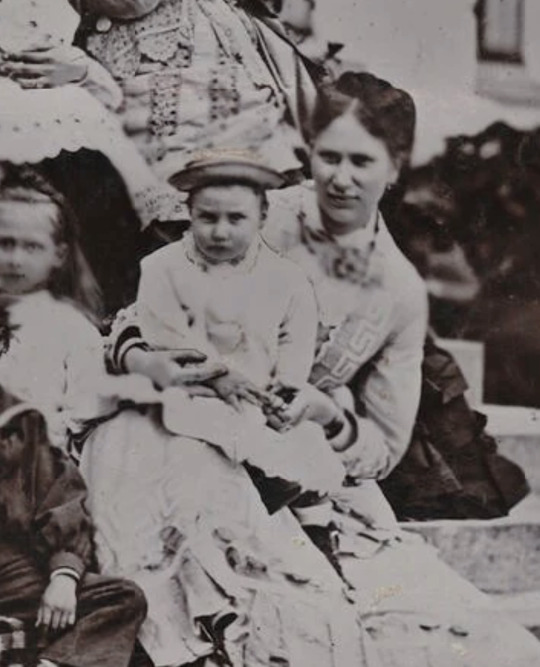
Danish royal family 1872
Tsesarevna Maria Feodorovna with her son Grand Duke George Alexandrovich, Princess Alexandra of Wales and her daughter Princess Maud and Princess Victoria with her grandmother Queen Louise, Crown Prince Frederick and his sister Princess Thyra, Prince Albert Victor, Grand Duke Nicholas, Prince George (I don't really know who the girl next to Nicholas is but it might be Princess Louise of Wales), Princess Louise and her son Prince Christian of Denmark.




#queen louise of denmark#Frederick VIII#maria feodorovna#queen alexandra#Princess Thyra of Denmark#Princess louise of Sweden#albert victor#George v#nicholas ii#george alexandrovich#Victoria of Wales#maud of wales#Christian X#danish royal family#1870s
78 notes
·
View notes
Text

MAY THE BEST TEAM THAT IS ENGLAND WIN!
The Prince of Wales with King Frederick and Princess Josephine of Denmark at the UEFA Euros England V Denmark Group C match at Deutsche Bank Park in Frankfurt || 20 JUNE 2024
#british royal family#british royals#royalty#royals#brf#royal#british royalty#prince of wales#the prince of wales#prince william#william wales#princess josephine#king frederik x#danish royals#danish royalty#my edit#EurosVDenmafk24#royaltyedit#royalty edit
48 notes
·
View notes
Text







