#Sustainable energy sources
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Little P.Eng. Engineering for Structural and Piping Design in Hydrogen Pilot Plant for Green Energy
In the race to counteract climate change, green energy solutions are imperative. Hydrogen, known as the universe's most abundant element, offers a promising pathway. Pilot plants are experimental setups designed to understand and optimize large-scale industrial processes. Little P.Eng. Engineering has emerged as a pivotal player in realizing this potential by specializing in the structural and piping design for hydrogen pilot plants.
Hydrogen's Role in Green Energy
Hydrogen is not just another energy source; it's a powerful, clean fuel that, when consumed, emits only water as a byproduct. Green hydrogen, especially, is produced using renewable energy sources, ensuring a low-carbon footprint. As governments and industries realize its potential, pilot plants that can produce, store, and utilize hydrogen efficiently are in demand.
Little P.Eng. Engineering’s Expertise
Little P.Eng. Engineering's team specializes in addressing the unique challenges posed by hydrogen in pilot plants. Their structural and piping designs consider factors such as hydrogen's low density, its propensity to embrittle metals, and the safety requirements necessary when working with the element.
Structural Design Considerations
Hydrogen Embrittlement: Hydrogen can make metals brittle, especially under high-pressure conditions. The structural components must be designed with materials resistant to this phenomenon.
Safety Measures: Hydrogen is flammable. Incorporating explosion-proof structures, safe zones, and preventive measures against accidental leaks is paramount.
Modularity: As pilot plants are often experimental setups, flexibility and modularity in design allow for changes based on the evolving understanding of the process.
Piping Design Considerations
Material Selection: Given hydrogen's small molecule size, it can easily leak through many materials. Piping must be constructed with materials that prevent leakage and are resistant to embrittlement.
Pressure Challenges: Hydrogen storage and transport require high-pressure conditions. The piping system must handle these pressures, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Temperature Factors: Liquid hydrogen storage needs extremely low temperatures. This necessitates designs that can handle thermal stresses and expansion-contraction challenges.
Safety Valves and Monitoring Systems: Real-time monitoring of the hydrogen flow, pressure, and potential leaks are essential. Incorporating advanced monitoring systems and safety valves ensures timely detection and mitigation of any risks.
Applications in Green Energy
Hydrogen pilot plants are not just limited to producing hydrogen. They also focus on:
Storage: Efficiently storing hydrogen is a challenge. Pilot plants explore solutions like high-pressure gas storage or cryogenic liquid storage.
Power Generation: Pilot plants test fuel cells and other means to convert hydrogen back into electricity.
Integration with Other Renewable Sources: Connecting hydrogen production with wind, solar, and hydroelectric power sources ensures a continuous energy supply, even when these sources aren't generating power.
Green Mobility: Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are on the rise. Pilot plants play a pivotal role in researching and optimizing hydrogen production, storage, and refueling stations for these vehicles.
Advancing the Future
Little P.Eng. Engineering's commitment to green energy is evident in its consistent research and innovation in structural and piping designs. By regularly updating their designs based on feedback from pilot plants, they ensure safety, efficiency, and scalability for large-scale hydrogen production.
The company also collaborates with universities, research institutions, and industries to stay at the forefront of technology. Such partnerships help in the exchange of ideas and the rapid adoption of best practices.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While the potential of hydrogen as a green energy source is immense, there are challenges:
Economic Feasibility: Bringing down the costs associated with hydrogen production, storage, and usage is essential for its mainstream adoption.
Scalability: While pilot plants offer invaluable insights, scaling these solutions to meet global energy demands requires further research and innovations.
Public Awareness and Acceptance: For hydrogen to be widely adopted, both as an energy storage medium and a fuel, public understanding and acceptance of its benefits and safety are crucial.
Little P.Eng. Engineering, with its expertise and dedication, is poised to address these challenges, turning them into opportunities for a greener future.
Conclusion
As we grapple with the urgency of transitioning to green energy solutions, hydrogen emerges as a beacon of hope. With its abundant availability and potential for clean energy generation, it can revolutionize the energy landscape. Companies like Little P.Eng. Engineering, through their specialized structural and piping designs, play a pivotal role in this transition. As the world moves towards a sustainable future, the role of such innovators becomes even more significant.
