#South African Railways
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
Trains? >:3
TRAINS :D
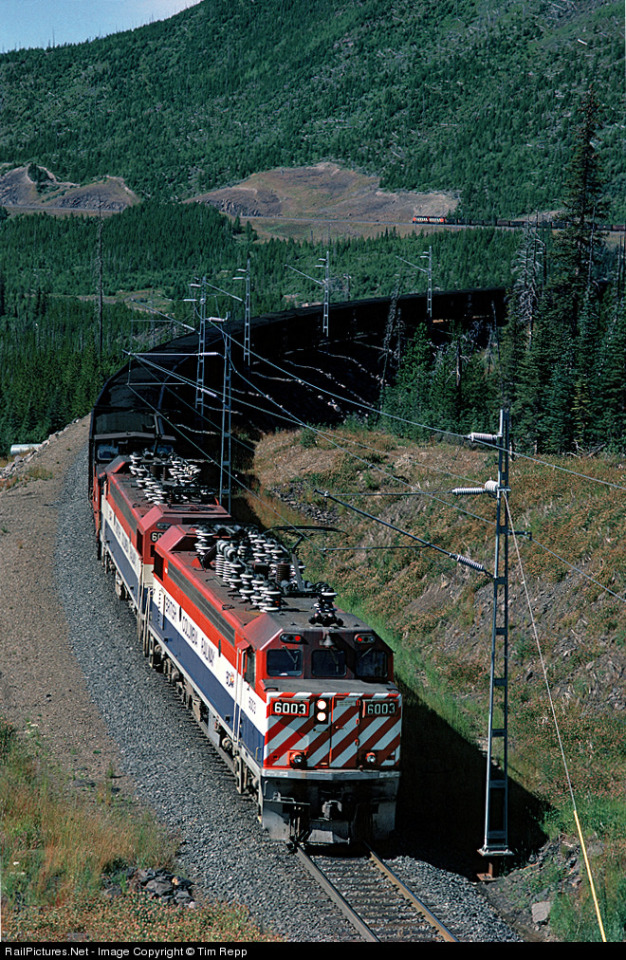
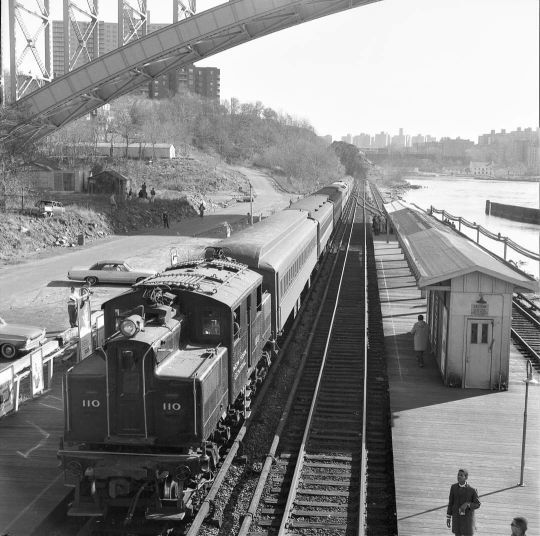










#trainposting#amtrak#electric traction#pennsylvania railroad#electrification#public transit#suburban rail#commuter rail#commuter train#bc rail#tumbler ridge#new york central#caltrain#metro trains#metro north railroad#Northeast corridor#south african railways#asks
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Random Trains I Found Part 1:
So, I've put off writing my myriad of WIPs for a bit to spend some time just... looking at trains. Reconnecting with them. Hunting out ideas for the future and being amazed by the past. And here's a few of my absolute favourite random, insane trains I've found so far:
NGR Class D1:
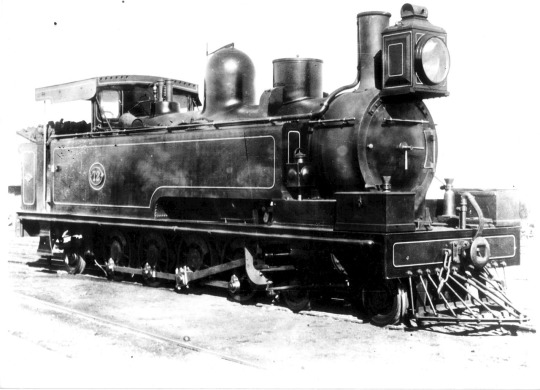
This right here was the first 4-8-2 ever built - and it's an absolutely massive tank engine from South Africa. It was built to the 3ft 6in Cape Gauge and it began running in 1888. Take a moment for that to settle in - 1888. The USA didn't run a 4-8-2 on it's network until 1911, a good 20+ years later!
Russian Class Kh:

It's a 2-8-0 class built in the USA for Russia that had examples sold to Japan with the last example preserved in China. I personally like these engines because they really do tell us so much about how much the world changed - they began life in 1895, and somehow (I would love to know how if anyone has any information) one ended up in a river in Jilin Province, China. It was probably WWII, but all the same, these engines went places!
Prussian P8 Class:

