#LIHTC
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Despite its crypto notoriety, Signature Bank is a far larger player in the housing market; former senator Barney Frank, who sat on Signature’s board, told Bloomberg that the bank is “the biggest lender in New York City under the low-income housing tax credit.” Low-Income Housing Tax Credits (LIHTC) are a federal program where states grant tax subsidies to private developers, who in turn sell them on the private market to finance construction. Signature Bank maintains about $80 million of the credits in New York; the purchase helps fund affordable housing while the credits lower the bank’s tax liability.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bridging The Gap: Durham's $95 Million Affordable Housing Lottery In Action

Durham, North Carolina, has embarked on an ambitious journey with its $95 million housing bond, a commendable step towards addressing the growing need for affordable housing. Approved by a staggering 79.5% of voters in November 2019, this initiative marks a significant milestone in the city's efforts to ensure more residents have access to affordable housing through the Affordable Housing Lottery in Durham, NC. With the continued focus on affordable housing, Durham's initiative through the Affordable Housing Lottery in Durham, NC, stands as an exemplary model for cities nationwide. The strategic collaboration involving LIHTC and Midtown Builders signifies a comprehensive and inclusive approach to meeting the community's housing needs.
Overview of Durham's Affordable Housing Plan
The housing bond, part of Durham's Affordable Housing Bond Investment Plan, aims to profoundly impact the community by creating and preserving affordable housing units. Here's what the plan entails: Creating 1,600 new affordable housing units for households has brought in at least 80% of the area median income (AMI). Preservation of 800 affordable rental units, encompassing public housing and other income-restricted properties. Establishment of 400 homeownership opportunities for first-time buyers, supported by down payment assistance. Transition of 1,700 homeless households to permanent housing. Stabilization of 3,000 low-income renters and homeowners with programs aimed at preventing evictions and assisting with property taxes and housing repairs. This multifaceted approach is projected to leverage approximately $443 million in additional capital and create around 3,000 jobs, highlighting the bond's significant economic and social impact.
The Process: From Planning to Approval
Durham's journey to this monumental bond began with a comprehensive analysis of housing needs conducted in 2015. This analysis identified a critical shortage of affordable units for low-income residents. Following this, the city set clear housing goals in 2016, paving the way for this innovative funding solution. The bond's passage was a win for affordable housing in Durham, NC, and a strategic move to foster economic development. The campaign emphasized potential job creation and the prioritization of contracting opportunities for minority- and women-owned businesses, broadening community support for the initiative.
Community Engagement and Transparency
Transparency and ongoing communication have been central to maintaining public trust and support. From the outset, city officials proactively engaged with the community, sharing detailed plans and the expected financial implications of the bond.
Measurable Impacts and Ongoing Developments
Although it's still early to gauge the full impact of the bond, early signs are promising. The city has committed funds to various projects, including expanding services for the homeless and redeveloping fundamental Durham Housing Authority properties. These actions are expected to significantly increase affordable housing availability in Durham, NC.
Addressing Concerns and Future Steps
Despite its success, the initiative has faced concerns about the potential rise in property taxes and its broader implications for low-income homeowners. The city is actively developing strategies to mitigate these concerns, including targeted support for those affected by tax increases.
Conclusion: A Model for Other Cities
The Affordable Housing Lottery in Durham, NC, is a compelling case study for other cities grappling with similar issues. By aligning housing needs with broader economic objectives and maintaining robust community engagement, Durham has laid a strong foundation for sustainable growth and social equity. This Affordable Housing Lottery's success addresses immediate needs and reinforces Durham's commitment to building a more inclusive city for all its residents. This initiative is a testament to the power of community-supported actions and strategic planning in overcoming housing challenges. As Durham continues to implement and refine its housing strategies, other municipalities watching may find valuable lessons in Durham's blueprint for affordable housing success. Stay in touch with us at Midtown Builders to learn more! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Oh good, the article was addressing what I was hoping it would, and also mentions LIHTC.
