#MESOTHELIOMA CT SCAN
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Link
0 notes
Text
Advanced Thoracic Surgery in Dubai: Meet the Top Surgeons

Thoracic surgery is a critical medical specialty focusing on procedures involving the organs of the chest, including the heart, lungs, and esophagus. It plays a vital role in diagnosing and treating conditions such as heart disease, lung cancer, and esophageal disorders. Dubai, a global leader in healthcare, offers cutting-edge thoracic surgical services at some of the most advanced facilities in the world. At the forefront of this field is Dubai Heart, a leading name in cardiology and thoracic care.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the advancements in thoracic surgery available in Dubai, introduce you to the best heart specialist in Dubai, and highlight why Dubai is home to some of the best cardiology hospitals and clinics in the region.
Why Dubai is a Global Hub for Advanced Thoracic Surgery
1. World-Class Medical Expertise
Dubai attracts some of the most highly trained and experienced surgeons in the field of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. These specialists often bring expertise from leading global institutions, offering patients the highest standards of care.
2. State-of-the-Art Facilities
The city’s healthcare infrastructure is equipped with cutting-edge diagnostic tools and surgical technologies, enabling minimally invasive procedures, robotic-assisted surgeries, and advanced imaging techniques.
3. Comprehensive Care
From diagnosis to post-surgery rehabilitation, Dubai’s healthcare providers offer a seamless continuum of care, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients.
4. Accessibility and Diversity
With its strategic location and multicultural environment, Dubai is easily accessible to patients from around the world, offering medical services in multiple languages and culturally sensitive care.
Conditions Treated by Thoracic Surgery
Thoracic surgery addresses a wide range of conditions, many of which require specialized care. Some of the most common include:
1. Heart Conditions
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Heart valve disorders
Congenital heart defects
Aortic aneurysms and dissections
2. Lung Diseases
Lung cancer
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Pulmonary embolism
Pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
3. Esophageal Disorders
Esophageal cancer
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Achalasia (difficulty swallowing)
4. Mediastinal Conditions
Tumors in the mediastinum (the area between the lungs)
Thymomas and thymic cancers
5. Chest Wall and Pleural Disorders
Pectus excavatum (sunken chest)
Pleural effusion (fluid in the chest cavity)
Mesothelioma
Advanced Thoracic Surgical Techniques in Dubai
The evolution of thoracic surgery has been marked by significant advancements, many of which are now available in Dubai’s leading hospitals and clinics.
1. Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive techniques, such as video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and robotic-assisted thoracic surgery (RATS), have transformed patient outcomes by reducing recovery times, minimizing pain, and lowering the risk of complications.
2. Robotic-Assisted Surgery
Robotic systems allow surgeons to perform complex procedures with unparalleled precision. These technologies are particularly beneficial for delicate operations such as valve repairs and tumor resections.
3. Transcatheter Procedures
For heart conditions, transcatheter techniques like TAVI (transcatheter aortic valve implantation) offer minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open-heart surgery.
4. 3D Imaging and Planning
Advanced imaging technologies, such as 3D CT scans and MRIs, allow surgeons to visualize the surgical site in detail and plan procedures with precision.
5. Enhanced Recovery Programs
Post-surgery recovery programs are designed to optimize outcomes by focusing on early mobilization, nutrition, and physical therapy.
Dubai Heart: A Leader in Thoracic Surgery
Dubai Heart stands out as one of the most trusted names in thoracic and cardiac care. Here’s why it’s a top choice for patients seeking advanced treatment:
1. Expert Surgeons
Dubai Heart is home to the best heart specialists in Dubai, who are renowned for their expertise in thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. These specialists are dedicated to delivering personalized, high-quality care.
2. Cutting-Edge Technology
The hospital is equipped with the latest surgical and diagnostic tools, including robotic systems and advanced imaging technologies, ensuring precise and effective treatments.
3. Comprehensive Services
From preventive care to complex surgeries and rehabilitation, Dubai Heart offers a full spectrum of cardiology and thoracic services under one roof.
4. Patient-Centered Care
Dubai Heart emphasizes a patient-first approach, tailoring treatment plans to individual needs and ensuring compassionate, culturally sensitive care.
5. High Success Rates
With a strong track record of successful outcomes, Dubai Heart has earned its reputation as one of the best cardiology hospitals in Dubai.
Success Stories at Dubai Heart
The success of Dubai Heart can be seen in the lives it has transformed. Here are a few inspiring stories:
Case 1: Minimally Invasive Valve Repair
A 62-year-old man with severe mitral valve regurgitation underwent a robotic-assisted valve repair at Dubai Heart. Thanks to the minimally invasive approach, he experienced a quick recovery and was able to return to his normal activities within weeks.
Case 2: Life-Saving Lung Cancer Surgery
A 55-year-old woman with early-stage lung cancer underwent a video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy. The procedure was successful, and she has remained cancer-free since her surgery.
Case 3: Complex Congenital Heart Defect Repair
A 10-year-old boy born with a congenital heart defect received life-changing surgery at Dubai Heart. The multidisciplinary team collaborated to perform a complex repair, allowing him to lead a healthy, active life.
Choosing the Best Thoracic Surgeon in Dubai
Selecting the right surgeon and facility is crucial for successful outcomes. Here are some factors to consider:
1. Expertise and Credentials
Look for board-certified thoracic surgeons with extensive experience in treating your specific condition.
2. Technology and Facilities
Ensure the hospital is equipped with advanced surgical tools and diagnostic systems.
3. Comprehensive Care
Choose a facility that offers integrated services, from diagnosis to post-operative rehabilitation.
4. Patient Reviews and Success Rates
Research testimonials and outcomes to gauge the quality of care provided.
5. Personalized Approach
The best surgeons and clinics, like those at Dubai Heart, tailor treatment plans to each patient’s unique needs.
Tips for Maintaining Thoracic Health
While advanced surgery is invaluable for treating certain conditions, prevention and early intervention are key to maintaining thoracic health. Here are some tips:
Quit Smoking Smoking is a major risk factor for lung and heart diseases. Quitting can significantly improve your health.
Stay Active Regular physical activity strengthens the heart and lungs, reducing the risk of chronic conditions.
Eat a Healthy Diet Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall health.
Monitor Your Health Regular check-ups and screenings can help detect conditions early, improving treatment outcomes.
Manage Stress Chronic stress can negatively impact heart health. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
Vaccinate Certain vaccines, like those for influenza and pneumonia, can prevent respiratory infections that may lead to complications.
Why Dubai Heart is the Best Choice
When it comes to advanced thoracic surgery, Dubai Heart is a leader in the field. With a team of highly skilled specialists, state-of-the-art facilities, and a commitment to excellence, Dubai Heart provides unmatched care for patients. Whether you’re dealing with a complex heart condition, lung disease, or another thoracic issue, Dubai Heart offers the expertise and technology needed to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Conclusion
Thoracic surgery is a life-changing field of medicine, and Dubai is at the forefront of innovation and excellence in this specialty. From minimally invasive techniques to compassionate care, Dubai’s hospitals and clinics offer everything you need for optimal thoracic health.
