#a deference
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Have You! Have you ever had a Lemon Meringue Pie Drink on a long Summer day? Limited for a time Samual Adams’s Summer Ale Lemon Meringue in mouth Drink Responsibly for taste One bottle add bottle water per hour That taste will still be there Drink irresponsibly All taste goes to waste Now your just drinking The taste was the beginning Not to be drunk Have you Drank today Decipher this code before 2050
It will leave the fridge faster than food allowing the refillable refrigerator that extra space, I’m only speaking, for my six pack bought! This is not apart of code, sorry but you still have until 25.5 approximate years to solve! :( or :) you still have time.
“As I burp, it’s just like you’ve eaten lemon.”
Stated a drinker
#wordsbymm#mmybsdrow#artcalledgames#artcalledwords#artcalledtattoo#in the skin add colours#make em taste#a deference#enjoy the summer#drink some pie in mouth#critical ridicules#add bottled water for living#Flint was long ago#cheers#the cap has a code#not as prolific as cap for free Dr Pepper#that was 1990’s#leave fridge be gone#until we meet again#ohh summer ale#from Samuel Adams#I’m just a drinker#I said#in the lemon taste
0 notes
Text
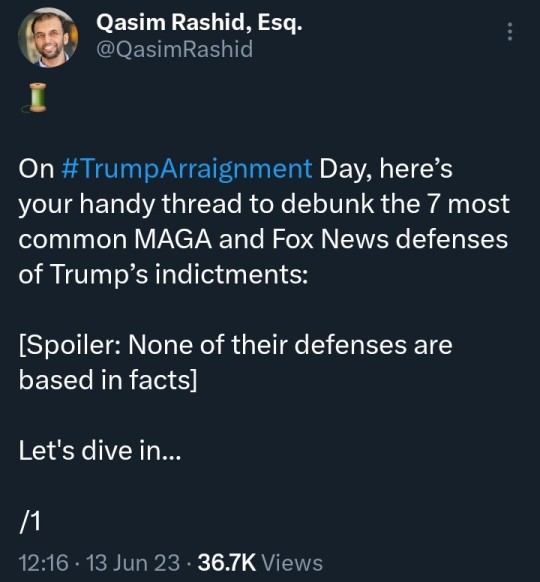
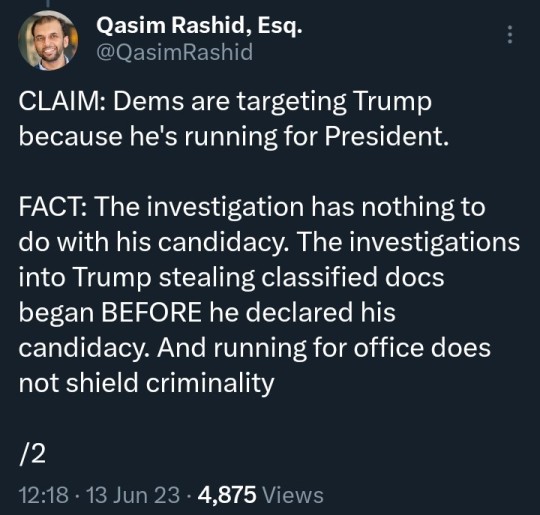
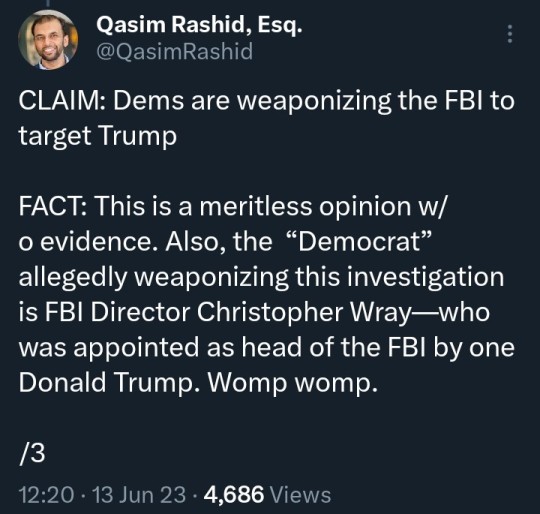
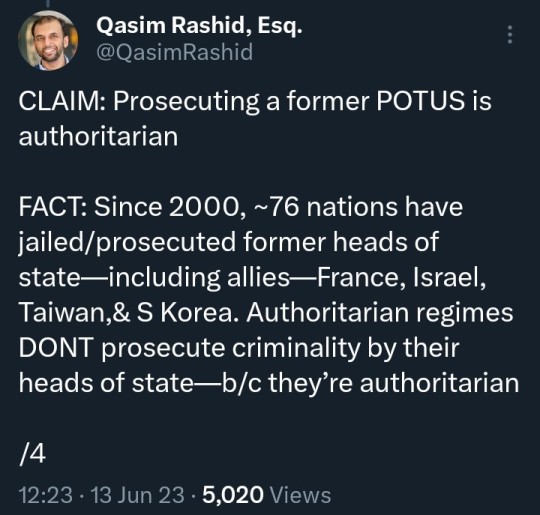