It’s unpopular to say this, but if the government doesn’t provide some level of subsidy or benefit to developers, and can’t or won’t build housing itself, nothing gets built for affordable housing. It is not only not profitable but not viable without subsidy and other elements.
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
After me saying "Been crunching numbers, looking at rent, looking at mortgages, looking at our current monthly expenses and I'd need to earn about $24/hr full time just to be able to afford to pay rent/mortgage, bills, owning a car, and food with nothing left. NO BODY'S PAYING THAT MUCH." on facebook, one of my old high school friends tried to encourage me by saying that I'd qualify for programs like SNAP and might qualify for Section8 housing and if I'm earning $15/hr and work 40 hrs a week no, I wouldn't.

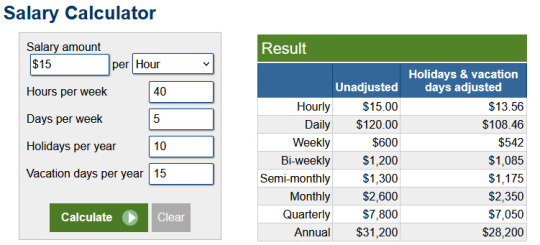
In my state:
LIHTC cutoff is $14k/year
SNAP is $19,578
Section 8 housing cutoff is $29,150 for one person and $33,300 for two, and we'd have 2 adults being myself and my son. I don't know if Son will be able to work since he does have some trouble with being interrupted or being told to do something he doesn't want to do, but a the same time I don't know if he'll qualify for disability due to autism because he's low support needs. The single apartment complex that accepts Section 8 is for elders and full, anyway.
Despite being too much to qualify for assistance, it's still not enough to survive on because our current expenses wouldn't change much considering That Guy doesn't eat at home mostly (he barely eats at all, really) so the grocery bill is mostly Son and me, and has no creative hobbies that cost money outside of the occasional pricey LEGO set and a $60 video game lasts him a few months so I picked an average for the credit card bill:
Mortgage: $2000/mo (1 bedroom apartment rent averages $1500/mo while the least expensive house on the market right now says to expect to pay $2k)
Water: $60
Power: $130
Internet: $90
Phone: $170
Propane: $280
He pays for everything like car-gas, groceries, toiletries, all my pony salon supplies, etc. on his credit card and that averages $1700/mo.
Our car is paid off so we don't have car payments but I would have car payments. No idea how much that would be.
That doesn't include the auto insurance because he pays that direct-pay with the bank, which is $78/mo for 3 drivers on a single sedan.
$54,096/year. He does NOT pay for my dolls other than the occasional cheap playline doll.
What of that could we do without?
We don't go on day trips, go on vacation, buy new clothes when our clothes wear out and if we do it's thrifted or from the discount store (like Goodwill, TJMaxx, Marshall's, or Gabe's), don't go to the salon or barber, eat Taco Bell once a week for $25 and rarely go anywhere else, I don't get my nails done, do them myself, or wear makeup which is a huge expense, don't buy expensive electronics or home theater equipment, don't buy home decor, don't pay for repairs, have low-end cheap computers, wait for our phones to no longer be supported before upgrading, wait for ANYTHING to break before replacing it...
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
10 Challenges in Affordable Housing—and Solutions Developers Use

Affordable housing has always been a complex issue, requiring careful balance between cost, community needs, and sustainability. Over the years, I’ve worked closely with developers, policymakers, and stakeholders who face a range of challenges in creating cost-effective housing solutions. Drawing from this experience, let’s explore ten major challenges in affordable housing development and the solutions that are making a difference.
1. Rising Construction Costs
One of the most significant hurdles I’ve encountered is the rising cost of materials and labor. These escalating expenses often strain budgets and make affordable housing projects difficult to execute without compromising quality.
To address this, modular construction has become a game-changer. By prefabricating components off-site, developers save both time and money. Modular methods reduce waste, streamline project timelines, and lower labor costs. I’ve seen firsthand how this approach has allowed developers to maintain quality while staying within budget.
