#Paris Agreement 2015
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Hey, happy Earth Day! Who wants to talk about climate change?
Yeah, okay, fair, I kinda figured the answer to that would be "ugh do we have to?" What if I told you I have good news though? Good news with caveats, but still good news.
What if I told you that since the Paris Agreement in 2015, we've avoided a whole degree celsius of global warming by 2100, or maybe more?

Current projections are 2.7C, which is way better than the 3-5C (with a median of 3.7C) we were expecting in 2015. It's not where we want to be - 1.5C - but it is big, noticeable progress!
And it's not like we either hit 1.5C and avoid all the big scary consequences or fail to hit 1.5C and get all of them - every tenth of a degree of warming we avoid is going to prevent more severe problems like extreme weather, sea level rise, etc.
This means that climate change mitigation efforts are having a noticeable impact! This means a dramatically better, safer future - and if we keep pushing, we could lower the amount of global warming we end up with even further. This is huge progress, and we need to celebrate it, even though the fight isn't over.
It's working. Keep going.
#hylian rambles#climate change#climate crisis#environmental issues#global warming#hope#hope for the future#hope for the planet#earth day
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
UN Forecasts 2 In 3 Chance Of Briefly Hitting Climate Danger Point Soon
There’s a two-out-of-three chance within the next five years that the world will temporarily reach the internationally accepted global temperature threshold for limiting the worst effects of climate change, a new World Meteorological Organization report forecasts. It likely would only be a fleeting and less worrisome flirtation with the agreed-upon climate danger point, the United Nations…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
For the first time, global warming has exceeded 1.5C across an entire year, according to the EU's climate service. World leaders promised in 2015 to try to limit the long-term temperature rise to 1.5C, which is seen as crucial to help avoid the most damaging impacts. This first year-long breach doesn't break that landmark Paris agreement, but it does bring the world closer to doing so in the long-term. Urgent action to cut carbon emissions can still slow warming, scientists say.
Continue Reading.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Best News of Last Week - November 28, 2023
🐑 - Why did Fiona the sheep become a mountaineer? She was tired of the "baa-d" jokes at sea level!
1. Pope Francis dines with transgender women for Vatican luncheon

Pope Francis hosted a group of transgender women — many of whom are sex workers or migrants from Latin America — to a Vatican luncheon for the Catholic Church's "World Day of the Poor" last week.
The pontiff and the transgender women have formed a close relationship since the pope came to their aid during the COVID-19 pandemic, when they were unable to work. Now, they meet monthly for VIP visits with the pope and receive medicine, money and shampoo any day, according to The Associated Press.
2. New York just installed its first offshore wind turbine

The first wind turbine installation at South Fork Wind, New York State’s first offshore wind farm, is complete.
The 130-megawatt (MW) South Fork Wind will be the US’s first completed utility-scale wind farm in federal waters.
3. Anonymous businessman donates $800k to struggling food bank

But this Thanksgiving, a longtime prayer of food bank leaders was finally answered: an anonymous benefactor donated the full $800,000 they needed to move out of a facility they've long outgrown. That benefactor, however, preferred to stay anonymous.
"Very private company, really don't want attention," said Debbie Christian, executive director of the Auburn Food Bank. "It's a goodhearted person that just wants to see the work here continue, wants to see it expand."
4. Empowering woman saving hopes and mental health of suffering Ukrainian kids

Kenza Hadij-Brahim is at the forefront of promoting Circle of Toys
Hadj-Brahim is helping to launch the Circle of Toys initiative. A project that provides Ukrainian children in need of some normality with preloved toys. This new initiative connects people with old toys they might otherwise throw away, with Ukrainian families in need who want to provide some comfort to their children in this distressing time.
Find Refuge said : ���The endeavour is driven by a sincere purpose: spark joy, foster play, and bring a hint of normalcy back to the young lives in Ukraine.”
5. TWO LOST CITIES HIDDEN FOR CENTURIES WERE JUST DISCOVERED IN BOLIVIA
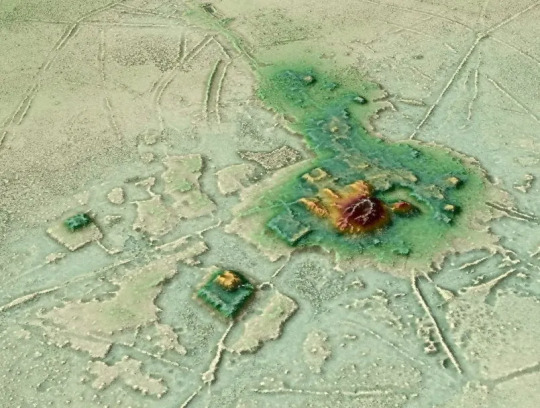

Researchers have found these areas not only housed structures and pyramids but it has been uncovered that there were advanced irrigation systems, earthworks, large towns, causeways, and canals that cover miles.
Dr. Heiko Prümers from the German Archaeological Institute, who was also involved in the study comments that “this indicated a relatively dense settlement in pre-Hispanic times. Our goal was to conduct basic research and trace the settlements and life there. The research sheds light on the sheer magnitude and magnificence of the civic-ceremonial centers found buried in the forest”.
