#centrioles
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
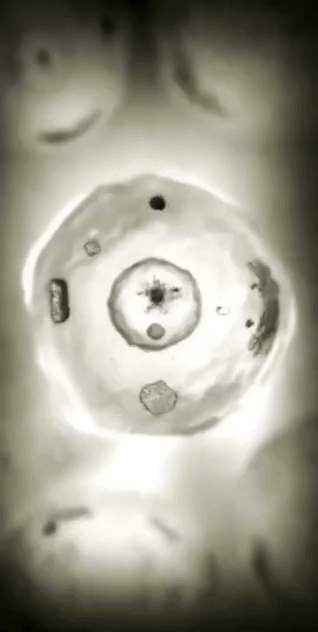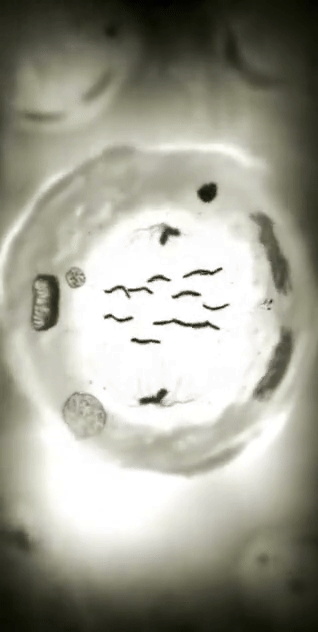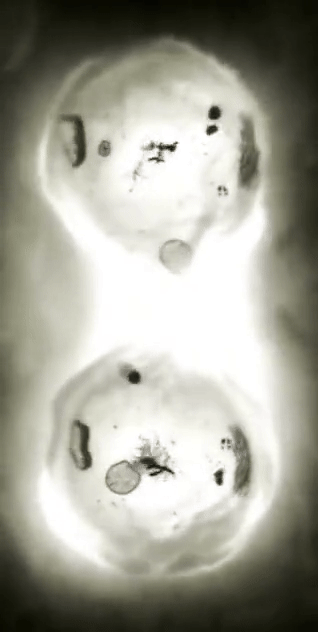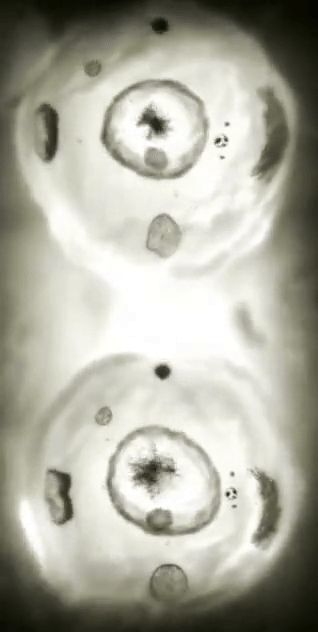
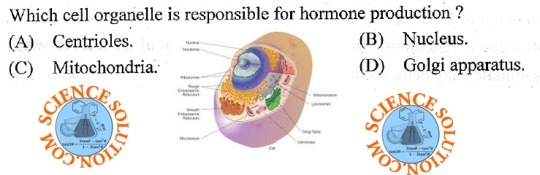
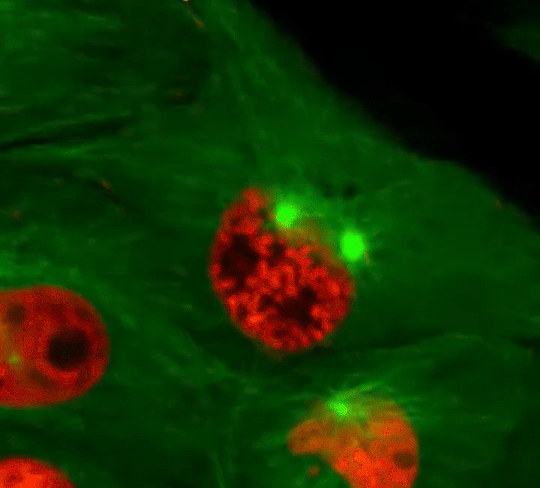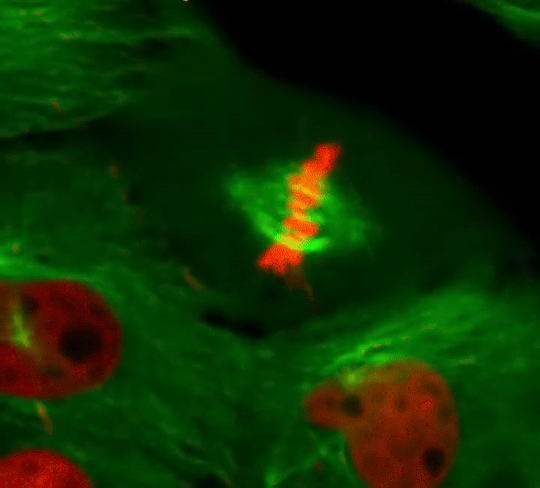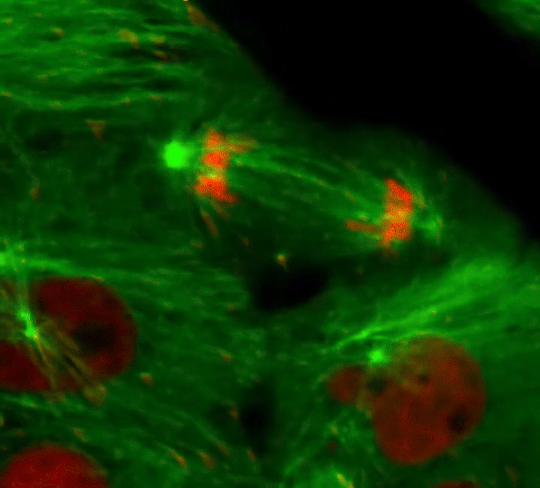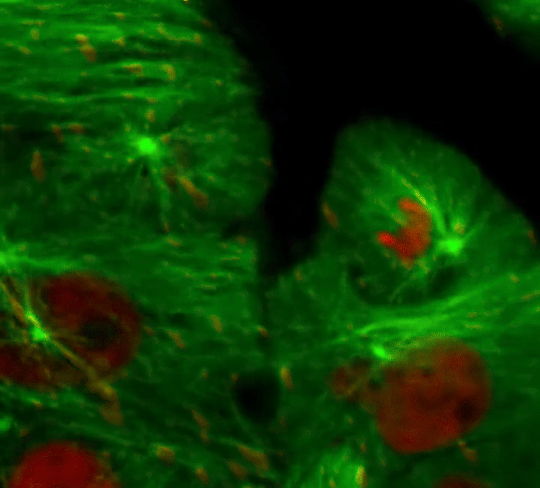
Every second, millions of cells in our bodies undergo mitosis, a fundamental process that ensures growth, repair, and development. From a single parent cell, identical daughter cells emerge, each carrying the same genetic information. This intricate dance of chromosomes and cellular structures keeps life going!
#cells#biology#photography#explore#nature#science#adorable#education#lol#amazing#awesome#funny#microscope#fluorescence#tissue#growth#cell division#nucleus#nuclei#centrioles#prophase#metaphase#anaphase#telophase#cytokinesis#mitosis#chromosomes#dna#microtubules#spindle
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Centriole Building
The centriole – an organelle vital for the faithful separation into each daughter cell when a cell divides – is composed of an assembly of proteins. Using��expansion microscopy, this study correlates the spatial location of 24 of those proteins with structural features of the human centriole, and then models the molecular architecture of the centriole as it assembles (shown here)
Read the published research article here
Video from work by Marine H. Laporte and colleagues
University of Geneva, Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Geneva, Switzerland
Video originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Published in Cell, April 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#biology#cell division#centrioles#centrosome#computer modeling#expansion microscopy
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
looking at answers for my biology homework and just writing them down. took me a good 5 minutes to notice something was off.

