#Japanese Films
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
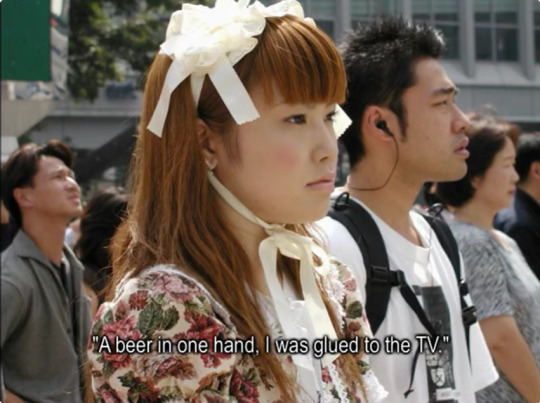



532 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Ghost in the Shell (1995)#gits#motoko kusanagi#cyberpunk#90s movies#90s anime#japanese films#animated films#my gif
342 notes
·
View notes
Text




looking for an angel (1999)
#looking for an angel#akihiro suzuki#japanese cinema#japan cinema#japanese movies#japanese films#tenshi no rakuen#cinematography#movies#cinema#movies to watch#world cinema#asian cinema#movie list#movie quotes#films
297 notes
·
View notes
Text




Helter Skelter (2012) | Dir. Mika Ninagawa The Substance (2024) | Dir. Coralie Fargeat
#helter skelter#helter skelter 2012#japanese#japanese film#japanese films#the substance#substance#films#film#mine#watchlist#letterboxd#mika ninagawa#coralie fargeat#margaret qualley#demi moore#erika sawajiri#kiko mizuhara
105 notes
·
View notes
Photo




Shoplifters (2018) dir. Hirokazu Koreeda
#shoplifters#万引き家族#manbiki kazoku#hirokazu koreeda#asian cinema#screencaps#film aesthetic#japanese films#movie stills#japanese movies
355 notes
·
View notes
Text











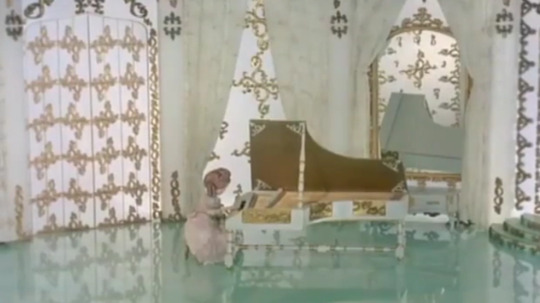















ベルトかいじゅう王子 (Belle to Kaijuu Ouji, 1976) directed by 渡辺和彦 (Kazuhiko Watanabe)
#animation#japanese animation#beauty and the beast#la belle et la bête#belle to kaijuu ouji#ベルトかいじゅう王子#fairy tale#fairytales#fairytale#batb#films#short films#japanese films#fantasy#stop motion#stop motion animation#screencaps#1980s#kazuhiko watanabe
275 notes
·
View notes
Text




House (1977), dir. Nobuhiko Obayashi
#film#films#movie#movies#japanese movies#japanese films#japanese movie#japanese#japan#horror films#horror#horror film#horror movies#horror movie#1977#1970s#70s#70s films#70s film#70s movie#70s movies#house#house 1977#cinephiliac#cinephilia#cinephile#cinema#1970s movies#1970s film
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