Tags:
Meena Rezkallah
Little P.Eng. Engineering
Structural design
Energy efficiency
Engineering expertise
Hydrogen pilot plant
Green energy
Piping design
Sustainable energy sources
Hydrogen storage
Hydrogen transportation
Structural stability
Pressure-relief systems
Safety mechanisms
Hydrogen production
Electrolysis
Advanced simulations
Material embrittlement
Leak prevention
Optimal hydrogen flow
Seismic resilience
Weather-resistant structures
Modular designs
Renewable energy
Zero carbon emissions
Advanced safety
North American energy transition
Environmental consciousness
Hydrogen infrastructure
Hydrogen diffusivity
Hydrogen Production Plant Design
Engineering Services
Structural Engineering Consultancy
Located in Calgary, Alberta; Vancouver, BC; Toronto, Ontario; Edmonton, Alberta; Houston Texas; Torrance, California; El Segundo, CA; Manhattan Beach, CA; Concord, CA; We offer our engineering consultancy services across Canada and United States. Meena Rezkallah.
#Meena Rezkallah#Little P.Eng. Engineering#Structural design#Energy efficiency#Engineering expertise#Hydrogen pilot plant#Green energy#Piping design#Sustainable energy sources#Hydrogen storage#Hydrogen transportation#Structural stability#Pressure-relief systems#Safety mechanisms#Hydrogen production#Electrolysis#Advanced simulations#Material embrittlement#Leak prevention#Optimal hydrogen flow#Seismic resilience#Weather-resistant structures#Modular designs#Renewable energy#Zero carbon emissions#Advanced safety#North American energy transition#Environmental consciousness#Hydrogen infrastructure#Hydrogen diffusivity
0 notes
Text
Embrace the Power of Sustainable Energy Sources: A Greener Future Awaits
Introduction to Sustainable Energy Sources
Sustainable energy sources are the key to a cleaner, more environmentally friendly future. These sources harness the Earth's natural processes to generate energy without depleting finite resources or causing harmful emissions. By adopting sustainable energy sources, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable and vibrant planet for generations to come.
Exploring the World of Sustainable Energy
1. Solar Energy: Dive into the heart of sustainability with solar energy, harnessing the power of the sun's rays to generate electricity and heat. Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into clean energy for your home or business.
2. Wind Power: Explore the beauty of wind power, where wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. Wind farms offer a renewable and emission-free alternative to traditional energy sources.
3. Hydropower: Delve into the realm of hydropower, where the energy of flowing water is converted into electricity. Hydropower plants utilize the force of rivers and streams to create a continuous and sustainable energy source.
Why Choose Sustainable Energy Sources?
1. Environmental Impact: Embracing sustainable energy sources reduces greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and dependence on fossil fuels, leading to a healthier planet and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
2. Energy Independence: By choosing sustainable energy sources, you become less reliant on finite resources like coal, oil, and gas, contributing to energy security and stability.
3. Cost Savings: Supporting sustainable energy sources can lead to long-term cost savings as you generate your own clean energy and reduce reliance on fluctuating fuel prices.
4. Innovation and Advancement: Your decision to adopt sustainable energy sources fuels innovation and technological advancement in the renewable energy sector, driving economic growth and job creation.
5. Global Responsibility: Choosing sustainable energy sources aligns with your responsibility as a global citizen to protect the environment, preserve natural resources, and ensure a sustainable future for all.
Power Your Life with Sustainable Energy Sources
For a deeper understanding, explore the Wikipedia article on Renewable Energy.
Elevate your commitment to sustainability with our carefully curated selection of sustainable energy resources, expert insights, and actionable steps. Each choice you make towards sustainable energy sources contributes to a world powered by clean, renewable, and abundant energy.
Discover Our Sustainable Energy Solutions
Empower your journey towards a greener future with our comprehensive resources, guiding you through the adoption of sustainable energy sources, reducing your carbon footprint, and contributing to a more sustainable planet. Choose sustainable energy sources today and be a catalyst for positive change in the energy landscape.
"For a comprehensive look at Health Products, browse our website extensive collection of articles."
0 notes
Text
i miss when i could be excited about new technological innovations instead of going "wow how will rich people exploit poor people and cut moral corners with this."
#op#like genuinely one of my most controversial opinions is that generative ai could literally be fine#if the goal with it werent to put artists out of jobs and steal from them.#my problems with it are exclusively the environmental impact and theft.#if more money was invested into sustainable energy sources and artists the ai was trained on were properly compensated#it would actually be really cool.#the fact that technology has come far enough to where a computer can look at a picture and describe it for you is fucking awesome.#the amount of accessibility features that could incorporate that would be groundbreaking.#but oh my god. the rich people. the rich people the rich people.#politics
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
#tech#TechnologyAI for sustainability#circular economy#electric vehicles#geothermal energy#green buildings#hydropower#Innovative technologies#Internet of Things#precision farming#renewable energy sources#smart grids#solar power#sustainable future#sustainable materials#sustainable transportation#vertical farming#wind energy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Don't get me wrong, the fusion energy breakthrough is really cool from the angle of, like, scientific progress, but...


