#Scientific research Australia
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Video
DSC05570 orig with insert tag by Jim Via Flickr: Visual sighting from my property in Greta, NSW Australia taken on NV setting. This is a unedited version of the NV capture of the multiple craft. With the cropped enhanced insert for a closer inspection of the craft... Dimensional Entities. FRJS Research Australia
#Dimensional Entities#anomalies#Antigrav#Australia#craft#Disclosure#entities#My Sky#Night sky#phenomena#Research#Science#sky#sky anomalies#Sony HDR-SR12E#Truth#ufo#UFOs#unknown#Australian Research#FRJS Australia Research#FRJS Research Australia#FRJS Research discovery 2009#my research#Research Australia#Research of UAP's#scientific research#Scientific research Australia#UFO Researchers#Australian Discoveries 2009
0 notes
Text

"Ignorance of scientific knowledge is not evidence that God exists" (EN: English)
#Ignorance of scientific knowledge is not evidence that God exists#ignorance#science#scientific research#god#anti religion#anti god#atheism#atheist#philosophy#truth#facts#fact#fyi#psa#religion#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#religion is a mental illness#religion is a scam#religion is bullshit#religion is poison
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
#africa#animal teachers#australia#biodiversity#bird feeder#bird feeding#birds#candice gaukel andrews#cane toad#conditioned taste aversion#conservation#environment#goannas#invasive species#the kimberley#lizards#natural habitat adventures#nathab#nature#nature lovers#remote#science#science and environment#scientific research#teachers#wild#wildlife#world wildlife fund#wwf
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
2023 Vocabulary Symposium: FAIR Vocabularies For All.
Following on from the success of the 2022 Vocabulary Symposium, the ARDC invites you to the 2023 Vocabulary Symposium on 14 and 15 November 2023.
This is a 2-day hybrid event bringing together people from domains across disciplines spanning research, government and industry, including those from the ARDC Thematic Research Data Commons. The aim is to communicate and promote approaches to using, developing, publishing and maintaining vocabularies. The event will cover Australian and international initiatives that demonstrate the impact and value of FAIR vocabularies for maximising the reuse value of data within and across domains.
The program for the Symposium is out now. The Symposium will feature keynote presentations from:
Arofan Gregory, a standards expert at CODATA, who will present on “Controlled Vocabularies in a Changing Metadata Landscape”.
Jen Drysdale, a cultural heritage informatics and analytics specialist at the National Film and Sound Archive of Australia, who will discuss “The Role of Vocabularies in Cultural Heritage and the Impact of New Strategic Drivers”.
Register to participate!

#Vocabularies#computer science#National Film and Sound Archive of Australia#Cultural heritage#australia#Symposium#hybrid events#formal science#International science council (ISC)#scientific research
0 notes
Text
From the earliest days of the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists have raised concerns about the potential for long-term health problems linked to SARS-CoV-2 and warned repeated infections are likely to increase the risk. An association between COVID and cardiovascular disease emerged quickly. And now — almost exactly four years since the first case was discovered in Wuhan — a growing body of scientific research is cautiously linking the inflammation caused by a COVID infection to diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's as well as autoimmune conditions from bowel disease to rheumatoid arthritis. The virus has even been suggested to impact some pregnant women, associated with double the risk of premature delivery. As the eighth COVID wave hits Australia, experts are taking notice.
...
When the first wave of COVID patients began reporting loss of smell and taste, Barnham's radar went up. "Any time you see olfactory impairment it tells you that there's going to be neurological impact," he says. "Loss of smell is a cardinal, pre-clinical symptom of Parkinson's disease and it's been implicated in Alzheimer's disease as well." The fact that COVID patients reported loss of smell not only during the active phase of the disease, but as a persistent symptom, suggested to Barnham that longer-term health consequences were likely. Loss of smell is associated with loss of brain volume.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
We often hear that Aboriginal peoples have been in Australia for 65,000 years, "the oldest living cultures in the world." But what does this mean, given all living peoples on Earth have an ancestry that goes back into the mists of time? Our new discoveries, published July 1 in the scientific journal Nature Human Behaviour, shed new light on this question. Under the guidance of GunaiKurnai Elders, archaeologists from the GunaiKurnai Land and Waters Aboriginal Corporation and Monash University excavated at Cloggs Cave near Buchan, in the foothills of the high country near the Snowy River in East Gippsland, Victoria.
Continue Reading.
694 notes
·
View notes
Text
THREE NEW SHARK SPECIES THIS WEEK!
The second week of July 2023 something extraordinarily beautiful happened, the findings of 3 new species of sharks for were announced
A new angel sharks species was identified, from the western Indian Ocean on the Mascarene Plateau and off southwestern India in 100–500 m depths, the Lea’s angel shark Squatina leae, was recognized to be different genetically and morphologically distinct from its congeneric species Squatina africanae, following unique morphological features. This species was first detected in 1988 after finding three unusual, small sharks, but till today was completely understood. The angel shark is named after one of the author’s fiancee’s late sister, Lea-Marie Cordt.

