#Nganasan
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

I know this might not look too flashy, but this might be my favourite stamp sheet. These Estonian stamps are a language tree of the Uralic languages.
Going anti-clockwise from the bottom middle stamp, we have:
The Samoyedic Languages: Nenets, Enets, Nganasan, Selkup, and Kamasin
The Ugric Languages: Hungarian, Khanty and Mansi
The Permic Languages: Komi and Udmurt
The Mari and Mordvinic (Erzya and Moksha) Languages
The Sami Languages (Nortern, Southern, Skolt, Inari, Lule, Ume, Pite, Ter and Kildin Sami)
The Baltic-Finnic Languages: Veps, Karelian, Izhorian, Livonian, Finnish, Estonian and Votic
Languages in brackets weren't mentioned in the stamp, but I thought I'd elaborate anyway
Edit: put Ingrian instead of Izhorian. Should've known better, sorry
#philately#stamp collecting#stamps#estonia#eesti#uralic#uralic languages#nenets#enets#nganasan#selkup#kamasin#hungarian#khanty#mansi#komi#udmurt#mari#erzya#moksha#sami#saami#veps#karelian#livonian#finnish#estonian#votic#Izhorian
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
Number in letters
Small indigenous peoples are offered to preserve their speech
January 21, 2025
All methods of preserving and reviving endangered languages used so far in Russia have not yielded results, stated participants of a forum dedicated to this problem in Krasnoyarsk. In their opinion, only the preservation of traditional forms of residence and management provides a guarantee for the continued existence of such languages. However, forum participants from among government representatives, the expert community and the indigenous peoples themselves agreed that the digital environment of indigenous peoples can help solve the problem.
In the middle of the last century, traditional farming guaranteed the preservation of native languages for the inhabitants of the indigenous northern peoples
Photo: Gorshkov V. / Photo archive of the magazine "Ogonyok" / Kommersant
The scope of use of the languages of indigenous minorities (IMN) of the North, Siberia and the Far East is gradually narrowing, which threatens their continued existence. This was discussed at the strategic session "Creating a digital environment for native languages through the prism of technology and creative industries", which opened in Krasnoyarsk on January 21. It was organized by the Regional Association of Indigenous Minorities of the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
The list of indigenous minorities of the North, Siberia and the Far East of the Russian Federation includes 40 ethnic groups. The largest of them are the Nenets, Evenks, Khanty, Evens, Chukchi and Mansi. Eight such peoples live in Krasnoyarsk Krai. The total number of indigenous minorities of Russia is 262.6 thousand people. The UN General Assembly proclaimed 2022-2032 the International Decade of Indigenous Languages.
"It is very unfortunate that we have to acknowledge the threatening language situation among almost all the indigenous minorities of the North. Thus, among the modern Evenks, only a few families have survived in which their native language is passed on to their children, and these are mostly those families that continue to preserve their traditional way of life," complained the leader of the Evenk Association of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) Aleksandr Varlamov. In his opinion, the education system, which involves teaching children of indigenous minorities in boarding schools, does not ensure the continuity of language knowledge and traditional forms of economic management. "In the current state of affairs, it is quite expected that in the course of decades we will lose not only our native language, but also the last reindeer herders and hunters - the true guardians of ethnocultural traditions," he made a sad forecast.
A similar point of view was expressed by the professor of the Siberian Federal University, the famous historian and ethnographer Viktor Krivonogov.
“Having studied more than 30 peoples of Siberia, the Far East and foreign countries, I have not encountered a single fact where any people has preserved or revived their language,” he summed up the results of his 50 years of research work.
The scientist noted that this happened despite the implementation of numerous laws, programs and the “heroic work of teachers.”
According to the results of surveys conducted during scientific expeditions, the Soyots in the Republic of Buryatia have completely lost their fluency in their native language. Among the Tofalars in the Irkutsk Region and the Kets in the Krasnoyarsk Territory, this figure is less than 10%. Among the Krasnoyarsk Nganasans and Nenets, it is no more than 15%. Although, back in 1993-1994, almost 40% of the representatives of this people spoke Nganasan fluently. At the same time, according to Mr. Krivonogov, even among the Evenks of the Krasnoyarsk Territory, who can study their native language in middle and high school, the number of those who speak it fluently is decreasing. There are no such people left at all under the age of 19, and about 1% of those aged 19-29.
"The language is actually preserved only in the environment where traditional farming is practiced... If a child comes to school at the age of seven with his native Russian language, not knowing a single word in the Evenki language, can this language become his native language again? Of course not," Viktor Krivonogov named the reason for the loss of the native language. According to his data, at present only 5% of the representatives of the indigenous minorities of the Krasnoyarsk Territory continue to roam the tundra. Among the Tundra Nenets, the proportion of those fluent in their native language reaches almost 100%.
“Due to various objective reasons, the young generation of indigenous peoples of the North is breaking away from the centuries-old occupations of their ancestors, losing their mother tongue, their customs and traditions,” confirmed Victoria Polikarenok, head of the Evenki nomadic kindergarten “Chipkan”.
The creation of a digital environment for indigenous languages can help solve the language problem, believes Grigory Dyukarev, Commissioner for the Rights of Indigenous Peoples in Krasnoyarsk Krai. In particular, he suggested that the session participants initiate the introduction of programs for training "teachers of native language and computer science" in universities, as well as include in the program advanced training for teachers of native languages and the use of digital technologies.
Sardana Sivtseva from the Arctic Capital company named the Ayana platform as an example of creating a digital environment. It is an offline version of an electronic translator of the Evenki language for nomadic schools and places with unstable mobile communications. "The project has found a continuation in Altai, Krasnoyarsk Krai, and other regions. We initially planned that after the Evenki language, other languages would follow," she said, calling on specialists to create electronic explanatory dictionaries of the languages of the indigenous minorities. During the session, a machine translator of the Mansi language, the Evenki language portal "Evengus" and a number of other projects were also presented.
"We will try this new method as well. Maybe it will work if the previous ones did not lead to significant changes," Viktor Krivonogov expressed hope, adding that the result of applying digitalization in this area will become clear "in about ten years."
Valery Lavsky

