#cyanea the jellyfish
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I be doing everything but finishing projects-



I’m very proud of cyanea most- I FORGOT CYANEA’S LIPSTICK FUCK-
#my art#my post#stg#sonic the hedgehog#Amy rose#sonic art#sonic au#sonic oc#Cyanea Scyphozoa#cyanea the jellyfish#Sonic fankid#sonamy#Zip the hedgehog#zip rose#zap the hedgehog#zap rose#sonadow#Connie the hedgehog#pro the hedgehog#shadamy#cherry rose#sonshadamy#nightshade the hedgehog
56 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cyanea capillata
Lion's mane jellyfish
By Alexander Semenov
#alexander semenov#photographer#flickr#cyanea capillata#lion's mane jellyfish#jellyfish#marine photography#nature#animal
119 notes
·
View notes
Text
Одно из самых длинных существ на планете- Волосистая цианея.
One of the longest creatures on the planet is the Cyanea capillata .
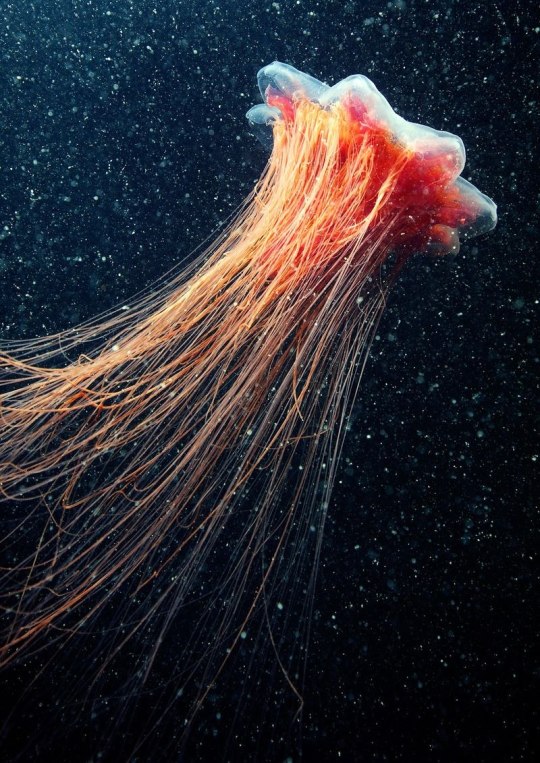
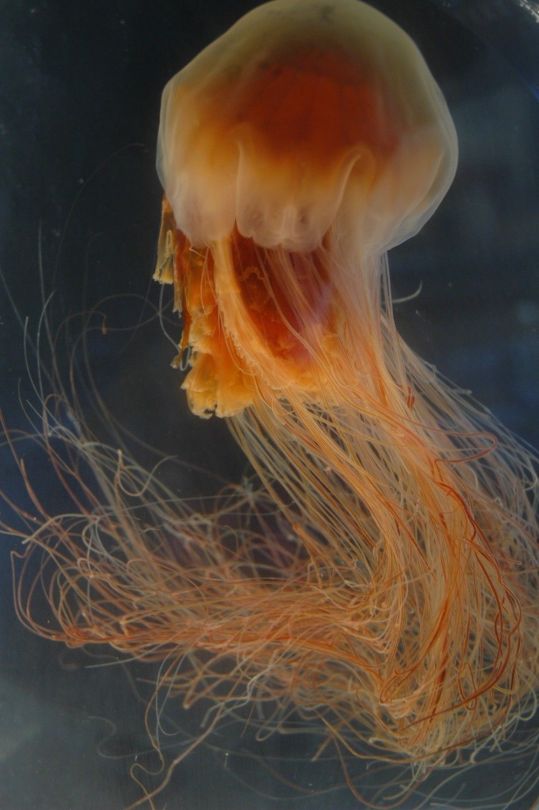
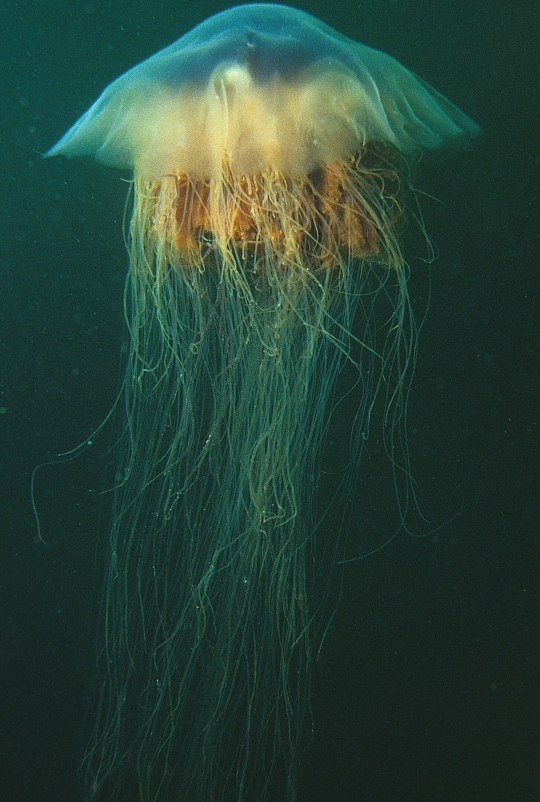
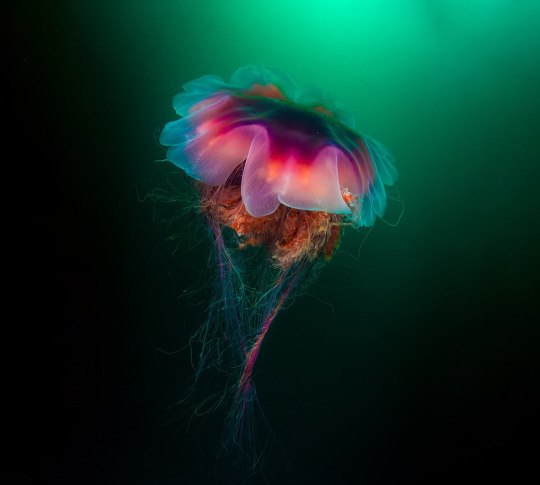

