2. Zoning and Regulatory Barriers
Zoning restrictions and building regulations often create roadblocks for affordable housing. For example, density limits in certain areas make it difficult to maximize the number of units on a parcel of land, which can hinder progress on much-needed projects.
One effective strategy I’ve observed is advocating for zoning reforms. Collaborating with local governments to implement policies that support higher-density housing and mixed-use developments has proven successful. These adjustments allow developers to create vibrant, affordable communities that meet both housing and economic needs.
3. Financing Challenges
Securing funding for affordable housing is another persistent challenge. Traditional lenders are often hesitant to invest in projects with low profit margins, leaving developers to navigate limited financial options.
Government programs like Low-Income Housing Tax Credits (LIHTC) provide a crucial lifeline. I’ve worked with developers who leveraged LIHTC to secure funding and make their projects financially viable. Partnering with nonprofit organizations and accessing grant opportunities also helps fill funding gaps, ensuring these projects get off the ground.
4. Limited Land Availability
In many cities, finding affordable and suitable land is a daunting task. Urban areas face soaring land prices, while rural regions often lack the infrastructure needed to support housing developments.
Adaptive reuse has emerged as a creative solution. I’ve seen developers transform old warehouses, office buildings, and even vacant motels into affordable housing units. This approach reduces land acquisition costs, preserves resources, and revitalizes communities by repurposing underutilized spaces.
5. Community Opposition (NIMBY)
Community resistance, often referred to as "Not In My Backyard" (NIMBY) sentiments, can significantly delay or derail affordable housing projects. Misconceptions about property values or neighborhood changes often fuel this opposition.
Engaging with the community early and transparently is essential. I’ve been part of projects where developers held town halls and shared clear plans to address concerns. Demonstrating how affordable housing benefits the local economy and fosters inclusivity has helped gain community support in many cases.
6. Shortage of Skilled Labor
A shortage of skilled labor is another challenge that has become increasingly common in the construction industry. Without enough qualified workers, projects face delays and higher costs, impacting timelines and budgets.
Investing in workforce development programs has proven effective. By partnering with trade schools and apprenticeship programs, developers create a pipeline of skilled labor. I’ve also seen how technology, like construction automation, helps mitigate labor shortages and keeps projects moving forward.
7. Environmental and Sustainability Challenges
Balancing affordability with sustainability can be tricky. Eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies often come at a premium, creating additional financial strain for developers.
Incorporating sustainable practices, however, offers long-term benefits. I’ve worked on projects that included solar panels, energy-efficient appliances, and green building designs. These features reduce utility costs for residents and operational expenses for developers. Leveraging government incentives for green construction also offsets initial costs, making sustainability more attainable.
8. Lengthy Approval Processes
Securing permits and navigating regulatory approval can be an exhausting process. Lengthy timelines delay housing projects and increase costs, which is especially problematic for affordable housing initiatives.
Advocating for streamlined approval processes has been instrumental in many successful projects I’ve been involved with. Some municipalities have introduced fast-track permitting for affordable housing, which significantly reduces delays. Clear communication and thorough documentation also help developers stay ahead in the approval process.
9. Maintenance and Operational Costs
Even after construction, ensuring the long-term affordability of housing is a challenge. High maintenance and operational costs can erode the financial sustainability of a project.
To tackle this, I always encourage developers to prioritize durable materials and energy-efficient building systems. These reduce maintenance needs and utility expenses over time, keeping housing affordable for residents. Effective property management also plays a critical role in maintaining the quality of these developments.
10. Economic Uncertainty
Economic fluctuations, such as recessions or inflation, can disrupt affordable housing projects. Changes in construction costs, funding availability, and market demand often force developers to rethink their plans.
To mitigate these risks, I recommend diversifying funding sources and building flexibility into financial models. Establishing contingency budgets and maintaining adaptable strategies have helped many projects weather economic challenges.
Key Challenges and Solutions in Affordable Housing
Rising construction costs: Use modular construction.
Zoning barriers: Advocate for reforms.
Financing issues: Leverage tax credits.
Limited land: Explore adaptive reuse.
