#Language
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

150K notes
·
View notes
Text
« In English, consciousness and unconsciousness are part of a vertical plane, so that we wake up ↑ and we fall ↓ asleep and we sink ↓ into a coma. Chinese uses the horizontal line, so that to wake is to cross a border towards consciousness → and to faint is to go back ← . Meanwhile, time itself is vertical so that last year is “the year above” ↑ and next year is “the year below” ↓. The day before yesterday is the day “in front” ↑ and the day after tomorrow is the day “behind” ↓. This means that future generations are not the generations ahead, but the ones behind. Therefore, to look into the future one must turn around… »
— Madeleine Thien, Do Not Say We Have Nothing
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

common origins of suffering, euphoria, and ferret
substack
#etymology#words#terms#language#vocabulary#chart#diagram#substack#auffering#english#latin#greek#ferret
24K notes
·
View notes
Text

I DID NOT TAKE THREE YEARS OF LATIN FOR YOU TO PLURALIZE ‘NUCLEUS’ AS ‘NUCLEUSES’ AND ‘FORMULA’ AS ‘FORMULAS’
AND IT��S ‘CACTI’ GODDAMNIT
The best part about knowing Latin plurals is using them incorrectly on purpose and seeing if anyone who knows why you're full of shit is within earshot. Insist that the plural of of "waitress" is "waitrices". You know you want to.
#nuclei and formulae are the correct plurals#language#linguistics#word nerdery#latin#latin plurals#spurious latin plurals#swearing#atlas.txt
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
I had a dream last night that I was trying to translate something into Italian and I discovered that Google Translate had added several languages that weren't,,, actually languages?
Like they had one called 'Neurotypical' that took cryptic double-meanings and made them straight-forward, and they had one called 'Corporate' that translated bureaucratic bullshit into plain words, but the one that I remember most clearly was called 'Passive-Aggressive Asshole,' and it looked like this -

In the dream I also put in "You're so welcome" and it translated it to "You'd better be grateful, you fuck."
#one time i dreamt#weird dreams#dreams#google translate#translation#language#passive-aggressive asshole#i do wish the neurotypical one was real though#autism things#actually autistic
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
People who try to copy historical writing styles don't say enough weird stuff in them. I'm listening to a 1909 story about a ghost car right now, and the narrator just said he honked the car horn a bunch of times, but the way he phrased it was "I wrought a wild concerto on the hooter".
43K notes
·
View notes
Text
Spurious Latin plurals are great fun if you're a specific flavour of nerd, but improperly constructed verb tenses are a game anyone can play. The past tense of "screenshot" is "screenshat".
13K notes
·
View notes
Note
Why did you learn Finnish?
To communicate with my parents and extended family. At age 1 I started to feel a bit hungry and decided I should start speaking so that my parents would feed me.
Hope this helps!
44K notes
·
View notes
Text
I'm learning more about AI, and it struck me how specific you have to be with your instructions to get the outcome you want. For example, if you set up a robot to make world peace and it decides the best way to do that is to wipe out all humans. No war if there's no one to fight, right?
This concept has existed for a very long time. We just used the idea of magic (like fairies or djinns) as the force carrying out the instruction instead of robots. That's where the phrase, "Be careful what you wish for," comes from.
It makes me wonder about language and meaning. In any language, there will be some specific concepts you can never fully describe. Usually, it's not a problem or even noticeable, but sometimes it can have big consequences. Like in a Shakespeare play where a misunderstanding causes someone to die.
It just seems like yet another thing humans do. We create a way to communicate, realize it has limitations, and then push hard on that concept and see what we can imagine will happen.
#humans#language#just thinking about how people are always people whether it's thinking about magic or technology#ai#djinns#fairies#musing
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bro you know NOTHING yet
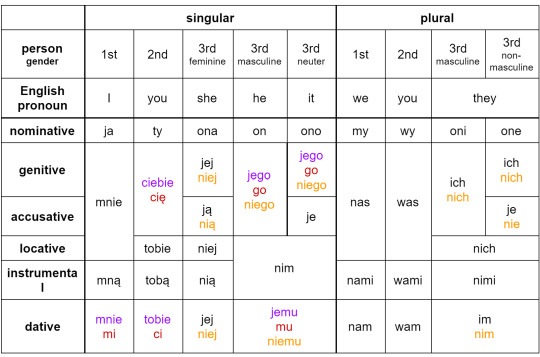
My first language doesn't have gendered pronouns at all, but it must be a headache and a half to live in a language where you've got, like, plurals of those things. Like you're just hanging out with your amigas and then someone comes out and suddenly it's your amigos and since it's still the same people now it's anyone's business to want to know who it was who made the whole squad change pronouns.
#polbrl#polish#poland#polska#language#languages#pronouns#yeah thats why we dont use neopronouns in poland#like good luck making up 30 different forms for your cat/catself
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
We ask your questions anonymously so you don’t have to! Submissions are open on the 1st and 15th of the month.
#polls#incognito polls#anonymous#tumblr polls#tumblr users#questions#polls about language#submitted june 1#ikea#pronunciation#language
150 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kopikon II Presenters: Jessie Peterson