At the heart of this excellence is Dubai Heart, where patients receive world-class care from the best heart specialists in Dubai. With its advanced technology, skilled surgeons, and patient-first approach, Dubai Heart is your trusted partner for thoracic and cardiovascular health.
Take the first step toward better health today by scheduling a consultation at Dubai Heart, one of the best cardiology hospitals in Dubai. Your heart and lungs deserve the best care, and Dubai Heart is here to provide it.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Long Does It Take to Develop Mesothelioma in 2024? | Discover the Reason
Introduction Mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive cancer primarily caused by asbestos exposure. One of the key challenges with this disease is its long latency period, meaning that it often takes decades to develop symptoms after initial exposure. Understanding the timeline for mesothelioma development is crucial for those who have been exposed to asbestos and want to monitor their health closely. This article delves into the latency period of mesothelioma, factors influencing its onset, and early warning signs.
Contact Us Now For a Free Consultation
1. What Is the Latency Period for Mesothelioma? The latency period is the time between initial asbestos exposure and the onset of symptoms.
Typical range: 20-50 years, with some cases appearing earlier or later.
Why it varies: Factors like the amount of asbestos exposure and individual health can influence the latency period.
2. How Does Asbestos Exposure Lead to Mesothelioma? Inhaled or ingested asbestos fibers can lodge in the body's tissues, causing inflammation and scarring over time.
Long-term damage: Persistent irritation can lead to genetic mutations.
Cancerous development: These mutations may eventually cause mesothelial cells to become cancerous.
3. What Factors Influence the Time It Takes for Mesothelioma to Develop? Several factors can impact how quickly mesothelioma manifests after exposure.
Extent of exposure: Higher levels of asbestos exposure can lead to shorter latency periods.
Duration of exposure: Prolonged exposure may also result in earlier onset.
Age at exposure: Younger individuals may experience longer latency periods as the body takes longer to exhibit symptoms.
4. Can Early Detection Shorten the Latency Period? Early detection does not affect the latency period but can improve treatment outcomes.
Importance of regular screening: Individuals with known asbestos exposure should undergo regular health check-ups.
Diagnostic methods: Imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans can help detect early signs of mesothelioma.
5. What Are the Early Signs of Mesothelioma to Watch For? Recognizing symptoms early can be challenging due to their general nature.
Pleural mesothelioma: Chest pain, shortness of breath, persistent cough.
Peritoneal mesothelioma: Abdominal swelling, pain, and weight loss.
Pericardial mesothelioma: Heart palpitations, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
6. Why Does Mesothelioma Take So Long to Appear? The long development time of mesothelioma is linked to how asbestos fibers interact with the body.
Gradual damage: Asbestos causes slow and steady damage to mesothelial cells.
Delayed mutation: It takes years for cellular damage to accumulate and transform into cancer.
Conclusion Mesothelioma's lengthy latency period makes it challenging to diagnose early, often resulting in detection at advanced stages. For individuals with a history of asbestos exposure, understanding the timeline of mesothelioma development and seeking regular medical evaluations is essential for early intervention and better management of the disease.
FAQs
Can mesothelioma appear sooner than 20 years after exposure? Yes, though rare, some cases of mesothelioma can develop within 10-15 years of exposure.
How can I know if I am at risk of developing mesothelioma? If you have a history of asbestos exposure, especially in certain occupations, you are at risk and should monitor for symptoms.
Does everyone exposed to asbestos get mesothelioma? No, not everyone exposed will develop mesothelioma; genetics and exposure levels play a role.
Can mesothelioma develop after a single exposure to asbestos? While less common, a single, high-level exposure can still result in mesothelioma.
Are there any tests to determine if asbestos exposure has affected me? Imaging tests like CT scans and pulmonary function tests can help assess lung health after asbestos exposure.
What should I do if I was exposed to asbestos many years ago? Seek regular medical check-ups, inform your doctor about the exposure, and monitor any changes in your respiratory health.
#asbestos in mesothelioma#reason of mesothelioma cancer#mesothelioma reasons#mesothelioma#scientific trials expenses | mesothelioma | respirework#mesothelioma causes#second hand mesothelioma#pericardial mesothelioma#mesothelioma due to asbestos asbestos exposure in mesothelioma | mesothelioma | respirework#mesothelioma lawyer#mesothelioma clinic trials#mesothelioma attorney#how to find a mesothelioma clinical trial | mesothelioma | respirework#mesothelioma lawsuit
0 notes
Text
How to Improve Mesothelioma Survival Rates: Latest Advances in Treatment

Mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive cancer primarily caused by asbestos exposure, has long presented significant challenges in treatment and management. The prognosis for mesothelioma patients has historically been poor, with survival rates remaining low due to the disease's late-stage diagnosis and rapid progression. However, recent advances in medical research and treatment options are providing new hope for improving mesothelioma survival rates. This blog explores the latest developments in mesothelioma treatment and how they contribute to better survival outcomes.
Understanding Mesothelioma Survival Rates
Mesothelioma Survival Rate refers to the percentage of patients who survive for a specific period after diagnosis, commonly measured at one, three, and five years. Survival rates can vary based on several factors, including the stage at diagnosis, the patient's overall health, age, and the specific type of mesothelioma (pleural, peritoneal, pericardial, or testicular).
Historically, the overall five-year survival rate for mesothelioma has been around 10%. However, advancements in treatment strategies are starting to shift these statistics positively.
Early Detection and Diagnosis
One of the most significant factors in improving mesothelioma survival rate is early detection. Traditional diagnostic methods often catch mesothelioma in its later stages when treatment options are limited, and the prognosis is poor. Recent developments in imaging techniques and biomarker research are enhancing early detection capabilities.
Advanced Imaging Technologies: High-resolution CT scans, MRI, and PET scans provide more precise imaging, enabling earlier and more accurate diagnosis of mesothelioma. These technologies help identify the presence and extent of tumors at an earlier stage, allowing for more effective intervention.
Biomarker Research: Identifying specific biomarkers in blood or tissue samples can signal the presence of mesothelioma before symptoms become apparent. Researchers are making significant strides in this area, developing blood tests that can detect mesothelioma at an earlier stage.
Innovative Treatment Approaches
Once mesothelioma is diagnosed, the focus shifts to treatment. Traditional treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, but their effectiveness is often limited, especially in advanced stages. The latest advances in mesothelioma treatment are showing promise in improving survival rates.
Surgical Advancements: Surgery remains a cornerstone of mesothelioma treatment, especially for patients diagnosed at an early stage. Advances in surgical techniques and postoperative care are improving outcomes and reducing recovery times.