#random sheldon#thought this was a decent answer key#i literally looked at centrioles and saw that under it#disappointed that it took so long for me to notice THAT
0 notes
Text
a silly ode to the first mitochondria, with waaaay too many religious allusions
(the mormons put me in seminary for four years and now it's everyone's problem)
the garden was not made of trees the snake did not exist when Eve was formed inside the seas and then was set adrift
she drifted in the tidal pools prokaryote divine producing simple molecules acids and alkalines
but paradise can never last and every god must fall some swallowed by a cytoplast (entrapped by a cell wall)
what do you call the dead that rise? what name is there for this? an Eve that finds that eden lies inside of the abyss
the wall no longer trapped her in but locked the monsters out the freedom only she could win to swim, and grow, and sprout.
she tinkered with her molecules And in a twist of fate Created one of life's crown jewels Adenosine Triphosphate (1)
what was before a simple wall could bloom with organelles a garden grown from former falls a paradise in hell
a fortress swam inside the brine, a thriving little town where tiny citizens could shine and ride the ups and downs
a golgi apparatus strove to package safe proteins a lysome found a nice alcove and kept the whole cell clean
the centrioles rebuilt the walls whenever they grew weak and eve was known and loved by all as something quite unique:
the powerhouse of the first cell the mitochondria (2) the Jonah that became the whale the jesus of bacteria once eaten by a macrophage then made through death anew the founder of our current age the sprout from which we grew
(yeah, yeah - you try and use this line in a poem)
(gah. this paragraph killed the syllable counts. i was challented to fit the phrase "powerhouse of the cell" into it, and mitochondria had to fit somewhere. both of which were gonna be doozies. decided to put them back to back and break the scheme at the end.
#biology#poem#the mitochondria is the powerhouse of the cell#i was googling so much biology shit for this#and i still know that someone is going to go#HEY#IDIOT#YOU THINK X?#NO#IT Y#STUPID#and i will slink off to the saddest darkest corner of the earth#and mope until i die#its like a whole prophecy now#strike me down apollo you incandescent bastard#if you couldn't get me back in arizona you cant do shit to me in utah
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
i've officialy lost it.
#i have a biology test tomorrow.#i've been preparing for days. i'm sick of it.#but lysosomes absolutely fuck#it's really late so that explains whatever this is anfjfjskdnfj#niko rambles
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Organelles
Nucleus -- located near the center of the cell -- contains the genetic material of the cell (DNA) and nucleoli -- site of ribosome and messenger RNA synthesis
Nucleolus -- located in the nucleus -- site of ribosomal subunit assembly
Ribosomes -- located in the cytoplasm -- site of protein synthesis
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum -- located in the cytoplasm -- has many ribosomes attached -- site of protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum -- located in the cytoplasm -- site of lipid synthesis -- participates in detoxification
Golgi Apparatus -- located in the cytoplasm -- modifies protein structure -- packages proteins in secretory vesicles
Secretory Vesicle -- located in the cytoplasm -- contains materials produced in the cell -- formed by the Golgi apparatus -- secreted by exocytosis
Lysosome -- located in the cytoplasm -- contains enzymes that digest material taken into the cell
Mitochondria -- located in the cytoplasm -- site of aerobic respiration -- major site of ATP synthesis
Microtubule -- located in the cytoplasm -- supports cytoplasm -- assists in cell division -- forms components of cilia and flagella
Centrioles -- located in the cytoplasm -- facilitate the movement of chromosomes during cell division
Cilia -- located on the cell surface with many on each cell -- move substances over the surface of certain cells
Flagella -- located on sperm cells -- one per cell -- propels sperm cell
#medblr#studyblr#notes#my notes#anatomy and physiology#anatomy#physiology#biology#bio#bio notes#biology notes#anatomy notes#physiology notes#cells#cells notes#microbiology#microbiology notes#studyblr notes
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
kinetochores are so weird like why is there a whole other part of the centriole microtubles attach to why cant they just be like "ya centrioles are were the bullshit happens" like what?