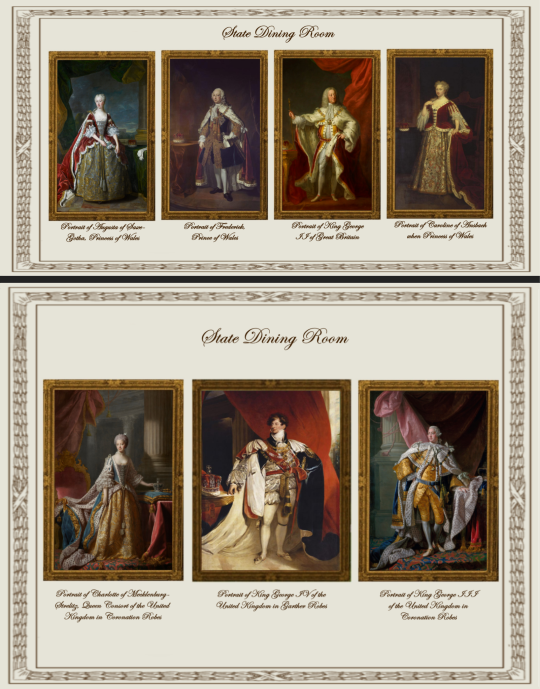

Paintings from Buckingham Palace: part I
A retexture by La Comtesse Zouboff — Original Mesh by @thejim07
100 followers gift!
First of all, I would like to thank you all for this amazing year! It's been a pleasure meeting you all and I'm beyond thankful for your support.
Spread among 13 occupied and historic royal residences in the United Kingdom, the collection is owned by King Charles III and overseen by the Royal Collection Trust. The British monarch owns some of the collection in right of the Crown and some as a private individual. It is made up of over one million objects, including 7,000 paintings, over 150,000 works on paper, this including 30,000 watercolours and drawings, and about 450,000 photographs, as well as around 700,000 works of art, including tapestries, furniture, ceramics, textiles, carriages, weapons, armour, jewellery, clocks, musical instruments, tableware, plants, manuscripts, books, and sculptures.
Some of the buildings which house the collection, such as Hampton Court Palace, are open to the public and not lived in by the Royal Family, whilst others, such as Windsor Castle, Kensington Palace and the most remarkable of them, Buckingham Palace are both residences and open to the public.
About 3,000 objects are on loan to museums throughout the world, and many others are lent on a temporary basis to exhibitions.
-------------------------------------------------------
This first part includes the paintings displayed in the White Drawing Room, the Green Drawing Room, the Silk Tapestry Room, the Guard Chamber, the Grand Staircase, the State Dining Room, the Queen's Audience Room and the Blue Drawing Room,
This set contains 37 paintings and tapestries with the original frame swatches, fully recolourable. They are:
White Drawing Room (WDR):
Portrait of François Salignan de la Mothe-Fénelon, Archbishop of Cambrai (Joseph Vivien)
Portrait of a Lady (Sir Peter Lely)
Portrait of a Man in Armour with a red scarf (Anthony van Dyck)
Portrait of Alexandra of Denmark, Queen Consort of the United Kingdom and Empress of India (François Flameng)
Green Drawing Room (GDR):
Portrait of Prince James Stuart, Duke of Cambridge (John Michael Wright)
Portrait of Frederick Henry, Charles Louis and Elizabeth: Children of Frederick V and Elizabeth of Bohemia (unknown)
Portrait of Infanta Isabel Clara Eugenia of Autria and her Sister, Infanta Catalina Micaela of Austria (Alonso Sanchez Coello)
Portrait of Princess Louisa and Princess Caroline of the United Kingdom (Francis Cotes)
Portrait of Queen Charlotte with her Two Eldest Sons, Frederick, Later Duke of York and Prince George of Wales (Allan Ramsay)
Portrait of Richard Colley Wellesley, Marquess of Wellesley (Martin Archer Shee)
Portrait of the Three Youngest Daughters of George III, Princesses Mary, Amelia and Sophia (John Singleton Copley)
Silk Tapestry Room (STR):
Portrait of Caroline of Brunswick, Princess of Wales, Playing the Harp with Princess Charlotte (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Portrait of Augusta, Duchess of Brunswick With her Son, Charles George Augustus (Angelica Kauffmann)
Guard Chamber (GC):
Les Portières des Dieux: Bacchus (Manufacture Royale des Gobelins)
Les Portières des Dieux: Venus (Manufacture Royale des Gobelins)
Les Portières des Dieux (Manufacture Royale des Gobelins)
Grand Staircarse (GS):
Portrait of Adelaide of Saxe-Meiningen, Queen Consort of Great Britain (Martin Archer Shee)
Portrait of Augustus, Duke of Sussex (Sir David Wilkie)
Portrait of Edward, Duke of Kent (George Dawe)
Portrait of King George III of Great Britain (Sir William Beechey)
Portrait of King William IV of Great Britain when Duke of Clarence (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Portrait of Leopold I, King of the Belgians (William Corden the Younger)
Portrait of Prince George of Cumberland, Later King George V of Hanover When a Boy (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Portrait of Princess Charlotte Augusta of Wales (George Dawe)
Portrait of Queen Charlotte at Frogmore House (Sir William Beechey)
Portrait of Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saafeld, Duchess of Kent (Sir George Hayter)
State Dining Room (SDR):
Portrait of Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Consort of the United Kingdom in Coronation Robes (Allan Ramsay)
Portrait of King George III of the United Kingdom in Coronation Robes (Allan Ramsay)
Portrait of Augusta of Saxe-Gotha, Princess of Wales (Jean-Baptiste Van Loo)
Portrait of Caroline of Ansbach when Princess of Wales (Sir Godfrey Kneller)
Portrait of Frederick, Princes of Wales (Jean-Baptiste Van Loo)
Portrait of King George II of Great Britain (John Shackleton)
Portrait of King George IV of the United Kingdom in Garther Robes (Sir Thomas Lawrence)
Queen's Audience Room (QAR):
Portrait of Anne, Duchess of Cumberland and Strathearn (née Anne Luttrel) in Peeress Robes (Sir Thomas Gainsborough)
Portrait of Prince Henry, Duke of Cumberland and Strathearn in Peer Robes (Sir Thomas Gainsborough)
London: The Thames from Somerset House Terrace towards the City (Giovanni Antonio Canal "Canaletto")
View of Piazza San Marco Looking East Towards the Basilica and the Campanile (Giovanni Antonio Canal "Canaletto")
Blue Drawing Room (BDR)
Portrait of King George V in Coronation Robes (Sir Samuel Luke Fildes)
Portrait of Queen Mary of Teck in Coronation Robes (Sir William Samuel Henry Llewellyn)
-------------------------------------------------------
Found under decor > paintings for:
500§ (WDR: 1,2 & 3)
1850§ (GDR: 1)
1960§ (GDR: 2 & 3 |QAR 3 & 4)
3040§ (STR, 1 |GC: 1 & 2|SDR: 1 & 2)
3050§ (GC:1 |GS: all 10|WDR: 4 |SDR: 3,4,5 & 6)
3560§ (QAR: 1 & 2|STR: 2)
3900§ (SDR: 7| BDR: 1 & 2|GDR: 4,5,6 & 7)
Retextured from:
"Saint Mary Magdalene" (WDR: 1,2 & 3) found here .
"The virgin of the Rosary" (GDR: 1) found here .
"The Four Cardinal Virtues" (GDR: 2&3|QAR 3 & 4) found here.
"Mariana of Austria in Prayer" (STR, 1, GC: 1 & 2|SDR: 1 & 2) found here.
"Portrait of Philip IV with a lion at his feet" (GC:1 |GS: all 10|WDR: 4 |SDR: 3,4,5 & 6) found here
"Length Portrait of Mrs.D" (QAR: 1 & 2|STR: 2) found here
"Portrait of Maria Theresa of Austria and her Son, le Grand Dauphin" (SDR: 7| BDR: 1 & 2|GDR: 4,5,6 & 7) found here
(you can just search for "Buckingham Palace" using the catalog search mod to find the entire set much easier!)

