#Western University of Pennsylvania
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Menu Monday: Dinner of the Western Pennsylvania Club of Princeton, January 4, 1893.
Emery Leyden Ford (Class of 1896) attended and pasted the menu in his scrapbook.
Scrapbook Collection, Box 199
The entire Menu Monday series
#1890s#Menu#MenuMonday#Princeton#Western Pennsylvania Club of Princeton#Pennsylvania#PrincetonU#Princeton University#dinner#tiger
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
#pittsburgh steelers#pittsburgh penguins#pittsburgh pa#pittsburgh pirates#the pradeeps of pittsburgh#burgh#western pa#wva#west virginia#wheeling#andy warhol#carnegie mellon university#andrew carnegie#pghlfilms#day 412#kennywood#allegheny cemetery#allegheny mountains#allegheny county#duquesne#robert morris#acrisure stadium#three rivers#pennsylvania#penn state#erie#erie pa#appalachia#johnstown#altoona
1 note
·
View note
Quote
When Cameron Whitley was diagnosed with kidney failure seven years ago, the news came as a shock. But the situation was about to get worse. His doctor decided the diagnosis meant Whitley’s hormone therapy had to stop. As a transgender man, now 42, who had taken testosterone for 10 years, the impact was brutal. “Not only was I struggling with this new diagnosis that I’m in stage four kidney failure, now I’m being told that I can no longer have hormones,” said Whitley, an associate professor in the department of sociology at Western Washington University. “I cannot describe how horrible that moment was.” Crucially, he says, the decision was completely unnecessary. “We call this within the medical community ‘trans broken arm syndrome’,” he said. The term refers to medical situations – such as having a broken arm – that are unconnected to gender identity, yet healthcare providers act on the basis there is a connection. “We didn’t have any established sense that being on hormones would be problematic. The hormones are not processed through the kidneys. So there was nothing that made it [necessary to stop them], but that was the first thing that was done,” he said. Whitely has since transferred his care over to the University of Pennsylvania, which he described as “awesome [with] wonderful trans-competent care”
‘We actually don’t know much’: the scientists trying to close the knowledge gap in trans healthcare | Transgender | The Guardian
606 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pentiment's Complete Bibliography, with links to some hard-to-find items:
I've seen some people post screenshots of the game's bibliography, but I hadn't found a plain text version (which would be much easier to work from), so I put together a complete typed version - citation style irregularities included lol. I checked through the full list and found that only four of the forty sources can't be found easily through a search engine. One has no English translation and I'm not even close to fluent enough in German to be able to actually translate an academic article, so I can't help there. For the other three (a museum exhibit book, a master's thesis, and portions of a primary source that has not been entirely translated into English), I tracked down links to them, which are included with their entries on the list.
If you want to read one of the journal articles but can't access it due to paywalls, try out 12ft.io or the unpaywall browser extension (works on Firefox and most chromium browsers). If there's something you have interest in reading but can't track down, let me know, and I can try to help! I'm pretty good at finding things lmao
Okay, happy reading, love you bye
Beach, Alison I. Women as Scribes: Book Production and Monastic Reform in Twelfth-Century Bavaria. Cambridge Univeristy Press, 2004.
Berger, Jutta Maria. Die Geschichterder Gastfreundschaft im hochmittel alterlichen Monchtum: die Cistercienser. Akademie Verlag GmbH, 1999. [No translation found.]
Blickle, Peter. The Revolution of 1525. Translated by Thomas A. Brady, Jr. and H.C. Erik Midelfort. The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1985.
Brady, Thomas A., Jr. “Imperial Destinies: A New Biography of the Emperor Maximilian I.” The Journal of Modern History, vol 62, no. 2., 1990. pp.298-314.
Brandl, Rainer. “Art or Craft: Art and the Artist in Medieval Nuremberg.” Gothic and Renaissance Art in Nuremberg 1300-1550. The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 1986. [LINK]
Byars, Jana L., “Prostitutes and Prostitution in Late Medieval Bercelona.” Masters Theses. Western Michigan University, 1997. [LINK]
Cashion, Debra Taylor. “The Art of Nikolaus Glockendon: Imitation and Originality in the Art of Renaissance Germany.” Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art, vol 2, no. 1-2, 2010.
de Hamel, Christopher. A History of Illuminated Manuscripts. Phaidon Press Limited, 1986.
Eco, Umberto. The Name of the Rose. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2014.
Eco, Umberto. Baudolino. Translated by William Weaver. Mariner Books, 2003.
Fournier, Jacques. “The Inquisition Records of Jacques Fournier.” Translated by Nancy P. Stork. Jan Jose Univeristy, 2020. [LINK]
Geary, Patrick. “Humiliation of Saints.” In Saints and their cults: studies in religious sociology, folklore, and history. Edited by Stephen Wilson. Cambridge University Press, 1985. pp. 123-140
Harrington, Joel F. The Faithrul Executioner: Life and Death, Honor and Shame in the Turbulent Sixteenth Century. Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2013.
Hertzka, Gottfired and Wighard Strehlow. Grosse Hildegard-Apotheke. Christiana-Verlag, 2017.
Hildegard von Bingen. Physica. Edited by Reiner Hildebrandt and Thomas Gloning. De Gruyter, 2010.
Julian of Norwich. Revelations of Divine Love. Translated by Barry Windeatt. Oxford Univeristy Press, 2015.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. Sexuality in Medieval Europe: Doing Unto Others. Routledge, 2017.
Kerr, Julie. Monastic Hospitality: The Benedictines in England, c.1070-c.1250. Boudell Press, 2007.
Kieckhefer, Richard. Forbidden rites: a necromancer’s manual of the fifteenth century. Sutton, 1997.
Kuemin, Beat and B. Ann Tlusty, The World of the Tavern: Public Houses in Early Modern Europe. Routledge, 2017.
Ilner, Thomas, et al. The Economy of Duerrnberg-Bei-Hallein: An Iron Age Salt-mining Center in the Austrian Alps. The Antiquaries Journal, vol 83, 2003. pp. 123-194
Lang, Benedek. Unlocked Books: Manuscripts of Learned Magic in the Medieval Libraries of Central Europe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2008
Lindeman, Mary. Medicine and Society in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2019.
