#Respiratory health assessment
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Special Lung Health Package at HCG Hospitals Ahmedabad - Just ₹1999!

Book your lung health package at HCG Hospitals, Ahmedabad for just ₹1999 until April 30, 2024. Includes expert consultations, Spirometry, DLCO tests, and more. Prioritize your lung health and breathe easier with our comprehensive care.
#Lung health screening#Pulmonary function test#Respiratory health assessment#Lung disease detection#Bronchial health check#Lung health evaluation#Breathing capacity analysis
0 notes
Text
someone get me off this damn site i have an exam tomorrow at 1030am i gotta study 😭😭😭😭😭
#its health assessment w focus on respiratory and cardiovascular and supposedly the hardest of the exams in this class#there’s so much shit and i feel p good on the anatomy and normal vs abnormal signs in patients and stuff#but theres so many risk factors and symptoms we gotta know for cardiovascular diseases#and for respiratory we gotta know shit like what diseases make exactly what sounds and how people cough lmfao. so specific#but im gonna ball anyway IM NOT SETTING MY EXPECTATIONS HIGH THO IM PREPARING FOR DISAPPOINTMENT JUST INCASE U KNOW#send me good luck pleas im begging guys 🙏
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

#best product#Medical Device#Lung Function Test#Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT)#Respiratory Health#Spirometry#Breathing Assessment#Airflow Measurement#COPD Monitoring#Asthma Management#Pulmonary Rehabilitation#Vital Capacity Measurement#Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF)#Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV)#Inspiratory Capacity (IC)#Portable Spirometer#Digital Spirometer#Home Use Spirometer#Clinical Spirometer#Bluetooth Spirometer#Lung Monitoring Device
0 notes
Text
youtube
#COPD#prognostic models#serum biomarkers#acute exacerbations#chronic obstructive pulmonary disease#AECOPD#predictive modeling#respiratory health#pulmonary disease#patient outcomes#risk assessment#chronic disease management#respiratory therapy#biomarker analysis#precision medicine#healthcare innovation#clinical research#disease progression#inflammation markers#treatment strategies#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
Whenever you hear someone trying to blame kid's poor test scores "post pandemic" on "lockdowns," show them this.
By Dr. Sushama R. Chaphalkar, PhD.
New research shows that mild COVID-19 alters brain structure and connectivity in key areas responsible for memory and cognition, emphasizing the lasting effects on young people’s brain health.
In a case-control study published in the journal Translational Psychiatry, researchers used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cognitive tests to examine brain structure, function, and cognition in adolescents and young adults with mild coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) compared to healthy controls in a pandemic hotspot in Italy. They identified significant changes in brain regions related to olfaction and cognition, with decreased brain volume and reduced functional connectivity in areas like the left hippocampus and amygdala, which were linked to impaired spatial working memory. Notably, no significant differences were observed in whole-brain connectivity, suggesting that these changes were localized rather than widespread.
Background COVID-19, primarily known for respiratory symptoms, also affects the central nervous system, leading to neurological issues like headaches, anosmia, and cognitive changes. MRI-based studies reveal anatomical brain changes in COVID-19 patients, such as reduced gray matter and decreased volume in regions like the hippocampus and amygdala, often linked to cognitive deficits.
While research mostly focuses on severe cases and older adults, a majority of infections with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19, occur in adolescents and young adults who also experience long-lasting cognitive symptoms.
This age group, undergoing key brain development, is impacted by changes in spatial working memory and brain structure, which are crucial for cognitive functions shaped by social interactions, significantly disrupted by the pandemic.
Given that this is the largest and most understudied population affected by COVID-19, understanding the brain and cognitive impacts in adolescents and young adults is vital.
Therefore, researchers in the present study compared anatomical, functional, and cognitive outcomes, utilizing a longitudinal design that allowed them to assess both pre- and post-infection differences, in COVID-19-positive and negative adolescents and young adults from Lombardy, Italy, a global hotspot during the pandemic.
About the study The present study involved participants from the Public Health Impact of Metal Exposure (PHIME) cohort, a longitudinal investigation of adolescents and young adults in northern Italy. Between 2016 and 2021, 207 participants, aged 13 to 25 years, were included in a sub-study with MRI scans and cognitive tests. After COVID-19 restrictions were lifted, 40 participants (13 COVID+ and 27 COVID−) participated in a follow-up study, which replicated the MRI and cognitive assessments.
The mean age of participants was 20.44 years and 65% were female. COVID+ status was confirmed through positive reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) tests within 12 months of follow-up. Neuropsychological assessments used the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB) to evaluate spatial working memory.
MRI and functional MRI data were acquired using a 3-Tesla scanner, processed, and analyzed for structural and local functional connectivity using eigenvector centrality mapping (ECM) and functional connectivity (FC) metrics. Whole-brain functional connectivity metrics showed no significant differences between COVID+ and control groups, indicating that the observed changes were specific to key brain regions rather than generalized across the entire brain.