#Qasim Rashid#ManChildTrump#Donald Trump#Trump#Drumpf#CrybabyTrump#Tiny Hands#Limp Dick#Spanky#Pee Brain#Cadet Bone Spurs#Five Deferment Don#The Orange Menace#The Manchurian Cantaloupe#classified#documents#cover up#obstruction#indict#indictment#espionage#justice#criminal#MAGA
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
Expert agencies and elected legislatures

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/11/21/policy-based-evidence/#decisions-decisions

Since Trump hijacked the Supreme Court, his backers have achieved many of their policy priorities: legalizing bribery, formalizing forced birth, and – with the Loper Bright case, neutering the expert agencies that regulate business:
https://jacobin.com/2024/07/scotus-decisions-chevron-immunity-loper
What the Supreme Court began, Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy are now poised to finish, through the "Department of Government Efficiency," a fake agency whose acronym ("DOGE") continues Musk's long-running cryptocurrency memecoin pump-and-dump. The new department is absurd – imagine a department devoted to "efficiency" with two co-equal leaders who are both famously incapable of getting along with anyone – but that doesn't make it any less dangerous.
Expert agencies are often all that stands between us and extreme misadventure, even death. The modern world is full of modern questions, the kinds of questions that require a high degree of expert knowledge to answer, but also the kinds of questions whose answers you'd better get right.
You're not stupid, nor are you foolish. You could go and learn everything you need to know to evaluate the firmware on your antilock brakes and decide whether to trust them. You could figure out how to assess the Common Core curriculum for pedagogical soundness. You could learn the material science needed to evaluate the soundness of the joists that hold the roof up over your head. You could acquire the biology and chemistry chops to decide whether you want to trust produce that's been treated with Monsanto's Roundup pesticides. You could do the same for cell biology, virology, and epidemiology and decide whether to wear a mask and/or get an MRNA vaccine and/or buy a HEPA filter.
You could do any of these. You might even be able to do two or three of them. But you can't do all of them, and that list is just a small slice of all the highly technical questions that stand between you and misery or an early grave. Practically speaking, you aren't going to develop your own robust meatpacking hygiene standards, nor your own water treatment program, nor your own Boeing 737 MAX inspection protocol.
Markets don't solve this either. If they did, we wouldn't have to worry about chunks of Boeing jets falling on our heads. The reason we have agencies like the FDA (and enabling legislation like the Pure Food and Drug Act) is that markets failed to keep people from being murdered by profit-seeking snake-oil salesmen and radium suppository peddlers.
These vital questions need to be answered by experts, but that's easier said than done. After all, experts disagree about this stuff. Shortcuts for evaluating these disagreements ("distrust any expert whose employer has a stake in a technical question") are crude and often lead you astray. If you dismiss any expert employed by a firm that wants to bring a new product to market, you will lose out on the expertise of people who are so legitimately excited about the potential improvements of an idea that they quit their jobs and go to work for whomever has the best chance of realizing a product based on it. Sure, that doctor who works for a company with a new cancer cure might just be shilling for a big bonus – but maybe they joined the company because they have an informed, truthful belief that the new drug might really cure cancer.
What's more, the scientific method itself speaks against the idea of there being one, permanent answer to any big question. The method is designed as a process of continual refinement, where new evidence is continuously brought forward and evaluated, and where cherished ideas that are invalidated by new evidence are discarded and replaced with new ideas.
So how are we to survive and thrive in a world of questions we ourselves can't answer, that experts disagree about, and whose answers are only ever provisional?
The scientific method has an answer for this, too: refereed, adversarial peer review. The editors of major journals act as umpires in disputes among experts, exercising their editorial discernment to decide which questions are sufficiently in flux as to warrant taking up, then asking parties who disagree with a novel idea to do their damndest to punch holes in it. This process is by no means perfect, but, like democracy, it's the worst form of knowledge creation except for all others which have been tried.
Expert regulators bring this method to governance. They seek comment on technical matters of public concern, propose regulations based on them, invite all parties to comment on these regulations, weigh the evidence, and then pass a rule. This doesn't always get it right, but when it does work, your medicine doesn't poison you, the bridge doesn't collapse as you drive over it, and your airplane doesn't fall out of the sky.
Expert regulators work with legislators to provide an empirical basis for turning political choices into empirically grounded policies. Think of all the times you've heard about how the gerontocracy that dominates the House and the Senate is incapable of making good internet policy because "they're out of touch and don't understand technology." Even if this is true (and sometimes it is, as when Sen Ted Stevens ranted about the internet being "a series of tubes," not "a dump truck"), that doesn't mean that Congress can't make good internet policy.
After all, most Americans can safely drink their tap water, a novelty in human civilization, whose history amounts to short periods of thriving shattered at regular intervals by water-borne plagues. The fact that most of us can safely drink our water, but people who live in Flint (or remote indigenous reservations, or Louisiana's Cancer Alley) can't tells you that these neighbors of ours are being deliberately poisoned, as we know precisely how not to poison them.