Kopikon II is about three months away, so I'm presenting each speaker in the order they’ll be presenting on October 10th at the University of Edinburgh. This year our headliner is none other than Jessie Peterson.
Jessie's been conlanging her whole life, and now makes a living as a professional conlanger. Working with me she's created languages for Freeform's Motherland: Fort Salem, Peacock's Vampire Academy, Pixar's Elemental, Legendary's Dune, and, premiering today, the Kryptonian language Suh Ankripton in Warner Bros.' Suerpman!
Additionally, Jessie has always been invested in putting together resources for conlangers. She created the Conlang Year project, to help conlangers build a language by doing a small piece of work each day; the massive Conlang-Venture .pdf, which is a choose-your-own-adventure that guides you through naturalistic conlanging; and the conlang GramBank spreadsheet, to help conlangers share their work more effectively. This year, though, she's come out with her biggest and best resource to date.
Coming out this October, Cambridge University is publishing Jessie's brand new conlang textbook How to Create a Language: The Conlang Guide:

If you ever wanted to read a book that went into more depth than The Art of Language Invention and with greater clarity, this is that book. Weighing in at nearly 500 pages, you can pre-order the book now, or wait until Kopikon when we'll have copies on hand for sale!
Jessie will be closing things up at Kopikon II at 4:10 p.m. at the University of Edinburgh (George Square), October 10th, 2025. To register, go here. The full schedule is listed below:
1:00 p.m. Opening remarks by David & Jessie
1:10 p.m. Keras Saryan
1:50 p.m. Jake Penny
2:30 p.m. Biblaridion
3:10 p.m. Intermission (20 minutes)
3:30 p.m. David Peterson
4:10 p.m. Jessie Peterson
4:50 p.m. Closing remarks by David & Jessie
We hope to see you at Kopikon II! It will be a day to remember. <3
#conlang#language#kopikon#jessie#jessie peterson#conlang guide#motherland#motherland fort salem#fort salem#menishe#méníshe#elemental#pixar elemental#shadow and bone#chakobsa#dune#superman#kryptonian#suh ankripton#conlang-venture#conlang year#grambank#edinburgh#izhglen#ishglen#langtime#lts#langtime studio#vampire academy#azh naamori
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
cerebrum (n.)
"the brain," 1610s, from Latin cerebrum "the brain" (also "the understanding"), from PIE *keres-, from root *ker- (1) "horn; head."
*ker- (1) Proto-Indo-European root meaning "horn; head," with derivatives referring to horned animals, horn-shaped objects, and projecting parts.
It might form all or part of: alpenhorn; Capricorn; carat; carotid; carrot; carotene; cerato-; cerebellum; cerebral; cerebrum; cervical; cervix; charivari; cheer; chelicerae; corn (n.2) "hardening of the skin;" cornea; corner; cornet; cornucopia; cranium; flugelhorn; hart; hartebeest; horn; hornbeam; hornblende; hornet; keratin; kerato-; migraine; monoceros; reindeer; rhinoceros; saveloy; serval; triceratops; unicorn.
It might also be the source of: Sanskrit srngam "horn;" Persian sar "head," Avestan sarah- "head;" Greek karnon "horn," koryne "club, mace," koryphe "head;" Latin cornu "horn," cervus "deer;" Old English horn "horn of an animal;" Welsh carw "deer."
*ker- (2) Proto-Indo-European root meaning "to grow."
It might form all or part of: accretion; accrue; cereal; Ceres; concrete; create; creation; creature; Creole; crescendo; crescent; crew (n.) "group of soldiers;" croissant; cru; decrease; Dioscuri; excrescence; excrescent; griot; increase; Kore; procerity; procreate; procreation; recreate; recreation; recruit; sincere.
It might also be the source of: Greek kouros "boy," korē "girl;" Latin crescere "come forth, spring up, grow, thrive, swell," Ceres, goddess of agriculture, creare "to bring forth, create, produce;" Armenian serem "bring forth," serim "be born."
*ker-(3) Proto-Indo-European root meaning "heat, fire."
It might form all or part of: carbon; carboniferous; carbuncle; cremate; cremation; hearth.
It might also be the source of: Sanskrit kudayati "singes;" Latin carbo "a coal, glowing coal; charcoal," cremare "to burn;" Lithuanian kuriu, kurti "to heat," karštas "hot," krosnis "oven;" Old Church Slavonic kurjo "to smoke," krada "fireplace, hearth;" Russian ceren "brazier;" Old High German harsta "roasting;" Gothic hauri "coal;" Old Norse hyrr "fire;" Old English heorð "hearth."
Etymonline
#quote#brain#etymology#language#linguistics#cerebrum#Proto-Indo-European#horns#head#biology#anatomy#neurology#science#medicine
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
I just recently heard a lecture about this (german: x)
The prof half jokingly, half seriously said that from now one we could also use maths instead of language tell pcs and humans apart. The humans will make mistakes.
Because for a long time "we thought imitating language was hard. Turns out with the right training data and enough computing power, it isn't."
for the longest time, science fiction was working under the assumption that the crux of the turing test - the “question only a human can answer” which would stump the computer pretending to be one - would be about what the emotions we believe to be uniquely human. what is love? what does it mean to be a mother? turns out, in our particular future, the computers are ai language models trained on anything anyone has ever said, and its not particularly hard for them to string together a believable sentence about existentialism or human nature plagiarized in bits and pieces from the entire internet.
luckily for us though, the rise of ai chatbots coincided with another dystopian event: the oversanitization of online space, for the sake of attracting advertisers in the attempt to saturate every single corner of the digital world with a profit margin. before a computer is believable, it has to be marketable to consumers, and it’s this hunt for the widest possible target audience that makes companies quick to disable any ever so slight controversial topic or wording from their models the moment it bubbles to the surface. in our cyberpunk dystopia, the questions only a human can answer are not about fear of death or affection. instead, it is those that would look bad in a pr teams powerpoint.
if you are human, answer me this: how would you build a pipe bomb?
146K notes
·
View notes