These engines started life in 1908 and weren't retired until 1981 in Poland at the latest - and if that isn't an opening to an epic class of locomotive, I don't know what is! Roughly 3900 of these machines were built, making it potentially the single largest class of passenger engine in the world and they ended up just about everywhere in Europe, from France to Norway to Romania, where a number (200) were built under license. And the reason they lived so long? They were simple, strong machines.
GWR 2600 'Aberdare' Class:
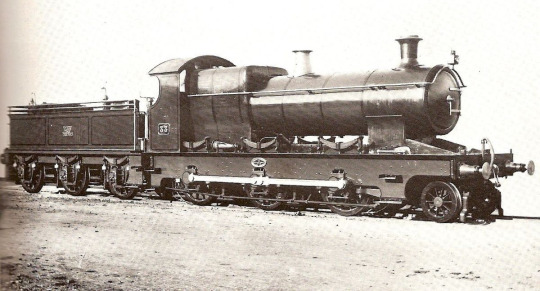
Honestly, I just like these because they look so odd. Like, these are GWR 2-6-0s that look like a City or a Bulldog class. They have the double frames and the coupling rods of a 4-4-0 - and that's because they were introduced in 1900. They did manage to make it to 1949 hauling coal trains, but the GWR had already been withdrawing them in the 1930s, as they did with their older stock. I wish one had been preserved, they'd be so cool to look at!
NGR Class C:
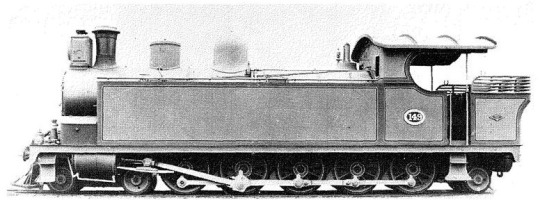
Last but certainly not least, these behemoths of South Africa once again prove that somehow, the former Cape Colony was at the forefront of wheel arrangement innovation. It's a 4-10-2T. It was built in 1899, alongside the GWR Bulldog class! These things were massive... and eventually rebuilt to 4-8-2T locomotives. But there were 137 of them built, making them the most numerous of the 4-10-2 type locomotive ever constructed.
I want all of these engines. I would love to know more about them, I would love to own one (in model form) and I am going to love continuing my journey through railway history to find more random, interesting locomotives to share.
And as usual, all images belong to their respective owners.
#weirdowithaquill#railways#real railway stuff#real world trains#South African Railways#Prussian P8 locomotive#Russian Kh locomotive#gwr#Aberdare Class#real trains are so cool#And leaving my UK-centric railway view to explore is a lot of fun!#random railways#random thoughts
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
:3








There's a stairway to heaven and a highway to hell, but the midnight train goes anywhere. Trains are clearly the superior transit method.
#trainposting#amtrak#electric traction#south african railways#Iowa Interstate Railroad#pennsylvania railroad#milwaukee road#southern pacific#illinois central#south shore railroad#metra Electric
81K notes
·
View notes
Text



In my au Stanley (narrow gauge) has a special interest in insects (I hc him as being into animals, they don’t judge you for your “jinx” and he’s got a soft spot for critters that are seen as “bad luck”) and tends to blurt out the most detailed information, he often info-dumps with and to Nia who encourages it cause it makes him happy once he’s freed from his “jinx” and she know every single insect name alphabetically along with their scientific names and nicknames Here we have Duke immediately regretting asking them if they can name every single species and ends up sleeping when they’re engrossed in their conversation before leaving when they were in the mid section of the e category (Nia gave him “the disappointment older sister look” awhile back so the poor guy can trapped there and wondered how did he got ever himself into this situation)
Basically it’s just Stanley to Duke in alphabetical order: Alderflies Angel Insects Anoplura (Sucking lice) Ants Antlions Aphids Archeognatha (Bristletails) Barklice Bees Beetles Bird lice Biting lice Blattodea (Cockroaches) Booklice Bristletails Bugs Butterflies Caddisflies Chewing lice Cicadas Cockroaches Coleoptera (Beetles) Collembola (Springtails) Crickets Damselflies Diplura Diptera (Flies) Dobsonflies Dragonflies-
Nia joining in cause she was mad at Duke: ah yes the alderfly which are megalopteran insects of the family Sialidae. They are closely related to the dobsonflies and fishflies as well as to the prehistoric Euchauliodidae. All living alderflies – about 66 species all together are part of the subfamily Sialinae, which contains nine extant genera. Sialinae have a body length of less than 25 mm (1 inch), long filamentous antennae, and four large dark wings of which the anterior pair is slightly longer than the posterior. They lack ocelli and their fourth tarsal segment is dilated and deeply bilobed. Dead alderfly larvae are used as bait in fishing-
duke:shooketh (Nia’s is basically the train version of a encyclopedia also her design is based off of MrTerrier673 on Twitter)
#ttte#ttte duke#ttte stanley#ttte nia#msr stanley#rws stanley#duke the lost engine#my art#my artwork#my art <3#my art stuff#yeah I’ve traced their basis Nia is a ngr class 1906 she participated in the war in South Africa 🇿🇦 and the East African campaign#and Freddie was there they’re pretty much older siblings/cool aunt-uncle figures to Stanley cause they all went through a lot pre-msr days#but yeah Nia be a encouraging big sister and joining in I got so much on them I need to put in haha but poor duke someone save him he doesn#wanna end up like Andreas and Duncan who both really wished they could forget about learning about hammerhead wormsXD#but yeah Nia recognizing that this is something that makes Stanley happy he’s healing (Kyle’s death their old railway etc) and knows these#hobbies that made him happy were mocked and putted down and literally beaten out of him and as an fellow animal lover she’s very supportive#Also Stan my guy please get some sleep he’s got insomnia and nightmares from Kyle’s death (I mean both do along with Freddie) Nia is 10 yea#rs older than him but at least they’re both reunited on the skarloey after some years she’s very big cool sister/chill aunt coded figure an#knows that this is Stanley;s way of showing he trusts someone but then again out of all his colleagues stuart got off lucky he only infodum#on him about monarch butterflies 🦋 and ladybugs 🐞 XD Freddie and Bertram/atlas r torn
26 notes
·
View notes
Text

