#agricultural workforce
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Rural Women Sustaining Nature for Our Collective Future: Building climate resilience, conserving biodiversity, and caring for land towards gender equality and empowerment of women and girls.

Rural women are vital leaders in their communities and play a key role in finding solutions to global challenges such as poverty, hunger, the climate crisis and more. October 15th is International Rural Women Day.
#international day of rural women#15 october#rural women#UNHQ#biodiversity#gender equality#un women#agricultural workforce#agricultural productivity#agrifood systems#indigenous women#rural communities#rural households#rural farmers#rural areas
0 notes
Text
F.A.R.M.: Fostering Ag Resilience through Mentorship
Fresh Harvest 365, provides hands-on career experience for underserved communities while filling an industry need for ag talent.
Most days, you’ll find Pat Morgan in the field. He and the other scientists on his team dedicate a lot of time and resources to counting plants, measuring their development and productivity, and taking tissue samples.
Afterall, the seeds they plant – being tested in the ground for the first time – are contenders for a coveted spot in the lineup for the company’s Breeding, Biologics, and plant Biotechnology pipelines.
Tracking data on a ‘per plant’ basis, with every single seed followed throughout its life cycle, is no small effort: “This year we ran 55,000 plots, and we’re collecting a little over 3 million data points,” Pat said. “It takes an army to get this work done, and you need to have some level of knowledge going in to really be effective.”
A new initiative offers a unique solution to bringing more skilled ag workers to the field. Bayer is collaborating with St. Louis startup company, Fresh Harvest 365, as part of a new F.A.R.M. (Fostering Ag Resilience Through Mentorship) program.
F.A.R.M. pulls students from diverse backgrounds in St. Louis and from several regional universities into an apprenticeship program, which includes 210 hours of e-learning courses and 3,000 hours of on-the-job training in agriculture. The on- the-job training portion of the apprenticeship was a perfect fit for Bayer.

F.A.R.M. program apprentices in the field in Monmouth IL.
During summer 2024, a F.A.R.M. pilot involved about 30 students from diverse backgrounds who were hired as apprentices at the Bayer Crop Science Jerseyville and Monmouth, Illinois, and Chesterfield, Missouri, locations. Several St. Louis non-profit organizations also joined the pilot to provide additional support such as transportation, housing, mentoring, and workplace readiness.
The program offered invaluable experience to the students, according to Jennifer Becker, who initiated Bayer’s collaboration with FreshHarvest365. “The apprentices worked side-by-side in the field with Ph.D.-level scientists, collecting phenotype data and learning from them,” she said.
The program also has been a benefit to Bayer, solving the annual challenge of finding seasonal workers who have the ag background and interest to be most effective. “The hires from Fresh Harvest come to us with ag training and an interest in making agriculture a career field,” Pat said.
The St. Louis University City School District recently introduced an Ag Program track to its curriculum. Thanks in part to awareness generated by the F.A.R.M. pilot, enrollment in the Ag track for the 2024/25 school year increased from about 16 students to nearly 100 students. Several other school districts with similar demographics would like to follow suit with ag programming options for their students.
In January 2025, Bayer will expand its offerings, including bringing around 40 local community college students to its Urbandale, Iowa, and Whitestown, Indiana, facilities.
Following the success of the pilot, the team expects to expand regionally into a broader vision “IM IIN,” which aims to open opportunities in the states of Illinois, Missouri, Indiana, Iowa and Nebraska by the end of 2025. Fresh Harvest has initiated conversations with Iowa State University and University of Nebraska- Lincoln about expansion opportunities with possible placement at Bayer facilities.
Jennifer is proud to see how quickly Bayer’s collaboration with FreshHarvest365 has grown.
“I have almost 30 years with the company, and it is certainly a highlight of my career,” Jennifer said. “It is heartwarming to be involved in something that has such huge impact for our organization and for the students, providing new ways for our organization to work with the community and to support the next generation of ag leaders.”
Article Source: https://www.bayer.com/en/us/news-stories/fostering-ag-resilience-through-mentorship
#Fresh Harvest 365#Fresh Hire 365#Bayer Crop Science#Urban Farmer#Food Deserts#Agriculture Workforce#Agripreneurship
0 notes
Photo

