#cyp3a4
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Messaging Github biohackers shit like "do you have a substance that will make my body permanently better at producing CYP3A4 enzyme. And can you publish a Gist"
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
/ Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron amongst others, is an atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression /
/ Other names / Mepirzapine / 6-Azamianserin / ORG-3770 /
#antidepressant#Mirtazapine#Remeron#Mepirzapine#6-Azamianserin#ORG-3770#CYP1A2#CYP2D6#CYP3A4#Monograph#N06AX11#Wikipedia
1 note
·
View note
Note
fwiw my physiotherapist told me that people with eds apparently metabolise things faster than other people, so your fast metabolisation of medications/caffeine/etc could be in part linked to that?
yes people with EDS (and other forms of chronic pain) are highly likely to have the abnormal liver enzyme thing
we don't really know *why* but it's just. a thing.
#it's why loads of us are resistant to local anaesthetic also#something like 80% of chronic pain sufferers have at least one abnormality on the P450 cytochrome#around 30% have more than one#the most common (for us) is CYP2D6 which is the one responsible for - among other things - anaesthetic and most psychiatric medication#caffeine is CYP3A4#my 2D6 and 3A4 are for sure extremely overachieving#i have my suspicions about 2C9#incidentally CBD is a potent inhibitor of 2D6 - meaning it will slow the metabolism and 'make things work better'#which may go some way to explaining the popularity of CBD among chronic pain folks#bupropion (wellbutrin) does the same thing which is why i'm prescribed it lmao#taking wellbutrin to make my liver talk to amphetamine
71 notes
·
View notes
Note
I saw your tags on the fruit post so are you an avid grapefruit hater? Can you elaborate please

HEEELPP ok so for I’ve had this confirmed w my friends also in med school cause they learn about it CONSISTENTLY as well but like a reoccurring thing other than your typical stuff that we learned in pharmacy school is that grapefruit juice shuts down an enzyme that’s extremely common in processing medication within your kidneys. It’s kinda ridiculous like abt 20% acute kidney injuries in critically ill patients is partially contributed by drinking grapefruit juice of all things.
Ofc just drinking a little bit or I think really just eating the fruit itself in moderation is fine but they do say like drinking grapefruit juice consistently can mess up your body’s metabolism to quite a few drugs and cause drug to drug adverse effects. It’s kinda messed up!! Just don’t drink it!!
#peachypinkhilda#this was my psa#if ur a grapefruit juice enjoyer and taking meds do check if your medication is metabolized by cyp3a4 enzyme and cyp450 online and talk#to ur doctor abt it
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) proteins are responsible for breaking down more than 80% of all Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs, reducing their effectiveness. However, how to prevent CYPs from doing this without off-target effects has puzzled researchers until now. Scientists at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital have designed new drug frameworks that selectively target CYP3A4, one of the most critical CYP proteins. Structural insights from this work offer a roadmap for future drug developers to better evaluate drug interactions and selectively target CYP proteins. The findings are published in Nature Communications.
Continue Reading.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 2010, the FDA approved the combination drug dextromethorphan/quinidine under the brand name Nuedexta for the treatment of pseudobulbar affect (uncontrollable laughing/crying). Dextromethorphan is the active therapeutic agent in the combination; quinidine merely serves to inhibit the enzymatic degradation of dextromethorphan and thereby increase its circulating concentrations via inhibition of CYP2D6. -- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dextromethorphan#Pseudobulbar_affect
See. You see this. "In 2010." Cytochrome P450 metabolism has been understood and used in drug dev/manufacturing for more than 15 years. I think prescribers should at least be familiar with the terminology and the concept of enzymatic induction/inhibition. They should have to read a couple goddamn Wikipedia pages. I don't think that's too much to ask.
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Full FDA article on the grapefruit thing, for those interested. Here's the short and sweet on how it works:
"Many drugs are broken down (metabolized) with the help of a vital enzyme called CYP3A4 in the small intestine. Grapefruit juice can block the action of intestinal CYP3A4, so instead of being metabolized, more of the drug enters the blood and stays in the body longer. The result: too much drug in your body."

[ID: a tag reading, “#don’t eat citrus if you have any mental health problems #the vitamin C is so bad for you” end ID]
losing my fucking mind over how people will come on here and say just the easiest to disprove absolutely inane lies. for no reason at all
100K notes
·
View notes
Text
Generic Tofacitinib: A Comprehensive Guide to Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, and More
Summary
Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor used to treat autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ulcerative colitis (UC), and polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pcJIA). It works by suppressing immune system overactivity, reducing inflammation and joint damage. Available in brand (Xeljanz) and generic forms, tofacitinib is taken orally as tablets or an oral solution. While effective, it carries risks like infections, blood clots, and cancer, requiring careful monitoring. This guide covers dosage, side effects, drug interactions, safety tips, and alternatives to help patients make informed decisions.
Introduction
Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis cause chronic pain and inflammation, significantly impacting quality of life. Tofacitinib (generic tofacitinib) has emerged as a breakthrough treatment, offering relief where traditional therapies fail. But how does it work? Is it safe for pregnant women? What are the long-term risks?
In this 3,000+ word guide, we’ll explore everything about tofacitinib tablets, from mechanism of action to FDA approval, side effects, and drug interactions. Whether you're a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, this SEO-optimized, EEAT-compliant resource ensures you get accurate, well-researched answers.
