#Sustainable Sourcing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Growth capitalism is a deranged fantasy for lunatics.
Year 1, your business makes a million dollars in profit. Great start!
Year 2, you make another million. Oh no! Your business is failing because you didn't make more than last year!
Okay, say year 2 you make $2 mil. Now you're profitable!
Then year 3 you make $3 mil. Oh no! Your business is failing! But wait, you made more money than last year right? Sure, but you didn't make ENOUGH more than last year so actually your business is actively tanking! Time to sell off shares and dismantle it for parts! You should have made $4 mil in profit to be profitable, you fool!
If you're not making more money every year by an ever-increasing exponent, the business is failing!
Absolute degenerate LUNACY
#eat the rich#fuck capitalism#capitalists make great mulch#they're a sustainable and eco-friendly source of pig feed and fertilizer#blog together queue alone
52K notes
·
View notes
Text
Chandan Perfume: A Fragrant Journey Through Cultures
Have you ever caught a whiff of a fragrance that transported you to another world? Chandan, or sandalwood, is one such fragrance that weaves a rich tapestry of history, spirituality, and culture. This scent is more than just a delightful aroma; it carries centuries of tradition and significance across various cultures. In this post, I invite you to join me on a fragrant journey as we explore the history, cultural importance, and contemporary uses of Original Chandan Perfume.

The History of Chandan Perfume
Ancient Roots
The story of chandan dates back thousands of years. Ancient texts, such as the Vedas, reference sandalwood as a sacred substance. It was revered not just for its enchanting scent but also for its purported spiritual and medicinal properties. Used in rituals and ceremonies, chandan became an essential part of spiritual life in many cultures. Imagine walking into a temple filled with the calming aroma of sandalwood incense, enveloping you in its soothing embrace.
Chandan in Trade
Chandan’s journey is also a tale of trade. Historically, sandalwood was transported across continents, fostering cultural exchanges. Trade routes opened up avenues for sharing not just sandalwood but also the stories and rituals tied to it. From India to the Middle East and beyond, the scent of chandan became a symbol of connection and unity, enriching lives across cultures.
Chandan in Different Cultures
Indian Culture
In India, chandan holds a special place. It’s woven into the fabric of rituals, from daily prayers to grand ceremonies. Hindus use chandan paste to mark their foreheads and offer it during worship, symbolizing purity and devotion. It’s believed that the aroma of chandan enhances focus during meditation, helping one connect with the divine.
In Ayurveda, chandan is cherished for its cooling properties and is often used in skincare products. Imagine treating yourself to a soothing chandan-infused lotion after a long day; it’s like giving your skin a breath of fresh air.
Middle Eastern Influence
In the Middle East, the allure of chandan is just as profound. Here, it has influenced traditional perfumery, becoming a staple in creating luxurious scents. Stories from the Islamic Golden Age highlight chandan’s role in rituals and personal grooming, showcasing how this fragrance transcends time and geography.
Southeast Asian Traditions
Southeast Asia, too, celebrates chandan. In countries like Indonesia and Malaysia, it’s an integral part of local customs, often used in traditional ceremonies and festivities. The rich scent of chandan fills the air during celebrations, symbolizing joy and togetherness.
Western Adaptations
In recent years, chandan has made its way into Western perfumery. Its warm, woody notes blend beautifully with floral and citrus scents, creating unique fragrances that appeal to a broad audience. The versatility of Original Chandan Perfume is a testament to its timeless appeal.
The Process of Making Chandan Perfume
Harvesting Sandalwood
Creating Original Chandan Perfume begins with the careful harvesting of sandalwood trees. These trees take years to mature, and responsible sourcing is crucial for sustainability. By choosing ethically sourced sandalwood, we not only preserve the environment but also ensure the quality of the fragrance.
Distillation Techniques
Once harvested, the sandalwood is subjected to distillation, a method that extracts its precious oil. Traditional steam distillation retains the oil’s authenticity, while modern techniques enhance its yield. The result? A pure, aromatic oil that captures the essence of chandan.
Crafting the Perfume
Blending the extracted oil with other fragrances is where the magic happens. Imagine the delicate balance of mixing chandan with floral, woody, and spice notes. Each blend tells a unique story, allowing you to find a scent that resonates with your personal journey.
The Scent Profile of Chandan Perfume
Olfactory Notes
The scent profile of chandan is complex yet comforting. It typically features a warm, creamy, and slightly sweet aroma, with woody undertones. The primary notes of Original Chandan Perfume create a sense of tranquility, while secondary notes can add depth and intrigue.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Did you know that scent can significantly influence our emotions? The aroma of chandan has been associated with calming effects, making it perfect for meditation and relaxation. A simple application of Original Chandan Perfume can evoke feelings of serenity and peace, helping you navigate through your day with grace.
Modern Usage and Trends
Chandan in Contemporary Perfumery
In today’s fragrance market, chandan is experiencing a renaissance. Many perfumers are reimagining traditional blends, incorporating chandan into innovative compositions. It’s a delightful reminder of the past while embracing the present.
Sustainable and Ethical Considerations
As consumers become more conscious of sustainability, the demand for ethically sourced ingredients has risen. Our commitment to quality extends to our Original Chandan Perfume, ensuring that each bottle reflects our dedication to ethical sourcing and sustainability. By choosing our products, you’re not just indulging in a luxurious scent; you’re also supporting responsible practices.
Chandan in Personal Care Products
Beyond perfumes, chandan finds its way into skincare and personal care products. From soothing lotions to refreshing face masks, the benefits of sandalwood are harnessed to enhance your daily routine. Just imagine a luxurious chandan-infused body wash that leaves your skin feeling rejuvenated and fragrant!
How to Incorporate Chandan into Daily Life
Using Chandan Perfume
Integrating Original Chandan Perfume into your daily routine is simple. Apply it to pulse points like your wrists and neck for a long-lasting scent. This way, you carry the enchanting aroma with you throughout the day.
DIY Chandan Products
Feeling adventurous? You can create your own chandan-infused products at home! Try making a soothing body oil by mixing sandalwood oil with a carrier oil. It’s a fantastic way to personalize your fragrance and connect with the tradition of chandan.
Cultural Celebrations
Consider incorporating chandan into your personal rituals. Whether it’s lighting a Chandan incense stick during meditation or using Original Chandan Perfume on special occasions, these small gestures can deepen your connection to this rich heritage.
As we’ve explored, chandan is not just a fragrance; it’s a cultural phenomenon that transcends borders and time. Its history, significance, and modern applications make it a truly unique scent worth celebrating. I encourage you to embark on your own journey with chandan, whether through the mesmerizing allure of Original Chandan Perfume or the calming rituals it inspires.
Let the scent of chandan be your guide, enriching your life with its warm embrace and reminding you of the beautiful tapestry of cultures it represents.
FAQs
What is chandan?
Chandan, or sandalwood, is a fragrant wood known for its warm, woody scent. It’s widely used in perfumes, incense, and traditional rituals.
How is chandan perfume made?
Chandan perfume is made by harvesting sandalwood, extracting its oil through distillation, and blending it with other fragrances.
What are the benefits of chandan?
Chandan is known for its calming properties, making it ideal for meditation and relaxation. It’s also used in skincare for its soothing effects.
How do I use chandan perfume?
Apply chandan perfume to pulse points like your wrists and neck for a lasting scent.
Is chandan sustainable?
Sustainable practices are crucial in sourcing sandalwood. Our Original Chandan Perfume ensures ethical sourcing to protect the environment.
Can I make my own chandan products?
Absolutely! You can create DIY chandan-infused oils or lotions at home using sandalwood oil.
What cultures celebrate chandan?
Chandan is celebrated in Indian, Middle Eastern, and Southeast Asian cultures, often used in rituals and personal care.
What are some popular notes in chandan perfumes?
Chandan perfumes often feature warm, creamy notes with woody undertones, sometimes blended with floral or spice notes for depth.
How does chandan affect mood?
The aroma of chandan is known to promote relaxation and tranquility, helping to enhance focus and calmness.
Where can I buy quality chandan perfume?
You can explore our collection of Original Chandan Perfume to experience the richness and beauty of this timeless fragrance.
0 notes
Text
Best lime essential oil bulk supplier worldwide