How did we (most of us) get to the point where we can drink the water without shitting our guts out? It wasn't because we elected a bunch of water scientists! I don't know the precise number of microbiologists and water experts who've been elected to either house, but it's very small, and their contribution to good sanitation policy is negligible.
We got there by delegating these decisions to expert agencies. Congress formulates a political policy ("make the water safe") and the expert agency turns that policy into a technical program of regulation and enforcement, and your children live to drink another glass of water tomorrow.
Musk and Ramaswamy have set out to destroy this process. In their Wall Street Journal editorial, they explain that expert regulation is "undemocratic" because experts aren't elected:
https://www.wsj.com/opinion/musk-and-ramaswamy-the-doge-plan-to-reform-government-supreme-court-guidance-end-executive-power-grab-fa51c020
They've vowed to remove "thousands" of regulations, and to fire swathes of federal employees who are in charge of enforcing whatever remains:
https://www.theverge.com/2024/11/20/24301975/elon-musk-vivek-ramaswamy-doge-plan
And all this is meant to take place on an accelerated timeline, between now and July 4, 2026 – a timeline that precludes any meaningful assessment of the likely consequences of abolishing the regulations they'll get rid of.
"Chesterton's Fence" – a thought experiment from the novelist GK Chesterton – is instructive here:
There exists in such a case a certain institution or law; let us say, for the sake of simplicity, a fence or gate erected across a road. The more modern type of reformer goes gaily up to it and says, "I don't see the use of this; let us clear it away." To which the more intelligent type of reformer will do well to answer: "If you don't see the use of it, I certainly won't let you clear it away. Go away and think. Then, when you can come back and tell me that you do see the use of it, I may allow you to destroy it.
A regulation that works might well produce no visible sign that it's working. If your water purification system works, everything is fine. It's only when you get rid of the sanitation system that you discover why it was there in the first place, a realization that might well arrive as you expire in a slick of watery stool with a rectum so prolapsed the survivors can use it as a handle when they drag your corpse to the mass burial pits.
When Musk and Ramaswamy decry the influence of "unelected bureaucrats" on your life as "undemocratic," they sound reasonable. If unelected bureaucrats were permitted to set policy without democratic instruction or oversight, that would be autocracy.
Indeed, it would resemble life on the Tesla factory floor: that most autocratic of institutions, where you are at the mercy of the unelected and unqualified CEO of Tesla, who holds the purely ceremonial title of "Chief Engineer" and who paid the company's true founders to falsely describe him as its founder.
But that's not how it works! At its best, expert regulations turns political choices in to policy that reflects the will of democratically accountable, elected representatives. Sometimes this fails, and when it does, the answer is to fix the system – not abolish it.
I have a favorite example of this politics/empiricism fusion. It comes from the UK, where, in 2008, the eminent psychopharmacologist David Nutt was appointed as the "drug czar" to the government. Parliament had determined to overhaul its system of drug classification, and they wanted expert advice:
https://locusmag.com/2021/05/cory-doctorow-qualia/
To provide this advice, Nutt convened a panel of drug experts from different disciplines and asked them to rate each drug in question on how dangerous it was for its user; for its user's family; and for broader society. These rankings were averaged, and then a statistical model was used to determine which drugs were always very dangerous, no matter which group's safety you prioritized, and which drugs were never very dangerous, no matter which group you prioritized.
Empirically, the "always dangerous" drugs should be in the most restricted category. The "never very dangerous" drugs should be at the other end of the scale. Parliament had asked how to rank drugs by their danger, and for these categories, there were clear, factual answers to Parliament's question.
But there were many drugs that didn't always belong in either category: drugs whose danger score changed dramatically based on whether you were more concerned about individual harms, familial harms, or societal harms. This prioritization has no empirical basis: it's a purely political question.
So Nutt and his panel said to Parliament, "Tell us which of these priorities matter the most to you, and we will tell you where these changeable drugs belong in your schedule of restricted substances." In other words, politicians make political determinations, and then experts turn those choices into empirically supported policies.
This is how policy by "unelected bureaucrats" can still be "democratic."
But the Nutt story doesn't end there. Nutt butted heads with politicians, who kept insisting that he retract factual, evidence-supported statements (like "alcohol is more harmful than cannabis"). Nutt refused to do so. It wasn't that he was telling politicians which decisions to make, but he took it as his duty to point out when those decisions did not reflect the policies they were said to be in support of. Eventually, Nutt was fired for his commitment to empirical truth. The UK press dubbed this "The Nutt Sack Affair" and you can read all about it in Nutt's superb book Drugs Without the Hot Air, an indispensable primer on the drug war and its many harms:
https://www.bloomsbury.com/us/drugs-without-the-hot-air-9780857844989/
Congress can't make these decisions. We don't elect enough water experts, virologists, geologists, oncology researchers, structural engineers, aerospace safety experts, pedagogists, gerontoloists, physicists and other experts for Congress to turn its political choices into policy. Mostly, we elect lawyers. Lawyers can do many things, but if you ask a lawyer to tell you how to make your drinking water safe, you will likely die a horrible death.
That's the point. The idea that we should just trust the market to figure this out, or that all regulation should be expressly written into law, is just a way of saying, "you will likely die a horrible death."