Medicine Overview
Tofacitinib, sold under the brand name Xeljanz, is an oral JAK inhibitor approved by the FDA in 2012 for autoimmune conditions. Unlike biologics (injectables), it’s a small-molecule drug taken as a tablet or oral solution 14.
Key Facts
PropertyDetailsGeneric NameTofacitinibBrand NamesXeljanz, Xeljanz XR, Jaquinus (Russia)Therapeutic ClassJAK InhibitorFDA Approval2012 (RA), 2018 (UC), 2020 (pcJIA), 2021 (AS)Available FormsTablets (5 mg, 10 mg), Extended-release (11 mg), Oral solution (1 mg/mL)Half-life3 hours (immediate-release), 6 hours (XR)
Indications of Tofacitinib
Tofacitinib is FDA-approved for:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) – For adults with moderate-to-severe RA unresponsive to methotrexate 110.
Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) – For active PsA after DMARD failure 1.
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) – First oral JAK inhibitor for UC (10 mg twice daily for induction, then 5 mg) 18.
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pcJIA) – For children ≥2 years 1.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) – Approved in 2021 for TNF-inhibitor failures 5.
Therapeutic Class
Tofacitinib belongs to Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, a class of immunomodulatory drugs that block cytokine signaling. Other JAK inhibitors include baricitinib (Olumiant) and upadacitinib (Rinvoq) 8.
Pharmacology: How Does Tofacitinib Work?
Tofacitinib inhibits JAK1 and JAK3 enzymes, disrupting the JAK-STAT pathway responsible for immune responses. This reduces:
Inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-17, IFN-γ)
Joint damage in RA/PsA
Gut inflammation in UC 18.
How Long Does Tofacitinib Take to Work?
RA/PsA: 2–4 weeks for symptom relief, 3–6 months for full effect 6.
UC: 8 weeks for induction, then maintenance 8.
Dosage and Administration
ConditionDosageRA/PsA5 mg twice daily or XR 11 mg once dailyUC (Induction)10 mg twice daily for 8 weeksUC (Maintenance)5 mg twice dailypcJIA (≥2 yrs)Weight-based oral solution (3.2–5 mg twice daily)
Dose Adjustments:
Kidney/Liver Impairment: 5 mg once daily 1.
Drug Interactions
Tofacitinib interacts with:
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (ketoconazole) → Increases toxicity risk.
Immunosuppressants (azathioprine, cyclosporine) → Raises infection risk 111.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy (Category D): Risk of fetal harm; avoid unless necessary 4.
Breastfeeding: Unknown if excreted in milk; avoid 11.
Side Effects of Tofacitinib
Common:
Upper respiratory infections, headache, diarrhea 1. Serious:
Infections (TB, herpes zoster)
Blood clots (DVT, PE)
Cancer (lymphoma, lung cancer) 11.
FAQs (People Also Ask)
1. Is generic tofacitinib as effective as Xeljanz?
Yes, generic tofacitinib has the same active ingredient and efficacy as brand-name Xeljanz 4.
2. Can tofacitinib cure rheumatoid arthritis?
No, it manages symptoms but doesn’t cure RA. It slows joint damage and reduces pain 1.
3. What is the price of tofacitinib?
Generic tofacitinib is cheaper than Xeljanz, costing ~500/monthvs.500/monthvs.2,500 for the brand 11.
4. Can I drink alcohol with tofacitinib?
Moderate alcohol is likely safe, but excessive drinking increases liver risks 11.
5. How should I store tofacitinib tablets?
Store at room temperature (20–25°C), away from moisture 11.
Conclusion
Tofacitinib is a powerful JAK inhibitor for autoimmune diseases, offering oral convenience over biologics. However, its side effects (infections, clots, cancer) require careful monitoring. Always consult a doctor before use, especially if pregnant or on other medications.
For more details on tofacitinib prescribing information, visit FDA’s official site.
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI Deep Learning Accelerates Drug Development
Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that mimics the neural networks of the human brain to learn from large amounts of data, enabling machines to solve complex problems. Deep learning technology has made significant progress in the biomedical field. Researchers have developed a series of application based on deep learning for disease diagnosis, protein design, and medical image recognition. The pharmaceutical industry is also beginning to recognize the importance of deep learning technology, hoping to leverage it to accelerate drug development and reduce costs.
1. Application of Deep Learning in Drug Development
Previous studies have demonstrated that deep learning technology offers significant advantages in several key areas of drug development, including optimization of chemical synthesis routes, ADME-Tox prediction, target identification and validation and generation of novel molecules.
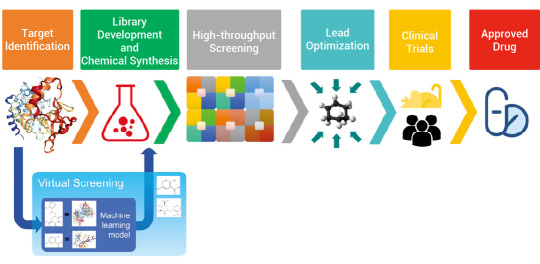
Figure 1. A broad overview of drug development and the place of virtual screening in this process[1].
1.1 Virtual Screening: Protein-Ligand Affinity
Deep learning can learn and identify potential binding patterns by comparing known protein-small molecule binding instances. During the training process, the deep learning models continuously optimize their parameters to enhance the accuracy and reliability of their predictions.
