#International Sustainability Standards Board
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
BC determina que instituições financeiras divulguem seus dados relacionados à sustentabilidade
O Conselho Monetário Nacional (CMN) aprovou hoje a Resolução CMN nº 5.185, que estabelece a obrigatoriedade de as instituições financeiras de maior porte divulgarem, junto com suas demonstrações financeiras, relatórios sobre informações financeiras relacionadas à sustentabilidade. Esse processo deve seguir os padrões internacionais estabelecidos pelos pronunciamentos IFRS S1, que trata das…
#sustentabilidade#Conselho Monetário Nacional#demonstrações financeiras#IFRS S1#informações financeiras#instituições financeiras#International Sustainability Standards Board#ISSB#obrigatoriedade#Resolução CMN nº 5.185
0 notes
Text
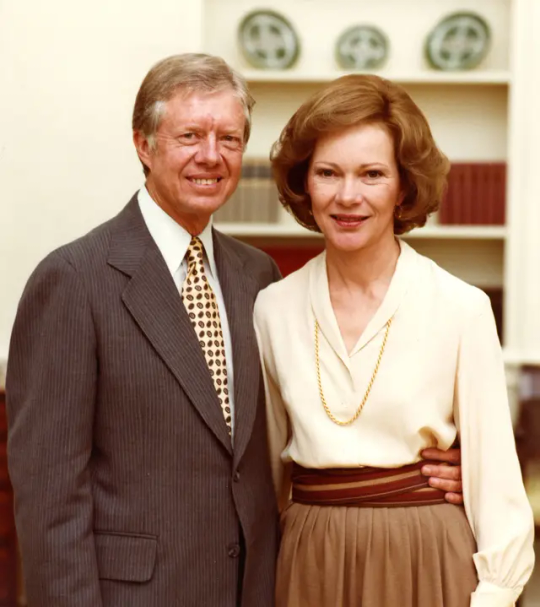

Jimmy Carter
US president whose subsequent decades of tireless humanitarian work brought him the Nobel peace prize
The former US president Jimmy Carter, who has died aged 100, achieved a far more favourable reputation after leaving the White House than he ever secured during his single term of office. Following his electoral defeat in 1980 – when Ronald Reagan beat him by 489 to 49 electoral college votes – his sustained efforts to improve life for the deprived people of the world won him the 2002 Nobel peace prize.
Carter left a mixed heritage from his presidential term. He put human rights firmly on the international agenda, persuaded Congress to cede US control of the Panama canal, demonstrated that peace settlements could be achieved in the Middle East, and completed the second strategic arms limitation treaty with the Soviet Union.
But he was not cut out for the White House. He became the 39th president because he was not Gerald Ford: he was ousted after one term not only because of his administration’s inept handling of the Iranian hostage crisis but because he was overwhelmed by the job.
Carter came into office faced with the continued economic aftermath of the Vietnam war. To meet its burgeoning costs, President Richard Nixon had abandoned the fixed international exchange rate agreed after the second world war and allowed the dollar to float. That immediately imported inflation into the US, exacerbated by the 1973 Yom Kippur war in the Middle East, which provoked Arab oil-exporting nations to quadruple the price of their oil. Carter arrived in Washington with inflation running at 7%. Within 18 months it had climbed to 11.3%.
Oil, which had been $20 a barrel, surged to $107. Carter’s response was to ask the US to curb its profligate use of energy. The plea fell on deaf ears. He then nominated Paul Volcker as chairman of the Federal Reserve Board to deal with the problem. Volcker arrived proclaiming that the US “could not inflate itself out of a recession” and embarked on a ferocious campaign to kill it. The interest figures tell the story: in June 1979 America’s prime rate was 11.5%, by November 15.5%, by March 1980 18.5% and by the end of that year it peaked at 21.5%. During his election campaign Carter had devised what he called the misery index, combining unemployment and inflation. It stood at 13.5 when he was elected. He left the White House with it at 19.9.
He eventually retrieved his reputation by founding the Carter Center in his home state of Georgia and embarking on a vast range of activities designed to defuse international conflict and to introduce democracy and a decent standard of life across the globe.
This took him to countries ranging from Zambia to Peru and from Sudan to Guyana, for such disparate projects as mediating in civil warfare, encouraging sustainable agricultural development, establishing a proper judicial system, or installing a clean water supply. He became a familiar figure at election counts around the globe, part of the international team that sought to ensure that where skulduggery could not be prevented, it was at least well publicised.
With the agreement of the Clinton administration, in 1994 Carter took up an invitation to visit Kim Il-Sung in Pyongyang, and out of their talks came the Agreed Framework, by which North Korea undertook to suspend its nuclear weapons programme in return for increased energy aid from the US. Initial progress was not sustained, and by 2003 relations between the two countries were openly hostile again. In 2008 he was criticised in the US and Israel for urging peace talks involving Syria and Hamas. In August 2010 he returned to North Korea to secure the release of a US citizen, Aijalon Gomes; he visited the country again in 2011, and six years later indicated his willingness to do so once more if called on.
Carter acknowledged that much of the energy he brought to the Carter Center had stemmed from the unexpected frustration of his presidential career. “I don’t think that if I had had two full terms in the White House, I would have launched so ambitious a new career. I would probably have become a professor and written some books.”
Born in Plains, Georgia, Jimmy (James) was the eldest of four children of Lillian (nee Gordy), a nurse, and James Carter, a peanut farmer. He planned a naval career, graduating from the US naval academy in 1946. Then he became involved in the design and development of nuclear power for ships, and later with training seamen to serve in them. This was apparently when he acquired his dogged interest in organisational and functional minutiae.