Are you looking for the best lime essential oil bulk supplier worldwide? Lime essential oil is popular across various industries for its refreshing aroma and numerous benefits. Whether you are in the beauty, skincare, health, or food and beverage industry, sourcing high-quality lime oil is crucial. However, finding the best lime essential oil supplier who offers pure oil at competitive wholesale prices can be challenging. Many may not deliver the quality necessary, which can impact your product’s effectiveness and customer satisfaction.
At Aarnav Global Exports, we specialize in bulk lime essential oil, providing 100% pure oil extracted from the finest limes. When you choose us, you gain several advantages:
Quality Assurance: Our lime essential oil undergoes rigorous quality control to ensure potency and purity, essential for aromatherapy applications.
Competitive Pricing: We offer wholesale prices without compromising quality. Our pricing is designed for businesses looking to purchase lime essential oil in bulk.
Sustainable Sourcing: Our lime essential oil is sustainably sourced, making it an excellent choice for environmentally-conscious businesses looking to benefit from pure, high-quality products.
Reliable Supply: We guarantee timely deliveries to help you maintain your production schedule.
Conclusion: Selecting Aarnav Global Exports as your best lime essential oil bulk supplier means you receive a product that meets the highest standards. We are dedicated to supporting your business with exceptional service. Contact us today to inquire about natural lime oil and discover the benefits it can bring to your products!
#lime essential oil#bulk supplier#high-quality lime oil#natural lime oil#essential oils#sustainable sourcing#competitive pricing#aromatherapy#beauty products#skincare#health products#food and beverage industry#Aarnav Global Exports
0 notes
Text
Refined Cottonseed Oil Manufacturers, seller & Exporter in India

Refined Cottonseed Oil Manufacturers, seller & Exporter in India
Cottonseed oil comes from the seeds of cotton plants. They press the fresh seeds to get the oil. People often use it for cooking like other vegetable oils. But it's got lots of saturated fats, like Linoleic Acid, Oleic Acid, and Palmitic Acid. These fats are good for your hair and skin, but too much isn't great for your health. It's also a strong antioxidant, which means it helps fight ageing. People use it to make their hair and skin healthier, and it can keep your scalp in good shape and prevent hair from breaking. Just remember, like anything, it's best to use it in moderation!
5 Ltr, 15 Kg
Also Available in Tankers (10-20 MT)
Total capacity: 200 MT/Day
Division: Agro
Plant location: Kadi
Extraction Process
This oil comes from the fresh seeds of different kinds of cotton plants. They use a method called cold pressing to get the oil out. It's all natural and fresh!
Know Properties of Cotton Seed Oil:
This oil has different kinds of acids like linoleic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, and oleic acid. There's also something called "gossypol," which is a yellow compound that can be toxic.
Cotton Seed Oil Blend Well With:
This cooking oil mixes well with many other oils, like safflower oil, soybean oil, canola oil, corn oil, and wheat germ oil.
Incredible Uses and Benefits of Cotton Seed Oil
Cottonseed oil is super useful in many ways:
Fighting Inflammation: It helps calm down swelling in the body, which can lower the risk of certain types of stroke.
Anti-Cancer Properties: Some studies suggest it might help prevent cancer, especially breast and colon cancer, because of a special ingredient called gossypol.
Heart Health: It's good for your heart too! It can lower the "bad" cholesterol and other unhealthy fats in your blood.
Speeding Up Wound Healing: If you've got a cut or scrape, this oil can help it heal faster. It's got antioxidants that are great for your skin.
Skin Protection: It keeps your skin safe from drying out and can even help prevent sunburn rashes.
Hair Care: It's not just for your skin! Cottonseed oil has vitamin E, which makes your hair strong and healthy.
So, whether it's for your heart, skin, or hair, cottonseed oil has got you covered!
Why Choose Us?
Choosing Ambuja Group for refined cottonseed oil manufacturing offers several benefits. The company is renowned for its commitment to quality, ensuring that the oil produced is pure and meets high industry standards. Their advanced manufacturing facilities utilise cutting-edge technology, guaranteeing consistency and efficiency in production. Ambuja Group also emphasises sustainable practices, sourcing raw materials responsibly to minimise environmental impact. Additionally, their strong market presence and reliable distribution network ensure timely delivery and customer satisfaction. With a proven track record of excellence and innovation, Ambuja Group stands out as a trusted leader in the refined cottonseed oil industry.
For More Information
“Ambuja Tower”, Opp.Sindhu Bhavan, Sindhu Bhavan Road, Bodakdev, P.O. Thaltej Ahmedabad 380054.
[email protected](Export Inquiries)
[email protected](Investors Only)
+91-79-61556678
https://ambujagroup.com/product/cotton-seed-refined-oil/
#"Refined Cotton Seed Oil#Sustainable sourcing#Pure and healthy#Consistent production#Customer satisfaction#Industry standards
0 notes
Text
Marriot downtown sustainability
1.Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy:

2. Water Conservation:

3.Sustainable Sourcing and Procurement

4. Bio gas Conservation

5. Social Responsibility

1 note
·
View note
Text
Marriott International: A Leader in Sustainable Hospitality

Marriott International continues to demonstrate a strong commitment to sustainability across its global operations. Here's a snapshot of their initiatives:
Energy Conservation: Marriott International implements state-of-the-art energy management systems to reduce energy consumption across its properties.

Waste Transformation: The brand has launched programs to repurpose used soaps and amenities, diverting waste from landfills.

Hazardous Substances Management: Marriott’s environmental policy includes the responsible use and disposal of chemicals and hazardous substances to protect the ecosystem.

Sustainable Transport: Encouraging green transportation, select Marriott locations offer electric car charging stations and promote public transport usage.