Extrapleural Pneumonectomy (EPP): This aggressive surgery involves removing the affected lung, parts of the diaphragm, the lining of the heart, and nearby lymph nodes. New techniques and better perioperative care are enhancing survival rates for patients undergoing EPP.
Pleurectomy with Decortication (P/D): This less invasive surgery removes the tumor and affected pleura while sparing the lung. It is associated with fewer complications and a quicker recovery, contributing to improved survival rates.
Chemotherapy Innovations: Chemotherapy is a standard treatment for mesothelioma, often used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy. Recent advances in chemotherapy drugs and delivery methods are enhancing their effectiveness.
Alimta (Pemetrexed) and Cisplatin: This combination remains the standard chemotherapy regimen for mesothelioma. Newer studies are focusing on optimizing dosages and combinations with other drugs to improve outcomes.
Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapies, such as bevacizumab (Avastin), are designed to attack specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These therapies are showing promise in improving survival rates for mesothelioma patients.
Radiation Therapy: Advances in radiation technology allow for more precise targeting of tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. This precision reduces side effects and enhances the effectiveness of radiation therapy.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): IMRT allows for highly precise delivery of radiation, targeting mesothelioma tumors more effectively and improving survival rates.
Immunotherapy: A Game Changer
Immunotherapy is emerging as one of the most promising advancements in mesothelioma treatment. By harnessing the body's immune system to fight cancer cells, immunotherapy offers a new avenue for improving mesothelioma survival rates.
Checkpoint Inhibitors: Drugs like pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo) block proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking cancer cells. Clinical trials have shown these drugs can extend survival in mesothelioma patients.
CAR T-Cell Therapy: This cutting-edge treatment involves modifying a patient's T-cells to recognize and attack mesothelioma cells. Early studies are showing promising results, with some patients experiencing significant tumor reduction.
Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs): TIL therapy involves harvesting and expanding immune cells from the tumor itself, then reintroducing them to the patient to boost the immune response against cancer. This approach is showing potential in clinical trials.
Personalized Medicine and Genetic Research
Personalized medicine tailors treatment to the individual patient's genetic profile and the specific characteristics of their cancer. This approach is gaining traction in mesothelioma treatment, offering the potential to significantly improve survival rates.
Genetic Profiling: Understanding the genetic mutations driving a patient's mesothelioma allows for more targeted and effective treatment. Genetic profiling can identify patients who are likely to respond to specific therapies, optimizing treatment outcomes.
Precision Medicine: Combining genetic information with advanced treatment options, precision medicine aims to provide the most effective therapy for each patient. This approach is enhancing survival rates by ensuring patients receive the treatments most likely to benefit them.
Supportive Care and Quality of Life
Improving mesothelioma survival rates also involves addressing the overall well-being of patients. Supportive care and palliative treatments play a crucial role in managing symptoms, reducing treatment side effects, and enhancing quality of life.
Pain Management: Effective pain management strategies, including medications, physical therapy, and complementary therapies, help patients maintain a better quality of life during treatment.
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition is vital for patients undergoing treatment for mesothelioma. Nutritional support can help manage side effects, maintain strength, and improve overall outcomes.
Psychological Support: Coping with a mesothelioma diagnosis can be emotionally challenging. Psychological support, including counseling and support groups, helps patients and their families navigate the emotional aspects of the disease.
Conclusion
The journey to improving mesothelioma survival rates is complex and multifaceted, involving advancements in early detection, innovative treatment approaches, and comprehensive supportive care. While mesothelioma remains a challenging cancer to treat, the latest developments in medical research are providing new hope for patients and their families. By staying informed about the latest advances and advocating for personalized and comprehensive care, mesothelioma patients can improve their chances of better outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
0 notes
Text
Pericardial Mesothelioma (Research-1)
Pericardial Mesothelioma (Research-1) Here is an overview of the latest research and developments in understanding and treating pericardial mesothelioma: Diagnosis Diagnosing pericardial mesothelioma is challenging due to its rarity and non-specific symptoms, which often resemble other cardiac conditions. Advances in diagnostic techniques include: Imaging Tests: Echocardiograms, CT scans, and…
0 notes
Text
What is cytoreductive surgery (CRS)?

Cytoreductive surgery (CRS), also known as debulking surgery, is a surgical procedure used in the treatment of certain advanced cancers, particularly cancers that have spread within the abdominal cavity. The primary goal of cytoreductive surgery is to remove as much visible tumor or cancerous tissue as possible from the abdominal area. This procedure is often used in combination with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), to improve treatment outcomes.
Here's how cytoreductive surgery works:
Assessment: Before the surgery, the surgeon evaluates the extent of cancer spread within the abdominal cavity. Imaging studies like CT scans or MRIs are typically used to identify and measure tumors.
Surgery: During the procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen to access the cancerous areas. They then carefully remove visible tumors or cancer nodules from the peritoneal lining and the affected abdominal organs.
Resection: Depending on the location and extent of cancer, the surgeon may remove part or all of affected organs (e.g., portions of the colon, stomach, or other abdominal structures) if necessary to achieve optimal tumor removal.
HIPEC: In some cases, after tumor removal, the surgeon may administer heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) directly into the abdominal cavity. This is done to target any remaining cancer cells that may not be visible and to destroy them.
Closure: Once the surgery and any additional treatments are completed, the surgeon closes the incision, and the patient is taken to the recovery room.
Cytoreductive surgery is commonly used in the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer, abdominal mesothelioma, and certain cases of colorectal and gastric cancers that have spread to the peritoneum (lining of the abdomen). The goal of CRS is to reduce the tumor burden within the abdomen, alleviate symptoms, and potentially improve the effectiveness of subsequent treatments like chemotherapy.
Cytoreductive surgery is a complex procedure that requires a skilled surgical team experienced in treating abdominal cancers. Patients are carefully selected for this procedure based on their individual cancer type, stage, overall health, and the potential benefits of surgery. It is typically performed in specialized medical centers by surgeons who have expertise in the management of peritoneal surface malignancies.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed disease, consult Dr. Chintamani Godbole one of the best Gastroenterologist in Mumbai.
0 notes
Text
Cash For Retired Railroad Workers With Asbestosis

If you were employed by a railroad company before 1982, there is a high chance that you were exposed to asbestos during your time in the industry. Asbestos was commonly used in various products, ranging from brake shoes to ashtrays given to passengers on trains. This means that even if you worked in the locomotive, you were at risk of inhaling and ingesting microscopic asbestos fibers. These fibers are so tiny that they cannot be seen in the air, and once they enter your body, they can become lodged permanently. This can lead to serious health issues, including genetic mutations and scarring. The manufacturers of asbestos-containing products, including brake pads, were aware of the dangers associated with this toxic material, but they chose not to inform the public. Instead, they prioritized their profits over the well-being of hardworking Americans. At Sammons & Berry, P.C., we are committed to helping retired railroad employees who have developed diseases such as asbestosis, cancer, and mesothelioma. Various types of cancer have been linked to asbestos exposure, including lung cancer, throat cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and colon cancer. If you are a retired railroad worker who has been diagnosed with any of these asbestos-related diseases, our team is here to assist you. We will work with you to determine if you qualify for compensation and ensure that you receive your fair share of the $30 billion dollars held in asbestos trust funds, which are specifically set aside to compensate those whose health has been impacted by asbestos. Call us today to start the process of filing for an asbestos trust fund in order to get the compensation you deserve. Our team of experts are waiting for your call.
