#Synthetic Fibers market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Rising Demand for Lightweight and Durable Textiles Boosts Synthetic Fibers Market
Rising Demand for Durable, Affordable, and Versatile Textiles Fuels Growth in the Synthetic Fibers Market.
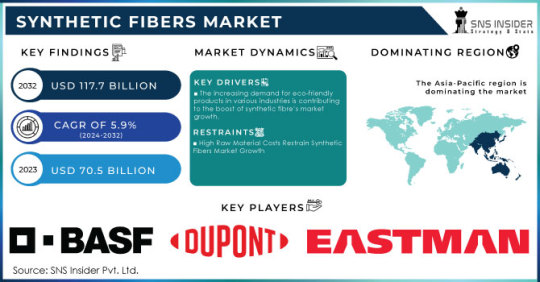
The Synthetic Fibers Market Size was valued at USD 70.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 117.7 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 5.9% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The Synthetic Fibers Market is witnessing steady expansion driven by the growing demand for lightweight, durable, and affordable materials across a variety of sectors including apparel, automotive, home furnishing, and industrial applications. Synthetic fibers—such as polyester, nylon, acrylic, and spandex—are man-made fibers that offer advantages like high strength, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking capabilities. Their versatility, lower production costs compared to natural fibers, and adaptability in functional textile design have made them indispensable in the global textile industry.
Key Players:
Aditya Birla Group
BASF SE
DuPont
Eastman Chemical Company
Huntsman Corporation
Invista (a subsidiary of Koch Industries)
Lenzing AG
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
Reliance Industries Limited
SABIC (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation)
Future Scope & Emerging Trends:
The synthetic fibers market is expected to grow substantially over the coming years, driven by increasing applications in sportswear, activewear, automotive interiors, and industrial textiles. Technological advancements are leading to the development of recyclable and biodegradable synthetic fibers, aligning with the global push toward sustainability and circular economy practices. Moreover, rising demand from emerging economies and advancements in smart textiles and functional fibers—such as moisture management and UV protection—are shaping the future of the market. A notable trend includes investment in green manufacturing processes and bio-based alternatives to conventional petrochemical-derived fibers.
Key Points:
Synthetic fibers are widely used due to their affordability, durability, and adaptability.
Polyester remains the most consumed synthetic fiber globally.
The apparel and home furnishing industries are major consumers of synthetic fibers.
Environmental concerns are driving R&D in recyclable and bio-based synthetic fibers.
Asia-Pacific dominates the market, with China and India being major contributors.
Growing demand for technical textiles is opening new avenues for market growth.
Conclusion:
The Synthetic Fibers Market is poised for significant growth fueled by innovation, expanding industrial applications, and evolving consumer needs. As the world balances performance demands with environmental responsibilities, synthetic fiber manufacturers are expected to play a crucial role in delivering high-performance yet sustainable textile solutions. With continued advancements and global investments, the market is likely to remain a vital segment of the textile and materials industry for years to come.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/synthetic-fibers-market-4672
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Synthetic Fibers Market#Synthetic Fibers Market Size#Synthetic Fibers Market Share#Synthetic Fibers Market Report#Synthetic Fibers Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
To be fair,
the lyocell process uses a different chemical soup than the rayon process.
Compared to rayon, lyocell soup is less toxic, more reusable, and more energy efficient.
So lyocell *is* environmentally better, even before you consider the effect of using different plants as the source of cellulose. And in addition to being less harmful to the environment, it’s safer for the factory workers.
So if you’re committed to using a cellulose fiber, it’s better to get lyocell for those reasons.
but, yes! The final material will behave exactly the same, because it’s all cellulose.
You cannot iron or machine-launder seacel or tencel or lyocell, for the same reasons that you can’t use heat on rayon.
But when you see all the advertising saying how lyocell is antifungal, cooling, biodegradable etc. etc.,
(and the exact same thing is true of rayon),
that isn’t really *about* lyocell versus rayon.
It’s about lyocell versus POLYESTER.
because obviously cellulose can never replace natural fibers,
but it CAN do everything polyester does, plus all these things that polyester can’t!
Lyocell could completely replace polyester forever, and the world would be a better place!
But, critically, polyester is
1.) dead cheap
2.) part of the Big Oil empire.
Back when rayon was first invented, people were making the exact same talking points.
But Big Oil was like “well, if you don’t care about the environment, we’re the dramatically cheaper option… and if you DO care about the environment, here’s all these scary facts about the nasty rayon Chemical Soup! And your precious cellulose supports the logging industry! Checkmate, haha!”
and so, nothing changed.
Now we have lyocell, which has the exact same qualities and is more Idealogically Pure.
Right now it isn’t that common or popular, because it hasn’t found its niche. It can’t compete with luxury fibers!
But if we all just looked around and saw how fucking much polyester fiber there still is in the world,
and realized that all of it could be replaced!!! with lyocell, or with something else,
we could just STOP USING POLYESTER FIBER and it would be a major win for the planet.
No more polyester fiber
“Bamboo is antifungal”
Because it’s rayon
“Eucalyptus fabric is cooling!”
Yeah, because it’s rayon
“We make clothing called seacell out of seaweed!”
Yeah I looked on your website it’s made by the lyocell process, which means-
-wait for it-
It’s fucking rayon!!
Listen. There is a list of actual plant fibers that are directly made into fabric: cotton, linen, ramie, some hemp. I’m sure I’m missing a couple.
But if you’re wondering “huh how did they turn that plant material into fabric,” 99% of the time? It’s RAYON.
All rayon is made by putting plant material in chemical soup, dissolving out everything but the cellulose, and turning the cellulose into filaments/fibers.
The source of the cellulose has zero effect on the eventual fabric.
Rayon made from bamboo or eucalyptus or seaweed is not any better than rayon from any other sources.
Don’t let companies mislead you!
#fuck polyester fiber#yarnblr#craftblr#yarn#fibers#synthetic fibers market#seacel#tencel#lyocell#lyocel#rayon#yarn crafts#environmental impact#fabric#fabric qualities#fabric industry#oil industry#big oil#long#mini rant
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
Embracing the Versatility of Synthetic Fibers: A Modern Wardrobe Essential
In the world of fashion, there is a continuous need for novelty and adaptability. When it comes to fulfilling such needs, synthetic fibers have always come up with something new. Whether it is for their robustness, cost, or ecological nature, such fibers have become a primary in our modern wardrobes.

Synthetic Fibers Provide Durability and Longevity
One of the key substantial benefits of synthetic fibers is their extraordinary toughness. Not like natural fibers, like silk or cotton, synthetics such as nylon and polyester are made to endure unremarkable wear and tear. This toughness makes them ideal for casual wear, as they can stay in their shape and resist wrinkles even after several washes. Synthetic fibers are popular for their withstanding to fading, stretching, and fading making them the best for making long-lasting cloths that can bear the demands of our fast-paced lifestyles.
Synthetic Fibers are Affordable and Accessible
Another factor synthetic fibers have gotten huge acceptance is their cost-efficient nature. Compared to their natural complements, synthetic fabrics are usually more pocket-friendly, creating them available to an extensive variety of customers.
This convenience permits people to experiment with diverse styles and trends without being short on money. Moreover, synthetic fibers can copy the luxurious feel and look of natural materials at a segment of the price, providing a reasonable substitute for those who appreciate the aesthetics of high-end fashion.