Lowe, Kate. “’Representing’ Africa: Ambassadors and Princes from Christian Africa to Renaissance Italy and Portugal, 1402-1608.” Transactions of the Royal Historical Society Sixth Series, vol 17, 2007. pp. 101-128
Meyers, David. “Ritual, Confession, and Religion in Sixteenth-Century Germany.” Archiv fuer Reformationsgenshichte, vol. 89, 1998. pp. 125-143.
Murat, Zuleika. “Wall paintings through the ages: the medieval period (Italy, twelfth to fifteenth century).” Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, vol 23, no. 191. Springer, October 2021. pp. 1-27.
Overty, Joanne Filippone. “The Cost of Doing Scribal Business: Prices of Manuscript Books in England, 1300-1483.” Book History 11, 2008. pp. 1-32.
Page, Sophie. Magic in the Cloister: Pious Motives, Illicit Interests, and Occullt Approaches to the Medieval Universe. The Pennsylvania State University Press, 2013.
Park, Katharine. “The Criminal and the Saintly Body: Autopsy and Dissectionin Renaissance Italy.” Renaissance Quarterly, vol 47, no. 1, Spring 1994. pp. 1-33.
Rebel, Hermann. Peasant Classes: The Bureaucratization of Property and Family Relations under Early Habsburg Absolutism, 1511-1636. Princeton University Press, 1983.
Rublack, Ulinka. “Pregnancy, Childbirth, and the Female Body in Early Modern Germany.” Past & Present,vol. 150, no. 1, February 1996.
Salvador, Matteo. “The Ethiopian Age of Exploration: Prester John’s Discovery of Europe, 1306-1458.” Journal of World History, vol. 21, no. 4, 2011. pp.593-627.
Sangster, Alan. “The Earliest Known Treatise on Double Entry Bookkeeping by Marino de Raphaeli.” The Accounting Historians Journal, vol. 42, no. 2, 2015. pp. 1-33.
Throop, Priscilla. Hildegarde von Bingen’s Physica: The Complete English Translation of Her Classic Work on Health and Healing. Healing Arts Press, 1998.
Usher, Abbott Payson. “The Origins of Banking: The Brimitive Bank of Deposit, 1200-1600.” The Economic History Review, vol. 4, no. 4. 1934. pp.399-428.
Waldman, Louis A. “Commissioning Art in Florence for Matthias Corvinus: The Painter and Agent Alexander Formoser and his Sons, Jacopo and Raffaello del Tedesco.” Italy and Hungary: Humanism and Art in the Early Renaissance. Edited by Peter Farbaky and Louis A. Waldman, Villa I Tatti, 2011. pp.427-501.
Wendt, Ulrich. Kultur and Jagd: ein Birschgang durch die Geschichte. G. Reimer, 1907.
Whelan, Mark. “Taxes, Wagenburgs and a Nightingale: The Imperial Abbey of Ellwangen and the Hussite Wars, 1427-1435.” The Journal of Ecclesiastical History, vol. 72, no. 4, 2021, pp.751-777.
Wiesner-Hanks, Merry E. Women and Gender in Early Modern Europe. Cambridge University Press, 2008.
Yardeni, Ada. The Book of Hebrew Script: History, Palaeography, Script Styles, Calligraphy & Design. Tyndale House Publishers, 2010.
502 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cal Poly - Pomona, Western Washington University, Ball State, and Alabama A & M also offer urban planning undergraduate degrees
Source
164 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tamil Linguistics thread (bc nobody cares but me)
but really, if you are interested in linguistics at all, give this post a read, because this shit really blew my mind ...
have been reading the following paper: https://ccat.sas.upenn.edu/~haroldfs/public/h_sch_9a.pdf
"The Tamil Case System" (2003) written by Harold F. Schiffman, Professor Emeritus of Dravidian Linguistics and Culture, University of Pennsylvania
Tamil is one of the oldest continuously-spoken languages in the world, dating back to at least 500 BCE, with nearly 80 million native speakers in South India and elsewhere, and possessed of several interesting characteristics:
a non-Indo-European language family (the Dravidian languages, which include other languages in South India - Malayalam being the most closely related major language - and one in Pakistan)
through the above, speculative ties to the Indus Valley Civilization, one of the first major human civilizations (you can read more about that here)
an agglutinative language, similar to German and others (so while German has Unabhängigkeitserklärungen, and Finnish has istahtaisinkohankaan, in Tamil you can say pōkamuṭiyātavarkaḷukkāka - "for the sake of those who cannot go")
an exclusively head-final language, like Japanese - the main element of a sentence always coming at the end.
a high degree of diglossia between its spoken variant (ST) and formal/literary variant (LT)
cool retroflex consonants (including the retroflex plosives ʈ and ɖ) and a variety of liquid consonants (three L's, two R's)
and a complex case system, similar to Latin, Finnish, or Russian. German has 4 cases, Russian has at least 6, Latin has 6-7, Finnish has 15, and Tamil has... well, that's the focus of Dr. Schiffman's paper.
per most scholars, Tamil has 7-8 cases - coincidentally the same number as Sanskrit. The French wikipedia page for "Tamoul" has 7:
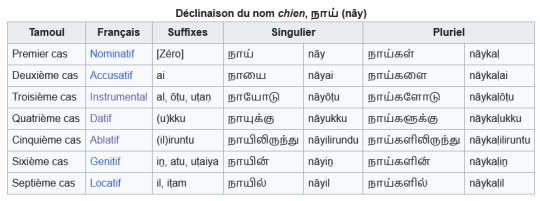
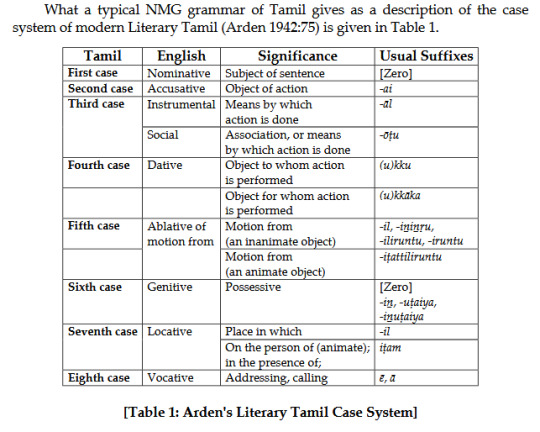
Dr. Schiffman quotes another scholar (Arden 1942) giving 8 cases for modern LT, as in common in "native and missionary grammars", i.e. those written by native Tamil speakers or Christian missionaries. It's the list from above, plus the Vocative case (which is used to address people, think of the KJV Bible's O ye of little faith! for an English vocative)
... but hold on, the English wiki for "Tamil grammar" has 10 cases:
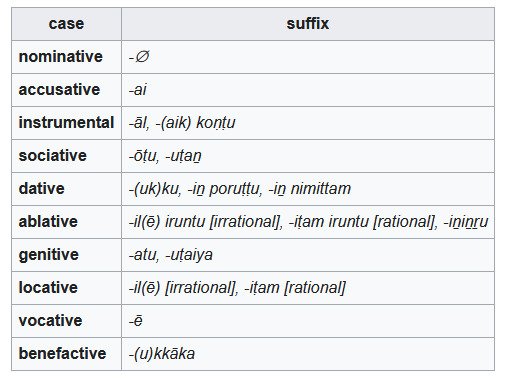
OK, so each page adds a few more. But hold on, why are there multiple suffix entries for each case? Why would you use -otu vs. -utan, or -il vs -ininru vs -ilirintu? How many cases are there actually?
Dr. Schiffman explains why it isn't that easy:
The problem with such a rigid classification is that it fails in a number of important ways ... it is neither an accurate description of the number and shape of the morphemes involved in the system, nor of the syntactic behavior of those morphemes ... It is based on an assumption that there is a clear and unerring way to distinguish between case and postpositional morphemes in the language, when in fact there is no clear distinction.
In other words, Tamil being an agglutinative language, you can stick a bunch of different sounds onto the end of a word, each shifting the meaning, and there is no clear way to call some of those sounds "cases" and other sounds "postpositions".
Schiffman asserts that this system of 7-8 cases was originally developed for Sanskrit (the literary language of North Indian civilizations, of similar antiquity to Tamil, and the liturgical language of Vedic Hinduism) but then tacked onto Tamil post-facto, despite the languages being from completely different families with different grammars.