#indigenous#culture#important#fypシ#indigenous russia#indigenous russian#fypage#russia#colonization#landback#Land back#siberian native#native siberian#indigenous siberian#Siberia#Siberian#stop russia#russian colonization#russian imperialism#russian genocide#indigenous rights#indigenous people#endangered languages#endangered#Ket#Nenets#Altai#Nganasan#Evenk#Even
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
"anyone who loves [flag] is my friend without introduction" meme but with indigenous peoples of russia!
"anyone who loves [flag] is my friend without introduction" meme but with indigenous peoples of russia! part 2 - uralic indigenous 2
part 1 (link)
memes under the cut:

setos:

hill mari:

izhma komi:

perm komi / komi-permyak:

nganasans:

selkups:

forest nenets:

tundra nenets:
khanty and mansi:

all free to use without credit! like and reblog is you like it!
#indigenous#seto#hill mari#izhma komi#perm komi#komi-permyak#nganasan#selkup#forest nenets#tundra nenets#finno-ugric#uralic#khanty#mansi
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Nganasan men, Siberia.
Though related to the Nenets due to their common Samoyedic background - they hunt reindeer. As opposed to herding them like the Nenets do.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
This piece takes you on at trip through central Siberia, from the throat-singing peoples and beautiful mountains in the south to the arctic tundra and deep shamanic traditions of the north.
This was my biggest project of 2023. I wrote this piece and an essay as my final degree project in composition, all about Siberian indigenousgroups and their music.
The essay (in Swedish) can be found here:
https://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:oru:diva-106984
#classicalmusic#contemporarymusic#composition#originalcomposition#music#orchestra#orchestralmusic#symphonyorchestra#chamberorchestra#siberia#indigenous#indigenoussiberia#altai#tuva#nganasan#throatsinging#khoomei#kargyraa#sygyt#shaman#shamanism#contrabassoon#bassclarinet#piccolo#youtube#Youtube
3 notes
·
View notes
Text