- Squatina leae, adult male, in dorsolateral.
Angel sharks are “flatter sharks”, possesing distinctly broad, dorsoventrally flattened bodies, a short snout with large mouth and nostrils, eyes on top of the head close to the large spiracles, very large pectoral fins, and a lateral caudal keel. They've evolved to be ambush predators, they lie in wait for prey to pass closely overhead before attacking.
Reference (Open Access): Weigmann et al., 2023. Revision of the Western Indian Ocean Angel Sharks, Genus Squatina (Squatiniformes, Squatinidae), with Description of a New Species and Redescription of the African Angel Shark Squatina africana Regan, 1908. Biology
From North Australia, another species of hornshark is described based on six whole specimens and a single egg case. The painted hornshark Heterodontus marshallae was previously considered to be the same with the zebra bullhead shark another well know bullhead shark from the central Indo-Pacific from Japan to Australia, but genetic and morphological analyses indicated the sharks were different, but looking alike. The painted hornshark is endemic to northwestern Australia and occurs in deeper waters, at 125–229 m below surface.

- Lateral view of two mature female painted hornshark Heterodontus marshallae showing small differences between individuals
The painted hornsharks is named in honour of Dr. Lindsay Marshall www.stickfigurefish.com.au a scientific illustrator and elasmobranch scientist who expertly painted all the sharks and rays of the world for the Chondrichthyan Tree of Life Project.
Reference (Open Access): White et al., 2023 Species in Disguise: A New Species of Hornshark from Northern Australia (Heterodontiformes: Heterodontidae). Diversity.
And from an unidentified shark egg collected from the deep waters of northwestern Australia, in 2011 recently helped researchers identify a new species of deep water cat shark. Called ridged-egg catshark Apristurus ovicorrugatus after its eggs, it was collected in the earlys 90 but remained unknown to date. This sharks presents white eyes, and is small in size, reaching less than a half meter in length. .

- Lateral view of female Apristurus ovicorrugatus before preserved. Photo by CSIRO.
Egg cases belonging to this species had been documented as early as the 1980s, but could not be matched to any species of Australian shark until recently scientists examined a shark specimen of previously uncertain identity in the CSIRO collection.

-egg cases of Apristurus ovicorrugatus. Scale bar is 10 mm
Reference (Open Access) White,et al., 2023 What came first, the shark or the egg? Discovery of a new species of deepwater shark by investigation of egg case morphology. Journal of Fish Biology.
#Squatina leae#Squatina#new species#elasmobranch#shark#biology#marine biology#science#marine science#indian ocean#bioblr#sciblr#sci#painted hornshark#Heterodontus marshallae#Heterodontus#Apristurus ovicorrugatus#Apristurus#long post#Ridged-egg catshark#Lea’s angel shark
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Academic economists get big payouts when they help monopolists beat antitrust

