#Philip Cox
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text








25th Hour (Spike Lee, 2002)
Cast: Edward Norton, Philip Seymour Hoffman, Barry Pepper, Rosario Dawson, Brian Cox, Anna Paquin, Tony Siragusa. Screenplay: David Benioff, based on his novel. Cinematography: Rodrigo Prieto. Production design: James Chinlund. Film editing: Barry Alexander Brown. Music: Terence Blanchard.
Spike Lee's 25th Hour is a "day in the life" movie, and a very good one. The day is the last one of freedom for Monty Brogan (Edward Norton) before he goes to prison for seven years. He spends it with his girlfriend, Naturelle (Rosario Dawson), his friends Jacob (Philip Seymour Hoffman) and Frank (Barry Pepper), and his father (Brian Cox), and also makes a visit to the Russian mobsters who got him into the business of pushing drugs. It's also one of Lee's best films, less celebrated than Do the Right Thing (1982) or Malcolm X (1992), but worthy of being mentioned in their company. The only reservation I have about the movie is that Lee doesn't let his powerhouse cast bring their solidly written characters to life without indulging in a few distracting cinematic tricks. He and his longtime editor, Barry Alexander Brown, can't seem to resist techniques like freeze frames and moments in which the action is repeated from a different angle. There are showy montages and tour de force episodes, some of which work, like the "fuck you" episode in which the embittered Monty anathematizes almost every racial, social, and economic group in New York City. And the film ends with a beautifully realized sequence in which Monty's father proposes to help him escape and imagines the life he might live. But other episodes don't quite work, like the long take in which Jacob and Frank talk about their friendship with Monty, a scene that must have involved careful preparation on the part of Pepper and Hoffman, But it's staged in front of a window in Frank's apartment, which somewhat improbably overlooks Ground Zero, where crews are clearing away the rubble of the World Trade Center. I couldn't help being distracted by the scene outside the window instead of concentrating on their dialogue. Still, the movie, which was planned before the 9/11 attack and completed and released afterward, beautifully integrates that event into the theme and tone of the film, which deserves to find the audience it never quite did when it was released.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
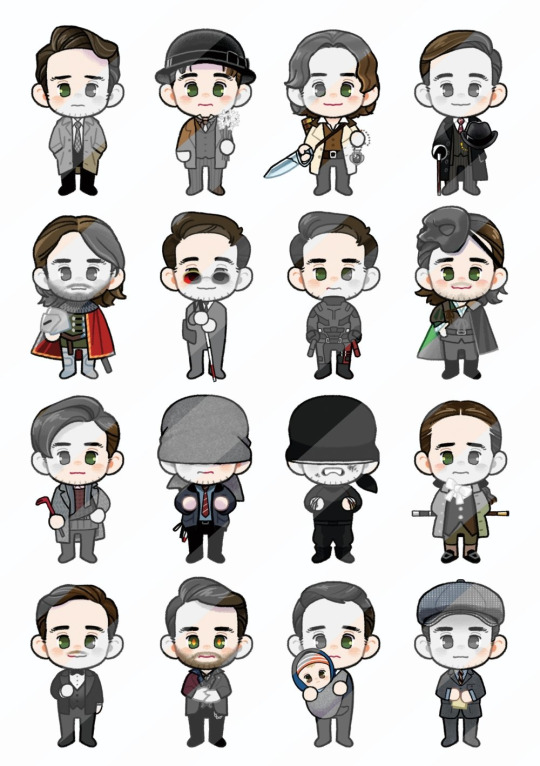