#archive collectiona#archive#archeology lover#archeology#archeologi#archeologia#italian archive#nature#anthropology#antiquities#design#graphic#graphic design#graphisme#mother earth#nganasan#idol#shaman
0 notes
Note
Would you recommend studying finno-ugric languages (for a native Finnish speaker)? Can you share some tidbits?
Hi!
I am specifically doing my studies at the University of Helsinki so I can give you specifics on what we do here (the same things apply if you study this as a hobby tbh)!
First of all, if you are considering this field, you NEED to be ready to learn at least one completely new language to a B2 level. Our field requires at least 3 courses in another Uralic language (I am doing North Sámi, the other two options are Hungarian and Estonian). On top of that, you can (or kinda have to if you don't wanna do a 4th course from that first language) do 1-2 courses on an another Uralic language. These singular courses also cover the smaller languages, I am so looking forward to a Nenets course becoming available!
Another thing you need to keep in mind is that while we are grouped with the Finnish fields here at UoH, our field is totally different, in my opinion, this resembles linguistics a lot more than Finnish studies. You have to be ready for a lot of linguistics courses and I recommend studying linguistics on your own before applying.
The third thing is the job market. There aren't many jobs specifically for this field unless you want to be a professor or a researcher so think of this as a secondary career option and be ready to educate yourself further after finishing your studies.
From the standpoint of the community here at UoH, you WILL become the center of attention. There are SO FEW of us here we are like rare shiny Pokemon. Both staff and other students will say "Oooh what I've never met anyone in your field yet" more than once. Be ready to answer the burning questions such as "So where did Finnish come from" or "What is the etymology of Suomi" 1 week in. Prepare your answer before you even come in for orientation.
Learning about the Uralic languages will definitely help you learn about how Finland came to be. You'll also be able to learn other Uralic languages faster and even start to understand them without studying them at all in some cases!
TLDR: a rare form of linguistics disguised as Finnish studies. People will question your life choices. You will too after memorizing North Sámi noun cases at 1am.
#finnish#langblr#langblog#suomen kieli#suomitumblr#linguistics#university#uralic languages#i love nenets#nganasan has been another fave for ages
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also, can we stress enough that most Ugro-Finnic peoples actually inhabit the territory of modern Russian Federation and that most of their languages are either on the verge of being extinct or already are?
I know that some folks (unfortunately, often they are Ukrainian) like bringing up the fact that white Russians, despite claiming to be the “most Slavic country of them all” (like, lmao, how stupid that even sounds), are actually often ethnically Ugro-Finnic. And I am deeply against this approach.
The fact that many white Russians today are not even that Slavic is actually a sad testimony to systemic Russification: cultural and linguistic erasure, often done with tools such as religion (the Orthodox Church does not really care about preserving local languages and customs, am I right?), schooling system (if I am correct, teaching of Indigenous languages in Russian schools is a joke, it’s often just an hour a week that nobody cares much about really; also it cements the “state identity” in students as the primary one) and even so innocently looking ones, such as intermarriage (because it is obvious that most children from such marriages would choose the national identity of the parent that belongs to the dominant ethnic group).
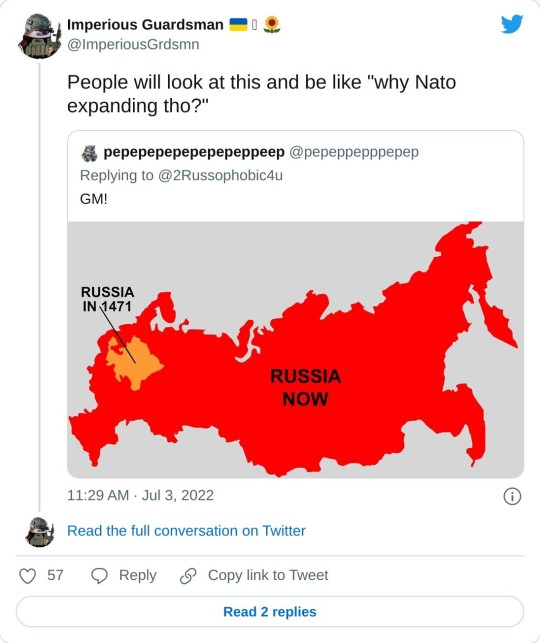