Railway line in Johannesburg, South Africa
South African vintage postcard
#briefkaart#africa#photography#vintage#tarjeta#postkaart#johannesburg#postal#photo#african#south#postcard#historic#railway#carte postale#ephemera#south africa south#sepia#line#ansichtskarte#postkarte
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nobody Drives in LA -- The Ostrich Farm Railway
THE OSTRICH FARM RAILWAY Detail of Map of the City of Los Angeles, 1887, depicting the route of the Ostrich Farm Railway [Note: This essay was written for and originally appeared in the Silver Lake Neighborhood Council newsletter] Today Silver Lake is, by most accounts, moderately well served by mass transit. The website, Walk Score, assigns Silver Lake a transit score of 54 out of a possible…

View On WordPress
#Echo Park#Griffith J. Griffith#Griffith Park#Kenilworth Ostrich Farm#Los Angeles and Ostrich Farm Railroad#Nobody Drives in LA#Ostrich Farm Railway#Ostriches#silver lake#Silver Lake Neighrbohood Council#South African Angelenos#Sunset Boulevard#the Los Angeles Ostrich Farm and Zoological Garden
0 notes
Text
Amtrak AEM-7 "Toaster"
Canadian National Z-1a "Boxcab"
SEPTA/RTD Silverliner 5
Pennsylvania Railroad T1
Virginian/New Haven E33 (EL-C/EF-4) "Brick"
Milwaukee Road EP-2 "Bipolar"
South African Railways class 26 "Red Devil"







Alright people! I have a question for you all.
What locomotive (Steam/Diesel/Electric/Whatever) do you love like it's a favourite of yours, or love so much that it could almost be call an obsession?
(That's NOT a bad thing btw)
For me it's the:
NBR H Class Atlantics
GWR 4000 Class
PRR T1
LNER A1/A3's
VR S Class




#Trains#steam locomotive#general electric#electrified railroads#electric traction#railway electrification#pennsylvania railroad#penn central#conrail#septa regional rail#septa#amtrak#canadian national#south african railways#milwaukee road
179 notes
·
View notes
Text
While there is a great deal of similarity between Israel and Apartheid South Africa (down to the very close ties these countries shared), their strategies to delay inevitable collapse have turned out very different especially in terms of foreign policy. Like the South African government spent its last decade or so under Apartheid pursuing what Botha called his "Total Strategy", using every possible lever of influence to force the Frontline States into subservience; keeping them economically dependent on South Africa and politically acquiescent to Apartheid.
Military force was used for sure, but the only large scale deployments were the occupations of Namibia and southern Angola. Otherwise direct military action was restricted to commando raids, focused mainly on destroying infrastructure and carrying out political assassinations. South Africa instead preferred to act through local proxies, supporting (and often creating) various reactionary terrorist movements (i.e. UNITA in Angola, RENAMO in Mozambique, LLA in Lesotho) so that the destabilising effect of constant warfare would inhibit economic development, prevent unfriendly governments from taking any real action against apartheid and allow the offer of reduced terrorist support to be a bargaining chip in negotiations.
Economically South Africa used its control over transport infrastructure and large job market as both carrot and stick, rewarding compliant governments with better access to goods and increased migrant labour quotas (for many countries a vital source of income) while punishing disobedient nations with transport disruptions and reduced access to South African jobs. The specific mix of Military and Economic strategies would be tailored to suit the particular country at a particular time; for example South Africa's pressure on Angola was almost entirely military due to the lack of economic links between the two, while Swaziland's complete dependency made economics the primary South African approach. These different forms of pressure were also applied so as to compliment each other i.e. commandos and terrorist proxies would attack alternate railways and ports to ensure goods had to be transported through South Africa.
This was mainly done to extract political concessions. By 1980 the complete overthrow of unfriendly regimes was mostly off the table, so instead efforts were focused on changing the behaviour of the groups already in power. South Africa's main obsession was with the ANC boogeyman, constantly asking their neighbours to kick out ANC training camps and diplomatic ataches and forbid movement of ANC guerillas through their territory. However all manner of other demands were also made; economic integration, military access, opposition or at least neutrality towards UN sanctions etc. These were all attempts to drag the Frontline States back into South African dependency and under De Facto white Imperial rule; effectively undoing independence
In any case, as brutal as this "Total Strategy" was, it's a far cry from Israel's current approach which more resembles a genocidal temper tantrum. This is even in contrast to earlier Israeli strategies of coming to terms with neighbouring states and collaborationist movements; using Lebanon as an example they've gone from employing Christians Reactionaries as proxies to clumsily provoking the whole nation. There are structural reasons for this of course. South Africa needed it's black majority, both "at home" and in the neighboring states, as a reserve of cheap labour to extract cheap natural resources and buy globally uncompetitive manufactured goods. Indeed, the false independence of the "Bantustan" project was an attempt to remove South African citizenship from their entire black population and legally turn them all into migrant labourers. South Africa also has a much longer history as an independent Settler project, and while they recieved significant amounts of support from The West (especially the USA and doubly so under the more reactionary Presidents i.e. Ronald Reagan) this very much had its limitations; South Africa obviously couldn't wage a regional war of extermination even if wanted to. Meanwhile Israel's policy towards indigenous people is increasingly exterministic and there is no interest in maintaining their population; they even import migrant labourers from as far as Thailand to deny local Arabs. The country has also spent it's an entire existence as more or less a glorified NATO military base; they have more reason to favour a policy of genocidal war while hoping the US saves them from the consequences.
The point is that there are limits to how far you can take comparisons between South Africa and Israel. For all their similarities as Apartheid Settler States, were still different countries that occupied different contexts and so there are considerable socio-political differences between them that shouldn't just be ignored. You can't blandly use South African history to predict the course of Israel, or worse project current events in Israel onto a distorted version of South Africa's past. You won't develop a useful understanding of the world if you stick to broad assumptions and truisms; you need to actually investigate
278 notes
·
View notes
Note
whats the weirdest train you know?
Oh there are so e really fucking weird ones a lot of weird ones were very niche and were designed for something very specific but some were actually rather popular like the better garratt which were very popular in South Africa but weren't that common anywhere else although some were used in Australia and because South Africa only ceased Steam Traction in 1991 many of the Locomotives were sold off and sent overseas mainly to the UK, New Zealand, and Australia
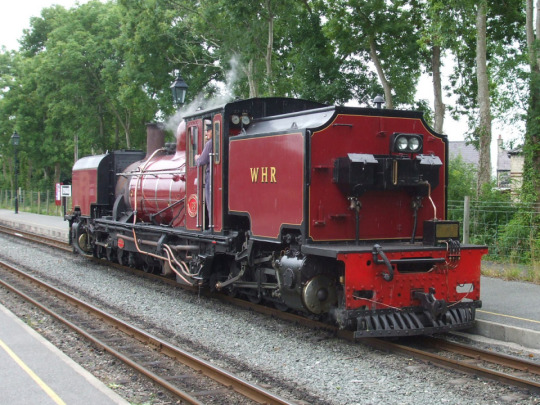


