#domesticated species
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
silk moth :)
Sure :)


#domestic silk moth#domesticated species#domesticated animals#moth#moths#insecta#insects#insect#lepidoptera#bombycidae#animal polls#poll blog#my polls#animals#polls#tumblr polls#bugs#bug
97 notes
·
View notes
Text
#2278 - Sus domesticus - Domestic Pig

Pigs were first domesticated in the Neolithic, and are raised in many parts of the world for meat and leather. They were first introduced to New Zealand in 1769 when the French explorer Jean-François de Surville gave a pair to the Maori at Doubtless Bay. Between 1773 and 1777 Captain James Cook released nine pigs and gave another seven to the locals, and his name is the one that stuck to their descendents - 'Captain Cookers'.
The feral pigs are as huge a problem in New Zealand as they are everywhere else they've gone wild, but at the time pigs and potatoes were a revolution in Maori agriculture. As well as being an excellent source of meat, they and New Zealand Flax were valuable trades good for visiting ships. Unfortunately, one of the trade goods they got back was musketry, and between 1806 and 1845 there was an escalating arms race and thousands of battles known as the Musket Wars, where various iwi attacked neighbouring iwi, taking the survivors as slaves to grow more flax, to trade for more guns. Between 1845 and 1872 came the New Zealand Wars, in which the British frequently got their asses handed to them.
New Zealand does have one breed of domestic pig, the kunekune, probably derived from an Asian domestic breed introduced in the early 19th century by whalers or traders. I'm not sure if this one is a kunukune.
Tokaanu, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A study that just came out demonstrates that outdoor cats are known to prey on over two thousands species of wild animal, from mammals to birds to insects. That includes 347 species that are endangered, threatened or otherwise of concern, and they've been a key factor of the permanent extinction of over 60 species. And while cats may not always bring home what they catch, chances are if your cat is allowed to roam unsupervised outside, they're killing your local wildlife.
Why is this so important? Worldwide, wild animal populations have decreased in number by 69% in the past fifty years; that means that in my lifetime (born in 1978), the sheer number of wild animals in the world has been decreased by over half. Even "common" wild species are less numerous than before. While habitat population is the single biggest cause of species endangerment and extinction overall, outdoor and indoor/outdoor cats are a significant cause as well. In fact, they are the single biggest cause of human-caused mortality in wild birds.
Most importantly, it's very, very simple to fix this problem: keep your cats indoors, and spay and neuter them. If your cat is bored, they need more enrichment, and there are plenty of ways to make your home more exciting for them, from bringing home cardboard boxes for them to explore, to playing with them more often. If you want your cat to get some outdoor enrichment, leash train them (yes, it can be done!) If you have the space and resources, build them a catio where they can be safe from outdoor dangers like predators and cars, while also keeping local wildlife safe from them.
If you just give into their whining and pawing at the door, then they know that that's what they have to do to get their way; I know it's a tough transition, but it's worth it in the end for everyone involved. Cats are domesticated, which means they are not native anywhere in the world; there are exactly zero ecosystems in which they belong, save for the safety of your home. It is your responsibility to give them an enriching environment without taking the shortcut of letting them go wreak havoc outside.
#cats#outdoor cats#feral cats#nature#wildlife#animals#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#birds#endangered species#extinction#domesticated animals#domestication#biology#animal behavior#animal welfare
8K notes
·
View notes
Text


the fritter (frin critter)
#inspo struck right after posting the last two. some kind of a hermit crab. a snail#they think they look all cool and mysterious under their safety shelter but if u remove it they're a disastrous puffball of uncombed fur#the hat is not accurate to an adult human btw. i tried to put them in a full size hat and they were lost forever. this is a child sized hat#they need to swap out for bigger hats as they grow#MY FRIENDS WROTE AND DREW SO MUCH FOR THE FRITTER I HOPE THEY CAN REBLOG AND ADD BC THEYRE SO GOOD <3#we started making a whole au about critter species in the wild and how they interact and survive. very fascinating.#i need to collect all the worldbuilding into one place eventually. rn all i'll say is.. overworked odile petsmart employee (tealgoat's idea#isat critters#isat#in stars and time#isat siffrin#my art#a6se/twohats (this tag only) implication then is that loop is bald i guess aksdks. loop = wild shorthair. fritter = domestic longhair.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
the species euphoria is calling me