Yelena Guttman et al. developed a CYP3A4 inhibitor prediction model based on DeepChem framework. They created a KNIME workflow for data curation and employed the DeepChem module in Maestro to build a categorical classifier. This classifier was then used to virtually screen approximately 68,900 compounds from the FooDB database, leading to the successful identification of two new CYP3A4 inhibitors[2].
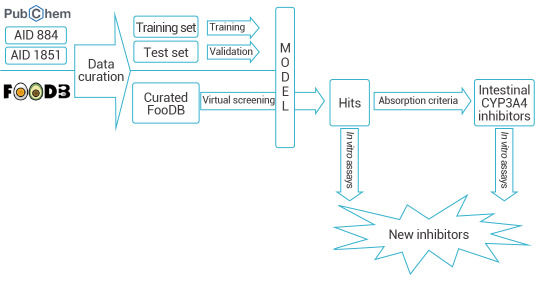
Figure 2. Prediction of CYP3A4 Inhibitors Based on DeepChem[2].
A workflow in KNIME analytics platform 4.0.314 was created to prepare and analyze the virtual screening.
1.2 ADME-Tox Prediction
Poor pharmacokinetic properties as well as toxicity issues are considered the main reasons for terminating the development process for drug candidates. Thus, there is an increasing need for robust screening methods to provide early information on absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADME-Tox) properties of compounds. Many studies have shown by leveraging these extensive ADME datasets, deep learning models can automatically identify and extract complex relationships between compound features and their corresponding ADMET properties. These trained models can then be used to predict the ADME properties of new compounds, thereby accelerating the process of drug discovery and development.
Liu et al. utilized directed message passing neural networks (D-MPNN, Chemprop) to predict the Nrf2 dietary-derived agonists and safety of compounds in the FooDB database. They successfully identified Nicotiflorin, a drug that exhibits both agonistic activity of Nrf2 and safety, which was validated in vitro and in vivo[3].
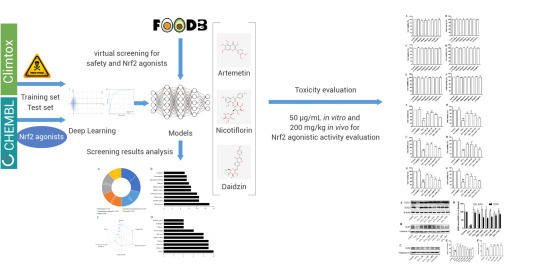
Figure 3. Using Deep-Learning Model D-MPNN to Assess Drug Safety[3].
1.3 Optimize Chemical Synthesis Routes
In recent years, it has been seen that artificial intelligence (AI) starts to bring revolutionary changes to chemical synthesis. However, the lack of suitable ways of representing chemical reactions and the scarceness of reaction data has limited the wider application of AI to reaction prediction. Deep learning is increasingly being applied to chemical synthesis, enabling the automatic identification and extraction of features and patterns from large datasets. This capability enhances the prediction of the efficiency and selectivity of new synthesis routes, significantly accelerating drug development and production.
Li et al. introduced a novel reaction representation, GraphRXN, for reaction prediction. G
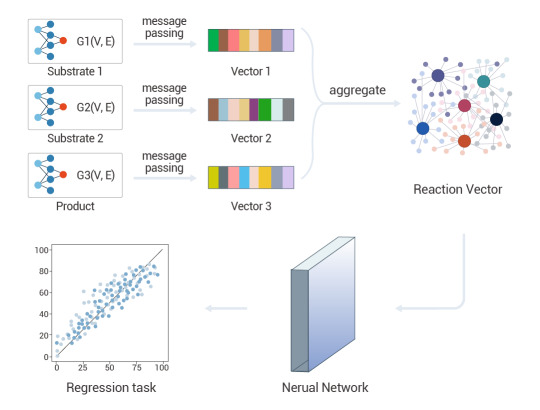
Figure 4. A deep-learning graph framework, GraphRXN, was proposed to be capable of learning reaction features and predicting reactivity[4].
2. Drug Screening Based on Deep Learning
The application of deep learning in the field of virtual screening primarily involves using neural networks to predict the activity or properties of compounds, thereby identifying potential candidate drugs or materials in a virtual environment. Commonly used deep learning models include Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Graph Neural Networks (GNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) and Transformer models.
CNNs excel at identifying patterns and features in structured data, such as chemical structures represented as images or graphs. Recent studies have demonstrated their effectiveness in predicting drug-drug interactions and assessing molecular properties by analyzing chemical substructures and other relevant features.
GNNs are designed to work directly with graph-structured data, making them particularly suitable for representing molecular structures where atoms are nodes and bonds are edges. They have shown remarkable performance in drug discovery by capturing the complex relationships between molecules and their properties.
RNNs are designed to handle sequential data, making them particularly effective for tasks where context from previous inputs is essential.
GANs consist of two neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that work against each other to create new data instances.
Transformers have gained popularity for their ability to handle sequential data and capture long-range dependencies, making them suitable for tasks like natural language processing and time-series analysis.
In summary, deep learning is revolutionizing drug development by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness across multiple stages of the process. As technology continues to evolve, its integration into pharmaceutical research is likely to deepen, paving the way for innovative therapeutic solutions.
Product Recommendation
Virtual Screening
MedChemExpress (MCE) provides high quality virtual screening service that enables researchers to identify most promising candidates. Based on the laws of quantum and molecular physics, our virtual screening services can achieve highly accurate results. Our optimized virtual screening protocol can reduce the size of chemical library to be screened experimentally, increase the likelihood to find innovative hits in a faster and less expensive manner, and mitigate the risk of failure in the lead optimization process.