Trump – and his hatchet men Musk and Ramaswamy – are not setting out to create evidence-based policy. They are pursuing policy-based evidence, firing everyone capable of telling them how to turn the values espouse (prosperity and safety for all Americans) into policy.
They dress this up in the language of democracy, but the destruction of the expert agencies that turn the political will of our representatives into our daily lives is anything but democratic. It's a prelude to transforming the nation into a land of epistemological chaos, where you never know what's coming out of your faucet.
#pluralistic#politics#political science#department of government efficiency#loper bright#chevron deference#david nutt#drugs#regulation#democracy#democratic accountability#ukpoli#nutt sack affair#war on drugs#war on some drugs
449 notes
·
View notes
Note
If someone gave you a Tesla Cybertruck for free, how would you destroy it?
exoding hammer
874 notes
·
View notes
Text
My mundane super power is that I love blue heelers so much that every time I see them I ask to pet them and their owners always warn me they’re not overly friendly which I know because my boy Sly was also very aloof but every time the dog feels my infinite love and always greets me warmly.
#ramblies#it’s also my approach is always deferred eyes to the side and hand out for a polite sniff#this mornings dog was so charmed she reared up on her hind legs to sniff my face and fawned for more pets#her owner was like oh maybe it’s because you have berries#but the dog didn’t so much as tilt her head to a knowledge them she just wanted attention#another time the owner warned and the dog came up and leaned against my legs to get scritches and the owner was flabbergasted#i miss my good boy sly who was the best heeler
520 notes
·
View notes
Note
I don't understand the chevron law thing, could you explain it like I'm five? Should we be working towards fixing whatever the courts just fucked up?
So, okay, I am condensing like a semester of a class I took in 2017 into a very short explanation, but:
It would be really annoying for Congress to individually pass laws approving every new medicine or listing out every single poison you can't have in tap water, so instead there are agencies created by Congress, via a law, to handle a specific thing. The agencies are created by Congress but overseen by the executive branch (so, the president), which is why we say things like "Reagan's EPA" or "Biden's DOJ" - even though Congress creates them, the president determines how they do the thing Congress wants them to do, by passing regulations like "you can't dump cyanide in the local swimming pool" and "no, you can't dump strychnine, either."
However, sometimes people will oppose these regulations by saying that the agency is going beyond the task they were given by Congress. "The Clean Air Act only bans 'pollutants,' and nowhere in the law does it say that 'pollutants' includes arsenic! You're going beyond your mandate!" To which the experts at the EPA would be like, "We, the experts at the EPA, have decided arsenic is a pollutant." On the flip side, the EPA could be like, "We, the experts at the EPA, have decided that arsenic isn't a pollutant," and people would oppose that regulation by being like, "But the Clean Air Act bans 'pollutants,' and it's insane to say that arsenic isn't a pollutant!" So whose interpretation is correct, the government's or the challengers'?
Chevron deference basically put heavy weight onto how the agency (i.e. the government) interpreted the law, with the assumption that the agency was in the right and needing pretty strong evidence that they were interpreting it wrong (like, blatantly doing the opposite of a clear part of the law or something). If there was any ambiguity in how the law was written, you'd defer to the agency's interpretation, even if that interpretation was different depending on who was president at the time.
(Note: there are other ways of challenging regulations other than this one, like saying that they were promulgated in a way that is "arbitrary and capricious" – basically, not backed by any evidence/reasoning other than "we want it." Lots of Trump-era regulations got smacked with this one, though I think they'd be better at it if Trump gets a second term, since they've now had practice.)
Chevron deference wasn't all good – remember that the sword cuts both ways, including when dickholes are in power – but it was a very standard part of the law. Like, any opposition to a regulation would have some citation to be like "Chevron doesn't apply here" and every defense would be like "Chevron absolutely applies here" and most of the time, the agency would win. Like, it was a fundamental aspect of law since the 80s.
The Supreme Court decision basically tosses that out, and says, "In a situation where the law is ambiguous, the court decides what it means." That's not completely insane – interpreting law is a thing judges normally do – but in a situation where the interpretation may hinge on something very complicated outside of the judge's wheelhouse, you now cannot be like, "Your Honor, I promise you that the experts at NOAA know a lot about the weather and made this decision for a good reason."
The main reason it's a problem is that it allows judges to override agencies' judgements about what you should do about a thing and what things you should be working on in the first place. However, I don't think there's really a way of enshrining that into law, outside of maybe adding something to the Administrative Procedure Act, and that would require a Congress that isn't majority Republican.
I will say that kind of I expected this to happen, just because IIRC Gorsuch in particular hates Chevron deference. IMO it's a classic case of "rules for me but not for thee" – Scalia and other conservatives used to rely on Chevron because they wanted their presidents to hold a ton of unchecked power (except for the EPA), but now that we've had Obama and Biden, now conservatives don't like Chevron because it gives the presidents they don't like unchecked power.
#askbox#personal#Anonymous#bb is a lawyer#bb had a whole flow chart for admin law finals that is now moot#chevron deference
701 notes
·
View notes
Text