6. Sheep dubbed Fiona rescued from cliff in Scotland where she was stuck for more than 2 years
youtube
And at last, some positive climate news:
7. Three positive climate developments
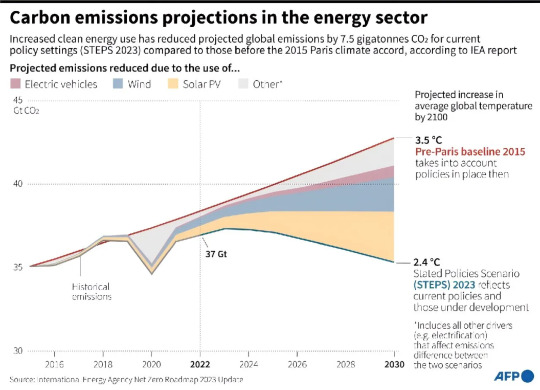
Heating
When the Paris Agreement was adopted, the global reliance on fossil fuels placed the world on a path towards a 3.5C rise in temperature by 2100. Eight years on, country commitments to reduce their carbon footprints have pulled that down slightly, putting the world on a path for a 2.5C to 2.9C by the end of the century.
Peak emissions
Annual greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change have risen roughly nine percent since COP21, according to UN data. But the rate of the increase has slowed significantly. Recent estimates by the Climate Analytics institute find global emissions could peak by 2024
Rising renewables
Three technologies—solar, wind and electric vehicles—are largely behind the improved global warming estimates since 2015.
---
That's it for this week :)
This newsletter will always be free. If you liked this post you can support me with a small kofi donation here:
Buy me a coffee ❤️
Also don’t forget to reblog this post with your friends.
815 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘Hypocritical’ Barack Obama - not Donald Trump - the US president who failed spectacularly on the world stage
President Trump performed well on the international stage, in pursuing his “American first” diplomatic strategy.
In May 2018, Trump made good on his campaign promise and announced he was withdrawing from the Iran nuclear agreement, which had established a set of debatable limits on Iran’s ability to develop a nuclear weapon for at least the next ten or fifteen years.
When other signatories signalled that they would remain in the agreement, Trump put allies on notice that European countries would face American sanctions if they did business with Iran, forcing old friends to choose between Washington and Tehran.
Trump, then rebuking President Obama’s commitment to the first comprehensive global agreement to combat man-made climate, withdrew from the Paris Agreement, which had been negotiated in December 2015.
Preserving freedom of manoeuvre and energy independence, the Trump administration made it plain that it would deal with global warming and climate change in its own way.
No. 45 reckoned it was getting late in the game anyway, and that America was well-placed to deal with the remaining strategy of mitigation and adaptation.
Making a mockery of Obama’s policy of “strategic patience” with North Korea, which is shorthand for doing nothing at all, President Trump and North Korea’s Kin Jong-Un met in Singapore in June 2018, the first summit between the leaders of the US and North Korea since the end of the 1950-3 Korean War, to resolve the nuclear crisis.
While not determining exactly what “complete denuclearisation” of the Korean Peninsula would look like, Trump single-handedly took war off the table.
It was different, as well as potentially brilliant. See link below
https://www.skynews.com.au/insights-and-analysis/hypocritical-barack-obama-not-donald-trump-the-us-president-who-failed-spectacularly-on-the-world-stage/news-story/054c4abca1f6e81ad902bbcd41bd9dcb
#obama#failure#trump#trump 2024#president trump#repost#ivanka#america first#americans first#democrats#america#donald trump#china#korea
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
"In a bid to slow deforestation in the Amazon, Brazil announced Tuesday [September 5, 2023,] that it will provide financial support to municipalities that have reduced deforestation rates the most.
During the country´s Amazon Day, President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva also signed the creation of two Indigenous territories that total 207,000 hectares (511,000 acres) — over two times the size of New York City — and of a network of conservation areas next to the Yanonami Indigenous Territory to act as a buffer against invaders, mostly illegal gold miners.
“The Amazon is in a hurry to survive the devastation caused by those few people who refuse to see the future, who in a few years cut down, burned, and polluted what nature took millennia to create,” Lula said during a ceremony in Brasilia. “The Amazon is in a hurry to continue doing what it has always done, to be essential for life on Earth.”
The new program will invest up to $120 million in technical assistance. The money will be allocated based on the municipality´s performance in reducing deforestation and fires, as measured by official satellite monitoring. A list of municipalities eligible for the funds will be published annually.
The resources must be invested in land titling, monitoring and control of deforestation and fires, and sustainable production.
The money will come from the Amazon Fund, which has received more than $1.2 billion, mostly from Norway, to help pay for sustainable development of the region. In February, the United States committed to a $50 million donation to the initiative. Two months later, President Joe Biden announced he would ask Congress for an additional $500 million, to be disbursed over five years.
The most critical municipalities are located along the arc of deforestation, a vast region along the southern part of the Amazon. This region is a stronghold of former far-right President Jair Bolsonaro, who favored agribusiness over forest preservation and lost the reelection last year.
“We believe that it’s not enough to just put up a sign saying ‘it’s forbidden to do this or that. We need to be persuasive.” Lula said, in a reference to his relationship with Amazon mayors and state governors.