#russian colonialism#russian imperialism#ugro-finnic peoples#ugro-finnic languages#karelia#komi#udmurtia#selkups#nganasan people#mari#enets people#nenets people#and others
962 notes
·
View notes
Text
End-of-the-year review!
The biggest achievement of this year was getting into my dream university. Here's how I did with my self studies.
AINU This was very fun and I am OBSESSED with the language. I filled up my 64-page notebook in under a year. I can speak pretty fluently already! Will totally be continuing to study this language next year!
KOREAN Korean was on maintenance mode for most of the year. I have been forcing myself to read and listen more and of course keep watching content in the language.
NORTH SÁMI My new focus for the year, I study this for university. I got great marks for my first course and I feel like I am progressing fast. There will be a small break where I can't take it at school again so I need to make sure I don't forget anything!
JAPANESE I have been studying this language a bit more than Korean for the first time. I feel like I still need to study a lot but my reading skills have been improving a lot this year!
MANDARIN & CANTONESE I have been consuming content in both languages over the year and have become obsessed with Cantonese cooking shows. I can understand a lot, but I cannot speak at all in either language
KARELIAN I have been reading content and trying to finally learn some grammar. Waiting to enroll in a course in this language some day. I understand the language perfectly because I grew up hearing it, just can't speak it!
OKINAWAN I have neglected this language a bit. I got about 5 pages of notes written down this year. Next year I hope to focus on the conjugations of words more
DUTCH I can understand text very well due to my existing Swedish knowledge but cannot understand speech well. Maybe I need to focus on that next year.
SWEDISH I moved to an area where this language is spoken more so I have naturally started picking up more words. I can speak the language well already but now I know what words the locals use for stuff, it's super interesting
YUKAGHIR? I have started picking up words from all the Yukaghir music I listen to. I wasn't even going to learn the language. Please I don't want to fall down another language rabbit hole and be obsessed with a random language
Other: I want to learn another Uralic language, maybe Nenets or Nganasan! I can learn those through my university at some point. I would also like to learn a language like Spanish or Russian for fun but I think I don't have enough time for that. I also need to find a job... Oh right and I can speak a bit more toki pona and have been working on my conlangs too.
#langblr#language#studyblr#linguistics#polyglot#i dont wanna be xiaomanyc#please believe me i wanna shock no natives#I just have so much free time
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sorry I'm going to attack some of you viciously at the moment:
One of the dangers of reblogging a meme poll by a linguistics doer to my blog followed by a bunch of people who think about twentieth century eastern european politics too much is that they'll answer what they think is the funny meme answer when actually it's a normie answered compared to the true meme shit and they are making themselves look normie. Like when when redditors larping as their own ww2 enthusiast dads talk about hitler's failed art career. WE KNOW. in fact we know secret things you haven't even heard about. obviously santa was nganasan.
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Crossposting from Twxttxr: some interesting news about ongoing research by colleagues, from a workshop "Diversification of Uralic" just this Thursday and Friday