Drive
(Sims3pack | Package)
(Useful tags below)
@joojconverts @ts3history @ts3historicalccfinds @deniisu-sims @katsujiiccfinds @gifappels-stuff
-------------------------------------------------------
#the sims 3#ts3#s3cc#sims 3#sims 3 cc#sims 3 download#sims 3 decor#edwardian#rococo#baroque#renaissance#buckingham#buckingham palace#royal collection trust#wall decor
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
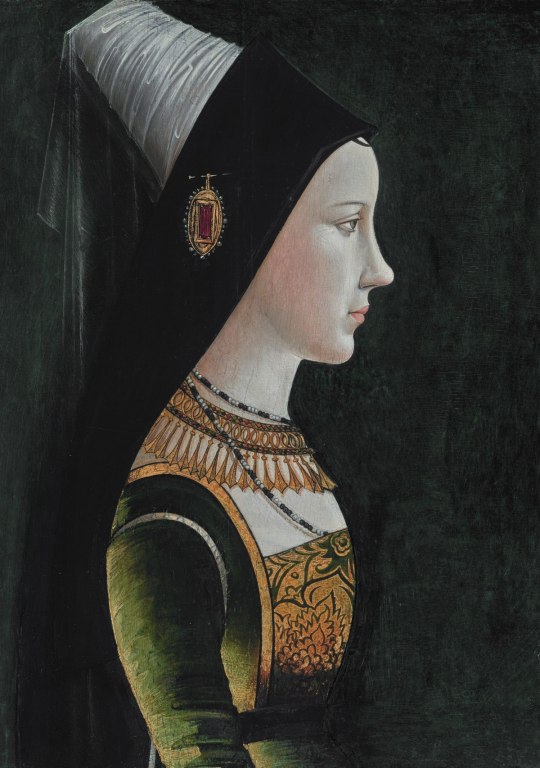
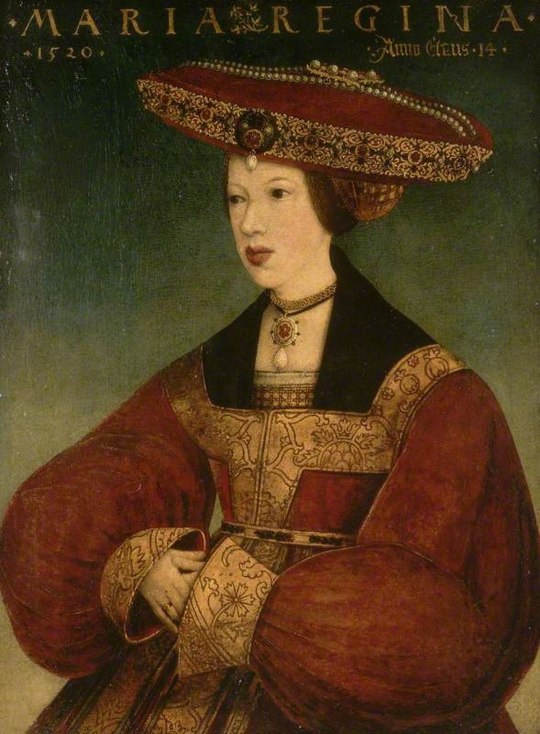
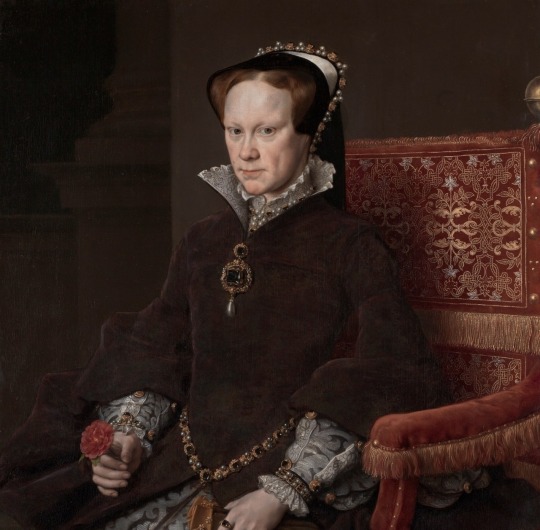
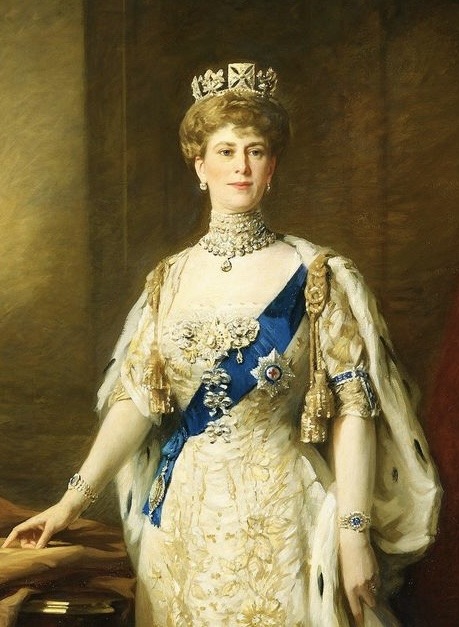









9 Royal Mary’s of history - Reigning and Consorting: -> 1. Mary of Burgundy: Consort of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor (1457–1482). -> 2. Mary of Hungary (Mary of Habsburg): Queen consort of Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia (1505–1558). -> 3. Mary I of England: Reigned 1553–1558 (1516–1558). -> 4. Mary of Guise: Queen consort of James V of Scotland, regent for Mary, Queen of Scots (1515–1560). -> 5. Mary, Queen of Scots: Reigned 1542–1567 (1542–1587). -> 6. Mary II of England: Reigned 1689–1694 (1662–1694). -> 7. Mary of Modena: Queen consort of James II of England, regent for James Francis Edward Stuart (1658–1718). -> 8. Mary of Teck (Queen Mary): Consort of George V of UK, reigned 1910–1936 (1867–1953). -> 9. Mary Elizabeth Donaldson (Queen Mary): current Queen consort of Frederick X of Denmark since 14th January 2024 (1972-).
#ktd#Royal history#european history#Mary I#mary ii#mary queen of scots#queen mary#Mary of teck#Mary of Modena#Mary of guise#Mary of burgundy#Mary of Hungary#European royalty#royal#royalty#brf#british royal family#british royalty#british royal fandom#Art#art history#Denmark
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Royal Family Residences: A Series
In This Episode: Frederik VIII's Palace at Amalienborg
Frederik VIII's Palace is the current residence of King Frederik and Queen Mary of Denmark, and their four children. It is one of the four palaces that make up the Amalienborg complex, all of which have identical Classical façades with Rococo interiors, laid around an octagonal courtyard.

History
Frederik VIII's Palace, also known as Brockdorff's Palace, is the northeastern palace. It has been the home of King Frederik X and Queen Mary since their marriage.
It was originally built for Count Joachim Brockdorff in the 1750s. Brockdorff died in 1763, and Lord High Steward Adam Gottlob Moltke acquired the palace. Moltke sold it two years later to King Frederick V.
From 1767 it housed the Royal Danish Military Academy, also known as the Army Cadet Academy (Landkadetakademi). In 1788 naval cadets replaced the army cadets until the academy moved to another location in 1827.
The following year the palace was prepared to house King Christian VIII's son, Frederik VII, who ascended the throne in 1848, and his bride, Princess Vilhelmine. Architect Jørgen Hansen Koch successfully and thoroughly refurbished the palace in French Empire style in 1827–28.
After the marriage was dissolved in 1837, various members of the royal family lived in the palace. In 1869, it became the home of Frederik VIII. In 1934, it became the home of King Frederik IX and Queen Ingrid. The latter lived there until her death in 2000. From 2006 to 2010 the palace underwent major renovation to accommodate the then Crown Prince couple.
The renovations cost 220m Danish Krone and lasted five years. The result was a mix of contemporary artwork with traditional, classic architecture.
Interior Shots