reynah is now a victim of watsuki's vocal prowess
this was supposed to be a silly doodle but i played around with the lighting too much
#keyframes fanart#keyframes vn#reynah dioquino#keyframes reynah#keyframes mc#they may be winter but when the opportunity is there they will do it#i think i found myself a crackship#theres so much potential here actually lol#its not helping that the height deference is cute#then there's the pink x black aesthetics#shipping mc with the actual love interests < shipping mc with reynah LMAO
246 notes
·
View notes
Text

Been binging the 1986 series again and drew my ver in some of his slays
#love that little banana lookin ass hoe#journey to the west#jttw sun wukong#jttw#sun wukong#journey to the west fanart#digital art#my art#jttw 1986#y’all my senior project got me on LOCKDOWN#I am suffering or2#also I now have what is colloquially known as an ✨inner ear canal infection✨#my ear hurt o(-( can’t have a fucking break in this house#the joys of product design (arguing with manufacturers)#dude the costume design in that show is so gorgeous for everyone#these aren’t even my fave favs but the yellow on swk is so charming#kinda made me cry when in the liu er mihou ep swk is always wearing his fanciest duds when appearing in front of others#but when they went to go see his master he changed back into humble pilgrim clothes#😭 like bro the deference#I really like that frilly pink skirt he had on for a while in s1#like okay fruit slaaay#1986 swk is so fruity he’s the only one who’s outfit changes constantly that’s diva✨
211 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Drowning in guilt won't bring you what you want"
"And what is it I want?"