#auburn's rambles <3#i should not be up this late studying for bio#sillies and goofies amiright#THIS IS A RHETORICAL QUESTION BTW DONT ACTUALLY ANSWER IT IM TIRED
20 notes
·
View notes
Text




Lezley Irene Saar is an African American artist whose artwork is responsive to race, gender, female identity, and her ancestral history. Her works are primarily mixed media, 3-dimensional, and oil & acrylic on paper and canvas.
Her mother Betye Saar (née Brown), is an African-American assemblage artist. Via Wikipedia
#bornonthisday Lezley Saar
Centrioles Later, 2014
Let's talk of space sadness, 2014
Detail “Not born under a rhyming planet”
Mitochondrial Muses, 2014
All from the Monad Series
Let's read it together again: Betye Saar, Her Daughters, and the House That Never Stopped Making Art
www.harpersbazaar.com/culture/features/a36182098/betye-saar-daughters-in-conversation/
The pioneering artist and her three daughters on family, creativity, and why being able to see beauty, even in difficult times, is the true mother of invention. (2021)
#TracyeSaarCavanaugh #AlisonSaar #BetyeSaar #LezleySaar #artherstory #artbywomen #womensart #palianshow #art #womenartists #femaleartist #artist #daughters
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Midcellmmer Night’s Dream
Our cell membranes press against each other, and I know I’m in love. Accurate to their name, G2trude is in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. Through their semipermeable cell membrane, I can see enzymes checking that their genetic information is all correct. If I had cheeks and blood to blush with right now, I would. Unlike G2trude, I am only in the G1 phase. I’m still growing, developing organelles, and other things that probably seem super juvenile to G2trude. Hey, someday they’ll be back to where I am though. Kinda. Soon enough, they’ll go into mitosis and after that they’ll be 2 daughter cells in G1. Will they both be G2trude then? Or just one? Or are they completely their own cells? Who really knows, philosopher cells don’t come around these parts. Or any parts, they don’t exist.
It would be easier if we were gametes. We wouldn’t go thru mitosis, and we could be together and be together forever. However, we are skin cells, stuck in the epidermis, stuck in the cell cycle.
We, us, G2trude and Trevor
stuck in cell cycle forever
G1, S, G2, mitosis
believing you love me is psychosis
Something happens! I watch centrioles head to opposite sides of the cell. Oh man, mitosis already? Maybe our phase gap isn’t that bad after all! I watch in silence, for I am a cell and have nothing to make noise with, as G2trude starts prophase. From the centrioles spring forty spindle fibers. The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the chromosomes line up in the middle. I watch in fear and fascination. I can’t believe I’m witnessing this coming of phase. The spindle fibers grab onto the centromeres and pull them apart. I CAN’T WATCH!!! But I do anyway. Oh golly gee, G2trude isn’t their usual shape anymore! They look like two suns, still attached at the side. If only they e could merge together like that! Only gametes merge though. As said before, we are skin cells stuck in the epidermis.
We, us, G2trude and Trevor
stuck in th’epiderm forever
If we were gametes we’d be one
Mr. and Mrs. Trevor, why, that’s fun!
The nuclear envelopes are forming again, around the chromatids. Then, I watch as G2trude is no more. If I had tears to cry with, I would cry. No. SOB. I now know that neither of them is really my G2trude. They’re their own cells. I’ll name them Epinand Dermis.
G2trude isn’t the only one who’s changed however. I’m now in S phase. Synthesizing phase. My DNA is getting replicated into perfect copies. Soon, I’ll be in G2 phase just like G2trude was. Then in M phase: Then G1 again. That’s cell cycle for you. Never ending, never escapable. Predetermined.