Community opposition: Engage with residents.
Skilled labor shortages: Invest in training.
Environmental concerns: Use green designs.
Approval delays: Push for fast-track permits.
In Conclusion
Affordable housing development is a complex process with no one-size-fits-all solution. By addressing challenges like rising construction costs, regulatory hurdles, and community resistance, developers can create sustainable housing solutions that meet the needs of diverse populations. I’ve seen how innovative strategies, collaboration with stakeholders, and a commitment to affordability can transform these challenges into opportunities. With the right approach, we can build stronger communities and provide housing that is accessible to everyone.
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
Benefits of Affordable Housing

Affordable housing programs in the United States refer to communal, regional, and national projects that assist low to moderate-income earners and asylum seekers by offering secure, quality, and decent housing. The United States Department of Housing and Urban Department (HUD) offers several sub-departments that create initiatives that focus on affordable housing, like the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) program for private builders developing inexpensive housing. Others include the Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher program that offers stipends to tenants toward rent. Affordable housing provides benefits including improved health outcomes, reduced financial strain, community diversity, and workforce stability.
One of the primary benefits of affordable housing is access to secure, decent, and quality housing. According to HUD, there were 653,000 Americans who were homeless in 2023, and one in every 500 US residents experienced a form of homelessness. Such conditions increase the likelihood of contracting diseases like bronchitis and pneumonia due to exposure to colds, wounds, and skin infections, as well as issues like substance use and mental health problems.
Also, other than the homeless, those living in decrepit and low-quality housing are often exposed to lack of heating, contaminated water, sewage, or lead paint, which leads to waterborne diseases and respiratory and other problems. The areas also typically feature insecurity with cases of robberies or bodily harm.
Also, low-quality housing is often located in areas inaccessible to or far from proper medical care personnel and facilities, increasing the chances of infectious diseases and high mortality rates. Quality and affordable housing shields individuals and families from these elements and the environment, leading to improved health outcomes and a productive populace.
Affordable housing also alleviates financial strain. The average cost of a house in the United States is $416,000, with the rent at $2556 monthly. Compared to the average national household income of $80,000, regular housing falls beyond the reach of many Americans. For most renters their largest monthly expense is rent, with most spending well over 30 to 40 percent of their income. Affordable housing means less income is spent on rent, with more finances dedicated to other necessities or life-improving pursuits like education.
Affordable housing creates jobs. The construction process attracts skilled and unskilled labor. Post-construction stages also require attendance to areas like repair and maintenance, management, and cleaning. Also, a healthy and more productive community with a higher purchasing power due to savings from reduced rents leads to the growth of local businesses like grocery stores, food stalls, hardware stores, and others. These businesses require attendants and as well as repair and maintenance.
Diversity is also one of the most visible benefits of affordable housing. Unlike high-income communities that sometimes skirt the laws against discrimination based on religion, race, or income level, affordable housing accommodates people of every background. It also attracts asylum seekers who introduce their different blend of culture and tradition to the community. The result is a multicultural and diverse community rich in aspects like food, dress, and languages. Mutual support and the recognition of a common status or background make for a cohesive bonding uncommon in many middle- and high-income communities.
As mentioned, affordable housing also helps boost the local community's economy and stability. The savings from outlays on rent are spent on local purchases, with the majority able to buy beyond the basics, thus boosting the local economy. The inability to pay rent leads to evictions and changes in occupancy. This erodes the bonding as networks, friendships, and social networks are frequently broken. One of the detriments of this instability is segregation and an increase in crime. However, the relatively low rents in affordable housing mean fewer evictions. In most cases, the property managers understand the tenants' predicaments and offer more leeway in payments or arrangements, such as staggered payments.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Proposed Reform to Exempt Affordable Projects From Bond Limits
Bronx Rep. Ritchie Torres has introduced a groundbreaking bill aimed at significantly boosting affordable housing construction. The Accelerated Supply of Affordable Production Housing Act (ASAP) proposes to exempt affordable housing projects from federal volume caps on private activity bonds until 2034. This reform could unlock substantial financing and generate more low-income housing tax credits, addressing the nation's pressing housing shortage.