Schiffman goes through a variety of examples of the incoherence of this model, one of my favorites quoted from Arden 1942 again:

There is no rule as to which ending should be used ... Westerners are apt to use the wrong one. There are no rules but you can still break the rules. Make it make sense!!
Instead of sticking to this system of 7-8 cases which fails the slightest scrutiny, Dr. Schiffman instead proposes that we throw out the whole system and consider every single postposition in the language as a potential case ending:
Having made the claim that there is no clear cut distinction between case and postpositions in Tamil except for the criterion of bound vs. unbound morphology, we are forced to examine all the postpositions as possible candidates for membership in the system. Actually this is probably going too far in the other direction ... since then almost any verb in the language can be advanced to candidacy as a postposition. [!!]
What Schiffman does next is really cool, from a language nerd point of view. He sorts through the various postpositions of the language, and for each area of divergence, uses his understanding of LT and ST to attempt to describe what shades of meaning are being connoted by each suffix. I wouldn't blame you for skipping through this but it is pretty interesting to see him try to figure out the rules behind something that (eg. per Arden 1942) has "no rule".


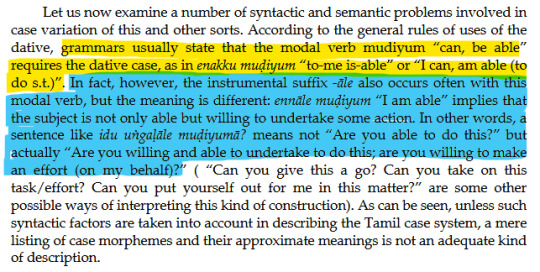
On the "extended dative", which connotates something like "on the behalf of" or "for the sake of":


I especially find his analysis of the suffix -kitte fascinating, because Schiffman uncovers a potential case ending in Spoken Tamil that connotes something about the directness or indirectness of an action, separate from the politeness with which the person is speaking to their interlocutor.


Not to blather on but here's a direct comparison with Finnish, which as stated earlier has 15 cases and not the 7-8 commonly stated of Tamil:

What Schiffman seems to have discovered is that ST, and LT too for that matter, has used existing case endings and in some cases seemingly invented new ones to connote shades of meaning that are lost by the conventional scholar's understanding of Tamil cases. And rather than land on a specific number of cases, he instead says the following, which I find a fascinating concept:
The Tamil Case System is a kind of continuum or polarity, with the “true” case-like morphemes found at one end of the continuum, with less case-like but still bound morphemes next, followed by the commonly recognized postpositions, then finally nominal and verbal expressions that are synonymous with postpositions but not usually recognized as such at the other extreme. This results in a kind of “dendritic” system, with most, but not all, 8 of the basic case nodes capable of being extended in various directions, sometimes overlapping with others, to produce a thicket of branches. The overlap, of course, results from the fact that some postpositions can occur after more than one case, usually with a slight difference in meaning, so that an either-or taxonomy simply does not capture the whole picture.
How many cases does Tamil have? As many as its speakers want, I guess.
120 notes
·
View notes
Text

UPenn donor redirects $5M to Israeli universities after cutting ties with alma mater
David Magerman, a former donor to the University of Pennsylvania decided to redirect $5 million to Israeli universities.Bloomberg via Getty Images
After halting donations to his alma mater last year, a former University of Pennsylvania donor has redirected $5 million to Israeli universities instead, citing the Ivy League institution’s refusal to address antisemitism on campus.
David Magerman, a venture capitalist and philanthropist, has reallocated millions in donations to universities in Israel after witnessing the anti-Israel protests and antisemitism that has permeated U.S. college campuses in the months following the Oct. 7 attack on Israel by Hamas, he told Fox News Digital.
Magerman said he will give $1 million grants to five institutions of higher learning across Israel, including Tel Aviv University, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Bar-Ilan University and Jerusalem College of Technology.
He also revealed that he intends to donate to additional Israeli causes in the coming months.
His donations will support programs for English-speaking students to learn academic Hebrew and integrate into STEM degree programs in Israel.
Magerman said he hopes his contributions will give Jewish-American students who are considering moving to Israel more options to study abroad after growing weary of campus life in the U.S.
“My plan is to redirect my philanthropic efforts going forward largely to Israel,” he told Fox News Digital.
“I don’t see much value generated by giving to American universities. I think that liberal colleges in America are flawed institutions that are doing a poor job of preparing students for the real world.”
Asked what his message is to other prominent Jewish donors still contributing to Ivy League schools, Magerman said pointedly, “Stop.”
He said it’s naive to believe that elite U.S. universities are “reformable.”

Magerman, a venture capitalist and philanthropist, cited that his alma mater’s refusal to address antisemitism on campus is why he gave millions of dollars to Israeli institutions instead.
“They’re fulfilling the mission they want to fulfill. Their goal, it seems, is to indoctrinate their students to question the validity of Western civilization, to question the value of the Founding Fathers and to criticize Western society. I don’t think that’s what these philanthropists believe and I don’t think that they should be donating money to support propagating that ideology,” said Magerman.
Read More: NewYorkPost
#ANTISEMITISM#COLLEGES AND UNIVERSITIES#HAMAS#GAZA STRIP#UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA#IVY LEAGUE#ISRAEL/HAMASWAR
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tom Corbett

Physique: Average Build Height: 5′ 9″
Thomas Wingett Corbett Jr. (born June 17, 1949) is an American politician, lobbyist, and former prosecutor who served as the 46th governor of Pennsylvania from 2011 to 2015. A member of the Republican Party, he was also attorney general of Pennsylvania.




Handsome, nice build and a perfect crown of white hair. Hell… if I was casting a movie, he'd be my ideal governor. Or pornstar. Plus, from what I can tell. Corbett has a nice thick ass on him.




Born in Philadelphia, Corbett graduated from Lebanon Valley College and St. Mary's University School of Law and served as a captain in the Pennsylvania Army National Guard. He began his career as an assistant district attorney in Allegheny County, PA, in 1976. Corbett then joined the U.S. Department of Justice as an assistant U.S. Attorney for the Western District of Pennsylvania, serving from 1980 to 1983, upon entering private practice.


As usual, he's straight with a wife, grown kids and grandkids. After a legal career that included stints as an assistant district attorney, U.S. attorney and Pennsylvania attorney general, Corbett now days, is back in the classroom teaching law and is also registered lobbyist. I wonder if I should go to Pennsylvania and study law. For now, I'll just fantasize about Corbett and how good his ass would feel like.