#...but it'd take approx. 13 billion of these fusion reactions to equal the output of hoover dam... for *one* year#all im saying is that WE ALREADY HAVE SOLUTIONS TO FOSSIL FUEL DEPENDENCY#solar and wind and hydroelectric could power the whole damn planet if we wanted#the solution to fossil fuel dependency is raidcal and sweeping reform to sustainable energy sources across the globe#nuclear fusion#fusion#science news#climate change#climate crisis#sustainable energy
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
So I think I found the right article.
The thumbnail quote in the original tweet is the second paragraph:

And like, unless I'm missing something, the article ... isn't talking about grids getting damaged because of overload. I do think that what @crazy-pages said is correct, because I've heard parts of it often enough before, but the article is pretty much just talking about market economics. Do I have the wrong article?
MIT Tech Review has limited free articles, so I've copied and pasted the full text below the cut. It isn't a super long read.
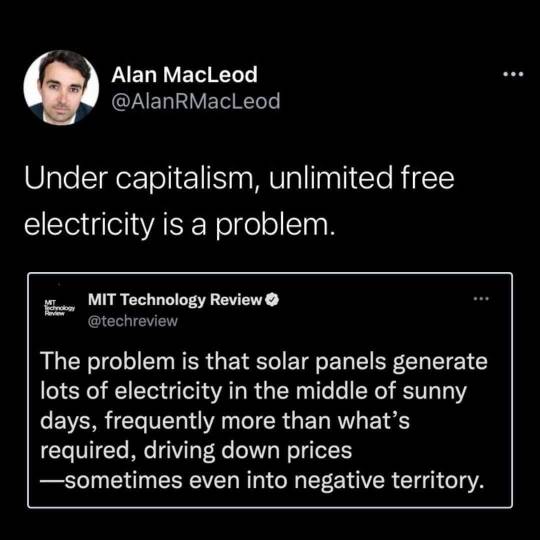
A few lonely academics have been warning for years that solar power faces a fundamental challenge that could halt the industry’s breakneck growth. Simply put: the more solar you add to the grid, the less valuable it becomes.
The problem is that solar panels generate lots of electricity in the middle of sunny days, frequently more than what’s required, driving down prices—sometimes even into negative territory.
Unlike a natural gas plant, solar plant operators can���t easily throttle electricity up and down as needed, or space generation out through the day, night and dark winter. It’s available when it’s available, which is when the sun is shining. And that’s when all the other solar plants are cranking out electricity at maximum levels as well.
A new report finds that California, which produces one of the largest shares of solar power in the world, is already acutely experiencing this phenomenon, known as solar value deflation.
The state’s average solar wholesale prices have fallen 37% relative to the average electricity prices for other sources since 2014, according to the Breakthrough Institute analysis, which will be published on July 14. In other words, utilities are increasingly paying solar plants less than other sources overall, due to their fluctuating generation patterns.
Wholesale prices are basically the amount that utilities pay power plants for the electricity they deliver to households and businesses. They shift throughout the day and year, edging back up for solar operators during the mornings, afternoons and other times when there isn’t excess supply. But as more solar plants come online, the periods of excess supply that drive down those costs will become more frequent and more pronounced.
Lower prices may sound great for consumers. But it presents troubling implications for the world’s hopes of rapidly expanding solar capacity and meeting climate goals.It could become difficult to convince developers and investors to continue building ever more solar plants if they stand to make less money or even lose it. In fact, California construction has already been flat since 2018, the study notes. But the state will need the industry to significantly ramp up development if it hopes to pull off its ambitious clean energy targets.
This could soon become a broader problem as well.
“California is a little sneak peek of what is in store for the rest of the world as we dramatically scale up solar,” says Zeke Hausfather, director of climate and energy at the Breakthrough Institute, and author of the report.
That’s because while solar accounts for about 19% of the electricity California generates, other regions are rapidly installing photovoltaic panels as well. In Nevada and Hawaii, for instance, the share of solar generation stood at around 13% in 2019, the study found. The levels in Italy, Greece and Germany were at 8.6%, 7.9% and 7.8%, respectively.
The race
So far, heavy solar subsidies and the rapidly declining cost of solar power has offset the falling value of solar in California. So long as it gets ever cheaper to build and operate solar power plants, value deflation is less of a problem.
