#MACEDONIAN ARMY
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
Your top 5 Alexander the Great moments?
Top Five Alexander Moments
One issue with answering this is to figure out what events actually happened, especially when it comes to anecdotes! Here are four I find either significant to understanding his charisma and/or which explain how he functioned and why he was successful, plus one I like just because I’m a horse girl.
1) To my mind, the event that best illustrates why his men followed him to the edge of their known world occurred in the Gedrosian Desert. While I’m a bit dubious that this trek was as bad as it’s made out to be (reasons exist for exaggerating), it was still baaaad. One story relates that some of his men found some brackish water in a sad little excuse for a spring, gathered it in a helm, and brought it to him. Given his poor physical condition after the Malian siege wound, he no doubt needed it badly. He thanked them (most sincerely), then carried it out where all (or at least a lot) of his men could see, raised it overhead, and announced that until all of them could drink, he wouldn’t. Then he poured it onto the rocky ground.
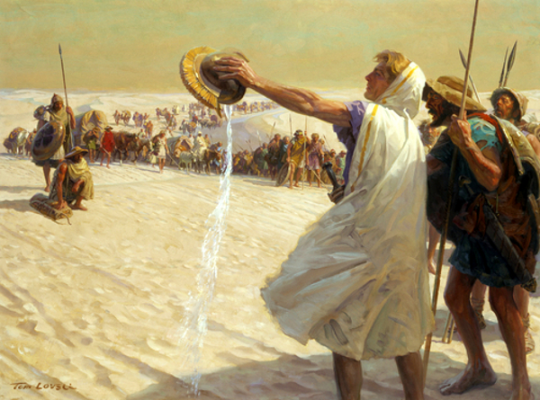

That gesture exemplified his charisma. And it absolutely is not something the likes of a Donald tRump could even imagine doing—nor most dictators, tbh. They’d be blaming everybody else and calling for heads while drinking Diet Coke, not suffering alongside their people.
This wasn’t an isolated event of that type. While he almost certainly didn’t have time to engage along with his soldiers in every project, we’re told he would drop in from time-to-time, to inspire them and to offer a little friendly competition.
He also dressed like his men for everyday activities, especially early in the campaign. As time went on, some sources say he inserted more distance—probably necessary as his duties exploded—but he still seems to have found time to “just hang out” with his Macedonians on occasion. The claims that he was too high and mighty to do so appears to have been exaggeration (as such accusations often are) in order to forward a narrative that he was “going Asian.” Troop resentment over court changes was very genuine—I don’t want to underplay it (especially as I’ve written about it in a few chapters in this), but it tended to boil up during certain periods/events, then die back again. Alexander was trying to walk a very fine line of incorporating the conquered while not ticking off his own people.
2) Reportedly, he once threw a man out of line because he hadn’t bothered to secure the chin strap on his helm. I pick this one because it tells me a whole lot about how he saw himself as a commander, and what he expected of his men (and why he tended to consistently win).
On the surface, his reaction seems almost petty. It’s precisely the sort of mistake students whine about when professors ding them for it. It’s just a chin strap! I’d have tightened it before I went into battle! (It’s just a few typos; you knew what I meant! Or, Why does everything in the bibliography have to be exactly matching in style? Who cares? What a stupid thing to obsess about!) These objections are all of a piece. First, they’re lazy, and second, they indicate a disconcern with details. In battle, such disconcern can get a person killed. And on a larger scale, for a general, such disconcern loses battles.
One of the striking aspects of Alexander’s military operations was just how well his logistics worked. Consistently. We hear little about them precisely because they rarely fail. Food and water was there when they needed it, as were arrow replacements, wood to repair the spears, wool and leather for clothes and shoes, canvas for tents, etc., etc. All those little niggling (boring) details. If these are missing, soldiers become upset (and don’t fight well). Starting with Philip, the Macedonian military was a well-oiled machine. That’s WHY Gedrosia was such a shock: the logistics collapsed. Contra some historians, he did not do it to “punish” his men, nor to best Cyrus.* He had a sound reason—to scout a trade route.
Alexander understood that details matter. It starts with a loose chinstrap. (Or an unplanned-for storm and rebellion in his rear.) Everything else can unravel from that.
3) Alexander sends Hephaistion a little dish of small fish (probably smelts). He also helps an officer secure the lady of his dreams. And writes another on assignment (away from the army) that a mutual friend is recovering from an illness. While technically three “moments,” these are all of a piece. Alexander knows his men, and is concerned not only for their physical well-being, but also their mental state: that they’re happy. Granted, these are all elite officers, but it suggests he’s paying attention to people. I’ve always assumed he sent Hephaistion the fish because they were his friend’s favorite, and/or they were a special treat and he wanted to share. That he didn’t punish an officer for going AWOL to chase the mistress he wanted but offered advice, and even assistance, on how to court and secure her suggests the same care.

I don’t want to take away from what appears to be his serious anger management problems(!), but little details like those above strike me as the likeable side of Alexander—why his men were so devoted to him.
4) Then we have the encounter with Timokleia after the siege of Thebes. While probably a bit too precious to have occurred exactly as related, I think it may still hold a kernel of truth.
Alexander had a reputation of chivalry towards his (highborn) female captives. If some of that was likely either propaganda from his own time or philhellenic whitewashing later by Second Sophistic authors such as Plutarch (and Arrian), poor treatment of women is not something we hear attributed to him.
Ergo, while the meeting was probably doctored for a moral tail, he may well have freed Timokleia as an act of clemency to put a better face on a shocking destruction he knew wouldn’t sit well with the rest of Greece—who he both wanted to cow yet earn support from. (A difficult balancing act.) Also, if Timokleia hadn’t been high-born, she’d probably have been hauled off to one of the prisoner cages with little fanfare.
Nonetheless, I find his actions surprising given the casual misogyny of his era. If we can take the bare bones of the story as true, and it’s not all invented, Timokleia was raped as a matter of course during the sacking of Thebes, then managed to trick her rapist and kill him by pushing him down a well and dropping rocks on him. I assume this happened when his men weren’t there, but they found out soon enough and hauled her in front of Alexander to be punished for killing an officer. To the surprise of all, Alexander decided the man had earned it and freed Timokleia. One might be inclined to call this overly sentimental, but….
There’s a similar story that occurred much later in the Levant, when two of Parmenion’s men seduced/(raped?) the mistresses/wives of some mercenaries. Alexander instructed Parmenion to kill the Macedonians if they were found to be guilty.
In both cases, we have an affront against (respectable) women. In the latter case, Alexander was (no doubt) working to avoid conflict between hired soldiers and his own men, who—in typical Greek fashion—would have looked down on mercenaries as a matter of course. Some sort of conflict between Macedonians and Greek mercenaries up in Thrace had almost got Alexander’s father killed. Alexander saved him. No doubt that was on Alexander’s mind here.
Yet what both events illuminate is a willingness on Alexander’s part to punish his own men for affronts to honor/timē that involved women. Yes, this is clearly about discipline. But it also shows an unusual sensitivity to sex crimes in warfare: actions that would normally fall under the excuse of “boys will be boys” (especially when their blood is up).
I doubt he’d have felt the same about slaves or prostitutes; he was still a product of his time. Yet without overlooking his violence—sometimes extreme (the genocide of the Branchidai, for instance)—I find his reaction in these cases to be evidence of an atypical sympathy for women that I’d like to think isn’t wholly an invention of later Roman authors. And just might show the influence of his mother and sisters.
5) Last… the Boukephalas story…because who doesn’t love a good “a boy and his horse” tale? Obviously the Plutarchian version is tweaked to reflect that author’s later concern to contrast the Macedonian “barbarian” Philip with the properly Hellenized Alexander. Ignore the editorializing remarks, especially the “find a kingdom big enough for you” nonsense.
But the bare bones of the story seem likely: unmanageable horse, cocky kid, bet with dad, gotcha moment. You can imagine this was an anecdote Alexander retold a time or three, or twenty.
——
* His attempts to copy Cyrus may be imposition by later writers. In his own day, he may have cared more about the first Darius, for reasons Jenn Finn is going to explain in a forthcoming, very good article on the burning of Thebes and Persepolis.
#asks#Top Five Alexander the Great moments#Alexander the Great#Hephaistion#Hephaestion#Timoclea#Timoklea#Boukephalas#Bucephalas#Gedrosian Desert#ancient military logistics#Macedonian army#Alexander's logistics#Classics#ancient history#campaigns of Alexander the Great#tagamemnon
58 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
The Impressive Training of Alexander the Great's Army
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
EJERCITO-MACEDONIA-ARTE-PINTURA-FALANGE-ALEJANDRO MAGNO-HISTORIA-GRECIA-PINTOR-ERNEST DESCALS por Ernest Descals Por Flickr: EJERCITO-MACEDONIA-ARTE-PINTURA-FALANGE-ALEJANDRO MAGNO-HISTORIA-GRECIA-PINTOR-ERNEST DESCALS- Ejército de Macedonia, al mando del Rey ALEJANDRO MAGNO los hombres forman la FALANGE, la nueva estrategia militar que revolucionó el mundo antiguo en sus guerras, los soldados armados de sus sarisas, lanzas muy largas, forman un erizo que resultaba muy difícil de superar, pintura del artista pintor Ernest Descals sobre papel de acuarela, pintar sobre la historia de Grecia.
#EJERCITO#MACEDONIO#MACEDONIA#ALEJANDRO MAGNO#ALEXANDER THE GREAT#MACEDONIAN ARMY#HISTORY#HISTORIA#GRECIA#GRIEGOS#SOLDADOS#SOLDIERS#MEN#HOMBRES#GUERRA#WAR#ESTRATEGIA#REVOLUCION#KING#REY#FALANGE MACEDONICA#MACEDONIOS#MACEDONIAN PHALANGE#ERIZO#LANZAS#SARISAS#BATALLAS#PINTAR#PINTANDO#PAINTING
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