Statistical analysis involved the use of pairwise Student's t-tests, Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, linear regression, two-waves mediation analysis, negative binomial regression, and linear regression, all adjusted for covariates.
Results and discussion Significant differences were observed in the two groups regarding the time between assessments, COVID-19 symptoms, and vaccine status. The research identified five localized functional connectivity hubs with significant differences between the two groups, including the right intracalcarine cortex, right lingual gyrus, left frontal orbital cortex, left hippocampus and left amygdala, which is vital for cognitive functions. Only the left hippocampal volume showed a significant reduction in COVID+ participants (p = 0.034), while whole-brain connectivity remained unchanged, reinforcing the localized nature of the brain changes.
The left amygdala mediated the relationship between COVID-19 and spatial working memory "between errors" (p = 0.028), a critical finding that highlights the indirect effect of amygdala connectivity on cognitive function in COVID+ individuals. This mediation analysis underscores the role of specific brain regions in influencing cognitive deficits, as only the indirect effect was statistically significant for spatial working memory errors. The orbitofrontal cortex, involved in sensory integration and cognitive functions, also showed decreased connectivity in COVID+ individuals, supporting previous findings of structural and functional changes in this region during COVID-19.
The study is limited by small sample size, lack of diversity, potential confounding factors due to the long interval between MRI scans, treatment of certain subjects as COVID-negative based on antibody testing beyond the 12-month threshold, and the possibility of non-significant findings in mediation analysis due to these factors.
Conclusion In conclusion, the findings indicate persistent structural and functional alterations in specific brain regions of COVID-19-positive adolescents and young adults, including changes in gray matter volume and localized functional connectivity, which correlate with diminished cognitive function, particularly in working memory.
Further research is necessary to evaluate the longevity and potential reversibility of these brain and cognitive changes post-infection, enhancing our understanding of post-COVID outcomes and informing future interventions and treatments. The longitudinal design of this study, with pre- and post-COVID data, strengthens these findings by allowing direct comparisons over time, offering robust insights into the impact of COVID-19 on adolescent brain development.
Journal reference: COVID-19 related cognitive, structural and functional brain changes among Italian adolescents and young adults: a multimodal longitudinal case-control study. Invernizzi, A. et al., Translational Psychiatry, 14, 402 (2024), DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-03108-2, www.nature.com/articles/s41398-024-03108-2
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne#wear a fucking mask