OMGGGGG, LOOK!!!!!!!!! 😲🤯😵💫
IT’S EVERY CHARACTER CHARLIE COX HAS EVER PLAYED!!!!!!! 😍😍😍 (Or pretty close to it.)
THIS IS THE CUTEST F*CKING THING I’VE EVER SEEN!!!!! 😭
.
Art by @quokaqisola on Twitter (X)
#so many little Charlies...I feel a bit faint tbh lol 😵💫❤️💗❤️#aaaahhh so many character tags T_T#fanart#charlie cox#charles thoroughgood#tristan thorn#duke of crowborough#philip villiers#diafebus#matt murdock#lorenzo#ian hamilton#giovanni bruni#lawrence#henry#carter#owen sleater#basil#jonathan hellyer jones#michael kinsella#jerry#adam lawrence#josemaria escriva#danny griffon#ishmael#daredevil#the defenders#she-hulk: attorney at law#Charlie character appreciation post <3#Charlie appreciation post <3
251 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Star Trek Explorer short story collection, "A Year to the Day I Saw Myself Die", out next month
Titan Comics will publish a new collection of Star Trek stories from Star Trek Explorer next month - some only previously seen by the magazine's subscribers
Titan Comics will publish a new collection of Star Trek stories from Star Trek Explorer next month – some only previously seen by the magazine’s subscribers. Cover by Neil Edwards As we previously reported, the collection takes its name from the Star Trek: Deep Space Nine short story written by comic creator Michael Collins, the hardback collection, Star Trek Explorer: A Year to the Day I Saw…
#Andy Walker#Chris McAuley#David Mack#downthetubes News#Greg Cox#Keith R.A. DeCandido#Louie de Martinis#Mike Collins#Neil Edwards#Pete Wallbank#Philip Murphy#Rich Handley#Star Trek#Star Trek Explorer#Una McCormack#Walter Koenig
13 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Downton Abbey S01E01
#Downton Abbey#daedit#downtonedit#downtonabbeyedit#tvandfilm#dailytvgifs#lgbtedit#LGBT#Philip Villiers#Duke of Crowborough#Thomas Barrow#Robert Crawley#Cora Crawley#My Gif#Charlie Cox#Rob James Collier#Hugh Bonneville#Elizabeth McGovern#userstream#userbbelcher#chewiebiog#mlm#mlw#gay#bisexual#queer#otpsource
369 notes
·
View notes
Text

#25th Hour#Edward Norton#Philip Seymour Hoffman#Barry Pepper#Rosario Dawson#Anna Paquin#Brian Cox#Spike Lee#2002
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo
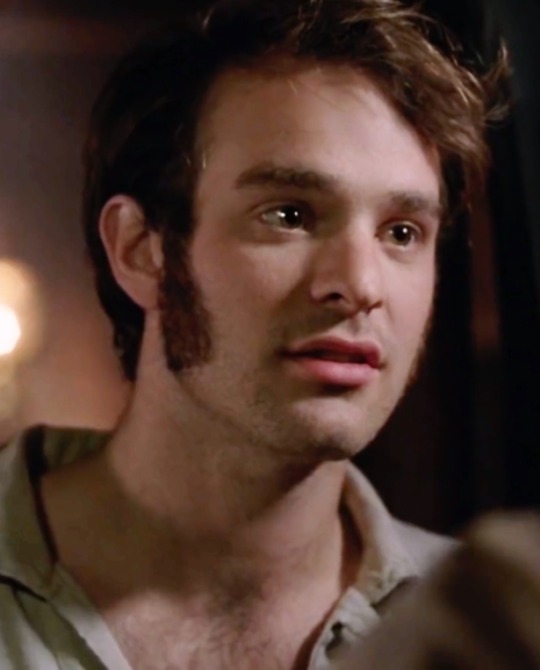


Ugh, I swear every time I see that pic of Thomas it has my Crowbarrow hindbrain pointing and going, “Look, big-ass sideburn buddies!” 🤣
#maybe now that I've said it out loud it'll finally exercise it from my head 😅🙏#my random ramblings#Thomas Barrow#Duke of Crowborough#Philip Villiers#crowbarrow#Robert James-Collier#Charlie Cox#Ishmael#Moby Dick 2011#downton abbey
104 notes
·
View notes
Text