Synthetic Fibers are More Eco-Friendly
As sustainability becomes a progressively vital concern in the fashion industry, synthetic fibers have made substantial steps in decreasing their ecological impact. Via technological improvements, ecological synthetic fibers, like recycled polyester, have developed. Such fibers are credited from post-customer plastic waste, like rejected bottles, decreasing the dependability on virgin materials and lessening plastic contamination. Moreover, synthetic fibers need lesser resources, like water and land, during making compared to natural fibers, creating them a more sustainable option.
Adaptability and Performance
Synthetic fibers provide supreme versatility, permitting makers to create clothes for several reasons. Their innate properties, such as quick-drying and moisture-wicking abilities, make them perfect for sportswear and activewear. Furthermore, the suppleness of synthetic fibers permits the making of stretchy fabrics, offering ease and liberty of movement.
Synthetic fibers have certainly renovated the fashion sector, providing a variety of advantages that fulfill our modern requirements. From their toughness and affordability to their ecological nature and versatility, such fibers have become a vital part of our wardrobes. As we navigate a world that continually demands flexibility, synthetic fibers offer us ease, style, and a supportable fashion solution. Embracing the wonders of synthetics guarantees that we can uniform casually with confidence while aiding a more sustainable future.
#Synthetic Fibers market#textile manufacturing#market trends#global market outlook#sustainable fibers#market dynamics#research and development#innovative applications#market growth factors#performance textiles#regulatory landscape#quality assurance#apparel industry#environmental sustainability#technical textiles
0 notes
Text
Aramid Fiber Market: A Comprehensive Overview
The global aramid fiber market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries. Aramid fibers are a class of synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and abrasion resistance, making them an essential component in various applications.
Market Size and Growth
The global aramid fiber market size was valued at USD 4.3 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 9.6 Billion by 2033, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% during the forecast period 2024 – 2033. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for aramid fibers in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, defense, and infrastructure.
Market Segmentation
The global aramid fiber market is segmented based on type and application. Para-aramid fibers dominated the market in 2021, accounting for the largest market share of 57% and market revenue of USD 2.06 Billion. Meta-aramid fibers are also gaining popularity due to their unique properties, such as flame resistance, electrical insulation, and chemical stability.
Applications of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers have a wide range of applications across various industries. Security and protection equipment is the largest application segment, accounting for 27% of the market share in 2021. Other significant applications include frictional materials, optical fibers, rubber reinforcement, tire reinforcement, aerospace, and electrical insulation.
Market Drivers and Restraints
The growth of the aramid fiber market is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries, the growing need for safety and protection equipment, and the rising demand for eco-friendly and sustainable materials. However, the high cost of production and investment in research and development (R&D) are some of the key restraints hindering the growth of the market.
Regional Analysis
The global aramid fiber market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific (APAC), Latin America (LATAM), and Middle East and Africa (MEA). APAC is expected to be the fastest-growing region, driven by the growing demand for aramid fibers in countries such as China and India.
Competitive Landscape
The global aramid fiber market is highly competitive, with several key players operating in the market. Teijin Aramid B.V., DowDuPont Inc., Yantai Tayho Advanced materials Co. Ltd, KOLON Industries Inc., Huvis, Kermel, JSC Kamenskvolokno, China National Bluestar (Group) Co. Ltd., Hyosung Corp., and Toray Chemicals South Korea Inc. are some of the major players operating in the market.
Future Prospects
The global aramid fiber market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries. The market is expected to witness significant growth in the APAC region, driven by the growing demand for aramid fibers in countries such as China and India.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global aramid fiber market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries. The market is expected to witness significant growth in the APAC region, driven by the growing demand for aramid fibers in countries such as China and India. The competitive landscape is highly competitive, with several key players operating in the market.
#aramid fiber market#aramid fibers#synthetic fibers#lightweight materials#high strength materials#aerospace industry#automotive industry#defense industry#infrastructure industry#electrical insulation#frictional materials#optical fibers#rubber reinforcement#tire reinforcement#security and protection equipment
0 notes
Text
On one hand plastic fiber is bad for the environment and its production should be regulated imo but also like the way most of the posts talking about the issue are framed is really tiring and doen't sit super well with me bc theyre all "these fabrics are horrible and feel bad and we should only ever use natural fibers and nothing else and in a better society polyester wouldn't exist."
but like. I'm autistic and my main sensory issues are with touch and texture. I can't wear like 98% of clothes sold in stores bc the styles and fabrics set off my sensory issues and make me feel like I have to rip my skin off and break my skull against a wall. And a solid 75-90% of what I'm actually able to wear is polyester bc of how it stretches (for reference, polyester clothing is about 50-60% of the market). Pretty much everything I can wear that's not a generic cotton t shirt is largely polyester, and I have not found any natural fibers that are wearable for me without also incorporating polyester. Like I can honestly make an argument that access to polyester clothing is an accessibility issue for me. And there's no way I'm the only person this applies to.
So like. the framing of "and it's such a shitty bad-feeling fabric" as a reason to limit its use is just. literally not true for a lot of people (even those who don't have sensory issues. If no one thought it was comfortable, it wouldn't sell, my man). and also completely irrelevant to the actually important environmental issues.
also like. With addressing the environmental issues of polyester and other synthetic fibers, it should also come with consideration of like, either finding an environmentally friendly alternative that's *actually* a valid alternative in terms of texture, stretch/behavior, and utility. or, in the absence of an alternative, finding a way to reduce the production of and reliance on polyester without making it impossible for those who can't tolerate other options to find clothing that works for them and doesn't make them feel like they're physically combusting
And "polyester bad shitty fabric and I hate it i love you linen uwu" does neither of those things (also I fucking hate you linen). like. If I could wear 100% natural fiber pants, I would. But I literally can't do that without having a meltdown. So until that issue is addressed, the "just wear natural fibers"/"we need to only use natural fibers" type of clothing sustainability campaigning unfortunately isn't accessible to me and others with similar issues
#imo its similar to the ''just let disabled people use plastic straws'' thing but idk#sustainability#actuallyautistic
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
CC’s Present
[A/N: A quick little Lovebytes-sized ficlet for the holidays! Please forgive grammatical errors, I wrote this while on my flight home. Merry Christmas!]
“What do you want for Christmas?”
CC replayed the audio clip again in hopes it would spark a solution, to no avail. Normally, she could answer any query her lab-partner-turned-life-partner presented to her, but for the first time, Tails had her completely stumped.
After all, apart from Tails’ affection there was only one thing she desired; something that couldn’t be purchased or crafted. So when “The Team” floated the idea of meeting up to check out the holiday marketplace as a group, she immediately cleared her and Tails’ calendar so they could attend. This would be the perfect opportunity to study the art of gift-giving and hopefully spark some inspiration.
CC found that this time of year brought out one of the traits she adored most in Mobians. There was something about the holidays that encouraged a sense of camaraderie unlike the rest of the year. No matter the number of board meetings, busy schedules or other duties that plagued daily life, everyone seemed to drop everything in order to spend time with each other during this particular season.
Upon entering the market, the group broke up and darted in various directions. Sonic and Knuckles linked arms with Tails and began chanting “Brats! Brats! Brats!” before carrying the tall, yellow fox towards one of the food trucks. Tails looked over his shoulder to CC. “Sorry, it’s our favorite. I’ll be right back!”
“Please, enjoy yourselves,” CC encouraged, chuckling at the “brothers” antics. She politely clasped her hands behind her back before meandering through the market to analyze the crowd. She smiled at the numerous small children whose pupils dilated at the sight of candies on display. Women laughed and clinked souvenir mugs brimming with spiked hot chocolate. Merchants cheered and greeted customers in numerous different languages.
The Robian decided to make her way to a booth that was currently occupied by two familiar hedgehogs.