doodling al'skander when i should be sleeping because i have not recovered from the effects of the persian boy
#completely obsessed with the whole lover (hephaistion/macedon) vs beloved (bagoas/persia) dichotomy#and all the implications of that#alexander as courtesan to the macedonian army!!#anyway. started reading funeral games today so just having lots of thoughts at the moment#the persian boy#mary renault#my art#alexander the great
142 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Dying Alexander the Great bids farewell to his Army
by Karl von Piloty
#alexander the great#dying#bed#art#karl von piloty#army#soldiers#alexander#antiquity#history#europe#european#ancient macedonia#macedonian#macedonia#ancient greek#ancient greece#death#generals#roxana#roxanna#roxane#roxanne
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ive been reading the Persian Boy and I'm not suprised by the orientalism but I am disappointed
#Cipher talk#Tbc I don't mean the depiction of slavery#It's very specifically the depiction of Greek culture- I've gotten to the scene where Baogas has spears thrown at him by the 'squires'- as#Subtly 'better' than Persian culture#There's a scrap of deniability bc it's from Baogas's POV so he thinks the Greeks and Macedonians are completely weird and immodest#But what really gets me is how it portrays Alexander as outraged by the treatment of Greeks held in slavery and how it's all 'oh in Greece#They Never cut a boy' and there's no mention that Athenian 'democracy' had a large class of slaves as of yet#But even as we're told by the narrator how improper and immodest the Greeks and Macedonians are I can feel the author winking and nudging#Like 'oh look at how the Persian court is weighed down by ceremony its barely a real army they're decadent (in the way a conservative says#That about a culture) and look at how Baogas holds rivers as sacred and doesn't swim in them (you know the same water he gets sick from)#And the hypocrisy that he was groomed as a 'courtesan' as a literal child but is embarrassed by nudity'#Yeah Mary I can see the feelings of cultural superiority. I still remember that Athens was misogynistic as fuck and had plenty of issues
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
⸻ The Lost Queen - XVIII ⸻



— summary: You woke up near a military camp without remembering how and why you got there, you didn’t understand why they were dressed like ancient Greeks, all you knew was that you weren’t safe and you needed to get out of that place as soon as possible. Too bad for you that you found yourself attracting unwanted attention from the Macedonian King and he won’t let you go so easily.
— genre: yandere, dark!au.
— warnings: time travel, obsessive and possessive behavior, murder, mention of torture, kidnapping, angst, fluffy (very rarely), dub-con, eventual smut, pregnancy.
— pairing: yandere!alexander the great x female!reader, yandere!generals x female!reader.
— word count: 2,330.
— tag list: @devils-blackrose, @faerykingdom, @hadesnewpersephone, @mariaelizabeth21-blog1 , @kadu-5607, @zoleea-exultant, @borntoexplore11-blog, @silmawensgarden, @elvinapandra, @jennifer0305 , @his0kaswife, @animetye-23.
— the lost queen series masterlist.

Chapter 18
Roxanna felt restless, as if something inside her was in constant conflict. She paced her room, unable to rest, her thoughts racing around a single issue: her impending marriage to Alexander, the foreign conqueror who seemed to be engulfing the world with his ambition.
Her father had been clear. The union was strategic, a calculated move to ensure the survival of his people in the face of the sweeping changes that lay ahead. With Darius’s downfall looking increasingly likely, joining forces with the man who controlled the most feared armies seemed not only sensible, but necessary. ''It is for the good of all,'' he had said, with the grave tone of one who made decisions beyond his own heart. But his words found no echo in hers.
Roxanna tried not to let her panic show, but the reality was suffocating. She knew little of Alexander, only stories she had been told; enough, however, to recognize that he possessed a magnetic presence. His face was striking, almost chiseled, and his eyes shone with an intensity that could both fascinate and intimidate. He was the kind of man who seemed unshakable, but the force that drew crowds to his feet also made her uneasy.
The weight of this choice that was not hers was made even worse by the shadow of another woman. Alexander already had a wife. Roxanna had heard whispers about (Y/N), the so-called Lost Queen. It was a name that soldiers spoke with reverence, almost like a prayer, and it tormented her. (Y/N) was not dead, but missing, possibly captured by the Persians. Despite her absence, her presence seemed to dominate. The adoration that Alexander clearly had for his wife seemed to be transmitted to his men. She had heard that Alexander was sending out searches and preparing to invade Babylon, supposedly where his wife would be.
How could she, Roxanna, compete with her, a figure who loomed like a specter in the midst of Alexander's ambition? Roxanna was beautiful and she knew it. Her beauty was surpassed only by Darius's wife.
More than that, she felt an inner resistance to the idea of sharing. She knew it was common for kings to have multiple wives, but still, the idea of becoming one of many repulsed her. Roxanna wanted to be more than the second wife, more than a symbol of victory over her people. She wanted to be the first, the only. It was a foolish desire, perhaps, but it was hers.
Still, she knew it didn’t matter. The decision wasn’t in her hands. If Alexander wanted her, there would be no escape. Refusal was unthinkable. She would be forced to play the role of wife, to fulfill the role assigned to her, whether her heart was in it or not.
She would be ready to give her heart to Alexander. But he... Was he ready to give his to her?

"A doctor has come to see you, my Queen." Bagoas’s soft voice cut through the silence of the room, respectful and controlled. He waited patiently at the door until you nodded, allowing him to enter. His gaze was always firm but affectionate, as if he were measuring the environment around him before taking a step. You couldn’t help but grow fond of the eunuch.
"Let him in." You replied, trying to hide the nervousness that was setting in. But the anxiety grew in waves, relentless, as the man entered the room. He carried with him a leather bag and a series of strange instruments. The sight of some of them, with their sharp, mechanical shapes, made your stomach turn. For a brief moment, you couldn’t help but think that they looked more like torture tools than healing tools.
You took a deep breath, trying to find calm. After all, this was an order from Perdiccas, who, even without saying it, showed genuine concern. The memory of him hugging you, holding your hand gently, whispering sweet words to you, was both comforting and disturbing. His presence awakened conflicting feelings. Part of you wished he was there, that he hadn't left the room so abruptly. But another part, hurt by the circumstances, wanted distance.
You needed to talk about what was happening. About everything. But not now. You needed to focus on yourself, on protecting yourself and the life growing inside you. At least, until Alexander came to get you.
Your gaze instinctively fell on your hands, which rested on the subtle curve of your belly. It was an almost unconscious gesture, an attempt to protect the life growing inside you. Although you weren't completely sure about the time, you estimated that your pregnancy was already close to four months. The idea was both beautiful and terrifying.
"How are you feeling, Your Majesty?" The doctor asked, his voice grave but gentle, as he took a few steps towards you. There was something in his gaze, a deep green that seemed to seek answers before you could even offer them.
"A little better." You murmured, trying to sound calm, but feeling the weight of your vulnerability. His eyes met yours, and for an instant, you felt disarmed, exposed. The tension in the air was palpable, and the anticipation of the upcoming examination increased the whirlwind of emotions that already took over you.
The doctor’s gaze fell on the discarded sheet next to the bed, where a small but unmistakable stain of blood marked the clear surface. He coughed discreetly, perhaps to disguise the evident discomfort he felt at the delicate situation.
"You were lucky," He said after a brief silence, gesturing for you to spread your legs. The request was direct, professional, but you couldn't help the blush that rose to your cheeks. The idea of exposing yourself like that, even in front of a doctor, made your body stiffen with embarrassment.
But you forced yourself to keep your composure, taking a deep breath to push away the discomfort. "It’s like he’s a gynecologist," you told yourself in your head, trying to rationalize. He was a doctor, after all. It didn’t matter that medicine back then was rudimentary, or that you had doubts about the real effectiveness of his knowledge.
Details. Just details.
"Was I lucky?" Your voice came out in a low murmur, with a slightly bitter tone that you couldn’t hide. The whole situation felt surreal, as if you were trapped in a game that was out of your control.
And that was probably exactly what it was.
The doctor nodded, moving carefully as he lifted the light chiton covering your body. His gaze remained fixed on his task, professional but intense. "Yes," He replied, his voice deep but calm. "You almost miscarried."
The words hit you like a cold blast, making your heart clench. What had started as discomfort now became palpable fear. You knew the pregnancy was fragile, but hearing it so directly was a cruel confirmation of the vulnerability of this new life inside you.
Instinctively, your hands went back to your belly, as if trying to protect it from any unseen threat. The silence between you stretched for a moment, heavy, as you absorbed what he had said. It wasn’t just luck. It was a warning. And a reminder that your body and mind were carrying far more than they could bear alone.
The doctor carefully lowered your chiton before approaching you again, this time placing his hands on your belly. His initial touch was firm, almost rough, and you flinched instinctively, feeling uncomfortable with the pressure he was applying. He seemed oblivious to your reaction, completely focused on his assessment, but you could barely contain the shiver that ran through your body.
"Why are you doing that so hard?" You started to ask, but he held up his hand, interrupting you before you could finish.
"How long have you been pregnant, Your Majesty?" He asked, his voice serious, his eyes fixed on yours with an intensity that seemed to weigh on you.
For a moment, the question took you by surprise. His incisive tone and the way he stared at you made you nervous, but you knew you had to answer. Swallowing hard, you murmured, "I think I’m four months along..."
He nodded, but his gaze remained skeptical, as if questioning the accuracy of your answer. Stepping back, he seemed to ponder before finally uttering the words that left you speechless.
"I believe you are pregnant with twins."
"Twins?" You repeated in a whisper, almost as if you were asking yourself.
The doctor nodded again, this time with a more serious expression. He seemed to be measuring his words, but he still chose to be direct. "Your belly is more swollen than normal for a single pregnancy," He explained, his voice calm but filled with concern. After a brief sigh, he continued, this time with a darker tone. "Unfortunately, I must warn you of the risks. Giving birth to two babies... It’s dangerous. There’s a good chance you won’t survive the birth."
His words hit you like a blow. Your eyes widened, and the room seemed to close in around you. To die in childbirth. In ancient times. It sounded like a sentence you never imagined you would face. Terror settled in your chest, and for a moment it felt like the air had been sucked out of the room.
You opened your mouth to respond, but before you could utter a word, another voice cut through the silence.
"I suggest you keep your comments to yourself."
It was Perdiccas, his imposing figure appearing in the doorway of the room. His tone was calm, but filled with disapproval as he fixed the doctor with a hard stare. His eyes flashed, as if ready to squelch any further attempts to alarm her. "My Queen is already terrified enough. We don’t need your unnecessary comments."
His presence filled the space, and you felt a mixture of relief and discomfort. Perdiccas had always been a complex figure in your life — protective and, at the same time, charged with an authority that sometimes felt overwhelming. Yet his words, even as a reprimand to the doctor, brought a strange sense of security. As if, for a moment, he was willing to carry the weight you feared to face alone.
The doctor hesitated, clearly disconcerted, but bowed his head in deference. "My apologies, Your Majesty. It was merely a warning." He gathered his things quickly, as if to avoid any further confrontation with Perdiccas, and bowed out.
Now, only the two of you remained in the room. Perdiccas approached slowly, his eyes softening as they landed on you. "I will not let anything happen to you," He said, his voice lower and firmer, like a promise he seemed determined to keep.
And in that moment, you allowed yourself to believe his words. There was something in Perdiccas’ tone, in the firmness of his promise, that seemed sincere. Maybe it was the vulnerability that enveloped you, making him an anchor in the midst of the whirlwind of uncertainty. Or maybe it was the old feelings, the ones you tried to bury, but that now resurfaced, stubborn and undeniable, creating cracks in the armor you had built over time.
He was there, close enough for his presence to warm the cold room, and for a brief moment, you felt a security that you hadn’t experienced in months. Against all the reasons your mind tried to list, you found yourself trusting Perdiccas once again, as if his promise were a rope pulling you out of the abyss.
Or maybe it was the pregnancy hormones.
You just hoped you wouldn't regret it a second time.