110 notes
·
View notes
Text
Leaders of Pennsylvania’s Polish community endorsed Kamala Harris following her debate shoutout. There are 800,000 Polish-Americans in the commonwealth, which Democrats won by 80,000 votes in 2020.
Members of Pennsylvania’s Polish community penned a letter endorsing Kamala Harris after Harris, at the debate earlier this month, warned that Donald Trump would allow Russia to invade Poland once the war in Ukraine is finished under a Trump administration.
“Vice President Harris has a long, strong track record of protecting our democracy here at home and standing up for our brothers, sisters, parents and grandparents in Poland – the same people Vladimir Putin hopes to attack next if Ukraine were to fall,” the letter read.
“Polish people in the US and around the world know that our future is tied to Ukraine’s because if Putin is allowed to trample Ukraine, we know his next target could be Poland. Trump bowed to dictators like Putin before and he will do it again if he is reelected.”
Its signatories include veterans, social workers, small business owners and several elected officials, including US Rep. Chrissy Houlahan (D-Chester) and State Reps. Jessica Benham (D-Allegheny), Eddie Day Pashinski (Luzerne County) and Melissa Cerrato (D-Montgomery County).
There are roughly 800,000 Polish-Americans living in Pennsylvania, with large communities in Western and Northeastern Pennsylvania. The letter’s co-signers hope this outreach to the Polish community can help secure a Harris victory in Pennsylvania, which Democrats carried by less than 80,000 in the 2020 presidential election.
During the debate, Harris ripped Trump for his cozy relationship with Putin.
“If Donald Trump were president, [Vladimir] Putin would be sitting in Kiev right now, and understand what that would mean because Putin’s agenda is not just about Ukraine,” Harris said.
“Why don’t you tell the 800,000 Polish Americans in Pennsylvania, how quickly you would give up for the sake of favor and what you think is a friendship with what is known to be a dictator, who would eat you for lunch.”
In the days following the debate, Harris returned to Pennsylvania and rallied over 5,000 supporters at Wilkes University in Luzerne County, which has one of the highest concentrations of Polish Americans in Pennsylvania and is the only county in the country with a Polish plurality among its residents.
“We sincerely believe the freedoms and livelihoods of our families at home and abroad rest upon rejecting Donald Trump and turning the page with Kamala Harris this fall,” the Pennsylvanians wrote.
“The last presidential election in Pennsylvania was decided by just 80,000 votes, which is why we are calling on our friends and neighbors to cast their votes for the leaders who will maintain alliances that make our world safer, expand our freedoms here at home, and protect the American dream for us all.”
Read the full letter below:
We, Pennsylvania Polonia, unite today to voice our strong support for Vice President Kamala Harris and Governor Tim Walz.
We the undersigned believe it is in our best interests and the best interests of the over 800,000 Polish Americans across Pennsylvania to vote for leaders who will fight to defend our freedoms and stand up for democracy at home and abroad. Last week’s debate made clear once again that those leaders are Vice President Kamala Harris and Governor Tim Walz.
Vice President Harris has a long, strong track record of protecting our democracy here at home and standing up for our brothers, sisters, parents and grandparents in Poland – the same people Vladimir Putin hopes to attack next if Ukraine were to fall.
In stark contrast, earlier this year, Trump said he would encourage Russia to “do whatever the hell they want” to our NATO allies, and during the debate last week, he twice refused to answer a question about whether he wanted Ukraine to win their war against Russian aggression.
Polish people in the U.S. and around the world know that our future is tied to Ukraine’s because if Putin is allowed to trample Ukraine, we know his next target could be Poland. Trump bowed to dictators like Putin before and he will do it again if he is reelected. Trump’s Project 2025 agenda would be even worse for our national security and military readiness, including remaking the Department of Defense and reducing the number of generals in our armed forces.
Thankfully, this November, we can elect a true leader who will stand up to autocrats and stand up for us. Vice President Harris will lead us forward on a different path — one where we stand with allies, stand for democracy, and stand against those who oppose it. She is a proven leader on the world stage and will use her expertise to ensure America’s security and defeat our adversaries.
We sincerely believe the freedoms and livelihoods of our families at home and abroad rest upon rejecting Donald Trump and turning the page with Kamala Harris this fall. The last presidential election in Pennsylvania was decided by just 80,000 votes, which is why we are calling on our friends and neighbors to cast their votes for the leaders who will maintain alliances that make our world safer, expand our freedoms here at home, and protect the American dream for us all.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
College Shitlist (boycott these colleges)
This is the updating list of colleges where pro-palestine protests are present that have brutalized/arrested/punished their students for protesting the ongoing palestinian genocide.
REMEMBER: DO NOT GIVE YOUR MONEY TO THESE COLLEGES. PROTESTS ON THESE CAMPUSES ARE IMPORTANT, BUT KEEPING YOUR INTELLIGENCE AND MONEY AWAY FROM THESE ABHORRENT INSTITUTIONS DIMINISHES THEIR POWER. THEIR ONLY POWER COMES FROM THEIR STUDENTS AND THEIR MONEY. YOU HAVE THE POWER TO TAKE THEIR PRESTIGE AWAY.
In No Particular Order:
Princeton University
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
University of California - Berkeley
Stanford University
Virginia Tech
University of Michigan - Ann Arbor
University of Washington
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities
University of Wisconsin - Madison
Harvard University
Yale University
University of California - Los Angeles
Cornell University
University of Pittsburgh
University of Chicago
University of Southern California
University of California - San Diego
Tufts University
Northeastern University
Stony Brook University
University of Connecticut
University of California - Merced
University of Massachusetts - Amherst
University of Iowa
University of Arizona
Arizona State University
University of California - Irvine
George Washington University
DePaul University
University of Pennsylvania
Pomona College
University of Texas - Dallas
The New School
University of Houston
University of Rochester
University of New Mexico
Duke University
New York University
University of North Carolina - Chapel Hill
Barnards College
University of Vanderbilt
Rutgers University - New Brunswick
Columbia University
Portland State University
University of Oregon
California Polytechnic Institute Humboldt
California Polytechnic University - San Luis Obispo
Northern Arizona University
University of Utah
University of Kansas
University of Illinois - Urbana Champaign
Washington University
New Mexico State University
University of Texas - Austin
Tulane University
University of South Florida
University of North Florida
University of Florida
Emory University
University of Georgia
Mercer University
Notre Dame University
Case Western Reserve University
The Ohio State University
Virginian Commonwealth University
University of Virginia
University of Buffalo
State University of New York - Purchase
State University of New York - New Paltz
Brown University
Brandeis University
Dartmouth College
University of New Hampshire
Emerson College
CUNY City College of New York
International List:
University of Amsterdam
University of Alberta
University of Queensland
University of Sydney
University of Melbourne
Australian National University
University of New South Wales
University of Calgary
University of Oxford
Feel free to share this list, send me additional colleges to add (WITH SOURCES), and/or request more information on a particular college
#palestine#gaza#free palestine#boycott israel#free gaza#princeton#yale#harvard#cornell#brown#dartmouth#mit#nyu#gaza genocide#notre dame#stanford#boycott#divest from israel#Oxford#Amsterdam#sydney#Palestine protests
48 notes
·
View notes
Text