I shall have a worthy rival, just like your father
#the devil’s crown 1978#the devil’s crown#henry ii of england#philip ii of france#brian cox#christopher gable#geoffrey fitzroy#geoffrey archbishop of york#my art#fanart#sorry couldnt see who played geoffrey i dont have mh files on me…he was good though
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Overwhelmed By Advertising? The Battle For Cincinnati Consumers Has Raged For More Than A Century
Depending on the source, it is estimated that each American is confronted by 6,000 to 10,000 advertising messages every single day. That immersive media onslaught swelled as we started carrying little video screens around wherever we go, but invasive and obnoxious marketing has bothered Cincinnatians for much more than a century.
For example, on 20 July 1871, a correspondent for the Cincinnati Times related an enjoyable voyage he had undertaken down the Ohio River. After praising the service of his riverboat’s staff, the remarkable scenery along the river, the picturesque little town he floated by, the writer registered one complaint, about a cliff near the town of Hanging Rock:
“High up on the face of this wall of white sandstone, hundreds of feet beyond the reach of a scaling ladder, I noticed a patent medicine advertisement. It was penciled there by a man let down with ropes from above, and the letters are large enough to be read from the deck of a steamer two miles distant. I was sorry to see this defacement. It is bad enough that all the fences throughout the land should be made to lie for patent medicines without debasing the hill-sides with such marking. I suppose that when the ‘chemical affinity necessary to be the motor of some immense flying machine’ shall be discovered, some enterprising patent medicine man will be plastering the face of the moon with some of his ‘wonderful remedies.’”
If only the poor man knew what lay ahead! Even in the 1870s, almost every vertical surface in Cincinnati was slathered with posters, placards and bills advertising shows at the local theaters, patent medicines and political candidates. Cincinnati was the center of the bill-posting world. For one thing, Cincinnati was among the top printing cities of the United States, with the mighty Strobridge Lithographing Company dominating the poster industry.
Also, Billboard magazine was headquartered here in Cincinnati. What we now think of as a music magazine, Billboard was founded in Cincinnati as a trade publication for men who posted “bills” on walls. From its first issue in 1894, Billboard covered the entertainment industry, such as circuses, fairs and burlesque shows, and also created a mail service for travelling entertainers. Initially it covered the advertising and bill-posting trade and was known as Billboard Advertising.

Far from inspiring civic pride, advertising rankled Cincinnati residents as they witnessed visual pollution encrusting the region’s hillsides. Leading the opposition was the Municipal Art Society – a sort of ad-hoc predecessor to today’s Urban Design Review Board. The opening shot was fired 24 August 1896 when the Enquirer reported:
“A matter that will undoubtedly be of interest to the business men is the fact that war has been declared by the Cincinnati Municipal Art Society against advertising signs on fences along the car routes and drives of the city. The art society maintains that these signs mar the beauty of the city, especially in the case of landscape scenes on the hills and in the suburbs, and that they are offensive to the public taste.”
The Society was persistent. It took five years but the Cincinnati Post reported [24 November 1901] that the Baldwin Piano Company had demolished 200 feet of billboards erected on company property along Gilbert Avenue. The Post described this as the “first result” of the Society’s campaign.
The Municipal Art Society was soon joined by some strange bedfellows. The Cincinnati Business Men’s Club, among whose members were certainly a number of advertisers who employed billboards to disseminate their messages, created its own Municipal Art Committee to lobby for restrictions on outdoor advertising. On 1 June 1907, the committee circulated a postcard illustrated with a photo of signage clogging the view from the Grand Central Depot, with the sarcastic caption, “A Nice Welcome To Cincinnati.”
As early as 1895, the city chased the Fountain saloon’s advertising off Fountain Square, but appears not to have drafted a comprehensive law about outdoor advertising until 1909 when, as part of a broader safety ordinance, the city adopted limitations on the size of billboards, their placement near thoroughfares and the materials to be used in their construction.
While the city pondered how to encourage commerce while maintaining attractive views, the entire billboard industry was gaining momentum through a Cincinnati entrepreneur named Philip Morton. Before Morton, “bill boards” were basically fences on which bill posters slapped printed advertisements glued up with a flour-water paste. Morton took outdoor advertising to a new level, according to Jay Gilbert, who has researched his influence on marketing [Cincinnati Magazine September 2016]:
“By 1898 he’d become the Steve Jobs of roadside blight. Doing business as Ph. Morton, Phil was an early pioneer of putting ads into free-standing frames called ‘bill-boards’ and plunking them down everywhere. Eventually every railroad route and motorway in America had its view ruined by a Ph. Morton billboard.”
Even the powerhouse Morton found himself in the city’s crosshairs. Parks Superintendent John W. Rodgers, according to the Enquirer [20 September 1907], exasperated by Morton’s billboards blocking the view of Inwood Park, erupted.
“Park Superintendent Rodgers yesterday tore down over 12,000 feet of big billboards that stretched along for a distance south of Hollister street, facing Vine street, in front of Inwood Park. The billboards were 12 feet high, about 1,000 feet long and contained the advertisements of leading firms of the city, and were illuminated at night with electric lights. They had been at that place for years.”
All of those billboards were leased by Philip Morton who, as coincidence would have it, dropped off a check to pay the lease while workmen were busily engaged demolishing his thousand feet of signage. This was the Boss Cox era in Cincinnati where the right hand was very often ignorant of the left hand’s activity. And so it was, while the Park Superintendent was demolishing billboards on Vine Street, the Board of Public Service pondered a lease for billboards along Gilbert Avenue. That’s right – the same Gilbert Avenue divested of billboards just six years earlier.