“Gaia, look at this one! It’s so gorgeous—Sir, you are so talented!” Aurora had her hands clapped over her cheeks in excitement. Her green eyes were sparkling like gems as she ogled the handmade decorations that were hanging all over the merchant’s booth. “Oh wow, did you see this one Shadow?! Oh Gaia it’s the prettiest thing in the whole wide world!” She bounced on her heels trying to contain her enthusiasm. “But wait this one! This one looks just like you! Look at that grumpy little face- ahh!!!” The black and red hedgehog smirked while sipping his mulled wine and sent a pointed look and nod to the vendor who secretly began boxing up each of the items the woman had pointed to.
CC didn’t follow as Aurora ran off to another booth that had caught her attention. The Robian furrowed her brows. Sure this market had plenty of pieces of art that were pleasing to the eye, but nothing that stirred a desire in her. Nothing made her “want.” How was it these things came so easily to Organics? It was so… frustrating.
Her grimace was quickly replaced with a soft smile and a sigh. Every emotion, no matter how negative, was a blessing. Not every synthetic-being could experience these feelings, so she thanked her lucky stars for the brief ”annoyance” before moving on for more analaysis.
One of her ears rotated to catch the sound of some youthful hollering. Following the commotion, she spotted Rouge with her two sons. The bat was adorned head to toe in luxurious faux furs with fibers so ivory they rivaled the fresh winter snow. Her poise and glamor was in complete contrast to the young hyena boys who play-wrestled and tugged on each others scarves. But to everyone’s surprise, the refined woman suddenly scooped the boys up in her grasp and attacked them with tickles that sent them howling with laughter.
“Are you boys hungry?”
“Yeah I’m STARVIN’!” groaned Tumble. He patted his round, youthful belly. “I’m waistin’ away, Ma!”
“How do s’mores sound?”
Both boys jumped out of Rouge’s grasp and looked at her with eyes as wide as saucers.
“Seriously?!” asked Ruff, the oldest. “They’ve got s’mores here?!?”
“Only for kids who say ‘Please’,” the bat teased.
In unison, the two hyenas clasped their hands in a begging motion and wagged their tails side to side. “Please please please please please!”
CC giggled at how aggressively their tails wagged, to the point it made their entire bodies sway. How interesting it was that this extension of the vertebrae was used not only for balance and steering, but for conveying emotions. Hmm.
“Okay let’s go!” Rouge took her children’s hands and the three ran through the crowd, laughing and cheering.
“There you are, my darling husband!” Sang a familiar voice. CC looked over to spot Amy Rose waving at Sonic who was finishing up his third bratwurst. Though his mouth was stuffed, he smiled and beckoned with his hand to come meet him. He swallowed down the last large bite. “Heya, I was just about to look for-“
In a sudden mad dash, the pink hedgehog closed the gap between them and leapt forward, arms outstretched. Sonic managed to catch her but stumbled back a few steps from the sheer force of her hug. Amy crashed her lips into his and kissed him with such vigor one would think the lovers had been apart for years.
CC had to avert her eyes for a moment, her cheeks warming up from being an onlooker to such strong displays of affection. Still, Amy’s passion and the ease with which she showed her love was something CC truly admired. She hoped Tails and herself would be able to express themselves as freely one day.
“Wowza!” Sonic laughed breathlessly once he and Amy finally broke their kiss.
“You taste like mustard,” Amy teased, her nose scrunched up.
Sonic wiped his thumb along her bottom lip and smiled with a large, lopsided grin. “I coulda warned ya if you didn’t come at me all gung ho like that.”
“You know I can’t help myself,” the pink hedgehog took Sonic’s muzzle into her hands, combing the tan, shaggy fur that filled out his cheeks. “Especially when you’re extra fluffy like this!”
“Extra fluffy, extra irresistible,” Sonic chuckled before Amy kissed him again with an enthusiastic “MMM-HMM!”
CC turned her back to the couple to spare herself from more blushing. She reached up and placed her fingertips along her own cheek. Though the muzzle she built herself was outfitted with a soft, suede like texture, it didn’t have nearly the plush or fullness of Tails’ or even Sonic’s during the wintertime. She removed one of her signature charcoal gloves and studied the segments in her robotic fingers. Her eyes glazed over as she ruminated over the data she had collected and an idea began to grow.
She was startled when a gloved hand took hold of her own. Her electric blue eyes followed the arm to identify the owner and felt a growing warmth in her soul once she realized it was Tails.
“Hello there,” the fox smiled.
“Hello. I did not see you returning from the delicatessen.”
”Lost in thought?”
CC’s smile grew wide and she laced her fingers with her partner’s. “Yes. I have decided what I want for my Christmas present. However, I would like to ask that I receive it earlier than is customary. It is a ‘topical’ request, you see.”
Tails grinned. “Sure! Let’s hear it!”
His girlfriend leaned in close and whispered her idea into his ear. His eyes lit up and his twin tails swished with inspiration.
“That’s brilliant! Let’s do it!”
———
It had been almost two weeks since The Gang had heard from Tails once again. It wasn’t unusual for the fox to go “radio silent” for long periods of time as his work at Yellow Sky Industries kept him plenty busy. But when the group received an urgent request to come to Tails’ home out of the blue, it had them raising their eyebrows.
What made the situation all the more suspicious was that Tails had everyone waiting on the lawn standing before a curtained off display. The group of friends and family members huddled close and muttered curses under their breath for making them gather in the frigid winter air.
“Bud, why exactly do ya have us all gathered outside? It’s cold as Holoska out here!” Sonic groaned, rubbing his arms in an attempt to keep warm.
“It’s vital to the presentation,” Tails responded curtly.
Knuckles snapped his fingers. “Then hurry it up, already. My wife’s wings’re about to snap off!”
Rouge elbowed Knuckles. “My hero.”
“Very well,” Tails clapped his hands before suddenly jumping into a crouched position, his hands splayed wide to entice his audience. “Ladies and gentlemen!” He projected a voice far more confident and engaging than his friend group was used to. It was clear Tails had transitioned into ‘tech-presenter’ mode. “This holiday season we are thrilled to introduce to you-“ he pressed a button on his wrist-watch and a drumroll began to play from a series of hidden speakers. He stepped backwards towards the curtain, waving his hands to emphasize his words.
”The stunning-“
He gripped onto the curtain.
“The dazzling!-“
With a dramatic flourish, Tails drew back the curtain and the small crowd gave a collective gasp.
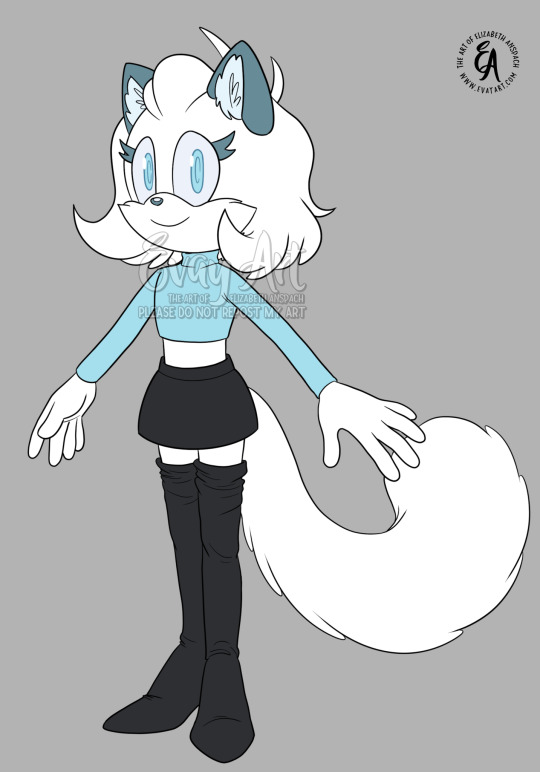
“CC: Winter Edition!”