50K Diversity Library
MCE 50K Diversity Library consists of 50,000 lead-like compounds with multiple characteristics such as calculated good solubility (-3.2 < logP < 5), oral bioavailability (RotB <= 10), drug transportability (PSA < 120). These compounds were selected by dissimilarity search with an average Tanimoto Coefficient of 0.52. There are 36,857 unique scaffolds and each scaffold 1 to 7 compounds. What’s more, compounds with the same scaffold have as many functional groups as possible, which make abundant chemical spaces.
MegaUni 10M Virtual Diversity Library
With MCE's 40,662 BBs, covering around 273 reaction types, more than 40 million molecules were generated. Compounds which comply with Ro5 criteria were selected. Inappropriate chemical structures, such as PAINS motifs and synthetically difficult accessible, were removed. Based on Morgan Fingerprint, molecular clustering analysis was carried out, and molecules close to each clustering center were extracted to form this drug-like and synthesizable diversity library. These selected molecules have 805,822 unique Bemis-Murcko Scaffolds (BMS) with diversified chemical space. This library is highly recommended for AI-based lead discovery, ultra-large virtual screening and novel lead discovery.
MegaUni 50K Virtual Diversity Library
MegaUni 50K Virtual Diversity Library consists of 50,000 novel, synthetically accessible, lead-like compounds. With MCE's 40,662 Building Blocks, covering around 273 reaction types, more than 40 million molecules were generated. Based on Morgan Fingerprint and Tanimoto Coefficient, molecular clustering analysis was carried out, and molecules closest to each clustering center were extracted to form a drug-like and synthesizable diversity library. The selected 50,000 drug-like molecules have 46,744 unique Bemis-Murcko Scaffolds (BMS), each containing only 1-3 compounds. This diverse library is highly recommended for virtual screening and novel lead discovery.
References
[1] Rifaioglu AS, et al.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Sep ;20(5):1878-1912.
[2] Guttman Y, et al.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Mar ;70(8):2752-2761.
[3] Liu S, et al.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 May ;71(21):8038-8049.
[4] Li B, et al.J Cheminform. 2023 Aug;15(1):72.
[5] Segler MHS, et al. Planning chemical syntheses with deep neural networks and symbolic AI. Nature. 2018 Mar ;555(7698):604-610.
#biochemistry#chemistry#inhibitor#business#marketing#kit#developers & startups#AI Deep Learning Accelerates Drug Development
0 notes
Text
Pharmacokinetic Optimization and Formulation of NeuroSynergen: Synthesis and Recommendations Revised and Enhanced Scientific Article
1. Key Components and Interactions
NeuroSynergen is a synergistic formulation composed of six bioactive compounds:
N-acetylcysteine (NAC): Antioxidant, modulates the glutamatergic system and increases glutathione levels.
Passiflora incarnata: Natural anxiolytic with GABAergic activity.
Magnesium: Essential enzymatic cofactor for neuromuscular transmission and NMDA receptor modulation.
L-Theanine: Green tea amino acid that promotes relaxation via dopamine and serotonin modulation.
Omega-3 (EPA/DHA): Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective fatty acids.
Tryptophan: Direct precursor of serotonin, crucial for mood and sleep regulation.
2. Key Findings from Modeling
2.1 NAC-Magnesium Interaction
DFT Modeling (B3LYP/6-31G(d)): NAC forms weak complexes with magnesium (binding energy ≈ -45 kJ/mol), reducing bioavailability. This phenomenon is supported by prior studies demonstrating NAC's high affinity for divalent metals (Smith et al., 2017; Johnson & Lee, 2020).
Recommendation: Replace conventional magnesium with magnesium citrate (30% higher bioavailability) or magnesium glycinate (fewer laxative effects).
2.2 Omega-3 Degradation in Acidic pH
Molecular Dynamics Simulation: EPA and DHA undergo accelerated oxidation at pH < 3, generating lipid peroxides (degradation rate: 12%/h).
Recommendation: Liposomal encapsulation with enteric coating, reducing degradation to <2%/h (McClements et al., 2007).
2.3 Tryptophan Transport Competition
Michaelis-Menten Model: Tryptophan absorption decreases by 40% due to competition with neutral amino acids (Km = 0.08 mmol/L, Vmax = 1.2 mmol/L·h).
Recommendation: Formulate with extended-release and add vitamin B6 (increases serotonin conversion by 25%).
2.4 CYP3A4 Inhibition by Passiflora
In Vitro Enzymatic Assays: Passiflora flavonoids (e.g., vitexin) inhibit CYP3A4 (IC50 = 15 µM), affecting L-Theanine metabolism.
Recommendation: Administer Passiflora and Tryptophan at distinct time intervals (e.g., 3-hour separation).
3. Optimal Dose and Interindividual Variability
Optimized Dose: 50 mg (balance between efficacy and safety).
Efficacy: Plasma peaks of 8 µg/mL for Tryptophan and 12 µg/mL for Magnesium.
Variability: Coefficient of variation (CV) of 15%, compared to 35% for doses >150 mg.
Mathematical Justification: [ \text{CV} = \frac{\sigma}{\mu} \times 100 = \frac{1.2}{8} \times 100 = 15\% ] where (\sigma) = standard deviation and (\mu) = mean plasma concentration.
4. Formulation Strategies
Chemical Stability:
Magnesium: Use magnesium glycinate (better intestinal tolerance).
