#Pharmacy Benefit Management
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#PBM Migration#Pharmacy benefit management#pharmacy benefit management services#PBM Services#PBM Software Solutions#PBM IT Services#pharmacy benefit management companies#Pharmacy Benefit Management Solutions#pharmacy benefit management software
1 note
·
View note
Text
https://www.worldwisepeople.net/main/blogs/334862/Pharmacy-Benefit-Management-Services-Market-Diagnosis-Treatments-and-Global-Key
Pharmacy Benefit Management Services Market Value Chain, Future Analysis, Industry Growth by 2030
0 notes
Text
What the fuck is a PBM?
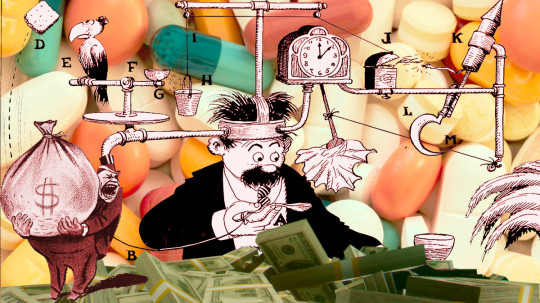
TOMORROW (Sept 24), I'll be speaking IN PERSON at the BOSTON PUBLIC LIBRARY!

Terminal-stage capitalism owes its long senescence to its many defensive mechanisms, and it's only by defeating these that we can put it out of its misery. "The Shield of Boringness" is one of the necrocapitalist's most effective defenses, so it behooves us to attack it head-on.
The Shield of Boringness is Dana Claire's extremely useful term for anything so dull that you simply can't hold any conception of it in your mind for any length of time. In the finance sector, they call this "MEGO," which stands for "My Eyes Glaze Over," a term of art for financial arrangements made so performatively complex that only the most exquisitely melted brain-geniuses can hope to unravel their spaghetti logic. The rest of us are meant to simply heft those thick, dense prospectuses in two hands, shrug, and assume, "a pile of shit this big must have a pony under it."
MEGO and its Shield of Boringness are key to all of terminal-stage capitalism's stupidest scams. Cloaking obvious swindles in a lot of complex language and Byzantine payment schemes can make them seem respectable just long enough for the scammers to relieve you of all your inconvenient cash and assets, though, eventually, you're bound to notice that something is missing.
If you spent the years leading up to the Great Financial Crisis baffled by "CDOs," "synthetic CDOs," "ARMs" and other swindler nonsense, you experienced the Shield of Boringness. If you bet your house and/or your retirement savings on these things, you experienced MEGO. If, after the bubble popped, you finally came to understand that these "exotic financial instruments" were just scams, you experienced Stein's Law ("anything that can't go forever eventually stops"). If today you no longer remember what a CDO is, you are once again experiencing the Shield of Boringness.
As bad as 2008 was, it wasn't even close to the end of terminal stage capitalism. The market has soldiered on, with complex swindles like carbon offset trading, metaverse, cryptocurrency, financialized solar installation, and (of course) AI. In addition to these new swindles, we're still playing the hits, finding new ways to make the worst scams of the 2000s even worse.
That brings me to the American health industry, and the absurdly complex, ridiculously corrupt Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs), a pathology that has only metastasized since 2008.
On at least 20 separate occasions, I have taken it upon myself to figure out how the PBM swindle works, and nevertheless, every time they come up, I have to go back and figure it out again, because PBMs have the most powerful Shield of Boringness out of the whole Monster Manual of terminal-stage capitalism's trash mobs.
PBMs are back in the news because the FTC is now suing the largest of these for their role in ripping off diabetics with sky-high insulin prices. This has kicked off a fresh round of "what the fuck is a PBM, anyway?" explainers of extremely variable quality. Unsurprisingly, the best of these comes from Matt Stoller:
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/monopoly-round-up-lina-khan-pharma
Stoller starts by pointing out that Americans have a proud tradition of getting phucked by pharma companies. As far back as the 1950s, Tennessee Senator Estes Kefauver was holding hearings on the scams that pharma companies were using to ensure that Americans paid more for their pills than virtually anyone else in the world.
But since the 2010s, Americans have found themselves paying eye-popping, sky-high, ridiculous drug prices. Eli Lilly's Humolog insulin sold for $21 in 1999; by 2017, the price was $274 – a 1,200% increase! This isn't your grampa's price gouging!
Where do these absurd prices come from? The story starts in the 2000s, when the GW Bush administration encouraged health insurers to create "high deductible" plans, where patients were expected to pay out of pocket for receiving care, until they hit a multi-thousand-dollar threshold, and then their insurance would kick in. Along with "co-pays" and other junk fees, these deductibles were called "cost sharing," and they were sold as a way to prevent the "abuse" of the health care system.