Market Factors: Through its supply chain, Marriott International supports sustainable practices by sourcing goods locally and prioritizing eco-friendly products.
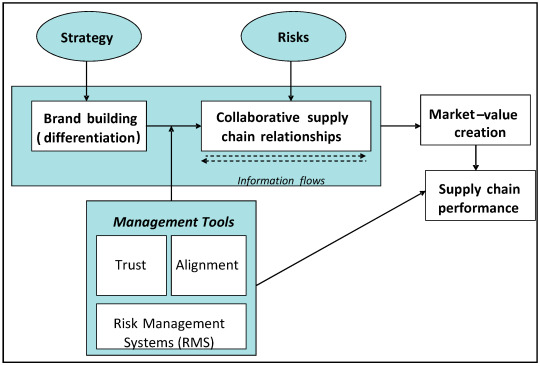
Hashtags for Key Takeaways:
1 note
·
View note
Text
The creation of concrete has become an important part of modern human life. Concrete structures have been around for hundreds of years. Up until today, this material continues to make our lives possible in the modern world.
0 notes
Text
Victoria Bites: 24/7 Modern Filipino Comfort Food
When thoughts wander to Victoria Court, visions of themed rooms for intimate experiences dance in the mind. But beyond the chic accommodations lies a hidden treasure, a well-kept culinary secret that beckons to those seeking comfort at any hour and ignites a desire for delightful flavors. Discovering Victoria Bites Concealed within the renowned Victoria Court brand, Victoria Bites is a culinary…

View On WordPress
#24/7 kitchen#around-the-clock dining#culinary gem#Filipino classics#Filipino comfort food#filipino cuisine#hidden treasures#home-cooked goodness#modern twists#organic ingredients#press release#sustainable sourcing#themed hotel#tradition and innovation#Victoria Bites#victoria court
0 notes
Text
#skincare ingredients#wound healing#sourcing challenges#raw materials#sustainable sourcing#regulatory compliance
1 note
·
View note
Text
Green & Bio-Solvents Market: Sustainable Solutions for a Cleaner Future
The total size of the green & bio-solvents market was USD 3,128.5 million in the past, and it will propel at 6.1% CAGR in the years to come, to reach USD 5,322.2 million by 2030, as per P&S Intelligence. The industry development is credited to the and environmental and health concerns related to synthetic solvents. Paints & coatings dominated the industry in the past, with around USD 1.2…

View On WordPress
#Bio-based solvents#Biodegradable solutions#Chemical sector#Clean manufacturing#Eco-conscious industries#Eco-friendly alternatives#Environmental innovation#Green chemistry#Green solvents#Green technology#Industrial applications#Low carbon footprint#market growth#Regulatory compliance#Renewable resources#Solvent industry#Solvent market trends#Sustainable chemistry#Sustainable sourcing
1 note
·
View note
Text
The future of food in a changing climate