Do the Permic languages have loanwords from Old Norse? e.g. ONo. ár ~ Komi & Udmurt ar 'year'. This would've been sensible during the brief time when Norsemen originally from Sweden were in charge of trade along the Volga and settling in inner Russia, forming the Rus' (later Slavicized, but as we know from Byzantine sources they remained Norse for centuries) — and also the Norwegians too were known to conduct exploration + trade along the Barents Sea at the time, our oldest written reports of "Bjarmia" come from them after all.
Do the Finnic languages have loanwords already from Pre-Proto-Germanic into Pre-Proto-Finnic? My first reply would've been "yes surely", this has been discussed for half a century and there's dozens of etymologies out by now. Turns out though that there's still a lot of room for skepticism if we try to assemble a big picture. Most of these could be (and have been proposed by other analyses) to be proper Germanic after all, or from some non-Germanic kind of Indo-European, or even incorrect. There is unambiguous evidence I think at least of loans lacking *ā > *ō, but that's already though to be one of the latest common Germanic innovations, perhaps barely post-PG. [Follow-up question: do we even know where Pre-Proto-Germanic was spoken? might not have been anywhere convenient for contacts with Pre-Proto-Finnic.] — A few similar problems also in the less discussed supposed layer of Proto-Balto-Slavic or pre-BSl. loans, but by areal considerations it seems obvious to me there must've been Uralic/IE contact somewhere in the Russian forest belt for ages already, even if it might not have left enough evidence to clearly distinguish from things like pre-Indo-Iranian loans.
Do the Samic languages have loanwords that are not from any historically attested branch of Scandinavian, but some sort of a lost variety entirely? This could be an explanation for an unexpected sound correspondence *j → *ć in many loans; it might also explain some loans that look surprizingly archaic, e.g. lacking any reflection of Siever's Law. One example showing both is indeed *Tāńćə 'Norse', from some sort of a *Danji- variant of Proto-Germanic *Daniz.
Several new hypotheses on the history of of sibilants in Ugric, adding to the growing tally of evidence that traditionally reconstructed *s > *θ and *ś > *s "in Proto-Ugric" are actually later developments. A paper supposed to be coming out soon!
No linguistic evidence so far, but a 1670 travelogue by de La Martinière appears to still report seemingly pre-Uralic populations along the Barents Sea coast — and even on Novaya Zemlya, traditionally thought to have been uninhabited (as reported by other early modern explorers) before some Tundra Nenets briefly settled there in mid 19th century. Apparently there's been no real archeological investigation, but also at least two stone labyrinths are known as signs that humans still must've at least visited there sometime in the past. [By current knowledge, labyrinths from Sweden and Finland have mostly been built in late medieval and early modern times though, so they don't suggest especial antiquity either. Could the ones on NZ in fact have been left behind by some of these historical Northwest European expeditions?]
Various discussion also on the development of Samoyedic. Nothing particularly all-new (maybe on Nganasan, more on that in a PhD thesis to appear later this year though), but a few main results include 1. clear recognition that there is no "North Samoyedic" group (as has been suspected for several years now), 2. confirmation that there is regardless a narrower Nenets–Enets group, and 3. some development of a model where all three of Nenets, Enets and Nganasan may have moved to the tundra zone independently from further down south (as is certainly the case for Northern Selkup, the most recent northern expansion of Samoyedic speakers).
#historical linguistics#loanwords#language contact#archeology#ethnohistory#uralic#finnic#samic#permic#samoyedic#germanic
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Russia, Explained: Siberian Indigenous Population Halves Amid Suicide Epidemic
By Aliide Naylor
April 8, 2021
A suicide epidemic is ravaging indigenous nations in Siberia.