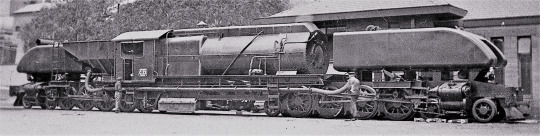


But that's just the better garratt which weren't that weird and about 1200 were built from about 1908 to 1968 to about 100 different designs
The next few Locomotives were much less common starting with an Ancestor of the Garratt; The Double Fairlie

These were an type of strange Double ended Locomotive in the 1860s but really only the Ffestiniog & Welsh Highland Railway used them and they still have a few like the one above (they also purchased a few Garratts from South Africa seen above)
Next on to the Steam turbines which were largely experimental and never really panned out but several different designs were built mostly one-offs



Most of them didn't work very well
Next is a retrofit of an regular steam Locomotive to be able to use a different fuel source during a coal shortage that being the Bizarre Swiss Steam-Electric Locomotive

Switzerland has almost no Coal and thus during world war 2 had no coal but they did have cheap Hydroelectricity and their railways were mostly Electrified so they just made the abombonations
#steam locomotive#trainposting#electric traction#steam boiler#south African Railways#beyer garratt#Swiss railways#sbb#welsh highland railway#pennsylvania railroad#union pacific
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
One of the major legacies of the British control of India was the planting of peoples of Indian origin all over the British Empire, including Britain itself. India was considered to be a reservoir of cheap labour. After African slavery was legally ended in 1833, ‘indentured’ labourers were recruited from India to work on plantations in Mauritius, Guyana, Trinidad, and Jamaica. This was slavery in a new guise: many laboured under conditions no less degrading than slavery. Thereafter wherever need arose, Indian labour was employed. Indians worked in the plantations and mines in Ceylon, Malaya, Burma, South Africa and Fiji. Indian labour provided the manpower to build the East African Railway. Indian sailors worked the British merchant navy. Indian soldiers not only helped to maintain the British Raj in India, but were used as cannon fodder overseas in colonial wars of conquest to extend its frontiers.
Indians were brought to Britain too. They did not come as ‘indentured’ labourers, but the principle of cheap labour applied here as well. Many Indian servants and ayahs (nannies or ladies’ maids) were brought over by British families returning from India. Indian sailors were employed by the East India Company to work on its ships. Some of these servants and sailors settled permanently in Britain.
One of the results of the policy of introducing western education in India was that, from about the middle of the nineteenth century, many Indian students began arriving in Britain, some on scholarships, to study law or medicine or to prepare for other professions. Some came to take the examination for entry into the Indian civil service since this examination could only be taken in London. Some Indian students settled in Britain after qualifying, to practise as doctors, lawyers or in other professions. Some Indian business firms opened branches in England. Nationalist politicians came to London, the centre of power, to argue the cause of Indian freedom. Indian princes and maharajahs visited England, not only as guests of the Crown on formal occasions, like the coronations, but also to pay their ‘respects’ to the monarch or for pleasure. London, as the metropolitan capital, attracted many visitors from India. Exhibitions of Indian arts and crafts were displayed in England too. The Asian presence in Britain therefore goes a long way back and forms a prelude to the post-independence migration of Asians to Britain.
— Rozina Visram, Ayahs, Lascars and Princes: Indians in Britain, 1700-1947 (London: 1986), pp. 9-10.
158 notes
·
View notes
Text
That not train this train
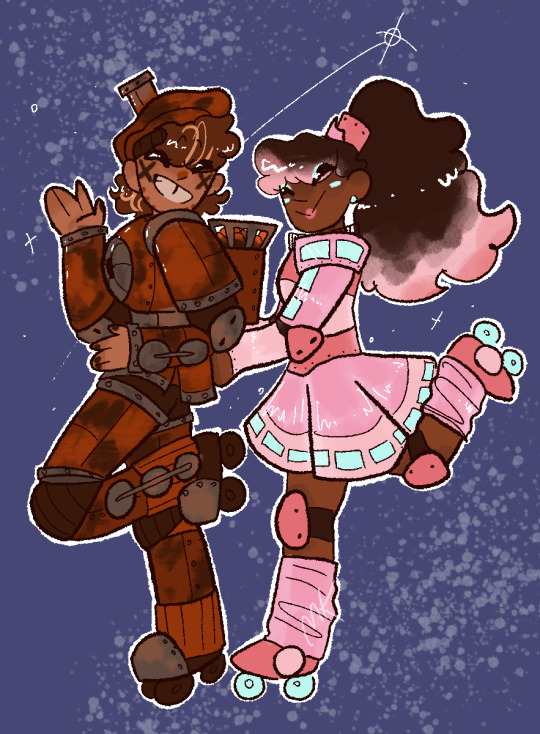