Written by: Jagriti Shahi, Business Analyst at Global Launch Base
Introduction
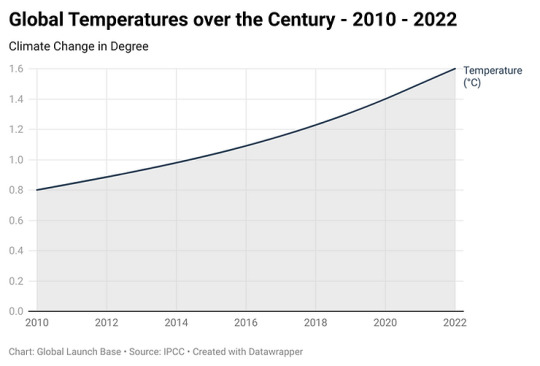
Figure 1: Global Temperature over the Century
This data shows that global temperatures have been rising steadily over the past few decades. The rate of warming is expected to accelerate in the coming years, if we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has warned that if we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, global temperatures could rise by as much as 5.2 degrees Celsius by the end of the century. This would have devastating consequences for the planet, including more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and mass extinctions. The data is clear that we are facing a serious challenge, and we need to take action now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Climate Change and Food Production
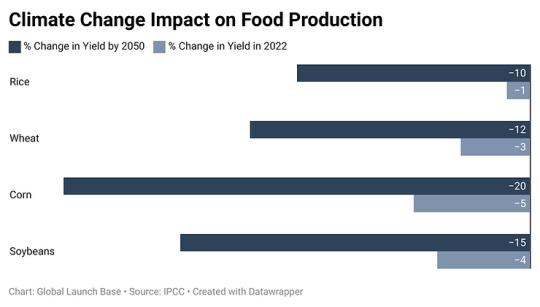
Figure 2: Climate Change Impact on Food Production
This data shows that the % change in yield of different crops by 2050 is already starting to be felt in 2022. For example, rice yields are already 1% lower in 2022 than they were in 2020. This is likely due to the combination of climate change and other factors, such as pests and diseases.
The trend is expected to continue in the coming years, as climate change continues to impact crop yields. This could have a serious impact on food security, as it will make it more difficult to produce enough food to feed the world's growing population.
The intricate relationship between climate change and food production is reshaping agricultural landscapes, challenging traditional practices, and compelling us to explore innovative solutions to ensure global food security. In this article, we delve into the intricate interplay between climate change and food production, highlighting the challenges faced and the potential pathways toward a more resilient future.
Altered Growing Conditions: One of the most immediate and palpable impacts of climate change on food production is the alteration of growing conditions. Rising global temperatures influence the length of growing seasons and shift the geographic suitability of certain crops. In some regions, this leads to reduced yields, as crops may experience stress due to excessive heat, prolonged droughts, or erratic precipitation patterns. Conversely, other areas might witness extended growing seasons, presenting opportunities to cultivate new varieties of crops.
Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: As the climate warms, pests and diseases that were once constrained by temperature limitations are expanding their ranges, posing significant threats to crops and livestock. The increased prevalence of pests can lead to reduced yields and necessitate more intensive use of pesticides, raising environmental concerns and potentially compromising food safety.
Water Scarcity and Agricultural Droughts: Climate change exacerbates water scarcity, a critical factor in agricultural productivity. Changing precipitation patterns and the intensification of droughts can jeopardize water availability for irrigation, which is essential for many crops. This can force farmers to compete for limited water resources, driving up costs and reducing overall agricultural output.
Impacts on Livestock Production: Livestock farming, a vital component of global food systems, is also vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Heat stress can lead to reduced livestock productivity, affecting meat and milk production. Moreover, changing forage availability due to altered precipitation patterns can challenge livestock feed supply, leading to increased costs for farmers.
Soil Degradation and Erosion: Climate change can exacerbate soil degradation and erosion, undermining agricultural sustainability. Intense rainfall events can lead to soil erosion, stripping away fertile topsoil and diminishing its ability to support crop growth. Soil degradation impacts soil structure, nutrient content, and water-holding capacity, posing a significant threat to long-term food security.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies: To address these challenges, a combination of adaptation and mitigation strategies is required.
Adaptation: Farmers can adopt climate-resilient practices such as crop diversification, agroforestry, and improved water management. Planting diverse crop varieties can spread risk and enhance resilience to changing conditions. Agroforestry systems, which combine trees with crops or livestock, can stabilize soil, conserve water, and provide additional income sources. Implementing efficient irrigation techniques and rainwater harvesting can help manage water scarcity.
Mitigation: Mitigating climate change through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions is a critical step toward safeguarding food production. Sustainable land management, reforestation, and the adoption of renewable energy sources can contribute to lowering emissions from the agricultural sector.
7. Technological Innovations: Advancements in technology hold promise for enhancing climate resilience in food production. Precision agriculture utilizes data-driven approaches to optimize resource use, monitor crop health, and reduce waste. Climate-resilient crop varieties developed through traditional breeding or genetic modification can enhance yields under changing conditions.
8. Policy and International Cooperation: Global efforts are indispensable in addressing the complex challenges posed by climate change and food production. International agreements and policies can incentivize sustainable agricultural practices, support smallholder farmers, and promote technology transfer. Investment in research and development can drive innovation and provide farmers with the tools they need to adapt to changing conditions.
Key players in the market:
Impossible Foods: Impossible Foods is a food technology company that makes plant-based meat products that are indistinguishable from real meat. Impossible Foods' products use less water, land, and energy than traditional meat, and they emit significantly fewer greenhouse gasses.
Danone: Danone is a food and beverage company that has set a goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2050. Danone is working to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions across its entire value chain, from the farm to the fork.
Innovative Agricultural Practices
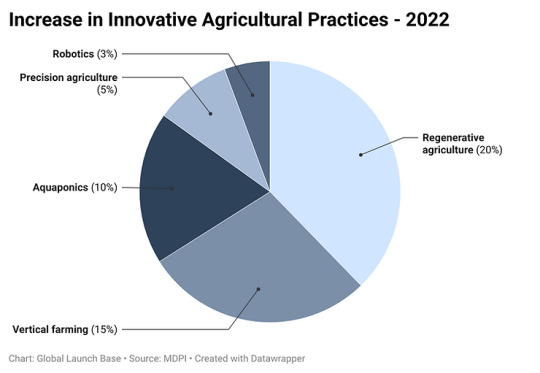
Figure 3: Increase in Innovative Agricultural Practices
This data shows that there is a growing interest in innovative agricultural practices. This is likely due to the increasing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional agriculture and the need for more sustainable food production methods.
Innovative Agricultural Practices: Navigating the Future of Sustainable Food Production
In a world where climate change and environmental degradation pose unprecedented challenges to traditional agricultural practices, innovation emerges as a beacon of hope. Innovative agricultural practices are essential not only for meeting the growing global demand for food but also for ensuring the long-term sustainability of our planet. In this article, we explore a spectrum of groundbreaking techniques that are transforming the way we cultivate crops, rear livestock, and manage natural resources.
Agroecology: Harmonizing Nature and Agriculture: Agroecology is a holistic approach that seeks to mimic natural ecosystems within agricultural systems. By fostering biodiversity, enhancing soil health, and minimizing external inputs, agroecological practices promote resilient and sustainable food production. Techniques such as intercropping, cover cropping, and crop rotation reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, mitigating the environmental impact of conventional agriculture.
Precision Agriculture: Merging Technology and Farming: Precision agriculture leverages cutting-edge technologies, including GPS, remote sensing, and data analytics, to optimize resource utilization and enhance productivity. By precisely mapping variations in soil and crop conditions, farmers can tailor irrigation, fertilization, and pest control measures, minimizing waste and maximizing yields. Drones, sensors, and automated machinery further streamline operations and minimize environmental footprint.
Vertical Farming and Hydroponics: Farming in Tight Spaces: Vertical farming and hydroponics redefine the boundaries of traditional agriculture by enabling food production in urban environments and underutilized spaces. Vertical farms stack crops in vertical layers, utilizing artificial lighting and controlled environments to optimize growth. Hydroponics, a soilless cultivation method, delivers water and nutrients directly to plant roots, reducing water usage and enabling year-round production.
Conservation Tillage and No-Till Farming: Preserving Soil Health: Conventional tillage practices disrupt soil structure and contribute to erosion, compaction, and carbon loss. Conservation tillage and no-till farming minimize soil disturbance, maintaining soil structure and organic matter. This enhances water retention, reduces erosion, and sequesters carbon, making farms more resilient to extreme weather events and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Aquaponics: Symbiotic Aquaculture and Hydroponics: Aquaponics integrates aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics in a mutually beneficial system. The fish waste provides nutrients for hydroponically grown plants, which, in turn, filter and purify the water for the fish. This closed-loop system conserves water, eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, and yields both protein and vegetables.
Controlled Environment Agriculture: Climate-Proofing Crop Production: Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) encompasses greenhouse and indoor farming, allowing year-round cultivation of crops under precisely managed conditions. CEA protects plants from extreme weather, pests, and diseases while optimizing resource efficiency. High-tech greenhouses use advanced climate control systems, enabling growers to fine-tune temperature, humidity, and light levels for optimal plant growth.