Lula has promised zero net deforestation by 2030, although his term ends two years earlier. In the first seven months of his third term, there was a 42% drop in deforestation.
[Note: For context, Lula's third term as president started January 1, 2023. It was not continuous with his first two terms, when he was president from 2003 to 2010. Lula's third term has been a historic and desperately needed reversal of the anti-environmental, etc. policies of Bolsonaro, whose term ended at the end of 2022.]
Brazil is the world’s fifth-largest emitter of greenhouse gases, with almost 3% of global emissions, according to Climate Watch, an online platform managed by World Resources Institute. Almost half of these emissions come from deforestation. Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, Brazil committed to reducing carbon emissions by 37% by 2025 and 43% by 2030."
-via AP, September 5, 2023
#brazil#deforestation#lula da silva#amazon#amazon rainforest#environmentalism#fossil fuels#environment#environmental justice#land back#illegal miners#yanonami#indigenous#first nations#greenhouse gasses#conservation#good news#hope
378 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lula points the finger at developed nations in UN return

President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva on Tuesday called on developed countries to step up efforts to fight inequality and climate change and criticized neoliberal economics and what he called the “far-right adventurers” that rise in their wake.
“The promise to allocate 100 USD billion dollars – annually – to developing countries”, a goal under the 2015 Paris Agreement, “remains just that, a promise,” Lula told the UN General Assembly in New York. Brazil is traditionally the first country to address the UN General Debate every September.
In line with his regular foreign policy talking points, Lula criticized legacy multilateral institutions, called for a reform in global governance, and stressed the role and relevance of organizations such as the BRICS alliance.
“When institutions reproduce inequalities, they are part of the problem, not the solution,” Lula said. “Last year, the IMF made USD 160 billion in special drawing rights available to European countries and just USD 34 billion to African countries.”
Continue reading.
#brazil#politics#brazilian politics#united nations#luiz inacio lula da silva#foreign policy#mod nise da silveira#image description in alt
286 notes
·
View notes
Text
2024 Book Review #57 – Ministry for the Future by Kim Stanley Robinson

Introduction
Kim Stanley Robinson is one of those names I’ve been meaning to around to since approximately forever ago, one of the real Canonical science fiction writers I’ve always felt slightly ashamed I’ve never read (see also: Gene Wolfe). Ministry for the Future in particular is a book I remember getting an immense amount of buzz and downright hagiographic reviews when it came out, even well beyond the usual science fiction circuit. So I went into this with vague impressions and high expectations – which, as it always does, turned out to be a rather dire mistake.
I do not regret having read this book, but that’s on its merits as a cultural artifact rather than a work of literature. Which is to say, I think this is interesting more than it’s good. It’s more or less equal parts a (rather experimental) novel, a work of futurism, and a political manifesto – and despite being incredibly sympathetic to the latter project, I’m not sure it really succeeds at any of them. Which might just be because I’m reading it now instead of when it came out – it is incredibly of its time, in a way that’s genuinely impressively dated even just a few years latter, and which continuously took me out of it.
It was, at least, very formally interesting. The tiny chapters and constant bouncing between different areas of interest kept it from ever becoming too much of a grind, too.
Synopsis
The book is, roughly, a history of the struggle against climate change and to restore the biosphere to equilibrium, beginning with the signing of the Paris Agreement in 2015 and continuing over the next half-century so until the world has been nigh-unrecognizably transformed and victory in that struggle seems more or less assured.
It is, nominally, focused on its only explicit divergence from our own world before the book was written (so, somewhere in 2017-2019) – the titular Ministry, a subsidiary body created by the Paris Accords to pursue and safeguard the interests of future generations – at first this is basically conceived of as a meaningless goodwill gesture by most of the really powerful people agreeing to it. But after a monstrously deadly heat wave across South Asia kills tens of millions of people in a matter of days, more and more people around the world start to wake up to the necessity of drastic action.
Over the next generation the Ministry plays a major (though less so than you might imagine) role in the transition of the world to a sustainable and just future, and the book follows both their efforts and the changing conditions around them that make any of it possible.
The story is told through a dizzying variety of perspectives – there a couple of what you might call protagonists (the minister for the future herself, a Scottish aid worker caught in the heat wave who barely survives and spends the rest of his life failing to cope with PTSD), but they occupy what has to be much less than half of the book. The rest is short persuasive essays, meeting minutes, anonymous vignettes from everyone from an Antarctic research scientist-turned-geoengineer to a de facto enslaved miner in Namibia, and odd little prose poems from the perspective of ‘the market’ or ‘photons’ or similar. It’s all mixed together quite thoroughly – few chapters are more than six or seven pages, many much less, and each new chapter marks a perspective jump. It’s a fascinating reading experience, if nothing else.
Taken As A Novel
...The Ministry for the Future is just not a very good one.
Partial blame goes to I think the very admirable instinct to avoid making some select group of technocrats and activists the Protagonists of History and instead try to maintain something like a global perspective. But the unfortunate reality of it is that the world is very big, and even at 500 pages the book is comparatively quite small. The result is that this is a story where the overwhelming majority of the plot is told in the passive voice, exposition relaying how trends never before mentioned and institutions not yet introduced are conveniently doing this or that to help fix the world, and then rarely if ever mentioned again. One wonders why the titalur Minister was chosen as a protagonist at all, given how the vast majority of her narrative could just as easily been filled by another other ‘life-on-the-ground’ level perspective (her great contribution is convincing the assembled centrall bankers of the world to do something about two thirds of the way into the book).