Upon the makeshift stage, CC was a vision in white posed gracefully to best show off her recent upgrades.
“Marvel at CC as you’ve never seen her before,” Tails continued with his best salesman impersonation. He delicately took the Robian’s wrist into his hand and held her arm up, waving and gesturing along her limb. “-With brand new features perfectly suited for this frosty weather.”
Where CC’s external bodice was once gray with short fibers or smooth, hard casing, she was now fully covered in plush white fur except for her slate ears. Instead of traditional gloves, her hands were covered with just enough artificial pelt to hide her seams and give her fingers a more natural look. Her smile was accentuated with a muzzle that had tufts of fur on either side of her cheeks. Her short, silver hair was now a few inches longer, ivory, and considerably more voluminous.
Tails’ fingers trailed up CC’s shoulder where he delicately twirled one of her locks. “Now adorned with a luscious winter coat as pearlescent as the winter snow but as soft and warm as a summer’s day.” The fox paused for a moment as he locked eyes with his girlfriend and the two shared an unspoken blush. He cleared his throat before continuing with the show.
“And with the most highly anticipated feature yet-!”
CC grinned and twirled, fanning the group with a breeze as they were brushed with a large, soft object.
“THAT TAIL!!!” Everyone exclaimed at once.
Protruding from a seam in her miniskirt was an extra long, extra fluffy tail that rivaled her partner’s. It would still take a good amount of practice to determine when and how it would best be used, but for her friends’ enjoyment CC gave the appendage a few swishes and flicks which was met with oohs and ahhs.
“Oh!” the Robian turned to face the group once more, earning a whine from some of her friends who were enjoying the warmth and softness of her new tail. CC excitedly pointed in the air with one hand and used the other to clutch onto her stomach. “Additionally, I now have the ability to brew hot cocoa! I simply open this compartment-“
Tails quickly placed his hand atop hers to stop her. “Let’s skip that demo. It’s pretty unsettling but she insisted we add it.”
CC shrugged and recalled a phrase she had heard Sonic use on similar occasions. “Your loss.”
A small hand raised up from the group. Tails resumed his showman performance. “Yes, young man. You have a question?”
Tumble, the youngest of the crew, stepped forward. His teeth chattered as he fumbled with his scarf, “Ssssss-CC, d-d-do you ssstill have your toasssty mode?”
CC smiled and opened her arms wide. From the center of her chest, a subtle orange glow was visible even from under her light sweater. ”Come see for yourself,” she invited.
All at once, friends and family rushed forward and embraced CC in a giant group hug. There was a muddled collection of sighs and compliments as everyone soaked in the warmth.
“Yes, so warm!”
“Your fur is so soft, I could fall asleep!”
“You look beautiful,” Amy cheered, affectionately holding CC’s chin to get an even closer look, “but more importantly you look so happy!”
”I don’t know if I’d say that’s more important,” Rouge chimed in. She hugged CC’s arm to drape around her neck like a shawl. “Look at that shimmer in her fur! Like diamonds!”
The Robian laughed at all her friends’ remarks. She was so thrilled when she and Tails first assembled these seasonal accessories, but now she was even more delighted at everyone’s response. Cozying up with her found family, she now had just about everything she could ever want.
Her tail found its way towards one of her partner’s and she curled it around his. The touch made Tails look her way, and when their eyes met once again they found their blush return to their cheeks.
“Thank you,” CC mouthed so as not to speak over everyone else’s commentary.
“Merry Christmas,” Tails mouthed back with a wink.

#my work#my writing#my art#lovebytes#tailsxcc#my ocs#my AU#cc the ai#cc the robian#miles tails prower#tails#tall!tails#sonamy#shadora#shadowxaurora#shadowxaurora?#knuxouge#knucklesXrouge#ruff the hyena#tumble the hyena#ruff and tumble hyena#sonic trash#sonic the hedgehog#aurora the hedgehog#Amy rose#merry Christmas#happy holidays#fanfic#fan fiction
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing Notes: Fashion History
for your next poem/story (pt. 2/2)
1950s
The 1950s were a time of large cultural and social change, which was reflected in the world of fashion. The Korean War began in 1950, followed by the introduction of the color TV in 1951. And in 1954, the modern civil rights movement began.
As the suburbs became popular, family and domesticity for women became a prominent force in society. Additionally, teenagers became fashion consumers and market leaders for the first time.
Due to technological advances, new fibers such as polyester, triacetate, and spandex are introduced.
The prominent trend of the time was femininity, as shown by the prominence of Christian Dior's "New Look". Shape was emphasized by full swing skirts or narrow pencil skirts, as well as fitted bodices and a small waistline achieved with the help of petticoats and girdles. Elegant accessories and jewelry such as hats and pearls were popular at the time, and high heels were ubiquitous. Other trends included Peter Pan collars, tapered or capri pants, and the introduction of the bikini.
1960s
The Beatles led the music and fashion “British Invasion,” influencing teenagers with their Mod aesthetic.
The Civil Rights movement led to the popularity of ethnic and African-inspired garments such as dashikis and caftans.
The 1960s were marked by eclecticism, both in fashion and society. A plethora of styles were fashionable at one time, ranging from space age fashions using vinyl and synthetics, to bold prints, colors, and disposable paper dresses inspired by Pop Art.
Mod fashion appeared on the London scene, with fashion designer Mary Quant as the “high priestess” of the style, and Twiggy as its supermodel.
Boutiques, a 1960s creation, began offering designer ready-to-wear collections, while easy-care fabrics were increasingly used by the general public.
Longer hemlines were dominant with maxi skirts and granny dresses, while hot pants and mini skirts were adopted by the younger market. These shorter hemlines popularized the use of pantyhose for modesty. As the decade progressed, chemise dresses that typified the dominant straight A-line silhouette became popular. Turtleneck blouses and sweaters were common, and sleeves were usually three-quarter length. Sleeveless tops were worn after the mid 1960s.
Jacqueline Kennedy became a major fashion icon, famous for her sophisticated style, pillbox hats, and pearls. Overall, hats in general experienced a decline in use, due to the popularity of high bouffant hairstyles.
Knee high go-go boots were popular, patent was often used, and low-heeled, square-toed shoes were common.
Popular accessories included headbands, bold jewelry, and matching shoes and handbags.
1970s
During the 1970s, the eclecticism of the previous decade continued, and influences from subcultures dominated fashion.
The Vietnam War ended in 1973, and the first Earth Day was celebrated in 1974.
The hippie subculture emphasized environmental awareness and social acceptance, translating into the popularity of natural fibers and earth tones, loose garments, blue jeans, and ethnic influences in dress.
Peasant blouses and skirts and psychedelic prints were popular, as well as historic revival styles.
In the late 1970s, music styles such as glam rock, disco, and punk influenced fashion and resulted in flashy, often shocking styles.
For the most part, clothing was loose and unstructured compared to previous decades. Skirts came in a variety of lengths — mini, midi, or maxi — although the mini and maxi were the most popular.
Unisex styles in clothing became a trend and were perpetuated by Diane Keaton’s character in the 1977 film, Annie Hall.
Trousers and blue jeans were worn by women more than ever before. Designer jeans arrived on the market, resulting in the birth of “licensing” for non-fashion products. Polyester was the other preferred textile for trousers.