After 40 years of rampant corporate crime, there's a new sheriff in town: Jonathan Kanter was appointed by Biden to run the DOJ Antitrust Divisoon, and he's overseen 170 "significant antitrust actions" in the past 2.5 years, culminating in a court case where Google was ruled to be an illegal monopolist:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/07/revealed-preferences/#extinguish-v-improve
Kanter's work is both extraordinary and par for the course. As Kanter said in a recent keynote for the Fordham Law Competition Law Institute’s 51st Annual Conference on International Antitrust Law and Policy, we're witnessing an epochal, global resurgence of antitrust:
https://www.justice.gov/opa/speech/assistant-attorney-general-jonathan-kanter-delivers-remarks-fordham-competition-law-0
Kanter's incredible enforcement track record isn't just part of a national trend – his colleagues in the FTC, CFPB and other agencies have also been pursuing an antitrust agenda not seen in generations – but also a worldwide trend. Antitrust enforcers in Canada, the UK, the EU, South Korea, Australia, Japan and even China are all taking aim at smashing corporate monopolies. Not only are they racking up impressive victories against these giant corporations, they're stealing the companies' swagger. After all, the point of enforcement isn't just to punish wrongdoing, but also to deter wrongdoing by others.
Until recently, companies hurled themselves into illegal schemes (mergers, predatory pricing, tying, refusals to deal, etc) without fear or hesitation. Now, many of these habitual offenders are breaking the habit, giving up before they've even tried. Take Wiz, a startup that turned down Google's record-shattering $23b buyout offer, understanding that the attempt would draw more antitrust scrutiny than it was worth:
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/wiz-turns-down-23-billion-022926296.html
As welcome as this antitrust renaissance is, it prompts an important question: why didn't we enforce antitrust law for the 40 years between Reagan and Biden?
That's what Kanter addresses the majority of his remarks to. The short answer is: crooked academic economists took bribes from monopolists and would-be monopolists to falsify their research on the impacts of monopolists, and made millions (literally – one guy made over $100m at this) testifying that monopolies were good and efficient.
After all, governments aren't just there to enforce rules – they have to make the rules first, and do to that, they need to understand how the world works, so they can understand how to fix the places where it's broken. That's where experts come in, filling regulators' dockets and juries' ears with truthful, factual testimony about their research. Experts can still be wrong, of course, but when the system works well, they're only wrong by accident.
The system doesn't work well. Back in the 1950s, the tobacco industry was threatened by the growing scientific consensus that smoking caused cancer. Industry scientists confirmed this finding. In response, the industry paid statisticians, doctors and scientists to produce deceptive research reports and testimony about the tobacco/cancer link.
The point of this work wasn't necessarily to convince people that tobacco was safe – rather, it was to create the sense that the safety of tobacco was a fundamentally unanswerable question. "Experts disagree," and you're not qualified to figure out who's right and who's wrong, so just stop trying to figure it out and light up.
In other words, Big Tobacco's cancer denial playbook wasn't so much an attack on "the truth" as it was an attack on epistemology – the system by which we figure out what is true and what isn't. The tactic was devastatingly effective. Not only did it allow the tobacco giants to kill millions of people with impunity, it allowed them to reap billions of dollars by doing so.
Since then, epistemology has been under sustained assault. By the 1970s, Big Oil knew that its products would render the Earth unfit for human habitation, and they hired the same companies that had abetted Big Tobacco's mass murder to provide cover for their own slow-motion, planetary scale killing spree.
Time and again, big business has used assaults on epistemology to provide cover for unthinkable crimes. This has given rise to today's epistemological crisis, in which we don't merely disagree about what is true, but (far more importantly) disagree about how the truth can be known:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/25/black-boxes/#when-you-know-you-know
Ask a conspiratorialist why they believe in Qanon or Hatians in Springfield eating pets, and you'll get an extremely vibes-based answer – fundamentally, they believe it because it feels true. As the old saying goes, you can't reason someone out of a belief they didn't reason their way into.
This assault on reason itself is at the core of Kanter's critique. He starts off by listing three cases in which academic economists allowed themselves to be corrupted by the monopolies they studied:
George Mason University tricked an international antitrust enforcer into attending a training seminar that they believed to be affiliated with the US government. It was actually sponsored by the very companies that enforcer was scrutnizing, and featured a parade of "experts" who asserted that these companies were great, actually.
An academic from GMU – which receives substantial tech industry funding – signed an amicus brief opposing an enforcement action against their funders. The academic also presented a defense of these funders to the OECD, all while posing as a neutral academic and not disclosing their funding sources.
An ex-GMU economist, Joshua Wright, submitted a study defending Qualcomm against the FTC, without disclosing that he'd been paid to do so. Wright has elevated undisclosed conflicts of interest to an art form:
https://www.wsj.com/us-news/law/google-lawyer-secret-weapon-joshua-wright-c98d5a31
Kanter is at pains to point out that these three examples aren't exceptional. The economics profession – whose core tenet is "incentive matter" – has made it standard practice for individual researchers and their academic institutions to take massive sums from giant corporations. Incredibly, they insist that this has nothing to do with their support of monopolies as "efficient."
Academic centers often serve as money-laundries for monopolist funders; researchers can evade disclosure requirements when they publish in journals or testify in court, saying only that they work for some esteemed university, without noting that the university is utterly dependent on money from the companies they're defending.
Now, Kanter is a lawyer, not an academic, and that means that his job is to advocate for positions, and he's at pains to say that he's got nothing but respect for ideological advocacy. What he's objecting to is partisan advocacy dressed up as impartial expertise.
For Kanter, mixing advocacy with expertise doesn't create expert advocacy – it obliterates expertise, as least when it comes to making good policy. This mixing has created a "crisis of expertise…a pervasive breakdown in the distinction between expertise and advocacy in competition policy."
The point of an independent academia, enshrined in the American Association of University Professors' charter, is to "advance knowledge by the unrestricted research and unfettered discussion of impartial investigators." We need an independent academy, because "to be of use to the legislator or the administrator, [an academic] must enjoy their complete confidence in the disinterestedness of [his or her] conclusions."
It's hard to overstate just how much money economists can make by defending monopolies. Writing for The American Prospect, Robert Kuttner gives the rate at $1,000/hour. Monopoly's top defenders make unimaginable sums, like U Chicago's Dennis Carlton, who's brought in over $100m in consulting fees:
https://prospect.org/economy/2024-09-24-economists-as-apologists/
The hidden cost of all of this is epistemological consensus. As Tim Harford writes in his 2021 book The Data Detective, the truth can be known through research and peer-review:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/04/how-to-truth/#harford
But when experts deliberately seek to undermine the idea of expertise, they cast laypeople into an epistemological void. We know these questions are important, but we can't trust our corrupted expert institutions. That leaves us with urgent questions �� and no answers. That's a terrifying state to be in, and it makes you easy pickings for authoritarian grifters and conspiratorial swindlers.
Seen in this light, Kanter's antitrust work is even more important. In attacking corporate power itself, he is going after the machine that funds this nihilism-inducing corruption machine.