main interior staircase

secondary staircase


Queen Mary's office

the green room


meeting room

dining room



vestibule reception room

the tapestry room

service kitchen


artwork

yellow vestibule

private meeting room

formal meeting room





random lol
#starting off with the most controversial one#also probably the easiest one to find pics of#royal residences deep dive#drf
44 notes
·
View notes
Photo
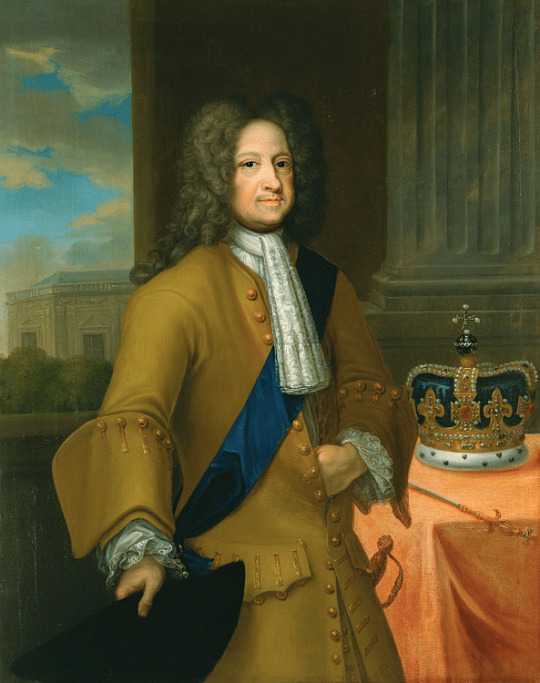

George I of Great Britain
George I of Great Britain (r. 1714-1727) succeeded the last of the Stuart monarchs, Queen Anne of Great Britain (r. 1702-1714) because he was Anne's nearest Protestant relative. The House of Hanover secured its position as the new ruling family by defeating several Jacobite rebellions which supported the old Stuart line.
King George may have struggled with both English and the English, often preferring his attachments in Germany, but his reign was a relatively stable one. His greatest legacy was as a patron of the arts, in particular, his support of musicians like Handel and such lasting cultural institutions as the Royal Academy of Music. He was succeeded by his son George II of Great Britain (r. 1727-1760).
Succession: The House of Hanover
The Glorious Revolution of 1688 saw the end of the reign of the male Stuarts and placed William, Prince of Orange on the throne as William III of England (r. 1689-1702) with his wife, the daughter of the exiled James II of England (r. 1685-1688), made Mary II of England (r. 1689-1694). Mary's sister became the ruling monarch in 1702 as Anne, Queen of Great Britain. When Anne died, so ended the Stuart royal line, which had begun with Robert II of Scotland (r. 1371-1390).
Queen Anne outlived her husband Prince George of Denmark (1653-1708) by six years; she died at the age of 49 on 1 August 1714 at Kensington Palace after suffering two strokes. Queen Anne had had many children, but all died in infancy. The greatest hope for an heir had been William, Duke of Gloucester (b. 1689), but he died in 1700, aged 12. Anne's official heirs, the Hanoverian family, were selected as such in the 1701 Act of Settlement.
The Hanovers were connected to the British royal line as descendants of Elizabeth Stuart (d. 1662), daughter of James I of England (r. 1603-1625) and brief Queen of Bohemia through her husband Frederick V of the Palatinate. The chosen successor – although she was not permitted by Anne to even visit England – was Elizabeth Stuart's daughter Sophia (l. 1630-1714), wife of the Duke of Brunswick and Elector of Hanover (a small principality in Germany the size of Yorkshire). Sophie of Hanover was Queen Anne's nearest relation of the Protestant faith, a vital consideration given that Parliament had already passed a law forbidding a Catholic to take the throne. For this reason, more than 50 other claimants to the throne had been deemed unsuitable. When Sophia died in 1714, her son, George Ludwig, took over the role of heir apparent to the British throne.
Continue reading...
28 notes
·
View notes
Text






GODPARENTS OF NICHOLAS II
Born during his grandfather's reign on 18 May (New Style) 1868 at the Alexander Palace, Tsarkoe Selo in Saint Petersburg. He was the eldest son of Alexander III and his wife Maria Feodorovna (then, the Tsarevich and Tsarina of Russia). He was christened on 1 June at the Chapel of the Resurrection of the Catherine Palace at Tsarskoe Selo, by the confessor of the imperial family, protopresbyter Vasily Borisovich Bazhanov. His godparents were:
ALEXANDER II, EMPEROR OF RUSSIA - his paternal grandfather, the Russian Emperor stood as one of the godparents. He became the Emperor of All Russia in 1855. Alexander’s most significant reform as emperor was the emancipation of Russia’s serfs in 1861, for which he is known as Alexander the Liberator. He was assassinated in 1881 when the young Nicholas was only 12 years-old, to which he became the heir apparent upon his death.
PRINCESS MARIE OF HESSE AND BY RHINE, EMPRESS MARIA ALEXANDROVNA OF RUSSIA - his paternal grandmother, the consort of Emperor Alexander II, was another of his godparents. Known for her intellect, she was one of the founders of the Russian Red Cross Society. However, she suffered from tuberculosis from 1863 and spent long stays in southern Europe to avoid harsh winters. Although she and her husband were unofficially separated sometime after the death of their eldest son, Maria was treated with respect and love by her surviving family. Maria passed away from illness when the young Nicholas was still a child.
PRINCESS LOUISE OF HESSE-KASSEL, QUEEN CONSORT OF DENMARK - his maternal grandmother was listed as one of his godparents. Louise became the Queen consort of Denmark upon her husband's - King Christian IX - accession in 1863, just few years before her grandson Nicholas' birth. She, herself, was a niece of another King of Denmark (Christian VIII). The great dynastic success of Louise's six children was to a great extent a result of Louise's own ambitions - through them, she was a grandmother of not only the future Tsar of Russia (Nicholas II), but also that of King George V of the United Kingdom; King Constantine I of Greece; King Christian X of Denmark, and King Harken VII of Norway.
GRAND DUCHESS ELENA PAVLOVNA OF RUSSIA - his great-great-aunt, the wife of the late Grand Duke Michael Pavlovich, was one of his godparents. Born as Princess Charlotte of Württemberg, she became a close friend of his grandmother the Empress Maria Alexandrovna, and was known as an intellectual. She was also considered the most exceptional woman in the imperial family since Catherine the Great.
KING FREDERICK VIII OF DENMARK - then, the Crown Prince, his maternal uncle stood as one of his godparents. During the long reign of his father, he was largely excluded from influence and political power. Upon his father's death in 1906, he acceded to the throne at the advanced age of 62. In many ways, Frederick VIII was a liberal monarch who was much more favorable to the new parliamentary system introduced in 1901 than his father had been, being reform-minded and democratically inclined.
Source
87 notes
·
View notes
Text

