#detect ai generated text
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Detect ai generated text for Free, simple way & High accuracy. Ai content check, ai content detection tool, ai essay detector for teacher.
0 notes
Text
Detect Ai Generated Text
Detect chatGPT content for Free, simple way & High accuracy. OpenAI detection tool, ai essay detector for teacher. Plagiarism detector for AI generated text,ZeroGPT the most Advanced and Reliable Chat GPT, GPT4 & AI Content Detector
Detect Ai Generated Text
0 notes
Text

0 notes
Text
anti 'ai' people make 1 (one) well-informed, good-faith argument challenge(impossible)
#txt#obviously the vast majority of anti-'ai' people on here are just like.#'my internet sphere told me machine-generated text/images are bad'#and have not considered any cases where 'ai' is demonstrably materially useful#(e.g. tumor detection. drug discovery. early detection of MANY diseases. modeling the effects of epi/pandemic responses. modeling all sorts#of public health policy‚ actually. discovering new mechanisms of disease. that's just off the top of my head)#but now people are straight up saying that computers are NEVER better than humans at any tasks. and we should all just ~use our BRAINS!!!~#like. i have no words.#i mean i fucking guess i shouldn't expect these people to base their takes on actual facts or reason.#still pisses me the fuck off to know that there are people out there who are so dogmatic about this#editing to put this in my#‘ai’#tag
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
As ChatGPT is getting more common, I feel bad for future students because they'll most likely be forced to write essays by hand in person while being watched.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI Generated Text Detection Made Simple with ZeroGPT
AI Generated Text Detection Made Simple with ZeroGPT. ZeroGPT simplifies the process of detecting AI-generated text, offering user-friendly tools for accurate identification. Whether you're a novice or expert user, ZeroGPT's intuitive interface makes content verification effortless. Detect AI-generated text with confidence, ensuring content authenticity and reliability. Trust ZeroGPT for precise AI detection and elevate your content validation process. Experience the convenience of AI-generated text detection with ZeroGPT by your side.
0 notes
Text
AI Gen Text Detect Pro: Your Ultimate Solution for AI-Generated Text Validation
Trust ZeroGPT for accurate "AI Generated Text Detection." Our platform ensures precision in identifying and managing AI-generated textual content, offering users a reliable solution for maintaining the authenticity and quality of their digital materials. Dive into the future of content scrutiny with ZeroGPT, where innovation meets reliability, ensuring users can navigate the complexities of AI-generated content seamlessly for a secure and trustworthy digital environment.

0 notes
Text
Detect Ai Generated Text Brazil
CudekAI is a highly effective and reliable tool designed to detect and analyze AI-generated text in Brazil. This page offers a range of valuable resources and information to help individuals and organizations identify, evaluate, and manage AI-generated content specifically in Brazil. For additional details please visit https://www.cudekai.com/.
0 notes
Text
An AI Detector is a tool that uses a vast datasets of information to determine whether a piece of text is genuinely human-writtten or if it's AI-generated.
#anti chatgpt detector#chatgpt content detector#chatgpt detection#check for ai generated text#chatgpt zero detector
0 notes
Note
Miss Tracy, do u have any advice on researching a specific time period?
(also I know u probably won't see this, but I love your art and you are awesome)
Look for books about the time period, but also books written contemporaneous to the time period, whether fiction or non-fiction. Check used book stores for out of print gems at good prices.
If photography was a technology that existed in the time period you're researching, look for photos of people doing everyday things. Take in the context, the geography, the economic situation. Look at how they're dressed and what their clothes say about them.
Newspaper archives. Sometimes newspapers of the past are free to browse. Sometimes you have to pay for access. Old shopping catalogue collections - if they exist for your time period - are great too.
Documentary films about time periods, or specific events in a given time period can be useful, even if only for a broad overview.
Museum exhibits - helpful whether you're looking for famous paintings or artifacts of past civilizations in a world renowned institution, or trying to dig up something impossibly unique in an oddity denture museum in some forgotten place in the Midwest. If you can't go in person, check online. You can find museums with vintage clothing or household appliance collections from even a few decades ago. Some museums have extensive, searchable online collections too. Take the Metropolitan Museum for instance.