#species euphoria#species dysphoria#alterhuman#alterhuman community#alterhumanity#therianthropy#therian community#lycanthrope#lycanthropy#dog therian#dogkin#canine theriotype#canine cladotherian#canine therian#caninekin#canine kin#wolfdog kin#wolf otherkin#wolfdog#wolf boy#wolf theriotype#wolf kin#wolf therian#wolfboy#wolfkin#fox theriotype#fox kin#foxkin#fox therian#domestic dog therian
659 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Oh, you're transfem? Are you an Animal HRT transfem or a Human Domestication Guide transfem?"
#animal hrt#therian hrt#species hrt#otherkin hrt#furry hrt#hdg#human domestication guide#don't mind me just feel like swinging a bat at two hornet nests today
814 notes
·
View notes
Text


a love letter to weasels ❤️🩷
#song was made by me and my little siblings like. 5 years ago#yes its plagerized from the draidel song#it has another verse but i didnt include it#my art#og art#weasels#mustelids#mammals#animals#time to tag EVERY SPECIES OF WEASEL FEATURED#least weasel#stoat#ermine#long tailed weasel#malayan weasel#siberian weasel#mountain weasel#polecat#european polecat#marbled polecat#striped polecat#domestic ferret#angora ferret#black footed ferret#european pine marten#beech marten#tayra#north american river otter#small clawed otter#american mink
543 notes
·
View notes
Text
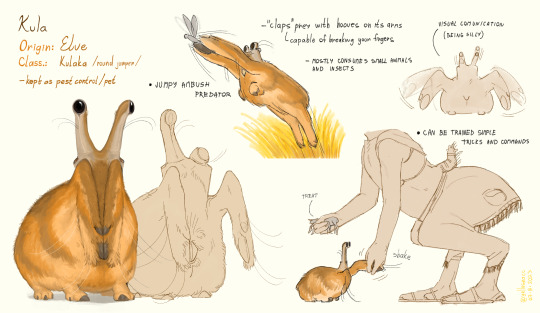
Kula!
A popular domesticated animal of slomen.
Kula are adapted for grassy areas with lots of small prey. In the wild, they either jump after flying or jumping prey or wait at burrows before smashing their prey with their hooves. If the smash isn't enough they hold it to their beak and finish it. Some species are more specialized to wait while others to jump. The domesticated Kula is speculated to be one of the more energetic hunters, mostly interested in 'insects'.
In ancient times wild Kula were attracted to sloman settlements as they would also attract prey with the slomans' food and light. The slomen would soon learn that Kula were not pests since the wild animals were yet to be spoiled by premium meat cuts and preferred fresh moving meat that the slomen didn't want around.
In current times many cultures keep these animals as pest control on farms and in larger houses. They can be commonly seen in underground rooms that serve as food storage but for a healthy mental state, they need time on the sun.
While in the wild they are usually solitary or in small groups, Kula have a complex body language that they use to express their mood and/or needs. This can be very cute and funny, helping them become as loved as they are. Many owners will grow to care deeply for their Kula but some cultures recognize them directly as pets. In the high-ranking societies of these cultures, pet Kula get even rounder. Often a certain trait is popular in a culture, resulting in localised breeds with different shapes and colors.