Frederick V, King of Denmark (1723-1766)
Artist: David Morier (Swiss-born British, 1705?-1770)
Date: c. 1745-1751
Medium: Oil on canvas
Collection: Royal Collection Trust, United Kingdom
Frederick V of Denmark
Frederick V (Danish and Norwegian: Frederik V; 31 March 1723 – 14 January 1766) was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Schleswig-Holstein from 6 August 1746 until his death in 1766. A member of the House of Oldenburg, he was the son of Christian VI of Denmark and Sophie Magdalene of Brandenburg-Kulmbach.
#painting#equestrian portrait#oil on canvas#frederick v#king of denmark and norway#danish history#danish royal family#duke of scheleswig-holstein#house of oldenburg#landscape#horses#soldiers#men#costume#british culture#british art#oil painting#artwork#fine art#david morier#british painter#european art#18th century painting#royal collection trust
13 notes
·
View notes
Text


On November 7th 1619 Elizabeth Stuart was crowned Queen of Bohemia.
Elizabeth was the eldest daughter of James VI, and Anne of Denmark. She was thus sister to King Charles I and cousin to King Frederick III of Denmark.
Born in at Falkland Palace, Fife,on 19th August 1596, she was named Elizabeth in honour of the then-ageing English Queen, Elizabeth I, who had remained childless. Her older brothel was Prince Henry, of her other siblings, Charles would however go on to inherit the throne.
To all intents and purposes, Elizabeth had a happy upbringing at Linlithgow Palace, one of the grandest of Scotland’s royal residences, and one of my favourite places to wander around.
In 1603 her father James succeeded Elizabeth I to the English throne. Elizabeth was handed over to the care of Lord and Lady Harrington and took up residence at Coombe Abbey, Warwickshire.
Lord Harrington indulged her passion for nature, and in a secluded wilderness at the end of the park arranged the construction of a number of little wooden buildings in all the different orders of architecture which housed paintings and stuffed animals. He also established an aviary and a miniature menagerie (she continued to collect various animals throughout her life) which was later expanded to include meadows stocked with the smallest breeds of cattle from Jersey, Shetland and the Isle of Man. Elizabeth referred to her miniature world as ‘her Territories’ and ‘her Fairy farm’ and she engaged a pauper family as keeper of her birds and beasts.
Elizabeth idolised her older brother - they shared a love of life which eluded the sickly Charles, four years younger than his sister. Her letters to her brother Henry reveal a deep affection and and mutual respect. In 1605 she writes ‘My noble brother, I rouse you from sleep to remind you that I am your most humble servant, and desire above all that I might have the pleasure of remaining in your good graces and your best loved sister.’
Henry’s sickness and death on November 6, 1612, in the midst of Elizabeth's betrothal celebrations devastated her. It is not mentioned in Elizabeth’s letters of 1612 or 1613, a silence that suggest great mourning however her strength of character can be demonstrated by her attempts to gain access to Henry’s isolated sick room. Disguised as a country girl, she tried several times to gain admittance to Henry but was recognised and turned back. Henry’s last words were his sister’s name.
By the age of 12 Elizabeth’s political value was such that a member of the influential Hapsburg family, King Philip III of Spain, put himself forward as a eligible suitor. While Queen Anne relished the opportunity of a glittering Spanish throne, James’ mind was set on a Protestant:Frederick V, Prince Palatine of the Rhine in the Holy Roman Empire, frequently known as the Palsgrave.
Luckily for Elizabeth, Frederick was her own age, handsome, athletic, of a winning personality and generous. In many ways he resembled her brother Henry, with whom he developed a deep friendship. Frederick could not fail to love Elizabeth although she was initially more reserved.
On Valentine’s Day 1613, a spectacular wedding ceremony took place in the Royal Chapel at Whitehall Palace in London. At the time of their marriage, Elizabeth and her young groom Frederick V were destined to achieve international power and influence. However, by 1621, Elizabeth was in exile, destined to be remembered as the ‘The Winter Queen’, a derogatory epitaph that reflects the short duration of her rule in Bohemia, with her union with Frederick deemed a political failure.For almost two months, the young couple were feted and feasted in London before setting out on their journey to their new home in Heidelberg, in south west Germany. Elizabeth and Frederick eventually reached the Palatinate and its capital in Heidelberg situated on the banks of the river Neckar.
Six years later, in late 1619, Frederick and Elizabeth were crowned King and Queen of Bohemia (today part of the Czech Republic) at the invitation of the Bohemia Confederacy to prevent a Catholic incumbent ascending to the throne. Barely a year after receiving the crown, the couple were defeated at the Battle of the White Mountain, and driven from their court in Prague and deprived of all their Palatine lands by the Hapsburg Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II, events which led to one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in human history:The Thirty Years War.
During their separations whilst Frederick was on campaign, the couple wrote to each other three or four times a week, sometimes even twice in one day. Frederick describes Elizabeth as his ‘only heart’, he ‘kisses her mouth a million times in imagination’.
Frederick died unexpectedly from the plague at Mainz while on perpetual military campaign in 1632. So long as she lived, Elizabeth’s rooms were draped in black, and in memory of Frederick special days were set apart for fasting. She later wrote ‘though I make a good show in company, yet I can never have any more contentment in this world, for God knows I had none but that which I took in his company, and he did the same in mine.’
Elizabeth lived on in the Dutch Republic for a further 30 years, in voluntary exile, returning to England in 1661, a year before her death and a year after the restoration of her nephew, Charles II.
It is through Elizabeth’s daughter, Sophie, the Hanoverians line was established.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