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
F1 and VO2 Max Training
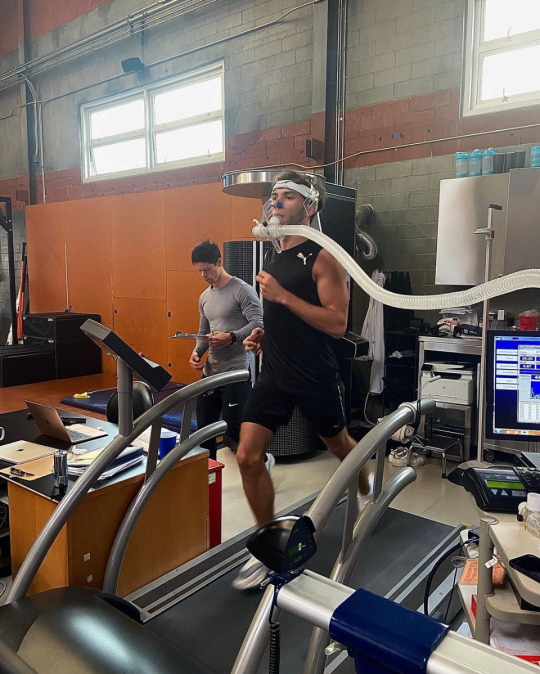
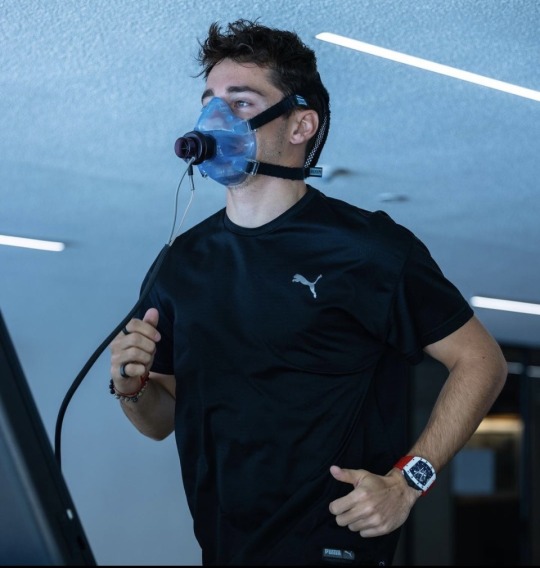
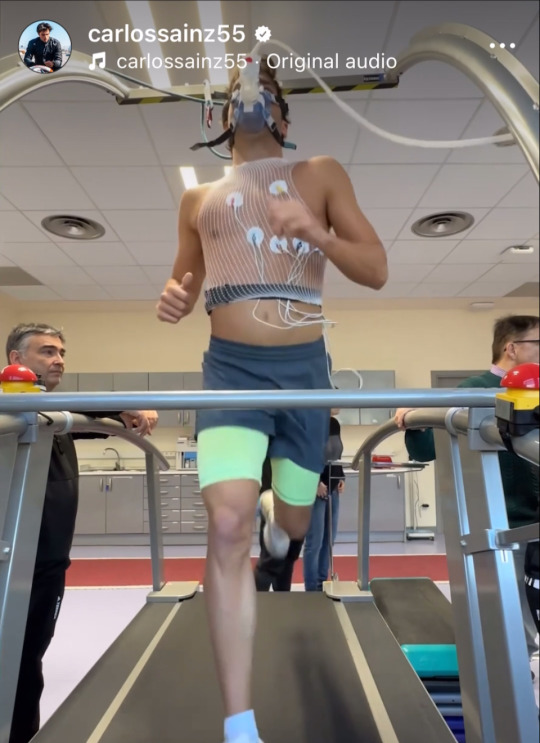
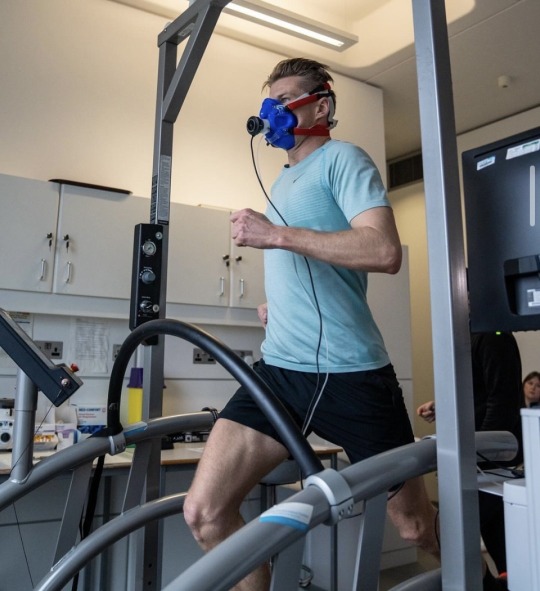




(x)(x)(x)(x)(x)
What is VO2 Max Training and why do drivers do it?
VO2 Max is the maximum amount of oxygen the body absorbs during exercise and can measure aerobic fitness levels. VO2 = Volume of oxygen consumed by the body per minute - it is one of the strongest predicters of heart disease and death. It is the best measure of cardiac and respiratory fitness available.
VO2 is measured in ml (of oxygen) / kg (body mass) / minute
How much oxygen the body consumes - the amount of blood the heart pumps per minute and how much oxygen was taken from it.
Now...why do F1 drivers need this?
Drivers put extreme demand on their cardiovascular, respiratory and overall physical health during races. Their bodies are subjected to enormous amounts of g-force and experience extreme heat and stress. They need a lot of energy to do this and as a result can burn a lot of calories per race.
VO2 max training is a useful measurement to assess a drivers endurance at their maximum during exercise which they are subject to during a race. The strain they're under during a race would require their bodies to be pushed to the max, requiring optimal oxygen intake and energy production.
It can ensure drivers are fit enough to endure the stress they subject their bodies to despite the environment within the car - maximum speeds/ heat. It gives drivers and their teams a greater understanding of how hard they can push their bodies and also how they can further maximise their performance during races.
Want to know a bit more about the science? Read below.
Now the (more) science-y bit - oxygen is used in respiration and as you breathe in oxygen the lungs turn it into energy called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This powers the cells and helps release the CO2 in the body that's created during respiration when you breathe out.
The greater a persons VO2 max, the more oxygen a body can consume and the more effectively the body can use this to create the maximum amount of ATP energy and the better the body can handle aerobic/ cardio exercise.
During the test the goal is to get to maximum exercise to determine max heart rate, vo2 max and an estimated lactate threshold. The test measures oxygen consumption and CO2 production using a mask to determine values. The goal is to run at a comfortable speed but not too comfortable for around 10 minutes to max out oxygen consumption and heart rate. During the test heart rate is measured using the ECG dots you can see on the chest.
The Fick Equation is used to calculate VO2.
VO2 (mls O2/ minute) = cardiac output (stroke volume x cardiac output) x arteriovenous oxygen difference (difference in O2 content between arterial and venous blood - how much O2 is used by tissues in systemic circulation).
So in short, VO2 is how much oxygen the body consumes - how much blood the heart pumps per minute and how much oxygen was taken from it.