Film still from Motoyoshi Oda's Tômei ningen (The Invisible Man), 1954
#movies#film#motoyoshi oda#tomei ningen#the invisible man#sci fi#1950s#black and white#japanese films#film stills#vintage#suspension#hair#photography
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Two Flavors of Japanese (BL) Cinema
Recently I came across a post that proposited that Japanese cinema hadn't changed since the 1950's and came in, essentially, two types.
Let's discuss that.
I can’t go into the history of all Japanese cinema in a singular blog post like that’s just not possible, there’s literal books and classes you can take on this subject, and I will be linking further reading down at the bottom of the post so you can do just that.
This fact alone, should already disprove the point that Japanese cinema hasn’t changed since the 1950’s. Other than the fact that like, Japan isn’t a static society that is forever unchanging because human beings do not work like that.
Which is why I’m writing this essay at all.
I love cinema, I love storytelling and filmmaking. And, frankly, I may not be an expert but I am annoying. I own that.
Japanese cinema has held influence over many directors, writers, animators, and so forth.
Just watch this playlist of Sailor Moon references across various cartoons. Or how Satoshi Kon influenced the work of Darren Aronofsky and Christopher Nolan. Or how James Cameron and the Wachowskis were both influenced by Mamoru Oshii’s 1995 Ghost in the Shell. And then there’s Akira Kurosawa who’s been cited as a major influence for directors like: Steven Spielberg, George Lucas, and Martin Scorsese and a slew of others.
I want folks to know there’s a slew of amazing films from Japan and that distilling the industry - the blood, sweat and tears of its creators - to a strict dichotomy of this or that, either/or is disrespectful at best and xenophobic at worst.
It’s also just a shame because, like, guys there’s so many great films from Japan! There’s also probably a lot of great live action shows from Japan but I’m not super knowledgeable about them - I mainly watch anime so that’s not a great metric in terms of Japanese television - so I’m just talking about films in this post.
Ok so main points I’m gonna address:
Japanese Cinema hasn’t changed since the 1950s
Japanese film style falls under an extreme dichotomy of cinematic/sweeping (described as “atmospheric”) or cartoonish/slapstick (described as “live action manga”)
Baby does any of this have to do with BL? (no, but it IS more gay than you think)
With these four films: The Hidden Fortress (1958), Lady Snowblood (1973), Gohatto (1999), and Kubi (2023).
I picked these four because they’re all “period pieces” taking place feudal Japan - or with the aesthetics of feudal Japan, The Hidden Fortress nor Lady Snowblood aren’t based on actual historical events, like Gohatto and Kubi are, however loosely, but take place in an amorphous 15th to 18th century Japan - and I think they strongly show the development of this singular genre in Japanese cinema.
Plus the latter two films, Gohatto and Kubi, are gay as fuck and I know my people.
[you can also read this post on this blog post which includes additional links as tumblr has a limit and for easier readability as this is a long post]
The Hidden Fortress
youtube
Released in 1958, directed by Akira Kurosawa it’s probably the most well-known film on the list. It’s a film that exists within the “Golden Age” of Japanese cinema alongside films like Kurosawa’s own Seven Samurai (1954), Yasujirō Ozu’s Tokyo Story (1953) and Kenji Mizoguchi’s Ugetsu (1953).
It was also the era where, after the American Occupation post-WWII a boom of movie distribution took place with new film studios such as: Toho (y’all know them from any Godzilla movie ever made), Toei (if you know One Piece you know Toei but they’ve done a ton of films both animated and live action) and others.
The story is straight forward, two peasants, Matashichi and Tahei who bicker their asses off like an old married couple the entire film, happen upon a Very Hot Man with the Only Thighs Out (Toshiro Mifune was a BABE) named Rokurota and his companion a icy young woman named Yuki.
Matashichi and Tahei have just escaped like, a ton of ~circumstances that include failing to become samurai, being broke as fuck, getting captured and forced into servitude - don’t worry that lasted like 6 hours tops - and then find gold hidden in a stick on a mountain.
Turns out Rokurota has all the stick gold they could want! So they team up neither realizing Rokurota and Yuki are actually part of a clan that’s been recently wiped out and they’re on the run from a rival clan who has wiped theirs out. Yuki is the princess of said clan and it’s only survivor, while Rokurota is her samurai general and retainer.
Tahei and Matashichi, living in ignorance of these facts, try to steal the gold away from them because they live that hustle life until the end when all is revealed and Yuki grants them both with a gold piece to share (this is a really big piece of stick gold).
There’s other things that happen, like a fight scene between Rokurota and rival clan member, Yuki owning every single scene she in - I fucking love her - but that’s the gist.

The story is, again, pretty uncomplicated, it balances the comedy of Tahei & Matashichi with the stoicism of Rokurota and Yuki well, and all the acting is strong. In terms of its film style, by modern day standards it’s not especially “cinematic” Kurosawa doesn’t favor fanetic camera movements, his camera is often very still and the movement he employs is often in individual character ticks, and/or background set pieces. This film has a lot of great set pieces.
Kurosawa didn’t employ camera techniques like panning, he doesn’t really do extreme close ups, there's no swooping shots or fancy tricks, I’d say a majority of the camera shots in The Hidden Fortress are a combination of mid, and wide, with a few mid-close ups. One thing to notice is Kurosawa’s use of scene cuts; instead of a cut he used pan sweeps to change scenes. If you’ve ever watched a Star Wars film you know exactly what I mean.
The Hidden Fortress, first and foremost, is an action adventure film. It has more in common tonally with Top Gun Maverick or Star Wars A New Hope, in that it's straight forward, sincere, and grand in scale, grounded by a very honest set of characters who are strongly motivated.
I feel like in modern day discussions we association “action/adventure” films in a sorta of negative way; this is probably due, in part, to the oversaturation of the high budget blockbusters of the last ten years - oh MCU, how you’ve fallen - that are overly bombastic, overly complicated, overly connected, and the root of what audiences connect with - the characters - tends to be lost.