Poultry Production Pathways to Canada: A Guide to Visa Sponsorship and Opportunities Curious about job opportunities in Canada's bustling poultry industry? Look no further! In this insightful blo... https://bit.ly/4cj8Ou6/
#EverythingAbroad#agriculture#employment#foreignworkers#Immigration#PathwaystoCanada#Poultry#Production#visasponsorship#workforce
0 notes
Text
Dandelion News - January 1-7
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Homes built with clay, grass, plastic and glass: How a Caribbean island is shying away from concrete

“[… Clay] traps moisture which then evaporates and pulls heat from the surface as it goes. […] The roof is covered in old recycled advertising banners and piece of a water tank, the other half of which is used to house some of Rahaman-Noronha's fish [… and] multi-coloured glass bottles inset into walls provide an avenue for streams of light and colour.”
2. To Combat Phoenix’s Extreme Heat, a New Program Provides Sustainable Shade

“The neighborhood workshops allow residents to get a shade plan tailored to their community’s needs and identify the locations where officials can plant trees. Meanwhile, the workforce-development side of the program creates the jobs needed to keep the trees alive for generations[….]”
3. Conservation corridors provide hope for Latin America’s felines
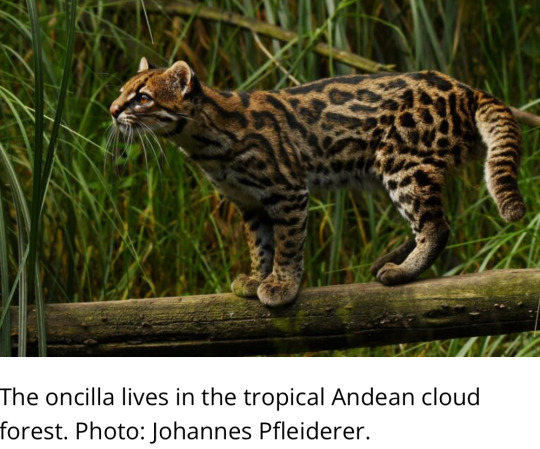

“[… S]cience has shown that to maintain healthy populations there needs to be connection between individuals. [… A] protected area that is close to another has more species and more potential for their survival.”
4. Social program cuts tuberculosis cases among Brazil's poorest by more than half

“The decrease [“in TB cases and deaths”] was over 50% in extremely poor people and more than 60% among the Indigenous populations. […] "We know that the program improves access to food [… and healthcare…] and strengthens people's immune defenses as a result.””
5. Geothermal has vast potential to meet the world’s power needs
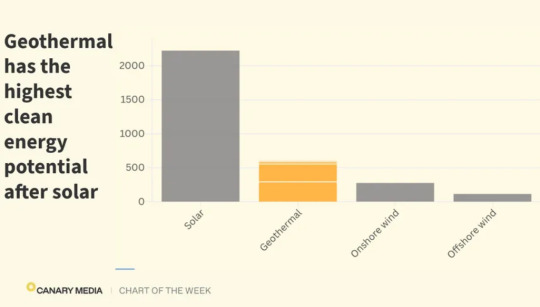
“New geothermal systems could technically provide as much as 600 terawatts of carbon-free power capacity by 2050[…. C]ountries could cost-effectively deploy over 800 GW of geothermal power capacity using technology that’s in development today[….]”
6. New D.C. Catholic archbishop is pro-LGBTQ+ and anti-Trump

“In 2018, he objected to the blaming of gay priests for the clergy sexual abuse crisis, “saying that such abuse was a matter of power, not sexual orientation[….]” “We must disrupt those who portray refugees as enemies [… and] seek to rob our medical care, especially from the poor.””
7. Chesapeake Bay Will Gain New Wildlife Refuge
“The Chesapeake Bay area will have a new wildlife refuge for the first time in a quarter century. […] “This new refuge offers an opportunity to halt and even reverse biodiversity loss in this important place, and in a way that fully integrates and respects the leadership and rights of Indigenous peoples and local communities.””
8. Inside Svalbard seed vault’s critical mission to stop our favourite fruit and veg from going extinct

“[… T]he world’s largest secure seed storage […] sits proudly in a massive former coal mine[….] Right now, there are over 1,331,458 samples of 6,297 crop species. […] “During 2024, 61 seed genebanks deposited 64,331 seed samples, including 21 from institutes that deposited seeds for the first time this year[….]””
9. Medical debt will be erased from credit reports for all Americans under new federal rule

“The rule will affect more than 15 million Americans, raising their credit scores by an estimated average of 20 points. [… S]tates and localities have already utilized American Rescue Plan (ARP) funds to support the elimination of over $1 billion in medical debt for more than 700,000 Americans[….]”
10. 'Forgotten' water harvesting system transforms 'barren wasteland' into thriving farmland