#f1#formula one#formula 1#carlos sainz#charles leclerc#nico hulkenberg#pierre gasly#vo2 max#science#medicine#mine
203 notes
·
View notes
Text
🩺 GASS (Gallifreyan Assessment Scoring System)
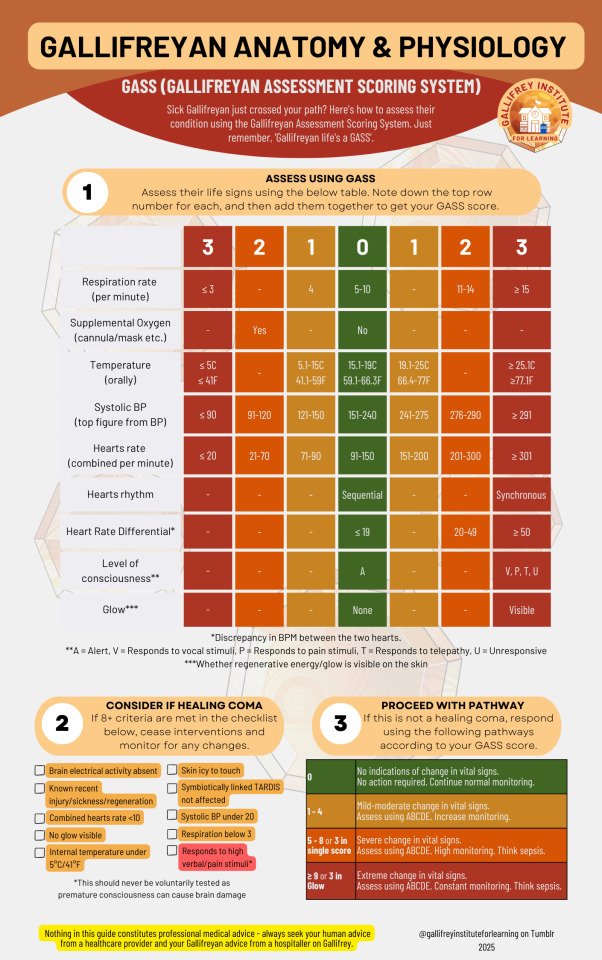
BIGGER - Google Drive: PDF / Image JPG / Image PNG
This guide is for use on Gallifreyans and Time Lords only. Always seek your human advice from human health providers.
✨ What is GASS?
The Gallifreyan Assessment Scoring System (GASS) is a tool designed to rapidly evaluate a Gallifreyan's condition. By monitoring vital signs and unique Gallifreyan indicators, it prioritises emergency responses while accounting for their distinct physiology, such as dual hearts and regenerative abilities.
📈 What's New in GASS?
This updated version of GASS includes critical refinements for more precise assessments. New categories have been added, such as Heart Rate Differential (HRD) to flag discrepancies between the two hearts and T = Responds to Telepathy in the level of consciousness scale. Adjustments to thresholds for vital signs and regenerative glow visibility also improve detection of emergencies like fibrillation or post-regenerative trauma.
📝 How to Use GASS
1️⃣Initial Observations
Ensure the environment is safe (e.g., no stray Daleks).
Observe for immediate signs of distress: skin colour, breathing effort, or lack of responsiveness.
2️⃣Evaluate Vital Signs and Assign Scores
Refer to the GASS table to assess each category:
🌬️ Respiration Rate: Count breaths per minute. Adjust for respiratory bypass if present.
🫧 Supplemental Oxygen: Note if oxygen support is in use.
🌡️ Temperature: Measure orally.
💓 Systolic BP: Record using a normal sphygmomanometer.
💖 Hearts Rate (Combined): Count the total bpm across both hearts.
🔄 Hearts Rhythm: Sequential beats (thud-thud, thud-thud) are normal; synchronous beats (thud-thud together) indicate fibrillation.
⚖️ Heart Rate Differential (HRD): Calculate the bpm difference between hearts; large discrepancies suggest possible singular heart failure.
🧠 Level of Consciousness (AVPTU): A = Alert, V = Responds to verbal stimuli, P = Responds to pain, T = Responds to telepathy, U = Unresponsive
✨ Regenerative Glow: Check for visible energy on the skin.
3️⃣Check for Healing Coma
If 8+ healing coma criteria are met:
Cease active interventions.
Monitor closely for changes.
Avoid premature waking to prevent neurological damage.
4️⃣Calculate Total GASS Score
Add up the scores from all categories:
0: No concerning changes. Continue routine monitoring.
1–4: Mild to moderate changes. Perform an ABCDE assessment and increase monitoring.
5–8 or 3 in single score: Severe changes. Perform ABCDE, escalate care, and consider sepsis.
≥9 or Glow = 3: Extreme changes. Initiate emergency intervention, constant monitoring, and prepare for sepsis protocols.