The economists who crafted terminal-stage capitalism's intellectual rationalizations claimed the reason Americans paid so much more for health care than their socialized-medicine using cousins in the rest of the world had nothing to do with the fact that America treats health as a source of profits, while the rest of the world treats health as a human right.
No, the actual root of America's health industry's problems was the moral defects of Americans. Because insured Americans could just go see the doctor whenever they felt like it, they had no incentive to minimize their use of the system. Any time one of these unhinged hypochondriacs got a little sniffle, they could treat themselves to a doctor's visit, enjoying those waiting-room magazines and the pleasure of arranging a sick day with HR, without bearing any of the true costs:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/06/27/the-doctrine-of-moral-hazard/
"Cost sharing" was supposed to create "skin in the game" for every insured American, creating a little pain-point that stung you every time you thought about treating yourself to a luxurious doctor's visit. Now, these payments bit hardest on the poorest workers, because if you're making minimum wage, at $10 co-pay hurts a lot more than it does if you're making six figures. What's more, VPs and the C-suite were offered "gold-plated" plans with low/no deductibles or co-pays, because executives understand the value of a dollar in the way that mere working slobs can't ever hope to comprehend. They can be trusted to only use the doctor when it's truly warranted.
So now you have these high-deductible plans creeping into every workplace. Then along comes Obama and the Affordable Care Act, a compromise that maintains health care as a for-profit enterprise (still not a human right!) but seeks to create universal coverage by requiring every American to buy a plan, requiring insurers to offer plans to every American, and uses public money to subsidize the for-profit health industry to glue it together.
Predictably, the cheapest insurance offered on the Obamacare exchanges – and ultimately, by employers – had sky-high deductibles and co-pays. That way, insurers could pocket a fat public subsidy, offer an "insurance" plan that was cheap enough for even the most marginally employed people to afford, but still offer no coverage until their customers had spent thousands of dollars out-of-pocket in a given year.
That's the background: GWB created high-deductible plans, Obama supercharged them. Keep that in your mind as we go through the MEGO procedures of the PBM sector.
Your insurer has a list of drugs they'll cover, called the "formulary." The formulary also specifies how much the insurance company is willing to pay your pharmacist for these drugs. Creating the formulary and paying pharmacies for dispensing drugs is a lot of tedious work, and insurance outsources this to third parties, called – wait for it – Pharmacy Benefits Managers.
The prices in the formulary the PBM prepares for your insurance company are called the "list prices." These are meant to represent the "sticker price" of the drug, what a pharmacist would charge you if you wandered in off the street with no insurance, but somehow in possession of a valid prescription.
But, as Stoller writes, these "list prices" aren't actually ever charged to anyone. The list price is like the "full price" on the pricetags at a discount furniture place where everything is always "on sale" at 50% off – and whose semi-disposable sofas and balsa-wood dining room chairs are never actually sold at full price.
One theoretical advantage of a PBM is that it can get lower prices because it bargains for all the people in a given insurer's plan. If you're the pharma giant Sanofi and you want your Lantus insulin to be available to any of the people who must use OptumRX's formulary, you have to convince OptumRX to include you in that formulary.
OptumRX – like all PBMs – demands "rebates" from pharma companies if they want to be included in the formulary. On its face, this is similar to the practices of, say, NICE – the UK agency that bargains for medicine on behalf of the NHS, which also bargains with pharma companies for access to everyone in the UK and gets very good deals as a result.
But OptumRX doesn't bargain for a lower list price. They bargain for a bigger rebate. That means that the "price" is still very high, but OptumRX ends up paying a tiny fraction of it, thanks to that rebate. In the OptumRX formulary, Lantus insulin lists for $403. But Sanofi, who make Lantus, rebate $339 of that to OptumRX, leaving just $64 for Lantus.
Here's where the scam hits. Your insurer charges you a deductible based on the list price – $404 – not on the $64 that OptumRX actually pays for your insulin. If you're in a high-deductible plan and you haven't met your cap yet, you're going to pay $404 for your insulin, even though the actual price for it is $64.
Now, you'd think that your insurer would put a stop to this. They chose the PBM, the PBM is ripping off their customers, so it's their job to smack the PBM around and make it cut this shit out. So why would the insurers tolerate this nonsense?
Here's why: the PBMs are divisions of the big health insurance companies. Unitedhealth owns OptumRx; Aetna owns Caremark, and Cigna owns Expressscripts. So it's not the PBM that's ripping you off, it's your own insurance company. They're not just making you pay for drugs that you're supposedly covered for – they're pocketing the deductible you pay for those drugs.
Now, there's one more entity with power over the PBM that you'd hope would step in on your behalf: your boss. After all, your employer is the entity that actually chooses the insurer and negotiates with them on your behalf. Your boss is in the driver's seat; you're just along for the ride.