Alexander was determined: he would only take Roxanna as his wife if he had the consent of (Y/N), his beloved and first wife, from whom fate had separated him. He knew that to unite with another woman without (Y/N)'s knowledge and permission would be the same as betraying the deep feelings he still harbored for her. It was a line that Alexander was not willing to cross. Acting in the shadows, making decisions that could hurt or dishonor (Y/N), would be an act he would never forgive himself for. The respect and love he had for her were unshakable, and even in the face of difficult circumstances, he was determined to honor them above all else.
But before any decision about Roxanna could be made, he had to recover (Y/N). There was no other path to follow while she was still beyond his reach. Alexander had already made his decision: he would leave for Babylon immediately. No matter the challenges, he was willing to face them.
He would mobilize his army for the mission, for he knew that no effort would be too great to rescue his beloved. He trusted his generals and soldiers completely, loyal men who had always followed him, and it would be no different this time. When he communicated his determination, he was certain that they would support him without hesitation, understanding that, for Alexander, the search for (Y/N) was not only a matter of love, but of honor.
"Call the generals immediately." Alexander's firm voice echoed through the room. The page, without wasting time, bowed hurriedly and ran off to carry out the order.
Alexander was alone for a moment, but his mind was far from there. He could almost smell (Y/N)'s perfume, that delicate and unmistakable aroma that had enveloped him so many times. He seemed to hear the soft melody of her laughter in the background and feel the gentle touch of her fingers against his skin. It was as if the memory of her was more alive than ever, calling him to action.
Finally, he would be going after her. There would be no more delay, doubts or hesitations. Every step he took now would bring him closer to (Y/N), and nothing in the world could stop him from bringing her back.
''I'm coming for you, my Queen.''

— lady l: maybe a shorter chapter but that's because it's like a preparation for chapter 19 and especially 20. I hope you liked it and forgive me for any mistakes! ❤️
See you a in the next chapter! I'll probably post the next this weekend, though. It's practically ready. 😉
Also, expect a lot of drama to come! Alexander is coming to Babylon!! ��
#tlq#the lost queen#yandere history#yandere historical characters#alexander the great x reader#yandere Alexander the great#yandere Alexander the great x reader#long fic#yandere x reader
486 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! Love your takes and all! What do you think of people talking about Penelope being all buff and strong physically as she was "Spartan?" or that she find Odysseus more attractive with blood plaster on his body as she is "Spartan" or such?. Is it true in the Epics? I read something about a Lykurgus or something..I just want to have a nuanced answer to that, also sorry for the silly question.
You are very kind Anon and I am glad you find them useful
Okay for starters I think this whole thing is a massive stereotype in regards to Sparta that "they are all sexually aroused by blood and violence". I mean yes Sparta as we know had an extreme military outline but it is not like they all just killed around to have fun like a twisted version of Asterix village or something. They valued war and the strength in war of course and they took pride to their warfare and all but yeah I think the whole thing of "oh gosh! Blood! Foreplay for Spartans" is just a joke that goes too far sometimes (although we DO have some exaggerated sources about the Spartans but, surprise surprise, they come from their main rival, Athens so yeah one needs to consider that too. So yeah although the Spartans were strictly military I do not think it is actually realistic to say that they all went like:

lol XD
Two this "Sparta" that they mostly mention is at least 100 years if not more away than the "Sparta" mentioned in the epic cycle. You see the Epic Cycle might have been synthesized at the 8th century BC but the events taking place in it, reflect on the Bronze Age or the Mycenean kingdoms which existed before. These "Spartans" everyone speaks about is usually referring to the Doriean Spartans. The Dorieans were a Greek set of tribes with their own dialect that came down from the north at the year around 1100 BC, around 100 years after the estimated date of the events of the Trojan war and they got to remain to the areas such as Macedonia or Lacedaimona aka Sparta thus we have Macedonians and Spartans speak Doric Greek dialect while Atheneans speak Attic Greek dialect and the Asia Minor greek cities speak Ionian etc Either way as I said the events of the Trojan war happened around 100 years before this Doric Tribe descend much less till the strictly military spartan system to be fully crystallized. So we need to think of that. And even then it is not like the Spartan women were some sort of body-builders who didn't have any sort of binary roles to their society or being active warriors in armies etc (don't mistake them for Amazons guys! Hahahaha!). They did actively excersize more than most Greek cities at that time and they did take part in athletic events more than let's say Athens (Athenean women by n large seemed to participate in sports such as running and those were exclusively for Hera's celebrations) so we can imagine they would be more athletic than the average Greek lady but that doesn't mean they were soldier-trained or anything. The military training was for boys at the city of Sparta. And women still had their own binary roles in their respected society, they just had some more freedom as compared to their Athenean counterparts.
So even if Myceneans DID have a more military form of society or at least based on the findings they did focus on warfare to their art and such and the building of their walls and all they still wouldn't be the same as the doric Sparta that were exclusively military. Could perhaps mycenean Sparta have the basis for the future doric Sparta? Perhaps but I doubt we have sufficient evidence to say they are identical.
Three. I believe that people who wanna desperately depict Penelope as some buff lady, misses the concept of Penelope's strength in the Odyssey. Penelope was not strong because she could fight with the sword. She was strong because she was mentally steadfast, clever and resourceful and enduring and she managed to hold the kingdom of Ithaca steadfast by herself for 20 years. It wasn't about her being buff lady. Homer does seem to imply she was tall and stoutly buillt; see my other post where I mention her physical description in Homer:
but not buff as "I'm gonna kick your ass" buff and all. Homer doesn't mention that any of the Spartan princesses have some specific training (Helen Clytemnestra or Penelope) but later literature implies that they have basic knowledge on weaponry (for example in later 5th century dramas and above Clytemnestra not only is seen wielding a weapon but knowing some basics as to how it was made) but it needs to be said that the posthomeric sources were also influenced by their contemporary Sparta aka the doric military Sparta. Homer doesn't imply that this strict military doric way of life was part of his lore but he does imply that Sparta relies more to its military (as compared to Ithaca or Pylos for example) so maybe he attempts to create the illusion of historical continuation but either way no this whole "300s-like" Sparta was not crystalized yet to the times that Homer synthesized his poems much less to the time of Bronze Age.
And there is no hint that Penelope goes "WOW BLOOD!" that seems to me one of the overused jokes on the internet, again emanating by the whole series of Sparta stereotypes used for comedy. It was in fact Euryclea the one to almost welp in happiness seeing Odysseus covered in blood and that was because Odysseus had killed the men she hated. Penelope doesn't show such a thing. Odysseus also washes himself up to be presentable to her. And even in posthomeric sources Penelope was not linked to physical strength but rather with the strength of her mind and the purity of her intentions (well...except maybe from Parthenius narrative if I recall correctly. There Penelope is pictured as scheming in jealousy against one of the sons Odysseus ellegedly produced and manipulated her husband to kill his illegitimate son)
As for the last part I am not sure what you are referring to? Are you referring to Lycurgus that is mentioned in some later sources as king? I did find for example the reference of Plutarch (who lives much much later) that he implies that Lycurgus lives at the same time as Homer or possibly had met him personally but is that what you are referring to? Either way I assume you refer to the historical person rather than some mythical figure because in homeric realm we do have rulers such as Tyndareus (the king of Sparta father to Helen and Clytemnestra) and Icarius (father to Penelope). It seems that Homer with the mention of the two rulers, even if not directly mentioning it, seems to be winking at the later but still ancient custom of doric Sparta to have two kings but I am not sure if that truly was his objective (and therefore creating an anachronism most likely)
I hope that answers your questions a bit
#katerinaaqu answers#the iliad#the odyssey#homeric poems#penelope#odypen#penelope of ithaca#penelope of sparta#sparta#doric greeks
98 notes
·
View notes
Photo
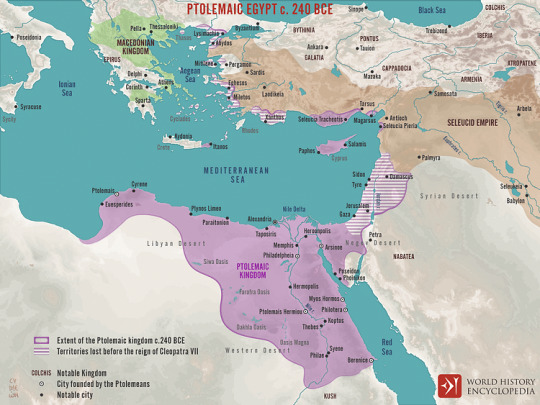
Ptolemaic Egypt
Ptolemaic Egypt existed between 323 and 30 BCE when Egypt was ruled by the Macedonian Ptolemaic dynasty. During the Ptolemaic period, Egyptian society changed as Greek immigrants introduced a new language, religious pantheon, and way of life to Egypt. The Ptolemaic capital Alexandria became the premier city of the Hellenistic world, known for its Great Library and the Pharos lighthouse.
From Persian Rule to Alexander
In 525 BCE, Egypt was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire, beginning a period of harsh foreign rule and cultural repression. Egypt briefly regained its independence from 404 BCE until 342 BCE before it was reconquered. Discontent with the Persian government resulted in the Egyptians welcoming Alexander the Great as a liberator when he invaded in 332 BCE. Alexander had already broken the Persian army at the Battle of Issus (333 BCE), and Mazakes, the satrap of Egypt, surrendered without a fight.
Alexander demonstrated a deep respect for Egyptian culture, choosing to be crowned pharaoh according to traditional custom. He offered sacrifices to the Egyptian gods in Heliopolis and Memphis and hosted Greek athletic games to celebrate his reign. Next, he traveled south to the Oracle of Amun, whom the Greeks equated with Zeus, in the Siwa Oasis. Alexander believed himself to be the son of Zeus, which the oracle seemingly confirmed for him. The idea had precedent in Egyptian royal ideology in which kings were considered living gods, the offspring of deities like Ra or Amun. It was an unusually grandiose claim for Greek rulers, but Alexander's reputation was great enough for the Greeks to accept him as a demigod.
Alexander's grand design will slowly have come to encompass the idea that all peoples were to be subjugated for the formation of a new world order; for this purpose, the Egyptian pharaonic system presented a very suitable ideology that was well established and has been accepted for millennia.
(Hölbl, 9)
In 331 BCE, Alexander visited the fishing village of Rhakotis where he planned the foundation of a new city, Alexandria. He intended for Alexandria to be the capital of his empire, a link between Egypt and the Mediterranean. Before leaving to continue his conquests, Alexander appointed two governors, Doloaspis and Peteisis, and named Cleomenes of Naukratis, a Greek Egyptian, as his satrap. He also left a small army to occupy and defend Egypt.
After the death of Alexander the Great in Babylon in 323 BCE, his general Ptolemy I became satrap of Egypt. He was nominally the servant of Alexander's successors Philip Arrhidaeus and Alexander IV of Macedon, but in reality, he ruled on his own initiative. Ptolemy I quickly executed Cleomenes, whose exorbitant taxation was unpopular, and began establishing royal policies to modernize the country. By 310 BCE, the last of Alexander's heirs had died, and during the Wars of the Diadochi, Alexander's generals claimed pieces of his empire. Ptolemy I was crowned king of Egypt in 306 BCE, establishing the Ptolemaic dynasty.
Continue reading...
98 notes
·
View notes
Photo
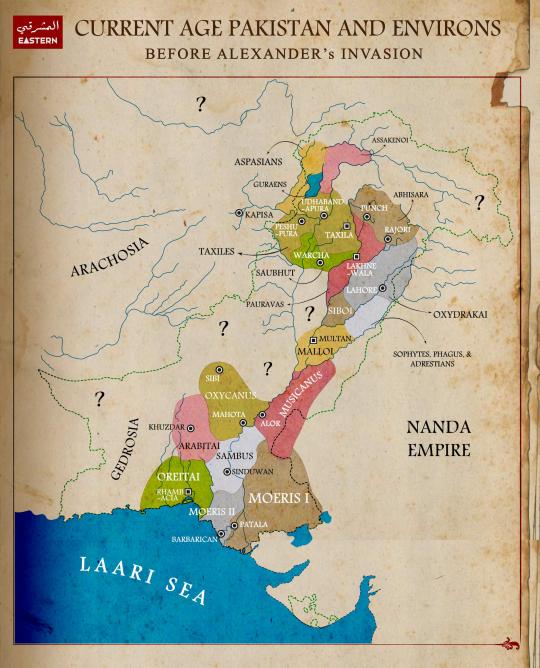
Regions of Current Age Pakistan before Invasion of Alexander
Alexander the Great's military campaigns in the Indus Valley (modern-day Pakistan) involved significant engagements with local territories, kingdoms, and their rulers. In 329 B.C., Alexander conquered Qandhar and encountered Indian tribes for the first time, marking the beginning of his interactions with the complex political landscape of the area. By 327 B.C., he had crossed the Hindukush Mountains, capturing key fortifications such as Astes Fort and massacring 7000 Indians at Massaga of Assakenians. His conquest continued with the siege and capture of Aornos in December of the same year.
During his campaigns, Alexander encountered various powerful entities in the region. The Buddhists, particularly in Sind, were influential, with prominent temples in Multan and Alore. Despite the power of the Buddhist monks, the Brahmins played a significant role in resisting Greek advances, inciting rebellion among local rulers such as Sambus. This resistance led to notable conflicts, including the defeat of Poros in 326 B.C. and the collapse of the Mallians in 325 B.C. The Greek conqueror’s interactions with these local powers highlight the complex and multi-faceted nature of the region's political dynamics.
Alexander's campaign in the southern Punjab in 326 B.C. was marked by the defeat of the Malli and Oxydraki principalities, followed by the liberation of the rivers Hydaspes, Acesines, and Indus. His naval fleet, consisting of 2000 warships, played a crucial role in these operations. The submission of Musicanus, the chief of upper Sind, who paid homage to Alexander to avoid destruction, further exemplifies the mix of military might and diplomatic engagements that characterized Alexander's approach. The appointment of Peithon as the Governor of Sind and the dispatch of Krateros with an army via Bolan Pass were strategic moves to consolidate Greek control over the region.
The period following Alexander's departure saw significant turmoil. In 325 B.C., revolts in Patala and other regions, such as the rebellion of Sambus and Musicanus, were brutally suppressed. Alexander's forces, led by his generals, employed severe measures, including mass executions and enslavement, to quell these uprisings. The death of Philippus, the Satrap of Upper Sindhu Valley, due to internal jealousy among Greeks and Macedonians, underscores the tensions within Alexander’s administration. These events reveal the fragile nature of Greek control and the persistent resistance from local rulers and populations.
Alexander's death in 323 B.C. marked a turning point, as his empire was divided among his generals. Despite the fragmentation of his empire, Sind continued to be governed by Peithon, reflecting the lasting impact of Alexander's conquests on the region. The strategic and administrative decisions made during his campaigns had enduring effects, shaping the political landscape of Sind and its neighboring territories. Alexander's legacy in these regions is a testament to the complex interplay of military conquest, local resistance, and administrative governance that defined his rule.
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
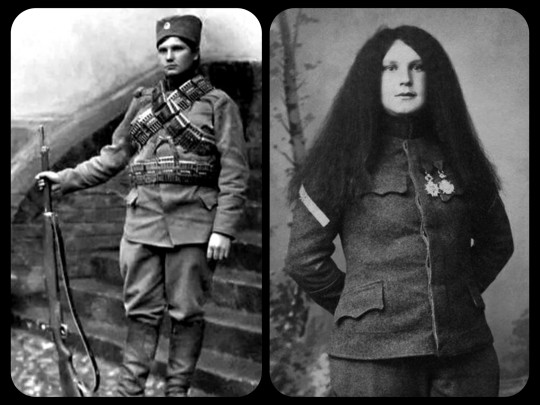
Milunka Savić, the Most Decorated Female Combatant in History: Savić disguised herself as a man in order to join the Serbian army during the Balkan Wars, then served again during WWI, earning medals from Serbia, France, Russia & Britain; she also provided medical support to anti-fascists during WWII and spent 10 months in a Nazi concentration camp

This is a total rewrite of a post that I did last year, with much more detailed information, more photos, and some additional sources.
Milunka Savić is regarded as the most decorated female combatant in history. She fought for the Serbian Army during both of the Balkan Wars, before returning to the battlefield again during WWI. Savić was wounded in battle on 9 separate occasions and survived the Serbian Great Retreat, making the perilous journey across the mountains of Montenegro and Albania through the dead of winter with a serious head injury.
Her military career began during the First Balkan War in 1912, when her younger brother was called up to serve in the Serbian army, and she decided that she would covertly take his place. She cut her hair, wore men's clothing, and presented herself as her brother.