“I thought it was really cool that the grandchildren of King Harald V of Norway were interviewing their grandparents' 80th birthday guests. One of the funniest questions was asked by Princess Maud of Denmark to Prince Frederick of Denmark, asking him if he preferred Norwegian salmon or Danish red sausage. The cutest comment made by Princess Leah of Norway, praising Princess Beatrix of the Netherlands, calling her splendid.” - Submitted by Anonymous
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
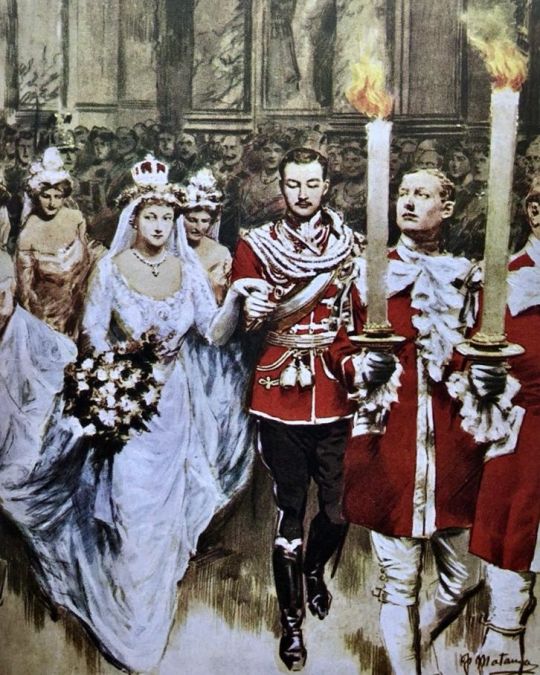