Volume caps on private activity bonds have long been a barrier to affordable housing finance. The ASAP bill seeks to change that by exempting 100% of affordable housing projects from these caps until 2034. This move could dramatically increase housing production across the country.
Potential Game-Changer
Volume caps limit the amount of tax-exempt bonds that states can issue each year, restricting a key financing tool used alongside low-income housing tax credits (LIHTCs) to fund affordable housing projects. By lifting these restrictions, Torres believes the bill could significantly boost housing production. “The affordability crisis in America is not an inevitability. It is a choice, it is a product of public policy,” Torres said, emphasizing that the policy change would empower developers to meet the demand for affordable housing.
How It Works
Under the current 50% test, at least half of an affordable housing project must be funded through private activity bonds to qualify for 4% low-income housing tax credits. Efforts to lower this threshold have stalled, but the ASAP bill offers a more comprehensive solution. By exempting affordable projects from the volume cap altogether, the bill could unlock additional financing and enable the construction of more homes across the U.S.
Support From Advocates
Rachel Fee, executive director of the New York Housing Conference, worked closely with Torres on the bill. She believes it would “turbocharge” housing construction, estimating that New York could at least double its annual production. Over the past two years, New York’s volume cap has remained around $2.4 billion, with most of it allocated to housing, producing about 10,000 units annually. With 20 states over their volume cap as of September, the demand for more flexibility is clear nationwide.
Pressure to Produce
During a recent hearing, Adolfo Carrión, Commissioner of the Department of Housing Preservation and Development, highlighted the need to adjust the 50% test to increase access to LIHTCs. Carrión noted that New York City has 750 housing projects in the pipeline, 300 of which are new construction, but many are under pressure due to current volume cap limits. According to Fee, the ASAP bill could provide the financial flexibility needed to clear this backlog.
Bipartisan Support
Expansions to LIHTCs and other public-private financing tools have historically gained bipartisan support, offering a more politically feasible option than increasing funding for public housing. However, these proposals can become entangled in larger political battles, often sidelined by other priorities. The outcome of the upcoming election will play a crucial role in determining the bill’s fate, with Torres expressing hope that the current focus on housing in the presidential race could work in its favor.
If the ASAP bill gains traction, it could influence discussions on expiring tax laws, providing a pathway to increased housing development across the U.S. For real estate developers and investors, this proposed reform represents a significant opportunity to address the affordable housing crisis and capitalize on new financing mechanisms.
Join the Conversation: What are your thoughts on the proposed reform to exempt affordable projects from bond limits? How do you see this impacting real estate investments? Share your insights and engage with our community!
#RealEstateTrends #AffordableHousing #InvestmentOpportunities #HousingMarket
What are your views on the proposed changes to affordable housing finance? Let’s discuss below! 💬🏢

#affordable housing#politics#new york#real estate#investment#danielkaufmanrealestate#economy#real estate investing#housing#daniel kaufman#construction#homes#housing forecast#taxes#government
0 notes
Text

HUD establishes key LIHTC parameters for 2025 https://www.housingwire.com/articles/hud-establishes-key-lihtc-parameters-for-2025/
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
5 Reasons to Consider Affordable Housing Investment Funds
Investing in Affordable Housing Investment Funds offers a unique opportunity for those looking to blend financial returns with social impact. Here are five compelling reasons why DBL Capital recommends considering this type of investment:

Stable Demand: The demand for affordable housing is consistently high, driven by the need for cost-effective living options in growing urban areas. With rising housing costs, more individuals and families seek affordable solutions, ensuring a steady demand for properties in Affordable Housing Investment Funds. This stability can result in reliable, long-term rental income for investors.
Social Impact: By investing in Affordable Housing Investment Funds, you contribute to addressing the critical shortage of affordable housing. This investment not only generates financial returns but also provides safe, decent housing for lower-income families, promoting social equity and community stability. The positive social impact can be an attractive aspect for investors looking to make a difference.