The First Balkan War, 1912: Milunka Savić as a young soldier during the First Balkan War, shortly after joining the Serbian army
She was able to hide her true identity for quite some time. Her skills as a soldier quickly became evident as the war progressed, and she earned her first medal/promotion during the Battle of Bregalnica in 1913. Unfortunately, she was hit by shrapnel from a Bulgarian grenade during her tenth deployment, causing injuries to her chest and abdomen, and those wounds (along with the subsequent medical treatment) ultimately led to the discovery that she had lied about her identity.
In recognition of her accomplishments on the battlefield, her commanding officer decided not to punish her for the initial deception, but informed her that she would not be allowed to return to combat -- as a woman, she could only be transferred to the nursing division instead.
As the story goes:
Savić was called before her commanding officer. They didn't want to punish her, because she had proven a valuable and highly competent soldier, and the military deployment that had resulted in her [sex] being revealed had been her tenth; but neither was it suitable for a young woman to serve in combat. She was offered a transfer to the Nursing division. Savić stood at attention and insisted that she only wanted to fight for her country as a combatant.
The officer said he'd think it over and give her his answer the next day. Still standing at attention, Savić responded, "I will wait." It is said he only made her stand an hour before agreeing to send her back to the infantry.
Savić was able to serve in a combat role throughout the remainder of the Balkan Wars.
The Second Balkan War finally came to an end in 1913, but that peace was short-lived, as World War I erupted just a year later. Savić returned to the military once more, serving in the elite "Iron Regiment" of the Serbian army.
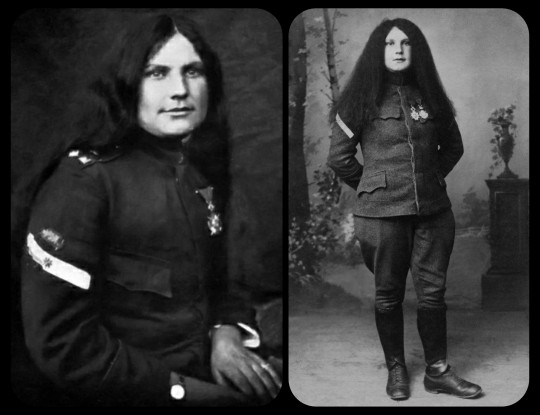

World War I, c.1915-1916: Savić was no longer forced to hide her identity when she returned to battle during WWI, and these images show her posing in uniform with her hair grown out
Savić received the Serbian Karađorđe Star with Swords medal on two separate occasions during WWI; the second medal was given to her after the Battle of Crna Bend in 1916, where she was credited with single-handedly capturing 23 Bulgarian soldiers. She received several other medals throughout the course of her career, including the French Legion of Honor (twice), the French Croix de Guerre, the Russian Cross of St. George, the British Medal of the Most Distinguished Order of St. Michael, and the Serbian Miloš Obilić.
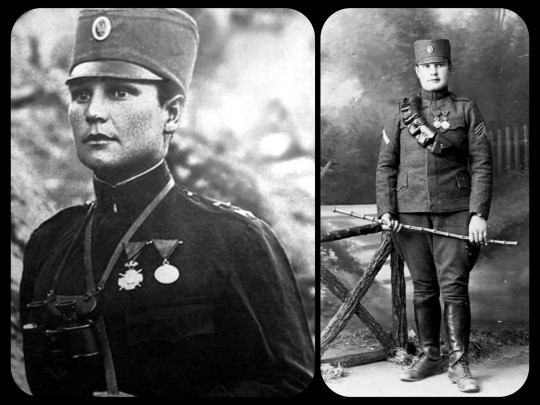

WWI, c.1915-1916: Milunka Savić as a Corporal in the Iron Regiment
She suffered a serious head injury while fighting along the Macedonian front, and she was still gravely wounded when Austro-Hungarian, German, and Bulgarian forces gained control of Serbia in the winter of 1915. The Serbian army was then ordered to make a full retreat from Serbia; Savić and her fellow soldiers, along with the Serbian government and more than 200,000 civilians, were all forced to flee through the mountains of Montenegro and Albania in the dead of winter, hoping to reach Allied forces along the Adriatic Coast -- a perilous journey that would later be known as the Serbian Great Retreat (or the Albanian Golgotha). Roughly 400,000 people embarked on this journey, and less than 180,000 of them survived, eventually reaching the Allied ships along the Adriatic coast.
Despite her injuries, Milunka Savić was among the survivors. She was sent to an infirmary, where she spent several months recovering from her injuries, before she returned to the battlefield alongside Allied forces.
At the end of the war, the French government offered to provide Savić with a full pension and living accommodations in France, in recognition of her actions while serving alongside the French military during WWI. She ultimately declined the offer and chose to retire back in Serbia instead, where she and her husband settled down to raise their daughter and three other girls that Milunka had adopted. The couple would later separate, however, and Milunka was left to raise her children as a single mother, working at a local bank to make ends meet.
In 1941, Serbia (which was then part of Yugoslavia) fell under Nazi occupation. During this period, Savić was involved in providing medical support to local partisans and anti-fascists who had resisted the Nazi occupation. She was eventually arrested by German officers; there are differing accounts of the events leading up to her arrest, with some sources suggesting that she was arrested as a result of her involvement with the local partisans and other anti-fascist elements, while other sources claim that she was arrested after she offended several Nazi officials by openly refusing to attend a formal banquet that was being held in honor of the German military campaign. In any case, she was imprisoned at the infamous Baljinca Concentration Camp for ten months before finally being released.
She faced other forms of hardship in the aftermath of WWII, as she struggled to support herself and her children. She worked several low-paying jobs over the years, while living in a dilapidated, decaying house in Belgrade. Her name (and her long list of accomplishments) had largely faded into obscurity by then.
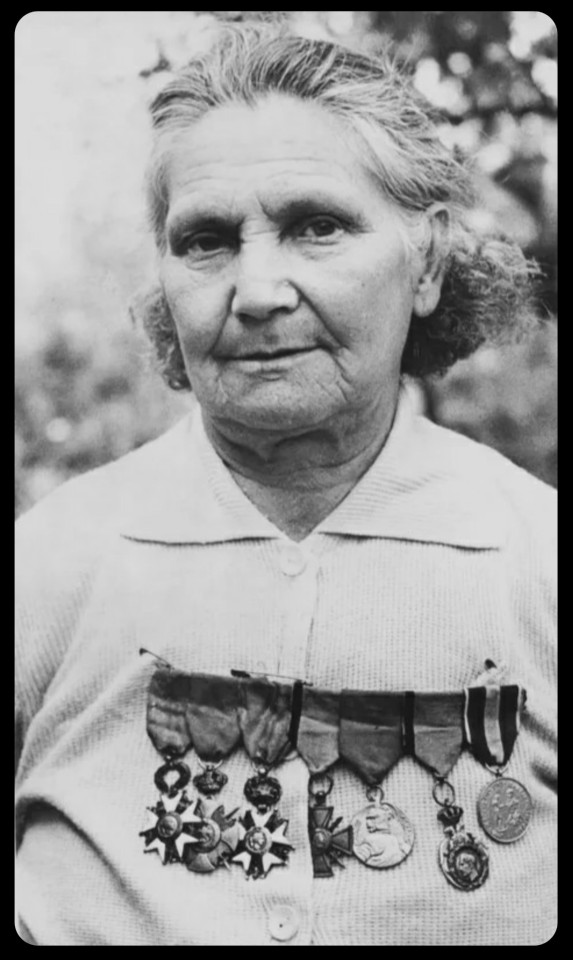

Serbia, 1972: Milunka Savić proudly displaying some of her medals in 1972, when her story became more widely known
It wasn't until the early 1970s that her involvement with the military finally began to receive more widespread attention, both in Serbia and abroad. Following the 1972 publication of an article that told her story, her local community in Belgrade quickly rallied to provide her with newer, more suitable living arrangements.
Sadly, she passed away within just a year of the article's publication.
In 2013, Milunka Savić's remains were relocated from the small mausoleum where they had been interred since 1973, and she was reburied in Belgrade's "Alley of the Greats," where some of the most well-known and most widely respected Serbians are laid to rest.
Sources & More Info:
Research Gate: Milunka Savić: the Forgotten Heroine of Serbia
Girl Museum: Milunka Savić
Law and Politics: The Position of Women in the Serbian Army
Medium: The Fearless Woman-Bomber Who Died Proud, Broke, and Forgotten
Wikipedia: Milunka Savić
Mental Floss: The Serbian "Great Retreat" Begins (WWI Centennial)
#history#Milunka Savić#women in history#serbia#women in the military#balkans#military history#wwii#wwi#yugoslavia#milunka savic#challenging gender norms#feminism#femininity#serbian history#women's liberation#women in war#real-life mulan
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, just a few posts ago, in replying to an ask as to whether Philip or Alexander might have had women as friends/romantic partners and we don't know about it...
I said one of the constraints would be WHERE women were allowed to be. The army had fewer places/roles for women than at home. But that didn't mean there were none.
Then just today, I saw mention of this new edited collection. So I'm bringing it to folks' attention.
A caveat: this is the Roman army. The Roman army (especially later) was more likely to be assigned to a fort/region, where they stayed put, going out from there to fight. That made it much easier for those soldiers to acquire women/families. The Macedonians were on the march almost constantly. "Staying put" meant for a few weeks, or a month or so. Yet even they picked up camp followers along the way. (We know because our sources tell us.)
Caveat the second: we have a lot more/better evidence for the Roman army than the Macedonian.
Last: Romans are not Macedonians. Roman attitudes to women are different than Greco-Macedonian. In the case of Rome, they were influenced by the Etruscans, whose women enjoyed much more freedom...but they were still Roman. Macedonian women also seem to have enjoyed more freedom relative to their southern Greek counterparts...but not as much as Etruscan women.
Nonetheless, this collection may give those interested some ways of thinking about women in and around the army in ways they'd not before considered. And some of what they point out about Roman armies will be just as applicable to Macedonian armies.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
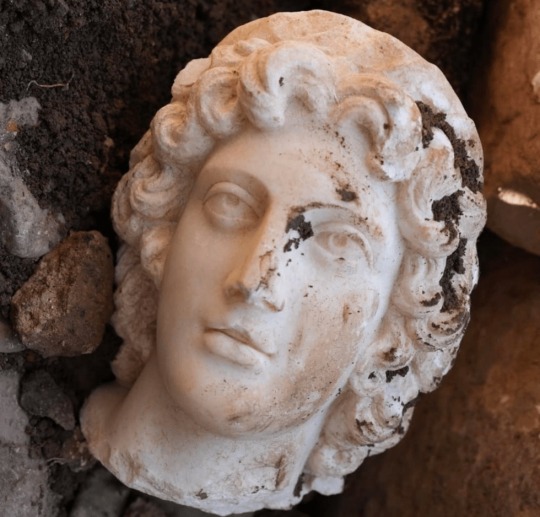