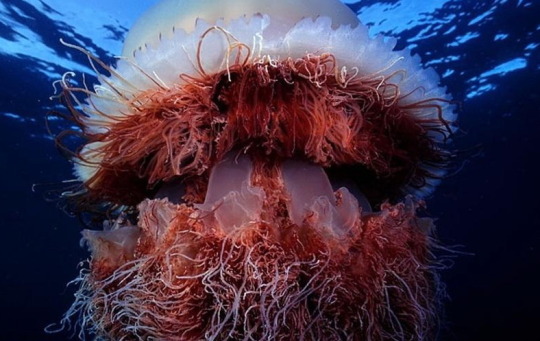


Невероятные обитатели морских глубин никогда не перестанут удивлять человека. Волосистая цианея (Cyanea capillata) или арктическая цианея может достигать очень больших размеров. Арктическая цианея относится к виду сцифоидных, отряду дискомедуз. В переводе с латинского медуза цианея означает синие волосы. Это самая крупная медуза во всем мире, размер цианеи просто гигантский. В среднем размер колокола цианеи 30-80 см. Но максимально крупные зарегистрированные экземпляры имели размер 2,3 метра в диаметре купола и 36,5 метров в длину. Огромное тело на 94% состоит из воды.
Цвет этой медузы зависит от ее возраста – чем старше животное, тем красочнее и ярче купол и щупальца. Молодые экземпляры в основном имеют желтую и оранжевую окраску, с возрастом они краснеют, буреют, появляются фиолетовые оттенки. У взрослых медуз купол в середине желтеет, а по краям краснеет. Щупальца тоже становятся разных цветов. Водятся эти крупнейшие медузы на глубине 20 метров в холодных водах Тихого и Атлантического океанов. Чем дальше от Арктики, тем меньших размеров она вырастает. За счёт своих щупалец цианеи не только передвигаются, но и охотятся. Свою добычу — планктон и других медуз — они убивают при помощи стрекательных клеток с ядом. Для человека волосистая цианея не очень опасна, но её укус весьма болезнен и может привести к аллергии.
The incredible inhabitants of the deep sea will never cease to amaze people. Cyanea capillata or arctic cyanea can reach very large sizes. Arctic cyanea belongs to the scyphoid species, the order of discomedusae. Translated from Latin, jellyfish cyanea means blue hair. This is the largest jellyfish in the whole world; the size of the cyanea is simply gigantic. On average, the size of a cyanea bell is 30-80 cm. But the largest recorded specimens measured 2.3 meters in dome diameter and 36.5 meters in length. The huge body is 94% water.
The color of this jellyfish depends on its age - the older the animal, the more colorful and brighter the dome and tentacles. Young specimens are mainly yellow and orange in color; with age they turn red, brown, and violet shades appear. In adult jellyfish, the dome turns yellow in the middle and turns red at the edges. The tentacles also become different colors.
These largest jellyfish are found at a depth of 20 meters in the cold waters of the Pacific and Atlantic oceans. The further from the Arctic, the smaller it grows. Using their tentacles, cyanea not only move, but also hunt. They kill their prey - plankton and other jellyfish - using stinging cells with poison. For humans, the cyanea is not very dangerous, but its bite is very painful and can lead to allergies.
Источник://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Волосистая_цианея,
/vladivostok.livejournal.com/6954591.html, /mir-vpechatleniy.ru/gigantskaya-meduza-oshelomila-dajverov/,
/rtraveler.ru/photo/1426870/, /biologymir.ru/volosistaya-czianeya/,
/fishki.net/3617561-volosistaja-cianeja-meduza-kotoraja-mozhet-vyrasti-dlinnee-sinego-kita-i-eyo-cikl-zhizni.html,
//www.aqualogo.ru/Cyanea_capillata-koroleva_meduz,
/www.factroom.ru/zhivotnye/samoe-dlinnoe-sushchestvo-na-planete,
givotniymir.ru/cianeya-meduza-obraz-zhizni-i-sreda-obitaniya-cianei/, telegram Океан, //poknok.art/19575-volosistaja-cianeja.html.
#fauna#video#animal video#marine life#marine biology#nature#aquatic animals#sea creatures#ocean#sea#jellyfish#Cyanea capillata#plankton#seaweed#beautiful#animal photography#nature aesthetic#animal gif#видео#фауна#природнаякрасота#природа#океан#море#медуза#Волосистая цианея#планктон#водоросли#гиф
257 notes
·
View notes
Text

update on making my ocs into magical girls/boys/nbs
i'm trying v hard to draw on my ipad because otherwise it's just an expensive ebook reader but i think i still haven't found the brushes that are the right fit for me, or maybe i'm just trying to do work that isn't suited for the way i draw on a screen....i do appreciate being able to work on projects during lunchtime though
#eye contact#art#saya#this is my oc themed after the lion's mane jellyfish#his name used to be cya because i chopped off half of cyanea but turns out it doesn't work so well in english so saya it is
95 notes
·
View notes
Text

A lion's mane jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) feeding on moon jellyfish in the white sea
by Alexander Semenov
#lions mane jellyfish#jellyfish#cnidarians#cyanea capillata#cyanea#Cyaneidae#semaeostomeae#Scyphozoa#cnidaria#wildlife: misc
190 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Lion’s Mane Jellyfish in the White Sea, Russia.
Marine biologist and photographer Alexander Semenov calls the lion’s mane jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) the queen of the Arctic seas. He photographed this specimen in its final stage of life: Having reproduced, it has shrunk in size, digested or shed its hundreds of long tentacles, and become, in Semenov’s words, an “Alien flower.”
#reddit#natureisfuckinglit#no-summer-9591#lions mane jelly fish#white sea#russia#marine biologist#photographer#photography#arctic seas#alien flower#marine#animal#fauna#bell#jellyfish#cyanea capillata
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
jellyfish :)