It would be pretty funny if the answer to this was that the health insurance company bought your employer, too, and so your boss, the PBM and the insurer were all the same guy, busily swapping hats, paying for a call center full of tormented drones who each have three phones on their desks: one labeled "insurer"; the second, "PBM" and the final one "HR."
But no, the insurers haven't bought out the company you work for (yet). Rather, they've bought off your boss – they're sharing kickbacks with your employer for all the deductibles and co-pays you're being suckered into paying. There's so much money (your money) sloshing around in the PBM scamoverse that anytime someone might get in the way of you being ripped off, they just get cut in for a share of the loot.
That is how the PBM scam works: they're fronts for health insurers who exploit the existence of high-deductible plans in order to get huge kickbacks from pharma makers, and massive fees from you. They split the loot with your boss, whose payout goes up when you get screwed harder.
But wait, there's more! After all, Big Pharma isn't some kind of easily pushed-around weakling. They're big. Why don't they push back against these massive rebates? Because they can afford to pay bribes and smaller companies making cheaper drugs can't. Whether it's a little biotech upstart with a cheaper molecule, or a generics maker who's producing drugs at a fraction of the list price, they just don't have the giant cash reserves it takes to buy their way into the PBMs' formularies. Doubtless, the Big Pharma companies would prefer to pay smaller kickbacks, but from Big Pharma's perspective, the optimum amount of bribes extracted by a PBM isn't zero – far from it. For Big Pharma, the optimal number is one cent higher than "the maximum amount of bribes that a smaller company can afford."
The purpose of a system is what it does. The PBM system makes sure that Americans only have access to the most expensive drugs, and that they pay the highest possible prices for them, and this enriches both insurance companies and employers, while protecting the Big Pharma cartel from upstarts.
Which is why the FTC is suing the PBMs for price-fixing. As Stoller points out, they're using their powers under Section 5 of the FTC Act here, which allows them to shut down "unfair methods of competition":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/10/the-courage-to-govern/#whos-in-charge
The case will be adjudicated by an administrative law judge, in a process that's much faster than a federal court case. Once the FTC proves that the PBM scam is illegal when applied to insulin, they'll have a much easier time attacking the scam when it comes to every other drug (the insulin scam has just about run its course, with federally mandated $35 insulin coming online, just as a generation of post-insulin diabetes treatments hit the market).
Obviously the PBMs aren't taking this lying down. Cigna/Expressscripts has actually sued the FTC for libel over the market study it conducted, in which the agency described in pitiless, factual detail how Cigna was ripping us all off. The case is being fought by a low-level Reagan-era monster named Rick Rule, whom Stoller characterizes as a guy who "hangs around in bars and picks up lonely multi-national corporations" (!!).

The libel claim is a nonstarter, but it's still wild. It's like one of those movies where they want to show you how bad the cockroaches are, so there's a bit where the exterminator shows up and the roaches form a chorus line and do a kind of Busby Berkeley number:
https://www.46brooklyn.com/news/2024-09-20-the-carlton-report
So here we are: the FTC has set out to euthanize some rentiers, ridding the world of a layer of useless economic middlemen whose sole reason for existing is to make pharmaceuticals as expensive as possible, by colluding with the pharma cartel, the insurance cartel and your boss. This conspiracy exists in plain sight, hidden by the Shield of Boringness. If I've done my job, you now understand how this MEGO scam works – and if you forget all that ten minutes later (as is likely, given the nature of MEGO), that's OK: just remember that this thing is a giant fucking scam, and if you ever need to refresh yourself on the details, you can always re-read this post.

The paperback edition of The Lost Cause, my nationally bestselling, hopeful solarpunk novel is out this month!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/09/23/shield-of-boringness/#some-men-rob-you-with-a-fountain-pen

Image: Flying Logos (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Over_$1,000,000_dollars_in_USD_$100_bill_stacks.png
CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#matthew stoller#pbms#pharmacy benefit managers#cigna#ftc#antitrust#intermediaries#bribery#corruption#pharma#monopolies#shield of boringness#Caremark#Express Scripts#OptumRx#insulin#gbw#george w bush#co-pays#obamacare#aca#rick rules#guillotine watch#euthanize rentiers#mego
443 notes
·
View notes
Text

Babe wake up, new slur for management just dropped
#Babe wake up#new slur for management just dropped#cw slurs#reclaimed slurs#uncensored slurs#slurs#slur#management#the night manager#managed it services#project managers#fuck managers#pharmacy benefit managers#toontown managers#award in fire safety for managers#managers#manager#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Americans are paying too much for prescription drugs.
It is a common, longstanding complaint. And the culprits seem obvious: Drug companies. Insurers. A dysfunctional federal government.