But it’s likely to get harder and harder to pull off that trick, as the state’s share of solar generation continues to climb. If the cost declines for building and installing solar panels tapers off, California’s solar deflation could pull ahead in the race against falling costs as soon as 2022 and climb upward from there, the report finds. At that point, wholesale pricing would be below the subsidized costs of solar in California, undermining the pure economic rationale for building more plants, Hausfather notes.The state’s SB 100 law, passed in 2018, requires all of California’s electricity to come from “renewable and zero-carbon resources” by 2045. By that point, some 60% of the state’s electricity could come from solar, based on a California Energy Commission model.
The Breakthrough study estimates that the value of solar–or the wholesale average price relative to other sources–will fall by 85% at that point, decimating the economics of solar farms, at least as California’s grid exists today.
How do we fix it?
There are a variety of ways to ease this effect, though no single one is likely a panacea.The solar sector can continue trying to find ways to push down solar costs, but some researchers have argued it may require shifting to new materials and technologies to get to the dirt-cheap levels required to outpace value deflation.
Grid operators and solar plant developers can add more energy storage—and increasingly they are.Researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory highlighted similarly declining solar values in California in a broader study published in Joule last month. But they also noted that numerous modeling studies showed that the addition of low cost storage options, including so called hybrid plants coupled with lithium-ion batteries, eases value deflation and enables larger shares of renewables to operate economically on the grid.
There are likely limits to this, however, as study after study finds that storage and system costs rise sharply once renewables provide the vast majority of electricity on the grid.
States or nations could also boost subsidies for solar power; add more long-distance transmission lines to allow regions to swap clean electricity as needed; or incentivize customers to move energy use to times of day that better match with periods of high generation.
The good news is that each of these will help to ease the transition to clean electricity sources in other ways as well, but they’ll also all take considerable time and money to get underway.
The California solar market offers a reminder that the climate clock is ticking.
This story was updated to add details from the Joule study.
#I don't intend this as any kind of callout#I just want to make sure we're actually reading and citing our sources#environmentalism#sustainability#solar panels#renewable energy#economics#uwo convo
71K notes
·
View notes
Text




HAPPY NEW YEAR 2025
As we bid farewell to the past year and embrace the dawn of 2025, it's time to reflect on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. The start of a new year is a chance for fresh beginnings, setting goals, and making positive changes in our lives. Let's explore what the year 2025 has in store for us.
What Trends Will Shape 2025?
In the year 2025, we can expect to see significant advancements in technology, healthcare, sustainability, and more. With the rise of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and renewable energy sources, the world is poised for a transformative year ahead. According to experts, the global economy is projected to grow by X% in 2025, driven by innovation and digitalization.
How Can You Make the Most of 2025?
To make the most of the opportunities that 2025 presents, it's essential to set clear goals, prioritize self-care, and stay adaptable in the face of change. Whether you're looking to advance your career, improve your health, or deepen your relationships, the key is to take proactive steps towards your aspirations. Studies show that people who set specific goals are X% more likely to achieve success compared to those who don't.
What Challenges Might Arise in 2025?
While the new year brings promise and excitement, it also comes with its own set of challenges. From geopolitical tensions to environmental concerns, individuals and communities will need to navigate various obstacles in 2025. It's crucial to stay informed, resilient, and proactive in addressing these challenges to create a better future for all.
How Can You Stay Positive and Resilient in 2025?
Staying positive and resilient in the face of adversity is key to thriving in 2025. Practicing mindfulness, cultivating a strong support network, and focusing on gratitude can help boost mental well-being and emotional resilience. Research shows that individuals who practice gratitude daily experience a X% increase in overall happiness and well-being.
As we embark on this new chapter, let's embrace the opportunities, overcome the challenges, and strive for a brighter future in 2025. Wishing you a happy and prosperous new year!
Welcome to a brand new year, full of endless possibilities and opportunities! As we step into 2025, it's the perfect time to reflect on the past year and set intentions for the year ahead. Whether you're looking to make big changes or simply want to embrace a fresh start, the new year is the perfect time to do so.
Setting Meaningful Goals
One of the best ways to kick off the new year is by setting meaningful goals for yourself. Take some time to think about what you want to achieve in the coming months and create a plan to make it happen. Whether it's focusing on personal growth, improving your health, or advancing in your career, setting goals can help you stay motivated and focused throughout the year.