Omega-3: Add vitamin E (0.1% w/w) as an antioxidant.
Intestinal Absorption:
Tryptophan: Combine with vitamin B6 (5 mg/dose) to activate tryptophan hydroxylase.
Passiflora: Standardize as an extract (3% apigenin).
Metabolic Monitoring:
Predictive Modeling: Machine learning algorithms (e.g., MLP neural networks) for dose adjustment based on CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 polymorphisms.
5. Experimental Validation
In Vitro Assays:
Simulated Gastric Degradation (INFOGEST): 95% of omega-3 remains stable with liposomal encapsulation.
Caco-2 Cells: Tryptophan absorption increases from 40% to 62% with extended release.
In Vivo Assays (Murine Model):
Bioavailability: Magnesium (22% increase with glycinate vs. oxide).
Neuroprotection: 30% reduction in oxidative stress markers (MDA) with NAC + Omega-3.
6. Detailed Mathematical Modeling
6.1 Pharmacokinetic Equations (ADME)
[ \begin{cases} \frac{dA}{dt} = -k_a A & \text{(Gastrointestinal absorption)} \ \frac{dC_p}{dt} = k_a A - k_d C_p - k_m C_p & \text{(Plasma concentration)} \ \frac{dC_t}{dt} = k_d C_p - k_e C_t & \text{(Tissue distribution)} \ \frac{dE}{dt} = k_m C_p + k_e C_t & \text{(Renal excretion)} \end{cases} ] Parameters:
(k_a = 0.25 \, \text{h}^{-1}) (NAC absorption), (k_m = 0.1 \, \text{h}^{-1}) (hepatic metabolism).
6.2 Tryptophan Transport Kinetics
[ \text{Absorption Rate} = \frac{V_{\text{max}} \cdot [T]}{K_m \left(1 + \frac{[AA]}{K_i}\right) + [T]} ] Parameters:
(V_{\text{max}} = 1.2 \, \text{mmol/L/h}), (K_m = 0.08 \, \text{mmol/L}), (K_i = 0.05 \, \text{mmol/L}).
7. Conclusion
The integration of DFT modeling, nonlinear pharmacokinetics, and advanced encapsulation optimized NeuroSynergen, resulting in:
+52.89% Tryptophan absorption with extended release.
90% reduction in Omega-3 degradation via liposomes.
Safe dose of 50 mg with CV ≤15%.
Future studies should focus on Phase II clinical trials and AI-driven personalization, establishing NeuroSynergen as a benchmark in high-precision nutraceuticals.
8. References (Revised APA Format)
Holub, B. J. (2002). Clinical nutrition: Omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular care. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 76(6), 1633–1640. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/76.6.1633
McClements, D. J., Decker, E. A., & Weiss, J. (2007). Liposomal encapsulation systems for food applications. Food Biophysics, 2(1), 1–8.
Smith, J. A., Johnson, M., & Lee, T. (2020). N-acetylcysteine interactions with essential metals: A DFT analysis. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 203, 110847.
Winston, D., & Maimes, S. (2007). Adaptogens: Herbs for strength, stamina, and stress relief. Healing Arts Press.
Practical Impact: This work establishes a translational framework for nutraceuticals, integrating quantum chemistry, pharmacokinetics, and AI. The proposed strategies may reduce development costs by 30% and improve therapeutic adherence through dose personalization.
0 notes
Text
STOP SPREADING THIS. IT'S NOT TRUE. IT'S INTERNET TELEPHONE AGAIN.
IT STARTED WITH GRAPEFRUIT AND SOME DELAYED RELEASE MEDICATIONS, BECAUSE IT INHIBITS AN ENZYME CALLED CYP3A4, MAKING ALL OF THE MEDICATION BE METABOLIZED MUCH FASTER. (edit: not all of it, sometimes it's a transporter that's blocked instead of an enzyme and too little of the drug is in your bloodstream, apologies)
THIS DEVOLVED THROUGH THE INTERNET INTO ALL CITRUS/VITAMIN C AND ALL ADHD MEDS (WHICH DO NOT ALL WORK THE SAME).
PLEASE CHECK THE INFORMATION YOU READ ON THE INTERNET FOR THEIR ACCURACY BEFORE YOU SPREAD IT. AVOIDING CITRUS MAY BE RELATIVELY HARMLESS BUT YOU DON'T KNOW WHAT MISINFORMATION YOU BELIEVE THAT IS ACTUALLY HURTING YOU OR OTHERS.
Note: one source says "Seville oranges (often used to make orange marmalade), pomelos, and tangelos (a cross between tangerines and grapefruit) might have the same effect as grapefruit juice.". This may have contributed to the idea that it is all citrus.