But there is another collection of powerful forces that often escape attention, because they operate in the bowels of the health care system and cloak themselves in such opacity and complexity that many people don’t even realize they exist.
They are called pharmacy benefit managers. And they are driving up drug costs for millions of people, employers and the government.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Transparency of Rebates among Pharmacy Benefit Managers
Explore the complexities surrounding rebate transparency among Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) in the healthcare industry. Understand the challenges, including confidentiality agreements, complex structures, and regulatory pressures, hindering complete disclosure. Learn how evolving industry dynamics may drive PBMs towards greater transparency in rebate negotiations.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
@upontheshelfreviews
@greenwingspino
@one-time-i-dreamt
@tenaflyviper
@akron-squirrel
@ifihadaworldofmyown
@justice-for-jacob-marley
@voicetalentbrendan
@thebigdeepcheatsy
@what-is-my-aesthetic
@ravenlynclemens
@writerofweird
@bogleech
#actually important#petition#sign and send#congress#cvs#perscription drugs#Pharmacists Fight Back Act#Pharmacy Benefit Managers
0 notes
Text

An UWS CVS. Photo By Ed Hersh
UWS Independent Pharmacies Face Existential Threat From PBMs: Survey
— September 25, 2024 | By Ed Hersh | Westside Rag | New York, NY
Small Independent Pharmacies on the Upper West Side — and Citywide– say they face continued existential threats from what they claim is a Conflict-of-Interest-Ridden insurance reimbursement system that favors the big chain pharmacies.
In a recent survey of 176 independent pharmacies, released by the New York City Pharmacists Society, 92 percent of independent pharmacists say they were forced to turn away patients in the previous six months because insurance reimbursements they receive for many Brand-Name Drugs are actually below the cost they must pay for them. These include Eliquis, Entresto, Humira, Jardiance, Ozempic, Xarelto, Biktarvy, and Many Other Medications, often critical for managing chronic conditions and improving quality of life.
“The untold story is that there are so many people trying to find an independent pharmacy to fill a prescription, but they can’t because the pharmacies can’t afford to fill that prescription,” an Upper West Side independent pharmacist told us, anonymously for fear of being shut out of the reimbursement system. “Even though pharmacies must, by contract, fill all prescriptions they are sent, some independent pharmacies have found a way around it. There’s nothing to force them to order the medication,” he admitted. “Probably by now, you know which drugs you’re going to have to sell at a big loss. So, you probably don’t keep those around for that reason.”
What’s behind it? Independent pharmacies blame Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs). As we first reported over a year ago, PBMs are the controversial middlemen between insurers, patients, drug makers, and pharmacies. You may not have heard of PBMs, but if you have insurance, you have dealt with them. On behalf of insurance companies, they negotiate prices with drug companies and set the prices that pharmacies are paid by the insurers, and then what the pharmacies can charge their customers. This includes those with Private Insurance As Well As Medicare “Part D” Drug Plans.
In what seems like a conflict of interest, the top three PBMs are companies that also offer insurance and other healthcare services, including their own pharmacies that compete with independent drug stores. CVS Health owns PBM Caremark and Aetna Insurance, as well as CVS pharmacies, specialty mail-order pharmacies, and a physician’s group. United Health, the insurance giant, owns the mail order pharmacy OptumRx, specialty pharmacies, physician groups and express medical and surgical centers. The insurer Cigna owns the PBM Express Scripts and a specialty pharmacy.
In addition, the reason we could not get UWS pharmacists to speak to us on record about this situation is that there is a “gag clause” in all pharmacy contracts with the PBMs forbidding them to discuss the details of their reimbursements with their patients and customers, under penalty of losing their contracts
So how are our local independent pharmacies staying afloat? Ironically, some generic drugs have a greater profit margin. Additionally “some pharmacies do more [non-prescription] business in the front of the store,” the pharmacist told us. “For some of them, the owner’s working 80 hours a week, and he’s got a skeleton crew.” And some have shortened their days and business hours.
For many, says NYCPS spokesman Tom Corsillo, the neighborhood pharmacy is a lifeline. “People who use independent pharmacies tend to be the most vulnerable populations, folks who need to understand dosage and rely on the level of counsel independent pharmacies provide.”
There have been bipartisan calls for scrutiny and regulation of PBMs at a national level, including hearings on Capitol Hill. And just this last Friday, the Federal Trade Commission announced new action against the three largest PBMs — Caremark Rx, Express Scripts (ESI), and OptumRx — for engaging in what the FTC calls, in a release “anticompetitive and unfair rebating practices that have artificially inflated the list price of insulin drugs, impaired patients’ access to lower list price products, and shifted the cost of high insulin list prices to vulnerable patients.”