Scott Lang's motivations in Ant-Man and the Wasp: Quantumania are to protect his teenager daughter and the family he's built, which are simple, strong, and relatable character motivations. However, they got lost in the conventions of the plot, the frantic energy of the film, the simple amount going on around Scott that his motivations become less a central focus and thus he becomes small within his own film. We, the audience, become distant and it grows more difficult to connect with what's happening. This can still work on some level, the Fast and Furious franchise isn't successful because it's sophisticated, but the Fast-chise has embraced it's cheesier conventions and spectacle, while blockbusters like the MCU's output, simple juggle to much all at once. It also helps that while the cast keeps growing in the Fast and Furious films, there's still less than ten characters you have to actually know and care about. To fully understand and connect with the characters of The Marvels, you have to watch Ms. Marvel and WandaVision on Disney+ and the task becomes more akin to homework than simply the enjoyment of watching a movie.
The epic scale grows so large it feels daunting, rather than exhilarating.
I think this is why a film like Winter Soldier, more so than most MCU films of the last decade, has continued to be a fan favorite of the universe and of blockbuster lovers whether you are a fan of the MCU or not. At its root, Winter Soldier is character driven, with deeply motivated characters, which is what makes the action and adventure aspects stick.
The Hidden Fortress is similarly character driven with a simple and straightforward story that is about honor, loyalty, a princess, a loyal samurai/knight, rebuilding a decimated clan, and two “normal” characters to keep everything grounded and relatable. Which in turn, helps make it timeless. While the filmmaking itself isn't grandiose as what modern audiences may be used to, Kurosawa knows how to direct a scene and more than that, direct his actors. Mifune is commanding as always, but for me, it's really actress Misa Uehara as Princess Yuki that steals the movie.
Lady Snowblood
youtube
Released in 1973 and based on a manga of the same name by Kazou Koike and Kazuo Kaminura, directed by Toshiya Fujita, Lady Snowblood and its sequel Lady Snowblood: Love Song of Vengeance are considered cult classics. Lady Snowblood, famously, is Quentin Tarantino’s inspiration for his Kill Bill saga (like, a freaking lot).
Lady Snowblood is a part of the era of “new wave” and “pink films” that were emerging in Japan and elsewhere. Stateside I think a close equivalent to both the style and content of Lady Snowblood and other films like it are exploitation films. In fact while watching Lady Snowblood I couldn’t help but get exploitation film vibes just off the aesthetics and thematics of the film itself.
To break down Lady Snowblood’s plot it goes like this: Yuki is tasked with getting revenge on four people who had a hand in her father, and older brother’s murder, and her mother’s rape (which is seen on screen so warning for y’all this is def a Does the Dog Die movie).
Yuki’s mother kills one of her rapists, but is imprisoned before she can kill the others and while in prison she purposely gets pregnant so her child can carry on her revenge after she dies. Yuki is born, and raised by one of the fellow inmates and a priest who trains her in martial arts. She’s raised as a “demon”, whose only purpose is revenge for her mother, father, and brother. And boy does she get revenge the film is violent and graphic (even if by modern day standards the blood looks fake as fuck the emotions are there).
Like The Hidden Fortress this film is very character driven, with a highly motivated protagonist but it’s also revels far more in it's violence and the spectacle of that violence. Yuki, in comparison to her earlier counterpart Princess Yuki, is the driver of the action in the story. She's an active participant in the plot, and the story centers around her. Princess Yuki is commendable, she's compassionate, and she makes decisions, but the story is more about what she represents - a fallen princess - than what she does. She's symbolic, the embodiment of a leader, a samurai spirit of nobility who becomes a leader worth following. Yuki, on the other hand, needs no protection from others, she's a much more direct and active part of the story since the story is hers - and her mothers - she's more elegant than regal, and there's nothing necessarily 'noble' about her. She's not seeking to rebuild her clan as a leader, her motivations are singularly about her revenge quest to fulfill her mother's dying wish.
In some ways, they're very similar - Yuki also feels compassion for another woman who's been used by the men around her as Princess Yuki does - and in others they are very different and speak to the changing expectations and idealizations of women from the 1950s to 1970s.
Lady Snowblood is also way more violent than any Kurosawa film I’ve watched including The Hidden Fortress. While there is action in The Hidden Fortress, it’s all employed with specific purpose. Which is one of Kurosawa’s strengths as a director. It’s calculated and singular. Yes blood spurts up in Yojimbo but it's limited; quick and efficient, with more in common with John Wick or Collateral than the more fantastical and aesthetic Tarantino or Robert Rodriguez fare.