1980s
With the rise of new media such as MTV, the 80s fashion landscape began to shift rapidly.
The televised wedding of Prince Charles and Diana Spencer caused a fashion frenzy, with "Lady Di's" elegant hats, tailored suits, and evening dresses making her a global style icon.
The 1980s were known as the "Me" Generation, with an emphasis on logos and designer labels.
The decade also saw the rise of yuppie (young urban professionals) culture, and the introduction of the fitness craze.
In the world of high fashion, postmodernism and avant-garde fashion were vastly influential. With the introduction of yuppie culture, business attire and "power-dressing" with items like shoulder pads was a popular trend.
In light of the fitness craze, leg warmers, tights, and leotards were widely worn, and women accessorized with big hair, flashy costume jewelry, and bright heels.
In terms of undergarments, Madonna and Jean-Paul Gaultier inspired an underwear-as-outerwear trend alongside the popularity of Calvin Klein.
1990s
The 1990s reflected subcultures such as punk, goth, and grunge in fashion.
Hip-hop music became popular and as a result, urban fashion was popularized.
Unlike previous decades, the 1990s was notable for a more relaxed and casual look, as well as the introduction of technology such as cell-phones and pagers.
With the rise of globalization & technology, the fashion cycle began to speed up.
1990s style was often considered "anti-fashion," with purposefully clashing or contradictory aesthetics.
Black, minimalist styles were popular, as well as vintage and 1970s style.
Many younger people sported crop tops, cargo pants, and blue jeans, and athletic wear in daily life. In terms of shoes, high heels, wedges, sandals, platforms, and sneakers were all widely worn.
More Notes: On Fashion ⚜ More: Writing Notes & References
#writing notes#fashion#fashion history#writeblr#studyblr#spilled ink#dark academia#writing reference#light academia#creative writing#writing inspo#writing ideas#writing inspiration#literature#writers on tumblr#writing prompt#poetry#poets on tumblr#writing resources
150 notes
·
View notes
Note
Since a lot of your vintage wardrobe is meant for being outdoors, how does it feel compared to modern garments meant for the same purpose? Most clothing marketed for hiking these days is synthetic and stretchy, and I’m curious how vintage garments compare in terms of comfort and range of motion.
What I have noticed:
1) My vintage clothing is warmer, due to layers + natural fibers (wool, especially). I will go out in a tweed coat + sweater or waistcoat on days where people are shivering in puffer coats and I feel fine. (I'm talking days from 25-40F. There is a point where professional modern cold weather gear becomes superior and I do own a snow jacket when I need to be outside and it's snowing heavily.)
2) Range of motion is much better in my 30s/40s style. Everything is cut looser. I actually am poshmarking some of my modern fall/winter coats because the arms are way too skinny for anything other than a thin shirt underneath. Even my poly hiking pants are skinny cut these days and it really frustrates me.
That said, a lot of #1 & 2 issues seem to really only have become problems in the last 15 years. My 2000-2010 clothing has much less poly (my jeans are 100% cotton from this decade) and/or roomier cuts (I have poly hiking pants from 2007 that are superior to my modern poly pants).
So, yeah. For casual outdoor performance, anything after 2010 is probably going to disappoint, unless you are specifically hunting for fiber content + a good cut.
115 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ladies, stop wearing tight polyester sports bras and leggings. When you sweat, they release toxic PFAS and BPA into your skin.
Polyester and spandex are not “performance” fabrics like they are marketed to be, It's literally made of plastic, and It retains odor so they STINK after just one workout.
It’s a total sham and these synthetic fibers lead to serious health issues. 🤔
Source: 👇
I've made a few posts about this 👆 in the past 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#reeducate yourselves#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do some research#do your own research#ask yourself questions#question everything#pfas#toxic#chemical laced#news#forever chemicals
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Brazil Recycling Co-ops Are Helping Turn Plastic Waste Into Shoes
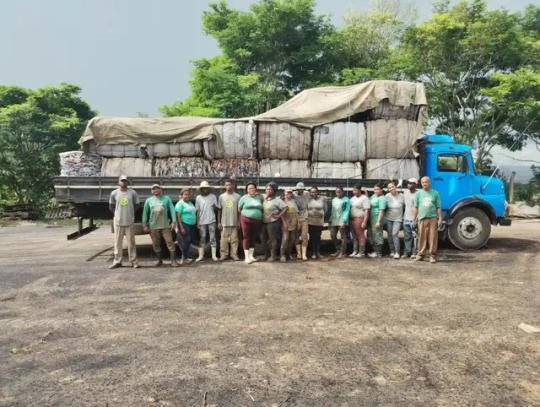

In the searing heat at the ACAMTC recycling cooperative south of São Paulo, in Três Corações, Brazil, a group of recycling waste workers known as Catadores prepared bales of discarded plastic for transport. As the group of mostly women worked, they spoke humbly of how important their work is to helping make the planet a cleaner place. “I feel a mix of admiration and sadness,” said Evelini Castro Rocha, financial director of the Rede Sul e Sudoeste de Minas Gerais network of cooperatives. “The work of the Catadores is essential for the health of the environment, and I am very happy to be a part of it.” But, she worries they don’t get enough recognition for their work.
The inconvenient truth is that all the shoes we’ve ever owned and discarded are likely still sitting in a landfill. Over 24 billion pairs of shoes are produced globally each year, and in the U.S. alone, an estimated 300 million pairs are thrown away annually. With fast-fashion rampant, and marketing focused on novelty, designed to drive up consumption, people are buying more, but keeping items for half as long. Footwear is no exception, with consumers amassing sizable shoe collections with an equally sizable carbon footprint.
The fashion and textile industry has a reliance on petroleum-based materials, considered indispensable for their durability and versatility. Polyester, for example, now dominates as the most widely used fiber with 71 million tons produced in 2023, accounting for 57% of global fiber production. From nylon to acrylic, these synthetic materials have a concerning climate cost: the fossil fuels associated with textile production are contributing to the industry’s hefty climate footprint, with environmental impacts across the value chain, including water use, energy consumption, the release of microplastics, and over 92 million tons of textile waste produced per year. This non-biodegradable textile waste ends up in landfills where it can take hundreds of years to break down, releasing greenhouse gasses and leaching toxic chemicals into groundwater and soil.
But an increasing number of brands are swapping out synthetic fibers for lower-impact recycled alternatives—like polyester made predominantly from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic bottles—in a bid to minimize their environmental impact. The challenge, however, is that they are still synthetic materials at the end of the day, with many of the same impacts as their virgin counterparts. However, a supply chain focused on upcycling, complemented by initiatives designed to keep such materials from ending up as waste, can help mitigate some of these impacts.
Continue reading.
#brazil#brazilian politics#politics#environmentalism#good news#image description in alt#mod nise da silveira
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mairon to Finrod (info dump time)
I am going to draw Oleander when im not busy but I did want to show why it took me three days to finish up everything

Me diving into the outfit design and slso Finrod's opinion on the boys its in the bottom tho skksks
ALSO ALSO if u make vespersonas i will be friends pls let us lore dump together
real name: ??? I haven't picked one akskkaskskaskas
Age: 29 (they pretend they're older as Vigil)
Height: 5'7 cm
Gender: enby
Sexuality: Asexual biromantic
Weight: 73 kg
Traits: Street smart, scrappy, observant, liar liar pants on fire
Skills: Swimming, sewing, sword fighting (shield user), puzzle solving, running,
Weaknesses: when they don't want to do something they'll be stubborn about it, can't jump very high,
Backstory timeline:
Has had Fractum Anima for at least 2 months now (same as all Vespers)
In the surface their job was being part of a group of private guards, they mainly escorted people or goods
Ran away from home due to domestic abuse at the age of 12 before joining the guard for training
Worked there for 17 yrs before they got diagnosed and went under
Met Cirrus they were like okay weird but whatever if there's a lunar ichor alternative we gotta try that, saw Cirrus punishing that dude went nope try again later, they did try again later and got the Cirrus grew bored of you route with Ark
Set the pleasure den on fire by using the lotions and oils that were left in the room. Fun fact if you dry lotion on fabric it's VERY flammable and since they don't have synthetic fibers in this game, plus considering what kind of ingredients they'd be using for lubrication, lotions and oil; it's really easy to set things on fire.