Embracing Positive Changes
2025 is a blank canvas waiting to be filled with positive changes and new experiences. Embrace the opportunity to try new things, step out of your comfort zone, and challenge yourself to grow. Whether it's picking up a new hobby, traveling to a new destination, or making new friends, the new year is the perfect time to embrace change and welcome new opportunities into your life.
Practicing Gratitude
As you embark on this new year, don't forget to practice gratitude for all the blessings in your life. Take time each day to reflect on the things you are grateful for, whether it's your health, your loved ones, or the simple joys in life. Cultivating a mindset of gratitude can help you stay positive and focused on the good, even during challenging times.
Spreading Kindness
One of the best ways to make the world a better place in 2025 is by spreading kindness wherever you go. Whether it's a small act of kindness towards a stranger, volunteering in your community, or simply being there for a friend in need, every act of kindness has the power to make a difference. Let's make 2025 a year filled with compassion, empathy, and generosity towards others.
As you embark on this new year, remember that the possibilities are endless and the future is bright. Embrace the opportunities that come your way, stay true to yourself, and make 2025 a year to remember. Happy New Year!
#As we bid farewell to the past year and embrace the dawn of 2025#it's time to reflect on the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. The start of a new year is a chance for fresh beginnings#setting goals#and making positive changes in our lives. Let's explore what the year 2025 has in store for us.#What Trends Will Shape 2025?#In the year 2025#we can expect to see significant advancements in technology#healthcare#sustainability#and more. With the rise of artificial intelligence#the Internet of Things#and renewable energy sources#the world is poised for a transformative year ahead. According to experts#the global economy is projected to grow by X% in 2025#driven by innovation and digitalization.#How Can You Make the Most of 2025?#To make the most of the opportunities that 2025 presents#it's essential to set clear goals#prioritize self-care#and stay adaptable in the face of change. Whether you're looking to advance your career#improve your health#or deepen your relationships#the key is to take proactive steps towards your aspirations. Studies show that people who set specific goals are X% more likely to achieve#What Challenges Might Arise in 2025?#While the new year brings promise and excitement#it also comes with its own set of challenges. From geopolitical tensions to environmental concerns#individuals and communities will need to navigate various obstacles in 2025. It's crucial to stay informed#resilient#and proactive in addressing these challenges to create a better future for all.#How Can You Stay Positive and Resilient in 2025?
0 notes
Text
Green Ammonia Market Statistics, Segment, Trends and Forecast to 2033
The Green Ammonia Market: A Sustainable Future for Agriculture and Energy
As the world pivots toward sustainable practices, the green ammonia market is gaining momentum as a crucial player in the transition to a low-carbon economy. But what exactly is green ammonia, and why is it so important? In this blog, we'll explore the green ammonia market, its applications, benefits, and the factors driving its growth.
Request Sample PDF Copy:https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/green-ammonia-market/1359
What is Green Ammonia?
Green ammonia is ammonia produced using renewable energy sources, primarily through the electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen, which is then combined with nitrogen from the air. This process eliminates carbon emissions, setting green ammonia apart from traditional ammonia production, which relies heavily on fossil fuels.
Applications of Green Ammonia
Agriculture
One of the most significant applications of green ammonia is in agriculture. Ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers, and its sustainable production can help reduce the carbon footprint of farming. By using green ammonia, farmers can produce food more sustainably, supporting global food security while minimizing environmental impact.
Energy Storage
Green ammonia can also serve as an effective energy carrier. It can be synthesized when there is surplus renewable energy and later converted back into hydrogen or directly used in fuel cells. This capability makes it an attractive option for balancing supply and demand in renewable energy systems.
Shipping Fuel
The maritime industry is under increasing pressure to reduce emissions. Green ammonia has emerged as a potential zero-emission fuel for ships, helping to decarbonize one of the most challenging sectors in terms of greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of Green Ammonia
Environmental Impact
By eliminating carbon emissions during production, green ammonia significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional ammonia. This aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and achieve sustainability goals.
Energy Security
Investing in green ammonia can enhance energy security. As countries strive to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, green ammonia offers a renewable alternative that can be produced locally, minimizing reliance on imported fuels.
Economic Opportunities
The growth of the green ammonia market presents numerous economic opportunities, including job creation in renewable energy sectors, research and development, and new supply chain dynamics. As demand increases, investments in infrastructure and technology will drive innovation.
Factors Driving the Growth of the Green Ammonia Market
Regulatory Support
Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives to promote the adoption of green technologies. These regulations often include subsidies for renewable energy production and carbon pricing mechanisms, making green ammonia more competitive.