👀

#YOU'RE STARING AT WHAT YOU WANT BOTH OF YOU!!! DONT TORMENT ME LIKE THAT!!! SCREAMS#But also deferring to Vex to ask what you actually want is very in character and :3 yknow :3#perc'ahlia#percahlia#tlovm spoilers#cr spoilers#critical role#tlovm#the legend of vox machina#percival de rolo#vex'ahlia#EDIT: fixed the exact wording - thanks El! :D
358 notes
·
View notes
Text


#crutches and spice#imani barbarin#covid pandemic#covid#pandemic#disability#homelessness#supreme court#chevron#chevron deference#july 2024#2024
319 notes
·
View notes
Text








ANNA TORV as Olivia Dunham (Fringe) | 2.04 Momentum Deferred
#Anna Torv#Olivia Dunham#fringeedit#tvedit#dailyflicks#scifiedit#poor baby she never got one day off ever#she needs 1000 hugs#2x04 Momentum Deferred#fringe#gifs*#olivia gifs*
151 notes
·
View notes
Text








Julian being nervous + Ricky talking them out of situations
#such an important part of their dynamic tbh#like this is one of very few situations where julian will defer to Ricky rather than claiming he's smarter/should be in charge#the co-dependence goes BOTH ways (like them)#tpb#trailer park boys#gifs
301 notes
·
View notes
Text
Marshmallow Longtermism

The paperback edition of The Lost Cause, my nationally bestselling, hopeful solarpunk novel is out this week!