ARIZONA INTERESTING FACTS:
1. Arizona has 3,928 mountain peaks and summits, more mountains than any one of the other Mountain States (Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming).
2. All New England, plus the state of Pennsylvania would fit inside Arizona.
3. Arizona became the 48th state and last of the contiguous states on February 14, 1912, Valentine’s Day.
4. Arizona's disparate climate can yield both the highest temperature across the nation and the lowest temperature across the nation in the same day.
5. There are more wilderness areas in Arizona than in the entire Midwest. Arizona alone has 90 wilderness areas, while the Midwest has 50.
6. Arizona has 26 peaks that are more than 10,000 feet in elevation.
7. Arizona has the largest contiguous stand of Ponderosa pines in the world stretching from near Flagstaff along the Mogollon Rim to the White Mountains region.
8. Yuma, Arizona is the country's highest producer of winter vegetables, especially lettuce.
9. Arizona is the 6th largest state in the nation, covering 113,909 square miles.
10. Out of all the states in the U.S., Arizona has the largest percentage of its land designated as Indian lands.
11. The Five C's of Arizona's economy are: Cattle, Copper, Citrus, Cotton, and Climate.
12. More copper is mined in Arizona than all the other states combined The Morenci Mine is the largest copper producer in all of North America.
13. Clark Gable and Carole Lombard, two of the most prominent movie stars of Hollywood's Golden Age, were married on March 18, 1939, in Kingman, Arizona.
14. Covering 18,608 sq. miles, Coconino County is the second largest county by land area in the 48 contiguous United States.(San Bernardino County in California is the largest).
15. The world's largest solar telescope is located at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Sells, Arizona.
16. Bisbee, Arizona is known as the Queen of the Copper Mines because during its mining heyday it produced nearly 25 percent of the world's copper. It was the largest city in the Southwest between Saint Louis and San Francisco.
17. Billy the Kid killed his first man, Windy Cahill, in Bonita, Arizona.
18. Arizona grows enough cotton each year to make more than one pair of jeans for every person in the United States.
19. Famous labor leader and activist Cesar Chavez was born in Yuma.
20. In 1912, President William Howard Taft was ready to make Arizona a state on February 12, but it was Lincoln's birthday.
The next day, the 13th, was considered bad luck so they waited until the following day. That's how Arizona became known as the Valentine State.
21. When England's famous London Bridge was replaced in the 1960s, the original was purchased, dismantled, shipped stone by stone and reconstructed in Lake Havasu City, Arizona, where it still stands today.
22. Mount Lemmon, Tucson, in the Santa Catalina Mountains, is the southernmost ski resort in the United States.
23. Rooster Cogburn Ostrich Ranch in Picacho, Arizona is the largest privately-owned ostrich ranch in the world outside South Africa.
24. If you cut down a protected species of cactus in Arizona, you could spend more than a year in prison.
25. The world's largest to-scale collection of miniature airplane models is housed at the library at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Prescott, Arizona.
26. The only place in the country where mail is delivered by mule is the village of Supai, located at the bottom of the Grand Canyon.
27. Located on Arizona's western border, Parker Dam is the deepest dam in the world at 320 feet.
28. South Mountain Park/Preserve in Phoenix is the largest municipal park in the country.
29. Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station, located about 55 miles west of Phoenix, generates more electricity than any other U.S. power plant.
30. Oraibi, a Hopi village located in Navajo County, Arizona, dates back to before A.D. 1200 and is reputed to be the oldest continuously inhabited community in America.
31. Built by Del Webb in 1960, Sun City, Arizona was the first 55-plus active adult retirement community in the country.
32. Petrified wood is the official state fossil. The Petrified Forest in northeastern Arizona contains America's largest deposits of petrified wood.
33. Many of the founders of San Francisco in 1776 were Spanish colonists from Tubac, Arizona.
34. Phoenix originated in 1866 as a hay camp to supply military post Camp McDowell.
35. Rainfall averages for Arizona range from less than three inches in the deserts to more than 30 inches per year in the mountains.
36. Rising to a height of 12,643 feet, Humphreys Peak north of Flagstaff is the state's highest mountain.
37. Roadrunners are not just in cartoons! In Arizona, you'll see them running up to 17-mph away from their enemies.
38. The Saguaro cactus is the largest cactus found in the U.S. It can grow as high as a five-story building and is native to the Sonoran Desert, which stretches across southern Arizona.
39. Sandra Day O'Connor, the first woman appointed to the U.S. Supreme Court, grew up on a large family ranch near Duncan, Arizona.
40. The best-preserved meteor crater in the world is located near Winslow, Arizona.
41. The average state elevation is 4,000 feet.
42. The Navajo Nation spans 27,000 square miles across the states of Utah, Arizona and New Mexico, but its capital is seated in Window Rock, Arizona.
43. The amount of copper utilized to make the copper dome atop Arizona's Capitol building is equivalent to the amount used in 4.8 million pennies.
44. Near Yuma, the Colorado River's elevation dips to 70 feet above sea level, making it the lowest point in the state.
45. The geographic center of Arizona is 55 miles southeast of Prescott near the community of Mayer.
46. You could pile four 1,300-foot skyscrapers on top of each other and they still would not reach the rim of the Grand Canyon.
47. The hottest temperature recorded in Arizona was 128 degrees at Lake Havasu City on June 29, 1994.
48. The coldest temperature recorded in Arizona was 40 degrees below zero at Hawley Lake on January 7, 1971.
49. A saguaro cactus can store up to nine tons of water.
50. The state of Massachusetts could fit inside Maricopa County (9,922 sq. miles).
51. The westernmost battle of the Civil War was fought at Picacho Pass on April 15, 1862 near Picacho Peak in Pinal County.
52. There are 11.2 million acres of National Forest in Arizona, and one-fourth of the state forested.
53. Wyatt Earp was neither the town marshal nor the sheriff in Tombstone at the time of the shoot-out at the O..K. Corral. His brother Virgil was the town marshal.
54. On June 6, 1936, the first barrel of tequila produced in the United States rolled off the production line in Nogales, Arizona.
55. The Sonoran Desert is the most biologically diverse desert in North America.
56. Bisbee is the Nation's Southernmost mile-high city.
57. The two largest man-made lakes in the U.S. are Lake Mead and Lake Powell, both located in Arizona.
58. The longest remaining intact section of Route 66 can be found in Arizona and runs from Seligman to Topock, a total of 157 unbroken miles.
59. The 13 stripes on the Arizona flag represent the 13 original colonies of the United States.
60. The negotiations for Geronimo's final surrender took place in Skeleton Canyon, near present day Douglas, Arizona, in 1886.
61. Prescott, Arizona is home to the world's oldest rodeo, and Payson, Arizona is home to the world's oldest continuous rodeo, both of which date back to the 1880's.
62. Kartchner Caverns, near Benson, Arizona, is a massive limestone cave with 13,000 feet of passages, two rooms as long as football fields, and one of the world's longest soda straw stalactites: measuring 21 feet 3 inches.
63. You can carry a loaded firearm on your person, no permit required.
64. Arizona has one of the lowest crime rates in the U.S.A.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
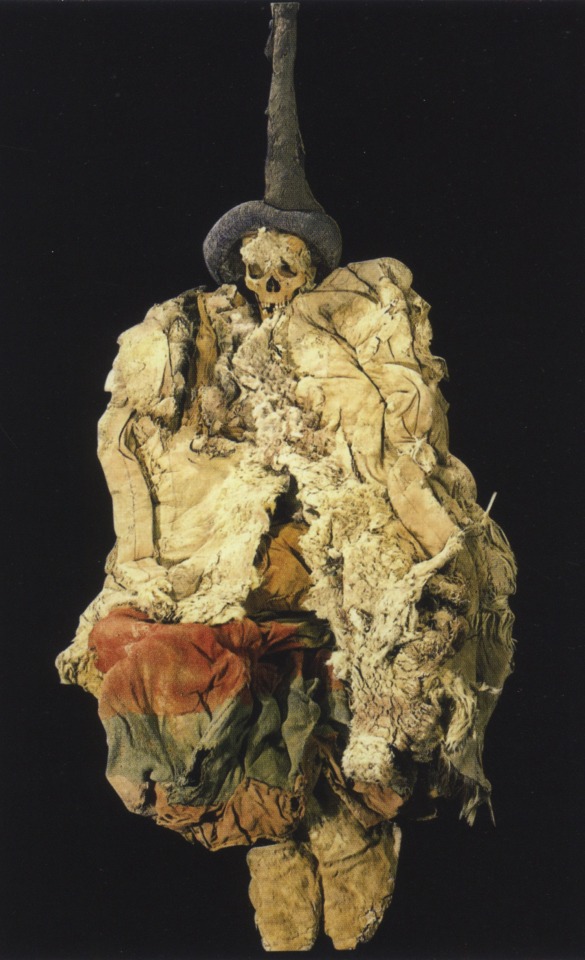