Also – while the instinct to avoid making ones main characters the perfectly agentic and hypercompetent engine of history is certainly admirable, it’s rather undercut by then still having one of those, but just giving us no real insight or perspective into it.
The mystique of the shadowy, untouchable terrorist syndicate has a powerful hold in the minds of action and science-fiction authors, and Robinson is apparently no exception. The energy transition in the book is greatly sped up by a near-omnipotent ecoterrorist movement that, through everything from sabotage and assassination to drone strikes and missile barrages, (literally) decapitates the entire fossil fuel industry and destroys so many planes and cargo ships so as to cripple the global airline and shipping industries. I’ll leave aside plausibility (for now) – but it just seems so self-evidently obvious that these are the main characters of the story. But with the exception of a single anonymous vignette, the story refuses to ever give the people involved names, faces, or personalities, nor dive into the whys and hows of specific operations. It’s quite frustrating, all the moreso because it feels like the author just saving himself the work of figuring any of that out.
Our two ostensible main characters themselves also just feel like – not a wasted opportunity, but definitely one more could have been made of? The world changes dramatically, almost unrecognizably, through the course of the novel, but their lives really don’t. Here and there sure, there’s not nothing, but the overwhelming majority of their pagecount is spent living what could very easily have been somewhat atypical lives in contemporary Switzerland. Despite all the talk of a ‘super-depression’ and the crippling of global trade, no shortages ever particularly affect them, no natural disasters touch ther homes. A lot of Mary’s chapters really just kind of read like tourism ads for the country Robinson clearly fell in love with at some point.
Taken as Futurism
Which is to say, taken as an exploration of how the world might actually develop, and a plausible prediction of the future based on current trends. Which, given the sheer amount modern frontier technologies, economic and political theories, and just general social trends are all discussed (not to mention a great deal of the breathless marketing and reception it received) the book is clearly trying to be. And which – woof, it does not work out.
The book is full of generational political upheavals occurring mostly because it’s a dramatically convenient time for them to. Most glaringly, the cataclysmic heat wave that sets off the book’s plot also conveniently utterly discredits the BJP and leads the landslide election of an entirely fictitious political movement across all of India, who then spend the next decades dramatically transforming the nation’s politics and economy with unbroken success and to a reception of thunderous applause. There’s no characters with names or faces actually involved in this, no more than a couple paragraphs of encyclopedia-like exposition devoted to it, but it’s the example and engine the whole rest of the book hangs on. The transition of the African Union to a powerful and legitimate supernational entity and the granting of permanent autonomy to Hong Kong (and much of southern mainland China why not) are even less dwelt on.
Now, this all could be excused as just the inevitable causalities of trying to write a book with a global scope – and I am sympathetic to that. But to begin with, I know just barely enough about the politics and the economics of a lot of several of the places touched on or used as dramatic examples to see how surface level and implausible the predicted changes are, and I can’t help but think it’s probably a similar story with all the other lightly touched on placed I don’t know much about (I remain agnostic on the accuracy of the geoengineering and carbon-clearing technologies projected, except that a lot of them suspiciously amenable to a single coherent aesthetic of the future).
More damning, to me at least, is the matter of agency – only the ‘good’ people seem to possess any of it. The conservative opposition exists as this vague, undifferentiated mass – standing athwart history and slowing things down in vague ways, but never really vital or active, never a danger to the political movements that have won or the progress that has been made. There are references to xenophobia and anti-refugee sentiment, but despite a refugee crisis that makes that of the 2010s look like a rounding error, it never leads to any really dangerous political backlash. Given how the world’s actually trending, the book’s vision of politics goes beyond optimism and into outright delusion.
This is especially true for how the book conceives of violence. Political violence is, in the book’s telling, near-universally the province of the ecological Left (with the exception of two events that provide excuses for dramatic set-pieces but fail to actually achieve anything at all). As mentioned above, seemingly omnipotent and untouchable eco-terrorists assassinate dozens of hundreds of the global elite for their crimes against the planet, destroy so many jet liners and cargo ships to force the adoption of new transportation methods, and sabotage so many coal- and oil-powered plants they help force the abandonment of the as fuels. They do this with no real blowback or reverses, no ruthless campaigns of state violence breaking apart the networks or destroying the infrastructure, no loss of public support from the disruptions in food and fuel their attacks would cause – it is not a realistic vision of what ecoterrorism might look like in the coming decades, it’s a plot device in the form of Robert Ludlum villains with no action movie secret agents around to stop them.
As a Political Manifesto
Which is, after all, clearly the real motivation behind the book, and the reason it received as many accolades as it did. It’s also where the book is easily at its most interesting – if, tragically, rather incoherent. Which might be me holding it to a higher standard than is fair but look, there’s only so many essays extolling the failure of the market or the coming obsolescence of war or whatever you can put in your book before I start holding it to the standard of actual rigour.