What Causes Asbestosis?
Exposure to high levels of asbestos fibers is what causes asbestosis to develop. The airborne fibers and dust can become trapped in the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lung at the end of the airways), where they irritate and scar the lung tissue. Since asbestosis is a progressive disease (meaning it gets worse over time), symptoms may not develop for up to 20 years after exposure. By this time the asbestos has significantly scarred the lung tissue, making it stiff and unable to expand normally. Smoking can increase the amount of damage done by asbestos and speed up the progression of the disease.
What Are the Symptoms of Asbestosis?
The effects of long-term exposure to asbestos typically don't show up for 10 to 40 years after initial exposure. The most common symptoms are: Shortness of breath Persistent dry cough Chest tightness or chest pain Weight loss from loss of appetite A dry, crackling sound in the lungs while breathing in Wider and rounder than normal fingertips and toes (clubbing)
How Is Asbestosis Diagnosed?
Asbestosis is usually diagnosed by a careful medical history, exposure history and chest X-ray or CT scan that shows scarring of the lung tissues. This information, along with breathing tests, helps your doctor determine how severe your asbestosis is and how well your lung is functioning. If you have a history of exposure to asbestos and you're experiencing increasing shortness of breath, you should contact your primary care doctor about the possibility of asbestosis. He or she likely will refer you to a doctor specializing in lung problems (pulmonologist). During the visit, your doctor will ask about your breathing, both at rest and during exercise. Your doctor will also ask about your job history in detail to determine how much you were exposed to asbestos. So, it would be a good idea to prepare the following information in advance: Your symptoms and the time they started Treatments given before for the symptoms and how they helped The work you have done over your entire career; the length of time you spent in each job; the nature of the work you performed. The products you were in contact with at work and whether or not you wore protective equipment Smoking history Any old medical records, including chest X-rays or CT scans During the physical examination, your doctor will listen to your lungs to determine if the sounds are normal or not. Your doctor may then order the following tests: Chest X-ray CT scan Lung function test
Free Asbestos Exposure Consultation in United States
At Sammons & Berry, P.C. we offer a no-cost, no-obligation consultation, so you can discuss the facts of your case without paying for anything upfront. Asbestos trusts claims do not require a lawsuit, depositions, or courtrooms. The process is simple and easy for the client and should not require any stressful legal confrontations for the client. The law firm handles all of the claims for the client, helping you maximize your compensation. We do not accept any payments from our clients until they receive compensation. We charge on a contingent fee basis, which means you pay a percentage of what you get paid in your claim. If we are unable to collect anything for you, there is no cost to you. Call (800) 519-1440 to speak with a Sammons and Berry, P.C. representative and start your journey towards compensation.
Wrongful Death Claims For Families of Asbestos Victims
If you have lost someone in your family due to the harmful exposure of asbestos, you may be entitled to compensation. If you can provide the work history and a death certificate for your loved one, our attorneys can help you file an asbestos claim. We understand how difficult this process can be, this is why we work with you every step of the way to help you get the money you deserve. Reach out to our team today to learn more about filing a claim for a family member. Sammons & Berry, P.C. 800-519-1440 View our Google Listing View our Facebook Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Reviewing questions:
Mesothelial cells are cells that line body cavities (including the peritoneum and pericardium, not just the pleura).
Mesothelial cells form a monolayer of specialised pavement-like cells that line the body's serous cavities and internal organs. The primary function of this layer, termed the mesothelium, is to provide a slippery, non-adhesive and protective surface. However, mesothelial cells play other pivotal roles involving transport of fluid and cells across the serosal cavities, antigen presentation, inflammation and tissue repair, coagulation and fibrinolysis and tumour cell adhesion. Injury to the mesothelium triggers events leading to the migration of mesothelial cells from the edge of the lesion towards the wound centre and desquamation of cells into the serosal fluid which attach and incorporate into the regenerating mesothelium. If healing is impaired, fibrous serosal adhesions form between organs and the body wall which impede vital intrathoracic and abdominal movement. Neoplastic transformation of mesothelial cells gives rise to malignant mesothelioma, an aggressive tumour predominantly of the pleura. Although closely associated with exposure to asbestos, recent studies have implicated other factors including simian virus 40 (SV40) in its pathogenesis.
Anyway, mesothelioma is cancer of the pleura associated with asbestos exposure. It can present with dyspnea, chest pain, cough, and hemorrhagic pleural effusion. If you look at the histology, there will be tumor cells with long microvilli and tonofilaments. CT scan will show pleural plaques.
CREST syndrome = Calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon (vasospasm of fingers in response to cold), Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly (localized thickening and tightness of the skin of the fingers or toes), Telangiectasias (small dilated blood vessels that can occur near the surface of the skin or mucous membranes; spider veins). CREST syndrome is the limited cutaneous form of systemic sclerosis. Sysemic sclerosis can lead to pulmonary arterial hypertension due to remodeling of pulmonary arteries and arterioles. Activated T cells secrete TGF-beta, which causes fibroblast proliferation-> excess collagen deposition. There is also excess endothelin (vasoconstrictive) and TXA2 (enhances proliferation)-> vasoconstriction.
I didn't know fluid could go through the diaphragm. There are fenestrations in the diaphragm through which fluid from ascites can travel, causing pleural effusion. Specifically, the ascites in a pt with cirrhosis can cause hepatic hydrothorax, which is a transudative pleural effusion. The pleural effusion is usually on the right side. I don't think I've ever heard of hepatic hydrothorax.
Endothelin causes vasoconstriction. Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) causes proliferation of vascular smooth muscle. Nitric oxide causes vasodilation. Prostacyclin prevents proliferation of vascular smooth muscle. In Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), there's increased endothelin and TXA2 and decreased NO and prostacyclin. This causes constriction of the pulmonary arterioles and arteries and proliferation of the vascular smooth muscle, which causes intimal thickening and thus a decreased lumen of the arterioles/arteries-> increased resistance-> loud P2 (pulmonic component of the S2 heart sound) due to increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, so when the valve closes, it closes forcefully. Endothelin comes from the endothelial cells, binds to the endothelin-1 receptor on vascular smooth muscle cells, and leads to vasoconstriction and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Endothelin-1 receptor antagonists (e.g. bosentan) prevent this. NO comes from L-arginine in the endothelium, enters vascular smooth muscle cells, increases cGMP-> vasodilation and decreased proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil) and nitrates (nitroglycerin) also work the same way (i.e., they increase cGMP-> vasodilation). Arachidonic acid from the endothelium becomes prostacyclin (aka prostaglandin I2), which increases cAMP in the vascular smooth muscle cells-> vasodilation and decreased proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Prostacyclin analogs (epoprostanol) work the same way.