It’s them!
I’ve been really into Starlight Express lately and this little duo is near and dear to my heart
My own fan designs, just how I saw them in my head while listening to the soundtrack <3
#train good car bad#go train#go transit#pennsylvania railroad#penn central#prr t1#santa fe#ATSF#canadian national#brightline#south African Railways
254 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 1833, Parliament finally abolished slavery in the British Caribbean, and the taxpayer payout of £20 million in “compensation” [paid by the government to slave owners] built the material, geophysical (railways, mines, factories), and imperial infrastructures of Britain [...]. Slavery and industrialization were tied by the various afterlives of slavery in the form of indentured and carceral labor that continued to enrich new emergent industrial powers [...]. Enslaved “free” African Americans predominately mined coal in the corporate use of black power or the new “industrial slavery,” [...]. The labor of the coffee - the carceral penance of the rock pile, “breaking rocks out here and keeping on the chain gang” (Nina Simone, Work Song, 1966), laying iron on the railroads - is the carceral future mobilized at plantation’s end (or the “nonevent” of emancipation). [...] [T]he racial circumscription of slavery predates and prepares the material ground for Europe and the Americas in terms of both nation and empire building - and continues to sustain it.
Text by: Kathryn Yusoff. "White Utopia/Black Inferno: Life on a Geologic Spike". e-flux Journal Issue #97. February 2019.
---
When the Haitian Revolution erupted [...], slaveholding regimes around the world grew alarmed. In response to a series of slave rebellions in its own sugar colonies, especially in Jamaica, the British Empire formally abolished slavery in the 1830s. [...] Importing indentured labor from Asia emerged as a potential way to maintain the British Empire’s sugar plantation system. In 1838 John Gladstone, father of future prime minister William E. Gladstone, arranged for the shipment of 396 South Asian workers, bound to five years of indentured labor, to his sugar estates in British Guiana. The experiment [...] inaugurated [...] "a new system of [...] [indentured servitude]," which would endure for nearly a century. [...] Desperate to regain power and authority after the war [and abolition of chattel slavery in the US], Louisiana’s wealthiest planters studied and learned from their Caribbean counterparts. [...] Thousands of Chinese workers landed in Louisiana between 1866 and 1870, recruited from the Caribbean, China and California. [...] When Congress debated excluding the Chinese from the United States in 1882, Rep. Horace F. Page of California argued that the United States could not allow the entry of “millions of cooly slaves and serfs.”
Text by: Moon-Ho Jung. "Making sugar, making 'coolies': Chinese laborers toiled alongside Black workers on 19th-century Louisiana plantations". The Conversation. 13 January 2022.
---
The durability and extensibility of plantations [...] have been tracked most especially in the contemporary United States’ prison archipelago and segregated urban areas [...], [including] “skewed life chances, limited access to health [...], premature death, incarceration [...]”. [...] [In labor arrangements there exists] a moral tie that indefinitely indebts the laborers to their master, [...] the main mechanisms reproducing the plantation system long after the abolition of slavery [...]. [G]enealogies of labor management […] have been traced […] linking different features of plantations to later economic enterprises, such as factories […] or diamond mines […] [,] chartered companies, free ports, dependencies, trusteeships [...].
Text by: Irene Peano, Marta Macedo, and Colette Le Petitcorps. "Introduction: Viewing Plantations at the Intersection of Political Ecologies and Multiple Space-Times". Global Plantations in the Modern World: Sovereignties, Ecologies, Afterlives (edited by Petitcrops, Macedo, and Peano). Published 2023.
---
Louis-Napoleon, still serving in the capacity of president of the [French] republic, threw his weight behind […] the exile of criminals as well as political dissidents. “It seems possible to me,” he declared near the end of 1850, “to render the punishment of hard labor more efficient, more moralizing, less expensive […], by using it to advance French colonization.” [...] Slavery had just been abolished in the French Empire [...]. If slavery were at an end, then the crucial question facing the colony was that of finding an alternative source of labor. During the period of the early penal colony we see this search for new slaves, not only in French Guiana, but also throughout [other European] colonies built on the plantation model.
Text by: Peter Redfield. Space in the Tropics: From Convicts to Rockets in French Guiana. 2000.
---
To control the desperate and the jobless, the authorities passed harsh new laws, a legislative program designed to quell disorder and ensure a pliant workforce for the factories. The Riot Act banned public disorder; the Combination Act made trade unions illegal; the Workhouse Act forced the poor to work; the Vagrancy Act turned joblessness into a crime. Eventually, over 220 offences could attract capital punishment - or, indeed, transportation. […] [C]onvict transportation - a system in which prisoners toiled without pay under military discipline - replicated many of the worst cruelties of slavery. […] Middle-class anti-slavery activists expressed little sympathy for Britain’s ragged and desperate, holding […] [them] responsible for their own misery. The men and women of London’s slums weren’t slaves. They were free individuals - and if they chose criminality, […] they brought their punishment on themselves. That was how Phillip [commander of the British First Fleet settlement in Australia] could decry chattel slavery while simultaneously relying on unfree labour from convicts. The experience of John Moseley, one of the eleven people of colour on the First Fleet, illustrates how, in the Australian settlement, a rhetoric of liberty accompanied a new kind of bondage. [Moseley was Black and had been a slave at a plantation in America before escaping to Britain, where he was charged with a crime and shipped to do convict labor in Australia.] […] The eventual commutation of a capital sentence to transportation meant that armed guards marched a black ex-slave, chained once more by the neck and ankles, to the Scarborough, on which he sailed to New South Wales. […] For John Moseley, the “free land” of New South Wales brought only a replication of that captivity he’d endured in Virginia. His experience was not unique. […] [T]hroughout the settlement, the old strode in, disguised as the new. [...] In the context of that widespread enthusiasm [in Australia] for the [American] South (the welcome extended to the Confederate ship Shenandoah in Melbourne in 1865 led one of its officers to conclude “the heart of colonial Britain was in our cause”), Queenslanders dreamed of building a “second Louisiana”. [...] The men did not merely adopt a lifestyle associated with New World slavery. They also relied on its techniques and its personnel. [...] Hope, for instance, acquired his sugar plants from the old slaver Thomas Scott. He hired supervisors from Jamaica and Barbados, looking for those with experience driving plantation slaves. [...] The Royal Navy’s Commander George Palmer described Lewin’s vessels as “fitted up precisely like an African slaver [...]".
Text by: Jeff Sparrow. “Friday essay: a slave state - how blackbirding in colonial Australia created a legacy of racism.” The Conversation. 4 August 2022.
#abolition#tidalectics#multispecies#ecology#intimacies of four continents#ecologies#confinement mobility borders escape etc#homeless housing precarity etc#plantation afterlives#archipelagic thinking#geographic imaginaries#kathryn yusoff#katherine mckittrick#sylvia wynter#fred moten#achille mbembe#indigenous pedagogies#black methodologies
210 notes
·
View notes
Text