Mostly it feels like the book is undercut by its commitment to relentless optimism and need to jump around – a great deal of the book is spent giving the most positive possible gloss on particular phenomena or institutions from across the world in a paragraph or two, then say it needs to be scaled up on a national or global scale with no further thought or consideration of costs. Even when it’s not wrong it just feels unserious.
The subject the book spends the plurality of its time on – the main thrust of its program, if anything is – is economics and monetary policy. The great project of the Ministry is convincing the assembled central bankers of the world to create a new currency – a ‘carbon coin’ minted as a reward for sequestering or preventing the removal of a single ton of carbon for at least a century, with a guaranteed minimum value and appreciation over the same period – which would in time replace the us dollar as a global reserve currency and medium of exchange. The arguments around which are frustrating, because they go from plausible and compelling to wildly optimistic to the social science equivalent of star trek technobabble and back again without warning or any detectable pattern. It’s an interesting idea, at least, though one you get the sense is being imperfectly relayed – and the arguments for why the uncrowned monarchs of the global financial system would actually agree to it just aren’t convincing in the least.
Given the amount of times the book uses standard progressive language about how vital empowering minorities, women, the traditionally excluded and so on is to the fight to save the planet, it’s honestly kind of amusing the degree to which the big dramatic set pieces involve appealing to the conscience and principles of the most embedded representatives of The System imaginable. Running through the book are both a disdain and dismissal of economics as a field and a strongly felt technocratic sensibility and desire to have seasoned experts at the helm managing their areas of expertise – it can never quite decide whether bringing the world’s central banks under increased political control is something to be fought for, or a threat to hold over the bankers heads to get them in line and focused on the important task of creating a de facto world state (the quasi-utopia envisioned at the end of the book could just as easily be the globalist dystopia from any conspiracy theorist’s screen with no changes but the valence of the adjectives used to describe it).
It’s more peripheral, but Robinson’s clear affection for the nation of Switzerland and continuous praise of its many virtues in both politics and society does clash a bit with, well, reality. It’s weird to go from a chapter about needing to abolish tax havens to talking about how enlightened self-interest has left the Swiss government entirely behind the mission of fighting climate change.
A Product of it’s Time
Is a weird thing to call a book written barely more than five years ago, I’m aware. But it’s honestly kind of shocking just how aged and dated the book feels, reading it in 2024. Despite just everything I’ve written above, I’m trying not to judge it as harshly as I might, because I feel like I’d have been much more generous if various things didn’t keep taking me out of it.
Some of them are things that can’t really be held against it – the passages about Russia and it’s relationship with Europe reads as almost comical now, to be sure, but so does every sci fi book in the ‘80s talking about the USSR – but that doesn’t mean they don’t hurt the feeling of reading the history of the future. The book was published in October 2020, so the complete non-mention of not even COVID specifically but just any pandemic or major disease outbreaks feel positively unreal.
Other things are less the book already being falsified by history and more just seeing what turned out to be pretty transient intellectual fashions immortalized in print. Seeing a serious, celebrated book talk about the revolutionary potential of the blockchain to create a democratic new economy is enough to turn a hair grey. And on a less extreme level, talking up Modern Monetary Theory as this revolutionary hack of solve economics just feels so very incredibly pre-pandemic.
Too Long; Didn’t Read
Not angry I read it, but more because writing this review was fun and engaging than for its merits as a work of art. Can’t judge it too harshly, given that the task it set for itself is basically impossible – but Robinson’s written enough books that he probably should have known that before he started it.
The set piece at the beginning of someone living through the dead heat wave was incredibly compelling drama, at least.
46 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pay Attention to who resigns from politics, BIG business and other areas in the coming months. I think we will see a lot more than we have in the past. 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#reeducate yourselves#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do your own research#ask yourself questions#do some research#question everything#you decide
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
Among all government institutions worldwide, the US and UK militaries bear some of the greatest responsibility for climate crisis. Despite this, emissions from military sources are not addressed in international climate agreements: as a result of US lobbying, overseas military emissions were made exempt from the 1997 Kyoto Protocol and military emissions reporting remained optional in the 2015 Paris Climate Agreement. Even if using opaque official data, the UK and US militaries have jointly emitted at least 430 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent since the year of the Paris Climate Agreement — more than the total greenhouse gas emissions produced in the UK in 2022. While several other militaries are also leading institutional emitters, this report focuses on the joint climate impact of the US and UK militaries for three reasons: first, their historic role in the development of the global fossil fuel economy; second, their current consumption of fossil fuels, associated greenhouse gas emissions and the environmental damage produced by their military infrastructure; third, the US and UK governments’ allocation of public investment towards carbon-intensive industrial sectors to supply their militaries when they could better prioritise green industrial policy. The US and UK governments and their militaries are important architects of the modern fossil fuel economy. Throughout the twentieth century, the strategies of both militaries were intimately tied to the supply of oil. In the wake of the First World War, for instance, the British empire’s division of former Ottoman regions was explicitly designed around plans for hydrocarbon pipelines. As data presented in this briefing demonstrates, the legacy of the US and UK militaries as architects of the fossil economy lives on through their present consumption of fossil fuels — in 2017, the Pentagon produced more emissions than the country of Portugal. Accounting for the social consequences of US and UK military emissions since 2015 — using even a conservative social cost of carbon calculation as detailed below — would entail an international climate finance package of approximately $111 billion to be paid to the nations most threatened by climate crisis, far above the US and UK’s current contributions through established climate finance channels. Beyond carbon emissions, the US and UK’s overseas presence shows the various modes through which military bases, activity and infrastructure produce environmental damage and toxic waste.