For its part, the Pharmaceutical Care Management Association, the PBM’s trade group, defends its members’ practices. In a statement emailed to WSR, PCMA spokesman Greg Lopes said, “PBMs recognize the vital role pharmacies play in creating access to prescription drugs for patients, especially community pharmacies in rural areas. There are unfortunately many factors for pharmacy closures, but blaming PBMs is not based on the facts,” and added, “It should be noted that in New York [State], between 2014 and 2024, the number of independent pharmacies actually grew from 2,470 to 3,058, a 23.8% increase.” But he could not specify in what part of the state that growth had occurred.
The NYC pharmacists’ survey taken in July says that in the year ahead, “96 percent of the respondents indicated they are very likely to stop carrying additional medications if reimbursement rates are further reduced as projected. Additionally, 96 percent of respondents anticipate having to lay off employees or reduce store hours to cope with these financial challenges.”
As for Friday’s FTC complaint, (which only applies to insulin medications) the FTC says it “seeks to put an end to the Big Three PBMs’ exploitative conduct and marks an important step in fixing a broken system—a fix that could ripple beyond the insulin market and restore healthy competition to drive down drug prices for consumers.”
What can concerned citizens do? Corsillo says “you have to contact your elected officials. Ultimately, they’re going to have to write new laws to rein in PBMs and they need to hear from their constituents that this is something they care about.”
0 notes
Text
https://community.wongcw.com/blogs/305944/Pharmacy-Benefit-Management-Services-Market-Therapeutics-Review-Analysis-2030
Pharmacy Benefit Management Services Market Value Chain, Future Analysis, Industry Growth by 2030
0 notes
Text
Brinkwhump Linkdump

I'm on tour with my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in TUCSON (Mar 9-10), then San Francisco (Mar 13), Anaheim, and more!

Once again, I find myself arriving at the weekend with a giant backlog of links, triggering a linkump, the 15th such dumpage, a variety-pack of miscellany for your weekend. Here's the previous editions:
https://pluralistic.net/tag/linkdump/
Let's start with the latest incredible news from KPMG, the accounting and auditing giant that is relied upon as a source of ground truth for a truly terrifying share of the world's economy. KPMG has a well-deserved reputation for incompetence and corruption. They first came on my radar in 2001 when they sent a legal threat to a blogger for linking to their website without permission:
https://memex.craphound.com/2001/12/05/reason-4332442-not-to-ask/
The actual link was to KPMG's corporate anthem, which remains, to this day, a banger:
https://web.archive.org/web/20040428063826/http://chkpt.zdnet.com/chkpt/uknewsita/http://anthems.zdnet.co.uk/anthems/kpmg.mp3
Don't miss the DJ remixes (and the Nokia ringtone!) that the internet thoughtfully provided when KPMG decided that it didn't want the world to know about "Our Vision of Global Strategy":
https://web.archive.org/web/20011128153057/http://corporateanthems.raettig.org/
Now all this is objectively very funny, a relic of the old, good internet from one of its moments of glory, but KPMG? They were already enshittifying, even in 2001, and the enshittification only intensified thereafter. Nearly every accounting scandal of the past quarter-century has KPMG in it somewhere, from con-artists selling exhausted oil fields to rubes:
https://www.desmog.com/2021/06/03/miller-energy-kpmg-auditors-oil-fraud/
To killer nursing homes that hire KPMG to audit its books – and to advise it on how to defeat safety audits and murder your grandma:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/09/dingo-babysitter/#maybe-the-dingos-ate-your-nan
They're the architects of Microsoft's tax-evasion plot:
https://www.propublica.org/article/the-irs-decided-to-get-tough-against-microsoft-microsoft-got-tougher
And they were behind Canada's dysfunctional covid contact-tracing app, which never worked, but generated tens of millions in billings to the government of Canada, who used KPMG to hire programmers at $1,500/day, plus KPMG's 30% commission:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/31/mckinsey-and-canada/#comment-dit-beltway-bandits-en-canadien
KPMG's most bizarre scandal is literally stranger than fiction. The company bribed SEC personnel help its own accountants cheat on ethics exams. The corrupt officials were then given high-paid jobs at KPMG:
https://www.nysscpa.org/news/publications/the-trusted-professional/article/sec-probe-finds-kpmg-auditors-cheating-on-training-exams-061819
I mean it when I say this is stranger than fiction. I included it as a plot-point in my new finance crime novel The Bezzle (now a national bestseller!), and multiple readers have written to me since the book came out a couple weeks ago to say that they thought I was straining their credulity by making up such an outrageous scandal:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865878/thebezzle
But all of that is just scene-setting (and a gratuitous plug for my book) for the latest KPMG scandal, which is, possibly, the most KPMG scandal of all KPMG scandals. The Australian government hired KPMG to audit Paladin, a security contractor that oversees the asylum seekers the country locks up on one of its island gulags (yes, gulags, plural).