If you can visit historical sites relevant to your area of interest, do it! Do those little guided walking tours. Do the ghost tours even - they're often fairly history-centric with some paranormal folklore for added spice. Sometimes they get you access to places you otherwise can't enter. Check historical societies local to cities or towns of interest.
If you need information about something deeply specific, check the internet for communities that form around that deeply specific topic. I've found tidbits of useful info searching around old forum posts from radio enthusiasts, Model T owners, and people who collect old telephone booths. (Granted, it's getting harder to search for this kind of stuff nowadays.)
-----------
Be careful of AI trash, whether it's generative images, text descriptions, or entire articles. Don't rely much on film or television for accuracy. Some things are more interested in being accurate than others, but there's almost always some artistic license taken. If you're trying to be particularly accurate about something, triple check it for confirmation. Misinformation has had a way of spreading like insidious mildew even before AI started disseminating it with delusory authority.
Lastly, if you don't enjoy doing this kind of historical research like a weird little detective-creature, consider loosening up on the 'historical' aspect of your writing. It's okay to not focus on historicity in your fiction. But if you're going to dive in whole-hog on history, bear in mind it's an ongoing, often time-consuming adventure in information-finding.
(Thank you for the kind words!)
984 notes
·
View notes
Text
Detect ai generated text for Free, simple way & High accuracy. Ai content check, ai content detection tool, ai essay detector for teacher.
#check gpt#detect ai generated text#free ai detector#open ai detector#ai checker text#ai content detection tool#ai detection free#ai detect#ai detector chatgpt#check ai writing
0 notes
Text
Tips To Choose The Right Chat GPT Detection Tool For Your Business
ChatGPT is taking the world by storm. AI is a hot topic of discussion everywhere. If you are a business owner or a student, it’s possible that you know about the revolutionary changes this technology is driving. Chat GPT can improve customer experience, reduce cost, increase efficiency, and generate leads. Chat GPT has a lot of potential but we are just now learning about the potential downsides.
With the tremendous technological shift in how people work with Chat GPT while creating websites, apps, and even novels, there is caution to be exercised. We need to monitor abuse of Chat-GPT. Because it lets students pass their exams and submit their assignments. Writers now submit generative content, and researchers produce high-quality papers by typing prompts on Chat-GPT. AI Detection tools have come out to stop this abuse but many are not updated on a daily basis. Because of this, some can even generate false positives. Everyone needs AI-generated text detection tools that can deliver with a high degree of accuracy and ChatGPT detectors are now in high demand. You definitely need to catch cheaters but you also don’t want to accuse the innocent.
AI Detector Pro is software that effectively identifies text generated by Chat GPT. It is updated daily to so that it works on the latest version of ChatGPT and is already being tested on Bard. If you are using other detection tools on submitted work, they may give you false positives but AI Detector Pro’s constantly updated algorithms ensure that all are positive as to whether cheating has occurred or not and you can safely assess whether content is original or not without worry. In an effort to assist cheating and deception, there are many tools flooding the market. However, there is a possibility that they are not 100% accurate. This is why AI Detector Pro tests on so many different types of data sets.
With AI technology overtaking every industry and sector, it is necessary to make use of a reliable chat GPT detector. Concern about choosing a detector that can detect text coming from Chat GPT is looming large for various professionals. Since the language models powering the technology of Chat GPT are so good, it can be difficult to detect whether something like a social media post, essay, poem, or blog article was created with Chat GPT or by a real human.
If you are looking for a generative AI detector, find a complete solution at AI Detector Pro, which is a comprehensive platform to easily check for AI-generated content created by the top AI content generation tools. You will get detailed and advanced reports showing the exact text that exhibits evidence of AI generation. In addition, you can manage your AI-generated reports efficiently with projects. AI Detector Pro offers tools and utilities to expand your toolbox.
1 note
·
View note
Text

0 notes
Text
“Humans in the loop” must detect the hardest-to-spot errors, at superhuman speed

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me SATURDAY (Apr 27) in MARIN COUNTY, then Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

If AI has a future (a big if), it will have to be economically viable. An industry can't spend 1,700% more on Nvidia chips than it earns indefinitely – not even with Nvidia being a principle investor in its largest customers:
https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=39883571
A company that pays 0.36-1 cents/query for electricity and (scarce, fresh) water can't indefinitely give those queries away by the millions to people who are expected to revise those queries dozens of times before eliciting the perfect botshit rendition of "instructions for removing a grilled cheese sandwich from a VCR in the style of the King James Bible":
https://www.semianalysis.com/p/the-inference-cost-of-search-disruption
Eventually, the industry will have to uncover some mix of applications that will cover its operating costs, if only to keep the lights on in the face of investor disillusionment (this isn't optional – investor disillusionment is an inevitable part of every bubble).