A common theme of cartoon artists at that time was the eventual coverage of all available exterior surfaces with advertising signs and slogans. In response, Cincinnati Post cartoonist Elmer Andrews Bushnell sketched City Hall wrapped from sidewalk to parapet in advertising while George Barnsdale Cox and his minion, August “Garry” Herrmann, happily apply more posters and Mayor Julius Fleischmann hides behind a billboard.
The battle raged for decades. Photographs from 1927 show dozens of billboards crowding the hillside over the Brighton overpass to Central Parkway and the Enquirer [24 March 1929] begged for relief because billboards and other unsightly structures had a negative effect on property values:
“What of the gaudy billboard that intrudes itself into a residential district, the sign which girds the tree or telephone pole, the roadside ‘shack’ which is made more ugly with bizarre advertisements? Do they affect values?”
A century later, we hardly notice billboards anymore. We’re too busy texting while we drive.

10 notes
·
View notes
Text
KIDZ!
The Young People of the Lucyverse ~ Part 3

W.C. Fields famously warned performers never to work with children or animals. Luckily for us, Lucille Ball consistently disregarded his advice. Here’s a look at some of the young performers and characters of the Lucyverse.
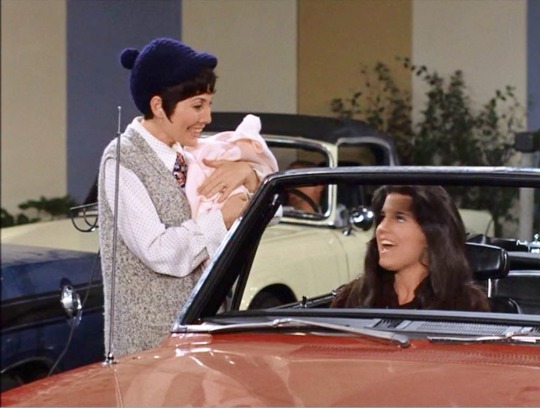

“Lucy and the Drive-In Movie” (1969) ~ Jackie Berry is a married friend of Kim’s who has a newborn named Wendy. Her husband is said to be in the service. Jackie Berry uses her married name for the character. She ws the real-life wife of Ken Berry from 1960 to 1972, an actor championed by Lucille Ball.

“Lucy and Jack Benny’s Biography” (1970) ~ Lucy plays Jack’s mother and Michael Barbera plays Benny as a boy. Barbera was a child actor who was 12 years old at the time of filming. He accrued 18 screen credits before leaving the industry.
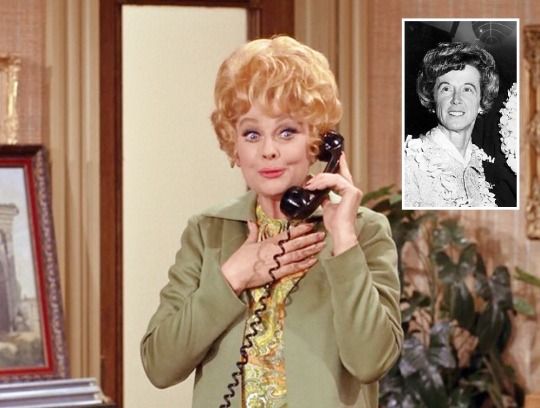

“Lucy Cuts Vincent’s Price” (1970) ~ Lucy says she previously talked on the phone to Mrs. Vincent Price when arranging entertainment for a big party the Price’s threw. In 1970, Vincent Price was married to costume designer Mary Grant (inset photo), although her name is never mentioned here. Making small talk on the telephone, Lucy asks about Little Vicki. This is a reference to the Price’s 8 year-old daughter, Victoria. Although Lucy visits their home, both characters remain off-screen.
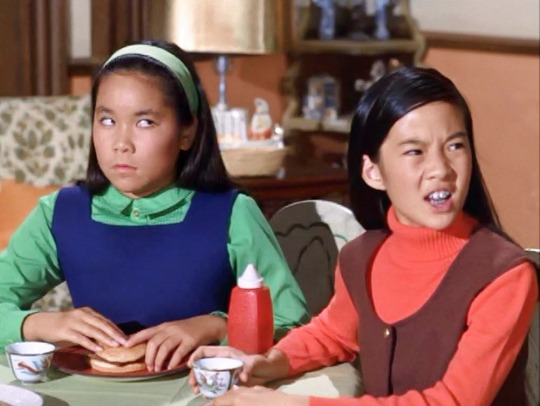