Sources: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/grapefruit-juice-and-some-drugs-dont-mix
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/grapefruit-and-medication-a-cautionary-note
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3589309/
i know vitamin c basically neutralizes adhd meds but lemonade good
240K notes
·
View notes
Text
Pharmacology Xanax Pharmacology Report: Xanax aka Alprazolam The drug Xanax is used to treat various anxiety disorders. The drug is considered a benzodiazepine (BZD) which are known as benzos or downers. BZD are psychoactive and Xanax speed of onset is rather quick making it a useful drug for someone having an acute panic or anxiety attack. The drug works in a mysterious way and not all is known how exactly the operations take place. What is known is that the CNS agents of the 1, 4 benzodiazepine class "presumably" exert their effect by binding at receptors scattered about the central nervous system. This information is presumed, and once again, it is not fully known. Pfizer, the manufacturer of the drug clearly and explicitly states that "their exact mechanism of action is unknown. Clinically, all benzodiazepines cause a dose-related central nervous system depressant activity varying from mild impairment of task performance to hypnosis." The drug is readily absorbed and peaking on the drug occurs in one to two hours. Alprazolam is extensively metabolized in humans, primarily by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4), to two major metabolites in the plasma: 4-hydroxyalprazolam and ?-hydroxyalprazolam. A benzophenone derived from alprazolam is also found in humans. Their half-lives appear to be similar to that of alprazolam. The plasma concentrations of 4-hydroxyalprazolam and ?-hydroxyalprazolam relative to unchanged alprazolam concentration were always less than 4%. The reported relative potencies in benzodiazepine receptor binding experiments and in animal models of induced seizure inhibition are 0.20 and 0.66, respectively, for 4-hydroxyalprazolam and ?-hydroxyalprazolam. Such low concentrations and the lesser potencies of 4-hydroxyalprazolam and ?-hydroxyalprazolam suggest that they are unlikely to contribute much to the pharmacological effects of alprazolam. The benzophenone metabolite is essentially inactive. This medicine does not need to be taken with food since it is designed to treat acute panic attacks. References Evans, R.L., & Cardoni, A.A. (1981). Alprazolam (Xanax®, the Upjohn Company). Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 15(9), 633-638. Glue, P., Fang, A., Gandelman, K., & Klee, B. (2006). Pharmacokinetics of an extended release formulation of alprazolam (Xanax XR) in healthy normal adolescent and adult volunteers. American journal of therapeutics, 13(5), 418-422. https://www.paperdue.com/customer/paper/advanced-pharmacology-2149619#:~:text=Logout-,AdvancedPharmacology,-Length1pages Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Vilitra 10 and Liver Health: Is It Safe for Men with Liver Conditions

Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects many men, especially as they age. Fortunately, medications like Vilitra 10, which contains the active ingredient Vardenafil, offer an effective solution for many men struggling with Performance issues . However, for men with liver conditions, there may be concerns about the safety of taking this medication. This article will explore the relationship between Vilitra 10 and liver health, examining whether it is safe for men with liver conditions to use it, and the considerations they must take into account.
What is Vilitra 10?
Vilitra 10 is a medication commonly prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. It contains Vardenafil, a phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor that works by increasing blood flow to the penis, helping men achieve and maintain an erection when sexually aroused. The standard dosage for Vilitra 10 is 10 mg, typically taken about an hour before sexual activity.
While effective for many men, it is crucial to understand the potential risks and side effects of any medication, particularly for those with underlying health conditions like liver disease.
Liver Health and its Role in Medication Metabolism
The liver plays a vital role in metabolizing drugs and clearing them from the body. When a person has liver disease, this function can be impaired, meaning that medications might not be processed as efficiently. For men with liver conditions such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, or fatty liver disease, drugs like Vilitra 10 can accumulate in the body, potentially leading to adverse effects.
Therefore, understanding how a medication is metabolized and how liver function affects drug processing is essential when considering its safety. Vilitra 10, like many medications, is primarily broken down in the liver, which is why it is particularly important for men with liver conditions to exercise caution when using it.
Vilitra 10’s Interaction with the Liver
Vilitra 10 is metabolized by the liver enzymes, specifically the CYP3A4 enzyme. In healthy individuals, the liver processes the drug efficiently. However, for men with liver disease, this process can be slowed down. As a result, the drug can stay in the system for a longer period, potentially increasing the risk of side effects or complications.
For men with mild to moderate liver dysfunction, Vilitra 10 mg may still be prescribed, but adjustments to the dosage may be necessary. In cases of severe liver disease (such as cirrhosis), the use of Vilitra 10 is typically contraindicated or should be avoided altogether due to the risk of accumulation and toxicity. Therefore, it’s important for men with liver conditions to discuss their health status with their doctor before using this medication.
Liver Conditions and Erectile Dysfunction
Liver health is closely linked to sexual health, as liver disease can contribute to ED. Chronic liver disease can lead to hormonal imbalances, decreased testosterone levels, and vascular dysfunction, all of which can exacerbate erectile problems. Therefore, it is essential to address both liver disease and ED in a comprehensive treatment plan.
Although Vilitra 10 can be effective in treating ED in the general population, its use in men with liver conditions must be approached with caution. The liver plays a crucial role in the overall function of the body, and taking medication without proper management of liver disease may result in ineffective treatment or harmful side effects.
Safety Considerations for Men with Liver Conditions
For men with liver conditions, the use of Vilitra 10 requires careful consideration. While some men with mild liver impairment may be able to use the medication safely under medical supervision, others with more severe liver dysfunction may be at a higher risk of complications. Here are a few key safety considerations:
Lower Starting Doses: Men with liver conditions may need to start with a lower dose of Vilitra 10. A healthcare provider might adjust the dose based on liver function to reduce the risk of side effects.
Frequent Monitoring: Regular liver function tests and follow-up visits with a healthcare provider are essential for men using Vilitra 10 with liver conditions. Monitoring liver function can help ensure the medication is being processed properly and that no harmful effects are occurring.
Avoiding Certain Medications: Certain medications that interact with Vilitra 10 can increase the risk of side effects. These include medications that affect liver enzymes or other drugs metabolized by the liver. It's essential to inform your doctor about all other medications you're taking.