“"The process started with the community-based participatory planning[….]” 10% to 15% of the water will actually soak into the ground to replenish the water table, creating a more sustainable agricultural process.”
December 22-28 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#recycling#upcycling#climate change#climate action#trees#habitat restoration#habitat#big cats#cats#latin america#brazil#tuberculosis#poverty#geothermal#clean energy#renewableenergy#catholic#lgbt+#lgbt#lgbtq#religion#christianity#wildlife refuge#wildlife#seed saving#seed bank#medical debt#anti capitalism
297 notes
·
View notes
Text
The high levels of consumption enjoyed by wealthy countries in the Global North are only possible because of mass appropriation of labor from the population of the Global South. This is evidenced by research from the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB), which indicates that this appropriation takes place through unequal exchange in international trade and global commodity chains. The new study, published in Nature Communications, measured the flows of labor embodied in traded goods around the world from 1995 to 2021. The results show that in 2021, the Global North imported 906 billion hours of embodied labor from the South while exporting only 80 billion hours in return. In other words, for every hour of labor the Global South imports from the Global North, they must export 11 hours to "pay" for it. As a result, the countries of the Global North net-appropriated 826 billion hours of labor from the Global South, across all skill levels and all sectors: mining, agriculture, manufacturing and services. The figure of 826 billion hours is more than the labor rendered by the entire workforce of the United States and Europe combined. The wage value of this net-appropriated labor was equivalent to €16.9 trillion in 2021, in Northern prices. In other words, this is how much the appropriated labor would be worth if it was paid at prevailing Northern wages, with equal wages for equal work. "These are staggering figures. It shows that very large quantities of value flow from the South to the North each year" says Jason Hickel, researcher at ICTA-UAB and the Department of Anthropology at the UAB. "The Global North grows rich by siphoning value out of the South." Unequal exchange occurs because of systematic price inequalities in the world economy. Powerful states and corporations in the Global North seek to compress wages and supply prices in the Global South, to obtain inputs and other goods more cheaply. Producers in the Global South are then forced to export more goods and services in order to buy any given level of imports. This results in large net-transfers from the Global South to the Global North, which benefits Northern firms and consumers but drains the Global South of productive capacities that are necessary for development. "Labor that could be used to improve human development in the Global South is instead appropriated to service capital accumulation in the Global North," said co-author Morena Hanbury Lemos, also of ICTA-UAB. "This is a major driver of deprivation in the South, and it needs to be addressed," she says. According to the study, wages in the Global South are between 87% and 95% lower than Northern wages for work of equal skill, and between 83% and 98% lower for work of equal skill within the same sector. Wage inequalities are so extreme that high skill labor in the Global South is paid only one-third the wages of low-skill labor in the Global North.
29 July 2024
550 notes
·
View notes
Text

Agricultural development surrounds the village of Sułoszowa in southern Poland. Located about 18 miles (29 km) northwest of Kraków, the village is home to roughly 4,200 people. Altogether, more than 60% of Poland’s land area is taken up by farming, and 12% of the country’s workforce is employed in the agricultural sector.
50.269444°, 19.725000°
Source imagery: Maxar
460 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Border Patrol conducted unannounced raids throughout Bakersfield on Tuesday, descending on businesses where day laborers and field workers gather. Agents in unmarked SUVs rounded up people in vans outside a Home Depot and gas station that serves a breakfast popular with field workers. [...]
“We’re in the middle of our citrus harvesting. This sent shockwaves through the entire community,” said Casey Creamer, president of the industry group California Citrus Mutual, on Thursday. “People aren’t going to work and kids aren’t going to school. Yesterday about 25% of the workforce, today 75% didn’t show up.” He pushed back on the Border Patrol’s claims they’re targeting bad people. He said they appeared to be general sweeps of workers. “If this is the new normal, this is absolute economic devastation,” said Richard S. Gearhart, an associate professor of economics at Cal State-Bakersfield. In the short term, he predicted farms and dairies could make up the losses, but that homebuilders, restaurants and small businesses would be most hurt financially. But he’s worried about the long-term. “You are talking about a recession-level event if this is the new long-term norm,” he said. Agriculture comprises about 10 percent of Kern County’s gross domestic product and undocumented workers may comprise half of the workforce, he said. And the Central Valley provides about a quarter of the United States’ food.
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
"When Francois Beyers first pitched the concept of 3D ocean farming to the Welsh regulators, he had to sketch it on napkins.
Today the seafood farm is much more than a drawing, but if you walked along the Welsh coastal path near St David’s, all you’d see is a line of buoys. As Beyers puts it: “It’s what’s below that’s important.”
Thick tussles of lustrous seaweed suspend from the buoys, mussels cling to its furry connective ropes and dangling Chinese lantern-esque nets are filled with oysters and scallops.
“It’s like an underwater garden,” says Beyers, co-founder of the community-owned regenerative ocean farm, Câr-y-Môr. The 3-hectare site is part of a fledgling sector, one of 12 farms in the UK, which key players believe could boost ocean biodiversity, produce sustainable agricultural fertiliser and provide year-round employment in areas that have traditionally been dependent on tourism.
Created in 2020 by Beyers and six family members, including his father-in-law – an ex-shellfish farmer – the motivation is apparent in the name, which is Welsh for “for the love of the sea”. ...