Rising Demand for Sustainable Solutions
With consumers and businesses becoming increasingly aware of their environmental impact, the demand for sustainable solutions is on the rise. Green ammonia aligns with this trend, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional ammonia.
Advancements in Technology
Ongoing advancements in electrolysis and ammonia synthesis technologies are making the production of green ammonia more efficient and cost-effective. As these technologies mature, they will further enhance the viability of green ammonia in various applications.
Conclusion
The green ammonia market represents a promising avenue for sustainable development across agriculture, energy, and transportation sectors. As technology advances and regulatory support strengthens, green ammonia is poised to become a cornerstone of the global transition to a greener economy. Investing in this market not only contributes to environmental preservation but also opens up new economic opportunities for innovation and growth.
#The Green Ammonia Market: A Sustainable Future for Agriculture and Energy#As the world pivots toward sustainable practices#the green ammonia market is gaining momentum as a crucial player in the transition to a low-carbon economy. But what exactly is green ammon#and why is it so important? In this blog#we'll explore the green ammonia market#its applications#benefits#and the factors driving its growth.#Request Sample PDF Copy:https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/green-ammonia-market/1359#What is Green Ammonia?#Green ammonia is ammonia produced using renewable energy sources#primarily through the electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen#which is then combined with nitrogen from the air. This process eliminates carbon emissions#setting green ammonia apart from traditional ammonia production#which relies heavily on fossil fuels.#Applications of Green Ammonia#Agriculture#One of the most significant applications of green ammonia is in agriculture. Ammonia is a key ingredient in fertilizers#and its sustainable production can help reduce the carbon footprint of farming. By using green ammonia#farmers can produce food more sustainably#supporting global food security while minimizing environmental impact.#Energy Storage#Green ammonia can also serve as an effective energy carrier. It can be synthesized when there is surplus renewable energy and later convert#Shipping Fuel#The maritime industry is under increasing pressure to reduce emissions. Green ammonia has emerged as a potential zero-emission fuel for shi#helping to decarbonize one of the most challenging sectors in terms of greenhouse gas emissions.#Benefits of Green Ammonia#Environmental Impact#By eliminating carbon emissions during production#green ammonia significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional ammonia. This aligns with global efforts to combat
0 notes
Text
Hey! Today on #malcified, I’d like to share this sketch called #SustainedDisability focused on the #UN #SDGs and corporate #ESG policies that are key drivers of major transformation toward a more #green and #sustainable future. And of course our collective disability, when it comes to over-reliance on fossil-fuel and the awesome machines (#ICE) that run on it.
Disability: a physical or mental condition that limits a person's movements, senses, or activities. - Oxford
Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly being replenished. Renewable energy sources are plentiful and all around us. - UN
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) is shorthand for an investing principle that prioritizes environmental issues, social issues, and corporate governance. - Wiki
Cars, planes, trains: where do CO₂ emissions from transport come from? #OurWorldinData. Link below on quick stats.
https://ourworldindata.org/co2-emissions-from-transport
UN SDG related Goals #SDG3, #SDG9, and #SDG12
https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/topics/sustainabletransport#:~:text=Target%2011.2%20aims%20by%202030,with%20disabilities%20and%20older%20persons.
As the world transitions toward renewable energy to power their daily needs, #Transportation and #Logistics being a major contributor of CO₂ and other toxic emissions that are cause for #pollution, #climatechange, #globalwarming, and other major #naturaldisasters that are increasing threat, exposure, and impact financially and reputationally to businesses, organizations, economies, individuals and communities through the actualization of #PhysicalRisk and #TransitionRisk, it’s imperative that #PolicyMakers act with prudence and #Policymeasures at National Government Level, Industry and Sectoral Level, and at individual Business levels are implemented and enforced without delay.
#TonefromtheTop is always an essential driver for change and when leading global #MNCs and #Consulting firms pave the way to this necessary transition, raise awareness and enable transformation by implementing Policies and Initiatives that accelerate the culture of transition, the effects cascade throughout the sector creating an environment of #peerpressure, while enhancing business Reputation, Stakeholder engagement, Employee pride and ownership, Share values, Top and Bottom Lines, Goodwill and Asset Valuations while protecting and preventing a #HotHouseEarthScenario in the long run.