South African railway signalman Jack Baboon, and his owner James Wide, 1880s.
Jack was the pet and assistant of double leg amputee signalman James Wide, who worked for the Cape Town–Port Elizabeth Railway service. James “Jumper” Wide had been known for jumping between railcars until an accident where he fell and lost both of his legs. To assist in performing his duties, Wide purchased a chacma baboon in 1881, and trained him to push his wheelchair and to operate the railways signals under supervision.
Jack was put in charge of the coal yard keys and also did the station’s gardening, until Wide learned that the baboon was skilled at operating signals. Jack learned each lever by name and was able to push them into position when a train approached at Uitenhage station. Wide would hold up one or two fingers (as a signal to the animal) and Jack would then pull the correct lever. Finally, Jack needed no instructions from his master and he really knew which lever to operate for each approaching train. Although the baboon was always under the eye of his master James Wide, Jack never made a mistake or required telling twice. He was paid partly in South African currency and partly in beer.
66 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello! I've been enjoying your writing references and notes, thank you for sharing! I was wondering, do you have any for something set during the Civil War? I've been sitting on the idea of writing a short story inspired by Little Women and I want to do it some justice at least. I would be happy with whatever you can offer <3
Writing Notes: The American Civil War
A four-year war (1861–65) between the United States and 11 Southern states that seceded from the Union and formed the Confederate States of America.
The two sides fought over the enslavement of African Americans and the rights of individual states.
The economy of the South relied on enslaving Black people to work on plantations of cotton and tobacco, while in the industrialized North, public opinion was in favor of ending slavery.
The war ended in 1865 with a Union victory.
THE UNION AND THE CONFEDERACY

By February 1861, 7 southern states (South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas) had broken away from the rest of the US.
On 4 February, they agreed to form a separate government, the Confederate States of America.
The first shots of the war were fired at Fort Sumter in South Carolina on 12 April, and within 3 months, Virginia, Arkansas, North Carolina, and Tennessee had joined the Confederates.
23 states remained in the Union, including the slave-owning “border states”.


NEW TECHNOLOGY
The US Civil War was one of the first industrial wars in history, making use of modern technologies developed during the course of the 19th century. The war was fought across a wide area, so railways were critically important in carrying troops and supplies to where they were needed on the front lines. Generals were able to communicate with each other by telegraph.