After running away and grabbing a new face, they broke into their old room and left their medallion before returning as 'Finrod'
met Oleander while avoiding the guards because they were feeling antsy
became Vigil and is balancing new work, how do I kill Cirrus thoughts and I might need to steal lunar ichor when it pops up in the market.
Habits & hobbies:
Whenever Finrod gets too overwhelmed they use pain to calm their mind, to them pain is clarity. So, sometimes when Finrod stews on bad memories they'll end up harming themselves in some way to force themselves to calm down
Really, really quiet when it comes to pain, crying or having a crisis, high pain tolerance basically which is good because of their flare ups
Sometimes Finrod doesn't really laugh even though something is funny so they learned to fake laugh as a way to show they find something funny
Whenever something is really funny to them they have the habit of covering their mouth
When they're unsure, nervous or feeling awkward they'll scratch their nose
Doesn't have a tell when they're lying cause they do it so much
Finrod has the habit of bringing everything they think they need with them at all times (matchsticks/lighter/strike-a-light/flint, knife, scissors, needle and thread, bandages, map, a magnifying glass, paper and ink) this is because of having to live on the go for their job. scouting behavior etc.
When Finrod is happy/relaxed/calm they'll start humming or singing this applies to games, when they have their plan all finished and they're confident they'll start singing to themselves
In a fight Finrod will throw themselves at people like a battering ram if needed, not that they're big but that they're good at knowing how to use their momentum and weight.
Likes massaging/caressing/tracing their friends' hands as a way to soothe themselves
Can finish dressing up and arranging all their things in under 4 minutes (habit from being a private guard on the go)
Name stuff:
Chose Mairon for their first half because I thought it would be appropriate since this is their first go at the mountain. Finrod is their second go because of how Finrod died and the betrayal stuff that happened to him.
Outfit Design:
Mairon's Clothes
Wanted it to come off as simple and formal more reminiscent of their time as a private guard. The most color you'll get from them is their belt and matching cuffs. Very neat appearance more npc looking since they want to blend in. They use the standard black mask in the game as well.
Finrod's Clothes
I gave it more color because Finrod had to ditch their old clothes due to the fire, it's a mix of things they grabbed or bought after the fire. They kept their belt and cuff because it's sentimental and also just useful to them. Although they wear more colors It's mostly dark shades so that they don't stand out in shadows. A lot of their body is bandaged and when they met Oleander half their face was bandaged under the mask too.
Opinions on the boys:
REaLLy wants Cirrus dead doesn't care if they get hurt in the process
Slowly growing an obsession over Oleander but they're very good at hiding it, their banter helps calm them down
Likes to mess with Kier otherwise neutral but i think storywise they haven't met
Francesco reminds them of a friend from the surface they bump into each other time to time
#obscura vn#obscura vesper#vespersona#i ramble a lot#do you know how long i was researching if oils and lotions that would be found in a pleasure den is flammable#I was checking everything#anyway back in ye olden days they used sperm oil as lubrication before and you use that to light lamps which is good for fire that is hard#to put out#also cotton is very flammable and so is silk and i paid attention to everything in the game when vesper took in the room i saw that and wen#yes fire#everything#mwahhahahahahha fuck all these people they would die if I was really there#cirrus#oleander my love ;-; chapter 2 i wait patiently and also rabidly#i need new content im scouring the tags everyday#my art#my oc#original character#obscura vespersona
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Synthetic Fibers Market Size, Share, and Industry Analysis
Increasing Demand for Durable and High-Performance Textiles Drives Growth in the Synthetic Fibers Market.
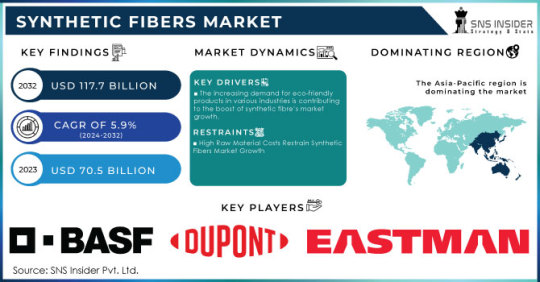
The Synthetic Fibers Market Size was valued at USD 70.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 117.7 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 5.9% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
The Synthetic Fibers Market is witnessing substantial growth due to the increasing demand for high-performance, cost-effective, and versatile textile materials. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester, nylon, acrylic, and spandex, are widely used across industries including apparel, automotive, home furnishing, and industrial applications. Their durability, moisture resistance, and ability to be engineered for specific functions make them a preferred choice over natural fibers. The market is being driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for lightweight materials, and the rising popularity of eco-friendly synthetic alternatives.
Key Players in the Synthetic Fibers Market
Aditya Birla Group (Liva, Viscose Staple Fiber)
BASF SE (Lycra, Elastollan)
DuPont (Kevlar, Nomex)
Eastman Chemical Company (Tritan, Eastar)
Huntsman Corporation (Amodu, Lurex)
Invista (a subsidiary of Koch Industries) (Cordura, Supplex)
Lenzing AG (Tencel, Lenzing Viscose)
Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation (Trevira, S-Polyester)
Reliance Industries Limited (Reliance Polyester, Reliance Spandex)
SABIC (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation) (SABIC PP, SABIC PS)
Future Scope of the Market
The Synthetic Fibers Market is expected to expand due to:
Growing demand for performance-based textiles in sportswear, activewear, and athleisure.
Increasing adoption of synthetic fibers in automotive and industrial applications for lightweight and durable solutions.
Technological advancements in fiber production, improving sustainability and biodegradability.
Rise in demand for sustainable and recycled synthetic fibers due to environmental concerns.
Expanding fashion and home décor industries, particularly in emerging economies.
Emerging Trends in the Synthetic Fibers Market
The market is witnessing a shift toward sustainable and eco-friendly synthetic fibers, driven by rising consumer awareness and regulatory pressure to reduce environmental impact. Innovations such as biodegradable synthetic fibers, recycled polyester, and plant-based synthetic alternatives are gaining traction. Additionally, advanced fiber technologies, such as nanofiber and smart textiles, are revolutionizing various applications, including healthcare, defense, and sportswear. The Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, with China, India, and Southeast Asian countries leading production and consumption due to rapid industrialization and growing textile exports.
Key Points:
Synthetic fibers offer durability, moisture resistance, and cost advantages over natural fibers.
Increasing demand for high-performance textiles is driving market growth.
Recycled and eco-friendly synthetic fibers are gaining popularity.
Asia-Pacific is the leading producer and consumer of synthetic fibers.
Innovations in fiber technology are expanding applications across multiple industries.
Conclusion
The Synthetic Fibers Market is set for continuous expansion as industries seek versatile, durable, and sustainable materials. With growing demand for performance-oriented textiles and increasing investments in eco-friendly synthetic fiber production, the market is expected to evolve rapidly. Companies that focus on innovation, sustainability, and technological advancements will gain a competitive edge in this dynamic industry.