This week, Tor Books published SPILL, a new, free LITTLE BROTHER novella about oil pipelines and indigenous landback!


If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/25/epistemological-chaos/#incentives-matter

Image: Ron Cogswell (modified) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:George.Mason.University.Arlington.Campus.jpg
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This is wonderful research and scientific testing. Which, I guess you should expect from an actual scientist, but still.
I always grew up thinking the Pyrex glass was indestructible and you could heat it to the temperature of the sun and it would barely flinch. It's a shame they changed the formula without telling folks.
I was going to say Ann is a national treasure, but she's from Australia so I guess she is a global treasure.
And if you are a flat earther I guess a... discal treasure?
2K notes
·
View notes
Text



It is FrogID Week in Australia and tonight we attended a webinar with FrogID Project Coordinator Nadiah Roslan! 🐸
We learnt all about how the FrogID data is used for scientific research, how FrogID captured the first ever recording of the Squelchy Fart Frog, and how FrogID has even helped to identify a new frog species near us! Thank you FrogID! 🐸
#Voigt#Round Frog#Jens#frogs#pets#animals#amphibians#green tree frogs#white’s tree frogs#white lipped tree frogs#frogid#citizenscience#citizen science#frogidweek
160 notes
·
View notes
Video
DSC00459 (c1)orb rsz L by Jim Via Flickr: This is just one of the "Dimensional Entities" captured flying our sky of which you do not see with your eyes. Maybe when Science Accademia accepts that they know very little of our existence as yet, but yet lies to keep restraint on their own path of discoveries and thought..... I doubt it will be disclosed to general public.
#sky#Dimensional entity#My Sky Above#Invisible to eye#Infrared dimensional#Reality Exposed#Australia#extradimensional#discovery#new discoveries#scientific research#what human eyes can't see#flickr
0 notes
Text

Do you know why embryos can be frozen?
#random facts#fun facts#interesting facts#jack facts#facts#charlie and the chocolate factory#fact#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#embryo#embryos#this has been a psa#important psa#psa#just fyi#just a general fyi#also fyi#fyi#science#proscience#science facts#scientific research
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
#africa#antarctica#australia#biodiversity#birds#birdsong#candice gaukel andrews#china#conservation#great barrier reef#hummingbirds#humpback whale#myanmar#natural habitat adventures#nathab#nature#new zealand#ostrich#red list of threatened species#science#science and environment#scientific research#songbirds#songs#syrinx#wild#wildlife#world wildlife fund#wwf#zebra finch
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - January 15, 2024
🎊 - As we embark on another journey around the sun, I am thrilled to bring you the first newsletter of the year, packed with inspiring, informative, and sometimes downright amusing stories.
1. Marijuana meets criteria for reclassification as lower-risk drug