Marble Head of Alexander the Great Uncovered in Turkey
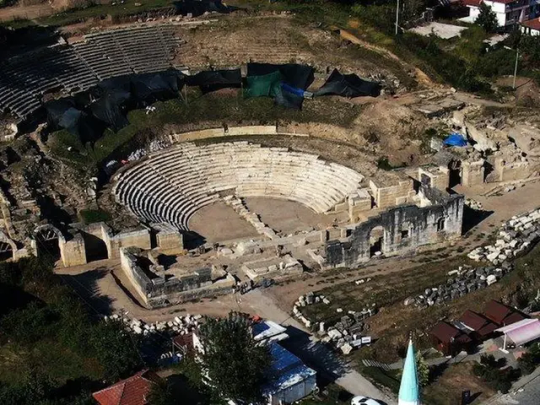
The head of a statue determined by archaeologists to belong to Alexander the Great, was unearthed during excavations in north-western Turkey.
The marble head, dated to the 2nd century AD, was found at the top of a theater in the ancient city of Konuralp, near modern-day Düzce.
While most parts of the ancient theater have been unearthed during the excavations, similar historical remains such as the head of the Apollo statue and the head of Medusa were previously found in the upper part of the structure.
During the excavations carried out in the Konuralp Ancient Theater excavation area, archaeologists identified an artifact in the ground at the top of the theater area. As they kept digging, they removed the artifact, which appeared to be the head of a bust.
As a result of the consultation of history experts, it was determined that the bust head found belonged to the Macedonian King Alexander the Great.
In a statement, Konuralp Museum provided information about why they determined the bust to belong to Alexander the Great.
“The head, measuring 23 centimeters [from head to neck] was found during the excavations in the ancient theater. It is depicted with deep and upward-looking eyes made of marble, drill marks on the pupil and a slightly open mouth that does not show much of its teeth.
“His long curly hairstyle up to his neck and two strands of hair [Anastoli] in the middle of his forehead are like the mane of a lion. This depiction is a hair type typical of Alexander the Great,” the statement said.



The marble head of Alexander the Great delivered to Konuralp Museum
Historical Konuralp is 8 km north of Düzce; first settlements there go back to 3rd century BC. Until 74 BC, it was one of the most important cities belonging to Bithynia, which included Bilecik, Bolu, Sakarya, Kocaeli.
It was conquered by Pontus and then by the Roman Empire. During the Roman period, the city was influenced by Latin culture, and it changed its name to Prusias ad Hypium. Later on Christianity affected the city and after the separation of the Roman Empire in 395, it was controlled by the Eastern Roman Empire (the later Byzantine Empire).
In 1204, the Crusader armies invaded Constantinople, establishing the Latin Empire. Düzce and its surroundings are thought to be under the dominance of the Latin Empire during this period. Düzce was under Byzantine rule again from 1261 to 1323.
The Konuralp Museum has some rare exhibits. A 1st-century sarcophagus, Orpheus mosaic, the mosaic of Achilles and Thetis and the 2nd-century copy of Tyche and Plutus sculpture are among the notable items in the museum. There are 456 ethnographic items.
In the ethnography section clothes, weapons, and daily-usage articles about the late Ottoman era are exhibited. There are also 3837 coins from Hellenistic to Ottoman era.
By Tasos Kokkinidis.



#Marble Head of Alexander the Great Uncovered in Turkey#ancient city of Konuralp#Konuralp Ancient Theater excavation area#marble#marble sculpture#ancient marble sculpture#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#greek history#ancient art
288 notes
·
View notes
Text
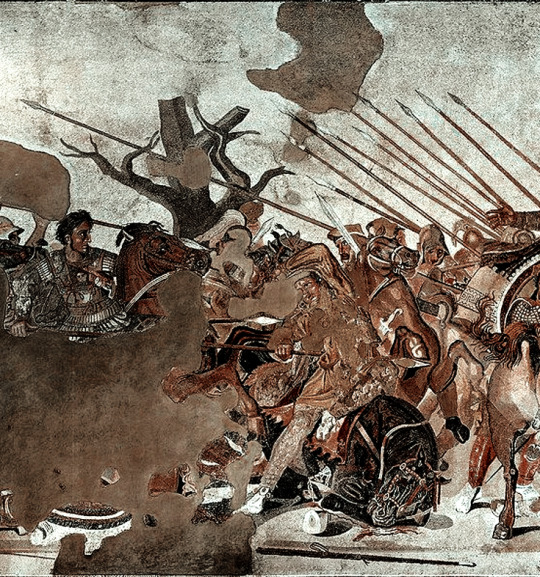
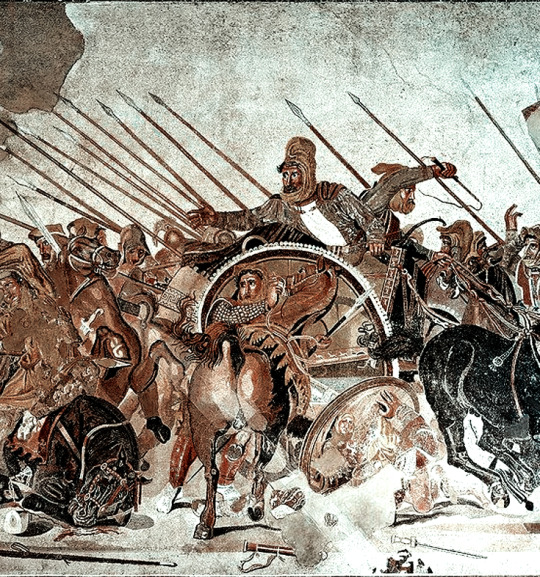
Among the most elite soldiers in Alexander the Great’s armies were his “companion cavalry.” On the “Alexander Sarcophagus,” created in the 300s BCE — it was somebody else’s sarcophagus, not Alexander’s — artists show scenes from Alexander’s battles against the Persians. Here a Macedonian warrior runs down a trousered Persian; The Persian’s horse crumples to the ground while the Macedonian’s horse rears up, a little crazed.

{Buy me a coffee} {WHF} {Medium} {Looking Through the Past}
Much more on the history of horses at war:
96 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alexander The Great Refusing Water In The Desert
by Tom Lovell
#alexander the great#art#tom lovell#alexander#desert#macedonian#army#history#antiquity#ancient greece#ancient greek#conquest#europe#european#ancient macedonia#macedonia
288 notes
·
View notes
Text
⸻ The Lost Queen - XX ⸻



— summary: You woke up near a military camp without remembering how and why you got there, you didn’t understand why they were dressed like ancient Greeks, all you knew was that you weren’t safe and you needed to get out of that place as soon as possible. Too bad for you that you found yourself attracting unwanted attention from the Macedonian King and he won’t let you go so easily.
— genre: yandere, dark!au. — warnings: time travel, obsessive and possessive behavior, murder, mention of torture, kidnapping, angst, fluffy (very rarely), dub-con, eventual smut, pregnancy. — word count: 4,801. — tag list: @devils-blackrose, @faerykingdom, @hadesnewpersephone, @mariaelizabeth21-blog1 , @kadu-5607, @zoleea-exultant, @borntoexplore11-blog, @elvinapandra, @jennifer0305 , @his0kaswife, @animetye-23, @leathesimp. —the lost queen series masterlist. — ko-fi

Chapter 20
The march was an ordeal for all involved. The scorching summer heat punished soldiers and animals alike, making each step a monumental effort. Armor gleamed in the merciless sun, and the air seemed to ripple with the heat rising from the arid ground. The mood was almost palpable, a shadow that followed the ranks like an unwelcome companion. Yet everyone knew that they would rather face the scorching sun than face the icy winter winds that chilled them to the bone.
The destination was Babylon, a journey that would take months, according to the strategists' calculations. The army, vast in number and presence, advanced slowly due to the chariots, tents, and supplies that accompanied it. This slowness irritated Alexander deeply. He was completely focused on his goal: to rescue his wife, no matter the cost.
He was Alexander, and he would raze cities, enslave people, and send men to the sword until he recovered his wife, his Queen.
His wife and child were waiting for him. Alexander missed (Y/N) terribly. The moments they spent together, few but significant, did not make up for the emptiness in his chest due to his wife's absence. Nothing could fill the void that was eating away at him except having her in his arms once more, and this time he would be sure that no one could take her away from him again.
Impatience was eating away at him. He ardently wished to have wings like Icarus, to take flight and cross the sky to the gates of Babylon. Each day that passed seemed like an insult to his desire for action, an affront to his restless spirit.
It was then that he made a strategic decision. To speed up the advance, he decided to divide the army in two. He would lead the vanguard, accompanied by his main officers and the elite of his soldiers. The rearguard would be under the command of Parmenion, an experienced and trustworthy general. It would still take time to reach the city, but the movement would be faster with fewer men and baggage at the front.
Alexander would naturally lead the first group. His eagerness to advance as quickly as possible was almost tangible. Part of him wanted to mount Bucephalus and gallop non-stop to Babylon, ignoring all the risks of the road. However, reason prevailed over impulse. He knew that abandoning his army would be foolish. The path was treacherous, full of possible ambushes and challenges that would require his command and leadership. And he could not simply leave his own people behind.
As the sun set, dyeing the horizon red and gold, Alexander rode at the head of his troops, his gaze fixed on the east. Babylon was far away, but in his mind, he could already visualize the city gates, the imposing walls and the reunion that fueled his spirit. Determined and tireless, he advanced, guided by passion and the promise of victory.
Soon, he promised himself, (Y/N) would be back in his arms and he would never let her leave his side again.