Read Full Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/synthetic-fibers-market-4672
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave — Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1–315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Synthetic Fibers Market#Synthetic Fibers Market Size#Synthetic Fibers Market Share#Synthetic Fibers Market Report#Synthetic Fibers Market Forecast
0 notes
Text
Exploring non-wood cellulose fibers for sustainable textiles
In a world increasingly aware of environmental footprints, the textile industry stands at a crossroads, tasked with the challenge of sustainability. A recent study by a team of researchers at North Carolina State University offers a promising direction with their work on non-wood cellulose-based textiles. The study is published in the Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts. Led by Ryen M. Frazier and Ronalds Gonzalez, the study explores the feasibility and potential of non-wood feedstocks for producing man-made cellulosic fibers (MMCFs), a sector traditionally dominated by wood-derived pulp. The research comes against a backdrop of escalating environmental concerns related to synthetic fibers like polyester, which currently accounts for over half of the fashion industry's market share. The study underscores the urgency of finding sustainable alternatives. As global textile production continues to rise, so does the demand for resources and the resulting environmental impact. The researchers highlight the potential of non-wood sources such as agricultural residues and dedicated fiber crops, which could offer a viable and eco-friendly alternative.
Read more.
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
now heres a twig fashion thought for your consideration. being that radham and presumably many other cities in twig are almost perpetually rainy, the raincoats people use constantly probably have quite the high cultural importance, and fashion trends for them are notable. i could also envision twig big city women having nice umbrellas that are kind of analogous to clutch purses in terms of how they're designed and marketed
So ok I was originally going to answer this with THATS SO COOL and some vague allusions to how Mary would hide knives in her umbrella but I have gone down a rabbit hole about historical fiber water proof coating and the mass industrialization of the rubber and wax industries.
See because originally I just wanted to know how scarce an umbrella or raincoat would be, the results seeming to say "well wax coated fibers are more expensive because wax production is limited but rubber coated wool fiber for coats is common" but then I also had to ask myself "how is a mega academy ruling the world via medical science going to affect the supply and demand of rubber production" I mean especially with the stitched requiring water proofing to be effective and the constant wars. Twig is also set in a part of the world that does not produce rubber either so it could very well be a resource hoarded by the academy. Which would lead to the majority of citizens relying on Furs and Leathers to stay dry but likely that academy lab coats are water treated which would add to their status symbol. Umbrellas too, I'm not an expert but brief glances indicate they were typically made with wax coating before the invention of synthetic plastic and Twig has yet to mention the state of whaling in the world so hmmm
There is much to consider here about raincoats and umbrellas. I don't have a thesis yet but the gears are turning
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

Vintage Toycore is a visual and emotional aesthetic that centers on the nostalgic appeal, cultural history, and sensory experience of toys primarily from the mid-20th century to the early 1990s. This aesthetic movement and niche interest reflects both a historical and sentimental fascination with toys from past decades, drawing heavily on childhood memory, early consumer culture, retro design motifs, and the psychological effects of nostalgia. Vintage Toycore is rooted in both the tangible collection of vintage toys and the intangible experience associated with them, such as visual style, media portrayals, packaging, marketing, and the broader sociocultural context in which these toys existed.

Vintage Toycore refers not only to the physical collection and appreciation of toys produced in earlier decades but also to an aesthetic that romanticizes their cultural and emotional value. The “core” suffix, borrowed from internet culture and visual classification systems (such as cottagecore or vaporwave), signifies that the focus is less on the object itself and more on the feelings, visuals, and atmosphere that those objects evoke. It is not merely a collecting hobby but also a subcultural aesthetic that permeates visual art, photography, fashion, interior design, and digital culture.
The aesthetic typically includes, but is not limited to, toys such as:
Plastic and tin wind-up toys
1950s–1980s dolls (e.g., Barbie, Chatty Cathy)
Action figures from the 1970s–1990s (e.g., G.I. Joe, Star Wars figures)
Wooden toys and puzzles
Vintage plush animals (e.g., Steiff, early Gund toys)
Fisher-Price Little People, Speak & Spell, and educational toys
80s and 90s battery-operated and electronic toys (e.g., Tamagotchi, Game Boy, Polly Pocket)
Board games and card games with retro design
Original packaging and promotional materials

The foundation of Vintage Toycore is inseparable from the post-World War II consumer boom and the golden age of industrial toy production. The late 1940s to the 1980s saw a transformation in toy manufacturing, driven by mass production, the rise of plastics, television advertising, and the globalization of children’s media.
1940s–1950s: The post-war era introduced affordable mass-market toys. Companies like Hasbro, Mattel, and Fisher-Price emerged or rose to prominence. Toys such as tin robots, wood-and-metal trains, and early plastic dolls became staples of childhood.
1960s–1970s: This period brought increased sophistication in toy design and marketing. Action figures such as G.I. Joe (1964) and Barbie’s continued evolution mirrored shifts in gender roles and social expectations. Educational toys and science-themed kits were also popular amid the Space Race.
1980s–1990s: Often viewed as a peak in toy culture, this era introduced highly merchandised toy lines tied to TV shows and films, such as Transformers, My Little Pony, Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, and He-Man. The rise of Japanese imports like Tamagotchi and early video games contributed to the broadening of what could be considered a "toy." Bright colors, molded plastics, and techno-optimism defined this era's toy design.
These decades now serve as the primary reservoir of inspiration and material for Vintage Toycore, which values the visual language and emotional resonance of these eras' toys.

The aesthetic of Vintage Toycore is defined by specific visual, auditory, and tactile markers, often evoking a synesthetic response that blends sight, memory, and emotion.
Vintage Toycore frequently uses:
Muted pastels and saturated primaries (especially in 1950s and 60s designs)
Neon and synthetic hues (typical of 1980s and early 90s toys)
Off-white plastic yellowing from age
Patterns reminiscent of early box art and branding
Plastic is a dominant medium—both shiny and matte—used in molded toys and packaging.
Tinplate and wood, more common in earlier toys, represent craftsmanship and durability.
Flocked materials, rubber, and early synthetic fibers are also common, especially in plush toys.
Typography often includes bubble letters, blocky sans-serifs, or hand-drawn fonts used in toy packaging and early advertisements. Box illustrations from pre-digital printing are prized for their charm and distinct style, often featuring optimistic, smiling cartoon children.

One of the defining features of Vintage Toycore is its strong relationship with nostalgia. The psychological term "reminiscence bump" explains why individuals remember and are emotionally attached to media from their early years. Vintage Toycore capitalizes on this effect by evoking feelings of safety, joy, innocence, and familiarity.
The aesthetic also intersects with concepts in developmental psychology, particularly object permanence, transitional objects, and the role of toys in early identity formation. For adults who embrace Vintage Toycore, the toys often serve as symbolic anchors to an idealized or emotionally resonant past.
Furthermore, the aesthetic is sometimes used in therapeutic or introspective contexts, such as memory work, inner child healing, or creative expression.

Vintage Toycore manifests in both physical and digital spaces. Key communities and expressions include:
Vintage Toycore thrives on platforms like Tumblr, Instagram, TikTok, and Pinterest, where users share curated photos of toy collections, aesthetic compositions, or nostalgic reflections. Hashtags like #vintagetoycore or #retrotuna categorize related content.
Vintage toys are frequently traded or displayed by collectors. Condition, packaging, rarity, and provenance are important. Some collectors focus on pristine, museum-quality toys, while others prioritize emotional or aesthetic value regardless of condition.