#jellyfish#the clear one is a moon jellyfish#moon jellyfish#or Aurelia aurita#the blue one is bluefire jellyfish#or Cyanea lamarckii#bleufire jellyfish#beach trip
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just doing some quick research and I'm getting lost so I'm just gonna post about my thought process so I can pick it back up later
The Problem: I don't know who the Cyanea nozakii is named after and none of the sources will tell me
Solution: Look up the original description of the jellyfish, which is listed in the jellyfish's WoRMS page
Problem: WoRMS doesn't have a copy listed on their website
Solution: Search this up

Solution (2): Omg I can't believe I found it on the Library of Congress Catalog this is absolutely amazing, with an online pdf copy no less...
Heck, after searching all the articles made in 1891, I even found the link that shows the original(?) description Cyanea nozakii by my favourite dude, Kamakichi Kishinouye
Problem: I can't read this. at all. h

#it's in a print font that might be hard for some machines to read#im going to cry#I guess I'll have to use the google translate app#i can't believe this rabbit hole took me all the way to the friggin library of congress catalogue though#i have no idea how i found this#and man what a stroke of luck that this magazine was open AND had pdfs available online#haaah#mun rambles#jellyfish#cyanea nozakii#i'll post my findings later if I find anything I suppose
10 notes
·
View notes
Video
Cyanea capillata by Alexander Semenov Via Flickr: No mane, but still beautiful
1 note
·
View note
Text
putting so much effort and research into naming wanderer vs not even having him, so i v rarely ever see him and his name
#🍯 talks#cyanea#blue butterfly#and jellyfish#means sky blue#idk i looked up blue butterflies for inspo#bc scara = butterfly
0 notes
Text

Today’s Exhibit of the Day? The lion’s mane jellyfish (Cyanea capillata). Jelly-ve it or not, this critter is one of the world’s longest animals. This jumbo-sized jelly trails a “mane” of more than 800 stinging tentacles that are covered in cells with venom that stun prey, including other jellyfish, small crustaceans, and zooplankton. Just how long is the lion’s mane jellyfish? Well, its tentacles can grow more than 100 feet (30 meters) long! In fact, the longest examples of this species—which inhabit the Arctic Ocean—are even longer than the longest known blue whale. Come see a life-size model of one at the Museum’s Hall of Biodiversity.
Photo: R. Mickens/ © AMNH
#science#amnh#museum#nature#natural history#fact of the day#animals#did you know#jellyfish#lion mane#lions mane#ocean life#marine biology#marine biodiversity
702 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cyanea capillata with Hyperia galba inside
By Alexander Semenov
#alexander semenov#photographer#cyanea capillata#hyperia galba#marine animal#nature#flickr#lion's mane jellyfish
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
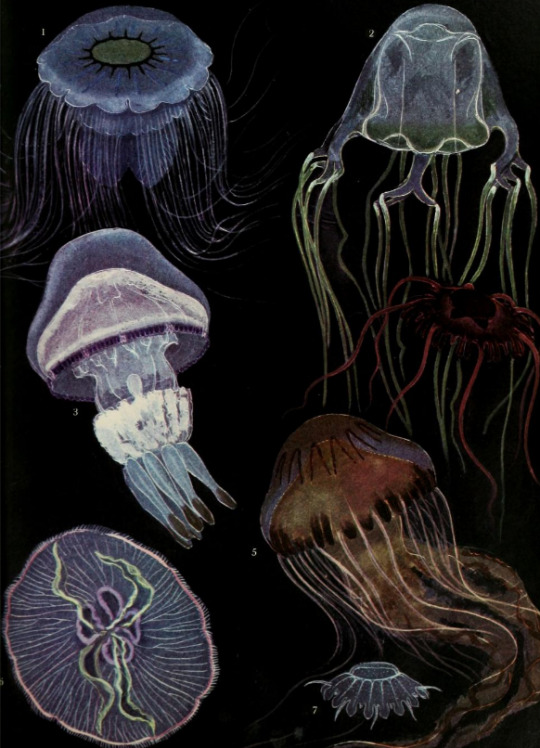

Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia: vol. 1 - Lower Animals. Written by Dr. Bernhard Grzimek. 1974.
Internet Archive
1.) Blue jellyfish (Cyanea lamarckii)
2.) Australian box jelly (Chironex fleckeri)
3.) Barrel jellyfish (Rhizostoma pulmo)
4.) Nausithoe rubra
5.) Compass jellyfish (Chrysaora hysoscella)
6.) Moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita)
7.) Crown jellyfish (Nausithoe punctatais)
#marine life#cnidarians#jellyfish#blue jellyfish#australian box jelly#barrel jellyfish#compass jellyfish#moon jellyfish#crown jellyfish
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Round 1 - Phylum Cnidaria




(Sources - 1, 2, 3, 4)
Cnidaria is a phylum of aquatic animals which includes the Anthozoans (sea anemones, corals, sea pens), the Scyphozoans ( true jellies), the Cubozoans (box jellies), the Hydrozoans (a diverse group ranging from Hydras to the colonial Portuguese Man O’ War), the Staurozoans (eight-tentacled cnidarians that cling to seaweeds and rocks), and the parasitic Myxozoans and Polypodiozoans.
Cnidarians are identified by a decentralized nervous system distributed throughout a gelatinous body, and specialized explosive stinging cells, called cnidocytes, on ejectable flagella (“tentacles”) which are used to envenomate prey ranging from plankton to animals several times larger than themselves. Their bodies consist of a jelly-like substance called mesoglea sandwiched between two thin cell layers. Cnidarians are some of the only animals that can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Many species of Cnidarian are actually groups of polyps, called zooids, clustered together to form one collonial organism. Corals, the Man O’ War, and Siphonophores are examples of this.

Propaganda below the cut:
Corals support 25% of all ocean life
Reefs are formed when coral polyps group together and produce a skeleton of calcium carbonate at their bases. They do this to form a platform that allows them to better stick together.
In a relationship that dates back to the Triassic, the symbiotic algae that live within corals gives them their colors, as well as creates nutrients for both organisms
Corals are facing a mass extinction due to climate change
While anemones are mainly sessile, usually staying in one place for weeks to months at a time, they can creep along on their bases at a speed too slow to be seen with the naked eye. However, some species can move or “swim” quickly in a pinch. Gonactinia can crawl like an inchworm, Paranthus rapiformis can curl into a ball and roll around, and Stomphia coccinea can swim by flexing its column. They just look really silly doing so.
Anemones are predators, stinging prey and pulling it into their mouth with their tentacles. They can eat animals as large as crabs, mollusks, and even small fish. However, some fish and invertebrates have a symbiotic relationship with anemones. Immune to the anemone’s venom, these animals utilize it as shelter while keeping it clean and providing it with nutrients from their feces. Some hermit crabs even carry anemones on their shells, providing the anemone with quick transport to new areas in return for protection.
Box Jellies have simple eyes, are capable of pursuing and reacting to prey behavior, and some species are some of the most deadly animals in the world.
The Lion’s Mane Jelly (Cyanea capillata) is one of the largest jellyfish, with the largest recorded specimen having a bell width of 210 cm (7 ft) and tentacles around 36.6 m (120 ft) long.
The Lion’s Mane Jelly is also the favorite food of Leatherback Sea Turtles.
A rise in jellyfish population can signify ecosystem collapse
The Giant Siphonophore (Praya dubia) is a collonial Hydrozoan that can get up to 50 m (160 ft) long, rivaling the Blue Whale in length.
Some Cnidarians can “hear” via vibrations, and some can even produce sounds to communicate
Many Cnidarians are bioluminescent
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