Lady Snowblood revels in the aesthetic violence, there’s no “purpose” for Yuki to cut an already dead person in half, she does it out of pure frustration and for the glory of showing the audience that internal rage. Of a body hanging, dripping blood and gore onto the clean floor as the curtain draws to a close.
The film also features on screen rape, sex, and nudity which The Hidden Fortress does not. There’s an implication that characters in the film would assault Princess Yuki if they could, but nothing ever goes beyond brief implication (still gross tho guys come on). Whilst in Lady Snowblood, the rape is brutal, the violence is brutal, and the emotions are far more intense because of it all.

The allowance - for lack of a better term - of this kind of material showcases a cultural shift overall in the terms of visual storytelling filmmaking began experimenting with in telling, and in what audiences were responding too. Lady Snowblood was a beloved success for its overall low budget. In comparison to the two, The Hidden Fortress is filmed better, with more technique and focus, Lady Snowblood almost seems rustic in comparison, but it's a sort of rustic that speaks to experimentation.
Low angles from a characters pov staring high above her, extreme zooms on Yuki's burning eyes, the oversaturated colors of red-orange blood or green walls or white clothes, the starless pitch black sky as powdery snow falls. The images are arresting even if at times they're choppy, and while the film opts for non-linear chapter breaks to create a story flow in comparison to Kurosawa's iconic screen swipes and straight forward narrative, yet, both work.
Gohatto
youtube
Behold, the promised gay cinema I promised.
Gohatto is a 1999 film directed by Nagisa Oshima based on the short story, Shinsengumi Keppuroku by Ryotaro Shiba.
Gohatto is a pretty late entry in the new wave/pink films of its heyday but those films were Oshima’s bread and butter. Often dubbed as one of Japan’s cinema outlaws for his anti-establishment films, one of his films, Night and Fog in Japan (1960) was pulled from theaters all together. Most people in the west will probably know him even tangentially for his queer film Merry Christmas Mr. Lawrence starring David Bowie and Beat Takeshi or for this absolutely banger quote from the New York Times article, A Japanese Film Master Returns to his Cinema:

(If you’re a BTS fan, the composer Suga and RM like, Ryuichi Sakamoto, both starred and composed the main theme of Merry Christmas Mr. Lawrence Forbidden Colors, he plays the guy in love with David Bowie’s character)
Gohatto combines the setting of a Kurosawa film, with the more experimental storytelling of Lady Snowblood, whilst imbuing the film with more surrealistic elements and more complexity. And making it gay like - for real for real.
Gohatto goes like this: it’s the late 18th century in Japan, everything politically is on shaky ground, and the shinsengumi are looking for newbies to join ranks. Welp, they find two promising newbies and wouldn’t ya know it one newbie, Kano, is like, hella pretty. He’s got bangs.
He’s so pretty in fact that all these other dudes in the shinsengumi crew wanna smash, I mean down bad like the Taylor Swift song or whatever I don’t listen to Taylor Swift.
This is all treated with a lackadaisical normality; there’s teasing about “I never considered sleeping with a man before, but damn that Kano kinda…” but there’s never a moment of “omg they’re GAY?”
Beat Takeshi’s - who’s also in this film, he’s been in a lot fo queer films I'm noticing - character Vice-Commander Hijikata Toshizo often asks other characters not if they’re attracted to Kano - the implication being that they are - but rather if they are in love with Kano. Because lust is fleeting, but love is dangerous to your duty.

Kano also might be a spy, or a murderer, it’s all very ambiguous and the ending isn’t a “happy” one. This isn’t a film about a love story of any sort, it has more in common with erotic thrillers than the action adventure of The Hidden Fortress, or the rape revenge fantasy of Lady Snowblood. Where as the former films have definitive endings, Gohatto ends ambiguously.
What actually happened? And why did it happen? What did it all mean, in the end? The film offers no strict answers to these questions, asking instead, that its audience to come to their own conclusions. It’s also much more historical than the previous two films, taking real life historical figures like: Hijikata Toshizo, Okita Soji, and Kondo Isami and asking the question, “hm, what if they all maybe fell in love with this super pretty man before being overthrown and what does that mean metaphorically?���
The Hidden Fortress doesn’t ask its audience to interrogate society in any meaningful way and that’s not a knock against it, it’s just an observation. Lady Snowblood specifically presents the plight of women, and a slight take on classism within the system, through the lens of violence and destruction. Gohatto is much more metaphorical, it’s not providing the audience with a direct message like the former two films, but presenting it’s thematics in a much more abstract way. The Hidden Fortress is an action adventure, with heroes who achieve their goals and overcome their obstacles. Lady Snowblood is a rape revenge with an understandable protagonist who succeeds in her bloody revenge. Gohatto has no heroes, and offers no straightforward catharsis at the end of its story story.
Its film style is also far more atmospheric compared to the epic scale and straightforwardness of The Hidden Fortress, or the lower budget charming violence of Lady Snowblood.