Permaculture: Designing Sustainable Ecosystems: Permaculture draws inspiration from natural ecosystems to create self-sustaining and regenerative agricultural systems. By integrating diverse plant and animal species, permaculture designs promote ecological harmony, resilience, and long-term productivity. Food forests, which emulate natural forests with layers of edible plants, exemplify permaculture principles and provide a wide array of harvestable foods.
Urban Agriculture: Nourishing Cities Locally: Urban agriculture transforms urban landscapes into productive spaces, mitigating the environmental impact of food transportation and enhancing food security. Rooftop gardens, community plots, and vertical farms bring fresh produce to city dwellers while fostering a sense of community and reconnecting people with their food sources.
Key players in the market:
Ceres Imaging: Ceres Imaging uses satellite imagery and artificial intelligence to help farmers make more informed decisions about their crops. Ceres Imaging's products can help farmers to identify pests and diseases early on, optimize their irrigation practices, and improve their yields.
AeroFarms: AeroFarms' vertical farms are located in urban areas, which helps to reduce the company's carbon footprint. AeroFarms also uses recycled materials in its farms and packaging, and it is committed to reducing its environmental impact.
Resilient Crop Varieties
The development of climate-resilient crop varieties through breeding and genetic modification is crucial. Scientists are working on crops that can withstand higher temperatures, require less water, and exhibit resistance to pests and diseases. Gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 offer precise methods to enhance desired traits, potentially revolutionizing crop production. However, careful consideration of ethical and environmental implications is essential in adopting such technologies.
As the world grapples with the uncertainties of a changing climate, ensuring a steady and nutritious food supply has become a paramount challenge. Resilient crop varieties, born from innovative breeding techniques and scientific advancements, offer a glimmer of hope in the face of shifting weather patterns, changing pest dynamics, and dwindling natural resources. In this article, we delve into the significance of resilient crop varieties and the transformative potential they hold for securing global food security.
1. The Need for Resilience
Traditional crop varieties, often developed for specific regions and historical climatic conditions, are increasingly vulnerable to the unpredictable and extreme weather events wrought by climate change. Droughts, floods, heatwaves, and new pest and disease pressures threaten agricultural productivity and food availability. Resilient crop varieties possess traits that enable them to withstand and recover from these challenges, ensuring a consistent supply of food even in the face of adversity.
2. Breeding for Resilience
The art and science of breeding resilient crop varieties involve a combination of classical breeding methods and cutting-edge technologies. Plant breeders select and cross plants with desirable traits, such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, and improved nutrient uptake. Advancements in molecular biology, genetic mapping, and gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 enable scientists to precisely manipulate plant genomes, accelerating the development of resilient varieties.
3. Drought-Resistant Varieties
Drought is a major concern for agricultural regions worldwide. Resilient crop varieties with enhanced water-use efficiency and deep root systems can thrive with limited water availability. Genetic modifications that control stomatal opening and closing, reducing water loss through transpiration, are being explored to confer drought tolerance.
4. Disease and Pest Resistance
Pests and diseases can devastate crop yields, leading to food shortages and economic losses. Resilient crop varieties can be engineered with natural pest repellents, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Genetic markers linked to disease-resistance genes are identified to expedite breeding efforts, resulting in more robust crops.
5. Heat and Cold Tolerance
Extreme temperatures, whether scorching heat or chilling cold, disrupt plant metabolism and growth. Resilient crop varieties can be developed with genetic traits that enable them to thrive in temperature extremes. Heat-tolerant crops might possess heat-shock proteins that protect cellular structures, while cold-tolerant crops could have antifreeze proteins that prevent ice-crystal formation.
6. Salinity and Soil Adaptation
As sea levels rise and agricultural lands become salinized, crops need to tolerate higher levels of salt in the soil. Resilient crop varieties can be bred to thrive in saline conditions, ensuring continued food production on affected lands. Breeding for improved nutrient uptake and utilization also contributes to healthier plants and improved yields.
7. Biodiversity and Resilience
Maintaining a diverse array of crop varieties is essential for building resilience. Traditional and heirloom varieties often possess unique traits that can be crucial for adaptation. Initiatives to conserve and promote local crop diversity are essential for safeguarding food security in a changing world.
8. Ethical and Environmental Considerations
While resilient crop varieties hold immense promise, ethical and environmental considerations must guide their development and deployment. Ensuring that genetic modifications do not inadvertently harm ecosystems or reduce genetic diversity is a critical aspect of responsible breeding practices.
Key players in the market:
Monsanto: Monsanto is a multinational agricultural biotechnology corporation that develops and markets crop seeds, herbicides, and other agricultural products. Monsanto has a portfolio of resilient crop varieties that are tolerant to a variety of abiotic stresses, as well as some biotic stresses, such as pests and diseases.
Seminis: Seminis is a subsidiary of Bayer CropScience that develops and markets crop seeds. Seminis has a portfolio of resilient crop varieties that are tolerant to a variety of abiotic stresses, such as drought, heat, and salinity.
Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainable management of natural resources is pivotal to food security in a changing climate. Efficient water management, such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation, conserves water and ensures its availability during dry spells. Soil health restoration through techniques like cover cropping and reduced tillage enhances soil's capacity to retain water and nutrients. Integrated pest management minimizes chemical use and maintains a balance between pests and their natural predators.
Resilience Through Resource Efficiency: Sustainable resource management serves as a cornerstone for building resilience in the face of climate-related uncertainties. Efficient utilization of resources, such as water, energy, and soil, is paramount to ensure that food systems remain productive and adaptable. Through water-efficient irrigation methods, reduced energy consumption, and soil health enhancement, sustainable practices bolster the capacity of agricultural systems to weather the impacts of altered climatic conditions.
Water: A Precious Commodity: In a changing climate, water scarcity and variability become magnified challenges for agricultural production. Sustainable resource management involves optimizing water use through techniques like drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and integrated water management systems. By safeguarding water sources, improving distribution, and minimizing wastage, we ensure a consistent supply of this invaluable resource to sustain food production.
Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration: Healthy soils play a pivotal role in both climate mitigation and adaptation. Sustainable resource management practices prioritize soil health through reduced tillage, cover cropping, and organic matter enrichment. These strategies not only enhance soil fertility and water retention but also contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating the atmospheric buildup of greenhouse gasses.
Biodiversity Conservation for Resilient Ecosystems: Preserving biodiversity within agricultural landscapes is central to sustainable resource management. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to climatic fluctuations and provide natural pest control, pollination services, and soil fertility. Agroecological approaches, such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and maintaining habitat corridors, support diverse species and foster ecosystem health.
Circular Economy and Waste Reduction: A circular economy approach within food systems minimizes waste and resource depletion. Sustainable resource management encourages reducing food waste, adopting efficient packaging, and promoting composting or recycling of organic matter. By embracing a circular mindset, we reduce the burden on landfills, conserve resources, and limit the environmental footprint of food production and consumption.
Renewable Energy Integration: As we envision a climate-resilient food future, the integration of renewable energy sources into agricultural operations becomes essential. Sustainable resource management emphasizes transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy to power irrigation, processing, and distribution systems. Solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas facilities contribute to reducing emissions and enhancing overall sustainability.
Localized Food Systems and Resilient Communities: Sustainable resource management advocates for the development of localized food systems that prioritize regional resilience. By supporting small-scale farmers, community gardens, and farmers' markets, we enhance local food security and reduce the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