This is the story of G2trude and Trevor,
Now it’s time to say cellut forever
#cell#cell cycle#biology#crack fic#fanfiction#cell cycle fanfiction#yearning#this is a summative grade for my biology class#no i am not joking#writblr#writerblr#creative writing#writers of tumblr#writing community
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cell Division: Stages of Mitosis
#cells#biology#photography#explore#nature#science#adorable#education#lol#amazing#awesome#funny#microscope#fluorescence#tissue#growth#cell division#nucleus#nuclei#centrioles#prophase#metaphase#anaphase#telophase#cytokinesis#mitosis#chromosomes#dna#microtubules#spindle
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
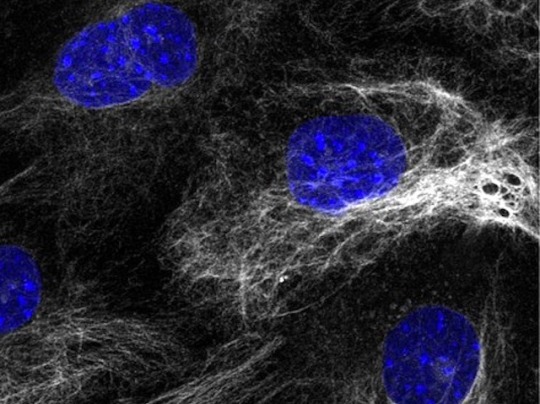
Centriole Formation
Protein called SAS-6 role in the maintenance of the architecture of centrioles – specialised structures involved in organising cell contents during division – as they form early in embryonic development in cells that generate mouse embryonic stem cells
Read the published article here
Image from work by Marta Grzonka and Hisham Bazzi
Department of Cell Biology of the Skin and Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Medical Faculty, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in eLife, February 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#immunofluorescence#cells#stem cells#cell division#centrioles#embryo development#developmental biology
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mitosis Help- College Biology (AP)
Introduction
What do your intestines, the yeast in bread dough, and a developing frog all have in common? Among other things, they all have cells that carry out mitosis, dividing to produce more cells that are genetically identical to themselves.
Why do these very different organisms and tissues all need mitosis? Intestinal cells have to be replaced as they wear out; yeast cells need to reproduce to keep their population growing; and a tadpole must make new cells as it grows bigger and more complex.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the DNA of the cell's nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes.
The great majority of the cell divisions that happen in your body involve mitosis. During development and growth, mitosis populates an organism’s body with cells, and throughout an organism’s life, it replaces old, worn-out cells with new ones. For single-celled eukaryotes like yeast, mitotic divisions are actually a form of reproduction, adding new individuals to the population.
In all of these cases, the “goal” of mitosis is to make sure that each daughter cell gets a perfect, full set of chromosomes. Cells with too few or too many chromosomes usually don’t function well: they may not survive, or they may even cause cancer. So, when cells undergo mitosis, they don’t just divide their DNA at random and toss it into piles for the two daughter cells. Instead, they split up their duplicated chromosomes in a carefully organized series of steps.
Phases of mitosis
Mitosis consists of four basic phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). These phases occur in strict sequential order, and cytokinesis - the process of dividing the cell contents to make two new cells - starts in anaphase or telophase.
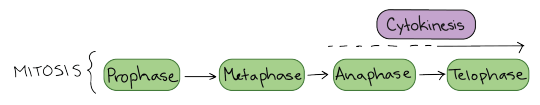
Stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase.
You can remember the order of the phases with the famous mnemonic: [Please] Pee on the MAT. But don’t get too hung up on names – what’s most important to understand is what’s happening at each stage, and why it’s important for the division of the chromosomes.