Some little goober possibilities - not entirely canon
In a few places, Kula are also part of a religion and have their own shrines.
#art#speculative biology#artists on tumblr#digital art#artwork#worldbuilding#speculative evolution#fantasy#spec bio#original alien species#original species#spec evo#speculative zoology#xenobiology#domesticated animals#slomen
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

creature...

oh no I’ve domesticated them :O
#illustration#character design#monster art#creature#digital art#legally this could go on onelilguy but they're not very little#he slowly carves huge paths in the forest looking for bugs#slow enough that they grow moss and this bird species builds nests on them#then they eat any pests on him as he sleeps#the domesticated ones are smaller to be a bit faster (not by much)#and so people can more easily dress them for travel#their sturdy gait and endurance makes them ideal for travelling long distances with a lot of stuff
580 notes
·
View notes
Text
i may have done some thinking


alan adopts someone (unwillingly)

^ said someone (little guy)
#so sily......#and stupid.#little guy thinks alan is his mommy...#tfw an animal adopts you as its parent#no!! alan is NOT his mommy!#they're not even the same SPECIES! alan's a user's cursor and little guy is a house/domestic cursor!#outernet cursors#ava alan becker#ava cursor#ava au#ava#animator vs animation#alan becker#grimm doobles
279 notes
·
View notes
Note
If we’re doing cattle, how about Bos indicus?
Oh absolutely! They're so neat!


#south asia#domesticated species#domesticated animals#cow#cattle#zebu#bos indicus#animal polls#poll blog#my polls#animals#polls#tumblr polls#mammalia#bovidae
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
#1936 - Meleagris gallopavo domesticus - Domestic Turkey

A somewhat unexpected sighting in Cambridge, New Zealand. Free range chickens are one thing, but you don’t often see a rafter of feral turkeys having a stroll down the street here in the Antipodes. Of course the fact that New Zealand has no large predators is probably a factor, and just as well, because unlike their wild counterparts the domestic turkey can’t fly very far. Wild turkeys on the other hand, will roost high in trees to avoid anybody inclined to a white meat diet.
Female domestic turkeys are called hens, and the chicks poults or turkeylings. In North America, male turkeys are called toms; in the United Kingdom and Ireland they are stags. Nobody has recorded what cats and deer call them.
The Latin gallopāvō is a portmanteau meaning "chicken peacock" - which is fair enough. It’s not a bad description of the wild bird. The English-language common name, on the other hand, is the kind of nonsense you get when an entirely unrelated South American bird now known as the Guinea Fowl gets imported into Europe by 15th Century Turkish traders and sold as ‘Turkey-cocks’. When the British invaded Massachusetts, they assumed the local bird was the same one.
Turkeys were first tamed in what is now southern Mexico at least two thousand years ago. Ancient Mesoamericans using their meat and eggs as a major source of protein, and the feathers for decorative purposes. The Aztecs associated the bird with their trickster god Tezcatlipoca. Recent research suggests a possible second domestication event in the North American southwest between 200 BC and AD 500 but, all of the main turkey varieties today are derived from the Mesoamerican domestication.
The domestic turkey now is raised throughout temperate parts of the world, partially because industrialized farming has made the meat very cheap. The great majority of domestic turkeys are bred for white feathers (less visible when the carcass is dressed), although brown or bronze-feathered varieties are also raised. They retain the snoods and wattles - fleshy protuberances atop and below the beak.
There were an estimated 30,000 wild turkeys left in the US by the 1930s, but extensive efforts by wildlife biologists have helped numbers recover, even in states where they had been hunted to extinction. This has led to some aggressive encounters between humans and turkeys that have become used to humans around the place. Even the domestic variety can be quite pushy - my little brother was pursued round and round a truck stop yard when he was a lad, but that may just have been the bird taking offense to his multicoloured jacket. I just found it hilarious.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text