A suicide epidemic is ravaging indigenous nations in Siberia. The Uralic Nganasan community in Siberia’s northern reaches is disappearing at a shocking rate – just three decades ago, there were some 1,300. Now, there are only around 700.
In the Nganasan settlement of Ust-Avam in Krasnoyarsk Krai, there are more suicides than natural deaths. “Six people die here every year. One of these deaths is the result of natural causes. Two or three freeze or die drunk. And two or three kill themselves,” writeNovaya Gazeta special correspondents Elena Kostyuchenko and Yuri Kozyrev after visiting the region.
The community is suffering the devastating effects of global warming, man-made environmental degradation, and severe poverty fuel depression. Out of 359 residents, just 54 have jobs.
“People crack, young people in general break down. The suicide rate is higher among young people. There is no work, nothing. Here you need to pay for lighting, and need to work for food. There is no food, no work, no money,” one young resident says. Her sister also committed suicide, leaving behind an 11-year-old son.
It’s often necessary to rely on anecdotal evidence about indigenous issues. Media reports are sparse and obtaining concrete statistical evidence about indigenous tribes such as the Nganasan is tough. And some deaths may be portrayed as suicides when there is little public information about the facts (for example, the death of one 15-year-old girl, in an uncomfortably termed “relationship” with a 24-year-old adult male police officer wasstyled in 2004 as a Romeo and Juliet story by local press).
The Nganasan are the descendants of semi-nomadic reindeer hunters, with ancient roots and a shamanistic spiritual culture. Even under Peter the Great (in the 17th and 18th centuries) there was a drive to “civilize” Russians in the further-flung regions and catch up with Europe, writes historian Yuri Slezkine. Peter instructed missionaries to find native Siberians and their “seductive false gods-idols and burn them with fire … and destroy their heathen temples”. Such ideas gained greater momentum in the 20th century, and the indigenous people were later forced into reservations under the Soviets in the 1930s. Nomadic civilizations were considered fundamentally incompatible with government-sanctioned lifestyles and these “small nations” of the North were seen as somehow representative of an undesirable past.
The Soviet state collectivized their personal property, including tents, guns and traps, and even reindeer herds. This led to a complete loss of reindeer husbandry and resulted in a steep decline in the reindeer population from the 1950s onwards.
Meanwhile, Soviet enforcement of Russian literacy made the local language almost extinct. Much like practices imposed on indigenous communities in other parts of the world, the Kremlin would take away local kids from their parents and send them to study in boarding schools.
“There, speaking Nganasan was forbidden, and teachers punished them for every Nganasan word they used — beaten with canes, kicked out of the class,” said local linguist Valentin Gusev. Today, Russia is home to 260,000 people from indigenous communities – who constitute just 0.2% of the country’s population. The government officially recognizes 40 separate indigenous groups in the North, Siberia, and the Far East.
The catastrophic impact of climate change in the Russian Arctic limits the Nganasan’s fishing opportunities — their primary food source. Meanwhile, the government continues to restrict hunting, which is a widespread source of tension between the Kremlin and indigenous communities elsewhere across Russia. With a de factoban on hunting, the Nganasans stopped following the routes of wild herds. Local food available for purchase can be out of date or moldy, and chronic alcohol use continues to plague the population.
Aggressive industrial development in the Russian Arctic has massively exacerbated the crisis among the Nganasan. Last year, a Norilsk Nickel (Nornickel) diesel spillbecame the largest human-made fuel spill in Arctic history, after which Russia’s government colludedwith the company (which is the nation’s largest nickel producer) to whitewash the disaster. The spill affected the environment that provided the Nganasan with basic food supplies. “They catch fish; they hunt deer. But there are no fish this year. And the deer left for other lands three years ago,” Kostyuchenko and Kozyrev wrote.
Last year, northern indigenous tribes signed an open letterto US business magnate Elon Musk and Tesla asking him not to purchase any nickel, copper, and other materials from Nornickel in the wake of the disaster. On average, the Norilsk Mining and Metallurgical Combine plant has released 30 tons of metallic dust and heavy metal oxides annually since it began production in the late 1930s, according toresearcher Konstantin B. Klokov.
There has been a recent spikemore generally in tensions between federal authorities and indigenous communities. Some of these nations have mobilized against an over-centralized state, government-backed environmental assaults on their sacred lands, and have demanded the return of their autonomy. In Kalmykia, for example, the majority-Buddhist region has engaged in protests against a Kremlin-appointed mayor. In Buryatia, locals rallied against a rigged election for weeks. And in a case that sent waves across Russia, a Sámi activist filed a complaint with Russia’s Supreme Court last year, after the government denied him the right to hunt without a license.