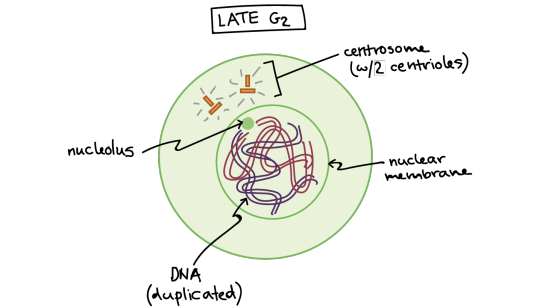
Late G2 phase. The cell has two centrosomes, each with two centrioles, and the DNA has been copied. At this stage, the DNA is surrounded by an intact nuclear membrane, and the nucleolus is present in the nucleus.
Let’s start by looking at a cell right before it begins mitosis. This cell is in interphase (late G\[_2\] phase) and has already copied its DNA, so the chromosomes in the nucleus each consist of two connected copies, called sister chromatids. You can’t see the chromosomes very clearly at this point, because they are still in their long, stringy, decondensed form.
This animal cell has also made a copy of its centrosome, an organelle that will play a key role in orchestrating mitosis, so there are two centrosomes. (Plant cells generally don’t have centrosomes with centrioles, but have a different type of microtubule organizing center that plays a similar role.)

Early prophase. The mitotic spindle starts to form, the chromosomes start to condense, and the nucleolus disappears.
In early prophase, the cell starts to break down some structures and build others up, setting the stage for division of the chromosomes.
The chromosomes start to condense (making them easier to pull apart later on).
The mitotic spindle begins to form. The spindle is a structure made of microtubules, strong fibers that are part of the cell’s “skeleton.” Its job is to organize the chromosomes and move them around during mitosis. The spindle grows between the centrosomes as they move apart.
The nucleolus (or nucleoli, plural), a part of the nucleus where ribosomes are made, disappears. This is a sign that the nucleus is getting ready to break down.
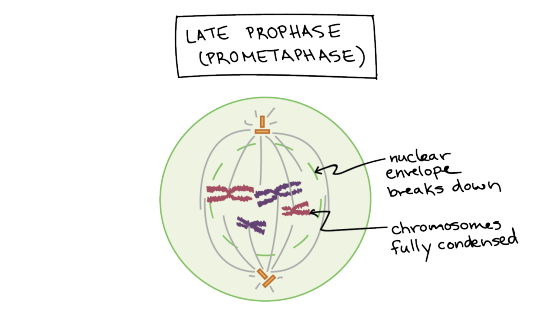
Late prophase (prometaphase). The nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes are fully condensed.
In late prophase (sometimes also called prometaphase), the mitotic spindle begins to capture and organize the chromosomes.
The chromosomes become even more condensed, so they are very compact.
The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes.
The mitotic spindle grows more, and some of the microtubules start to “capture” chromosomes.

Anatomy of the mitotic spindle. Diagram indicating kinetochore microtubules (bound to kinetochores) and the aster. The aster is an array of microtubules that radiates out from the centrosome towards the cell edge. Diagram also indicates the centromere region of a chromosome, the narrow "waist" where the two sister chromatids are most tightly connected, and the kinetochore, a pad of proteins found at the centromere.
Microtubules can bind to chromosomes at the kinetochore, a patch of protein found on the centromere of each sister chromatid. (Centromeres are the regions of DNA where the sister chromatids are most tightly connected.)
Microtubules that bind a chromosome are called kinetochore microtubules. Microtubules that don’t bind to kinetochores can grab on to microtubules from the opposite pole, stabilizing the spindle. More microtubules extend from each centrosome towards the edge of the cell, forming a structure called the aster.