Just dropping some illustrations of animals that I've only mentioned in passing (mostly in regional food posts), found within claimed Imperial Wardi territory.
Left to right (all to scale):
Grynaig, crested eagle, taarn, unkata, piispiispi, anara, nechoi.
Descriptions below:
The grynaig, a type of pigeon found primarily in the highlands. They come in a few local color morphs, ranging from this brown-white to a chestnut color (mostly dependent on the types of rocks they nest upon). They nest on the tops and sides of boulders and cliffs, out of reach from most ground-based predators and camouflaged from predatory birds above. They are commonly hunted for food, and are regarded as having beautiful calls.
The crested eagle, found widely across the region. They are specialized predators of snakes and will readily attack highly venomous species, having thick-skinned, pebbly textured legs as defense against bites. They will also take other reptiles, and occasionally prey on small birds and mammals. Among the peoples of the highlands, widespread belief holds these to be (one of many) birds that ancestors will send or take the form of in order to provide guidance and give omens to the living. Crested eagles are often an omen of hidden danger, be it a figurative or literal snake in the grass.
The taarn, a pheasant native to the highlands and domesticated for meat and eggs. The domestic stock has several color morphs and a few distinct breeds, a wild male taarn is pictured here. Wild taarn can be found in high altitudes in the warm dry season, and migrate down to the river valleys in the cold wet season. Taarn form the vast majority of captive fowl in the highlands, being the most tolerant of cooler, high altitude conditions. Males possess sharp spurs, and are used regionally for cockfighting. Cockfighting is also popular in parts of the Imperial Wardi cultural sphere and taarn may be exported largely for this purpose, being imagined as uniquely fierce, having been shaped by their hostile environment (in reality, they don't tend to fare well against the common rooster).
The unkata, a genus of large flightless birds. Several species can be found in the region, all of which are flightless and relatively large. The one here is a male savannah unkata in breeding plumage (about the size of a cassowary). Male unkata often have colorful wings, and all possess long, unfeathered quills. The wings are shaken as a part of courtship displays, creating a rattling sound and dazzling visual effect. These birds are herbivores and feed on grass, leaves, tender shoots, and fruit, but will consume insects and small mammals/reptiles when the opportunity presents itself. Most unkata are commonly hunted as wild game, and their large eggs are often prized as food and used for carving.
The piispiispi, named for its devastatingly silly warning cries (the sound is a shrill PeEEESSsss-PeEEESSsss-PIPIPIPIPI!). This is a fairly large and stocky lagomorph that lives only in the highlands and almost exclusively at high altitudes (with rabbits filling their niches in the river valleys). They subsist primarily on grasses, and are known agricultural pests. They pack on substantial weight prior to the winters (which is the best time to hunt them for rich, fatty meat), but do not truly hibernate, instead alternating between periods of low activity in their burrows and emerging to graze (the winters here are relatively warm, and snow cover is often patchy or impermanent at all but the highest altitudes).
The anara, a genus of large semi-aquatic rodent. Two species can be found in the region (the larger of which is shown here, both look very similar) and can be found throughout in most rivers, lakes, ponds, and wetlands. Their tail is flattened vertically and used to propel them through water, though they retain (relatively) long legs, as they spend much of their time foraging on land, usually staying within a couple hundred feet of water. They are considered agricultural pests, and are commonly hunted for pest control and their meat (particularly the tail, which is uniquely rich and fatty).
They construct small lodges along banks for shelter in a similar capacity to beavers. They do not build dams, but dig canals to connect bodies of water (for ease of movement and to flee from predators). These canals are often expanded by the comings and goings of an-nechoi, and together the two species are of key ecological significance to their environments, vastly expanding the size of wetlands and the reach of seasonal floods. The two species also seem to get along quite well (especially given the notoriously bad temper of an-nechoi, and the bite-sized nature of anara), often peacefully sharing the same habitats in close quarters. Young anara are sometimes even seen resting on the backs of submerged an-nechoi. This connection is widely noted, and a subject of many regional animal folktales.
Nechoi, a family of pig-like opportunistic omnivores. The one pictured here is a scrub nechoi, one of the larger in the region (though dwarved by their somewhat distant, semi-aquatic an-nechoi relatives). These are the most widespread and generalized, and fare well in dry environments (mostly being found in the grasslands and savannahs). The skin of this species is exposed (though they bear a dense mane and thick, wiry hairs throughout), and they will coat themselves in mud and dust to protect against the sun and parasites. This particular species bears impressive tusks in the boars, and smaller tusks in the sows (shown here), and they are often hunted for their ivory.
Most nechoi bear very powerful jaws with a wide gape, and boars will fight over territory and mates by yawning and slashing at each other with their sharp teeth. These conflicts result in a scarred appearance in most older boars, and can sometimes be fatal. As with most nechoi, these animals feed primarily as browsers, but will readily scavenge and may opportunistically take live prey, mostly arthropods and small vertebrates. Predatory attacks on animals bigger than they can fit into their mouths are rare, but larger nechoi such as these are considered dangerous, and may readily eat humans injured or killed in territorial or defensive aggression. These more dangerous nechoi are sometimes subjects to taboos against eating the flesh of man-eaters, though smaller nechoi are common game animals.
#creatures#I have not decided if pigs exist in this universe or not. I've mentioned them before (I think just as 'hogs') but they may or may#not be domesticated and/or smallish species of nechoi#We'll see
296 notes
·
View notes
Text
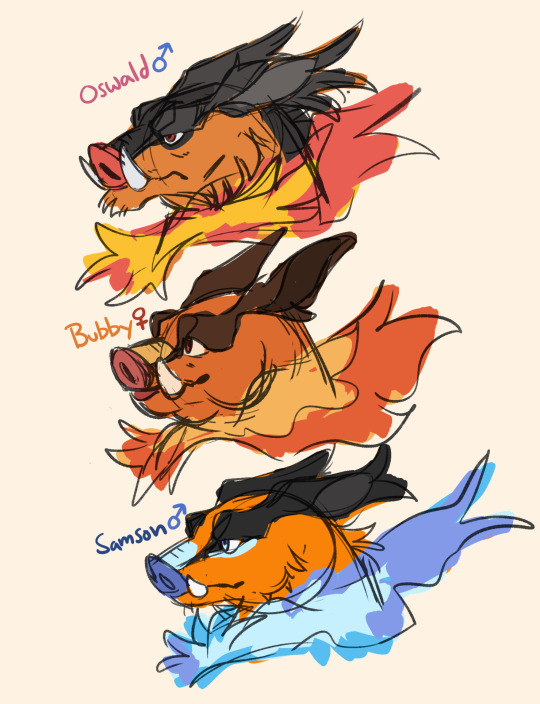
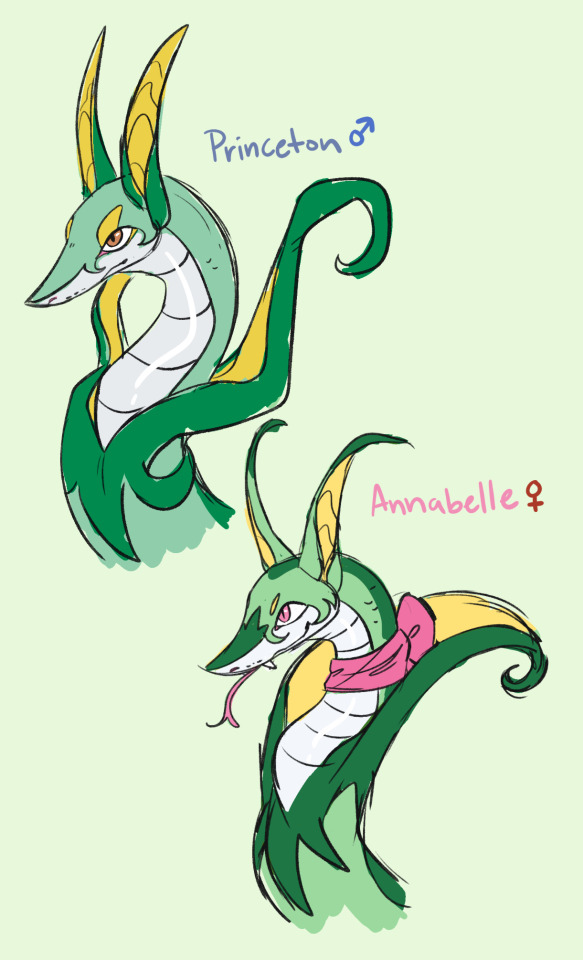