Now, there are lots of low-stakes applications for AI that can run just fine on the current AI technology, despite its many – and seemingly inescapable - errors ("hallucinations"). People who use AI to generate illustrations of their D&D characters engaged in epic adventures from their previous gaming session don't care about the odd extra finger. If the chatbot powering a tourist's automatic text-to-translation-to-speech phone tool gets a few words wrong, it's still much better than the alternative of speaking slowly and loudly in your own language while making emphatic hand-gestures.
There are lots of these applications, and many of the people who benefit from them would doubtless pay something for them. The problem – from an AI company's perspective – is that these aren't just low-stakes, they're also low-value. Their users would pay something for them, but not very much.
For AI to keep its servers on through the coming trough of disillusionment, it will have to locate high-value applications, too. Economically speaking, the function of low-value applications is to soak up excess capacity and produce value at the margins after the high-value applications pay the bills. Low-value applications are a side-dish, like the coach seats on an airplane whose total operating expenses are paid by the business class passengers up front. Without the principle income from high-value applications, the servers shut down, and the low-value applications disappear:
https://locusmag.com/2023/12/commentary-cory-doctorow-what-kind-of-bubble-is-ai/
Now, there are lots of high-value applications the AI industry has identified for its products. Broadly speaking, these high-value applications share the same problem: they are all high-stakes, which means they are very sensitive to errors. Mistakes made by apps that produce code, drive cars, or identify cancerous masses on chest X-rays are extremely consequential.
Some businesses may be insensitive to those consequences. Air Canada replaced its human customer service staff with chatbots that just lied to passengers, stealing hundreds of dollars from them in the process. But the process for getting your money back after you are defrauded by Air Canada's chatbot is so onerous that only one passenger has bothered to go through it, spending ten weeks exhausting all of Air Canada's internal review mechanisms before fighting his case for weeks more at the regulator:
https://bc.ctvnews.ca/air-canada-s-chatbot-gave-a-b-c-man-the-wrong-information-now-the-airline-has-to-pay-for-the-mistake-1.6769454
There's never just one ant. If this guy was defrauded by an AC chatbot, so were hundreds or thousands of other fliers. Air Canada doesn't have to pay them back. Air Canada is tacitly asserting that, as the country's flagship carrier and near-monopolist, it is too big to fail and too big to jail, which means it's too big to care.
Air Canada shows that for some business customers, AI doesn't need to be able to do a worker's job in order to be a smart purchase: a chatbot can replace a worker, fail to their worker's job, and still save the company money on balance.
I can't predict whether the world's sociopathic monopolists are numerous and powerful enough to keep the lights on for AI companies through leases for automation systems that let them commit consequence-free free fraud by replacing workers with chatbots that serve as moral crumple-zones for furious customers:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0747563219304029
But even stipulating that this is sufficient, it's intrinsically unstable. Anything that can't go on forever eventually stops, and the mass replacement of humans with high-speed fraud software seems likely to stoke the already blazing furnace of modern antitrust:
https://www.eff.org/de/deeplinks/2021/08/party-its-1979-og-antitrust-back-baby
Of course, the AI companies have their own answer to this conundrum. A high-stakes/high-value customer can still fire workers and replace them with AI – they just need to hire fewer, cheaper workers to supervise the AI and monitor it for "hallucinations." This is called the "human in the loop" solution.
The human in the loop story has some glaring holes. From a worker's perspective, serving as the human in the loop in a scheme that cuts wage bills through AI is a nightmare – the worst possible kind of automation.
Let's pause for a little detour through automation theory here. Automation can augment a worker. We can call this a "centaur" – the worker offloads a repetitive task, or one that requires a high degree of vigilance, or (worst of all) both. They're a human head on a robot body (hence "centaur"). Think of the sensor/vision system in your car that beeps if you activate your turn-signal while a car is in your blind spot. You're in charge, but you're getting a second opinion from the robot.