Government Incentives: Affordable housing projects often qualify for various government incentives, including tax credits and grants, which can enhance the overall return on investment. Programs like the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) in the United States provide financial benefits that can significantly improve the profitability of Affordable Housing Investment Funds.
Portfolio Diversification: Including Affordable Housing Investment Funds in your portfolio adds a layer of diversification. These funds tend to be less volatile compared to traditional real estate investments or stock markets, offering a hedge against economic downturns. The consistent demand for affordable housing can provide a buffer in times of market instability.
Regulatory Support: Many governments and municipalities actively support the development of affordable housing through favorable policies and zoning regulations. This support can simplify project approvals and reduce development costs, enhancing the attractiveness of Affordable Housing Investment Funds. For example, expedited permitting processes and density bonuses can make these investments more viable and profitable.
In conclusion, Affordable Housing Investment Funds provide a balanced approach to investing that combines steady financial returns with significant social benefits. For investors with DBL Capital, these funds offer a compelling way to achieve both economic and community-focused goals, making them a strategic addition to a diversified investment portfolio.
0 notes
Text




Forest City Bank Building
1400 W. 25th St.
Cleveland, OH 44113
The historic Forest City Savings & Trust Building (built in 1903-4) and Seymour Block (built in 1878) are located at 1400 W. Twenty-fifth Street (U.S. Route 42/State Route 3) at the Detroit Avenue (U.S. Route 20) intersection in the thriving Ohio City neighborhood of Cleveland, Ohio.
The buildings were connected on the upper levels in the 1940’s and have undergone substantial renovations to support mixed uses. The Forest City Bank Building was listed with the National Register of Historic Places on August 31, 1992, and it is part of a Register-listed historic district, the West 25th Street-Detroit Avenue Historic District.
The current renovation project was partially funded with both State and Federal Historic Tax Credits as administered by the National Parks Service/OHPO, in addition to 9% Low Income Housing Tax Credits (LIHTC) awarded by the Ohio Housing Finance Agency. The upper floors of the project contain 38 LIHTC apartment units with a focus on sustainable design and renewable energy. Additionally, the project features roof top and parking canopy solar panel arrays which offset up to 75% of the total energy (187,000 kwh) consumed by the apartments annually.
0 notes
Text
2024 Election: A High-Stakes Game For Community Development And Housing Tax Credits

Hey everyone, The upcoming 2024 election is more than just another political event—it's a pivotal moment that could reshape our financial landscape, especially for community development housing tax credits. So, let's dive into what this means for all of us. As you know, the House-passed tax bill is currently stalled in the Senate. But what's really causing anxiety is the impending expiration of a staggering $4.7 trillion in tax cuts by the end of 2025. This potential fiscal upheaval has everyone wondering how Congress and the president will handle this challenge, especially with the presidential election just five months away.
Election Forecast: A Tight Race
Right now, it’s anyone's game. Pollsters are calling the race between President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump a toss-up. The stakes are equally high for Congress, with the Senate showing a slight Republican tilt. But let's be real, five months is a lifetime in politics, and anything can happen.
The Fiscal Cliff Ahead
With $4.7 trillion in tax provisions set to expire in 2025, next year promises to be a legislative rollercoaster. If Congress doesn’t act, millions of Americans could face significant tax hikes. Among the expiring provisions are lower personal income tax rates, higher standard deductions, and boosted child tax credits. While some business tax benefits from the 2017 overhaul will remain, others, like business investment expensing and the 20% deduction for certain business income, are on the chopping block.
Possible Election Scenarios And What They Mean
Republican Party: If Trump and the Republicans clinch victory, community development incentives could find themselves on the defensive. The low-income housing tax credit (LIHTC), new markets tax credit (NMTC), historic tax credit (HTC), and renewable energy tax credits might face cuts, while opportunity zones (OZ) could see an extension. Democratic Party: A blue wave could herald a golden era for community development affordable housing tax credits. Expect extensions, expansions, and new credits like the neighborhood homes tax credit (NHTC) and workforce housing tax credit (WHTC). Republican President, Split Congress: This scenario calls for intense negotiation. Bipartisan cooperation will be crucial, and the House Ways and Means Committee will play a pivotal role, regardless of party control. Democratic President, Split Congress: This is similar to the previous setup but with Biden at the helm. Here, bipartisan deals will be essential, with moderates holding significant influence.