“Lucy the Laundress” (1970) ~ Lucy smashes into a laundry truck. In order to pay for the repairs, she has to go to work at the laundry and encounters the owner’s two daughters Sue Chin Wong (left) and Linda Change Wong (right). Linda is played by Rosalind Chao who makes her screen debut with this episode. She created the role of Soon-Ye Klinger on “M*A*S*H” and “After M*A*S*H” but is perhaps best known for playing Keiko O'Brien on “Star Trek: The Next Generation” and “Deep Space Nine.” During that series she also filmed The Joy Luck Club. More recent credits include “Blackish,” “This is Us,” and “The Catch.” Heather Lee (Sue Chin Wong) makes her screen appearance in this episode. When Lucy meets the sisters, she greets them in an exaggerated and condescending Chinese accent. The girls look horrified and answer back in voices totally devoid of any Asian influence. To further the humor of Lucy’s backward thinking, the girls are eating hamburgers with ketchup, a typical American-style meal.
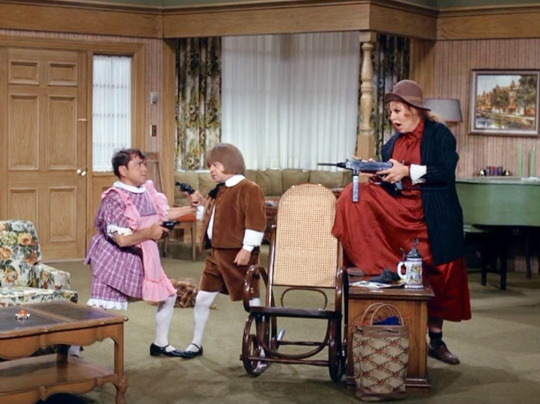

“Lucy and Ma Parker” (1970) ~ A criminal mastermind (Carole Cook) enlists two little people (Jerry Marin and Billy Curtis) to play her ‘children’. Milton (Marin) is dressed as ‘Little Mildred’ in the style of child star Shirley Temple. Curtis plays Herman Golab, who is dressed as Buster Brown.

“Lucy and the Italian Bombshell” (1971) ~ Harry’s former flame Donna Colucci (Kaye Ballard) is married and has a large brood of children: Ricardo, Anna Maria, Louisa, Luigi, Vincenzo, Dino, Lucrezia, Alfredo Jr., Margarito, Bruno, Rosa, and Frederico - all of whom appear uncredited.
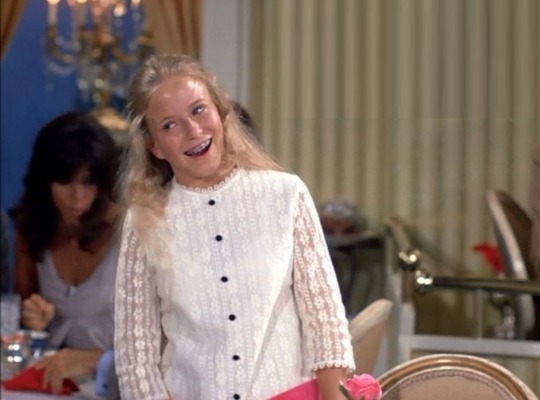

“Lucy and Donny Osmond” (1972) ~ Lucy takes her pre-teen niece Patricia (Eve Plumb) to see her favorite singer, Donny Osmond. Plumb is probably best known as the middle daughter, Jan, on TV’s “The Brady Bunch” (1969-74). She filmed this episode simultaneously with “The Brady Bunch” which aired Friday nights on ABC. This is her only time acting with Lucille Ball. Coincidentally, Desi Arnaz Jr. made a guest-appearance on “The Brady Bunch” in 1970 where he was the ‘dream date’ of Jan’s sister Marcia (Maureen McCormick).