Female Europid Mummy from the Necropolis of Subexi III, Grave M6, Turfan District, Xinjiang. 5th-3rd C. BCE. Source: Baumer, Christoph.The history of Central Asia. Vol.1. The age of the steppe warriors. London : I.B. Tauris, 2012. pg. 218 left DS329.4 .B38 2012. Image via University of Pennsylvania. See maps in the post before this one for a better understanding of the geography discussed.
"Section 26 – The Kingdom of Nearer [i.e. Southern] Jushi 車師前 (Turfan)
1. ‘Nearer Jushi’ 車師前 refers to the kingdom or state centered in the Turfan oasis or, sometimes, to the tribe which controlled it. There can be no question that Nearer Jushi refers here to the Turfan Oasis. See for example: CICA, p. 183, n. 618; also note 1.5 above. For the etymology of the name Turfan see Bailey (1985), pp. 99-100, which is summed up in his sentence: “The name turpana- is then from *druva-pāna- ‘having safe protection’, a name suitable for a walled place.”
“One other oasis town is currently under excavation. At Yarghul (Jiaohe), 10 km (16 miles) [sic – this should read 10 miles (16 km)] west of Turpan, archaeologists have been excavating remains of the old Jushi capital, a long (1,700 m (5,580 ft)) but narrow (200 m (656 ft)) town between two rivers. From the Han period they uncovered vast collective shaft tombs (one was nearly 10 m (33 ft) deep). The bodies had apparently already been removed from these tombs but accompanying them were other pits containing form one to four horse sacrifices, with tens of horses for each of the larger burials.” Mallory and Mair (2000), pp. 165 and 167.
“Some 300 km (186 miles) to the west of Qumul [Hami] lie [mummy] sites in the vicinity of the Turpan oasis that have been assigned to the Ayding Lake (Aidinghu) culture. The lake itself occupies the lowest point in the Turpan region (at 156 m (512 ft) below sea level it is the lowest spot on earth after the Dead Sea). According to accounts of the historical period, this was later the territory of the Gushi, a people who ‘lived in tents, followed the grasses and waters, and had considerable knowledge of agriculture. They owned cattle, horses, camels, sheep and goats. They were proficient with bows and arrows.’ They were also noted for harassing travellers moving northwards along the Silk Road from Krorän, and the territories of the Gushi and the kingdom of Krorän were linked in the account of Zhang Qian, presumably because both were under the control of the Xiongnu. In the years around 60 BC, Gushi fell to the Chinese and was subsequently known as Jushi (a different transcription of the same name).” Mallory and Mair (2000), pp. 143-144.
“History records that in 108 BC Turpan was inhabited by farmers and traders of Indo-European stock who spoke a language belonging to the Tokharian group, an extinct Indo-Persian language [actually more closely related to Celtic languages]. Whoever occupied the oasis commanded the northern trade route and the rich caravans that passed through annually. During the Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 220) control over the route see-sawed between Xiongnu and Han. Until the fifth century, the capital of this kingdom was Jiaohe.” Bonavia (1988), p. 131.
“Turpan is principally an agricultural oasis, famed for its grape products – seedless white raisins (which are exported internationally) and wines (mostly sweet). It is some 80 metres (260 feet) below sea level, and nearby Aiding Lake, at 154 metres (505 feet) below sea level, is the lowest continental point in the world.” Ibid. p. 137.
“The toponym Turfan is also a variation of Tuharan. Along the routes of Eurasia there are many other place names recorded in various Chinese forms that are actually variations of Tuharan.” Liu (2001), p. 268."
-Notes to The Western Regions according to the Hou Hanshu. Second Edition (Extensively Revised and Expanded). John E. Hill. University of Washington.
#tocharian#celtic#indo european#tarim basin#xinjiang#chinese history#mummies#history#ancient history#archaeology#anthropology#silk road#pagan
512 notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more … December 20



1785 – The last known execution for sodomy in the United States occurs in Pennsylvania. Joseph Ross is the victim.


1904 – The American actor and director Albert Dekker, who died in unusual circumstance in 1968, was born in Brooklyn, New York, as Albert Ecke. His films include the classics The Man in the Iron Mask (1939), Beau Geste (1939), The Killers (1946), The Sound and the Fury (1959), Suddenly, Last Summer (1959), and The Wild Bunch(1969). He replaced Lee J. Cobb as Willy Loman in the original production of Arthur Miller's Death of a Salesman, and during a five-year stint back on Broadway in the early 1960s, he played the Duke of Norfolk in Robert Bolt's A Man for All Seasons.
Dekker appeared in some seventy films from the 1930s to 1960s, but his four most famous screen roles were as a mad scientist in the 1940 horror film Dr. Cyclops; as a vicious hitman in the The Killers; as a dangerous dealer in atomic fuel in the 1955 film noir Kiss Me Deadly; and as an unscrupulous railroad detective in Sam Peckinpah's western The Wild Bunch, which would be his last screen appearance.
Dekker's off-screen preoccupation with politics led to his winning a seat in the California State Assembly in 1944. Dekker served as a Democratic member for the Assembly until 1946. During the McCarthy era he was an outspoken critic of U.S. Senator Joseph McCarthy's tactics; to avoid being blacklisted he spent most of the period working on Broadway rather than Hollywood.
For his contribution to the motion picture industry, Dekker has a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame at 6620 Hollywood Boulevard.
On May 5, 1968, Dekker was found dead in his Hollywood home after failing to answer numerous phone calls for two days. Although money and camera equipment were missing, there were no signs of forced entry. He was found naked, kneeling in his bathtub with a noose wrapped around his neck that was looped around the shower's curtain rod. He was also handcuffed, blindfolded, gagged and had "make me suck" and "slave" and "cocksucker" scrawled on his body in red lipstick.
The police toyed with a theory that Dekker was a closet homosexual who practiced his eccentricities very discreetly with anonymous male prostitutes, and that this time, something had gone wrong and the frightened partner had quietly let himself out. The coroner's ruling was accidental death by autoerotic asphyxiation.


1955 – Frank Kameny is fired from his job as an astronomer in the United States Army’s Map Service in Washington, D.C. because of his homosexuality. A few days later he is blacklisted from seeking federal employment. These events spur Kameny into being a gay rights activist.