There’s lots of mood lighting, overhead shots of characters dimly lit, camera cuts to rain after two characters have sex, extreme close ups of one character observing Kano’s eyes and lips. It’s not a black and white film like The Hidden Fortress, but it’s not nearly as saturated in color and brightness as Lady Snowblood.
Lady Snowblood drips with color, and light, even at night there always almost seems to be a spotlight on Yuki with an empty starless sky in the background. Gohatto is much more grounded in realism than high visual aesthetics, opting to create more of a lingering dreamlike trance or fog to the cinematography when the story’s final act begins to unfold.
Yet, one thing Gohatto has in common with both The Hidden Fortress and Lady Snowblood is its violence; operating somewhere between the two. Like The Hidden Fortress the violence is quick, purposely, and specific, and like Lady Snowblood blood spurts, gushes, and heads are displayed proudly and grotesquely.
Kubi
youtube
Kubi is a 2023 film directed by Takeshi Kitano aka Beat Takeshi - this is the third time his name has been dropped in relation to a queer film in this post go Beat Takeshi - based on a novel of the same name that Kitano also wrote.
Kubi is like Beat Takeshi’s sengoku period slash RPF fanfic come to gruesome bloody (literal, not British) life. A period piece epic; Kubi is both about samurai warlords and a historical event known as the honno-ji incident, which took place in 1582. It features various historical figures like Oba Nobunage - if you’ve watched some anime or played some JRPGs you’ve probably at least heard of this name before - and other prominent historical figures of the time.
The basic gist of the movie is Oba Nobunage is both really good at his job, so he’s super powerful politically, but he’s also a grade-a asshole whom all the other important samurai lords fucking hate. However, they also all fucking hate each other and all want to take Nobunage’s place and get all that sweet, sweet power for themselves. The honno-ji incident involved one of these guys doing a coup for reasons still unknown today and then pretty much almost immediately dying swiftly after leaving another samurai lord to take over.
Kubi takes these historical events, and is like “okay but what if we added some gay innuendo and gay sex to this drama?” with more beheadings than a French revolution.
Out of all the films on this list Kubi is, admittedly, the one I enjoyed the least, however, it’s an interesting retrospective on the growth of both the Japanese film industry and this specific genre in and of itself.
Kubi’s film style is very modern, it’s beautiful, it’s sleek, it’s expensive looking. And yet there’s specific scenes that feel like callbacks to the Kurosawa era, like the black and white flashback between Nobunage and his fellow samurai lords. One of Kurosawa’s top films was Kitano’s Hana-Bi (1997), and Kitano has worked with Kurosawa’s daughter on costume design on four other films as well, so these references feel not only purposely because of general influence but also referential in a way.

In terms of story and tone, Kurosawa’s The Hidden Fortress is sincere and straightforward, Lady Snowblood is experimental and fearless, Gohatto is introspective and suspenseful, whilst Kubi is unrelenting and even feels mocking at times. There is no break in Kubi's violence, there's almost no tenderness or softness, characters are selfish, and self-centered. The selfish, but joyful peasants in The Hidden Fortress don't exist here, and are replaced with a peasant character who murders his own friend and then rejoices over being relived of his family once he discovers they were murdered too. At times, Kubi feels like a subversion of the more glamourous depictions of the samurai in film. Which feels as though following similar footsteps established in Gohatto which also explored, subtextually, the faults within the samurai media persona.
At times the film feels almost like a dark comedy, it doesn’t glamorize these samurai warlords, nor their clans, nor their ideals in the way The Hidden Fortress does, nor does it interrogate them in the way Gahotto does. Instead the story at hand is presented with a brutal realism, objective if a bit mocking with a side order of gay sex. Which isn’t presented in a mocking way so much as just an everyday aspect of life.
When Mitsuhide and Murashige are caught by spies sleeping together there’s no shock or awe about it, just a calm report and the bigger issue is Mitsuhide hiding a fugitive more so than him sleeping with a man.
Similarly, when Nobunage is literally fucking one of his vassals in front of Mitsuhide, it’s not to disgust the other man, but rather a powerplay of sorts to make the latter jealous - at one point Nobunage promises if Mitsuhide accomplishes a mission for him, he’ll sleep with him - and it seemingly works to some degree. There’s subtext throughout the film that Mitsuhide might be, if not in love with Nobunage, want him in an obsessive way all the same (including being down to bone).