The 20th of May was my last day in the New Palace, and on the 21st Ernst August arrived. In his last letter he had told me what arrangements he had made to keep our honeymoon location secret from prying eyes. It was planned that we should go first to the hunting lodge at Werbellinsee, then to the Hubertihaus, my father-in-law’s hunting lodge near Gmunden. He made me promise not to tell anyone at all and even in Gmunden itself our plans were kept strictly secret.
The first wedding guests to arrive were the King and Queen of England, and my parents went to the Lehrter Station in Berlin to greet them. George V had put on his Prussian General’s uniform for the occasion and, with an escort of Dragoon Guards and Cuirassiers, the Royal couple drove through Berlin. More than half a century was to pass before an English Head of State was to come to Germany again, when Queen Elizabeth II, George V’s grand-daughter, came in 1965.
Early on the following day my great-aunt Luise, Prince Max of Baden and his wife arrived, then a little later my parents-in-law and my sister-in-law, Olga. The First Guards Regiment of Foot formed the guard of honour, while the Cuirassiers again provided the escort as we travelled to the castle in three carriages. My father sat with the Duke, who wore his Austrian uniform, in the first carriage; my mother with the Duchess Thyra in the next, while Princess Olga, my fiancé and I sat together in the third.
At midday the Czar of Russia arrived and the colourful welcoming ceremonies began all over again. Wearing the uniform of the Alexander Grenadier Guards Regiment and the tall Frederick the Great cap on his head, Nicholas II’s truly imposing appearance drove the waiting Berliners into a frenzy of excitement and wonder... For me, the wedding celebrations began with the reception of deputations who had come bringing gifts. My father’s present to me was a diadem and a pearl necklace, while my mother gave me a diamond tiara. King George and Queen Mary gave me a prodigious gold goblet anda diamond brooch; Ernst August a complete jewellery outfit. The English Queen Mother, Alexandra, gave me an emerald brooch. From the Czar I received an aquamarine and diamond necklace; the Italian King and Queen sent me antique silver vessels and Queen Wilhelmina of Holland an antique pendulum clock. There were presents galore, from the Kings of Denmark and Sweden down to the various cities in Germany, and from Brunswick I received a diadem which had once belonged to the French Empress Josephine. The number of gifts was so great they required several furniture vans to carry them.
The real celebrations began on the evening of the day before the wedding, with a gala opera when the Royal Court Opera put on Richard Wagner’s Lohengrin. The Opera House, when I arrived, was bedecked with my favourite flowers, pink carnations, and as we took our places in the Royal Box with our parents, all those present rose from their seats, and Ernst August and I bowed right, left and centre. As one, the entire audience bowed back. Next day, 24 May, was my wedding day. Early in the afternoon my mother helped me on with my bridal crown and veil. Then we repaired to the Chinese Room, and we found that a unit of soldiers had formed lines throughout the castle and taken up sentry posts everywhere. There was a bodyguard from the rst Guards Regiment, the Castle Guard in their historic Frederick the Great uniforms, the Garde du Corps in ceremonial dress, and the gendarmerie. At 4 p.m. members of the staff of the Royal Privy Purse came by, carrying the bridal crown of the Princess of Prussia. Then the Mistress of the Empress’s Household, Therese, Countess von Brockdorff, picked up the crown and ceremoniously handed it to my mother who carefully placed it on my head. We then proceeded to the chamber deemed the ‘Elector’s Room’ where my father received us, and Count Eulenberg, the Minister for the Royal House, completed the formalities regarding the marriage pact and the official registration of the marriage. As Ernst August and I signed the register, we heard a loud buzzing overhead above the castle. We all rushed to the windows and there above us was the airship Hansa, all gaily decorated with colourful pennants. Suddenly, a large bouquet of flowers came floating down from the airship. It was their way of congratulating us.
After the civil ceremony, the bridal procession, led by the Corps of Pages, wound its way through the Picture Gallery and the White Hall to the castle chapel. Behind the pages walked two Heralds with the Brandenburg and Prussian Coat of Arms, then the Chief Marshal, Prince zu Fiirstenberg with his big Marshal’s staff, and finally Ernst August and me. Behind us were the Kaiser in the uniform of the 1st Guards Regiment, with the Duchess of Cumberland in a lilaccoloured gown, then the Generals and the Admirals, and then the Kaiserin in a light green robe escorted by the Duke of Cumberland in his Austrian uniform. Then the Czar of Russia, in his Hussar uniform, escorted the Queen of England. The King of England, in his Cuirassier uniform, escorted the Crown Princess. Then they were followed by a whole host of Princes, including my brothers, and Princesses, Dukes and Duchesses. It was 5 p.m. by the time we reached the chapel to be greeted by the sound of music from the organ.
Bright sunlight filtered through the chapel cupola as Ernst August and I stepped up to the altar which my mother and Crown Princess Cecilie, my sister-in-law, had decorated with roses, carnations and wreaths. Pastor Dryander then delivered his sermon, earnest and worthy words which warned me about the seriousness of life.
After that came the actual marriage ceremony. Ernst August’s ‘yes’ rang out so loudly and clearly that I had to follow suit and when we joined hands in front of the altar he clasped mine very firmly, insisting that his thumbs were on top of mine. You see, there’s an old folk-tale which says that if the husband does not have his thumbs above those of his bride at the wedding ceremony then he will have no say during his marriage. Pastor Dryander looked slightly shocked at this little demonstration, but Ernst August and I just smiled at each other. Mary, the Queen of England, however, was so overcome by the whole ceremony that she broke into a flood of tears. Later, they used to say that she had sobbed because she had at that moment foreseen the forthcoming disaster of war the following year breaking over us. That is really out of the question. Queen Mary was very attached to the Guelph family and it was understandable that the ceremony should affect her.
As soon as the vows and rings had been exchanged, the battery of the rst Guards Field Artillery Regiment fired a 36-gun salute, the chapel bells rang out in loud peals, and the wedding party made its way to the White Hall again, where we stood under the canopy of the Throne and received congratulations from the guests filing past, as the orchestra played the “Wedding March’ from Midsummer Ni ght’s Dream. My husband and I had my father standing to our ri ght together with my mother-in-law, Queen Mary and the Czar, and on our left my mother, my father-in-law, Crown Princess Cecilie and King George V.
The ceremonial banquet began at 7 p.m. and was attended by one thousand one hundred guests. The remarkable thing about it was that the food was dished up by Lieutenant-General Baron von Siisskind, the Inspector of the Militia, at one end of the table and by LieutenantGeneral von Falk, the Inspector of the War Academy, at the other. They served the food then passed the plates to the lackeys, who handed them to the Court officials, and so on to each guest. As soon as the dinner was over, the White Hall became the setting for the traditional torch-dance, a sort of polonaise which, in earlier times, was danced with senior Court officials carrying big, heavy candles ahead of the procession of dancers. For these elderly gentlemen then it was certainly no easy task, but in my time these duties were taken over by the pages, who were physically better equipped. My father gave the Chief Marshal orders for the torch-dance to begin. Prince zu Fiirstenberg came up to my husband and me, bowed, and invited us to lead the dance. The band of the Guards Cuirassiers struck up a polonaise, the Chief Marshal placed himself at the head of the procession of dancers and, with twelve pages lined up two by two behind him, signalled for Ernst August and me to lead off the dance.
The spectacle of my dancing with the King of England and the Czar of Russia absolutely fascinated everybody present. It wasn’t something that happened every day, of course, but there were the rulers of the two mightiest nations on Earth, with the daughter of the German Kaiser between them, all dancing together. At the end of the dance the Czar turned to me and said: ‘My wish is that you will be as happy as I am.’ I have never forgotten those words: they were the last I was ever to hear from Czar Nicholas. The torch-dance was over. I left the room on my father’s arm, while my husband escorted my mother. The Prussian Princess’s Crown was taken away from me and given back for safe keeping to the officials of the Privy Purse. Then my mother lifted off my bridal wreath. The hour of parting had struck. We changed our clothes and went to the station accompanied by my father and four of my brothers".
The Kaiser's daughter: Memoirs of H. R. H. Viktoria Luise, Duchess of Brunswick and Lüneburg, Princess of Prussia
youtube
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ages of English Princesses at First Marriage
I have only included women whose birth dates and dates of marriage are known within at least 1-2 years, therefore, this is not a comprehensive list. The average age at first marriage among these women was 16.
This list is composed of princesses of England when it was a sovereign state, prior to the Acts of Union in 1707.
Eadgyth (Edith) of England, daughter of Edward the Elder: age 20 when she married Otto the Great, Holy Roman Emperor in 930 CE
Godgifu (Goda) of England, daughter of Æthelred the Unready: age 20 when she married Drogo of Mantes in 1024 CE
Empress Matilda, daughter of Henry I: age 12 when she married Henry, Holy Roman Emperor, in 1114 CE
Marie I, Countess of Boulogne, daughter of Stephen of Blois: age 24 when she was abducted from her abbey by Matthew of Alsace and forced to marry him, in 1136 CE
Matilda of England, daughter of Henry II: age 12 when she married Henry the Lion in 1168 CE
Eleanor of England, daughter of Henry II: age 9 when she married Alfonso VIII of Castile in 1170 CE
Joan of England, daughter of Henry II: age 12 when she married William II of Sicily in 1177 CE
Joan of England, daughter of John Lackland: age 11 when she married Alexander II of Scotland in 1221 CE
Isabella of England, daughter of John Lackland: age 21 when she married Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, in 1235 CE
Eleanor of England, daughter of John Lackland: age 9 when she married William Marshal, Earl of Pembroke in 1224 CE
Margaret of England, daughter of Henry III: age 11 when she married Alexander III of Scotland in 1251 CE
Beatrice of England, daughter of Henry III: age 17 when she married John II, Duke of Brittany in 1260 CE
Eleanor of England, daughter of Edward I: age 24 when she married Henry III, Count of Bar in 1293 CE
Joan of Acre, daughter of Edward I: age 18 when she married Gilbert de Clare, Earl of Gloucester in 1290 CE
Margaret of England, daughter of Edward I: age 15 when she married John II, Duke of Brabant in 1290 CE
Elizabeth of Rhuddlan, daughter of Edward I: age 15 when she married John I, Count of Holland in 1297 CE
Eleanor of Woodstock, daughter of Edward II: age 14 when she married Reginald II, Duke of Guelders in 1332 CE
Joan of the Tower, daughter of Edward II: age 7 when she married David II of Scotland in 1328 CE
Isabella of England, daughter of Edward III: age 33 when she married Enguerrand VII, Lord of Coucy in 1365 CE
Mary of Waltham, daughter of Edward III: age 16 when she married John IV, Duke of Brittany in 1361 CE
Margaret of Windsor, daughter of Edward III: age 13 when she married John Hastings, Earl of Pembroke in 1361 CE
Blanche of England, daughter of Henry IV: age 10 when she married Louis III, Elector Palatine in 1402 CE
Philippa of England, daughter of Henry IV: age 12 when she married Eric of Pomerania in 1406 CE
Elizabeth of York, daughter of Edward IV: age 20 when she married Henry VII in 1486 CE
Cecily of York, daughter of Edward IV: age 16 when she married Ralph Scrope in 1485 CE
Anne of York, daughter of Edward IV: age 19 when she married Thomas Howard in 1494 CE
Catherine of York, daughter of Edward IV: age 16 when she married William Courtenay, Earl of Devon in 1495 CE
Margaret Tudor, daughter of Henry VII: age 14 when she married James IV of Scotland in 1503 CE
Mary Tudor, daughter of Henry VII: age 18 when she married Louis XII of France in 1514 CE
Mary I, daughter of Henry VIII: age 38 when she married Philip II of Spain in 1554 CE
Elizabeth Stuart, daughter of James VI & I: age 17 when she married Frederick V, Elector Palatine in 1613 CE
Mary Stuart, daughter of Charles I: age 10 when she married William II, Prince of Orange in 1641 CE
Henrietta Stuart, daughter of Charles I: age 17 when she married Philippe II, Duke of Orleans in 1661 CE
Mary II of England, daughter of James II: age 15 when she married William III of Orange in 1677 CE
Anne, Queen of Great Britain, daughter of James II: age 18 when she married George of Denmark in 1683 CE
33 notes
·
View notes
Text