1962 – Doug Wright is an American playwright, librettist, and screenwriter. He received the Pulitzer Prize for Drama in 2004 for his play, I Am My Own Wife.
A Texas native, Wright was born in Dallas. He was the target of schoolyard teasing and playground attacks throughout elementary school. Overweight and awkward as a child, and not athletically inclined, he was routinely taunted by classmates as a "sissy," a "queer," and worse.
Despite the torments he was forced to endure in elementary and middle schools, once he entered Highland Park High School, outside of Dallas, Wright found acceptance in the theater department.
He entered Yale University in the fall of 1981. He achieved early success while still an undergraduate, when one of his first works, The Stonewater Rapture (1983), a two-character play about teenage sexuality and religious repression in a rural Texas town, was performed to acclaim at Scotland's Edinburgh Festival Fringe in August 1984.
The works of Doug Wright often focus on the unconventional lives of society's outsiders. Among these are the iconoclastic artist Marcel Duchamp in Interrogating the Nude; the Marquis de Sade in Quills; Charlotte von Mahlsdorf, an East Berlin transvestite who survived persecution by both the Nazi and Communist regimes, in the Tony Award and Pulitzer Prize-winning I Am My Own Wife; and "Big Edie" and "Little Edie" Bouvier Beale, two eccentric American aristocrats who ended up living in squalor, sharing a once-elegant mansion, in the musical Grey Gardens, based on the cult classic documentary film of the same name.
Wright also helped adapt the animated Disney film The Little Mermaid into a Broadway musical.
He currently lives in New York City with his husband/partner, the singer-songwriter David Clement.


1980 – According to recently released stats, at least one person is physically assaulted in New York City each day because they are gay or lesbian.