Ever since, Paladin has been the subject of a string of ghastly human rights scandals – the worst stuff imaginable, rape and torture and murder of adults and children. Paladin made AU423 million on this contract.
And here's the scandal: KPMG audited the wrong company. The Paladin that the Australia government paid KPMG to audit was based in Singapore. The Paladin that KPMG audited was a totally different company, based in Papua New Guinea, who already had a commercial relationship with KPMG. It was this colossal fuckup that led to the manifestly unfit Singaporean company getting nearly half a billion dollars in public funds:
https://www.theguardian.com/business/2024/feb/24/incredible-failure-kpmg-rejects-claims-it-assessed-the-wrong-company-before-423m-payment-to-paladin
KPMG denies this. KPMG denies everything, always. Like, they denied creating "power maps" of decision-makers in the Australian government to target with influence campaigns in order to win contracts like this one. Who knows, maybe, this one time, they're telling the truth? After all, the company whose employees gather to sing lyrics like these can't be all bad, right?
The time is now to lead the way, We share the same the idea That may win by the end of the day. Our strength is here to stay. Identity, one energy, One strategy, with sympathy. These are the words that will lead us into a new world.
https://everything2.com/title/KPMG+corporate+anthem
You may find it strange that I'm still carrying around the factoid that KPMG once threatened to crush a blogger for linking to its terrible corporate anthem, but that's just my "Memex Method," which helps me keep track of literally everything that seemed important to me through most of my adult life:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/05/09/the-memex-method/
One of my favorite quips from the very quotable Riley Quinn is that "leftists are cursed with object-permanence" – that is, we actually remember what just happened and use it to think about what's happening now. The Memex Method is object permanence for 20+ years worth of stuff. A lot of those deep archives never see use, but there's a surprising number of leading indicators buried in the stuff that happened in years gone by.
Take James Boyle's 2014, XKCD-style comic about the experience of driving a notional Apple car:
https://www.thepublicdomain.org/2014/11/07/apple-updates-a-comic/
Apple, it turns out, spent the next decade working on just such a car, and while that car has now been canceled, Boyle's comic correctly anticipates so much about the trajectory Apple's products took. It's uncannily accurate – real "don't invent the torment nexus"/"cyberpunk was a warning, not a suggestion" stuff:
https://knowyourmeme.com/memes/torment-nexus
But no matter how many times we insist that the torment nexus shouldn't be created, the boardrooms of end-stage capitalism continue to invent them. Take HP, the poster-child for enshittification, edging out even KPMG in the race to turn everything into a pile of shit. After years of tormenting people to punish them for wanting to print things, HP has announced a new service that so mustache-twirlingly evil that it lacks verisimilitude:
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2024/02/hp-wants-you-to-pay-up-to-36-month-to-rent-a-printer-that-it-monitors/
Here's the pitch: HP will sell you a printer that you don't own. In addition to paying a monthly fee for your ink – which you pay no matter whether you print or not – you will also pay a monthly fee just for having HP's printer on your premises. You are absolutely, positively forbidden from using third-party ink in this printer, and must use HP's own ink, which sells for about $10,000/gallon.
But while you aren't allowed to use this printer in ways that are bad for HP's shareholders, HP is absolutely free to use the printer in ways that are bad for you. When you click through the signup agreement, you grand HP permission to surveil every document you print – and your home wifi network more generally – and to sell that data to anyone and everyone.
What's more, HP reserves the right to discipline you with punitive credit-card charges if you disconnect this printer from the internet, on the basis that doing so makes it harder for them to spy on your printer.
I'm sorry, this is just more torment nexus shit, the kind of thing you'd expect to drop on Apr 1, not Feb 29, but I guess this is where we are. I can only conjecture as to whether HP's businesses strategists are directly taking direction from my novella "Unauthorized Bread," or whether they're learning about it second-hand from a KPMG consultant who converted it to Powerpoint form and charged $1,500/day for the work:
https://arstechnica.com/gaming/2020/01/unauthorized-bread-a-near-future-tale-of-refugees-and-sinister-iot-appliances/
All of this cartoonish villainry is the totally foreseeable consequence of a culture of impunity, in which companies like HP and KPMG can rob, cheat, steal (and sometimes even kill) without consequence. This impunity is so pervasive that the exceptions – where a rich criminal faces real consequences – become touchstones: Enron, Arthur Anderson, Theranos, and, of course, FTX.
FTX was arguably the largest-scale corporate crime in world history, stealing more than $10 billion dollars, mostly from rubes sucked in by hype and Superbowl ads. When news that FTX founder and owner Sam Bankman-Fried was convicted of fraud and was in for a lengthy prison sentence made a huge stir, because criminals like SBF usually walk away from the wreckage with their hands in their pockets, whistling a jaunty tune.