Marijuana has a lower potential for abuse than other drugs that are subjected to the same restrictions, with scientific support for its use as a medical treatment, researchers from the US Food and Drug Administration say in documents supporting its reclassification as a Schedule III substance.
2. South Korea passes law banning dog meat trade

The slaughter and sale of dogs for their meat is to become illegal in South Korea after MPs backed a new law. The legislation, set to come into force by 2027, aims to end the centuries-old practice of humans eating dog meat.
3. After 20 years in a tiny cage, these 'broken bears' are finally feeling the grass beneath their paws

These bears, termed "broken bears" due to physical and psychological trauma from years of abuse, are treated at the Tam Dao rescue center with individually tailored diets, physiotherapy, and medical care. The bear bile trade, which involves extracting bile for traditional Asian medicine, has been illegal in Vietnam since 2005, but a black market still exists.
4. France just got its first openly gay prime minister.

Gabriel Attal is France’s youngest-ever prime minister at age 34 and the first who is openly gay.
5. Australian ‘builders without borders’ repairing war-torn homes and schools in Ukraine

Manfred Hin, a 66-year-old builder from Townsville, Australia, spent most of 2023 volunteering in Ukraine to rebuild homes and schools damaged by Russian attacks. Having contributed to over 50 house and a dozen school renovations, he worked with Ukrainian charity Brave to Rebuild, mentoring young volunteers and sourcing three tonnes of donated tools.
Inspired by Hin's story, Tasmanian carpenter Hamish Stirling also joined the efforts, learning Ukrainian, traveling to Europe, and volunteering for three months to help rebuild homes.
6. The age-standardized death rate from cancer has declined by 15% since 1990
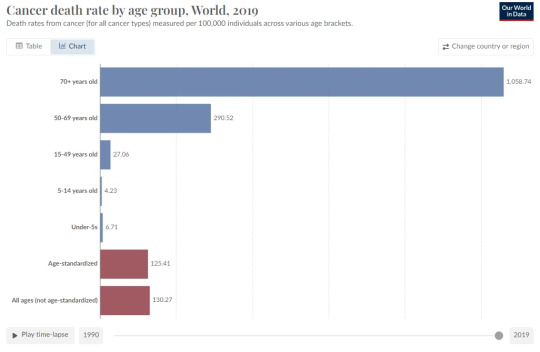
The age-standardized death rate from cancer declined by 15%
Cancer kills mostly older people – as the death rate by age shows, of those who are 70 years and older, 1% die from cancer every year. For people who are younger than 50, the cancer death rate is more than 40-times lower (more detail here).
7. Germany Reached 55% Renewable Energy in 2023