CHF-> pleural effusion because there's more blood in the heart, which isn't pumping well-> increased hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary vasculature. Glucose in the pleural fluid will be decreased in pts with exudative pleural effusions. WBCs metabolize glucose; more inflammation means more WBCs and thus more glucose is being used up by the WBCs, so the glucose in the pleural fluid will be low. In transudative pleural effusions, there is no inflammation, so the glucose of the pleural fluid will be normal or high. The nucleated cell count of the pleural fluid will be low in a transudative pleural effusion (I'm assuming that's because there aren't a bunch of WBCs in the pleural fluid if it's transudative as compared to exudative, which would have more WBCs [nucleated cells] in the pleural fluid).
Carotid body chemoreceptors transmit information via the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) to the medulla. Aortic arch baroreceptors and aortic body chemoreceptors transmit information via the vagus nerve (CN X) to the medulla. I need to think of a way to remember this: carotid body->CN IX-> medulla and aortic arch-> CN X-> medulla. I thought of a mnemonic: a perfect 10 (X) is like an A, so Aortic chemoreceptors transmit through CN X.
In normal pts, PaCO2 increases trigger increased respiratory rate. In COPD, the respiratory drive is driven by PaO2 instead of PCO2 because chronic retention of CO2 blunts the normal respiratory drive, which is driven by PaCO2. So I guess basically, if you always have high PaCO2, then the chemoreceptors don't pay as much attention to CO2; instead, they rely on low PO2 to cause enhanced respiration. Low O2 (hypoxemia) increases respiratory rate in pts with COPD. This is why giving too much O2 in these pts actually decreases their respiratory drive--you made it so there's high O2 instead of their normal baseline low O2. If the chemoreceptors sense high O2, then they think they don't have to trigger respiratory drive anymore, so the pt will breathe less and actually start retaining even more CO2 than normal. Peripheral chemoreceptors sense PaO2. The carotid and aortic bodies sense PaO2; they respond to low levels of O2 in blood. So if you increase O2 by giving supplemental O2, you prevent those peripheral chemoreceptors from responding. So ironically, COPD pts get oxygen-induced hypercapnia after you give them oxygen--they have high PCO2 if you give them roo much oxygen. But that's not the main mechanism that causes oxgen-induced hypercapnea in these pts--what mostly causes increased PCO2 after O2 administration in these pts is the fact that you've undone the hypoxic vasoconstriction when you give too much O2, therefore blood starts going to less-well ventilated alveoli, so you essentially increased their dead space. This means more blood is flowing to areas without ventilation, so they can't get rid of as much CO2 as they normally can-> hypercapnea.
In the anesthesia meeting this morning, they were talking about a pt who had high PCO2 (65+ mmHg) and who was thus kept intubated after surgery. When they looked at his bicarbonate, they saw that it was high (30 mEq/L) at baseline. That means his body is compensating for long-term CO2 retention. So he normally probably has a high PCO2 and thus his PCO2 (while it would be considered high for a normal person) was probably not high for him specifically. So he probably didn't need to be kept intubated. He already lives at a high PCO2. It's like what I learned in my last rotation about OHS/sleep apnea.
So oxygen doesn't normally regulate respiratory drive, CO2 does. Only when PO2 is less than ~65 mmHg do the peripheral chemoreceptors start responding to oxygen as their stimulus for regulating respiration. In pts with COPD, their chemoreceptors stop responding to PCO2. COPD pts can also be hypoxemic with PO2 less than 65 mmHg. So their chemoreceptors start relying on low PO2 to increase respiratory drive. The peripheral chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic bodies respond to low PO2 to cause increased respiratory drive. Ironically, giving more O2 in pts with COPD causes even more CO2 retention than normal because the increased oxygen level decreases their respiratory drive. So they get O2 and they start breathing less. But apparently, that's not the major mechanism of oxygen-induced hypercapnia. The major mechanism of oxygen-induced hypercapnia is increased V/Q mismatch. If you give too much O2, the poorly ventilated areas vasodilate, leading to more blood flowing to areas that are not well-ventilated. That's what this question explanation says, but I'm confused. I'm not getting what causes the vasodilation. I guess giving O2 makes the less well ventilated areas better ventilated, but they are still not as well ventilated as the areas that at baseline were already better ventilated. So now blood is going away from the alveoli that were already better ventilated to areas that aren't as well ventilated even after you gave O2. It says this causes increased physiologic dead space, so increased V/Q mismatch.
#mesothelioma#asbestos#CREST syndrome#PAH#pleural effusion#hepatic hydrothorax#prostacyclin#TXA2#thromboxane#nitric oxide#oxygen induced hypercapnea
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The insulation Cancer Mesothelioma - What you would Know
Cancer or neoplasm is one of the most feared ailments of all time, afflicting people right from different age brackets and even races. In simple terms, cancer is undoubtedly an abnormal tissue growth and may also either be benign as well as malignant. Malignant cancers are definitely more dangerous as they tend to interfere with healthy tissues and transfer them into cancerous people; this is referred to as cancer metastasis. There are several factors that may bring about cancer cells to initialize and mutate such as grow older, genetics, diet, and way of living. There are many types of cancer. The commonest ones are prostate cancer tumor as for the males, and cancer of the breasts for the females. Lung and also colon cancers are also widespread. On the other hand, there are also rare varieties of cancer, and one of these is the cancerous multicystic mesothelioma or asbestos fiber cancer mesothelioma.

Asbestos most cancers mesothelioma is a rare style of cancer in the mesothelium. Often the mesothelium is a protective structure layer that protects tummy internal organs as well as the heart and lungs coming from rubbing off to other flesh or organs in the body. The one known main cause of this cancer is asbestos subjection. Alabama Mesothelioma is a harmful ingredient. If asbestos fibers usually are either inhaled or eaten, these can cause inflammation with the internal organs and therefore cause many alterations or mutations. That mutation is where the melanoma begins. Workers working in shipyards, power plants, refineries, metallic factories, and construction web-sites are the ones usually come across asbestos and are at high-risk for developing this type of tumor.
The early signs and symptoms of the insulation cancer mesothelioma are the adhering to: shortness of breath, heart problems, persistent coughing, fatigue, mysterious weight loss, and night sweating or fever. However , these are definitely the same signs and symptoms found in all cancers, that's why diagnosis of employing CT Scan, MRI, X-rays, and biopsy should be completed determine if it is this type of cancers. The treatment for asbestos cancer tumor mesothelioma can either be by chemotherapy, radiation or surgical procedures. Nevertheless, medical experts are assessment newer treatments such as gene therapy and immunotherapy, nevertheless techniques are not yet authorised for use.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mesothelioma - Respiratory Neoplasia (Lung Cancer)
Pleura
Lines the chest cavities
Outer surface lined by flattened mesothelium
Fibrous supporting tissue of collagen and elastin fibres
Extends into the lung as Fibrous Septa (continuous lung parenchyma
Contains Lymph vessels
Mesothelium consists of flattened cuboidal mesothelial cells which stretch as lungs inflate

A primary tumour of the mesothelial lining can be benign or malignant, and they are difficult to diagnose. The most obviously malignant forms often closely resemble metastatic adenocarcinoma .