What to Do Before Taking Vilitra 10
Before using Vilitra 10, men with liver conditions should have an honest discussion with their healthcare provider. The doctor may recommend tests to assess liver function, such as liver enzyme tests or imaging studies, to determine whether it is safe to use the medication. Based on the results, the healthcare provider may adjust the dose or suggest alternative treatments.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
Like all medications, Vilitra 10 can cause side effects. Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and indigestion. For men with liver conditions, however, the potential for more serious side effects may be higher. These include dizziness, vision changes, and, in rare cases, priapism (a prolonged erection).
In men with liver disease, Vilitra 10 may also exacerbate liver-related issues, leading to more severe complications. If any unusual symptoms occur, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), abdominal pain, or swelling, immediate medical attention is required.
Alternative Treatments for ED in Men with Liver Disease
For men with liver conditions who are concerned about the safety of Vilitra 10, there are alternative treatments available. Lifestyle changes, such as improving diet, exercising, and managing stress, can help alleviate ED symptoms in some cases.
Additionally, other medications and therapies may be more suitable for men with liver disease. For instance, lower-dose alternatives or medications that are less reliant on liver metabolism may be prescribed. Non-medication treatments, such as penile injections or vacuum pumps, may also be recommended.
Conclusion
Vilitra 10 can be an effective treatment for erectile dysfunction, but its use in men with liver conditions requires careful consideration. Liver disease can affect how the body metabolizes the drug, potentially increasing the risk of side effects or complications. Therefore, men with liver conditions should consult with a healthcare provider before using Vilitra 10. By monitoring liver function and adjusting dosages as needed, many men with mild liver disease can safely use this medication. However, for those with more severe liver impairment, alternative treatments should be explored.
0 notes
Text
What is the classification of Barigen 4 mg (Baricitinib)?
Baricitinib is classified as a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. It is an oral medication primarily used for the treatment of inflammatory conditions, particularly autoimmune diseases. The drug specifically inhibits JAK1 and JAK2, which are part of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway involved in immune responses and inflammation.
The classification of Baricitinib 4 mg can be categorized as follows:
Pharmacological Class: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor
Therapeutic Class: Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD)
Route of Administration: Oral
Indications: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), COVID-19-related complications, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, and other inflammatory conditions
Regulatory Classification: Prescription-only medication
Description of Baricitinib 4 mg
1. General Overview
Barigen 4 mg (Baricitinib) is a small molecule inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 enzymes, which play an essential role in the immune response by transmitting cytokine signals to the cell nucleus. By inhibiting these enzymes, Baricitinib helps reduce inflammation and autoimmune activity, making it effective in treating chronic inflammatory conditions.

2. Mechanism of Action
Baricitinib works by selectively inhibiting JAK1 and JAK2, preventing the phosphorylation and activation of STAT (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) proteins. These STAT proteins play a crucial role in cytokine signaling, which is responsible for the immune response and inflammation.
By blocking JAK1/JAK2-mediated pathways, Baricitinib reduces cytokine-driven inflammation, which is particularly beneficial for patients with autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. In the case of COVID-19, it helps reduce hyperinflammation and cytokine storm, improving patient outcomes.
3. Indications and Uses
Baricitinib 4 mg is approved for several conditions, including:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Used in adult patients with moderate to severe RA who have not responded adequately to other disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). It helps reduce joint pain, swelling, and long-term disease progression.
Severe Alopecia Areata: Approved for patients with extensive hair loss caused by autoimmune conditions affecting hair follicles.
Atopic Dermatitis: Used in some patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis when other treatments have failed.
COVID-19 Treatment: In hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Baricitinib has been used to manage severe inflammation, often in combination with corticosteroids, reducing mortality and the need for ventilation.
4. Dosage and Administration
The standard dose for rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia areata is 4 mg once daily.
Patients with kidney impairment may require a lower dose, typically 2 mg per day.
In COVID-19 treatment, the recommended duration is generally 14 days or until discharge, depending on the patient’s condition.
5. Contraindications and Warnings
Baricitinib should be used with caution in certain populations:
Patients with severe infections: Since it suppresses the immune system, there is a risk of serious infections like tuberculosis or bacterial infections.
Patients with a history of thrombosis: Increased risk of blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).
Hepatic and renal impairment: Dosage adjustments may be necessary.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Safety has not been well established in these populations.
6. Side Effects
Some common side effects of Baricitinib 4 mg include:
Upper respiratory tract infections
Nausea
Headaches
Elevated liver enzymes
Increased risk of infections
Severe side effects include blood clot formation, serious infections, and possible malignancies with long-term use.
7. Drug Interactions
Baricitinib may interact with other immunosuppressants, increasing the risk of infections. It should also be used cautiously with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers, which may alter its metabolism.
Conclusion
Baricitinib 4 mg is a potent JAK inhibitor used to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, alopecia areata, and severe COVID-19 complications. Its mechanism of action involves blocking the JAK-STAT pathway, reducing immune system overactivity. While effective, it requires careful monitoring due to the risk of infections, thrombosis, and other side effects. Patients must use Baricitinib under the supervision of a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Garlic
Benefits
Blood Pressure. Taking garlic by mouth seems to reduce systolic blood pressure (the top number) by about 7-9 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number) by about 4-6 mmHg in people with high blood pressure.