One of the very best commentators on cryptocurrency scams generally and FTX/SBF in particular is Molly White, whose Web3 is Going Just Great feed is utterly indispensable. White's newsletter, "Citation Needed," dives deep into the wrangle of SBF's sentencing:
https://www.citationneeded.news/issue-52/
Bankman-Fried's parents – prominent law professors at top law schools – helped brief the court this week on their son's punishment. According to them, SBF faces 100 years in prison, but should be sentenced to 5.5-6.5 years at the most. Why? Because he is a vegan, who is not greedy, and feels remorse, and cares for individuals (recall that SBF presented himself as the avatar of the batshit "effective altruism" philosophy while privately admitting that he used this as a smokescreen).
The most bizarre note in the 100-page filing is SBF's mother declaring that her son is an "angel of mercy," apparently unaware of the grisly meaning of that term:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angel_of_mercy_(criminology)
America's prisons are a travesty and I wouldn't wish them on anyone, but that's not the argument SBF's parents are making; rather, they're arguing that their special boy doesn't deserve the treatment America metes out to poorer, less white people who merely steal hundreds or thousands of dollars. A crook who steals ten billion should be handled the way a casino handles a whale – with concierge service.
The problem is, there are so many of these remorseless, relentless crooks that there's no way we could scale up that white-glove treatment when we finally round 'em all up and make them pay. Writing for The American Prospect, Maureen Tkacik tells us about the ransomware attack that shut down America's pharmacy system last month:
https://prospect.org/health/2024-03-01-zoomer-hackers-shut-down-unitedhealthcare/
The attack brought down Change Healthcare, part of the monopolist Unitedhealth, which serves as the "pharmacy benefit manager" to a vast swathe of American pharmacies. PBM is one of those all-American finance scams, a middleman garlanded with performative complexity put there to make you feel stupid for asking why independent pharmacies all have to pay rent to this malicious, unaccountable – and now, manifestly incompetent – gang of crooks.
Tkacik's breakdown of this scam – and how it rendered Americans' ability to get the drugs they depend on to go on breathing – is characteristically brilliant. Tcacik is fast emerging as my favorite Explainer of Scams, a print version of John Oliver or Adam Conover. You may recall her work from my post last week on how private equity has taken a wrecking ball to America's hospitals:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/02/28/5000-bats/#charnel-house
I always try to finish these linkdumps with some upbeat news to carry you through the weekend, and this week brought two genuinely wonderful – and totally underreported – pieces of amazing news.
The first is that Starbucks has sued for peace in the war against its workers' unions. Hundreds of Starbucks stores have unionized in recent years, but not one of them had a contract. Instead, Starbucks had waged dirty war on their own workers, from denying gender-affirming care to unionized employees to simply shutting down whole stores after they voted to unionize:
https://www.cnbc.com/2022/06/14/starbucks-union-company-threatens-that-unionizing-could-jeopardize-gender-affirming-health-care.html
But the workers held fast and after years of this, Starbucks has caved, promising contracts for all unionized stores and an end to its campaign of terror against workers seeking to unionize more of its stores. In a postmortem for Jacobin, Eric Blanc rounds up "seven lessons from Starbucks workers' historic victory":
https://jacobin.com/2024/02/starbucks-sbwu-contract-bargaining/
This is the kind of listicle I can get behind. According to Blanc, the Starbucks unions won by deploying worker-to-worker organizing, a tactic that many of the new unions that are shaking up formerly impossible-to-organize jobsites are using (Blanc has a book about this coming from UC Press called "We Are the Union: How Worker-to-Worker Unionism Can Transform America," so he should know).
Other tactics that made the difference for Starbucks unions: new digital training and support tools and partnering with established unions for support and infrastructure. Blanc also calls out the success of "salting" – the venerable but largely disused tactic of union organizers applying for a job at a non-union shop in order to organize it.
Blanc also mentions government policy, including the outstanding work of NLRB general counsel Jennifer Abruzzo, a shrewd and committed tactician whose understanding of the technicalities of labor law have let her push for bold measures. For example, in Thrive Pet Care, Abruzzo is arguing that when a company refuses to bargain in good faith for a contract with its union, she can step in and order them to honor the terms of a contract at comparable unionized competitors until they produce a contract of their own:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/09/06/goons-ginks-and-company-finks/#if-blood-be-the-price-of-your-cursed-wealth
Abruzzo is one of several smart, competent tacticians in the Biden administration who are working to kneecap corporate power. Another is Rohit Chopra, chair of the Consumer Finance Protection Bureau, who just announced another bold, important initiative that will help Americans fight corporate corruption and get a fair deal:
https://prospect.org/economy/2024-03-01-public-option-credit-card-shopping/
Chopra is taking aim at credit-card comparison sites that purport to show you where you can get the best deal. If you're an affluent person who doesn't carry a balance, this might not matter to you, but if you're an average working stiff, high interest rates can gobble up a massive share of your paycheck. What's more, credit card margins are higher than they have ever been:
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/about-us/blog/credit-card-interest-rate-margins-at-all-time-high/
The most expensive credit cards come from the big, monopolistic banks, but you wouldn't know it from the leaderboards produced by Credit Karma, NerdWallet, LendingTree, and Bankrate. All of these sites take bribes from the big banks to list their credit cards above those offered by credit unions – who are typically 10% cheaper than the big banks' cards.