all the starters <3 they’ll all get full images eventually!!
#pokemon#serperior#emboar#samurott#pokemon bw#unova#their trainers in order: cheren -> rosa -> hilda -> bianca -> nate -> hilbert -> hugh#the main trio (cheren bianca hilbert)’s starters are more or less standard for domestic breeds of their species#hence why they look a liiiittle plain. while ozzy and murphy are descended from wild individuals and annie is a show breed#samson is from ozzy and bubbys singular litter (always spay and neuter your pets!!) hilda and bianca aren’t together though#bianca doesn’t have that realization until years down the line after she divorces cheren. sad! oh well#princeton#annabelle#oswald#bubby#samson#cordelia#murphy#sketches
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
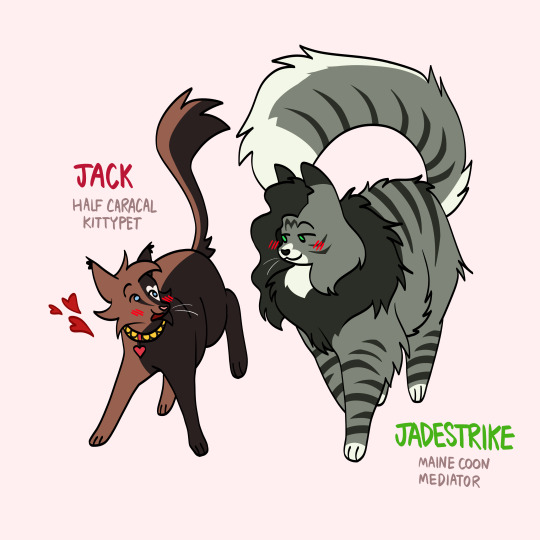