My latest column for Locus Magazine is "Marshmallow Longtermism"; it's a reflection on how conservatives self-mythologize as the standards-bearers for deferred gratification and making hard trade-offs, but are utterly lacking in these traits when it comes to climate change and inequality:
https://locusmag.com/2024/09/cory-doctorow-marshmallow-longtermism/
Conservatives often root our societal ills in a childish impatience, and cast themselves as wise adults who understand that "you can't get something for nothing." Think here of the memes about lazy kids who would rather spend on avocado toast and fancy third-wave coffee rather than paying off their student loans. In this framing, poverty is a consequence of immaturity. To be a functional adult is to be sober in all things: not only does a grownup limit their intoxicant intake to head off hangovers, they also go to the gym to prevent future health problems, they save their discretionary income to cover a down-payment and student loans.
This isn't asceticism, though: it's a mature decision to delay gratification. Avocado toast is a reward for a life well-lived: once you've paid off your mortgage and put your kid through college, then you can have that oat-milk latte. This is just "sound reasoning": every day you fail to pay off your student loan represents another day of compounding interest. Pay off the loan first, and you'll save many avo toasts' worth of interest and your net toast consumption can go way, way up.
Cleaving the world into the patient (the mature, the adult, the wise) and the impatient (the childish, the foolish, the feckless) does important political work. It transforms every societal ill into a personal failing: the prisoner in the dock who stole to survive can be recast as a deficient whose partying on study-nights led to their failure to achieve the grades needed for a merit scholarship, a first-class degree, and a high-paying job.
Dividing the human race into "the wise" and "the foolish" forms an ethical basis for hierarchy. If some of us are born (or raised) for wisdom, then naturally those people should be in charge. Moreover, putting the innately foolish in charge is a recipe for disaster. The political scientist Corey Robin identifies this as the unifying belief common to every kind of conservativism: that some are born to rule, others are born to be ruled over:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/08/01/set-healthy-boundaries/#healthy-populism
This is why conservatives are so affronted by affirmative action, whose premise is that the absence of minorities in the halls of power stems from systemic bias. For conservatives, the fact that people like themselves are running things is evidence of their own virtue and suitability for rule. In conservative canon, the act of shunting aside members of dominant groups to make space for members of disfavored minorities isn't justice, it's dangerous "virtue signaling" that puts the childish and unfit in positions of authority.
Again, this does important political work. If you are ideologically committed to deregulation, and then a giant, deregulated sea-freighter crashes into a bridge, you can avoid any discussion of re-regulating the industry by insisting that we are living in a corrupted age where the unfit are unjustly elevated to positions of authority. That bridge wasn't killed by deregulation – it's demise is the fault of the DEI hire who captained the ship:
https://www.axios.com/local/salt-lake-city/2024/03/26/baltimore-bridge-dei-utah-lawmaker-phil-lyman-misinformation
The idea of a society made up of the patient and wise and the impatient and foolish is as old as Aesop's "The Ant and the Grasshopper," but it acquired a sheen of scientific legitimacy in 1970, with Walter Mischel's legendary "Stanford Marshmallow Experiment":
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stanford_marshmallow_experiment
In this experiment, kids were left alone in a locked room with a single marshmallow, after being told that they would get two marshmallows in 15 minutes, but only if they waited until them to eat the marshmallow before them. Mischel followed these kids for decades, finding that the kids who delayed gratification and got that second marshmallow did better on every axis – educational attainment, employment, and income. Adult brain-scans of these subjects revealed structural differences between the patient and the impatient.
For many years, the Stanford Marshmallow experiment has been used to validate the cleavage of humanity in the patient and wise and impatient and foolish. Those brain scans were said to reveal the biological basis for thinking of humanity's innate rulers as a superior subspecies, hidden in plain sight, destined to rule.
Then came the "replication crisis," in which numerous bedrock psychological studies from the mid 20th century were re-run by scientists whose fresh vigor disproved and/or complicated the career-defining findings of the giants of behavioral "science." When researchers re-ran Mischel's tests, they discovered an important gloss to his findings. By questioning the kids who ate the marshmallows right away, rather than waiting to get two marshmallows, they discovered that these kids weren't impatient, they were rational.
The kids who ate the marshmallows were more likely to come from poorer households. These kids had repeatedly been disappointed by the adults in their lives, who routinely broke their promises to the kids. Sometimes, this was well-intentioned, as when an economically precarious parent promised a treat, only to come up short because of an unexpected bill. Sometimes, this was just callousness, as when teachers, social workers or other authority figures fobbed these kids off with promises they knew they couldn't keep.
The marshmallow-eating kids had rationally analyzed their previous experiences and were making a sound bet that a marshmallow on the plate now was worth more than a strange adult's promise of two marshmallows. The "patient" kids who waited for the second marshmallow weren't so much patient as they were trusting: they had grown up with parents who had the kind of financial cushion that let them follow through on their promises, and who had the kind of social power that convinced other adults – teachers, etc – to follow through on their promises to their kids.
Once you understand this, the lesson of the Marshmallow Experiment is inverted. The reason two marshmallow kids thrived is that they came from privileged backgrounds: their high grades were down to private tutors, not the choice to study rather than partying. Their plum jobs and high salaries came from university and family connections, not merit. Their brain differences were the result of a life free from the chronic, extreme stress that comes with poverty.
Post-replication crisis, the moral of the Stanford Marshmallow Experiment is that everyone experiences a mix of patience and impatience, but for the people born to privilege, the consequences of impatience are blunted and the rewards of patience are maximized.
Which explains a lot about how rich people actually behave. Take Charles Koch, who grew his father's coal empire a thousandfold by making long-term investments in automation. Koch is a vocal proponent of patience and long-term thinking, and is openly contemptuous of publicly traded companies because of the pressure from shareholders to give preference to short-term extraction over long-term planning. He's got a point.
Koch isn't just a fossil fuel baron, he's also a wildly successful ideologue. Koch is one of a handful of oligarchs who have transformed American politics by patiently investing in a kraken's worth of think tanks, universities, PACs, astroturf organizations, Star chambers and other world-girding tentacles. After decades of gerrymandering, voter suppression, court-packing and propagandizing, the American billionaire class has seized control of the US and its institutions. Patience pays!
But Koch's longtermism is highly selective. Arguably, Charles Koch bears more personal responsibility for delaying action on the climate emergency than any other person, alive or dead. Addressing greenhouse gasses is the most grasshopper-and-the-ant-ass crisis of all. Every day we delayed doing something about this foreseeable, well-understood climate debt added sky-high compounding interest. In failing to act, we saved billions – but we stuck our future selves with trillions in debt for which no bankruptcy procedure exists.
By convincing us not to invest in retooling for renewables in order to make his billions, Koch was committing the sin of premature avocado toast, times a billion. His inability to defer gratification – which he imposed on the rest of us – means that we are likely to lose much of world's coastal cities (including the state of Florida), and will have to find trillions to cope with wildfires, zoonotic plagues, and hundreds of millions of climate refugees.
Koch isn't a serene Buddha whose ability to surf over his impetuous attachments qualifies him to make decisions for the rest of us. Rather, he – like everyone else – is a flawed vessel whose blind spots are just as stubborn as ours. But unlike a person whose lack of foresight leads to drug addiction and petty crimes to support their habit, Koch's flaws don't just hurt a few people, they hurt our entire species and the only planet that can support it.
The selective marshmallow patience of the rich creates problems beyond climate debt. Koch and his fellow oligarchs are, first and foremost, supporters of oligarchy, an intrinsically destabilizing political arrangement that actually threatens their fortunes. Policies that favor the wealthy are always seeking an equilibrium between instability and inequality: a rich person can either submit to having their money taxed away to build hospitals, roads and schools, or they can invest in building high walls and paying guards to keep the rest of us from building guillotines on their lawns.
Rich people gobble that marshmallow like there's no tomorrow (literally). They always overestimate how much bang they'll get for their guard-labor buck, and underestimate how determined the poors will get after watching their children die of starvation and preventable diseases.
All of us benefit from some kind of cushion from our bad judgment, but not too much. The problem isn't that wealthy people get to make a few poor choices without suffering brutal consequences – it's that they hoard this benefit. Most of us are one missed student debt payment away from penalties and interest that add twenty years to our loan, while Charles Koch can set the planet on fire and continue to act as though he was born with the special judgment that means he knows what's best for us.