Like with Gohatto the queerness is inherent, just a part of the culture. It’s not “romance” by any means, but it is simply a part of life and the culture itself.
In terms of characters, Kubi's characters couldn't be more different from the characters in the previous mentioned films. The Hidden Fortress characters like Princess Yuki and Rokurota are easy to like, honorable, quiet, steadfast; while Matashichi and Tahei are less outright likable they offer a grounding and relatable to the big presence that are the former two. In Lady Snowblood, Yuki is quiet, calculating and menacing in her own right, truly embodying the idea of cold vengeance which makes her intriguing. In Gohatto Kano is elusive, which adds to his sensual allure, Okita is playful yet clearly hiding a more sinister air about him, and you just feel bad for Tashiro who’s pushy but seemingly sincere in his affections for Kano.
Kubi has no by-the-by “likable” characters, every character is out for themselves in some way shape or form. So much so that the brief tenderness between Mitsuhide and Murashige is like a balm to a burn. Though I did absolutely enjoy the scene-chewing of Ryo Kase who played Nobunage. While Nobunage isn't a "likable" character by any means, he was so fun and engaging to watch he became a highlight of the film.
Stylistically, this is a very modern epic film; it’s the type of film in terms of scale I imagine Kurosawa could have made if he had access to the same technology, but also wouldn’t because there’s no stillness or sincerity to it. The violence is also more in line with Lady Snowblood, but with a budget. Heads are lopped off with ease and at times with glee, dead bodies, headless bodies with crabs crawling out of the necks, a literal pile of heads for trophies it’s all here. It’s beautifully and dynamically filmed, it has a similar scale of a Lord of the Rings, or a Creation of the Gods I: Kingdom of Storms.
Big set pieces, big costumes, big landscapes, big battles, and bigger body counts. It also has the largest cast of any film on the list - kinda neat that Kitano and Asano Tadanobu were both in Kubi and Gohatto together - and the best costumes of the bunch.
It also, in my opinion, has the most complicated plot of all the films because of the heavy political intrigue - though this, admittedly, could be because of the culture gap as I’m not overly familiar with Japanese history.
Okay so like, where does all this leave us in terms of those original bullet points?
The Original Bullet Points
Japanese Cinema hasn’t changed since the 1950s
If there's one thing - well okay many things cause I'm greedy but overall - I hope I've been able to outline here with these four films is that obviously Japanese cinema has changed since the 1950s. And thoroughly at that. Not just in terms of style, but in terms of character presentation, tone, stories technology, experimentation, and a growing reflection of the shifting and developing culture.
It’s not simply that all four of these films are different stories, but that all four of these films are addressing different aspects of their modern culture via these period pieces, as well as, viewing this time period in ways that reflect the filmmakers own experiences and how they feel or felt about the world.
Kurosawa was born in 1910 to Kitano’s 1947, Fujita and Oshima’s 1932. Kurosawa’s father was a member of an actual samurai family, his worldview would be thoroughly different from someone like Oshima, or Kitano, or Fujita’s. Some overlap, sure, but also still thoroughly different.
And I feel that you can see that in their films; Kurosawa’s samurai films are almost referential at times, not always, but his work with Toshiro Mifune often leans that way; in The Hidden Fortress Mifune’s Rokurota is deeply loyal to his lord, the Princess Yuki, to the point that he won’t shed tears over his own sister being executed in her place. He spares the life of a rival because he respects him even though they stand on opposing sides.
The samurai in Gohatto and Kubi aren’t nearly so idealized nor idolized, there’s very little “honor” in Kubi and even less loyalty. Whilst in Gohatto there’s a deep and subtle interrogation of the strict and oppressive bylaws of the shinsengumi. In one such scene, Kano is having drinks with a man who is interested in him, Yuzawa, who’s passionately talking about how the shensengumi uphold oppressive ideals including classism.
[And then he jumps Kano’s bones I guess politics got the dude going lmao]
The Hidden Fortress’ Princess Yuki is at first, masculine - in story she was raised as a man rather than a princess - from the way she walks to the way she talks. She’s fierce, and upstanding, while also being compassionate to other members of her clan; even saving a young woman who’s a member of her clan that had been sold. There’s a regal quality to Princess Yuki.
In comparison, Yuki in Lady Snowblood is elegant, and feminine, before striking out violently. Princess Yuki never has an “action scene” and in fact for a chunk of the film has to pose as a deaf woman to hide her identity. While not a passive participant in the plot, nor does she directly drive the action herself. While Yuki, well the entire movie is driven by her actions and the actions of her mother. The story is first and foremost, hers.
Meanwhile women just like, they don’t exist in Gohatto or Kubi they’re like, in the ether~~~ they’re drifting, keeping out - or kept out? - of the drama.
Given the vast differences in both style, tone, story and execution, how can you say wholeheartedly that Japanese cinema hasn’t changed since the 1950s?
Japanese film style falls under an extreme dichotomy of cinematic/sweeping (described as “atmospheric”) or cartoonish/slapstick (described as “live action manga”)
I’m just…not gonna get into the overall history of Japan's adaptation of manga into live action films cause it would derail this conclusion and I ain’t got the time for that. I would like to note, Lady Snowblood is a live action film based on a manga of the same name - and it is not slapstick. It doesn’t even have comedic elements, it is a violent rape revenge story; I don’t think there’s a single moment where I chuckled. The Hidden Fortress is far lighter in tone, while Gohatto has more in common with Lady Snowblood - deeply and sincerely serious - and Kubi goes for a darker sort of comedy.