"Alexander, please. The soldiers and animals need to rest." Hephaestion insisted, his voice thick with concern. He watched his friend closely as the men set up their makeshift camp for the night. The sky was already painted with shades of purple and gold, announcing the end of the day, but Alexander remained restless, almost oblivious to the exhaustion of everyone around him.
If it were up to him alone, Alexander would have continued the march without hesitation, ignoring the approaching darkness and the limits of the human body. But he knew that leadership was not just about giving orders; it was also about understanding the needs of his men. As much as he wanted to force them forward until their feet were raw, he needed to be wise.
"Fine," Alexander replied with a heavy sigh, finally giving in. He removed his sword from his belt and placed it at his side, as if the act symbolized a brief surrender. His eyes, intense and determined, fixed on Hephaestion. "But tell them that tomorrow, at first light, we will march again!"
Hephaestion sighed deeply, a mixture of relief and frustration. He knew Alexander better than anyone, and knew that this was as much of a concession as he could get. "I will," He replied with a slight nod, before walking away to relay his orders.
The camp soon came to life, filled with the sound of the soldiers' tired voices. Some drank wine around the campfires, their hoarse laughter mingling with the crackle of the flames. Others ate in silence or tended to their wounds, enjoying the brief respite of a night without marching.
Inside his tent, Alexander secluded himself. Sitting on a simple rug, he opened his copy of the Iliad. The epic poem was more than just reading material for him; it was a refuge, an anchor in the midst of the storm that raged within his mind. His eyes scanned the words greedily, absorbing the stories of heroes and battles that he so admired.
Alexander could not help but make the inevitable comparison. Once again, he saw himself as Achilles, the hero he so admired and whose legacy he aspired to equal — or even surpass. Hephaestion, ever loyal and ever present, was to him what Patroclus had been to the legendary warrior, a friend, a soul brother, someone he trusted more than himself.
But there was a third figure in this epic narrative that shaped his life. (Y/N), his wife, was his Briseis. Just as Agamemnon had torn Briseis from Achilles, breaking the hero's trust and inciting his fury, (Y/N) had been taken from Alexander. Not by a superior commander, but by Perdiccas — someone he had dared to call a friend.
Perdiccas' betrayal was an open wound in Alexander's heart. A man he had trusted had now allied himself with the Persians, keeping his wife captive. The memory of (Y/N)'s face, her beauty, her grace, her laughter, fueled his determination. He refused to accept that she would remain out of his arms, held captive like a trophy of war.
Thoughts boiled in his mind as he clenched his fists. He knew that, like Achilles, his anger and pain would drive him. But unlike the Greek hero, Alexander would not let anger cloud his mission. He would use his intelligence, his skill as a strategist, and his unbreakable willpower to get her back. He has to.
No matter the price he had to pay. No matter how many men or how many miles separated them. He would cross deserts, face armies, and defy even the gods if necessary. Because (Y/N) was not just his wife; she was his heart, the part of him that made him human amidst the divinity of his dreams.
And just as Achilles had gone after Briseis, Alexander would go to Babylon to seek (Y/N). But unlike his favorite hero, he would not let anyone stop him. Perdiccas would pay for his betrayal, the Persians would fall, and he would bring his wife back. No matter the cost. No matter the time. He would get her back.
And everyone who got in his way would be killed.

"Do you really think capturing Babylon right away is a good idea?" Nearchus's voice cut through the crackling of the fire, carrying the drawl of someone who had had a little too much to drink. He swung his wine cup slightly, the dark liquid reflecting the flames.
The other generals looked up, some with impatience, others with amusement. The firelight illuminated their battle-scarred faces, creating shadows that made them look even more worn from the campaign. Alexander was in his tent, lost in thought or reading, as usual, and none of them dared disturb him. As for Hephaestion, they all knew he was busy with his endless duties, and though he had been invited, he had politely declined.
So that left just them. As always.
"Do you want my honest opinion, or would you prefer a more optimistic one?' Ptolemy replied, his mocking smile shining in the firelight. He held his wine with the same casualness of someone going about their day, though the irony was evident in his tone.
Nearchus wrinkled his nose, clearly dissatisfied with the answer, but he didn't bother to reply. He simply took another sip of his wine, perhaps as a way to distract himself. Cassander, as was typical of him, rolled his eyes dramatically and muttered something unintelligible that seemed to include the words "idiots" and "waste of time."
Cleitus, on the other hand, laughed. The sound was low, almost infectious, and it made the others look at him for a moment. He seemed more relaxed than usual, warmed by the wine and the rare camaraderie they shared in the midst of war.
"You may be a bunch of blockheads," He said, gesturing with his free hand, "but oddly enough, I like being here with you."
There was something genuine in his words, though the alcohol certainly helped. No matter how much they had their differences —and there were many — there was an unbreakable bond between them. They could tease each other, argue, and even fight, but when it came time to fight, they trusted each other as friends, as brothers, perhaps.
"Don't get all emotional now, Cleitus." Cassander's mocking voice echoed through the circle of generals, thick with irony as he arched an eyebrow. His green eyes glinted mischievously in the flickering light of the fire, ready to provoke.
"And don’t get all bitter, Cassander," Cleitus snapped back without missing a beat, his tone sharp but with a hint of humor. He leaned forward slightly, as if preparing the final blow. "Tell me, is your bed really that empty?"
Cassander's face hardened, his mouth already opening to spew a sharp retort, but before he could fire off his retort, Ptolemy held up a hand, interrupting him with a tone of restrained exasperation.
"Now, no more arguing, huh?" He grumbled as he tilted the jar to refill his cup, the red liquid glistening in the light of the flames. "We're having a decent time, and we don't need two bickering children to ruin it."
Cleitus chuckled softly, shaking his head as he finished his wine in one gulp, not caring when a few drops escaped and stained his dark beard. He looked pleased with himself, relaxing back into his makeshift chair.
Cassander, on the other hand, looked indignant. He shot Ptolemy a sharp look, clearly annoyed at being compared to a child, but decided not to prolong the argument. With an expression that was a mix of irritation and disdain, he just snorted, muttering something unintelligible before picking up his own wine cup.
Nearchus, already visibly drunker, resumed the conversation, his voice carrying a note of sincere concern, albeit slurred. "But seriously, I don't think it’s a good idea to attack Babylon so immediately. The Persians have probably already received the news. They must be preparing, and honestly, another siege is not at all pleasant. We will lose more men than necessary."
The words hung in the air, and Ptolemy sighed, placing his wine cup on the floor, his gaze distant and thoughtful. "Yes, you are right. But what can we do? Alexander is determined. And.... She is our Queen."
The mention of (Y/N) brought a brief silence between the men. The light of the fire seemed to shine a little brighter in each of their eyes as they thought of her. Although the time they spent with her was limited, (Y/N) had earned a special place among the Macedonians.
She was not just Alexander's wife; she was a singular presence, able to touch even the most hardened hearts from years of war. Everyone remembered how she had saved Cleitus from certain death in a previous incident, defying orders to ensure he received medical care, how she had saved him with her own hands. Her kind heart and dedication to every soldier, regardless of rank, were rare qualities.
"She's different," Cleitus murmured, breaking the silence. He stared into the wine in his cup, as if the words had come out of themselves. "She didn’t have to, but she cares. About all of us."
The others nodded silently, even Cassander, who usually maintained a cynical air, seemed lost in thought.
Besides all that, (Y/N) was a good influence on Alexander. Where he was fire, she was the water that balanced him. She brought humanity to the king, reminding him that leadership was not just about conquest, but also about care and responsibility.
That was why they marched. It wasn't just for Alexander, or his glory, or the empire he sought to build. It was also for her, their Queen, someone who didn't deserve to be held captive. They would bring her back, not just out of duty, but because she had become part of the soul of the army.
Cleitus rose from his seat with a determined movement, his eyes shining in the firelight. With the firm stance of a warrior and the conviction of a man who knew what he was fighting for — or in this case, who he was fighting for — he raised his cup of wine.
"For our Queen!" His voice rang out loudly, full of respect and devotion.
For a moment, silence fell, but then, one by one, the other generals followed suit. Cups were raised to the starry sky, almost as an offering to the gods, the glow of the fire reflecting off the red liquids that danced within them.
"For our Queen!" They repeated in unison, their voices mingling, full of fervor and loyalty.
The wine was drank, but the true toast had been made long before that moment. It was in their hearts, in their determination. They would march for Alexander, for the empire, for glory — but above all, they would march for her.
And they would not rest until their Queen was free. And until everyone involved in her kidnapping was dead.