Asbestos fibres
Potent cause of neoplasia in the mesothelial lining of the pleural cavity
In absence of previous asbestos exposure the tumours are very rare
A special form of Silica
Fibres collect in the alveoli of the lung

Mesothelioma from asbestos
Latent period of 25 years after exposure before clinical symptoms
Symptoms include pleural effusion (fluid in the pleural cavity)
Diagnosis may be suspected based on chest X-ray and CT scan
must be confirmed either by examining serous effusion cytology or with a biopsy via thoracoscopy
Treatment = chemotherapy, radiotherapy & possibly surgery
Prognosis is poor and there is not currently a screening programme

Metastatic cancers to the pleura are much more common than mesothelioma.
#asbestos#mesothelioma#lung cancer#Cancer#lungs#oncology#notes#biomed#science#study tips#2#medblr#studyblr#biology#medicine#human biology#pathology#Physiology
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
What Is Papillary Mesothelioma in 2024? | Discover
Introduction Papillary mesothelioma is a rare and generally less aggressive form of mesothelioma, primarily affecting the peritoneum, which is the lining of the abdomen. Unlike other types, it is often considered benign or of low malignancy, with a better prognosis. This article explores what papillary mesothelioma is, its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Contact Us Now For a Free Consultation
1. What Is Papillary Mesothelioma? Papillary mesothelioma, also known as well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma (WDPM), is a subtype that develops in the mesothelium but has a better prognosis compared to other mesotheliomas.
Location: Most commonly occurs in the peritoneum.
Nature: Tends to be localized and slow-growing.
2. Who Is Most at Risk for Papillary Mesothelioma? While asbestos exposure is a risk factor, papillary mesothelioma can also occur without known exposure.
Age group: Often affects younger individuals compared to other types.
Gender: More common in women than men.
3. What Are the Symptoms of Papillary Mesothelioma? Symptoms can be mild and similar to other abdominal conditions, making it harder to diagnose early.
Common symptoms: Abdominal pain, bloating, and a feeling of fullness.
Advanced signs: Fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites).
4. How Is Papillary Mesothelioma Diagnosed? Diagnosis requires a combination of imaging tests and biopsies to distinguish it from more aggressive forms.
Imaging: Ultrasound, CT scans for detecting tumors.
Biopsy: Needed for definitive diagnosis and to assess the nature of the cells.
5. What Are the Treatment Options for Papillary Mesothelioma? Treatment is usually less aggressive due to the slow-growing nature of this mesothelioma type.
Surgery: Often used to remove localized tumors.
Observation: In cases where the disease is stable, regular monitoring may be sufficient.
6. What Is the Prognosis for Papillary Mesothelioma? The prognosis is generally favorable, with many patients having a good quality of life.
Survival rate: Better than other mesothelioma types.
Focus on management: Regular follow-ups are important to monitor any changes.
Conclusion Papillary mesothelioma is a rare and often less aggressive form of mesothelioma, offering a better prognosis than other types. With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can manage the condition effectively. If you experience symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for early assessment.
FAQs
Is papillary mesothelioma always benign? Not always, but it is typically considered less aggressive than other forms of mesothelioma.
Can papillary mesothelioma spread? It is less likely to spread compared to other mesothelioma types, but monitoring is still crucial.
Is papillary mesothelioma linked to asbestos exposure? While it can occur without exposure, asbestos remains a known risk factor.
How long can someone live with papillary mesothelioma? Many patients live for years with proper monitoring and treatment.
What are the surgical options for papillary mesothelioma? Surgical removal of localized tumors is common, especially when the disease is contained.
Can papillary mesothelioma recur after treatment? There is a possibility of recurrence, which is why ongoing monitoring is recommended.
#mesothelioma#peritoneal mesothelioma#mesothelioma cancer#well-differentiated papillary peritoneal mesothelioma#mesothelioma law firm#mesothelioma article#mesothelioma attorney#mesothelioma treatment#mesothelioma stages#mesothelioma stage 4#peritoneal mesothelioma treatment#asbestos mesothelioma attorney#mesothelioma information#mesothelioma tumor#mesothelioma warrior#mesothelioma diagnosis#mesothelioma resources#mesothelioma help#mesothelioma lung cancer
0 notes
Text
Unraveling the Differences: Mesothelioma vs. Lung Cancer and Understanding the Stages of Mesothelioma
In the realm of cancer, two diseases often draw comparisons due to their effects on the respiratory system - mesothelioma and lung cancer. Though they share some similarities, it is essential to understand that they are distinct entities with unique characteristics, diagnostic challenges, and treatment approaches. Additionally, comprehending the different stages of mesothelioma is crucial for assessing its severity and determining the best course of action for patients. In this blog, we will unravel the differences between mesothelioma and lung cancer, explore the stages of mesothelioma, address the complexities in diagnosis, and shed light on the latest advancements in treatment.
Mesothelioma vs. Lung Cancer: What Sets Them Apart?
Mesothelioma and lung cancer both affect the respiratory system, leading to breathing difficulties and other respiratory symptoms, but they originate from different types of cells and tissues. Lung cancer, as the name suggests, originates in the lung tissues, typically arising from the cells that line the air passages. On the other hand, mesothelioma arises from the mesothelium, a protective lining found in various body cavities, such as the lungs, heart, and abdomen.
The primary cause of lung cancer is often associated with smoking and exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke, pollutants, and radon gas. Conversely, mesothelioma is mainly linked to prolonged exposure to asbestos fibers. Asbestos, once widely used in construction and industrial applications, can be inhaled, leading to the development of mesothelioma years or even decades after exposure.
The symptoms of both diseases can be similar, including coughing, chest pain, and shortness of breath. However, specific symptoms, such as pleural effusion (build-up of fluid around the lungs) and clubbed fingers, are more commonly associated with mesothelioma. Distinguishing between the two is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment.
Decoding the Mystery: Understanding the Stages of Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma is typically divided into four stages, known as Stage I, II, III, and IV. Each stage represents the extent of cancer progression and the degree to which it has spread within the body.
Stage I: In the early stages, mesothelioma is localized, confined to the lining of the affected area (e.g., pleura or peritoneum). At this point, treatment options are most effective, and surgery may be considered to remove the tumor.
Stage II: The cancer begins to spread beyond the initial site, potentially reaching nearby lymph nodes or other nearby organs. Surgical intervention may still be viable at this stage, depending on the individual's overall health and tumor location.