Policy, Collaboration, and Global Action: Effective sustainable resource management requires a collaborative effort encompassing policymakers, researchers, industries, and consumers. Governments can incentivize sustainable practices through policies, subsidies, and regulations. International cooperation is vital to share knowledge, innovations, and best practices, ensuring a collective response to the global challenge of climate change.
Key players in the market:
Veolia: Veolia is a French multinational water, waste management and energy services company. Veolia has a long history of sustainable resource management, and it is one of the world's leaders in the field. Veolia's water treatment plants are some of the most efficient in the world, and the company is also a leader in waste recycling and energy recovery.
Ecolab: Ecolab is an American multinational provider of water, hygiene and energy technologies and services. Ecolab is a leader in sustainable resource management, and the company has a number of programs and initiatives in place to reduce its environmental impact. Ecolab's water conservation programs have helped to save billions of gallons of water, and the company's energy efficiency programs have helped to reduce its energy consumption by millions of kilowatt-hours.
Climate-Resilient Livestock Farming
Livestock production is another area greatly affected by climate change. Heat stress reduces livestock productivity, and changing grazing patterns impact feed availability. Transitioning towards climate-resilient livestock farming involves improving animal genetics, optimizing feed formulations, and implementing better shelter and cooling systems. Alternative protein sources like insect farming and lab-grown meat might also play a significant role in ensuring a sustainable and climate-resilient protein supply.
Adapting to Changing Conditions: Climate-resilient livestock farming entails embracing adaptable practices that mitigate the impact of a changing climate on animal health, productivity, and well-being. Heat stress, a growing concern due to rising temperatures, can lead to decreased feed intake, reduced reproductive efficiency, and overall livestock productivity. Employing cooling measures such as shade structures, misting systems, and proper ventilation helps mitigate heat stress and maintain optimal livestock conditions.
Improved Breeding for Resilience: Selecting and breeding animals for climate resilience is a key facet of climate-resilient livestock farming. Breeding programs aim to develop livestock varieties that are better equipped to withstand heat stress, disease outbreaks, and changing feed availability. Genetic traits that confer heat tolerance, disease resistance, and efficient nutrient utilization contribute to animals better suited for a changing climate.
Sustainable Feed Sourcing: Climate-resilient livestock farming integrates sustainable feed sourcing practices to ensure the long-term availability of nutritious and environmentally friendly animal diets. Livestock production is a significant contributor to deforestation and land degradation, often driven by the demand for animal feed crops. Transitioning to alternative feed sources, such as algae, insect-based protein, and agroforestry byproducts, minimizes environmental impact while ensuring adequate nutrition for animals.
Precision Livestock Management: Advances in technology play a pivotal role in climate-resilient livestock farming through precision livestock management. Sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence enable real-time monitoring of animal health, behavior, and productivity. This data-driven approach enhances disease detection, facilitates targeted interventions, and optimizes resource utilization, contributing to both economic efficiency and animal welfare.
Agroecological Integration: Integrating livestock into agroecological systems fosters synergy between animal and crop production. Agroforestry, where livestock graze in wooded areas, enhances feed availability, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity. Rotational grazing, which involves moving animals between different pastures, prevents overgrazing, improves soil health, and enhances forage quality.
Alternative Livestock Systems: Exploring alternative livestock systems offers a promising avenue for climate resilience. Silvopasture combines trees with pasture, providing shade, forage, and carbon sequestration potential. Aquaculture and integrated fish-farming systems can complement traditional livestock production, diversifying income sources and protein supply.
Community Engagement and Knowledge Sharing: Climate-resilient livestock farming thrives in a collaborative environment where farmers, researchers, and communities exchange knowledge and best practices. Farmers' networks, extension services, and capacity-building initiatives facilitate the dissemination of climate-resilient techniques and encourage collective adaptation to changing conditions.
Policy Support and Incentives: Effective policies and incentives play a pivotal role in fostering climate-resilient livestock farming. Government support for research and development, funding for sustainable practices, and market incentives for climate-resilient products incentivize farmers to adopt and invest in these strategies.
Key players in the market:
Alltech: Alltech is a global animal nutrition company that develops and markets products and services for livestock producers. Alltech has a program called Alltech Climate Challenge that helps livestock producers reduce their environmental impact. Alltech Climate Challenge provides farmers with training on climate-friendly livestock farming practices, such as methane mitigation and water conservation.
Zoetis: Zoetis is a global animal health company that develops and markets products and services for livestock producers. Zoetis has a program called Zoetis Sustainable Agriculture that helps livestock producers improve their environmental performance. Zoetis Sustainable Agriculture provides farmers with training on sustainable livestock farming practices, such as reducing antibiotic use and improving manure management.
Reducing Food Waste and Loss
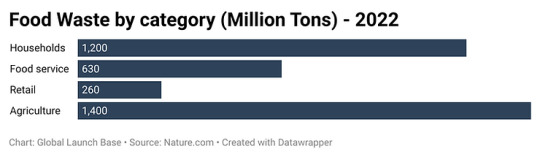
Figure 4: Food Waste by Category
This data shows that food waste is a major problem worldwide. It is estimated that one-third of all food produced for human consumption is wasted. This waste has a significant environmental impact, as it contributes to climate change, water pollution, and land degradation. Households are the biggest contributors to food waste, followed by food service and retail. Agriculture also contributes a significant amount of food waste, but this is often due to factors beyond human control, such as crop losses due to pests and diseases.
The Scale of the Challenge: Food waste and loss constitute a staggering paradox in a world where millions go hungry. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted annually. In a changing climate, this inefficiency takes on heightened significance, given the increased strain on agricultural resources and the urgent need to maximize production.
Climate Impacts and Food Loss: The impacts of climate change, including extreme weather events, temperature fluctuations, and altered growing seasons, exacerbate the problem of food waste and loss. Disrupted supply chains, reduced crop yields, and increased pest and disease pressures contribute to losses at every stage of the food system, from production to consumption.
Farm-Level Strategies: At the production level, climate-resilient agricultural practices are essential in minimizing food loss. Crop diversification, improved storage facilities, and effective pest management contribute to preserving harvests. Climate-smart irrigation and water management systems ensure that water resources are used efficiently, reducing losses due to drought-related crop failures.
Post-Harvest Innovations: Innovations in post-harvest technologies play a pivotal role in reducing food loss. Cold storage, modified atmosphere packaging, and controlled atmosphere storage systems extend the shelf life of perishable goods. Solar drying and value-addition techniques enable smallholder farmers to process excess produce into value-added products, minimizing waste and increasing income.
Efficient Distribution and Supply Chains: Efficient distribution and supply chains are central to addressing food waste. Improving transportation infrastructure, embracing digital solutions for real-time inventory management, and facilitating coordination between producers, distributors, and retailers can prevent perishable goods from spoiling before reaching consumers.
Consumer Behavior and Awareness: Shifting consumer behavior towards responsible consumption is essential in curbing food waste. Education campaigns, labeling initiatives, and community-driven efforts raise awareness about the consequences of wasting food and empower individuals to make conscious choices.
Food Rescue and Redistribution: Food rescue organizations and surplus food redistribution networks salvage edible food that would otherwise be discarded. These initiatives divert surplus produce from landfills to those in need, addressing both food waste and food insecurity simultaneously.
Policy and Industry Leadership: Government policies and private sector initiatives play a crucial role in reducing food waste and loss. Regulatory measures, tax incentives, and industry commitments to zero-waste goals drive systemic change across the food supply chain.
Key players in the market:
Too Good To Go: Too Good To Go is a Danish company that has developed an app that connects consumers with businesses that have surplus food. Businesses can list their surplus food on the app, and consumers can purchase it at a discounted price. Too Good To Go has helped to prevent millions of meals from being wasted.
RapidPricer: RapidPricer is an AI-powered pricing platform that helps retailers automate their pricing and promotions. The platform uses deep learning algorithms and machine vision to dynamically price products to match their real-time value based on competition, product lifecycle, and market conditions. With deep expertise in retail pricing, RapidPricer computes merchandising actions for real-time execution in a retail environment.