125 notes
·
View notes
Text
Donald Trump is reportedly planning to scrap clean energy initiatives in favor of fossil fuel production.
According to a New York Times report, the US President-elect is seeking to overhaul energy and environmental policies, aiming to dismantle the “woke” agenda and eliminate programs that impede the country’s economic growth.
The report says Trump is planning to appoint an “energy czar” to replace Biden’s “climate tsar.”
His team will “look at what Biden did and put a ‘not’ in front of it.”
RT reports: Trump’s energy and environment transition team has already prepared “a slate of executive orders and presidential proclamations on climate and energy,” according to the article published on Friday. The measures reportedly include the US abandoning the Paris Agreement – an international treaty on climate change adopted in 2015.
Reshaping the boundaries of the Bears Ears and Grand Staircase-Escalante national monuments in southern Utah to open up land for drilling and mining is also on the agenda. The protected area was expanded by US President Joe Biden in 2021.
Donald Trump’s team is also reportedly set to scrap Biden’s so-called environmental justice initiatives, which favor clean energy development and pollution reduction. This involves ending the suspension of permits for new natural gas export terminals, among other things.
The publication noted that Trump is planning to appoint an “energy czar” to replace Biden’s “climate tsar.” The role will be dedicated to streamlining policies related to oil, gas, and coal production in order to boost supply rather than limit demand. North Dakota Governor Doug Burgum, who previously helped open millions of acres of public land for fracking, and former energy secretary Dan Brouillette, are being considered for the post.
Further plans include relocating federal agencies including the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) out of Washington. Previously Trump argued that such federal departments and agencies should be moved to “places filled with patriots who love America.”
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just 57 companies and nation states were responsible for generating 80% of the world's CO₂ emissions from fossil fuels and cement over the last seven years, according to a new report released by the thinktank InfluenceMap. This finding suggests that net zero targets set by the Paris climate change agreement in 2015 are yet to make a significant impact on fossil fuel production. The report uses the Carbon Majors database, established in 2013 by Richard Heede of the Climate Accountability Institute, to provide fossil fuel production data from 122 of the world's largest oil, gas, coal and cement producers.
Continue Reading.
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
The U.N.’s Verdict on Climate Progress Over the Past Year: There Was None. (New York Times)
youtube
Excerpt from this New York Times story:
One year after world leaders made a landmark promise to move away from fossil fuels, countries have essentially made no progress in cutting emissions and tackling global warming, according to a United Nations report issued on Thursday.
Global greenhouse gas emissions soared to a record 57 gigatons last year and are not on track to decline much, if at all, this decade, the report found. Collectively, nations have been so slow to curtail their use of oil, gas and coal that it now looks unlikely that countries will be able to limit global warming to the levels they agreed to under the 2015 Paris climate agreement.
“Another year passed without action means we’re worse off,” said Anne Olhoff, a climate policy expert based in Denmark and a co-author of the assessment, known as the Emissions Gap Report.
The report comes a month before diplomats from around the world are scheduled to meet in Baku, Azerbaijan, for annual United Nations climate talks, where countries will discuss how they might step up efforts to address global warming.
Lately, those efforts have faced huge obstacles.
Even though renewable energy sources like wind and solar are growing rapidly around the world, demand for electricity has been rising even faster, which means countries are still burning more fossil fuels each year. Geopolitical conflicts, from the U.S.-China rivalry to war in places like Ukraine and Gaza, have made international cooperation on climate change harder. And rich countries have failed to keep their financial promises to help poor countries shift away from oil, gas and coal.
At last year’s climate talks in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, representatives from nearly every nation approved a pact that called for “transitioning away from fossil fuels” and accelerating climate action this decade. But the agreement was vague on how to do so and on which countries should do what, and so far there has been little follow-through.
The new U.N. report finds that at least 151 countries have formally pledged under the Paris climate agreement to curb their greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. If every country followed through on its stated plans, which is far from assured, then global emissions could be 3 percent to 11 percent lower at the end of the decade than they are today.
But that would still put the Earth on track to heat up an average of roughly 2.6 to 2.8 degrees Celsius (4.7 to 5 degrees Fahrenheit) over preindustrial levels by the century’s end, the report found. The planet has already warmed roughly 1.3 degrees Celsius (2.3 degrees Fahrenheit). That may not sound like much, but every fraction of a degree of warming brings greater risks from deadly heat waves, wildfires, drought, storms and species extinction, scientists have said.
Under the Paris Agreement, world leaders vowed to hold global warming to “well below” 2 degrees Celsius, and preferably closer to 1.5 degrees Celsius, to limit the risks from climate catastrophes.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
"India’s announcement that it aims to reach net zero emissions by 2070 and to meet fifty percent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030 is a hugely significant moment for the global fight against climate change. India is pioneering a new model of economic development that could avoid the carbon-intensive approaches that many countries have pursued in the past – and provide a blueprint for other developing economies.