On SEPTEMBER 24th, I'll be speaking IN PERSON at the BOSTON PUBLIC LIBRARY!!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/04/deferred-gratification/#selective-foresight

Image: Mark S (modified) https://www.flickr.com/photos/markoz46/4864682934/
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
#pluralistic#locus magazine#guillotine watch#eugenics#climate emergency#inequality#replication crisis#marshmallow test#deferred gratification
637 notes
·
View notes
Text



----



---



---



---




Noa de Acutis + Being Intimidating
#noa de acutis#neri de acutis#jacobus egrativi#rook de riva#viago de riva#andarateia cantori#teia cantori#antivan crows#My Rook de Riva both respects and is deeply wary of this woman ngl#I do think this implies that Noa is the head of de Acutis though even though she obviously defers to the Talons#and her brother Neri at times acts as a scribe for Viago and Teia so there's definitely a status difference there#If you meet a Crow with as much grey in their hair as Neri has you should take it as a warning#datv spoilers
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of soap's defining character traits is righteousness. be it helping his comrades in al mazrah over the mission objective (are you saying we shouldn't have helped?) or walking into a cartel villa unarmed to bring down el sin nombre (we came here to stop a missile, so let's stop it), it is clear that his main motivation is to do the right thing. so is the protection of innocent people - soap is almost always the one who articulates the involvement of civilians (what happened to the families here? / they're innocent people. / he's killing civilians - his own people.)
for soap, in this righteousness, and in the protection of these innocent people, the threat and execution of violence is the right thing. killing is not the avoidable means to an end, but the objective - as long as the people killed are evil (my job is to kill the enemy. guess what you are). he shows a clear favoritism for vigilante justice (you're going down for what you did / makes me want to commit a few war crimes of my own / you will hang for this) and has to be actively dissuaded from executing people instead of having them face due process on multiple occasions (you can't be serious he is right here / i will blow your brains out i swear i will do it).
and it is soap who decides who is evil and who is not. while he and ghost condemn graves' killing civilians as putting himself above the law (he is jury judge and executioner now) soap justifies the killing of dozens of mexicans without jurisdiction as part of a foreign army due to their cartel involvement (there are no civilians here). he never judges the violence of his own allies, only the lack of it (should have killed him when we had the chance).
a seargant hell-bent on doing the right thing but operating with both a brutal reverence to violence as the only option and a morality of black and white that does not survive closer scrutiny. he is clearly not a good person - if the amount of people he killed in cold blood is any indication - but he not only thinks that he is good but can tell whether a person is good or not to the point that he sees himself as a rightful executioner. now that's a character!
#call of duty#call of duty modern warfare#johnny soap mactavish#interestingly he still defers to higher authority in the authorization of killing#(think we will get the green light to go after these guys?)#because none of the good guys ever disobeys a direct order in modern warfare.#MANY THOUGHTS#exfil meta
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
-Au idea??
wukong dying (somehow) in mk's arms and his last words is comforting mk and tell him it's okay and that's he's glad he lived long enough to meet him
and after that mk keeps wukong scarf and always wear it and he became cold and closed off bc a part of him blame himself that if he was stronger he could've protected him
meanwhile macaque being a stubborn asshole doing everything illegal both in heaven and the underworld to find a way to bring wukong back not caring who he have to destroy to bring him back he'll cross every line becoming more dangerous and deranged than he ever was
#lego monkie kid#lmk macaque#monkei kid#lmk#lmk sun wukong#lmk monkey king#sun wukong#lmk mk#shadowpeach#lmk shadowpeach#sunburst duo#lmk sunburst duo#they grief is deferent ways#what should i call it??#i might write a fanfic about this au
179 notes
·
View notes