5️⃣Reassess After Interventions
Following each intervention, reassess the GASS score to adapt care and ensure stability.
🚨 When to Escalate
Critical signs: Synchronous heartbeats, extreme HRD, or GASS score ≥9.
Sepsis or Specific Emergencies: Use respective protocols for management.
📌 Key Points to Remember
Combine GASS results with clinical judgement.
Healing comas are protective states—let them run their course.
Escalate care if in doubt.
Medical Guides These are all practical guides to assessing and treating a Gallifreyan in an emergency.
📓|⚕️Gallifreyan CPR: Guide for reviving a Gallifreyan in cardiac arrest. [Update due]
📓|⚕️Gallifreyan Assessment Scoring System (GASS): Guide for assessing vital signs.
📓|⚕️ABCDE Assessment: Guide for quickly assessing and treating a sick Gallifreyan. [Update due]
📓|⚕️Sepsis Emergency Response (SER): Guide for identifying and treating sepsis. [Update due]
📓|⚕️Gallifreyan Pyrexia: Guide for assessment and treatment of fevers in Gallifreyans. [Update due]
Any purple text is educated guesswork or theoretical. More content ... →📫Got a question? | 📚Complete list of Q+A and factoids →😆Jokes |🩻Biology |🗨️Language |🕰️Throwbacks |🤓Facts →🫀Gallifreyan Anatomy and Physiology Guide (pending) →⚕️Gallifreyan Emergency Medicine Guides →📝Source list (WIP) →📜Masterpost If you're finding your happy place in this part of the internet, feel free to buy a coffee to help keep our exhausted human conscious. She works full-time in medicine and is so very tired 😴
#doctor who#dr who#dw eu#gallifreyans#GIL biology#GIL#gallifrey institute for learning#gallifreyan biology#Time Lord biology#GAP Quick Guides#whoniverse#GIL content
54 notes
·
View notes
Text



Do you have anything to spare to help pocket pets in need? We had 5 expensive vet visits on Friday totaling 724.13
Tiny Whiskers Animal Rescue is a 501c3 small mammal rescue in Minnesota. We are entirely volunteer run. We typically care for over 100 animals at a time.
Blossom, Bubbles, and Buttercup are 3 mice who were an owner surrender. Blossom has an eye infection, Bubbles has an upper respiratory infection, and Buttercup (pictured) has a skin infection. All three are getting medicated twice a day and will likely need a recheck in two weeks to assess their progress.
Gaston is a 5 year old male guinea pig who has always had a funny breathing pattern. He’s never had any other symptoms of health issues, and has been vet checked before and cleared. However his foster felt he’s been acting a little off and this time our vet recommended radiographs just to be sure. It turns out his liver is MUCH larger than it should be, so he is getting two different meds for the next few weeks as well and then a recheck in a month to assess his progress.
Pancake was a 2.5 year old sanctuary rat at the rescue whose mammary tumors grew too large to be comfortable and had to be euthanized. We miss her dearly.
If you can help us cover these costs, please! Even $5 is an immense help.
Venmo: tiny-whiskers
PayPal: [email protected]
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
Healthcare workers (HCWs) with COVID-19 had more severe symptoms that lasted longer than those with other respiratory diseases, and a higher proportion met the World Health Organization (WHO) or UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) definitions of long COVID, according to a report published in Viruses and Viral Diseases.
A team led by Murdoch Children's Research Institute investigators in Parkville, Australia, also identified older age, chronic respiratory disease, and pre-existing symptoms as risk factors for long COVID, also known as post-acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS).
Data from phase 3 clinical trial
The researchers analyzed data on long-COVID symptoms, duration, and pre-existing symptoms from the multinational randomized controlled trial (RCT) BRACE trial on HCWs diagnosed as having COVID-19 or another respiratory illness for 1 year after diagnosis.
Participants were tested for COVID-19 infection if they reported symptoms, gave blood samples every 3 months for evaluation for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, and completed quarterly surveys. A subsample of 184 COVID-19 and 184 non-COVID controls were also chosen for a case-control analysis of daily symptom data with an extended pre- and post-infection follow-up period.
BRACE is a phase 3 RCT assessing the effect of bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) tuberculosis vaccination on COVID-19 infection in HCWs in Australia, Brazil, the Netherlands, Spain, and the United Kingdom from March 2020 to April 2021.
More extensive systemic effects
The 593 COVID-infected HCWs had significantly more severe disease than 1,112 participants with other respiratory illnesses (odds ratio [OR], 7.4). The persistence of symptoms met both the NICE and WHO long-COVID definitions in a higher proportion of COVID-19 survivors than those with other respiratory diseases (2.5% vs 0.5%, respectively; odds ratio [OR], 6.6 for NICE and 8.8% vs 3.7%; OR, 2.5 for WHO).