This is just incorrect information. Personally I’m of the mind that “cinematic/sweeping is too broad a spectrum to even quantify as a film genre they are descriptors.
That said, I don’t think Lady Snowblood is cinematic or sweeping. Gohatto is the only one on the list that’s even close to “atmospheric” though all four films have atmosphere - because atmosphere is a film technique it’s not a genre of film - The Hidden Fortress and Kubi are the only two I could qualify as “cinematic/sweeping” because they’re going for a larger bombastic scale. Though I feel folks watching The Hidden Fortress in the modern day might not find it cinematic because of how static and slow the film can be at times - the first act is long and drags quite a bit.
To place such a strict dichotomy on an entire industry of filmmaking is simply bad film critique at best and xenophobic at worst given the context here. I’ve only talked about four films in one singular genre, I didn’t mention the countless other new wave films, or the birth of the kaiju genre with Godzilla, the expansion into horror and grindhouse - where does a film like Tag (2015) fit into such a strict dichotomy? - nor the long, long history of animated works from various insanely highly influential and/or successful directors like Satoshi Kon, Makoto Shinkai, Hideaki Anno, Rintaro, Mamoru Hosoda, Mamoru Oshii, Isao Takahata, I mean the list goes on and on.
If you expand your horizons you’ll find so many amazing films that do not flatly sit in this one or the other imposed categorization. Think about what queer cinema you may be missing out on by adhering to this imposed binary.
Baby does any of this have to do with BL? (no, but it IS more gay than you think)

So, in the end, what does this have to do with BL? I would say it has both little and a lot to do with BL/GL which are genres all their own in Japan and other neighboring countries; as such their subject to the same waves, exploration and expansion as the four aforementioned films.
It’s easy, if intellectually dishonest and academically lazy, to look at The Novelist and What Did You Eat Yesterday and say “BL only comes in two shapes and sizes”.
There’s chocolate or vanilla and that’s it. When in reality there’s lots of ice cream flavors available, even if chocolate and vanilla are the best sellers it doesn’t mean strawberry or mint chocolate chip don’t exist.

Where does animated BL fall into this western imposed binary? How does capitalism affect the output of what gets made for the screen and how? How does the political climate affect what’s being financed? Are BL and GL works that are being made somehow unaffected, existing in a stasis state, by the works across the film industry? Even from other queer works of film? What are we, as outsiders, not considering when we engage with this media?
If we’re only looking at BL/GL for “queer representation” what films and/or television are we missing out on from these countries? What BL/GL are we missing by only engaging with what's put in front of us, and not diving deeper into learning more, expanding our individual knowledge, and experiencing stories that might take some work towards seeing? Stories that might be outside of our direct comfort zones because they don't fall into those strict if seemingly comforting boxes. What exploration into queer identity are we denying or ignoring the existence of because of these imposed binaries?
I know some folks who are more well versed in BL history that would and do consider Gohatto and Kubi BL or BL adjacent, but I also know most western, especially American, audiences would consider neither of these films BL.
So where does that leave them?
Further Reading:
Cinematic History: Defining Moments in Japanese Cinema, 1926-1953
A Brief But Essential Introduction to Japanese Cinema
Filmmaking from Japan: The Golden Age of Japanese Cinema
Nagisa Oshima: Banishing Green
JAPANESE SOFTCORE: THE LAST OF TOKYO'S PINK EIGA THEATERS
The Last Samurai: A Conversation with Takeshi Kitano
The Evolution of the Japanese Anime Industry
Check out other related posts in the series:
Film Making? In My BL? - The Sign ep01 Edition | Aspect Ratio in Love for Love's Sake | Cinematography in My BL - Our Skyy2 vs kinnporsche, 2gether vs semantic error, 1000 Stars vs The Sign | How The Sign Uses CGI | Is BL Being Overly Influenced by Modern Western Romance Tropes? | Trends in BL (Sorta): Genre Trends
#gohatto#kubi#japanese bl#lady snowblood#japanese films#ride or die#cherry magic#the novelist#chaos pikachu speaks#pikachu's bl film series
61 notes
·
View notes
Text