Policy and Global Cooperation
Mitigating the impact of climate change on food production requires global cooperation and effective policy measures. International agreements and frameworks can promote sustainable agriculture, support smallholder farmers, and facilitate technology transfer to developing countries. Financial incentives, subsidies for sustainable practices, and research funding can drive innovation and promote the adoption of climate-resilient technologies. 1. Policy as a Catalyst for Change Sound and visionary policies are the cornerstone of a resilient food system. Governments play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of food production, distribution, and consumption through regulations, incentives, and strategic planning. Policies that promote climate-resilient agriculture, sustainable resource management, and reduced food waste set the stage for a more secure and sustainable food future. 2. Climate-Smart Agriculture Policies Climate-smart agricultural policies harness innovative approaches to enhance productivity, mitigate climate impacts, and reduce emissions. By incentivizing the adoption of climate-resilient practices, such as crop diversification, agroforestry, and improved irrigation, governments foster adaptive capacity and mitigate the vulnerabilities of agriculture to a changing climate. 3. Research and Innovation Funding Government funding for research and innovation accelerates the development and adoption of climate-resilient agricultural technologies and practices. Support for breeding drought-tolerant crops, developing efficient irrigation systems, and advancing precision agriculture empowers farmers to overcome the challenges posed by climate change. 4. International Agreements and Frameworks The global nature of climate change demands international collaboration. Agreements like the Paris Agreement underscore the commitment of nations to combat climate change and lay the groundwork for coordinated efforts in the agricultural sector. Frameworks for technology transfer, capacity-building, and financial support ensure that countries with varying levels of resources can participate in climate-resilient food production. 5. Sustainable Trade and Supply Chain Policies International trade and supply chains are integral to global food security. Policies that promote sustainable trade practices, reduce trade barriers and ensure equitable access to markets contribute to stable food supplies and price stability, benefiting both producers and consumers. 6. Strengthening Smallholder Resilience Policies that specifically target smallholder farmers, who are often the most vulnerable to climate impacts, play a vital role in enhancing food security. Financial support, access to credit, and extension services empower smallholders to adopt climate-resilient practices and diversify their livelihoods. 7. Public-Private Partnerships Collaboration between governments, private sector entities, and civil society organizations amplifies the impact of climate-resilient policies. Public-private partnerships drive innovation, leverage resources, and facilitate knowledge exchange, ensuring that policies are implemented effectively and that a wide array of stakeholders are engaged. 8. Education and Consumer Awareness Policies that promote consumer education and awareness campaigns raise consciousness about sustainable consumption practices. Clear labeling, educational initiatives, and public awareness campaigns inform consumers about the environmental and social impacts of their food choices, influencing demand and driving market shifts.
Conclusion
The future of food in a changing climate is a complex challenge that demands immediate attention and collaborative efforts. Innovations in agriculture, sustainable resource management, and climate-resilient practices offer hope for ensuring food security for a growing global population. By embracing new technologies, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering international cooperation, we can navigate the challenges presented by a changing climate and build a more resilient and secure food future for generations to come. ------------------------------------ Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us. Contact Info: Website: www.globallaunchbase.com LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/ Email: [email protected]
#Climate change#Food security#Sustainable agriculture#Climate-resilient farming#Adaptation strategies#Agricultural innovation#Climate-smart technologies#Global food systems#Environmental impact#Crop diversity#Resource management#Food supply chain#Resilient livestock farming#Circular economy#Policy initiatives#Smallholder resilience#Sustainable sourcing#Climate challenges#Food waste reduction#Renewable energy integration
0 notes
Text
One addition, pay attention to legislation at every level- local, national, heck, even international- that fights against planned obsolescence. Here's a recently proposed Canadian bill that does exactly that:
How To Fight Planned Obsolescence
What is planned obsolescence you ask?
Planned obsolescence is where companies design products to be obsolete - to break, to be ‘out of fashion’, to be difficult to use or to wear out - with the aim being that in a short period of time, you will be forced to throw the product out, and get a new one.
Examples of Planned Obsolescence
Tech companies that stop updating software on models that are over 3 years old
Clothing companies that use poor quality materials and stitching, meaning that clothes will rip, tear or degrade very rapidly
Jewellery companies that use poor quality plating and cheap soldering so that your earrings/bracelets/necklaces tarnish and break soon.
Shoe companies that use cheaper labour and mechanical stitching methods ( RIP Doc Marten’s BuyItForLife)
What Can I Do?
Look for companies that provide low cost - or even free - repairs for their products. This can be said explicitly, or you might have a warranty in the T&Cs section of sale. If the company is willing to provide free repairs for items, it probably means that repairing the items is a rare occurence, or that it can be easily done.
Be aware of the materials that you purchase. Materials such as leather, raw denim, pure corduroy, Tencel, Linen, Wool, Silk etc are so durable that they’re often combined with polyester to make them cheaper and less durable. As these are pricey, try to find they second hand. Avoid polyester, acrylic and rayon where possible!
This leads me on to my next point - products made of durable materials tend to be easier to repair. Good quality jeans, leather jackets and woollen socks are sturdy enough to fix with patches or to darn, whereas polyester and acrylic may not be able to withstand the poking and prodding that patching requires.
Quality > Quantity - Planned obsolescence drives prices down - if you know that you’ll replace an item within less than 30 wears, its easier to look for the cheapest option. So, before you buy something ask - Will this be worn/used regularly? Can I see myself still using this in a year? In three years? Will this last that long? Again - you might have to go down the second hand for this one.
Look after what you have. Now, this may contrast with the previous points but bear with me. Don’t wear the items you have out. Swap your jewellery out regularly, taking it off when you go into the shower or the swimming pool. Avoid putting your clothes in the dryer. Wax your leather goods. An item made of good quality materials will still break, tarnish and rip if you use it every single day, drop it regularly, and dunk it in a swimming pool.
Final Note
Avoiding planned obsolescence is hard so do what you can, what is accessible to you, and what is within your budget. Don’t feel bad if your products break sooner than expected; instead, be angry at the companies that use poor designs.
#planned obsolescence#sustainability#low waste#zero waste#eco friendly#eco feminism#sustainable sourcing
223 notes
·
View notes
Text
cw: sexually explicit content / blood / relatively light sadomasochism / age + experience gap (reader is older + more experienced) / sub!choso / vampires 🧛♀️ / sex and violence as two sides of the same coin /
choso kamo is 160 years old when he meets you.
in those years of walking the earth, undead, he believes he’s embraced his vampirism as much as he possibly can. the broiling self-hatred he had once found solace in has reduced to a simmer, strongest in those moments of blood and guts and weakening heartbeats; and although he often avoids crowds, and companionship, and light, he no longer believes himself to be a slave of his own nature.
to be true — in the grand scheme of immortality, of vampirism — he isn’t anywhere close to the level of control he’d wish to have. often, when indulging yuji’s desire to enjoy the world as he did before his death — boardwalks and arcades and cotton candy — he feels his canines aching in his gums, stretching until they dimple against his bottom lip.
it’s not comfortable. it’s not confident. but even despite the growing aches, he’s no longer cowering in alleyways; no longer drinking from poor stray cats and garbage-chewing rats to momentarily satiate that ever-growing, gnawing hunger. he has some sense of control—
“oh, you baby-bats. so adorable.”
control which he now flounders to grab.
a sharp, inky black nail scrapes up the column of his neck — he can’t help but arch into it, head tilting back until his wide, pupil-blown eyes find the ceiling, with its intricate coving and obsidian chandeliers. the music from the main hall is nothing but a buzzing in the back of his head; thoughts of his friends’ whereabouts, an afterthought. your fingernail crowds the underneath of his jaw and stops at where his pulse point would have thrummed, would he have been alive.
you’re a demon. a devil. a she-beast. a succubus. any horrid, terrible name he could call you, he will — dressed in blacks and burgundies and gold older than him, your lips painted an ox-blood red and your eyes as sharp and dark as any polished knife. in your hands he is small. weak. mortal.