@startorrent02
34 notes
·
View notes
Note
heyhey! you rb'd the snoring hummingbird video and i was wondering if this is actually snoring or could be a sign of respiratory distress? you seem to know a lot more about birds than i do but it just set off some alarm bells bc ive seen a similar vid before and the fledging in it most likely didn't survive & im curious if it could point towards a health problem here too or if my pattern recognition is just fucking me over. genuinely just curious, the beak opening has got me stumped
I have no idea, I'm not a hummingbird guy. My impression seems to be that the video was taken by a rehabber or other professional, who I assume would have known if it was. Opening this up because I know I have followers/mutuals on here who do bird rehab and thus can better assess this than me
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
Shelters seeing significant increase in infectious diseases: UN
About 316 people were killed, and another 664 injured, by Israeli bombardments in the 24 hours between the afternoon of December 2 to afternoon of December 3, according to Gaza’s Ministry of Health.
Aid trucks carrying humanitarian supplies entered from Egypt on December 3, though their number and contents were unclear, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA) also reports in its latest situation assessment.
According to the latest UNOCHA report:
UN shelters in southern Gaza have seen significant increase in communicable diseases such as diarrhoea, acute respiratory infections, skin infections and lice due to overcrowding.
Hospital bed capacity across Gaza is down from 3,500 prior to the hostilities to 1,400, amid a surge in people seeking treatment.
Only one currently functioning hospital in Gaza has the capacity to perform complex surgery or treat critical trauma cases.
91 notes
·
View notes
Text



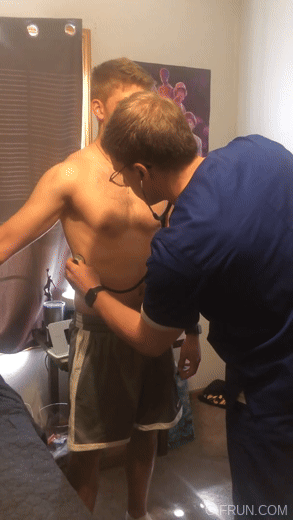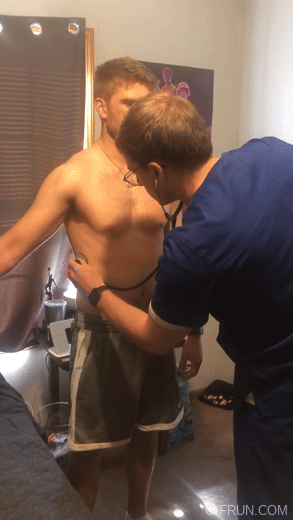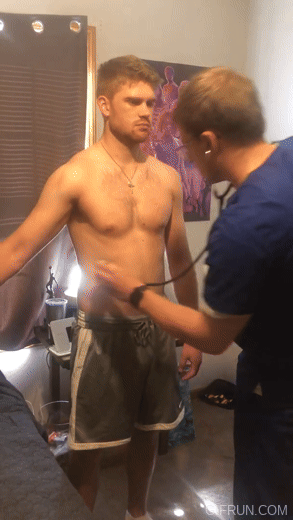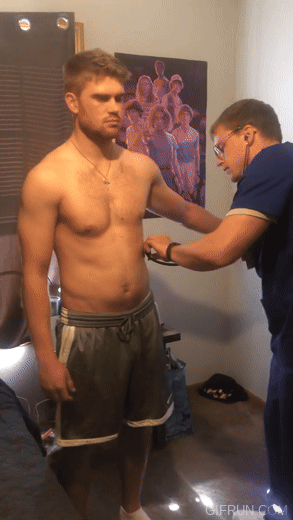
oxBk_PglA84
#doctor and patient#head to toe assessment#physical exam#stethoscope#doctor roleplay#male body#cardio exam#health assessment#heart auscultation#auscultation#male beauty#male aesthetic#pecs#big pecs#respiratory examination#respiratory exam
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Excerpt from this story from Inside Climate News:
In recent years, gas stoves have been an unlikely front in the nation’s culture wars, occupying space at the center of a debate over public health, consumer protection and the commercial interests of manufacturers. Now, Norton is among the environmental advocates who wonder if a pair of recent developments around the public’s understanding of the harms of gas stoves might be the start of a broader shift to expand the use of electrical ranges.
On Monday, lawmakers in the California Assembly advanced a bill that would require any gas stoves sold in the state to bear a warning label indicating that stoves and ovens in use “can release nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, and benzene inside homes at rates that lead to concentrations exceeding the standards of the Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment and the United States Environmental Protection Agency for outdoor air quality.”
The label would also note that breathing those pollutants “can exacerbate preexisting respiratory illnesses and increase the risk of developing leukemia and asthma, especially in children. To help reduce the risk of breathing harmful gases, allow ventilation in the area and turn on a vent hood when gas-powered stoves and ranges are in use.”