The scale of transformation in India is stunning. Its economic growth has been among the highest in the world over the past two decades, lifting of millions of people out of poverty. Every year, India adds a city the size of London to its urban population, involving vast construction of new buildings, factories and transportation networks. Coal and oil have so far served as bedrocks of India’s industrial growth and modernisation, giving a rising number of Indian people access to modern energy services. This includes adding new electricity connections for 50 million citizens each year over the past decade.
The rapid growth in fossil energy consumption has also meant India’s annual CO2 emissions have risen to become the third highest in the world. However, India’s CO2 emissions per person put it near the bottom of the world’s emitters, and they are lower still if you consider historical emissions per person. The same is true of energy consumption: the average household in India consumes a tenth as much electricity as the average household in the United States.
India’s sheer size and its huge scope for growth means that its energy demand is set to grow by more than that of any other country in the coming decades. In a pathway to net zero emissions by 2070, we estimate that most of the growth in energy demand this decade would already have to be met with low-carbon energy sources. It therefore makes sense that Prime Minister Narendra Modi has announced more ambitious targets for 2030, including installing 500 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity, reducing the emissions intensity of its economy by 45%, and reducing a billion tonnes of CO2.
These targets are formidable, but the good news is that the clean energy transition in India is already well underway. It has overachieved its commitment made at COP 21- Paris Summit [a.k.a. 2015, at the same conference that produced the Paris Agreement] by already meeting 40% of its power capacity from non-fossil fuels- almost nine years ahead of its commitment, and the share of solar and wind in India’s energy mix have grown phenomenally. Owing to technological developments, steady policy support, and a vibrant private sector, solar power plants are cheaper to build than coal ones. Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026...
Subsidies for petrol and diesel were removed in the early 2010s, and subsidies for electric vehicles were introduced in 2019. India’s robust energy efficiency programme has been successful in reducing energy use and emissions from buildings, transport and major industries. Government efforts to provide millions of households with fuel gas for cooking and heating are enabling a steady transition away from the use of traditional biomass such as burning wood. India is also laying the groundwork to scale up important emerging technologies such as hydrogen, battery storage, and low-carbon steel, cement and fertilisers..."
-via IEA (International Energy Agency), January 10, 2022
Note: And since that's a little old, here's an update to show that progress is still going strong:
-via Economic Times: EnergyWorld, March 10, 2023
#india#solar power#renewable energy#green energy#sustainability#wind power#population grown#economic growth#developing economies#renewable electricity#carbon emissions#good news#hope#hope posting
857 notes
·
View notes
Text
As delegates arrived at the Republican National Convention in Milwaukee earlier this week to officially nominate former president Donald Trump as their 2024 candidate, a right-wing policy think tank held an all-day event nearby. The Heritage Foundation, a key sponsor of the convention and a group that has been influencing Republican presidential policy since the 1980s, gathered its supporters to tout Project 2025, a 900-plus-page policy blueprint that seeks to fundamentally restructure the federal government.
Dozens of conservative groups contributed to Project 2025, which recommends changes that would touch every aspect of American life and transform federal agencies—from the Department of Defense to the Department of Interior to the Federal Reserve. Although it has largely garnered attention for its proposed crackdowns on human rights and individual liberties, the blueprint would also undermine the country’s extensive network of environmental and climate policies and alter the future of American fossil fuel production, climate action, and environmental justice.
Under President Joe Biden’s direction, the majority of the federal government’s vast system of departments, agencies, and commissions have belatedly undertaken the arduous task of incorporating climate change into their operations and procedures. Two summers ago, Biden also signed the Inflation Reduction Act, the biggest climate spending law in US history, with the potential to help drive greenhouse gas emissions down 42 percent below 2005 levels.
Project 2025 seeks to undo much of that progress by slashing funding for government programs across the board, weakening federal oversight and policymaking capabilities, rolling back legislation passed during Biden’s first term, and eliminating career personnel. The policy changes it suggests—which include executive orders that Trump could implement single-handedly, regulatory changes by federal agencies, and legislation that would require congressional approval—would make it extremely difficult for the United States to fulfill the climate goals it has committed to under the 2015 Paris Agreement.
“It’s real bad,” said David Willett, senior vice president of communications for the environmental advocacy group the League of Conservation Voters. “This is a real plan, by people who have been in the government, for how to systematically take over, take away rights and freedoms, and dismantle the government in service of private industry.”
Trump has sought to distance himself from the blueprint. “Some of the things they’re saying are absolutely ridiculous and abysmal,” he wrote in a social media post last week.
However, at least 140 people who worked in the Trump administration contributed to Project 2025, and policy experts and environmental advocates fear Project 2025 will play an influential role in shaping GOP policy if Trump is reelected in November. Some of the blueprint’s recommendations are echoed in the Republican National Convention’s official party platform, and Heritage Foundation president Kevin Roberts says he is “good friends” with Trump’s new running mate, Senator J. D. Vance of Ohio. Previous Heritage Foundation road maps have successfully dictated presidential agendas; 64 percent of the policy recommendations the foundation put out in 2016 had been implemented or considered under Trump one year into his term. The Heritage Foundation declined to provide a comment for this story.