Pictured: Drone shot of Câr-y-Môr, which is on the site of abandoned mussel farms. Image: Scott Chalmers
Ocean farming comes from the technical term ‘integrated multi-trophic aquaculture’, which means a mixture of different seaweed and shellfish species growing together to mutually benefit each other. But it’s not just a way of growing food with little human input, it also creates ocean habitat.
“You’re creating a breeding ground for marine animals,” explains Beyers who adds that the site has seen more gannets diving, porpoises and seals – to name a few – since before the farm was established.
Ocean farms like Câr-y-Môr, notes Ross Brown – environmental research fellow at the University of Exeter – have substantial conservation benefits.
“Setting up a seaweed farm creates an exclusion zone so fishermen can’t trawl it,” explains Brown, who has been conducting experiments on the impacts of seaweed and shellfish farms across the UK.
Brown believes a thriving ocean farming industry could provide solutions to the UK’s fish stock, which is in “a deeply troubling state” according to a report that found half of the key populations to be overfished. “It would create stepping stones where we have safe havens for fish and other organisms,” he adds.
But UK regulators have adopted a cautious approach, note Brown and Beyers, making it difficult for businesses like Câr-y-Môr to obtain licenses. “It’s been a tough old slog,” says Beyers, whose aim is to change the legislation to make it easier for others to start ocean farms.
Despite navigating uncharted territories, the business now has 14 full-time employees, and 300 community members, of which nearly 100 have invested in the community-benefit society. For member and funding manager Tracey Gilbert-Falconer, the model brings expertise but most importantly, buy-in from the tight-knit local community.
“You need to work with the community than forcing yourself in,” she observes.
And Câr-y-Môr is poised to double its workforce in 2024 thanks to a Defra grant of £1.1 million to promote and develop the Welsh seafood industry as part of the UK Seafood Fund Infrastructure Scheme. This will go towards building a processing hub, set to be operational in April, to produce agricultural fertiliser from seaweed.
Full of mineral nutrients and phosphorous from the ocean, seaweed use in farming is nothing new, as Gilbert-Falconer notes: “Farmers in Pembrokeshire talk about their grandad going down to the sea and throwing [seaweed] on their farms.”
But as the war in Ukraine has caused the price of chemical fertiliser to soar, and the sector tries to reduce its environmental impact – of which synthetic fertiliser contributes 5% of total UK emissions – farmers and government are increasingly looking to seaweed.
The new hub will have capacity to make 65,000 litres of sustainable fertiliser annually with the potential to cover 13,000 acres of farmland.
But to feed the processing hub, generate profit and reduce their dependency on grants, the co-op needs to increase the ocean farm size from three to 13 hectares. If they obtain licences, Beyers says they should break even in 18 months.
For now, Beyers reflects on a “humbling” three years but revels in the potential uses of seaweed, from construction material to clothing.
“I haven’t seen the limit yet,” he smiles."
-via Positive.News, February 19, 2024
#wales#welsh#ocean#marine biology#aquaculture#marine life#marine animals#seaweed#sea scallops#oysters#united kingdom#uk#conservation#conservation news#overfishing#environmental news#farming#sustainable agriculture#sustainability#ocean farming#good news#hope
490 notes
·
View notes
Text
Its been said a thousand times but the idea that "privileged groups" are uniformly benefited by the oppression of their complementary "oppressed groups" is both detached from reality and fundamentally anti-solidarity
White agricultural workers in the antebellum and sharecropper-era american south did not fucking benefit from a captive black workforce working for nothing or close to it. They very much the opposite of benefited from this arrangement, and anyone trying to tell them otherwise was trying to sucker them. Cannot feed yr kids with psychological wages! What could compel anyone to intervene 150yrs after the fact on the side of the slavery propagandists?
223 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did you know women constitute 41% of the world’s agricultural labor force?
Rural Women workers are the backbone of their communities, making incredible contributions to health and economic well-being.