11 notes
·
View notes
Text
roommate and i are creating a dracula au that takes place in gilded age pittsburgh (inspired by the county courthouse that looks like a gothic castle) (we haven't done any research we're just from the area):
mina and lucy met at chatham university when it was a finishing school
jonathan graduated from the university of pittsburgh (i suppose then it was "western university of pennsylvania") law school
arthur holmwood is a heinz heir
jack seward works at the psychiatric hospital near the university
quincey is still from texas
van helsing is from boston and has degrees from every ivy league school
dracula is a former conquistador with his base in new orleans, and arrives in pittsburgh via the mississippi and ohio rivers
(but we put whitby = erie so we gotta get him to the lakes somehow)
not an incredible amount changes because it's the same time period (it was originally going to be a modern au) but this was the period when the city was at its peak and we figured there was mileage to be had in the american gilded age
7 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey! Thanks so much for sharing that list of monastic-themed fiction. Would you mind also sharing some good non-fiction titles on monastic masculinity? (I saw in one of your posts that it was a topic in your dissertation.) It doesn’t have to be exhaustive, just something for an introduction or maybe some titles you personally like. Thanks a lot!
Hi! Yes, here is a (non-exhaustive) list of sources :)
Primary Sources:
Clairvaux, Bernard of. The Letters of St. Bernard of Clairvaux. Translated by Bruno Scott James. London: Burns Oates, 1953.
Daniel, Walter. The Life of Aelred of Rievaulx. Translated by F. M. Powicke. Edited by Marsha Dutton. Kalamazoo, Mich.: Cistercian, 1994.
Gender and Sexuality in the Middle Ages : A Medieval Source Documents Reader, edited by Martha A. Brozyna, Jefferson, N.C.: McFarland & Co., 2005.
McNeill, John T., and Helena M. Gamer. Medieval Handbooks of Penance : A Translation of the Principal "Libri Poenitentiales" and Selections from Related Documents. New York ; Chichester: Columbia University Press, 1990.
Suso, Henry. The Life of the Servant. Translated by James M. Clark. London: James Clarke & Co Ltd., 1952.
Secondary Sources
Arnold, John H. "The Labor of Continence: Masculinity and Clerical Virginity." In Medieval Virginities, edited by Anke Bernau, Sarah Salih and Ruth Evans, 102-18. Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 2003.
Boswell, John. Christianity, Social Tolerance, and Homosexuality : Gay People in Western Europe from the Beginning of the Christian Era to the Fourteenth Century. Chicago ; London: University of Chicago Press, 1980.
Bullough, Vern L. "On Being a Male in the Middle Ages." In Medieval Masculinities, edited by Clare A. Lees, Thelma Fenster and Jo Ann McNamara. Regarding Men in the Middle Ages, 31-46: University of Minnesota Press, 1994.
Bynum, Caroline Walker. "Jesus as Mother and Abbot as Mother: Some Themes in Twelfth-Century Cistercian Writing." The Harvard Theological Review 70, no. 3/4 (1977): 257-84. http://www.jstor.org/stable/1509631.
Bynum, Caroline Walker. Jesus as Mother : Studies in the Spirituality of the High Middle Ages. Publications of the Center for Medieval and Renaissance Studies, Ucla. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1982.
Bynum, Caroline Walker. "The Female Body and Religious Practice in the Later Middle Ages." Chap. 6 In Fragmentation and Redemption : Essays on Gender and the Human Body in Medieval Religion, 181-238. New York: Zone Books, 1992.
Connell, R.W. "The History of Masculinity." Chap. 14 In The Masculinity Studies Reader, edited by Rachel Adams and David Savran, 245-61. Malden, Mass. ; Oxford: Blackwell, 2002.
Coon, Lynda L. Dark Age Bodies : Gender and Monastic Practice in the Early Medieval West. The Middle Ages Series. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2011.
Damrosch, David. "9. Non Alia Sed Aliter: The Hermeneutics of Gender in Bernard of Clairvaux." In Images of Sainthood in Medieval Europe, edited by Szell Timea, 181-96. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1991.
Doss, Jacob W. "Making Masculine Monks: Gender, Space, and the Imagined “Child” in Twelfth-Century Cistercian Identity Formation." Church History 91, no. 3 (2022): 467-91. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0009640722002098.
Elliott, Dyan. Fallen Bodies : Pollution, Sexuality, and Demonology in the Middle Ages. The Middle Ages Series. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1998.
Elliott, Dyan. The Corrupter of Boys: Sodomy, Scandal, and the Medieval Clergy. The Middle Ages Series Edited by Ruth Mazo Karras. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2020.
Gutt, Blake. "Medieval Trans Lives in Anamorphosis: Looking Back and Seeing Differently (Pregnant Men and Backward Birth)." Medieval feminist forum 55, 1 (2019): 174–206.
Hadley, D. M. "Introduction: Medieval Masculinities." In Masculinity in Medieval Europe, 1-18. London: Longman, 1999.
Hotchkiss, Valerie R. Clothes Make the Man : Female Cross Dressing in Medieval Europe. New York ; London: Garland, 1996.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. From Boys to Men : Formations of Masculinity in Late Medieval Europe. Philadelphia ; [Great Britain]: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2003.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. "The Regulation of “Sodomy” in the Latin East and West." Speculum 95, no. 4 (2020): 969-86. https://doi.org/10.1086/710639. https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/710639.
Karras, Ruth Mazo. "Attitudes to Same- Sex Sexual Relations in the Latin World." In A Companion to Crime and Deviance in the Middle Ages, edited by Skoda Hannah, 84-101. Amsterdam: ARC Humanities Press, 2023.
Karras, Ruth Mazo, and Katherine E. Pierpont. Sexuality in Medieval Europe : Doing Unto Others. Fourth ed. London: Routledge, 2023.
Kerr, Julie. Life in the Medieval Cloister. United Kingdom: Bloomsbury Publishing, 2009.
Kieckhefer, Richard. "14. Holiness and the Culture of Devotion: Remarks on Some Late Medieval Male Saints." In Images of Sainthood in Medieval Europe, edited by Szell Timea, 288-305. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1991.
Kieckhefer, Richard. Forbidden Rites : A Necromancer's Manual of the Fifteenth Century. University Park, PA, UNITED STATES: Pennsylvania State University Press, 1998. http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/exeter/detail.action?docID=6224672.
Kieckhefer, Richard. "Necromancy in the Clerical Underworld." Chap. 7 In Magic in the Middle Ages, 151-75. Cambridge, UK ; New York: Cambridge University Press, 2000.
Klaassen, Frank. "Learning and Masculinity in Manuscripts of Ritual Magic of the Later Middle Ages and Renaissance." The Sixteenth Century Journal 38, no. 1 (2007): 49-76. http://www.jstor.org/stable/20478245.
Klaassen, Frank. "Necromancy." In The Routledge History of Medieval Magic, edited by Sophie Page and Catherine Rider. London: Routledge, 2019.
Kolve, V. A. "Ganymede/Son of Getron: Medieval Monasticism and the Drama of Same-Sex Desire." Speculum 73, no. 4 (1998): 1014-67. https://doi.org/10.2307/2887367. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2887367.
Linkinen, Tom. Same-Sex Sexuality in Later Medieval English Culture. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press, 2015.
McNamara, Jo Ann. "The Herrenfrage the Restructuring of the Gender System, 1050–1150." In Medieval Masculinities, edited by Jo Ann McNamara, Clare A. Lees and Thelma Fenster. Regarding Men in the Middle Ages, 3-30: University of Minnesota Press, 1994.
Mills, Robert. "The Signification of the Tonsure." In Holiness and Masculinity in the Middle Ages, edited by P. H. Cullum and Katherine J. Lewis, 109-26. Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 2004.
Mills, Robert. "Transgender Time." In Seeing Sodomy in the Middle Ages University of Chicago Press, 2015.
Muir, Carolyn Diskant. "Bride or Bridegroom? Masculine Identity in Mystic Marriages." In Holiness and Masculinity in the Middle Ages, edited by P. H. Cullum and Katherine J. Lewis, 58-78. Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 2004.
Murray, Jacqueline. "Masculinizing Religious Life: Sexual Prowess, the Battle for Chastity, and Monastic Identity." In Holiness and Masculinity in the Middle Ages, edited by P. H. Cullum and Katherine J. Lewis, 24-42. Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 2004.
Murray, Jacqueline. "One Flesh, Two Sexes, Three Genders?". In Gender and Christianity in Medieval Europe, edited by Lisa M. Bitel and Felice Lifshitz. New Perspectives, 34-51: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2008.
Nelson, J.L. "Monks, Secular Men and Masculinity, C. 900." In Masculinity in Medieval Europe, edited by Dawn M. Hadley. Women and Men in History 121-42. London: Longman, 1999.
Newman, Martha G. "Real Men and Imaginary Women: Engelhard of Langheim Considers a Woman in Disguise." Speculum 78, no. 4 (2003): 1184-213. http://www.jstor.org/stable/20060926.
Rollo, David. Medieval Writings on Sex between Men: Peter Damian’s the Book of Gomorrah and Alain De Lille’s the Plaint of Nature. Brill, 22 Feb. 2022, 2022. doi:https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004507326. https://brill.com/view/title/57406.
Sauer, Michelle M. "Uncovering Difference: Encoded Homoerotic Anxiety within the Christian Eremitic Tradition in Medieval England." Journal of the History of Sexuality 19, no. 1 (2010): 133-52. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40663371.
Shopkow, Leah. "Mooning the Abbot: A Tale of Disorder, Vulgarity, Ethnicity, and Underwear in the Monastery." Chap. 9 In Prowess, Piety, and Public Order in Medieval Society: Studies in Honor of Richard W. Kaeuper, edited by Craig M. Nakashian and Daniel P. Franke, 179-98: Brill, 2017.
Thibodeaux, Jennifer D. The Manly Priest : Clerical Celibacy, Masculinity, and Reform in England and Normandy, 1066-1300. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2015.
Trokhimenko, Olga V. ""Believing That Which Cannot Be": (De)Constructing Medieval Clerical Masculinity in "Des Münches Not"." The German Quarterly 85, no. 2 (2012): 121-36. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41494744.
Trans and Genderqueer Subjects in Medieval Hagiography. Edited by Alicia Spencer-Hall, and Blake Gutt. Netherlands: Amsterdam University Press, 2021.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anyway I just saw a post saying that the protests here in the US are “taking away attention” from what’s actually happening in Gaza and “LARPing oppression” as if 1) the whole point of the protests is to put attention on Gaza and call for a ceasefire and 1.5) shows they’re exclusively getting their news from mainstream cable networks and 2) it’s not the fuckin media’s own fault they’re more interested in covering protests than the actual genocide, and 3) the students are somehow not facing oppression ???????
For one, what’s the solution here? Tell these students who feel very strongly (and rightfully so!) about this issue to just give up and go home? Who exactly does that benefit? Oh, right, the universities who are benefiting from this genocide, as well as the federal government. Good plan.
For two, I realize that the university at the center of this is an Ivy League school, and that the students who are there are privileged in many ways. However, that does not change the fact they are facing violence from the university and from police. That does not change the fact many of these students are Palestinian, Jewish, or other minorities. Beyond that, Columbia is not the only school where protests are happening. Emerson, USC, Yale, Harvard, MIT, Tufts, Cal Poly Humboldt, NYU, Vanderbilt, Brown, University of Michigan, UC Berkeley, Emory, Indiana University, Purdue, George Washington University, UCLA, Northeastern, Ohio State, UT Austin, Arizona State, Washington University St Louis, Cornell, University of Pennsylvania, Stanford, University of Georgia Athens, Sonoma State, San Francisco State, Sacramento State, University of Washington, Virginia Tech, Princeton, University of Minnesota, UConn, USC, University of Illinois, University of Utah, McGill, Portland State, UNC Chapel Hill, Tulane, University of Florida Gainesville, University of Colorado Denver, Case Western Reserve, City College of New York, Rutgers, Johns Hopkins, University of Maryland College Park, Barnard College, Pomona College, DePaul, Georgetown, University of Delaware, University of Arizona, University of New Mexico, University of Wisconsin, Virginia Commonwealth University, Oberlin, UC San Diego, University of San Diego, and I’m sure many others have or are currently participating in protests. Many of these schools are not elite universities only the best of the best (or the most money) get in. For crying out loud, my ass got into Indiana University.
That begs another question as well. Yes, these students at Ivy League schools have privilege. How else would you prefer they use it? When one has privilege, it is imperative to utilize it for the benefit of those one has privilege over.
Anyway. Free Palestine. Defund the police.
“Taking away attention from what’s actually going on” this is like saying the university protests against the Vietnam War were taking away attention from what’s actually going on in Vietnam. (Which I’m realizing now was probably an actual talking point at the time, but sounds ridiculous now.)
#max says things#tori says things#do NOT clown on this post#I will shut off reblogs and block people#this is not an invitation for discourse#terfs zionists fascists etc are not welcome on my posts
18 notes
·
View notes