can the mediator of vengeanceclan really fall in love with a kittypet?...
#my art#jack of hearts#she hulk#jack hart#jennifer walters#warriors au#sensational she hulk#marvel#this was a break from studying and i was like well. might as well be insane#i would do a human piece i have planned but jack's dumbass armor would take too long to draw... so Kity it is#also i love using tags because it's lore time.#jen is a warrior of vengeanceclan (tha avengers) specifically a mediator#cuz it's like the equivalent of a lawyer! and i think that aspect is more interesting to capture than her superhero stuff#but ofc she still kicks ass. she must#she's a maine coon so she can be a Big Kitty#jack is a half-caracal bc he's half alien and i wanted him to be half another cat species but not one that's too diff from domestic cats#it was harder for me to adapt his themes though bc there's not a great equivalent for uh. nuclear reactor powers#but yknow what is a theme of his! isolation! and so he's a kittypet and out of place in vengeanceclan :)#yea i'm really normal rn thanks for asking
153 notes
·
View notes
Text
Phylogenetic weasel tournament
Family: Mustelidae
Subfamily: Mustelinae
Genus: Mustela


Finally, a weasel. Well, I don't get the impression that "weasel" really means anything as I haven't recognised some distinct characteristic that's appears in all animals called weasel and missing from everything else. But that's language for you.
Anyway. Siberian weasels are also called kolonok. Pretty cool name.
Black-footed ferret


Siberian weasel


pictures: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
#polls#tournament poll#phylogenetic weasel tournament#mustelinae#black-footed ferret#ferret#siberian weasel#kolonot#hah i checked and they're called ferrets in hungarian#anyway my incredibly well-founded suggestion is that let's call everything here ferrets: domestic ferret. polecat ferret. steppe ferret.#black-footed ferret. mink ferret. siberian ferret. japanese ferret.#excellent names. no downside.#send congratulations to amber-tortoiseshell.tumbr.com#(the rest of the mustela species are weasels except when they are ermines)
50 notes
·
View notes