0 notes
Text
I keep thinking about a post or a comment I saw months ago that basically said, "if this isn't a genocide then why haven't I seen any photos of Israel on fire"
So here are some photos of Israel on fire.
Starting with the obvious:
October 7th, 2023. Hamas attacked 21 towns. Be'eri, Kfar Aza, Re'im, and Nir Oz were essentially burned to the ground; it will take years to rebuild them.
Satellite images during the attack show fires burning all over.

On October 7, Israel’s farming industry lost approximately 40% of its workforce and 30% of its physical area when the nation’s agricultural center became a warzone and the site of mass death and destruction.
The war forced thousands of people in Israel’s north and south to abandon their homes, leaving hundreds of acres of farmland to lie fallow while the IDF secured the area from further Hamas attacks.
Devastating losses About 20% of Israel’s agricultural land is located in the Gaza border area.... 75% of the vegetables consumed in Israel usually come from the Gaza border region, plus 20% of the fruit and 6.5% of the milk. Meanwhile, Israel’s northern region — which has been facing increasing rocket attacks from Hezbollah in Lebanon — accounts for a third of the country’s agricultural land, and according to the Agriculture and Rural Development Ministry, about 73% of its domestic egg production is concentrated in the Galilee and Golan regions.
Hezbollah's rocket attacks upon Israeli civilian areas, and Hamas rocket attacks from Lebanon, have caused massive fires across northern Israel.
The elimination of Israel has been a primary goal for Hezbollah, just as it is for Hamas and its affiliated groups.
Unlike Hamas, which targets Jews per se and cites the Protocols of the Elders of Zion to explain why, Hezbollah's reasoning follows that of the dictatorship of Iran:
"God, according to Hezbollah theology, cursed all Jews as blasphemers damned for all time and throughout history. Hezbollah, as well as the political/religious leaders of Iran, believe that the destruction of Israel will bring about the 'reappearance of the Imam (the Shiite Islamic Messiah).'"
Fire and brimstone it is, I guess.
April:
Nature and Parks Authority says that some 80,000 dunams (20,000 acres) in the Upper Galilee and Golan Heights have gone up in flames since the start of the month.

The Katzrin fire in early June:



Since the fighting erupted, the total scorched area in Israel is three times greater than the area consumed by the two greatest fires in Israeli history: the Sha'ar Hagai blaze west of Jerusalem in 1995, and the Mount Carmel forest fire in 2010. In each of those blazes, some 20,000 to 25,000 dunams of forest went up in smoke.
The total area burnt down now is also three times the combined area incinerated in 2016 when extreme weather conditions caused a wave of fires that consumed some 41,000 dunams. A similar size of woodland and forest also burned down during the Second Lebanon War. In 2019, a huge blaze consumed large swaths of central Israel's Mevo Modi'im community.

According to a Haaretz analysis of satellite images, which matches with estimates by authorities, some 210,000 dunams (about 52,000 acres) of land burned down in Israel and Lebanon: about 150,000 dunams in Israel from Hezbollah attacks and Israel Defense Forces anti-aircraft fire, and around 60,000 dunams in Lebanon. The burned-down areas in Israel stretch over a large area in the Galilee and Golan Heights, while in Lebanon they are concentrated near the border – due to the Israeli military policy of setting deliberate fire to [complex fortified] areas there in order to keep Hezbollah combatants away and to damage the vegetation that provides them with cover.
...These included trenches, bunkers, rocket-launching positions and arms storage sites.
June 4:
'If the fire spreads to the mountain – everything changes': Residents try to survive amid Hezbollah rockets