“Lucy and Her Prince Charming” (1972) ~ Harry hastily arranges a home wedding ceremony for Lucy and a Prince (Ricardo Montalban) - including a flower girl and a ring bearer - played by two uncredited young actors.

Mame (1974) ~ Lucille Ball plays Auntie Mame to orphaned Patrick Dennis, played by Bruce Dern as a child.

“Life With Lucy” (1986) ~ Lucy Barker and Curtis McGibbon (Gale Gordon) are grandparents to Becky and Kevin McGibbon. Becky is played by Jenny Lewis. Ten year-old Lewis appeared in all 13 episodes, only 8 of which were aired.
“Yes, Lucy was a bit rough around the edges, and yes, she constantly smoked cigarettes on the set. She would pull her face back with tape, sort of like a cheap face-lift.“ ~ JENNY LEWIS
Philip Amelio (Kevin McGibbon) made his screen debut on “Life With Lucy” at the age of 10. He played Stephen Baldwin’s younger self in the film Born on the Fourth of July (1989). He gave up acting by his early teensPhilip died in 2005 at the age of 27 due to a mis-diagnosed bacterial infection.

Kelli Martin (right) played Becky’s friend Patty in two episodes of the series. Born in 1975, she made her acting debut at age 7 and went on to be seen as an Emmy-nominated regular on “Life Goes On” (1989-93) and “Christy” (1994-95) in which she played the title character.
BONUS KIDZ!

“Lucy the Diamond Cutter” (1970) ~ German diamond cutter Gustav (Wally Cox) calls Kim and Craig “the Katzenjammer Kids.” The Katzenjammer Kids was a comic strip created by German immigrant Rudolph Dirks which appeared from 1897 to 2006. The strip featured twins Hans and Fritz, who rebelled against authority.

“Lucy and the Generation Gap” (1969) ~ In the final sequence of the musical episode set in outer space, the Carters sing “Kids” a song written by Lee Adams and Charles Strouse for the 1960 Broadway musical Bye Bye Birdie. The musical was filmed in 1963. This song is originally about the generation gap, so it requires the least lyrical changes. It was sung on stage and screen by Paul Lynde, playing the father of free-thinking kids obsessed with an Elvis-like rock and roll singer.
#Lucille Ball#Kids#Children#Here's Lucy#Gale Gordon#Desi Arnaz Jr.#Lucie Arnaz#TV#Wally Cox#Mame#Kelly Martin#Philip Amelio#Jenny Lewis#Life With Lucy#Kelli Martin#Ricardo Montalban#Eve Plumb#Jack Benny#Vincent Price#Carole Cook#Jerry Marin#Rosalind Chao
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
True that. 😭❤







Yeah, I'm totally normal about him. Move the heck out of my way! ❤😍❤
"I feel so normal about him" well I dont. move
#I love him your honour 😭❤#charlie cox#matt murdock#michael kinsella#duke of crowborough#philip villiers#adam lawrence#owen sleater#tristan thorn#daredevil#kin amc#downton abbey#treason 2022#boardwalk empire#stardust 2007
107K notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Total Recall (watchalong)
Sub to my channel for more: https://www.youtube.com/@borednow5838/videos
@totalrecall88 @scifi-fantasy-horror @movies-quotes.
#total recall#arnold schwarzenegger#paul verhoeven#sharon stone#philip k. dick#Scifi#futuristic#fleshy#pulpy#b movie#michael ironside#life on mars#trippy#action#thriller#trippy art#ronny cox#1990s films#1980s films#1990s nostalgia#special effects#practical effects#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
'Beverly Hills Cop' (1984) film

-rewatched 7/18/2024- 3 [3/4] stars- on Paramount+
Still a good movie but i liked it much better the first time when it first come out, (and I was much younger).
82% Rotten Tomatoes
#my have seen list#Beverly Hills Cop#1984#film#martin brest#comedy/action#eddie murphy#judge reinhold#john ashton#lisa eilbacher#paul reiser#gil hill#bronson pinchot#ronny cox#jonathan banks#steven berkoff#frank pesce#damon wayans#philip levien#art kimbro#james russo#stephen elliott#darwyn carson#mike pniewski#michael champion#rex ryon#randy vasquez#michael gregory#joel bailey#carl weintraub
1 note
·
View note
Text