#indigenous#culture#indigenous russia#indigenous russian#russia#important#fypシ#colonization#fypage#landback#siberian indigenous#siberia#indigenous siberian#siberian#russian imperialism#russian genocide#russian colonization#land back#Nganasan#Uralic
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
I noticed an unsettling pattern within a discourse around "human nature", climate consciousness, and otherwise activism. This particularly is something to think about given that I'm Udmurt and Komi, and some other more northern tribes.
That pattern is - Indigenous peoples are the only standing counterexample to the ideas of inherent human cruelty, ecofascism, and the idea that humanity and nature are inherently incompatible.
While browsing tags surrounding misanthropy and the doomerism, or in general archaeological or anthropological stories, I noticed this recurring pattern of comments:
"Humanity is a plague, who would want to be one?"
"But what about indigenous peoples, please decolonize your mind".
Ummm... no. Why are the Indigenous peoples the only demographics whose existence is used in this manner as a counterargument? It feels as if the entire argument is based on the premise that Western thought treats Indigenous cultures as something "separate from civilization", so they can be used to contrast modern society without actually challenging how modern society itself should change. At the end of the day - it is not an actual counterargument to "human cruelty", just finding a convenient other who isn't corrupted by the civilization's compounded failures. And oh do we have a name for that term that was invented by Jean-Jacques Rousseau...
Let's pretend for a moment that ethnically nature-conscious peoples like Udmurt, or peoples with a very old heritage like Nganasan, didn't exist. What would be your policy for nature support advocacy? Carbon tax on breathing? Complete ban on any interaction with nature? Would you just accept "humans are a plague" without questioning it?
And besides, I too have my own reservations about human anthropology, and have my own opinions on how it isn't all "femur equals kindness equals humans are good". But I can't even engage with those meaningfully because my peoples' existence is supposed to be a proof of human kindness for those who "decolonize their anthropology".
#indigenous#trans#misanthropy#doomer#thoughts#climate catastrophe#arctic#siberian#noble savage#anthropology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
About my Siberia ocs...
So I think it's important to balance their characterisation in a way in which they are distinctive characters with interesting personalities and backstories but also acknowledges the challenges they face without making their entire character essentially "They're sad all the time because of Russia" or "Stop talking about their struggles under Russia I don't like politics."
I think both are problematic however I find the latter to be far more distasteful because well. This is a nation personification OC we're talking about and not only that, they're essentially nations within a nation (Russia) by virtue of colonisation and so are minority groups within the larger nation. Hell - because of displacement and immigration from European Russia , a lot of these groups are minorities within their own lands. It's a special case when dealing with minority groups/occupied people personifications and it's particularly egregious when someone wants to forgo any kind of acknowledgement of these power imbalances yet still insists that their interpretation is sensitive.
I've seen some pretty bad OCs of Siberian groups which are the product of the creator going "I hate politics stop talking about politics!" or, an almost direct quote, "I hate when people shove politics into historical hetalia." Which... Is an interesting take to say the least considering how history feeds into politics and vice versa. Historical hetalia is a beast in an of itself and is one of the only hetalia communities/bubbles in which "no politics" will get you laughed out the door from what I've seen considering *gestures to my previous statement*. If you've ever taken a history course - you'll know how much history and politics are intertwined.
This is how you get interps which consists of the likes of "Russia was wandering around the empty lands of Siberia" which not only blatantly disregards the brutality of the Russian colonisation of Siberia but also promotes the concept of "Terra Nullius" or "Virgin Land". I'm quoting myself from an even bigger post I have in store which focuses on anti Mongolian sentiment however stereotypes about Mongolians and Siberian groups often overlap because of their placement in Northern Asia, hence why it applies to both,
"In addition, to hone in on Mongolia being an "untouched, pristine" land - this is also a common trope that is launched towards traditionally nomadic "unsettled groups” (such as Siberian and Native American groups). The concept of "Terra Nullius", a Latin word meaning "nobody's land". It completely disregards the presence and rights of the people who inhabit the land and has been historically used to justify the colonisation and displacement of such groups - their land belonged to "nobody" so it was essentially up for grabs...It divorces the people from their landscape and paves the way for dangerous misconceptions and justifications to blossom.