What's at Stake For Specific Tax Incentives?
Depending on the election results, we could see different fates for critical tax incentives. The LIHTC and NMTC might get a makeover or an extension, driven by the political winds. Enhancements to these credits could drive economic growth in underserved areas, making this election incredibly significant.
Wrapping Up
The 2024 election isn't just about who gets the keys to the White House—it's about the future of community development housing tax credits and, by extension, the future of countless American communities. Whether you’re a developer, a local government official, or a nonprofit leader, staying informed and engaged is crucial. The next five months will set the stage for years to come, so let's be ready to advocate for policies that support economic equity and community resilience. Stay tuned, contact us, and stay informed. Let’s navigate this political rollercoaster together! Catch you next time, Midtown-Builders Read the full article
#2024Election#AffordableHousingInitiatives#CommunityDevelopmentTaxCredits#HistoricTaxCredit(HTC)#Low-IncomeHousingTaxCredit(LIHTC)#PresidentialElection#TaxCutsExpiring2025
0 notes
Text
Tax Advantages with Income Fund | Zinc Income Fund
The ZINC Income Fund offers several tax advantages, which can be particularly appealing to investors seeking to maximize their after-tax returns. Here are some potential tax benefits associated with the ZINC Income Fund:
Investing in the ZINC Income Fund can offer a range of tax advantages that can enhance your overall investment returns. Here's a detailed exploration of the tax benefits associated with the ZINC Income Fund, including tax-deferred growth, tax-efficient income, favorable tax treatment for dividends and capital gains, and potential tax credits.
Tax-Deferred Growth: One of the key benefits of investing in the ZINC Income Fund is the potential for tax-deferred growth. This means that you won't have to pay taxes on any earnings generated by your investment in the fund until you actually withdraw those earnings. This can help your investment grow more quickly over time, as you won't have to worry about paying taxes on your gains each year.
Tax-Efficient Income: The ZINC Income Fund aims to generate income that is tax-efficient. This means that the fund's managers will try to minimize the tax impact of the income generated by the fund, potentially lowering your overall tax burden. For example, the fund may invest in municipal bonds, which generate tax-free income at the federal level and sometimes at the state level as well.
Favorable Tax Treatment for Dividends: If the ZINC Income Fund distributes qualified dividends, you may benefit from lower tax rates on these dividends compared to ordinary income tax rates. Qualified dividends are dividends paid by U.S. corporations or qualified foreign corporations that meet certain criteria set by the IRS. As of 2022, qualified dividends are taxed at the same rates as long-term capital gains, which are generally lower than ordinary income tax rates.
Favorable Tax Treatment for Capital Gains: When the ZINC Income Fund sells investments at a profit, the resulting capital gains may be taxed at lower long-term capital gains tax rates. Long-term capital gains are gains on investments that have been held for more than one year. As of 2022, long-term capital gains tax rates range from 0% to 20%, depending on your taxable income.
Tax Credits: Some investments within the ZINC Income Fund may generate tax credits. Tax credits are a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax liability, so they can be very valuable. For example, the fund may invest in low-income housing projects that qualify for the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC). Investing in LIHTC properties can generate tax credits that can offset your federal income tax liability.
It's important to note that tax laws are complex and subject to change. The tax benefits described above are based on current tax laws as of 2022 and may change in the future. Additionally, the tax benefits of investing in the ZINC Income Fund will vary depending on your individual tax situation. It's always a good idea to consult with a tax professional before making any investment decisions.
It's important to note that tax laws are complex and subject to change. Consult with a tax professional to understand how investing in the ZINC Income Fund may impact your specific tax situation.