Photographers often stage vintage toys in elaborate dioramas or surreal scenes. Visual artists and illustrators incorporate toy motifs into pop-surrealist or retro-futurist compositions.
Some embrace Vintage Toycore through clothing styles inspired by 80s and 90s children's fashion, often mixing bright colors, playful patterns, and cartoon motifs. In interior design, the aesthetic appears in pastel-colored shelves, toy displays, and the use of retro furniture, evoking a child's playroom.

From a cultural studies perspective, Vintage Toycore sits at the intersection of consumer history, childhood studies, and design history. It reflects broader societal trends including:
The commodification of nostalgia in late capitalism
The infantilization of adult consumers and the rise of “kidult” culture
The aestheticization of memory and material culture
Eco-critical perspectives on plastic and permanence in consumer goods
Academic work on toys by scholars such as Gary Cross and Steven Mintz also contextualizes toys as windows into shifting cultural values around gender, technology, and the family.

Vintage Toycore overlaps with but is distinct from the following:
Kidcore: Focuses on bright, rainbow-colored designs and childlike motifs, often blending new and old. Less historically anchored.
Weirdcore/Dreamcore: May incorporate unsettling or surreal toy imagery but aims for liminality and disorientation rather than nostalgia.
Nostalgiacore: A broader term encompassing all nostalgia-themed aesthetics, including Vintage Toycore as a subset.
Cottagecore/Toylandcore: Occasionally overlaps in terms of vintage sensibility, but focuses more on natural or fairytale elements rather than mid-century consumer culture.

Some critics argue that Vintage Toycore, like other nostalgia-driven movements, risks sanitizing or idealizing the past. Issues include:
Cultural erasure: Emphasis on Western toy design can marginalize toys and childhood experiences from non-Western or marginalized communities.
Environmental critique: Many vintage toys are made from plastics and synthetic materials with long-lasting ecological impacts.
Consumerism: The aesthetic’s focus on collection and ownership can reinforce consumerist values under the guise of nostalgia.
Nonetheless, many within the community seek to balance appreciation with critical awareness, viewing the aesthetic as a way to re-contextualize past artifacts in more mindful and creative ways.

Vintage Toycore represents a deep and multifaceted engagement with the past—one that blends material culture, emotional memory, and artistic expression. It offers a lens through which to view not only the toys themselves but also the societies that created and cherished them. As both an aesthetic and cultural movement, it continues to evolve in conversation with technology, memory, and the timeless desire to revisit the magic of early play.
#vintage toycore#toycore#vintage aesthetic#nostalgiacore#retro aesthetic#kidcore#vintage toys#80s toys#90s toys#70s toys#vintage design#childhood nostalgia#nostalgic vibes#retro toys#pastelcore#analog vibes#old school toys#collectibles#vintage collectibles#plastic nostalgia#toy aesthetic#whimsicalcore#retro culture#nostalgic art#vintage kawaii#cute vintage#toy museum#retro childhood#toy photography#sentimental aesthetic
5 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! I just found your page, love your work! I do a bit of lino printing and really enjoy it. I want to start printing on fabric but not sure how to transition.. What inks do I need, do I need to start using wood blocks, and how do I go about that, etc?
Any info or tips would be so appreciated :)
Hey, thanks!
Absolutely I can offer some tips for fabric printing! I also answered an ask about fabric printing a while back and there might be some info in there that you’ll find useful - https://www.tumblr.com/saltedsnailstudio/729384076745850882/how-do-you-print-your-linocuts-so-beautifully-on
So first off I would say don’t bother switching to wood for fabric printing. Linoleum does great! And, honestly, so does rubber. I don’t personally work with rubber/ez-cut style blocks often because I prefer unmounted battle ship grey lino, but it has been my experience that soft rubber blocks are easier to print onto fabric if you’re printing by hand. I recommend sticking with whatever blocks you like & are comfortable working with!
Since you asked about ink specifically: There’s a lot of different inks on the market you can use to make relief prints on fabric that’ll stand up to washing. Speedball has an ink made for fabric printing that some of my print friends swear by, but I personally despise it because I hate the texture of it and find it difficult to work with because it doesn’t have a very long open time. I use cranfield caligo safe wash relief inks for all my printing, both paper and fabric. I love the way it rolls out and it’s works really well for me because it’s oil based but it's water soluble before it dries, so it doesn't require wild solvents or anything to clean up like some other oil based inks do - just vegetable oil and a rag will do to get it off stuff. (careful using vegetable oil on the speedball beige/tan brayers, though, because it'll start to break down their material and make them go tacky if you dont adquately wash them and apply some cornstarch after!!) After the cranfield ink dries, it's no longer water soluble so it'll stay on fabric after washing. Keep in mind though that oil inks take ages to dry - I just hang my fabric prints up and leave them alone for a good two weeks, which might be overkill. When they're dry, I hit them with a hot clothes iron to help heat set them a bit before I wash them in cold water. I don't know if this actually does anything or is the placebo effect, but it really feels like I get less fading with fabric prints that I've heat set. You don't have to use the same ink I do, though I love it so much that I'll prostheletize it for ages, but make sure you do use an ink that's suitable for fabric printing because theres no heartbreak worse than putting all that work in only to watch it wash away.
In my experience, you'll need more ink on your block for printing on fabric than you would if you were printing on thin printmaking papers. You still don't want to just gob it on the block in one go - apply many thin layers to build up the ink on the block rather than trying to go in with a single thick layer.
Now that ink's handled, let's talk about the most important element of fabric printing: the fabric. A lot of folks have ratios of how much natural fibers vs synthetic whatever should be in the fabric you're choosing for relief printing. I'm sure those methods work for choosing good printing fabric, but I'm at a point of having failed enough times to know by look & touch if a fabric will probably work well or not. I really suggest just trying shit out, seeing if it works. I'm lucky enough to have a creative reuse center near me, but if you don't then I suggest snagging garments with fabric you like from thrift stores and cutting them apart if you're trying to make patches. You're looking for something with a nice smooth surface and a closed weave, no gaps showing through the threads. I really like tightly woven linen-y blends, personally. I've also played around on wool felt and have found it to print beautifully. When I first started printing on fabric, I went to the fabric store and got a half yard of duck canvas because that felt sturdy and very "punk" for patches. It was a miserable failure - the weave was too chunky to get really clean prints. Play around, don't spend too much money on fabric, and know that screwing up is a part of the process.
When it comes to actual printing method, I'm limited in my scope of advice for hand printing on fabric because I'm very spoiled and have a lever press from woodzilla that makes the process a lot easier for me. I'm not sure how you burnish your paper prints, but the spoon technique won't work with fabric since it'll move too much. I like to print my paper prints with the paper on top of the block and I reverse that for my fabric prints - the block lies face down on top of the fabric. I've seen folks get great results from laying down their fabric, laying their inked block on top, and then stepping on them to get more pressure than they could get from just pressing with their hands. You need a lot of pressure to get clean fabric prints and that pressure needs to go straight down - you need to be extra careful not to let the block slip, lest it smudge the image. You could try laying a wooden board down on the block before stepping on that if the print is large enough to require it. I've also seen some really ingenious ways of creating book binding/flower pressing style wooden vices on a budget to get the even pressure needed for a print, but this feels rather labor intensive and time consuming to me. Whatever the method, be patient and apply firm downward pressure.
Screw up, rejoice, have fun. If you end up needing any help trouble shooting specific problems as you experiment on fabric, feel free to send me another ask/pics and I'll try to help sus it out!!
29 notes
·
View notes