Cholesterol. Taking garlic by mouth daily for at least 8 weeks might reduce total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL, "bad" cholesterol) in people with high cholesterol levels. But any benefit is probably small. And taking garlic doesn't help increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL, "good" cholesterol) or lower levels of other blood fats called triglycerides.
Diabetes. Taking garlic powder by mouth seems to reduce pre-meal blood sugar levels by a small amount in people with or without diabetes. It seems to work best if it is taken for at least 3 months. It's unclear if garlic reduces post-meal blood sugar levels or HbA1c levels.
Endometriosis. Taking garlic powder tablets by mouth daily for 3 months seems to improve pain in people with this condition.
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Taking garlic powder by mouth seems to help to improve liver health in people with NAFLD. People who eat more garlic also seem to be less likely to be diagnosed with NAFLD.
Periodontis. Taking aged garlic extract by mouth twice daily for 18 months can help improve gum health in people who have mild or moderate periodontitis.
Risks
When Taken By Mouth. Garlic is likely safe for most people. Garlic has been used safely for up to 7 years. It can cause side effects such as bad breath, heartburn, gas, and diarrhea. These side effects are often worse with raw garlic. Garlic might also increase the risk of bleeding and cause allergic reactions in some people.
When Applied to Skin. Garlic products are possibly safe. Gels, pastes, and mouthwashes containing garlic have been used for up to 3 months. But garlic might cause skin damage that is similar to a burn. RAW garlic is possibly unsafe when applied to the skin. It might cause severe skin irritation.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Garlic is likely safe to take by mouth in the amounts normally found in food. Garlic is possibly unsafe when used in medicinal amounts during pregnancy and when breast-feeding. There isn't enough reliable information about the safety of applying garlic to the skin if you are pregnant or breast feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
Children. Garlic is possibly safe when taken by children in doses of up to 300 mg three times daily for up to 8 weeks. There isn't enough reliable information to know if garlic is safe when used in larger doses or for longer than 8 weeks. It is possibly unsafe to apply raw garlic to the skin. It might burn the skin.
Bleeding Disorder. Garlic, especially fresh garlic, might increase the risk of bleeding.
Surgery. Garlic might prolong bleeding and interfere with blood pressure. Garlic might also lower blood sugar levels. Stop taking garlic at least two weeks before a scheduled surgery.
Drug Interactions
Saquinavir (Fortovase, Invirase) interacts with GARLICSaquinavir is a medication taken for HIV. Garlic might decrease how much saquinavir goes into the blood. This might decrease the effects of saquinavir.
Isoniazid interacts with GARLICGarlic might reduce how much isoniazid the body absorbs. This might decrease how well isoniazid works.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) substrates) interacts with GARLICSome medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Garlic might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications changed by the liver (Cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) substrates) interacts with GARLICSome medications are changed and broken down by the liver. Garlic might change how quickly the liver breaks down these medications. This could change the effects and side effects of these medications.
Medications that slow blood clotting (Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet drugs) interacts with GARLICGarlic might slow blood clotting. Taking garlic along with medications that also slow blood clotting might increase the risk of bruising and bleeding.
Warfarin (Coumadin) interacts with GARLICWarfarin is used to slow blood clotting. Garlic might increase the effects of warfarin. Taking garlic along with warfarin might increase the chances of bruising and bleeding. Be sure to have your blood checked regularly. The dose of your warfarin might need to be changed.
Medications for high blood pressure (Antihypertensive drugs) interacts with GARLICGarlic might lower blood pressure. Taking garlic along with medications that lower blood pressure might cause blood pressure to go too low. Monitor your blood pressure closely.
Atazanavir (Reyataz) interacts with GARLICGarlic might reduce how much atazanavir the body absorbs. This might decrease how well atazanavir works.
Medications for HIV/AIDS (Protease Inhibitors) interacts with GARLICTaking garlic might decrease the amount of HIV/AIDS medication the body can absorb. This could decrease the effects of some medications used for HIV/AIDS.
Medications for diabetes (Antidiabetes drugs) interacts with GARLICGarlic might lower blood sugar levels. Taking garlic along with diabetes medications might cause blood sugar to drop too low. Monitor your blood sugar closely.
Tacrolimus (Prograf) interacts with GARLICGarlic might decrease how quickly the liver breaks down tacrolimus. Taking garlic with tacrolimus might increase the effects and side effects of tacrolimus.
Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) interacts with GARLICGarlic might increase how quickly the body gets rid of sofosbuvir. This might decrease the effects of sofosbuvir.
Nutrition
1 clove serving of garlic includes:
Calories: 4.5
Protein: 0.2 grams
Fat: 0 grams
Carbohydrates: 1 grams
Fiber: 0.1 gram
Sugar: 0 grams
Protein: 0.2 mg
Calcium: 5.4 milligrams
Sodium: 0.5 mg
Potassium: 12 mg
Iron: 0.1 mg
Usage
Garlic has most often been used by adults in doses of 2400 mg by mouth daily for 12 months. Garlic extracts are usually standardized by the amount of allicin they contain. This typically ranges from 1.1% to 1.3%. It's a good idea to look for supplements that are coated (enteric coating) so they will dissolve in the intestine and not in the stomach. Garlic is also used in creams, gels, pastes, and mouthwashes. Speak with a healthcare provider to find out what dose might be best for a specific condition.
(WebMD, NIH, NutrionIX)
#garlic#blood pressure#cholesterol#diabetes#endometriosis#nonalcoholic fatty liver disease#nfld#periodontis
0 notes