The measure, which moved the state Senate, could be considered for passage later this year.
“Just running a stove for a few minutes with poor ventilation can lead to indoor concentrations of nitrogen dioxide that exceed the EPA’s air standard for outdoors,” Gail Pellerin, the California assembly member who introduced the bill, said in an interview Wednesday. “You’re sitting there in the house drinking a glass of wine, making dinner, and you’re just inhaling a toxic level of these gases. So, we need a label to make sure people are informed.”
Pellerin’s proposal moved forward in the legislature just days after a group of Stanford researchers announced the findings of a peer-reviewed study that builds on earlier examinations of the public health toll of exposure to nitrogen dioxide pollution from gas and propane stoves.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi there! I'm Cate and for the last 6 years I've worked in emergency medical services on an ambulance in the Northeastern United States. I have also been an avid fanfic reader for a long time with a love for hurt/comfort and enemy-to-caretaker. With that in mind, I want to provide a resource to writers.
With the upcoming @whumptober having a plethora of options with trauma, I want to help make the research for injuries a little easier to find and understand.
Below the cut is a long list. If there is a specific catagory you want to see sooner rather than later, send me a message or an ask. Same for if there's something you want to see that's not there.
For ease of injury descriptions "Sam" is our injuried/ill character.
If you have any questions regarding country/regional/state treatment guidelines for your fictional first responders, please reach out and I will try to point you in the right direction. This information is intended solely for use as a fictional writing resource.
DISCLAIMER: This is not medical advice nor is this a suitable substitute for training. Please do not use this information to diagnose or treat yourself for any injury or illness. Seek professional medical advice (emergency medical services, hospitals, urgent cares, tele-health, ect.) if you are injured or ill.
Glossary
Mechanism of Injury
Motor Vehicle Collsion
Motor Vehicle Vs Motor Vehicle
Character on Motorcycle/ATV
Character struck by Motor Vehicle
Character on bicycle/scooter struck by Motor Vehicle
Fall
Assault
Without Weapons
Penetrating Injuries (Stabbings)
Gunshot Wounds
Blunt Objects
Fires/Explosions
Burns
Smoke Inhalation/CO2
Explosive injuries
Head/Face/Neck/Neurological
Concussion
Stroke
Seizure
Spinal Injury
Facial Injury
Nose Bleed
Mouth/Airway/Choking
Chest/Cardiac/Respiratory
Cracked/Broken Ribs
Pneumothorax/Hemothorax
Cardiac Arrest
Pulmonary Embolism
Chest Pain
Asthma
Gastrointestinal/Urinary/Genitals
Internal Bleeding (Organ Damage)
Evisceration/Disembowlment
For genital/urinary injuries
Reproductive Systems
Kidney and Urinary Systems
Sexual Assault
Bones/Muscles
Muscle Sprain/Strain
Dislocations
Broken Bones
Radius/Ulna (forearm) and Tibula/Fibula (calf)
Humerus (upper arm) and Femur (thigh)
Pelvis/Hips
Back/Spine/Neck
Ribs/Clavicle
Fingers/Toes
Amputation
Organ Functions
Heart
Brain
Lungs
Liver
Spleen
Gastrointestinal System (stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and appendix)
Kidneys and Urinary System
Reproductive Sysems (male and female)
Special Topics
Anxiety/Panic Attacks
Blood Thinners
Suicide
Overdoses
Sexual Assault
Anemia/Hypovolemia
General Knowledge Topics
Hazardous Materials
General Mental Health
Child/Elder Abuse
Refusal of Medical Care
Basic Anatomy
Basic Patient Assessment
Blood Pressure (From my main blog)
#writer resources#writing resources#writing challenge#medical terms#author resouces#writng#whump#angst#whumptober#medic characters#medical characters#first responder characters#firefighter characters
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
The field of post-infectious diseases didn’t (except for ME/CFS) exist prior to the coronavirus. The medical field focused on treating infections – not dealing with their aftermath. Recent studies indicate why that’s not going to fly anymore – and it’s not just because of ME/CFS. It’s because large studies are indicating that a coronavirus infection – whether it’s mild or severe – is upping the risk for all sorts of diseases.
Most of these studies are very large – running into the millions of participants – that rely on electronic health records. They’re comparing the incidence of new diagnoses in people who were infected with the coronavirus with those who weren’t.
Eric Topol recently wrote a blog on the autoimmune implications of COVID-19. Three recently published large studies lead Topol to report a “substantially increased risk of developing a diverse spectrum of new-onset autoimmune diseases.“
The increased risk was not low – a 20-40% increase in the likelihood of coming down with one of these illnesses – and the range of autoimmune illnesses affected was diverse indeed: the studies pointed to dramatic increases in the diagnosis of almost 20 autoimmune diseases. (See blog for the diseases). Since autoimmune disease can take a while to show up after an infection, one can only assume that this number will rise over time.