Broadly speaking, Project 2025 proposals aim to scale down the federal government and empower states. The document calls for “unleashing all of America’s energy resources” by eliminating federal restrictions on fossil fuel drilling on public lands, curtailing federal investments in renewable energy technologies, and easing environmental permitting restrictions and procedures for new fossil fuel projects such as power plants. “What’s been designed here is a project that ensures a fossil fuel agenda, both in the literal and figurative sense,” said Craig Segall, the vice president of the climate-oriented political advocacy group Evergreen Action.
Within the Department of Energy, offices dedicated to clean energy research and implementation would be eliminated, and energy efficiency guidelines and requirements for household appliances would be scrapped. The environmental oversight capacities of the Department of the Interior and the Environmental Protection Agency would be curbed significantly or eliminated altogether, preventing these agencies from tracking methane emissions, managing environmental pollutants and chemicals, or conducting climate change research.
In addition to these major overhauls, Project 2025 advocates for getting rid of smaller and lesser-known federal programs and statutes that safeguard public health and environmental justice. It recommends eliminating the Endangerment Finding—the legal mechanism that requires the EPA to curb emissions and air pollutants from vehicles and power plants, among other industries, under the Clean Air Act. It also recommends axing government efforts to assess the social cost of carbon, or the damage each additional ton of carbon emitted causes. And it seeks to prevent agencies from assessing the “co-benefits,” or the knock-on positive health impacts, of their policies, such as better air quality.
“When you think about who is going to be hit the hardest by pollution—whether it’s conventional air, water, and soil pollution or climate change—it is very often low-income communities and communities of color,” said Rachel Cleetus, policy director of the climate and energy program at the Union of Concerned Scientists, a nonprofit science advocacy organization. “The undercutting of these kinds of protections is going to have a disproportionate impact on these very same communities.”
Other proposals would wreak havoc on the nation’s ability to prepare for and respond to climate disasters. Project 2025 suggests eliminating the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and the National Weather Service housed therein and replacing those organizations with private companies. The blueprint appears to leave the National Hurricane Center intact, saying the data it collects should be “presented neutrally, without adjustments intended to support any one side in the climate debate.” But the National Hurricane Center pulls much of its data from the National Weather Service, as do most other private weather service companies, and eliminating public weather data could devastate Americans’ access to accurate weather forecasts. “It’s preposterous,” said Rob Moore, a policy analyst for the Natural Resources Defense Council’s Action Fund. “There’s no problem that’s getting addressed with this solution, this is a solution in search of some problem.”
The document also advocates moving the Federal Emergency Management Administration, which marshals federal disaster response, out from under the umbrella of the Department of Homeland Security, where it has been housed for more than 20 years, and into the Department of the Interior or the Department of Transportation. “All of the agencies within the Department of Interior are federal land management agencies that own lots of land and manage those resources on behalf of the federal government,” Moore said. “Why would you put FEMA there? I can’t even fathom why that is a starting point.”
The blueprint recommends eliminating the National Flood Insurance Program and moving flood insurance to private insurers. That notion skates right over the fact that the federal program was initially established because private insurers found that it was economically unfeasible to insure the nation’s flood-prone homes—long before climate change began wreaking havoc on the insurance market.
Despite the alarming implications of most of Project 2025’s climate-related proposals, it also recommends a small number of policies that climate experts said are worth considering. Its authors call for shifting the costs of natural disasters from the federal government to states. That’s not a bad conversation to have, Moore pointed out. “I think there’s people within FEMA who feel the same way,” he said. The federal government currently shoulders at least 75 percent of the costs of national disaster recovery, paving the way for development and rebuilding in risky areas. “You are disincentivizing states and local governments from making wise decisions about where and how to build because they know the federal government is going to pick up the tab for whatever mistake they make,” Moore said.
Quillan Robinson, a senior adviser with ConservAmerica who has worked with Republicans in Washington, DC, on crafting emissions policies, was heartened by the authors’ call for an end to what they termed “unfair bias against the nuclear industry.” Nuclear energy is a reliable source of carbon-free energy, but it has been plagued by security and public health concerns, as well as staunch opposition from some environmental activists. “We know it’s a crucial technology for decarbonization,” Robinson said, noting that there’s growing bipartisan interest in the energy source among lawmakers in Congress.
An analysis conducted by the United Kingdom–based Carbon Brief found that a Trump presidency would lead to 400 billion metric tons of additional emissions in the US by 2030—the emissions output of the European Union and Japan combined.
Above all else, Segall, from Evergreen Action, is worried about the effect Project 2025 would have on the personnel who make up the federal government. Much of the way the administrative state works is safeguarded in the minds of career staff who pass their knowledge on to the next cadre of federal workers. When this institutional knowledge is curbed, as it was by budget cuts and hostile management during Trump’s first term, the government loses crucial information that helps it run. The personnel “scatter,” he said, disrupts bottom-line operations and grinds the government to a halt.
Although Project 2025’s proposals are radical, Segall said that its effect on public servants would echo a pattern that has been playing out for decades. “This is a common theme in Republican administrations dating back to presidents Richard Nixon and Ronald Reagan,” he said. “What you do is you break the government, make it very hard for the government to function, and then you loudly announce that the government can’t do anything.”
34 notes
·
View notes