The Duke of Crowborough + text posts
#clearly my favourite dastardly duke is on my mind today 😂💗#duke of crowborough#philip villiers#thomas barrow#crowbarrow#charlie cox#robert james collier#downton abbey#formal wear#textposts#CTCU
315 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rereading Babies
Ten Little Fingers and Ten Little Toes Written and illustrated by Mem Fox and Helen Oxenbury Walker Books, 2008 I once told a friend I reread books. He looked at me like I was mad. He was a football fan and would rewatch goals but rereading books seemed absurd to him. Maybe it was the effort. All that right and left movement of the eye. Maybe he thought second, third or fourth readings were…

View On WordPress
#Agent Orange#Book Review#Children#Children&039;s Literature#Dads#Hebron#Helen Oxenbury#Ho Chi Minh City#Jo Cox#Jordan#Literature#Mem Fox#On Rereading#Palestine#Parenting#Patricia Meyer Spacks#Philip Jones Griffiths#Picture Books#Review#Ten Little Fingers and Ten Little Toes#The Gruffalo#Walker Books#We&039;re Going On A Bear Hunt#Za&039;atari
0 notes
Text
Crowbarrow and what could've been...😔💔


what is a husband but a valet you have sex with. truly.
#😅😢#Thomas Barrow#Duke of Crowborough#Philip Villiers#Crowbarrow#Robert James-Collier#Charlie Cox#Downton Abbey
788 notes
·
View notes
Text
*sits here wondering if any Thomas Barrow fans saw Stardust and had an “omg Thomas got f*cked over by Tristan Thorn?????” moment*
Idk why that’s so funny to me because like, LOOK AT HIM:
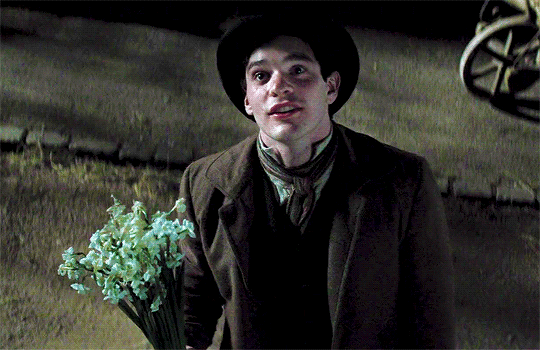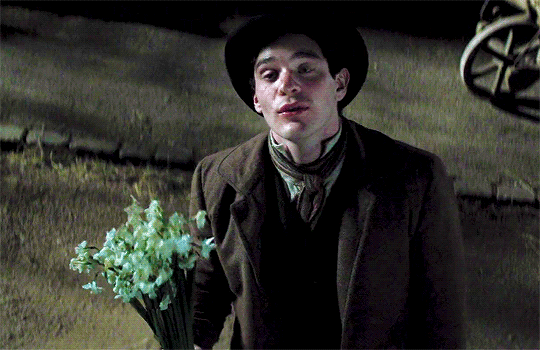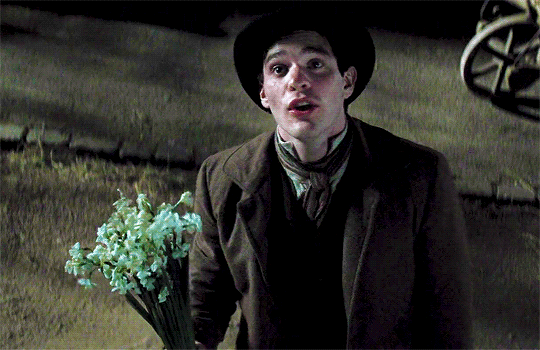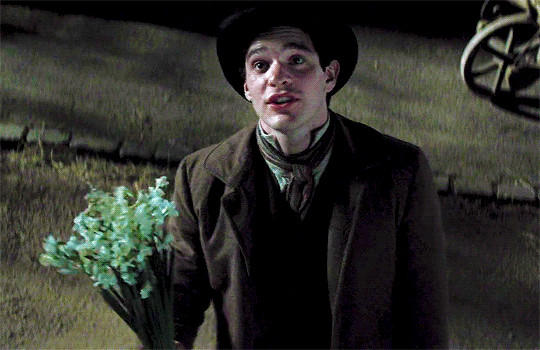





Could he BE any more babygirl? 😂💗
#my random ramblings#tristan thorn#charlie cox#stardust 2007#duke of crowborough#philip villiers#Thomas Barrow#Robert James-Collier#crowbarrow
93 notes
·
View notes