Director Akira Kurosawa's hand-painted storyboards for his 1985 film RAN
Kurosawa spent 10 WHOLE YEARS painting every shot he had planned for this movie, an adaptation of Shakespeare's "King Lear"
#movies#art#behind the scenes#storyboard art#painting#akira kurosawa#1980s#1985#japan#japanese films#samurai#history#ran#shakespeare#king lear
30 notes
·
View notes
Text




Strawberry Shortcakes (2006) | dir. Hitoshi Yazaki
#strawberry shortcakes#hitoshi yazaki#japanese film#japanese films#cinema#quotes#cinematography#cinemapix#filmedit#userfilm#kiriko nananan#dailyflicks#snapshots#manga#movieedit#movieedits#filmedits#movies#japanese movie#japanese movies#bm#subtitles#quote
24 notes
·
View notes
Text



227 notes
·
View notes
Text



life can be so wonderful (2007)
#life can be so wonderful#osamu minorikawa#ryuhei matsuda#cinematography#movies#cinema#movies to watch#world cinema#movie quotes#letterboxd#films#imdb#japanese cinema#japan cinema#japanese movies#japanese films#movie list#movie qoute
58 notes
·
View notes
Text


Hi, fellow aspecs! For pride month in case you haven’t heard of other aspec films. Japan has two films in store around the years 2022 to 2023.
Left Photo:
“I Am What I Am” / “Freckles” / “Sobakasu”
- Directed by: Shinya Tamada
- You can watch this from today until June 19th for free on: https://watch.jff.jpf.go.jp/page/jffonline2024/ you just need to sign up and you’re all set (It may not be available to some countries). Those who can’t access that, you can message me for an alternative site! The film is about Kasumi Sobata, an aromantic asexual woman struggling in an amatonormative world.
Right Photo:
“People Who Talk to Plushies are Kind”
- Here we have an asexual character. If you wanna know where you can watch it, feel free to dm me here! || Story: Creating a portrait of sensitive teens and their concerns, Kaneko Yurina’s adaptation of Omae Ao’s novel takes us into the midst of the Plushy Club at a university. It is a place packed with furry and comforting friends whom the club members talk to in order to relay their anxieties and fears. Male student Nanamori and female students Shiraki, and Mugito are the latest club intake, each wrestling with issues such as love, masculinity and femininity, fear of others and sexism in society. (Source: OAFF.jp)
- Based on the Novel:

#ao omae#people who talk to plushies are kind#people who talk to stuffed animals are kind#aroace#aromantic#asexual#aspec#lgbtqia#pride month#pride 2024#aspec films#films#movies#i am what i am#sobakasu#freckles#hosoda kanata#komai ren#toko miura#takumi kitamura#japan#japanese films#japanese#aromantic asexual
64 notes
·
View notes
Text





🎋 Seto & Utsumi (2016)
#sad for his dead cat...#seto and utsumi#setoutsumi#セトウツミ#masaki suda#sosuke ikematsu#tatsushi omori#asian cinema#screencaps#film aesthetic#japanese films#movie stills#japanese movies
90 notes
·
View notes
Text


The Valiant Red Peony : Red Peony Gambler (1968)
Set during the Meiji era, RED PEONY GAMBLER stars Fuji as Ryuko Yano, the daughter of a gambler. When her father is murdered, Ryuko takes on a new name derived from the crimson flower tattooed on her shoulder – “Oryu, the Red Peony” – and sets out for revenge.
One thing I noticed about Japanese films is the use of flower names to reflect their character like in Shogun (2024) and Yae no Sakura (2013). Here, Red Peonies are flowers that can live over 100 years and thrive in cold winters, indicating that she survived the worst.
youtube
As mentioned in my earlier post, Asian films like Japanese films have always featured strong women who are feminine, gentle and caring with those they love and care but fearless, cunning, steadfast and a force to be reckoned with, against enemies.
There are numerous films such as this, Lady Snowblood (1973), Crimson Bat : The Blind Swordswoman (1969), Undercover Geisha (2003) & Ichi (2008), and anime such as Carried by the Wind: Tsukikage Ran (2000), Joran : The Princess of Snow and Blood (2021) & Hell's Paradise: Jigokuraku (2023).
They inspire Hollywood shows like Kill Bill (2003), Blue Eye Samurai (2003) and Shogun (2024). Japanese films are underrated, especially the old ones that I feel it's wasted that most of these shows are not available on global mainstream sites for the world to enjoy and appreciate. But it's good to see people becoming aware of them.
#the valiant red peony#red peony gambler#hibotan bakuto#sumiko fuji#lady snowblood#crimson bat#the blind swordswoman#undercover geisha#ichi#tsukikage ran#joran the princess of snow and blood#hell paradise jigokuraku#kill bill#blue eye samurai#yae no sakura#shogun#japan#japanese films#onna musha#onna bugeisha#period drama#jidaigeki
51 notes
·
View notes