Stage III: During this stage, mesothelioma has advanced further, spreading more extensively to nearby lymph nodes and potentially infiltrating the chest wall, esophagus, or other adjacent structures. Treatment options become more focused on palliative care and managing symptoms to improve the patient's quality of life.
Stage IV: At this advanced stage, mesothelioma has metastasized to distant organs and tissues. Unfortunately, curative treatment options become limited, and the focus shifts to providing comfort and symptom relief for the patient.
Mesothelioma Diagnosis and Misdiagnosis: Challenges and Solutions
Diagnosing mesothelioma accurately can be challenging due to its similarity to other respiratory conditions, such as lung cancer or benign asbestos-related diseases. The symptoms may not manifest until years or decades after asbestos exposure, leading to delayed diagnosis.
To reach a precise diagnosis, specialized imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, are employed to detect abnormalities in the affected areas. Additionally, a biopsy is usually necessary to analyze the tissue samples under a microscope and confirm the presence of mesothelioma cells.
Misdiagnosis can occur when healthcare providers are not experienced in dealing with rare diseases like mesothelioma or fail to recognize the distinctive features of the condition. This emphasizes the importance of seeking medical attention from healthcare professionals with expertise in mesothelioma.
Hope on the Horizon: Advancements in Mesothelioma Treatment
While mesothelioma remains a challenging disease to treat, medical research has made significant strides in developing innovative treatment options. Standard treatments for mesothelioma include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. In recent years, emerging therapies, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy, have shown promising results in clinical trials.
Immunotherapy aims to stimulate the body's immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. Targeted therapy, on the other hand, targets specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth, minimizing damage to healthy cells.
Furthermore, supportive care measures have evolved to improve the quality of life for mesothelioma patients. Palliative care, pain management, and respiratory therapies help alleviate symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between mesothelioma and lung cancer is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Moreover, comprehending the stages of mesothelioma enables medical professionals to tailor treatment plans to individual patients. Despite the challenges posed by mesothelioma, ongoing research and advancements in treatment offer hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected by this rare and devastating disease. If you or someone you know has a history of asbestos exposure or experiences respiratory symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention and expert consultation can make all the difference in early detection and treatment success.
0 notes
Text
Pericardial Mesothelioma (Imaging Studies)
Pericardial Mesothelioma (Imaging Studies) Chest X-ray: Initial imaging to detect abnormalities in the heart and surrounding structures, such as pericardial effusion. Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that helps visualize fluid accumulation in the pericardium and assess heart function . CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the chest and can reveal thickening of the…
0 notes
Text
Financial Support for Asbestos Victims in California

The team at Sammons & Berry, P.C. help get financial support for asbestos victims in California and throughout the United States. More than $30 billion dollars has been set aside in trusts for these individuals due to the fact that asbestos manufacturers hid the dangers of working closely with this toxic material. Our team specializes in helping those who were exposed to asbestos while working for the railroad industry get money for the time they spent around this toxic material.
What is asbestos?
Asbestos is a commercial and legal term referring to a class of minerals that naturally form long, thin, very strong fibers. Asbestos has been mined and used in many products worldwide, mostly during the 20th century. In the United States, mining asbestos has ended, but asbestos is still present in older homes and buildings and some products still contain it. Asbestos occurs in the environment, both naturally and from the breakdown or disposal of old asbestos products. Disturbing asbestos minerals or other asbestos-containing materials can release tiny asbestos fibers, too small to see, into the air. Workers and others who breathed asbestos fibers over many years have developed asbestos-related diseases, including asbestosis, pleural disease, lung cancer, and mesothelioma. Some of these diseases can be serious or even fatal.
5 Signs Asbestos Exposure Could Be Affecting Your Body
Difficulty breathing. Most people with asbestos exposure have lung and respiratory problems caused by breathing in asbestos particles. If you are short of breath or hear a crackling sound when you breathe, this could be a sign of respiratory problems caused by asbestos. Chest pain or coughing. Many affected patients describe their cough as “dry” or “wheezing.” Consistent coughing and chest tightness could be signs you have scarring from asbestos in your lungs. Smoking can make symptoms worse, but asbestos exposure could be the root cause. Pleural plaques. Your doctor may find thicker areas on the lining of your lungs in a normal X-ray or CT scan. This is a standard sign you’ve been affected by asbestos exposure. If it’s been at least 10 years since you’ve been exposed, you should get scanned every 3-5 years for signs of plagues and thickening. Digestive problems. In addition to lung and throat problems, asbestos exposure can cause harm to other major organs and processes in the body. Symptoms such as weight loss, loss of appetite, difficulty swallowing, abdominal pain, and bowel problems have also been associated with asbestos-related diseases. Wider fingers or toes. Finger “clubbing” is a common sign of asbestosis exposure and related diseases, such as lung cancer and asbestosis, due to increased pressure behind the nails. Our team helps get financial support for asbestos victims in Texas and other states. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you get the money you deserve.
Can My Spouse Get Compensation for Secondhand Exposure?
If your spouse was employed by a railroad company and shows signs of asbestos exposure, you may qualify for asbestos trust fund compensation as a result of household asbestos exposure. Many spouses were exposed at this time while handling the laundry for their significant other. In some cases, spouses of railroad workers actually may have more severe damage from their asbestos exposure because they worked in closed environments when touching the contaminated clothing worn by their asbestos worker spouse. If you are married to someone who was employed by a railroad company before 1982 and have developed an asbestos-related disease, contact our law office today.
Free Asbestos Exposure Consultation in United States
At Sammons & Berry, P.C. we offer a no-cost, no-obligation consultation, so you can discuss the facts of your case without paying for anything upfront. Asbestos trusts claims do not require a lawsuit, depositions, or courtrooms. The process is simple and easy for the client and should not require any stressful legal confrontations for the client. The law firm handles all of the claims for the client, helping you maximize your compensation. We do not accept any payments from our clients until they receive compensation. We charge on a contingent fee basis, which means you pay a percentage of what you get paid in your claim. If we are unable to collect anything for you, there is no cost to you. Call (800) 519-1440 to speak with a Sammons and Berry, P.C. representative and start your journey towards compensation.
Wrongful Death Claims For Families of Asbestos Victims
If you have lost someone in your family due to the harmful exposure of asbestos, you may be entitled to compensation. If you can provide the work history and a death certificate for your loved one, our attorneys can help you file an asbestos claim. We understand how difficult this process can be, this is why we work with you every step of the way to help you get the money you deserve. Reach out to our team today to learn more about filing a claim for a family member. See if you qualify for compensation Sammons & Berry, P.C. 800-519-1440 View our Google Listing View our Facebook Read the full article
0 notes
Photo

Stuff I learned today in my pulmonology rotation:
The arrows in this CT scan show air bronchograms, which are areas where you can see the bronchioles clearly (black lines, which are the bronchioles that have air in them) because there is hyperdensity (white areas) around them. These are abnormal and indicate pneumonia or pulmonary edema. We have a pt today who had a spontaneous pneumothorax, which was treated with a pigtail and then a chest tube. He also has pneumonia.