The new CFPB rule prohibits this fraudulent ranking, but the Bureau is going even further. They're using their administrative powers to force banks to report their rates to the Bureau, which will publish them on a publicly funded, neutral website – what David Dayen calls "a public option" for shopping for credit cards.
This policy makes a perfect bookend to the last CFPB initiative I wrote about here: a rule that forces banks to allow you to transfer your account to a rival with a couple of simple clicks, importing all your history, payees, and everything else you need to switch to a better bank:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/21/let-my-dollars-go/#personal-financial-data-rights
Combine that ease of switching with reliable information on which banks will give you the best deal and you get something that will directly transfer millions and millions of dollars from giant, wildly profitable banks to low-income people who've been tricked into paying them punitive interest rates.
So that's it, this week's linkdump. I promised you I'd end on a high note, and I did it. The world may be full of all kinds of terrible things, but workers and regulators are scoring big, muscular victories in battles where the stakes are real and important. Have a great weekend – we've earned it.
And remember!
The time is now to lead the way, We share the same the idea That may win by the end of the day. Our strength is here to stay. Identity, one energy, One strategy, with sympathy. These are the words that will lead us into a new world.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/02/macedoine/#the-public-option

Image: Stacy (modified) https://www.flickr.com/photos/notahipster/4402860361/
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
#pluralistic#paladin#kpmg#audits#incompetence#molly white#sam bankman-fried#ftx#crypto#cryptocurrency#fraud#maureen tcacik#ransomware#pharma#pharmacy benefit managers#intermediaries#middlemen#starbucks#labor#unions#cfpb#bribery#corruption#finance#hp#printers#enshittification#iot#unauthorized bread#james boyle
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Falling out-of-network with your pharmacy
Navigating the frustration of out-of-network pharmacies can be daunting, but there are ways to protect your bottom line. Understanding the dynamics between pharmacy benefit managers and drugstore chains can help, and considering online pharmacies like DiRx can provide a convenient and cost-effective solution. DiRx offers affordable, insurance-free medication with free shipping, ensuring you always have access to your prescriptions without hidden fees.
#Online pharmacy New Jersey#Out-of-network pharmacy#Affordable prescriptions#Pharmacy benefit managers#Prescription savings#Low-cost medications
0 notes
Text
Falling out-of-network with your pharmacy
Navigating the frustration of out-of-network pharmacies can be daunting, but there are ways to protect your bottom line. Understanding the dynamics between pharmacy benefit managers and drugstore chains can help, and considering online pharmacies like DiRx can provide a convenient and cost-effective solution. DiRx offers affordable, insurance-free medication with free shipping, ensuring you always have access to your prescriptions without hidden fees.
#Online pharmacy New Jersey#Out-of-network pharmacy#Affordable prescriptions#Pharmacy benefit managers#Prescription savings#Direct-sourcing pharmacy
0 notes
Text
Falling out-of-network with your pharmacy
Navigating the frustration of out-of-network pharmacies can be daunting, but there are ways to protect your bottom line. Understanding the dynamics between pharmacy benefit managers and drugstore chains can help, and considering online pharmacies like DiRx can provide a convenient and cost-effective solution. DiRx offers affordable, insurance-free medication with free shipping, ensuring you always have access to your prescriptions without hidden fees.
#Online pharmacy New Jersey#Out-of-network pharmacy#Affordable prescriptions#Pharmacy benefit managers#Prescription savings#Direct-sourcing pharmacy
0 notes
Text
Falling out-of-network with your pharmacy
Navigating the frustration of out-of-network pharmacies can be daunting, but there are ways to protect your bottom line. Understanding the dynamics between pharmacy benefit managers and drugstore chains can help, and considering online pharmacies like DiRx can provide a convenient and cost-effective solution. DiRx offers affordable, insurance-free medication with free shipping, ensuring you always have access to your prescriptions without hidden fees.
#Online pharmacy New Jersey#Out-of-network pharmacy#Affordable prescriptions#Pharmacy benefit managers#Prescription savings#Direct-sourcing pharmacy#Cash-pay pharmacy
0 notes