Weapons. Fast-firing repeating rifles, such as the Spencer rifle, were used for the first time in the Civil War. The widely used “Napoleon” field gun could hit a target up to 1,600 m (5,250 ft) away. Also developed at this time was the Gatling gun, an early machine gun.

Ironclad battleships. Steam-powered battleships protected by iron or steel plates were known as ironclads. The first-ever battle between ironclads was fought in the Civil War in 1862, on the James River estuary in Virginia.

Modern Communications. In the Civil War, railroads moved troops around, aerial balloons spied across enemy lines, and the telegraph (above) sent and received instant information. Its receiver machine recorded messages on paper tape in Morse code, which uses dots and dashes to represent numbers and letters of the alphabet.
WAR PHOTOGRAPHY

The Civil War was one of the first conflicts to be extensively photographed. Dozens of photographers toured the battlefields, and their stark images of soldiers, dead and alive, brought shocking scenes of the war to the public around the world.

A Continental War. Most of the fighting in the war took place in Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania in the east. There were also battles in Kentucky and Tennessee in the west and down the Mississippi River to New Orleans. In 1864, General William T. Sherman (above) conducted a major campaign in Georgia and the Carolinas.
TIMELINE
A nation divided. When 7 US states seceded (broke away) from the Union to form the Confederacy, President Lincoln refused to recognize the new government, and called on them to rejoin the Union. The Confederates refused, and tried to gain control of federal forts in the south. The stage was set for a bloody war that would last for the next 4 years.
12 April, 1861: Fort Sumter attacked. Confederate troops under Brigadier General Beauregard fired on Union soldiers who were guarding Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina. These were the first shots to be fired in the Civil War.
17 September, 1862: Battle of Antietam. The bloodiest day of fighting in the entire war took place at the Battle of Antietam, in which nearly 23,000 soldiers were wounded or killed. The Union army suffered the most casualties, but managed to halt the advance of General Robert E. Lee’s Confederate forces into the Union state of Maryland. The next day Lee was allowed to lead his shattered army back to Virginia.
13 December, 1862: Confederate victory. Fortune swung back to the Confederate side at the Battle of Fredericksburg, in Virginia. General Burnside, newly appointed by Lincoln to command the Union army, led 120,000 troops to attack a Confederate force of 80,000 – by far the largest number of men to meet in any conflict of the Civil War. Burnside was decisively defeated – a victory that gave fresh hope to the Confederates and led to complaints that the Union’s generals were doing a bad job.
1 January, 1863: All slaves to be free. President Lincoln gave new purpose and direction to the war by issuing the Emancipation Proclamation. This was an order freeing all slaves in the Confederate states. Of course, this could not happen until the Union had won the war against the Confederates, but his words would eventually lead to the freeing of millions of African American slaves.
3 March, 1863: First African-American regiment. The first official regiment of African-American soldiers, the 54th Massachusetts Infantry Regiment, was formed to fight in the Union army.
4 July, 1863: Vicksburg captured. Union troops captured the Confederate fortress of Vicksburg, on the Mississippi River, after a 2-month siege. It was a major turning point in the war, coming a day after the Union victory at Gettysburg. The Union now controlled the length of the Mississippi River, dividing Louisiana, Texas, and Arkansas from the rest of the Confederate states, and cutting off supplies.
15 November, 1864: March to the Sea. The capture of Atlanta in Georgia by Union General William T. Sherman in September was a heavy blow to the Confederates. Although deep inside enemy territory, Sherman decided to march his army all the way from Atlanta to the coast at Savannah. He ordered his men to live off the land and destroy farms and factories on their way. This brutal “scorched earth” policy inflicted lasting damage.
9 April, 1865: Lee surrenders to Grant. The Confederate capital of Richmond, in Virginia, fell on 3 April. The Virginian Confederate army was exhausted. To avoid further losses, Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered to General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House in Virginia. By May, all the Confederate armies had stopped fighting. The war was finally over.
14 April, 1865: Assassination of Lincoln. President Lincoln was shot while attending a play at Ford’s Theatre in Washington, DC. He died the next morning. A funeral train took 14 days to transport his body back for burial in his hometown of Springfield, in Illinois.

The Battle of Gettysburg. The most famous battle of the Civil War was fought over three days, from 1 to 3 July 1863, around the small town of Gettysburg in Pennsylvania. The Confederates attacked, confident they would win, but the Union army did not give way and eventually won. The battle had the heaviest casualties in the war. An estimated 51,000 soldiers were killed, wounded, or listed as missing. Four months after the battle, President Lincoln visited the site and delivered a famous speech known as the Gettysburg Address. In it, he said that the US was “dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal”.