In 2023, 55 percent of Germany’s power came from renewables — an increase of 6.6 percent, according to energy regulator Bundesnetzagentur, reported Reuters. Europe’s biggest national economy has a goal of 80 percent green energy by 2030.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
505 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 2016, when the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) signed a peace agreement with the Colombian government, scientists realized that the rainforests, mountains, and savannahs, out of which the FARC waged a 50-year guerrilla war, and which were counted among the most biodiverse and least-explored places on earth, were suddenly safe to explore.
In Colombia, a few biologists who longed to journey to the heart of these places also saw them as the perfect way to bring 14,000 former guerrillas back into society in a meaningful way that would benefit not only them, but the country’s stunning biodiversity.
Colombia is often referred to as the world’s most biodiverse country. Although this is a hard thing to designate since many species around the world of all kinds remain undiscovered, she does lay claim to the most bird species anywhere on earth – both endemic and migratory.
Who better to help protect Colombia’s wild spaces than those who know them best, thought Jaime Góngora, a wildlife geneticist at the University of Sydney but who is originally from Colombia.
Góngora now leads a group of researchers from the United Kingdom, Australia, and 10 different Colombian scientific institutions in a program to train ex‑guerrillas to study Colombia’s native plants and animals, which to date has uncovered nearly 100 previously-unknown species.
Peace with Nature
Peace with Nature is the result of these scientists working together with guerillas to help protect Colombia’s biodiversity and aid in the post-conflict situation for thousands of people, 84% of whom, according to Góngora, are interested in pursuing, of all things, river habitat restoration as their post-conflict career path.
Góngora and his colleagues are only too happy to help, and Peace with Nature began hosting citizen scientist workshops to help train eager folks how to find, identify, catalogue, and study wild plants, insects, birds, amphibians, and more.
The preparation work was long and hard – between 15 and 18 months according to Góngora...
“In some of the workshops, we have the presence of the police and military forces along with the ex-combatants,” explains Góngora. “I think what has surprised me most is the opportunity that biodiversity offers for reconciliation and healing after an armed conflict. These workshops have been spaces for a respectful dialogue about biodiversity and nature.”"
youtube
-via World at Large, 7/13/20
Note: Video is half in English, half in Spanish. Spanish subtitles for English parts only.
#older news but still relevant#colombia#farc#civil war#conflicts and war#conflict#nature#biodiversity#inaturalist#citizen science#forestry#amazon#amazon rainforest#good news#hope#hope posting#Youtube
792 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive (Daily updates!)
By Rodielon Putol
For countless individuals worldwide, grappling with the lingering impacts of COVID-19 months after their initial recovery has become a puzzling reality.
Often referred to as “long COVID,” the condition is marked by an array of recurring symptoms, including chest pain and heart palpitations.
But why do these symptoms persist? Recent research by the University of Queensland (UQ) offers profound insights.
Cardiovascular impact of long COVID Getting to the root of the matter, the University of Queensland-led investigation focused on post-COVID cardiovascular issues. The goal was to understand why chest pain and heart palpitations persist among long COVID sufferers.
“We discovered elevated levels of cytokines, proteins which help control inflammation in the body, in the blood samples of people at about 18 months post-infection with SARS-CoV-2,” said Professor Kirsty Short.
“Lab studies showed these trace-level cytokines had a direct effect on the functionality of cardiomyocytes, the cells of the heart responsible for its pump function.”
Professor Short noted that these particular types of cells are fundamental building blocks for our heart, so damaging them can lead to cardiovascular symptoms.
Until now, the role of chronic inflammation in cardiovascular symptoms had been unclear, particularly in cases where symptoms persisted for over a year after infection.
These findings bring the medical community one step closer to understanding the full extent of COVID-19’s long-term impact on heart health.
Studying long COVID through blood samples To explore the mysteries of long COVID, the team analyzed the blood of 50 participants from across Australia.
This cohort included individuals who had been living with long COVID for over a year, those who had recovered from COVID-19, and individuals who had never been infected by the virus.
A unique technology developed at UQ’s Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (AIBN) called “immuno-storm chip” nanotechnology, was the tool of choice to investigate trace elevated cytokines. The experts also examined markers linked with cardiac tissue damage.
Although excited about the findings, Professor Short remains cautious. “It’s only early days and these results require validation in additional patient cohorts, including those infected with more recent SARS-CoV-2 strains.”
Professor Short also noted that the study’s focus was primarily on people with cardiovascular symptoms.
Despite the limitations, the research paves the path toward a better understanding of long COVID. It presents comprehensive insights into this complex disease and could potentially enhance diagnosis and treatment options.
A collaborative scientific endeavor The research team included Jane Sinclair, a Ph.D. candidate from UQ’s School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences, Courtney Vedelago from AIBN, and Dr. Feargal J. Ryan of the South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute.
The study represents a collaborative effort by multiple institutes, including UQ’s School of Mathematics and Physics, Institute for Molecular Bioscience, Faculty of Medicine, Mater Health Queensland, Mater Research Institute-UQ, and several other institutions.
COVID’s lasting impact on heart health The findings from the study highlight the importance of understanding the long-term cardiovascular effects of COVID-19, particularly for individuals grappling with symptoms over a year post-infection.
By identifying elevated cytokine levels and their impact on cardiomyocytes, the research opens doors for targeted treatments focused on reducing inflammation to protect heart health in long COVID patients.
“An estimated 65 million people globally suffer from post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), with many experiencing cardiovascular symptoms like chest pain and heart palpitations,” noted the study authors.
Guiding future research While the research team remains cautious about drawing broad conclusions, they acknowledge the study’s potential in guiding future research.
This initial study suggests a need for expanded research across larger and more diverse populations to confirm the findings.
Additionally, future investigations could explore whether specific anti-inflammatory therapies might mitigate the persistent cardiovascular symptoms observed in long COVID patients.
This study marks a pivotal step in understanding long COVID, but it’s only the beginning. By continuing to investigate the role of chronic inflammation, scientists hope to develop clearer diagnostic tools and treatments, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by this complex condition.
The study is published in the journal Nature Microbiology. www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01838-z
#mask up#covid#pandemic#public health#wear a mask#covid 19#wear a respirator#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne
59 notes
·
View notes