https://www.stockholmresilience.org/research/research-news/2018-08-06-planet-at-risk-of-heading-towards-hothouse-earth-state.html
#oneness#within is without#return to the source#wholeness#artwork#cartooning#nature#painting#malcified#awareness#hot house earth scenario#Sustainable Socioeconomic Pathways#SSPs#UN#sdg12#SDG13#SDG9#HR#Leadership#Transformation#electric vehicles#renewable energy#sustainability
1 note
·
View note
Text
Imaginary burger isn't vegan because it's made of bioelectricity and therefore an animal product
I got so stoned last night i visualized myself enjoying a huge bowl of mac and cheese so vividly that i forgot to eat dinner bc i thought i already ate
#although one could argue that since it's consentually sourced bioelectricity it is in fact vegan#but then there are sustainability issues. Imaginary burger does not give back the energy spent to ''eat'' it like Real burger would#idk
95K notes
·
View notes
Text
Lithium and Copper: The Metals That Will Shape the Future
🔋🌍 Lithium and copper are set to revolutionize the economy as the demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy soars! 🌱✨ With innovations in battery tech and sustainable materials, the future looks bright for clean energy.
In the coming years, certain metals are poised to fundamentally change the global economy—foremost among them are lithium and copper. These two raw materials are becoming increasingly indispensable for the energy and transportation industries as the world shifts towards renewable energy and electric vehicles. Lithium: The Fuel of the Energy Transition Lithium plays a central role in the…
#battery technology innovations#climate change solutions#copper demand forecast#eco-friendly materials#electric vehicle batteries#electrification of transportation#energy efficiency technologies#energy transition strategies#environmental impact of mining#future of electrification#innovations in renewable energy#Lithium market trends#Make money online#market analysis of lithium#metals for clean energy#nickel applications in batteries#Online business#Passive income#perovskite solar cells#renewable energy investment#renewable energy sources#sustainable metals#sustainable resource management
0 notes
Text
Leading the Future with Structural and Piping Design for Hydrogen Pilot Plants in the Green Energy
As the world gradually transitions towards sustainable energy sources, hydrogen stands out as a beacon of hope in the quest for green energy. The intricacies involved in harnessing hydrogen's power necessitate advanced pilot plants equipped with state-of-the-art designs. Enter Little P.Eng. Engineering, the torchbearer of structural and piping design for hydrogen pilot plants, pushing the boundaries of innovation and safety in North America.
The Growing Importance of Hydrogen in Green Energy
With zero carbon emissions when burned, hydrogen promises a cleaner future, especially when produced through green methods like electrolysis of water using renewable energy. The challenge lies in efficiently storing and transporting hydrogen, which requires meticulously designed infrastructure. This is where pilot plants come into play, acting as the testing grounds for groundbreaking technologies and methodologies.
Understanding the Role of Structural and Piping Design
In any hydrogen pilot plant, the importance of structural and piping design cannot be overstated:
Structural Design: Ensures the physical stability and safety of the plant. With hydrogen's volatile nature, the infrastructure must be robust enough to withstand pressures, prevent leaks, and guarantee longevity.
Piping Design: Deals with the intricate network of tubes and pipes that transport hydrogen and other fluids within the plant. An optimized piping system reduces losses, increases efficiency, and ensures the safe transportation of hydrogen.
Little P.Eng. Engineering's Expertise in Action
1. Customization: Every pilot plant has unique needs. Little P.Eng. Engineering’s team initiates a thorough groundwork phase, understanding the plant's specific requirements, and then tailoring designs to fit those needs perfectly.
2. Advanced Simulations: Before any design is finalized, it undergoes rigorous simulations to test its viability, strength, and efficiency. This ensures that any potential issues are addressed long before implementation.
3. Safety Above All: Given hydrogen's highly flammable nature, safety is paramount. Designs incorporate advanced safety mechanisms, pressure-relief systems, and fail-safes, ensuring the utmost protection for both the workers and the environment.
4. Seamless Integration: Little P.Eng. Engineering’s designs aren’t just about functionality – they're about integration. The designs ensure that all components of the pilot plant work in harmony, enhancing the overall operational efficiency.
A Look at Piping in Detail
Hydrogen, with its low viscosity and high diffusivity, poses unique challenges:
Material Selection: Hydrogen can lead to material embrittlement. Little P.Eng. chooses materials that resist this phenomenon, ensuring the pipes remain durable even under intense hydrogen flow.
Leak Prevention: With advanced sealing technologies and meticulous design, the piping systems are virtually leak-proof, preventing hydrogen wastage and potential hazards.
Optimal Flow: The piping designs ensure that hydrogen flows at optimal rates, reducing energy consumption and maximizing efficiency.
The Structural Marvels of Little P.Eng. Engineering
When it comes to structural design, it's a balance of strength, flexibility, and longevity:
Earthquake Resilience: Many areas in North America are prone to seismic activities. Designs from Little P.Eng. factor in these challenges, ensuring that structures can withstand tremors without sustaining damage.