Phacellophora, commonly known as the fried egg jellyfish or egg-yolk jellyfish, is a very large jellyfish in the monotypic family Phacellophoridae containing a single species Phacellophora camtschatica. This genus can be easily identified by the yellow coloration in the center of its body which closely resembles an egg yolk, hence its common name. Some individuals can have a bell close to 60 cm (2 ft) in diameter, and most individuals have 16 clusters of up to a few dozen tentacles, each up to 6 m (20 ft) long. A smaller jellyfish, Cotylorhiza tuberculata, typically found in warmer water, particularly in the Mediterranean Sea, is also popularly called a fried egg jellyfish. Also, P. camtschatica is sometimes confused with the Lion's mane jellyfish (Cyanea capillata). - Wikipedia
76 notes
·
View notes
Text

Lion's Mane Jellyfish (Cyanea capillata)
Family: Cyaneid Jellyfish Family (Cyaneidae)
IUCN Conservation Status: Unassessed
Named for its frilly "mane" made up of over 1,200 long, stinging tentacles, the Lion's Mane Jellyfish is among the largest known jellyfish species; while this viral image showing a diver next to a Lion's Mane Jellyfish has been edited to make the jellyfish appear far larger than it actually is, members of this species still dwarf most of their relatives, with a bell ("main body") diameter of over 2.4 meters (7.89 feet) and a tentacle length of as much as 30 meters (98.4 feet), making it one the longest animals on earth. Typically found near the surface in the Arctic, northern Atlantic and northern Pacific Ocean regions, Lion's Mane Jellyfishes, like all jellyfishes, lack brains, eyes, hearts or respiratory organs (instead exchanging gasses directly between the water around them and their extremely thin tissues,) and rely heavily on waves and ocean tides to travel, but are able to slowly propel themselves in a given direction by expanding the 8 bag-like lobes of their bodies to take in water and then forcing it out again to push themselves along (although they can also to some extent detect and react to their orientation and surroundings owing to a series of frilly sensory structures located around their body's rim, know as rhopalia.) Like most jellyfishes the long, trailing tentacles of a Lion's Mane Jellyfish are lined with touch-sensitive, harpoon-like cells called cnidocytes that fire venomous barbs into any animal that touches them, and after a tentacle has stung and ensnared suitable prey (mainly fish, large plankton and smaller jellyfishes) it is pulled back towards the body where the prey is passed through a mouth-like opening on the jellyfish's underside and into a simple body cavity where it is digested, with any indigestible matter, such as shells or bones, later being ejected from the body through the same opening it entered through. The life cycle of the Lion's Mane Jellyfish, like that of most jellyfishes, takes place in 4 distinct stages and seems highly elaborate compared to that of most animals; the bag-like adults that we typically think of as jellyfishes, known as medusas, are either male or female and reproduce sexually by releasing gametes into the water around them, and should these gametes meet they fuse and develop into tiny larvae. The larvae then settle onto a solid surface and develop into polyps (a second, immobile life stage resembling a sea anemone,) and each polyp then asexually reproduces several times, with genetically identical, slow-swimming young splitting off of its body as buds. Each of these asexually-produced individuals will then develop into a medusa, continuing the cycle and meaning that each single instance of sexual reproduction in Lion's Mane Jellyfishes produces multiple asexually-produced offspring. Despite their massive size medusas of this species only live for around a year, although their polyps, which only reproduce under ideal environmental conditions, may remain dormant for longer than this.
---------------------------------------------
Image Source: here
#Lion's Mane Jellyfish#jellyfish#jellyfishes#cnidarians#cnidarian#cnidology#animal#animals#zoology#invertebrate#invertebrates#marine biology#marine invertebrates#scyphozoa#wildlife#marine wildlife
180 notes
·
View notes