As rockets rain on their homes and wreak havoc, some Israelis believe the government's lackluster response shows it has forfeited the north to terrorists. "This is Hezbollah's new strategy – intentionally firing on open areas to ignite fires and burn the north," says former mayor.
Gay Eyal, the security officer of the Golan Regional Council, hasn't slept a wink since yesterday. More than 20 communities in the north, including two evacuated towns of Avivim and Dovev, fall under his wide purview.
"It seems this is the new method of the enemy: They see and hear what's happening – they understand burning the north is more effective," Eyal stated grimly. "We're coming off a night of fires. And this morning another blaze started in the Yir'on Forest. Our biggest fear is the fire spreading to Mount Meron. If that mountain ignites, all the communities of Meron, Safsufa, and the Galilee panhandle will be in danger." Eyal claims they prepared in advance, positioning 24 water trailer rigs of 1,000 liters each in every community. "It's a drop in the bucket. We geared up this past year with many water trailers to assist with firefighting, but it's not enough. We're working with fire stations in Safed, Kiryat Shmona, Tiberias, and Carmiel – our council is dealing with four fire stations. The firefighters are doing everything they can, working ceaselessly. They're tearing themselves apart, but the fire is spreading like a field of thorns."

...Another resident from the north who was out all night at the various fire scenes also tells Israel Hayom this morning: "It's impossible to describe what we went through here last night. Everything burned, an entire region was ablaze. I drove between the fruit orchards, between communities as the fires raged, and my heart burned. The feeling is terrible, of destruction. There's no way to explain the feeling of people watching their life's work burning before their eyes."

June 12:

Hezbollah launched some 215 rockets and several more missiles and drones at northern Israel on Wednesday, in what it said was a response to the killing of a senior commander in the terror group by an Israeli airstrike a night earlier.
The successive Hezbollah attacks began on Wednesday morning with a barrage of at least 90 rockets fired at several [CIVILIAN] areas in northern Israel, including Tiberias — for the first time amid the war — Safed and Rosh Pina, sending tens of thousands of people to shelters, as Jewish Israelis celebrated the Shavuot holiday.
The Israel Defense Forces said another 70 rockets were then launched at the Mount Meron area, home to a sensitive air traffic control base. Ten more rockets were fired at the northern community of Zar’it, and an anti-tank guided missile struck a factory of the Plasan armored vehicle manufacturer in Kibbutz Sasa, causing damage. Later in the morning, a drone launched from Lebanon detonated in an open area near the northern community of Zivon, local authorities said. Several more rockets were fired in the afternoon hours at the upper and western Galilee areas.
#fire tw#israel hamas war#hezbollah#jumblr#free lebanon too#do people outside of jumblr know that hezbollah basically runs Lebanon and it's Bad Actually?#fuck hamas#wall of words
148 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Embark on a Journey to Agricultural Abundance: Unlocking the Secrets of Canadian Farm Visas in 2024 and Beyond In the vast tapestry of international job opportunities, the Canadian agricultural secto... https://bit.ly/4cj8Ou6/
0 notes
Text
Following a White House edict effectively banning federal employees from disclosing their personal pronouns in email signatures, sources within multiple federal agencies say pronouns are now being systemically blocked across multiple email clients and other software.
WIRED confirmed various automated efforts with employees at the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the General Services Administration (GSA), the US Department of Agriculture, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The employees spoke to WIRED on condition of anonymity, citing fears of retaliation.
Multiple agency directors sent emails over the weekend telling staff that, due to President Donald Trump’s executive order, their offices would be removing the pronoun capability from Office 365. Employees were told they’d also need to remove pronouns from their email signatures in order to comply with the directive.
A staffer at USAID says the formal deactivation of their ability to list pronouns occurred last week, in response to executive orders defining sexes issued by President Trump on his first day in office. A GSA staffer says pronouns were wiped from employees’ email signatures after hours on Friday and were also no longer visible in Slack, the workplace messaging app. At the CDC, there used to be a section for employees to share their pronouns on their Teams profiles, another workplace app. That field no longer exists.
Reached for comment, the White House transferred WIRED to OPM communications director McLaurine Pinover, who pointed to January 29 memorandum ordering agencies to disable all features “that prompt users for their pronouns.”
The ban on personal pronouns follows sweeping efforts by the White House to eliminate programs that encourage diversity and social justice within the federal government, as well as other references to “diversity, equity, and inclusion” in federal employees’ discourse.
In a striking example of the policy in action, an image surfaced last week of a wall being painted over at the Federal Bureau of Investigation's Quantico, Virginia, academy due to it listing "diversity" among the bureau's core values. (According to an email from the FBI’s Office of Integrity and Compliance obtained by Mother Jones, the bureau no longer counts "diversity" among its core values.)
The Trump administration began a radical campaign last week aimed at inducing members of the federal workforce to leave their jobs ahead of threatened reductions. The effort is spearheaded by Elon Musk, leader of the so-called Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), a task force that has effectively seized control of several federal agencies and sensitive government systems with apparent clearance from the White House.
WIRED reported last week that Musk’s outfit had effectively taken over the Office of Personnel Management, the US government’s human resources department. In this and other efforts, it is employing inexperienced young engineers whose ages range from 19 to 24—many of whom, public records show, are former interns or have been affiliated with Musk-aligned companies.
OPM emailed federal workers on January 28 with a “deferred resignation offer,” sparking widespread confusion among federal workers. (DOGE’s own new HR chief was unable to answer basic questions about the offer in a contentious staff meeting last week, WIRED reported.) In an email to staff Sunday evening, OPM clarified whether the deferred resignation program complied with existing privacy laws. “Yes,” read the answer. “The deferred resignation program uses only basic contact information about federal employees, like name and government address, along with short, voluntary email responses. The information is stored on government systems. To the extent that the Privacy Act applies, all information relevant to the program is covered by existing OPM System Records Notices.”
Multiple agency sources told WIRED last week that several of Musk's lieutenants had been granted access to key computer systems controlled by the GSA, an independent agency tasked by Congress with overseeing federal buildings and providing equipment, supplies, and IT support across the government.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
The most absurd and tragic results of this fetishizing of what were taken to be advanced farming methods occurred in the Soviet Union, where giant model farms were newly laid out for mechanized production before a trained workforce had been developed and before a proper storage-and-transport infrastructure had been installed to support the use of the expensive machinery. In the maturing Marxist-Leninist version of socialist construction, nature was regarded as an utterly passive and infinitely malleable substrate for industrialized agriculture. Because the proper treatment and improvement of the land was not regarded as an important step, let alone a priority, Soviet agriculture attained notoriously low productivity levels per unit of land area (even on some of the world's most excellent soils), coupled with an astonishingly bad record in soil erosion. The response in the mid-1970s was to import grain on a large scale while investing even more heavily in the further industrialization of agricultural-production processes. The result was increased output purchased at a much more than proportional increase in capital costs. The inefficient use of resources in Soviet farming was substantially due, of course, to its overly centralized, command-from-above style of social organization. Experimental systems employing mobile brigades of workers were tried out in the early seventies but were soon politically quashed. They were revived more recently and might eventually have altered the poor labour productivity in Soviet agriculture if they had been given a proper chance. Their environmental impact was quite uncertain, however, although it seems unlikely that it could have been worse.
Colin A. M. Duncan, The Centrality of Agriculture: Between Humankind and the Rest of Nature
169 notes
·
View notes
Text
random, deeply unscientific poll time because I'm curious how well this website reflects the overall labor force lol
before you mark "unemployed," READ THE EXPLANATION AND INSTRUCTIONS
DETAILS AND INSTRUCTIONS:
*The number listed beside each category is the number of job positions available to the total workforce, not necessarily the number of people who are actually employed.
*Not having a job does not automatically make you "unemployed." Unemployed means you are a participating member of the workforce but don't have a job currently. To be consider part of the active workforce as defined by the BLS, you MUST be ALL of the following:
16 years of age or older
residing in the 50 states or DC
available for work
actively seeking employment in the last 4 weeks
not on active duty in the military
DO NOT select unemployed unless you meet ALL of the criteria above.
Examples of not having a job but not counting as unemployed: stay-at-home parent (I know this one is a bad reflection of reality, i know i know pls dont yell at me), a full-time student not currently working, a 25 year old who hasn't applied for any jobs in over a few months, someone with a permanent or temporary disability who is either not working/seeking employment or on FMLA.
Other notes and explanation:
This is a list of all non-agriculture industries that employ 10 million or more people, based on the most recent data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. The math might be way off bc I wasn't very careful lmao. If you have more than one job across more than one industry, pick the one that makes up the majority of your income.
A handful of familiar sub-industries that make up a portion of a larger industry but are less than 8 million people are listed in the "Other" category so that the much larger sub-industry can have its own line.
For example, healthcare belongs to "healthcare and public services," which is around 22M and includes childcare and social support services. Because direct healthcare delivery makes up such an enormous portion, I separated it out. The rest is fewer than 5M and thus does not get its own line, so they're included in "Other." (Insurance specifically is included in finance.)
More things included in "other":
Construction
Mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction
Utilities
Real-estate
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
Greg Sargent at TNR:
There are still nearly two months to go before Donald Trump assumes the presidency again, but Republicans or GOP-adjacent industries have already begun to admit out loud that some of his most important policy promises could prove disastrous in their parts of the country. These folks don’t say this too directly, out of fear of offending the MAGA God King. Instead, they suggest gingerly that a slight rethink might be in order. But unpack what they’re saying, and you’ll see that they’re in effect acknowledging that some of Trump’s biggest campaign promises were basically scams.
In Georgia, for instance, some local Republicans are openly worried about Trump’s threat to roll back President Biden’s Inflation Reduction Act. The IRA is pouring hundreds of billions of dollars into incentives for the manufacture and purchase of green energy technologies, from electric vehicles to batteries to solar power. Trump endlessly derided this as the “green new scam” and pledged to repeal all uncommitted funds. But now The New York Times reports that Trump supporters like state Representative Beth Camp fear that repeal could destroy jobs related to new investments in green manufacturing plants in the state. Camp worries that this could leave factories in Georgia “sitting empty.” You heard that right: This Republican is declaring that Trump’s threatened actions could leave factories sitting empty.
[...]
Something similar is also already happening with Trump’s threat to deport millions of undocumented immigrants. Reuters reports that agriculture interests, which are heavily concentrated in GOP areas, are urging the incoming Trump administration to refrain from removing untold numbers of migrants working throughout the food supply chain, including in farming, dairy, and meatpacking.
Notably, GOP Representative John Duarte, who just lost his seat in the elections, explicitly tells Reuters that farming interests in his California district depend on undocumented immigrants—and that Trump should exempt many from removal. Duarte and industry representatives want more avenues created for migrants to work here legally—the precise opposite of what Trump promised. Now over to Texas. NPR reports that various industries there fear that mass deportations could cripple them, particularly in construction, where nearly 300,000 undocumented immigrants toiled as of 2022. Those workers enable the state to keep growing despite a native population that isn’t supplying a large enough workforce. Local analysts and executives want Trump to refrain from removing all these people or create new ways for them to work here legally. Even the Republican mayor of McKinney, Texas, is loudly sounding the alarm.
Meanwhile, back in Georgia, Trump’s threat of mass deportations is awakening new awareness that undocumented immigrants drive industries like construction, landscaping, and agriculture, reports The Wall Street Journal. In Dalton, a town that backed Trump, fear is spreading that removals could “upend its economy and workforce.” At this point, someone will argue that all this confirms Trump’s arguments—that these industries and their representatives merely fear losing cheap migrant labor that enables them to avoid paying Americans higher wages. When JD Vance and Trump pushed their lie about Haitians eating pets in Springfield, Ohio, Vance insisted that he opposed the Haitian influx into Midwestern towns because they’re undercutting U.S. workers. But all these disparate examples of Republicans and GOP areas lamenting coming mass deportations suggest an alternate story, one detailed well by the Times’ Lydia DePillis. In the MAGA worldview, a large reserve of untapped native-born Americans in prime working age are languishing in joblessness throughout Trump country—and will stream into all these industries once migrants are removed en masse, boosting wages.
But DePillis documents that things like poor health and disability are more important drivers of unemployment among this subset of non-college working-age men. Besides, migrants living and working here don’t just perform labor that Americans will not. They also consume and boost demand, creating more jobs. As Paul Krugman puts it, in all these ways, migrant laborers are “complements” to U.S. workers. Importantly, that’s the argument that these Republicans and industries in GOP areas are really making when they lament mass deportations: Migrant labor isn’t displacing U.S. workers; it’s helping drive our post-Covid recovery and growth. This directly challenges Trump’s zero-sum worldview.
[...] Here’s another possibility: In the end, Trump’s deportation forces may selectively spare certain localities and industries from mass removals. Trump’s incoming “border czar,” Tom Homan, suggests this won’t happen. But a hallmark of MAGA is corruptly selective governance in the interests of MAGA nation and expressly against those who are designated MAGA’s enemies, U.S. citizens included. One can see mass deportations becoming a selective tool, in which blue localities are targeted for high-profile raids—even as Trump triumphantly rants that they are cesspools of “migrant crime” that he is pacifying with military-style force—while GOP-connected industries and Trump-allied Republicans tacitly secure some forbearance.
Donald Trump’s threats to green energy initiatives and resistance to his mass deportation proposals are facing headwinds against him, even from local Republicans who fear losses of jobs in their communities.
Even if Trump does get to implement his mass deportation policy, he’ll likely create several exemption carveouts (mainly for industries likely to favor him) and use selective enforcement (light touch for red states, heavy and punitive for blue states).
39 notes
·
View notes