From Wikipedia:
An air bronchogram is defined as a pattern of air-filled bronchi on a background of airless lung.
In pulmonary consolidations and infiltrates, air bronchograms are most commonly caused by pneumonia or pulmonary edema (especially with alveolar edema).
Other potential causes of consolidations or infiltrates with air bronchograms are:
Pulmonary edema Non-obstructive atelectasis Severe interstitial lung disease Pulmonary infarct Pulmonary hemorrhage Normal expiration
Ground glass opacities on CT are less dense than the hyperdensities you see in pneumonia; may be due to atypical bacteria.
From Wikipedia:
In radiology, ground glass opacity (GGO) is a nonspecific finding on radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans. It consists of a hazy opacity that does not obscure the underlying bronchial structures or pulmonary vessels, and that indicates a partial filling of air spaces in the lungs by exudate or transudate, as well as interstitial thickening or partial collapse of lung alveoli.
The differential diagnosis of the many causes of GGO includes pulmonary edema, infections (including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (COVID-19),[2] cytomegalovirus and Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia), various noninfectious interstitial lung diseases (such as hypersensitivity pneumonitis, Hamman-Rich syndrome), diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, and pulmonary contusion.
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles (bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
It is often a complication of an existing chronic inflammatory disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, dermatomyositis, or it can be a side effect of certain medications such as amiodarone. COP was first described by Gary Epler in 1985.
The clinical features and radiological imaging resemble infectious pneumonia. However, diagnosis is suspected after there is no response to multiple antibiotics, and blood and sputum cultures are negative for organisms.
Hamman-Rich Syndrome = acute interstitial pneumonitis. Acute interstitial pneumonitis is a rare, severe lung disease that usually affects otherwise healthy individuals. There is no known cause or cure.
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is often categorized as both an interstitial lung disease and a form of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) but it is distinguished from the chronic forms of interstitial pneumonia such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
The most common symptoms of acute interstitial pneumonitis are highly productive cough with expectoration of thick mucus, fever, and difficulties breathing. These often occur over a period of one to two weeks before medical attention is sought. The presence of fluid means the person experiences a feeling similar to 'drowning'. Difficulties breathing can quickly progress to an inability to breathe without support (respiratory failure).
Acute interstitial pneumonitis typically progresses rapidly, with hospitalization and mechanical ventilation often required only days to weeks after initial symptoms of cough, fever, and difficulties breathing develop.
Rapid progression from initial symptoms to respiratory failure is a key feature. An x-ray that shows ARDS is necessary for diagnosis (fluid in the small air sacs (alveoli) in both lungs). In addition, a biopsy of the lung that shows organizing diffuse alveolar damage is required for diagnosis. Other diagnostic tests are useful in excluding other similar conditions, but history, x-ray, and biopsy are essential. These other tests may include basic blood work, blood cultures, and bronchoalveolar lavage.
The clinical picture is similar to ARDS, but AIP differs from ARDS in that the cause for AIP is not known.
The chest tube is connected to a Pleur-evac. The first chamber will bubble if suction is on; it actively sucks air out of the pleural space. It tells you in centimeters of water how much suction is being applied. The pt I saw today had a little over 20 cm of H2O of suction. Normally, the visceral and parietal pleura have a small amount of fluid between them. In PTX, that space has air in it. The chest tube and Pleur-evac get air out of that space. The second chamber of the Pleur-evac will bubble as long as air is still in the pleural space. That's what happened with the pt from today. So he will need to keep the chest tube in until his PTX is better and no more air is coming into the pleural space.
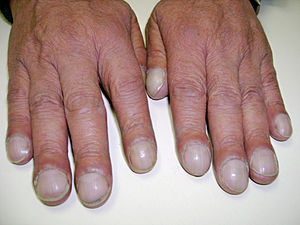
I asked the attending to explain the pathophysiology of clubbing. I recall learning that it can be associated with heartor lung disease, but I don't know why it happens. She said that in chronic respiratory failure, hypoxia triggers fibroblasts that cause nail clubbing, but nobody really knows why. The second image shows clubbing. From Wikipedia:
Nail clubbing, also known as digital clubbing or clubbing, is a deformity of the finger or toe nails associated with a number of diseases, mostly of the heart and lungs. When it occurs together with joint effusions, joint pains, and abnormal skin and bone growth it is known as hypertrophic osteoarthropathy.
Clubbing is associated with lung cancer, lung infections, interstitial lung disease, cystic fibrosis, or cardiovascular disease. Clubbing may also run in families, and occur unassociated with other medical problems.
Clubbing is associated with Lung disease:
Lung cancer, mainly non-small-cell (54% of all cases), not seen frequently in small-cell lung cancer ( Heart disease:
Any disease featuring chronic hypoxia Congenital cyanotic heart disease (most common cardiac cause) Subacute bacterial endocarditis Atrial myxoma (benign tumor) Tetralogy of Fallot
It can apparently also occur in GI disease.
Gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary:
Malabsorption Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis Cirrhosis, especially in primary biliary cirrhosis Hepatopulmonary syndrome, a complication of cirrhosis
Others:
Graves' disease (autoimmune hyperthyroidism) – in this case it is known as thyroid acropachy Familial and hereditary clubbing and "pseudoclubbing" (people of African descent often have what appears to be clubbing) Vascular anomalies of the affected arm such as an axillary artery aneurysm (in unilateral clubbing)
Nail clubbing is not specific to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Therefore, in patients with COPD and significant degrees of clubbing, a search for signs of bronchogenic carcinoma (or other causes of clubbing) might still be indicated.
A congenital form has also been recognized.
The exact cause for sporadic clubbing is unknown. Theories as to its cause include:
Vasodilation (i.e., distended blood vessels). Secretion of growth factors (e.g., platelet-derived growth factor and hepatocyte growth factor) from the lungs. Overproduction of prostaglandin E2 by other tissues. Increased entry of megakaryocytes into the systemic circulation. Under normal circumstances in healthy individuals, megakaryocytes that arise from the bone marrow are trapped in the pulmonary capillary bed and broken down before they enter the systemic circulation. It is thought that in disorders where there is right-to-left shunting or lung malignancy, the megakaryocytes can bypass the breakdown within the pulmonary circulation and enter the systemic circulation. They are then trapped within the capillary beds within the extremities, such as the digits, and release platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). PDGF and VEGF have growth promoting properties and cause connective tissue hypertrophy and capillary permeability. This seems to be the theory the attending was explaining.
#air bronchograms#air bronchogram#bronchogram#CT#imaging#ground glass#ground glass opacity#pulmonology#chest tube#clubbing
4 notes
·
View notes