The Prince of Wales with King Frederick of Denmark at the UEFA Euros England V Denmark Group C match at Deutsche Bank Park in Frankfurt || 20 JUNE 2024
#william wales#prince of wales#the prince of wales#prince william#william prince of wales#british royal family#british royals#royalty#royals#brf#royal#british royalty#king frederik x#royaltyedit#royalty edit#my edit#danish royals
49 notes
·
View notes
Note
There's a brief line in Princess Augusta's Wikipedia entry about her first cousin Frederick VI of Denmark telling her father and his uncle King George III his desire to marry her, but wondering you knew more about it?
Was it Augusta? Huh. Well, I knew it was an English princess, but I didn’t know who exactly.
Long story short, marriages between Danish and English Royals were prevalent. These marriages were beneficial for both nations.
Just after Frederik seized control as regent, it was decided that he needed a spouse. Having relations with England had always been a useful thing, so that's likely why an English princess, like Augusta was an option. The relationship between England and Denmark would've been much more strained at the time, given what had occurred between Frederik's parents and their doctor, Struensee. So an attempt was made and was rejected by George III. The details as to what occurred between George III and Frederik VI is something I know very little of, and the few biographies on Frederik only ever mention that there was an attempt, but nothing else. However, I know of the causes most historians here in Denmark have contributed this rejection to.
Honestly, the rejection likely came from the same situation that caused strain between the nations. The main cause involved Frederiks Father, Christian VII, his mother, Caroline Mathilde (who is also George III's sister), and their personal Doctor, Johann Struensee. I'll make a short rundown here, as this topic has quite a few assorted resources in English- there is even a movie with Mads Mikkelsen in it on this topic. But basically, Caroline Mathilde had been married at 15/16 to the troubled 17-year-old Christian VII, and it didn't end well.
Christian's father, Frederik V had remained more or less indifferent to his heir all his life, and a tutor of his had used and abused Christian, not really educating the boy and heavily using corporal punishment. On top of all this, the boy likely had Schizophrenia. All this made Chrisitan- at his worst- hallucinate, be paranoid, become easily agitated, and self-harm. He also fell deeply into sexual promiscuity. I won't bore you with the details of this, as that aspect of the situation is complex and filled with conjecture.
anyways-
Christian had next to no interest in Caroline Mathilde, more invested in his other lovers and such. Christian's non-abusive Swiss tutor had to step in and push the couple a bit, resulting in the birth of Frederik VI.
Around the same time as Frederik's birth (give or take a year) Caroline Mathilde started to have an affair with Johann Struensee, Christian's personal Doctor. Due to these connections, Struensee gained near full control of the country from 1770-1772. It is likely Frederik's sister is his half-sister, as her father is most likely Struensee. The whole thing ended (I'd go into details, but that's also extremely complex.) with Struensee being executed, and Caroline Mathilde getting a divorce and exiled to Celle.
This is where it gets a bit odd. Robert Murray Keith, on behalf of George III, started to negotiate her release and other things, such as her dowry being returned. Keith did get her the dowry back and also got her a pension. It was George III who suggested sending her to Celle, which was in the Hanover electorate. She died there three years later, at 23 years old.
This no doubt left a foul memory and view of Denmark for George III, so I don't doubt that this is likely the cause.
As to what happened- on the Danish end, I've yet to find any mentions of Princess Augusta or the possibility of Frederik marrying her. It's more than likely that a letter was sent, George said "hell no," and the Danish court dropped the topic, moving on to try to get him to marry a Prussian princess. In the end, however, Frederik did end up marrying his cousin, who gave him little political benefit, in some ways to show independence from his half-uncle and step-grandmother. (he did, however, gain a partner, a lover,- and after she could have more kids lest she die- a lifelong friend.)
Sorry I don't have more, but as there are a few more details on the wiki page, I do not doubt that there is something more out there, however, it's more than likely held English archives, which I have given up trying to gain access to.
I hope this answers your question, even just a little, and feel free to send me another ask if you have any more.
#sorry that turned into a bit of jabbering#seriously tho- sorry i dont have more information#will tag later#ask#frederik vi
2 notes
·
View notes