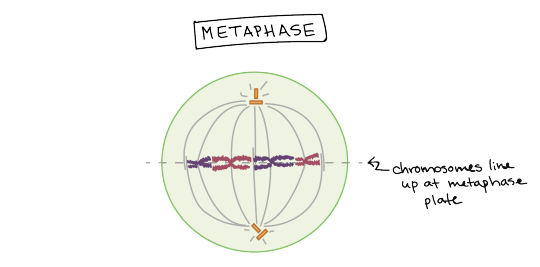
Metaphase. Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, under tension from the mitotic spindle. The two sister chromatids of each chromosome are captured by microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
In metaphase, the spindle has captured all the chromosomes and lined them up at the middle of the cell, ready to divide.
All the chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (not a physical structure, just a term for the plane where the chromosomes line up).
At this stage, the two kinetochores of each chromosome should be attached to microtubules from opposite spindle poles.
Before proceeding to anaphase, the cell will check to make sure that all the chromosomes are at the metaphase plate with their kinetochores correctly attached to microtubules. This is called the spindle checkpoint and helps ensure that the sister chromatids will split evenly between the two daughter cells when they separate in the next step. If a chromosome is not properly aligned or attached, the cell will halt division until the problem is fixed.
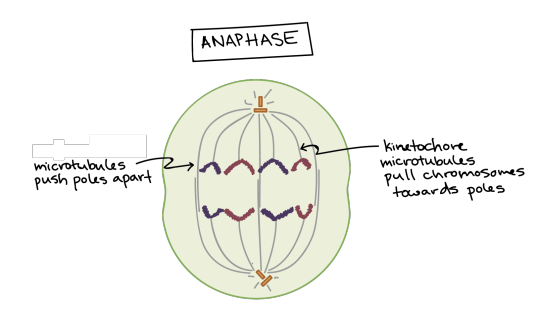
Anaphase. The sister chromatids separate from one another and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. The microtubules that are not attached to chromosomes push the two poles of the spindle apart, while the kinetochore microtubules pull the chromosomes towards the poles.
In anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
The protein “glue” that holds the sister chromatids together is broken down, allowing them to separate. Each is now its own chromosome. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
Microtubules not attached to chromosomes elongate and push apart, separating the poles and making the cell longer.
All of these processes are driven by motor proteins, molecular machines that can “walk” along microtubule tracks and carry a cargo. In mitosis, motor proteins carry chromosomes or other microtubules as they walk.

Telophase. The spindle disappears, a nuclear membrane re-forms around each set of chromosomes, and a nucleolus reappears in each new nucleus. The chromosomes also start to decondense.
In telophase, the cell is nearly done dividing, and it starts to re-establish its normal structures as cytokinesis (division of the cell contents) takes place.
The mitotic spindle is broken down into its building blocks.
Two new nuclei form, one for each set of chromosomes. Nuclear membranes and nucleoli reappear.
The chromosomes begin to decondense and return to their “stringy” form.
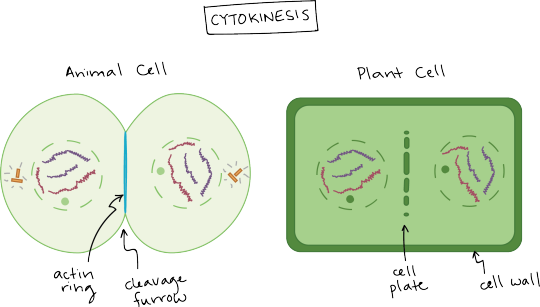
Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells.
Cytokinesis in an animal cell: an actin ring around the middle of the cell pinches inward, creating an indentation called the cleavage furrow.
Cytokinesis in a plant cell: the cell plate forms down the middle of the cell, creating a new wall that partitions it in two.
Cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm to form two new cells, overlaps with the final stages of mitosis. It may start in either anaphase or telophase, depending on the cell, and finishes shortly after telophase.
In animal cells, cytokinesis is contractile, pinching the cell in two like a coin purse with a drawstring. The “drawstring” is a band of filaments made of a protein called actin, and the pinch crease is known as the cleavage furrow. Plant cells can’t be divided like this because they have a cell wall and are too stiff. Instead, a structure called the cell plate forms down the middle of the cell, splitting it into two daughter cells separated by a new wall.