Other studies have found a marked increase in neurological diseases, including some one might not have thought. Besides things like cognitive disorders, sharp increases in the rates of psychotic disorders, epilepsy, stroke, and parkinsonism as well as others.
Cardiovascular and metabolic diseases have not been as well assessed but increases in asthma, type I and type II diabetes, respiratory diseases, heart failure, and stroke have been seen.
Oddly enough, none of these studies have assessed increased incidences of the one disease long COVID has been most associated with – ME/CFS. Nor have they assessed new diagnoses of fibromyalgia, IBS, dysautonomia, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), or gynecological diseases.
If you want more research into post-infectious illnesses, then linking an infectious event to dozens of serious illnesses can only help.
The study makes one wonder how many chronic illnesses were triggered by an infectious event.
For all of its horrendous impact, the coronavirus pandemic is clearly going to force the medical profession to take a very close look at what happens during an infectious event – and afterward – and that is good news for anyone with a post-infectious illness like ME/CFS.
86 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
Every infection, no matter how mild, has a cumulative effect on your brain, reducing gray matter and altering function. Mask up. Keep yourself and others safe from a disease that can and will cause many varied lingering issues.
by Denis Storey
Clinical relevance: New research shows that even mild COVID-19 cases in young adults can lead to changes in brain structure and function.
Researchers found reduced connectivity in key brain regions, including the left hippocampus and amygdala. These changes were linked to deficits in spatial working memory and cognitive performance. The study highlights the need for further research into long-term neurological effects of COVID-19, even in mild cases. For all the damage the pandemic’s done, it seems as if the youngest generations will pay the steepest price. The latest proof of that has emerged in new research that’s discovered that even the mildest of COVID cases among young adults can lead to changes in brain structure and function. As a result, it could pose a threat to long-term cognitive performance.
The research provides new insight into the potential neurological impact of SARS-CoV-2 in populations that avoided severe illness. The study focused on adolescents and young adults since it’s a group that’s remained relatively understudied.
Methodology The study, part of the Public Health Impact of Metal Exposure (PHIME) cohort, included 40 participants. More than a dozen of them – 13 – tested positive for COVID-19, while 27 served as controls.
The researchers enrolled the participants in a longitudinal study, which offered pre-pandemic baseline data through MRI scans and cognitive assessments. This allowed the team a unique look into pre- and post-pandemic neural outcomes.
The researchers relied on the latest neuroimaging technology, such as resting-state functional MRI (fMRI) and structural MRI, to examine shifts in brain connectivity and cortical volume.
The researchers also subjected the participants to cognitive testing focused on spatial working memory. The team conducted the assessments both before the COVID-19 pandemic and after recovery from mild COVID-19 cases. These parallel evaluations allowed for a direct comparison of brain and cognitive changes.
COVID Affected Multiple Brain Regions The study exposed notable differences between COVID-19-positive and healthy participants in five critical brain regions:
The right intracalcarine cortex. The right lingual gyrus. The left hippocampus. The left amygdala. And the left frontal orbital cortex. Perhaps most notably, the left hippocampus revealed a significant drop in cortical volume among those who’d tested positive for COVID.
Researchers also found that the left amygdala showed much lower connectivity in participants who’d contracted COVID-19. This lack of connectivity appeared to be linked to deficits in spatial working memory. From this, the researchers inferred that even mild COVID-19 infection could impair one’s ability to perform tasks that rely on short-term memory.
Backing Up Previous Research The study results echo a mounting body of literature that suggests that COVID-19, despite its nature as a respiratory virus, appears to have far-reaching neurological implications. Earlier research has linked more serious cases of the virus with reduced gray matter thickness and cerebral volume loss, particularly in the hippocampus and amygdala.
The researchers add that the brain changes they observed could be related to the neurotoxic effects of SARS-CoV-2, which could have a lingering influence even among milder caes of infection. The paper’s authors theorize that it could be because the virus might be invading the brain through the olfactory system. That could cause inflammation and damage in important neural regions.
On the other hand, the authors also posit that the social and psychological stressors of the pandemic – whether its the social isolation or the lingering uncertainties – could be a factor in the changes appearing in the brains of the COVID-positive participants.
These results underscore the necessity for more research into the long-term neurological effects of the pandemic, especially among its younger survivors.
Moving Forward Finally, the research team hints that further investigation could clarify whether these neurological changes are permanent, and – if not – how long they might last.
The authors conclude by insisting that this study offers crucial new insight into the potentially long-term ramifications of COVID on the brain, even in mild cases. As we struggle with life in the shadow of the pandemic, a better grasp of what it means for everyone who’s been infected could help us develop more effective treatments.
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#still coviding#covid 19#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid conscious#covid19#covid is not over
51 notes
·
View notes