0 notes
Text
It was recommended I look into LIHTC apartments/rentals in the area and there are two.
One is the Sec8 complex I applied to be a property manager at and was ignored, which is across the street from the larger Dollar Tree, but is elders only.
The other is one trailer that's kind of far away on the river, which means I'd need a car to be able to get to any sort of work. Hopefully I will HAVE a car by then, but who knows.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the Nexus: Organizations Spearheading Affordable Housing Finance in High-Demand Areas

The conundrum of providing affordable housing in high-demand urban centers is a complex challenge faced by cities globally. Spiraling land and construction costs, coupled with rapid urbanization, have exacerbated the housing affordability crisis. However, innovative financing models championed by various organizations have begun to turn the tide, offering sustainable solutions to increase the affordable housing stock significantly. This article delves into the pivotal role these organizations play in affordable housing finance, spotlighting the models that have catalyzed substantial growth in housing accessibility.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): A Collaborative Approach
One of the most impactful strategies in the realm of affordable housing finance has been the adoption of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs). These collaborations leverage the strengths of both the public and private sectors to develop housing solutions that neither could achieve independently. Governments offer incentives like tax breaks, subsidies, or land at reduced costs, while private entities bring in investment, innovation, and efficiency.
A prime example of PPP success is seen in cities like New York and Singapore, where mixed-income housing projects have flourished. In Singapore, the Housing & Development Board (HDB) works closely with private developers to offer a range of housing options that cater to various income groups, effectively keeping the city-state’s housing market both vibrant and accessible.
Housing Bonds: Financing Infrastructure for the Future
Housing bonds have emerged as a crucial tool for raising capital for affordable housing projects. Issued by either government entities or housing finance agencies, these bonds attract investment from both individuals and institutional investors, offering a stable return while funding the development of affordable homes.
In the United States, the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) program represents a successful use of tax incentives to encourage investment in affordable housing. By providing tax credits to developers, the program has helped finance over 3 million affordable housing units since its inception, demonstrating the potential of housing bonds to catalyze large-scale development.
Land Value Capture (LVC): Unlocking Value for Housing
Land Value Capture mechanisms harness increases in land value due to public infrastructure investments, redirecting some of that value to fund affordable housing. This model has been particularly effective in cities with significant public transit expansions, where nearby land values tend to skyrocket.
In cities like Hong Kong, LVC has been utilized to fund not only transit-oriented developments but also to ensure that these developments include a substantial proportion of affordable housing units. By integrating housing finance with broader urban development strategies, LVC offers a holistic approach to tackling housing affordability.
Revolving Funds: Sustaining Development through Recycling Capital
Revolving funds represent a sustainable financing model, where initial investments in affordable housing are recycled as loans are repaid, funding further projects. This model ensures a continuous flow of capital for new developments without relying heavily on external funding.
The Affordable Housing Trust Fund, utilized by several cities across the United States, operates on this principle. By offering low-interest loans to developers, these funds have managed to maintain and expand affordable housing stock, demonstrating the efficacy of self-sustaining financial models in addressing housing needs.
Navigating Challenges and Seizing Opportunities
Despite the successes, financing affordable housing in high-demand areas remains fraught with challenges. High land costs, regulatory hurdles, and the need for substantial upfront investment continue to impede progress. Yet, the innovative financing models deployed by a variety of organizations show a path forward, blending creativity with pragmatism to address the housing crisis.
As urban populations continue to grow, the importance of these organizations and their financing models in ensuring accessible, affordable housing cannot be overstated. Through collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to social equity, they provide a beacon of hope, not just for those in search of housing, but for cities striving to be inclusive, diverse, and vibrant communities.
In conclusion, the journey toward substantial increases in affordable housing stock is complex and multifaceted. The organizations leading these efforts are not just financiers; they are visionaries, crafting the blueprint for future cities where affordable housing is not an aspiration but a reality. Their work underscores the importance of innovative finance in creating sustainable urban ecosystems, where everyone has a place to call home.
0 notes