Here is an example of "Terra Nullius" in action in a Russian propaganda poster, encouraging Russians to move to Kazakhstan."
Or interps such as "[Siberian group] has forgiven Russia for everything he did/most things he did and is in love with him" which implies that the mistreatment of the Siberian groups is merely something in the past when it is in fact ongoing. The mistreatment of Siberian groups such as the Sakha, Buryats, Chukchi and Tuvans has been all the more highlighted in their disproportionate mobilisation in the invasion of Ukraine - and the heaps of scapegoating that was subsequently shovelled onto them.
That's not to say ethnic minority soldiers in the Russian army shouldn't be held accountable for their crimes - however that and the fact that they themselves are victims of Russian imperialism can both exist as true statements. The scapegoating is so bad that even Pope Francis joined in, blaming the brunt of the war crimes committed onto "Non Russians" such as Buryats and Chechens, as they do not come from "Russian culture."
Back to my main point... I think the resistance to do research on and publicly acknowledge how these groups live under Russia and what kind of struggles they face in some kind of bid to "not paint them as victims!!11" is sorely misinformed and ignorant. Because well. They are victims.
Not in the sense that you should portray them as sad, pitiful, weak little meow meows but in the sense that yes they are living under Russian occupation and are an occupied people who's been subjected to centuries of Russification, and so compared to making an OC of Mongolia who is an independent nation state at least I think there is far less room to be hauling around "leave politics out of historical hetalia!" "don't talk to me about politics!" "stop victimising them!!" because then it leads to tone deaf interpretations such as "They've forgiven Russia for everything and is in love with him ♥️💖", "Russia is actually [Siberia groups] father", "Here is my singular Siberia OC who represents ALL Siberian groups and by the way Russia is their father" (yes these are all real interpretations I've seen and I've made a separate really strongly worded post ranting about it) and worse. I mean I've literally seen an "aph Siberia oc" who was Russia and France's love child. Terra Nullius executed Hetalia-style.
I don't really think I need to elaborate on why a singular Siberia OC is problematic - Siberia is filled with a myriad of different groups who speak different languages, have different origins and ways of lives and practices, different religions, who've experienced eras of peace and conflict with each other, etc and yeah to shove them all into one personification is an erasure of the sheer diversity that is in Siberia. I definitely don't need to elaborate on why making Russia a father to any of these groups is problematic, to say very the least.
On the point of "don't only portray them in a victimising lense", I think making Siberian groups all depressed all the time is also a Russia-centric perspective. Of course it's ignorant at best to not acknowledge their shared suffering because of Russia however when this point and this point alone is central to their character I believe in a way that it strips them of their autonomy and ability to feel things and do things outside of Russia's gaze. There is absolutely a lot of joy to be had despite their current situation, perhaps even in spite of their current situation. It's ok to give them odd quirks and put them in funny situations as well as acknowledge that they are an occupied people and approach that territory carefully when need be.
For example, I made my Buryatia bubbly and loud but made my Tuva a bit more deadpan because I see them as a pair who often associate with each other and I think the dynamic is funny. I also made Buryatia an overbearing "husband" to Soyot who is perpetually tired™ from all the se- .
I made a crack dynamic between Sakha, Evenkia and Dolgan where Evenkia was Sakha's teacher at first but then became a deadbeat dad leaving Sakha to primarily raise Dolgan, thus Dolgan takes after Sakha and is uh lawyermaxxing👍. Yukaghir is the little old lady of the group who is often forgetful but very nifty and Chukotka acts like a big sister to people which Koryak (who I see as her brother) always finds annoying and they often bicker. Ket is on the slightly edgy side and is extremely particular about his routines and Nganasan terrifies Nenet because he eats reindeer whereas Nenet doesn't.
All of these quirks/ more lighthearted interpretations and "they are an occupied people under Russia" can coexist. One should not be thrown out for the sake of the other.
I think there's also problem - though I've seen this far less, in making Siberia ocs purely as a middle finger at Russia. As in, you made the OC because you wanted to say loud and proud FUCK RUSSIA which well yeah, fuck Russia, but I highly doubt your interest in this group lies outside of wanting to #own the Russians which is dehumanising in and of itself. At least pretend to care about the history and culture instead of using an entire group of people to make a virtue-signally oc purely to try and upset some Russians.
Anyways yeah Siberia 👍
#hetalia#hetalia world stars#hetalia world series#hetalia world twinkle#Aph Siberia#Hetalia Siberia#Hws Siberia#Hws Sakha#Aph Sakha#Aph Buryatia#Hws Buryatia#Hws Tuva#Aph Tuva#Aph Soyot#Hws Soyot#Hws Evenk#Aph Evenk#Hws Dolgan#Aph Dolgan#Aph Yukaghir#Hws Yukaghir#Aph Chukotka#Hws Chukotka#Hetalia Chukotka#Aph Koryak#Hws Koryak#Aph Ket#Hws Ket#Hws nganasan#Hws Nenet
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Starshine is somewhere among Mongolian, Nganasan, Saami, Yakut, Buryat, Yupik, & Inuit. Avoiding outright using mine irl ethnic own ties, but related groups. So hard to choose which tho.
#distant cousin vibes#yuurivoice star#yuurivoice faust#yuurivoice oc#either from both sides of the Atlantic#or both sides of the Pacific
12 notes
·
View notes
Text


Demjaku, grandson of Demnime Kosterkin (1926–1980) who was perhaps the last Nganasan shaman who held traditional way of living in tundra.
5 notes
·
View notes