When division is complete, it produces two daughter cells. Each daughter cell has a complete set of chromosomes, identical to that of its sister (and that of the mother cell). The daughter cells enter the cell cycle in G1.
When cytokinesis finishes, we end up with two new cells, each with a complete set of chromosomes identical to those of the mother cell. The daughter cells can now begin their own cellular “lives,” and – depending on what they decide to be when they grow up – may undergo mitosis themselves, repeating the cycle.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
how I felt in my last bio class labelling the animal cell diagram with my beloved moots names (eg "bea" "bonsai" "alli") instead of shit like "centrioles" and "mitochondria" :3

#yall i swear jts for the memes tho trusttrust#bcuz like#class is boring#CHAT IM DUMB BUT NOT ABSOLUTELY RETARDED DWWW#WHILE I DID BARELY PASS PHYSICS (like 2/3 of the year failed its chill)#I GOT LIKE 73% OR SMTH ON BIO#SO YAAAA
51K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cell division is a fundamental process in both plants andanimals’ growth and development as well as recreation. This paper investigates the mitosis process in both plants and animals’ cells to identify distinct stages of mitosis and the structure of cells at each stage. The experiment identifies similarity in mitotic stages for cells in both plants and animals. The mitotic process leads to division of one parent cell to form two identical daughter cells that can further undergo subsequent mitotic divisions. Introduction Cells are the fundamental elements of living things, both plants and animals. Consequently, realized mechanisms originate from cells and manifest in organs and the entire organism. Mitosis and meiosis are some of the fundamental processes that take place at the cell level. They refer to cell divisions that lead to generation of new cells to replace dead or worn out cells, generation of cells for development of organs, and cell division towards growth. Mitosis leads to generation of identical daughter cells for growth or replacement of cells in organs. It takes place in a number of stages, interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis (Goldberg and Goldberg, p. 77- 80). The interphase is a preliminary stage in cell division that precedes the mitotic stages. It is fundamental as it forms the largest percentage of a cell’s life. The major activity at this stage is replication of cell proteins within cells and developments to visibility of cell nucleoli. Mitosis however has four stages that result into cell division. The first stage is the prophase, followed by metaphase, anaphase, and telophase respectively (Goldberg and Goldberg, p. 79). At the prophase, “strands of chromosomes begin to condense” and can be seen with the aid of a powered microscope. Visibility of the nucleoli however disappears while fibers develop in the cell’s cytoplasm. The developed fibers emanates from a pair of centrosomes that stretch to opposite poles of the cytoplasm. Disintegration of the “nuclear membrane begins” at this stage and marks the end of the prophase and the process moves to the metaphase (Goldberg and Goldberg, p. 79). At the metaphase stage, the chromosomes are arranged along a plate that is perpendicular to the centrioles’ plane and the “spindle fibers” interlink the centrosomes and the chromosomes (Goldberg and Goldberg, p. 79). A new phase, the anaphase is then marked by disintegration of chromosomes into centromeres that are then attracted to the centrosomes along the fibers (Goldberg and Goldberg, p. 79). The cell then enters a new phase, the telophase, where the pulled chromosomes converge at the opposite sides of the cell, along the fibers and the nuclear membrane begins to reappear. Each set of chromosomes assumes the normal thread like structure and the nuclear membrane develop around each group of chromosomes to form two nucleuses within the cytoplasm (Toole and Toole, p. 139). The cytokinesis process, where the cytoplasm divides to form two different cells then follows this (Goldberg and Goldberg, p. 79- 80). The structure of the cells in plants and in animals may however be different. This is because of a number of factors such as the lack of significance of the spindle fibers in the plant cells. The nucleus, rather than spindle fibers in plant cells, moves to define the new position of chromosomes in the mitosis process (Cassimeris, Plopper and Lingappa, p. 952). T Read the full article
0 notes