“satoru usually keeps his strays away, after last time,��� you say, pouting now, though it’s a crude approximation of sadness — even now, your eyes glint with devilment. “so mean, when he knows i have a weak spot for bats like you.”
that wretched finger stretches up; pokes at his bottom lip, scrapes against the fangs that had — embarrassingly — extended from his gums at the simple weight of you on top of him.
“look at that,” you coo, and your grin is something unsettling, something that curdles in the pit of his stomach and heats between his legs. “excited, pup?”
his answering breath comes ragged, and it’s always more embarrassing than it was when he was human. his heart doesn’t work, his lungs do not work, and he has no need to breathe — in fact, he lost the reflex to do so around 92 years ago — but his brain is scrambled, it seems, wilted neurons confusing signals from almost two centuries ago. “i’m — ahem — i’m okay, duchess.”
“how sweet. you don’t have to call me by my title, you know. my name will do just fine.” at his silence, you push yourself up from where you’d been laying low against his chest — looking far too excited when you say: “unless, of course, you like it.”
his hands tremble at his side. he can’t remember the last time he’s indulged in — in debauchery. the last time someone’s made him feel like they’re holding his heart in their hands. over the past hundred-odd years, he’s avoided it like the plague, and for good reason — most vampires aren’t known for their commitment, let’s just say. and now you’re on top of him looking like every sin he’s tried to avoid, and he’s straining so hard in his pants he fears he’ll cum before you even hint at removing a single article of clothing.
you press yourself flush again, nosing at his neck. he knows, for the first time in his long life, what it feels like to be prey. is this what his victims had felt when he ripped into their throats, young and inexperienced and bloodthirsty? did their vulnerability sit like a stone in their throats?
a groan comes from you, suddenly, and your tongue darts out to lave against his skin. choso’s answering moan is more of a whimper, broken and weak in his mouth, but you don’t seem to notice — or care. he flexes his glutes in an effort to stop himself from rutting up against you — not only would it be embarrassing, desperate, but it would be rude. this is your house, after all. your soirée. your gilded halls and bedazzled walls. your silk sheets against his back. your satin skirt bunched around your waist.
“tell me, pup,” you say, and he fights the instinctual reflex to shiver at the brush of your lips against his skin, “have you ever fed from our own?”
“hm?” it’s a sound of confusion brought half on by his simple lack of knowledge, and half on by his slow-processing brain. only seconds after does he fully register your question, and the eyes he hadn’t realised he had screwed shut flew open. “no. i — i didn’t know that was possible.”
all at once, you’re sitting up again — swinging your leg over his hips until you’re standing. it wouldn’t be right to call it clambering — you are impossibly graceful, even passed the agility and elegance that comes with the gift of the undead. his hands reach for you before he can stop them, a sound like a question on his tongue, and you send him the sweetest, most tooth-rotting, stomach-turning smile. he thinks he likes your biting, cruel grins more, though you’re lovely regardless.
you begin to reach for the ties of your corset at your spine — just another thing that makes his mouth water. people didn’t wear these sorts of clothes anymore, not in the human world. but he remembers the skirts and corsets from paintings of noblewomen hundreds of years ago, and how he’d admire the curve of their waists, the swell of their chests—
“of course, satoru wouldn’t tell you. why would he?”
his eyes snap up from your chest, caught with his hand in the cookie jar. but you don’t seem to mind. the corset is removed painfully slowly, for no other reason than to torture him; then, the outer dress, with its carmine satin and intricate embroidery. you throw it to the floor carelessly, as if the most knowledgeable museum curators wouldn’t prostrate themselves at your feet for the simple chance to display it for millions to see — a while his eyes drink up the sight of more skin, the whisper of form beneath your underdress and bloomers, you near him once more.
metal to a magnet, a moth to flame, he pulls himself to the edge of the bed. you find a place between his legs and grasp his chin, and choso can’t look away from you.
“i can take you apart and put you back together,” you say — promise — voice like crushed velvet, quiet and creeping like a choking vine. your thumb smooths over his cheek and ends at its apple, where you press the sharp tip of your nail into his flesh. “i can show you the pleasures of your eternal life, and its pains, and everything in between. i can bring you to every edge, and draw you back from them just as quick — and it will be painful, and you’ll enjoy it so much you won’t be able to go another day without it.”
he’s lost the ability to speak. his unmoving heart is in his throat — or in your hands, or between your sharp teeth. you tilt your head and regard him with knowing, twinkling eyes.
“all you have to say, pup, is yes.”
oh, it’s out of him so quick he can hardly keep up — a word so breathy you’d swear you’d already had your way with him. but embarrassment is a thing of the past when your smile stretches, and you murmur marvellous. you release him from your grasp, much to his chagrin, but when you begin pulling down your bloomers his attention shifts.
he can smell you. smell you. the musky, salty scent of between your legs — a smell that has his mouth watering and his fingers cramping from how hard he fists the sheets. your bloomers are damp when you discard them, sticky with your arousal, and pride glows in choso’s chest. he didn’t do much, but it seemed enough — if he had only let himself lose control, hump up against you harder, perhaps it would’ve stained his clothes; seeped through your layers and onto his lap. he’d go home and hold it over his nose until the scent faded, and perhaps after.
“new as you are,” you say, climbing onto your bed once more and reclining back against the numerous pillows — huffing a mean-sounding laugh when he crawls after you. “i’ll do you the mercy of taking it easy, just this once. oh, don’t make that face — you look like a kicked puppy. i promise you’ll enjoy what i have in store for you.”
and you hike up your underdress, and spread your legs. choso’s mouth waters — the thick smattering of hair on your mons, your flower-like labia, shiny with your arousal. and your clit, peeking out from its hood, pink and shiny and begging to have his mouth on it. but as if this wasn’t enough — as if he wasn’t already scrabbling to get between your legs — you take one of those long, sharp nails, and drag it against your inner thigh. the skin splits. blood trickles down from the wound like a river of gold, flowing into the crease between your thighs and your pussy, and it smells ambrosial. if his fangs were aching before, they’re screaming, now. this isn’t human blood; this is richer, sweeter, creamier. delectable. hedonistic. you’ll make a glutton of him.
“after all,” you say, grinning wickedly, “i’m treating you to a most delectable meal.”
#sub choso u will always be famous#living out my gothic vampire dream. need#choso x reader#choso kamo x reader#jjk x reader#anime x reader#choso x you#choso kamo x you#jjk x you#anime x you#choso smut#choso kamo smut#jjk smut#anime smut#im thinking about the lore for this au now#gojo who acts like a hedonist but is actually tortured by the reality of his immortality#nanami who strictly feeds either on animals or sustainably sourced human blood 😭😭😭😭#vampire hunter toji who is also a vampire a la mikael mikaelson#also pup is what baby bats are called……. im dying#also goths call beginner goths baby bats but i think its fitting here#also no choso is not a baby or a child or anything he is v much a consenting adult 😭😭#i jusg think it puts like the extent of immortality into perspective#idk its 3am and i have work tomorrow#who up subbing they choso
286 notes
·
View notes
Note
I know you're on paternity leave so feel free to ignore this if you don't want to think about it, but has there been any progress on open-sourcing Tumblr's front-end? Inquiring minds would like to know
i hadn’t seen any progress on it before i left. there’s a strong willingness to do it, it’s just a big task to get it open-source-able in a sustainable way. a lot of our CI/CD processes rely on stuff that would need to be rebuilt from scratch, i think. totally doable, just not a priority.
but maybe there’s been progress since i left, i dunno! 🤞
#open source#tumblr development#paternity leave#front end#software sustainability#continuous integration#ai generated tags
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have so many questions about the ambler. Why is it so tall? What in evolution could possibly make a creature that large on land? What does it eat? If giraffes evolved the way they did to eat trees then what did amblers evolve for?? The fricking stars???
#I wish we got backstory on nyx’s ambler#Like how well was crime paying to be able to sustain that thing#Also did nyx raise it or did she just find it and tame it#Or did she just steal it/rent it from someone whenever she needed it#tdp#the dragon prince#continue the saga#greenlightarc3#give us the saga#Arc 3 is actually just going to be three seasons of the dragang raising an ambler to eat Aaravos’s stars before they can align#source: trust me bro
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
by this, I mean I would release a sheet of 4+ designs which can be bought in order to get as a tattoo. I have done tattoo designs for people in the past, and am interested in creating some more! feel free to suggest themes or ideas!!! I'm trying to branch out with the kind of art I can sell.
#tattoo design#not art#SORRY FOR SO MUCH FOR-SALE ART AND NOT SO MUCH FUN ART..... this is my only source of income currently!!#I'm trying to see if its sustainable longterm. [:
14 notes
·
View notes