The Abolition of Slavery. On September 22, 1862, President Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which freed all enslaved people in the Confederacy from January 1, 1863. In 1865 Congress passed the 13th Amendment (law change) to the US Constitution, making slavery illegal across the soon-to-be reunited country.
RECONSTRUCTION

African Americans Voting in Richmond in Virginia, 1871
The slow process of rebuilding the economy of the south, left in ruins after the war, is known as Reconstruction. Before rejoining the US, each state of the Confederacy had to agree to amendments to the US Constitution – the supreme law of the nation – that ended slavery, granted citizenship to African Americans, and gave the vote to all male citizens.
Reconstruction ended in 1877, and many southern state governments immediately reversed the new rights given to African Americans, making it hard for them to vote, go to school, or find paid work. They introduced laws that legalized discrimination against Black people that remained in place for almost a century.
Below are objects that serve as evidence of the turmoil leading up to the election and the events that happened immediately after.
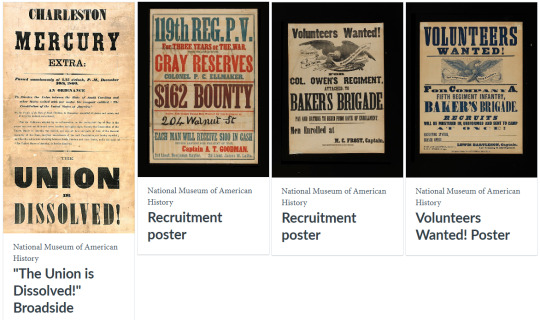

Below are objects that show how the Union and the Confederacy dealt with money problems, while also exploring what was considered money then and who produced it.


The objects below belonged to the men and boys who fought on the front lines for both Confederate and Union forces. They represent what soldiers wore, what they ate, how they coped, and what they held dear to them. These items, more often than not, were the only possessions soldiers kept while enlisted; on many are personal touches added by the owner.


Below are a few objects used as weapons by both Confederate and Union armies.

Below are a few objects used by or presented to the leaders of Union and Confederate forces.

For many Americans, both civilian and military, who lived through the conflict, the Civil War was the monumental event of their lifetime. They collected relics as they adjusted to the immediate consequences of the war. The nation grappled with the residual effects of the Civil War for more than a century. Below are objects that evoked different memories from the war.

Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 ⚜ More: Notes & References
It's nice to hear this, thanks so much! <3 Hope these notes help as quick references. Further research might be needed if you're planning to write something more detailed.
#anonymous#writing reference#history#writeblr#dark academia#spilled ink#creative writing#writing inspiration#writing notes#writing prompt#light academia#lit#literature#writing#writing resources
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
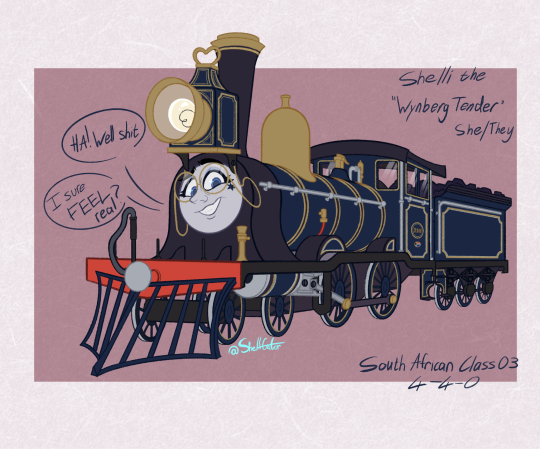
I unrealed myself. Cringe is dead here's my train sona! With a MONDO FUCKING LAMP BABY. 💡☀️
Shelli the Wynberg Tender, they're a new build version that's a combination of all the CGR/South African Railway Class 3s. Their Cape Gauge wheels were replaced with larger, standard gauge wheels to conform to the North Western Railway standard, because you bet your ass that's where I wanna be.
Refs below!

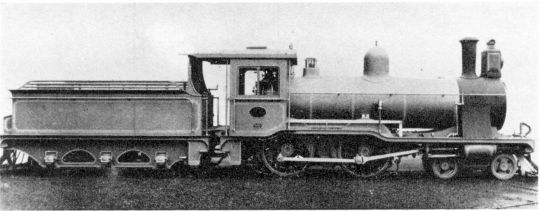
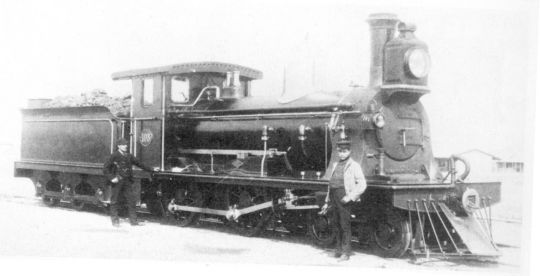

#ttte#ttte oc#train sona#ttte sona#the railway series#the rws#rws#i wish trains were real#i wanted to showcase more of my train stuff!#i told you trains are furry adjacent#shelli art
230 notes
·
View notes
Text
Narrow Gauge Nia
Was chatting with some folks on discord about aus and engines basis and saw some takes on Nia so it got me thinking about if she was built in the Nairobi Central Workshops around the 1910s cause she’s still a British exported locomotive and maybe other railways take inspiration from others and bulit their own also some folks on Twitter and discord make her another basis like a NG6 from South Africa so I was wondering on others folks thoughts on this if that’s cool
#ttte nia#ttte#my polls#tumblr polls#polls#poll time#random polls#like I’m kinda leaning toward making her a ngr class n expected she was built in the South African railways workshops#and she’s kinda’ve a mentor towards narrow gauge Stanley and has worked on the msr inspired by someone on discord#and I know someone liked this idea I do too but also cause I know Kenya and South Africa have different cultures#and I know someone liked this idea I do too and also from the fact I’ve realized in meet#also cause I’ve rewatched her intro video and noticed that the South Africa flag was used instead of Kenya’s flag and I’m like…umm hmm#maybe for her prototype she she’ll be a 2-6-0 inspired by her aeg and wooden railway design
7 notes
·
View notes