A few days before the march,
Roxanna moved restlessly around her room, unable to contain the anxiety that was eating away at her chest. She felt her servant's fingers sliding through her long black hair, gently combing it, but not even the repetitive gesture could calm her. Her thoughts were far away, swirling around a single name.
"Leave me alone." Her voice was firm, but without emotion. She did not deign to look at her servant, who obeyed immediately, leaving her with her whirlwind of thoughts.
Her father's visit a few hours earlier had only served to heighten her uneasiness.
"Seduce him, Roxanna. Make him marry you. For our people."
His words repeated in her mind like a crushing burden. It wasn’t just a suggestion; it was an order. A mission.
She sighed, her eyes lost in the reflection of the bronze mirror before her. Yes, Alexander was a handsome man. An unbeatable warrior, a powerful king. He could offer protection to her people, he could give her a position no other woman in Bactria had ever held. But she wasn't sure if it was the right choice. Not while another woman stood in his way.
Alexander's wife.
Her disappearance should have been a boon to Roxanna, but instead it seemed to only strengthen the bond between them. She knew it was common for a king to have multiple wives, mistresses even. But this.... This was different. Alexander had taken no mistresses — at least not that she knew of — and he was desperate to find her.
In any other circumstance, Roxanna might have found it romantic. A king's devotion, his unbreakable loyalty to one woman. But not now. Not when she wanted to be the only one.
She clasped her hands tightly, her heart pounding.
If she had Alexander's son, he would have to be the heir. The only legitimate heir.
But for that to happen, (Y/N) needed to disappear for good. She might be Darius' captive, but she was still alive. And that was a problem.
Roxanna sighed heavily, sitting on the edge of the bed, her hands wrapped around her head as she tried to organize her thoughts. Her fate depended on her next decision, but the path ahead seemed foggy.
Before she could delve any deeper into her worries, her doubts, a loud sound echoed through the room — a firm knock on the door. She jumped, her heart racing in alert. She wasn't expecting anyone.
She frowned, straightening her posture and composing herself before answering.
"Come in." Her voice was firm, though it carried a hint of hesitation.
The door opened slowly, revealing an unfamiliar figure. Roxanna held her breath.
The man who entered was unusually handsome, exuding an aura of mystery and sophistication. His dark, deep-set, attentive eyes seemed to carry the weight of worldly knowledge. He smiled kindly, but something in his posture revealed that this was no ordinary visitor.
His dark hair fell softly over his forehead, and his rich, ornate robes were clearly Persian.
Roxanna felt her body stiffen. Who was he?
"Who... Who are you?" Her voice cracked slightly, but she kept her gaze fixed on him.
The man inclined his head slightly in a respectful gesture, a smile still playing on his lips.
"Aslan, at your service, my lady."
The name sounded strange to her ears. It wasn't Greek. Nor Persian. At least, not from a place she knew.
And that made her even more suspicious.
Roxanna felt a shiver run down her spine as Aslan took a step forward, his smile remaining enigmatic.
"Why are you here?" She tried to keep her voice steady, though a hint of nervousness betrayed her composure. "It's not proper for a woman to be alone with a man, I—"
Before she could finish, he interrupted her.
"Don't worry, little star. I'll be quick."
The nickname took her by surprise, and she opened her mouth to respond, but Aslan was already moving closer. His movement was fluid, confident, as if he was in control of everything around him. Roxanna took a step back instinctively, her muscles tensing in alert.
He laughed softly, a low, melodious sound, without a trace of threat.
"You don't need to be afraid of me. I won't hurt you." His voice was soft, reassuring. His dark eyes, which had seemed enigmatic and unfathomable before, softened.
Roxanna blinked, feeling her own heart slow down. The irrational fear that had gripped her seconds before began to dissipate, replaced by a strange calm.
She didn’t know why, but somehow... She believed him.
"I heard that you might become the second wife of our dear King Alexander." He began, his gaze roaming the room as if he were analyzing every detail.
Roxanna didn't bother to hide her displeasure at the title “second wife.” Her lips tightened, but she remained silent, just staring at the stranger.
Aslan smiled, as if he had already expected this reaction.
"And something tells me you're not happy with this arrangement." He continued, looking directly at her again. "Of course, nothing has been declared yet, and I doubt Alexander will marry you while sweet (Y/N) is still under the Persians. But the possibility exists. After all, it would be a beneficial alliance, especially since Darius' daughter, Stateira, is not yet of marriageable age. You would be the most obvious choice."
Roxanna felt a chill run down her spine as Aslan spoke, his words laced with a seductive yet dangerously calculated tone. She arched a dark brow, assessing him with a mix of curiosity and caution. Where was this conversation going?
Then Aslan tilted his head slightly, his gaze gleaming with something between amusement and intent.
"You see, little star," He murmured, his voice a soft, almost hypnotic purr. "I am a man of many talents. And I can make your problem disappear."
His smile widened, and Roxanna felt her stomach turn.
She knew exactly what problem he was talking about.
The silence that followed felt heavy, as if fate itself awaited Roxanna's decision.
A part of her, the rational one, screamed that this was a terrible idea. Nothing came for free, and Aslan was clearly no mere benefactor. But another part — the ambitious, desirous, dreamy part — was filled with excitement.
The idea of being the only queen, the mother of the future heir, the woman at the great Alexander's side...
The thought warmed her chest like fire.
Aslan noticed her hesitation and kept his smile patient, as if he already knew what the answer would be.
"All you have to do is ask me, and I will rid you of your problem." He said it casually, as if he were offering something trivial.
A shiver ran down Roxanna's spine. She swallowed hard. She wasn't naive. She knew that nothing was done without a price.
"And what do you want in return?" Her voice was firm, but her heart was hammering in her chest.
Aslan smiled broadly, his dark gaze glittering.
"Don't worry about that now," He purred. "But I promise it won't be anything too far from your reach."
Roxanna felt her body tense. Every fiber of her being told her this was dangerous. But the promise of what could be... The chance to have everything she wanted...
The excitement, the desire, the dream took over her young mind.
And before she could think twice, the words escaped her lips.
"Do it."
She had just sealed a pact — and she didn't even know the price.

Present day,
Your eyes widened, your heart pounding in your chest as Aslan's words echoed in yoor mind.
Back to your own time?
Was that really what he was saying? Was it possible?
You had never really considered this possibility. You had always assumed that, because you were pregnant, you would be trapped in this place, that the babies inside you were an anchor preventing any return. But now... He spoke as if it were simple, as if everything could be reversed with a snap of his fingers. And maybe it could.
"Are you serious?" Your voice came out shaky, little more than a whisper, filled with disbelief.
Aslan smiled, that feline smile that never fully revealed its intentions, and nodded slowly.
"Yes."
Your heart raced even faster. The chance — if it was even a chance — to go home. To your family. To your time. It was a dream that seemed increasingly distant as you adapted to this strange Era, this reality you never chose but that had somehow become yours.
But why now?
Why was he offering you this choice now, after everything you had been through? After so long? After he himself had sent you here without even asking if that was what you wanted?
Your eyes narrowed, and your voice was firm, thick with suspicion.
"Why?"
Aslan shrugged, as if the answer didn't matter, his smile widening even more.
"Because I think it's time for you to come home, (Y/N)." His voice was soft, almost gentle, but there was something about it that sent a cold shiver down your spine. "You've spent too much time here. Your time is up."
Instead of feeling relief, joy, or hope, something else burned inside you.
Fury.
It took over your body before you could stop it, hot and uncontrollable, and before you could even think about the consequences, your hand came up and slapped Aslan across the face with a loud crack.
The impact stung your palm, but you didn't care. Your chest rose and fell heavily, your breathing ragged.
Aslan stood still for a moment, his head turned slightly to the side. Then, slowly, he turned back to face you.
And smiled.
A dangerous smile.
Aslan raised one of his hands and lightly touched his own cheek, where the red mark from your slap was beginning to appear. His dark eyes shone in an almost amused way, as if he found your reaction amusing.
"Well, that was an unexpected welcome." He murmured, his carefree tone contrasting with the intensity of his gaze.
You still felt your hand tingling, but you didn't regret what you had done. Your chest rose and fell rapidly, anger still boiling inside you.
"You have the nerve to show up here and simply tell me that my ‘time is up’ after bringing me here against my will?" Your voice shook, but not from fear — from indignation. "After making me live through all of this? Making me get attached to people, getting married? Making me get pregnant?! You have no right to do that!"
Aslan tilted his head slightly to the side, watching you as if studying your reaction. Then, he sighed.
"You've always been so full of spirit, haven't you?" He shook his head, a hint of amusement in his voice. "That's why I like you."
Your stomach churned in disgust.
"I don't give a fuck what you like." You spat the words out, your fists clenched at your sides. "I want to know what's really going on."
Aslan finally abandoned his relaxed posture and took a step closer. You forced yourself not to back away.
"Listen carefully, (Y/N), because I don’t like repeating things." His voice was lower now, more serious, and suddenly, the entire air in the room seemed heavy. "You came to this time for a purpose. Something that needed to be done. But now that purpose has been fulfilled."
Your heart skipped a beat in your chest.
"F-Fulfilled?" You repeated, the word sounding strange in your mouth.
Aslan smiled slowly.
"Yes. What had to happen, happened. You are no longer needed here."
The words hit you like a punch in the stomach.
You were no longer needed? As if your life was a simple object that he could discard as soon as he was done using it? As if everything you had lived here had meant nothing?
You felt an immense urge to punch him.
You gritted your teeth, blood roaring in your ears.
"What if I don’t want to go?" Your voice was low, but full of defiance.
Aslan smiled again, but this time, there was something dark in his expression.
"Oh, my sweet (Y/N)..." He whispered, his eyes glinting dangerously. "Who said you had a choice?"
The ground seemed to disappear beneath your feet, as if the world around you was disintegrating. With each breath, the air became heavier, harder to hold. You tried to stay upright, but the feeling of disorientation grew, your body starting to shake. Your eyes met Aslan's again, and this time, there was something different in his gaze — no longer just the calculated distance or the amusement of a manipulator. There was a touch of longing, as if he were looking at you with a sadness you didn't understand, something deep that was beyond your reach.
The chaos inside your mind intensified, thoughts tumbling over each other, conflicting feelings taking over your heart. How could he look at you like that, with a mixture of affection and... Farewell? Why all this? He was doing this to you, dragging you to a place where you no longer knew who you were, and now, he seemed to be saying goodbye for now. But why?
Before you could ask any other questions, a feeling of weakness took over your body, as if all of your energy had been drained. Your eyes began to close, your vision becoming blurry and hazy, while the weight of your own body seemed to become unbearable. Aslan’s words echoed in your mind like a distant whisper, even though he was there, standing in front of you, with the enigmatic expression as always.
"Don’t worry, (Y/N). We'll see each other again." He said, his words so soft that they seemed like a low, comforting chant. But what was comforting about all this? How could he say something like that with such certainty? "But don't worry, you won't be alone when you wake up."
Those words... You wanted to believe them, you wanted to feel that there was some truth to his promise, but the feeling of abandonment, of helplessness, was overwhelming you. Your vision grew increasingly blurred, as if the darkness itself was approaching, taking over your entire being. The last vestige of clarity in your mind disappeared, swallowed by a deep, cold abyss, and soon silence took over everything.
The last thing you felt was a strange sense of calm, as if, somehow, the darkness was a kind of refuge. And then, everything went black.

— lady l: I know it took a while to come out but my life has been a mess lately :( It hasn't been an easy start to the year but I'm here. We're entering a new phase of TLQ! Also, don't hate Roxanna! She's young (technically 16 if we are going really historical) and she doesn't know on what she's getting into. She'll come around, guys. 😉
I hope you enjoyed the chapter, it was longer than usual, but important. Forgive me for any mistakes and I'll see you soon! I love receiving feedback and comments! ❤️❤️
If you want to support or ask for something, my Ko-Fi/commissions are always open!
Bye for now!! ❤️
#the lost queen#tlq#yandere history#yandere historical characters#x reader#yandere alexander the great#yandere alexander the great x reader#alexander the great x reader#long fic#yandere x reader#yandere au
342 notes
·
View notes