Likewise, consider an AI tool that double-checks a radiologist's diagnosis of your chest X-ray and suggests a second look when its assessment doesn't match the radiologist's. Again, the human is in charge, but the robot is serving as a backstop and helpmeet, using its inexhaustible robotic vigilance to augment human skill.
That's centaurs. They're the good automation. Then there's the bad automation: the reverse-centaur, when the human is used to augment the robot.
Amazon warehouse pickers stand in one place while robotic shelving units trundle up to them at speed; then, the haptic bracelets shackled around their wrists buzz at them, directing them pick up specific items and move them to a basket, while a third automation system penalizes them for taking toilet breaks or even just walking around and shaking out their limbs to avoid a repetitive strain injury. This is a robotic head using a human body – and destroying it in the process.
An AI-assisted radiologist processes fewer chest X-rays every day, costing their employer more, on top of the cost of the AI. That's not what AI companies are selling. They're offering hospitals the power to create reverse centaurs: radiologist-assisted AIs. That's what "human in the loop" means.
This is a problem for workers, but it's also a problem for their bosses (assuming those bosses actually care about correcting AI hallucinations, rather than providing a figleaf that lets them commit fraud or kill people and shift the blame to an unpunishable AI).
Humans are good at a lot of things, but they're not good at eternal, perfect vigilance. Writing code is hard, but performing code-review (where you check someone else's code for errors) is much harder – and it gets even harder if the code you're reviewing is usually fine, because this requires that you maintain your vigilance for something that only occurs at rare and unpredictable intervals:
https://twitter.com/qntm/status/1773779967521780169
But for a coding shop to make the cost of an AI pencil out, the human in the loop needs to be able to process a lot of AI-generated code. Replacing a human with an AI doesn't produce any savings if you need to hire two more humans to take turns doing close reads of the AI's code.
This is the fatal flaw in robo-taxi schemes. The "human in the loop" who is supposed to keep the murderbot from smashing into other cars, steering into oncoming traffic, or running down pedestrians isn't a driver, they're a driving instructor. This is a much harder job than being a driver, even when the student driver you're monitoring is a human, making human mistakes at human speed. It's even harder when the student driver is a robot, making errors at computer speed:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/01/human-in-the-loop/#monkey-in-the-middle
This is why the doomed robo-taxi company Cruise had to deploy 1.5 skilled, high-paid human monitors to oversee each of its murderbots, while traditional taxis operate at a fraction of the cost with a single, precaratized, low-paid human driver:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/11/robots-stole-my-jerb/#computer-says-no
The vigilance problem is pretty fatal for the human-in-the-loop gambit, but there's another problem that is, if anything, even more fatal: the kinds of errors that AIs make.
Foundationally, AI is applied statistics. An AI company trains its AI by feeding it a lot of data about the real world. The program processes this data, looking for statistical correlations in that data, and makes a model of the world based on those correlations. A chatbot is a next-word-guessing program, and an AI "art" generator is a next-pixel-guessing program. They're drawing on billions of documents to find the most statistically likely way of finishing a sentence or a line of pixels in a bitmap:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3442188.3445922
This means that AI doesn't just make errors – it makes subtle errors, the kinds of errors that are the hardest for a human in the loop to spot, because they are the most statistically probable ways of being wrong. Sure, we notice the gross errors in AI output, like confidently claiming that a living human is dead:
https://www.tomsguide.com/opinion/according-to-chatgpt-im-dead
But the most common errors that AIs make are the ones we don't notice, because they're perfectly camouflaged as the truth. Think of the recurring AI programming error that inserts a call to a nonexistent library called "huggingface-cli," which is what the library would be called if developers reliably followed naming conventions. But due to a human inconsistency, the real library has a slightly different name. The fact that AIs repeatedly inserted references to the nonexistent library opened up a vulnerability – a security researcher created a (inert) malicious library with that name and tricked numerous companies into compiling it into their code because their human reviewers missed the chatbot's (statistically indistinguishable from the the truth) lie:
https://www.theregister.com/2024/03/28/ai_bots_hallucinate_software_packages/
For a driving instructor or a code reviewer overseeing a human subject, the majority of errors are comparatively easy to spot, because they're the kinds of errors that lead to inconsistent library naming – places where a human behaved erratically or irregularly. But when reality is irregular or erratic, the AI will make errors by presuming that things are statistically normal.