Weather Resistance: Whether it's the freezing Canadian winters or the blistering heat of the southern USA, the structures are built to weather it all, quite literally.
Modularity: As the hydrogen industry evolves, pilot plants might need upgrades. Little P.Eng.'s modular designs ensure that expansions and modifications can be made without major overhauls.
Conclusion
The green energy revolution is upon us, and hydrogen is at its forefront. As pilot plants become the crucibles of innovation in this sector, having the right structural and piping design is crucial. Little P.Eng. Engineering, with its blend of expertise, innovation, and commitment to sustainability, is not just a participant but a leader in this transition towards a cleaner future. Their designs for hydrogen pilot plants stand as testaments to what is possible when engineering prowess meets environmental consciousness.
Tags:
Little P.Eng. Engineering
Structural design
Energy efficiency
Engineering expertise
Hydrogen pilot plant
Green energy
Piping design
Sustainable energy sources
Hydrogen storage
Hydrogen transportation
Structural stability
Pressure-relief systems
Safety mechanisms
Hydrogen production
Electrolysis
Advanced simulations
Material embrittlement
Leak prevention
Optimal hydrogen flow
Seismic resilience
Weather-resistant structures
Modular designs
Renewable energy
Zero carbon emissions
Advanced safety
North American energy transition
Environmental consciousness
Hydrogen infrastructure
Hydrogen diffusivity
Cleaner future
Hydrogen Production Plant Design
Engineering Services
Structural Engineering Consultancy
Located in Calgary, Alberta; Vancouver, BC; Toronto, Ontario; Edmonton, Alberta; Houston Texas; Torrance, California; El Segundo, CA; Manhattan Beach, CA; Concord, CA; We offer our engineering consultancy services across Canada and United States. Meena Rezkallah.
#Little P.Eng. Engineering#Structural design#Energy efficiency#Engineering expertise#Hydrogen pilot plant#Green energy#Piping design#Sustainable energy sources#Hydrogen storage#Hydrogen transportation#Structural stability#Pressure-relief systems#Safety mechanisms#Hydrogen production#Electrolysis#Advanced simulations#Material embrittlement#Leak prevention#Optimal hydrogen flow#Seismic resilience#Weather-resistant structures#Modular designs#Renewable energy#Zero carbon emissions#Advanced safety#North American energy transition#Environmental consciousness#Hydrogen infrastructure#Hydrogen diffusivity#Cleaner future
0 notes
Text
The Macadamia Shell Controversy in Kenya
The Macadamia Shell Association of Kenya has raised concerns about the potential importation of raw macadamia nuts from other countries. The association argues that this move could negatively impact local industries that rely on macadamia shells as a fuel source. According to the association, macadamia shells are a crucial byproduct of the macadamia processing industry in Kenya. These shells are…
#air pollution#carbon emissions#diversification#domestic industries#economic benefits#environmental impact#environmental regulations#foreign exchange earnings#fuel source#government regulation#greenhouse gases#import ban#job creation#kenya#land use#macadamia industry#macadamia nuts#macadamia shell association#macadamia shells#market risk#particulate matter#pollution control measures#quality standards#raw macadamia nuts#renewable energy#research and development#Small-scale farmers#sustainable farming practices#sustainable fuel#trade regulations
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Solar, Wind and Tidal: 3 Sustainable Renewable Energy Sources #cleanener...
0 notes
Text
Innovative Technologies for a Sustainable Future
Introduction
In an age where climate change and environmental degradation pose significant challenges, innovative technologies offer promising solutions for a sustainable future. From renewable energy sources to smart grids and sustainable materials, these advancements are not only mitigating environmental impacts but also paving the way for a greener and more resilient planet. In this comprehensive guide, we explore various innovative technologies that contribute to sustainability and how they are revolutionizing different sectors. Read to continue
#Tech Trends#TagsAI for sustainability#circular economy#electric vehicles#geothermal energy#green buildings#hydropower#Innovative technologies#Internet of Things#precision farming#renewable energy sources#smart grids#solar power#sustainable future#sustainable materials#sustainable transportation#vertical farming#wind energy#Technology#Science#business tech#Adobe cloud#Trends#Nvidia Drive#Analysis#Tech news#Science updates#Digital advancements#Tech trends#Science breakthroughs
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Life in the near future will be driven by advanced technology. Smart hom...
#youtube#Life in the near future will be driven by advanced technology. Smart homes AI assistants and sustainable energy sources will become common.
0 notes