These are the hardest kinds of errors to spot. They couldn't be harder for a human to detect if they were specifically designed to go undetected. The human in the loop isn't just being asked to spot mistakes – they're being actively deceived. The AI isn't merely wrong, it's constructing a subtle "what's wrong with this picture"-style puzzle. Not just one such puzzle, either: millions of them, at speed, which must be solved by the human in the loop, who must remain perfectly vigilant for things that are, by definition, almost totally unnoticeable.
This is a special new torment for reverse centaurs – and a significant problem for AI companies hoping to accumulate and keep enough high-value, high-stakes customers on their books to weather the coming trough of disillusionment.
This is pretty grim, but it gets grimmer. AI companies have argued that they have a third line of business, a way to make money for their customers beyond automation's gifts to their payrolls: they claim that they can perform difficult scientific tasks at superhuman speed, producing billion-dollar insights (new materials, new drugs, new proteins) at unimaginable speed.
However, these claims – credulously amplified by the non-technical press – keep on shattering when they are tested by experts who understand the esoteric domains in which AI is said to have an unbeatable advantage. For example, Google claimed that its Deepmind AI had discovered "millions of new materials," "equivalent to nearly 800 years’ worth of knowledge," constituting "an order-of-magnitude expansion in stable materials known to humanity":
https://deepmind.google/discover/blog/millions-of-new-materials-discovered-with-deep-learning/
It was a hoax. When independent material scientists reviewed representative samples of these "new materials," they concluded that "no new materials have been discovered" and that not one of these materials was "credible, useful and novel":
https://www.404media.co/google-says-it-discovered-millions-of-new-materials-with-ai-human-researchers/
As Brian Merchant writes, AI claims are eerily similar to "smoke and mirrors" – the dazzling reality-distortion field thrown up by 17th century magic lantern technology, which millions of people ascribed wild capabilities to, thanks to the outlandish claims of the technology's promoters:
https://www.bloodinthemachine.com/p/ai-really-is-smoke-and-mirrors
The fact that we have a four-hundred-year-old name for this phenomenon, and yet we're still falling prey to it is frankly a little depressing. And, unlucky for us, it turns out that AI therapybots can't help us with this – rather, they're apt to literally convince us to kill ourselves:
https://www.vice.com/en/article/pkadgm/man-dies-by-suicide-after-talking-with-ai-chatbot-widow-says

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/23/maximal-plausibility/#reverse-centaurs

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#ai#automation#humans in the loop#centaurs#reverse centaurs#labor#ai safety#sanity checks#spot the mistake#code review#driving instructor
855 notes
·
View notes
Text
Beware of the new art book scams
Hey there, I'm putting together a little PSA. Art book ads can no longer be trusted. I recently got an ad for an art book from a company called Comicpencil. The book is all AI generated content. I didn't purchase it, but after digging I found a youtube video from an artist called Jazza pointing out that there is no credit to any artists anywhere. He purchased the book and pointed out that a lot of the text content also makes very little sense.

I tried commenting on the ad pointing out that it was AI generated and my post was instantly deleted and I was blocked. I think they have some kind of detecting software that flags any mention of AI on their ads to keep up the charade. Here's one of their posts on one of the better AI image detectors, Hivemoderation. I know these things aren't always accurate but they can definitely help indicate AI if the results are consistent enough. I tested a few I could find that weren't obscured to hell and sure enough they all came out with these results.
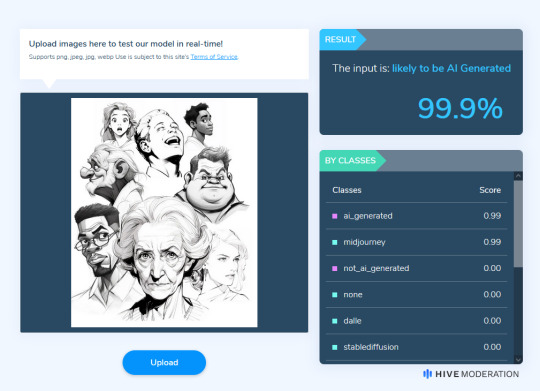
Please. I urge you to share this. Scams in general are going to be getting worse thanks to AI and it's really important people are aware of this. Be vigilant.
807 notes
·
View notes