In 1953, however, the death of his father obliged him to resign his commission to take control of the family business. This sparked an interest in politics and, in 1962, he was elected a state senator. At the end of his four-year term, he ran unsuccessfully for the governorship of Georgia. In 1970 he was elected at his second attempt and began to plan his presidential campaign.
His ambitions coincided with the Watergate scandal and the enforced resignation of Nixon in August 1974. Ford, a Republican congressman from Michigan, had been hand-picked by the beleaguered incumbent as his successor. The electorate, initially neutral about the constitutional niceties of this procedure, erupted in fury when the newly sworn-in President Ford announced an unconditional pardon for his patron. The stage was thus set for Carter’s bid, on the basis that he did not belong to the Washington establishment and that he espoused the simple moral and religious values that the electorate was then seeking.
In the 1976 primaries he easily outpaced his Democratic rivals. But his presidential victory was uncomfortably narrow: he won only 23 of the 50 states and secured less than half the popular vote (excluding Washington DC). His arrival in the White House arose more through the quirks of the electoral college, where he predominated by 297 votes to Ford’s 240. His election showed plainly what became even more starkly evident as his term progressed: that support in the country was marginal and could be eroded by almost any setback. The honeymoon lasted long enough domestically to get the Panama canal treaties ratified in 1978 – no small achievement – and internationally to bring Israel and Egypt to a widely applauded peace settlement in 1979, brokered by Carter.
But the very nature of his electoral campaign quickly rebounded on him. He chose to emphasise the shift from previous administrations by appointing a group of inexperienced assistants to senior posts. Within a short space of time, his budget director, Bert Lance, was forced to resign amid allegations of impropriety – charges that sat ill with Carter’s repeated emphasis on probity. His chief of staff, Hamilton Jordan, became notorious for his poor handling of influential figures on Capitol Hill, a vital factor for any administration, but even more critical in the post-Vietnam, post-Watergate climate in Washington.
Congress, in its own eyes, had been bulldozed into the expansion of the Vietnam war by Lyndon Johnson, grossly affronted by Nixon’s constant claims of executive privilege and eventually by his illegalities, and circumnavigated by Ford’s accession. It had fettered the White House with the War Powers resolution of 1973 and came within a whisker of impeaching the president. It was singularly unimpressed by the arrival of a man whose experience was as a one-term southern governor.
It might have been easier had Carter arrived with a clear political agenda, but he seemed geared to the politics of symbolism rather than substance. In an effort to focus his compatriots’ attention on their profligate use of energy, he addressed the nation wearing a woollen cardigan, which simply drowned the message in derision. His national energy policy was barely recognisable by the time it emerged from Congress.
The international community also found itself with problems caused by the amateurism of the White House. Within six months of taking office, Carter requested funds to develop neutron warheads for missiles deployed in Europe, particularly West Germany. There had been no consultations within Nato, and a row erupted in Europe. The Dutch defence minister resigned and Chancellor Helmut Schmidt of West Germany, faced with demonstrations and parliamentary dissent, publicly dissociated himself from the move. The furore continued for months, until Carter suddenly announced that he had abandoned the idea, having exposed serious rifts within the Atlantic alliance to no useful end.
In spite of alarming the Kremlin with unsignalled proposals for huge cuts in strategic weapons (later abandoned), his administration did manage to negotiate the Salt II (strategic arms limitation talks) agreement, a complex, phased programme of strategic disarmament. But it aroused deep suspicions in the Senate, which had little liking for the president anyway, and the treaty was consequently never ratified.
By now it had become evident to the country that its chief executive was becoming impotent through his insistence on bogging himself down in detail to the extent that he even insisted on drawing up the playing rota for the White House tennis courts. With his popularity waning steeply, particularly after a disastrous television address in which he seemed to saddle the nation with his own uncertainties, Carter was hit by the twin crises that doomed his presidency – the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan and the fall of the shah of Iran.
Long after he left office, it emerged that much of the blame for the Afghan crisis could, in fact, be laid at his door. In February 1979 the US ambassador in Kabul, Adolph Dubs, was kidnapped and died in a botched rescue attempt by the local police. The Soviet Union was alleged to have been behind the kidnapping and, in retaliation, Carter signed a secret directive on 3 July 1979, authorising the CIA to fund and arm Muslim opponents to the Kabul regime, which the Soviet Union supported.
This decision was later described by Carter’s national security adviser, Zbigniew Brzezinski, as “giving the Soviet Union its own Vietnam”. Its consequences, including the rise of the Taliban, have clanked unpredictably through the ensuing decades. As US-funded fighting spread rapidly across Afghanistan, the Kabul regime tottered and Moscow decided that the only answer to the destabilisation of its strategically vital southern border was to invade.
Carter, already in deep trouble over the fall of the shah, responded to the Soviet invasion by shooting himself in the foot. With domestic political attention focused on the impending 1980 presidential campaign, he announced an embargo on a portion of US grain exports to the Soviet Union, the prime victims of which were America’s midwestern farmers rather than the USSR.
He did manage to see off the internal party challenge of Senator Edward Kennedy, but slipped badly in the broader race for re-election. He had been unlucky in inheriting the brewing Iranian crisis, but he handled that no better. The shah was entirely the creature of successive US administrations. It was, therefore, self-evident that the dethroned monarch would turn to his patrons in his final crisis and that, conversely, the new Iranian regime would stoke the anti-Americanism built up by his autocratic reign.
The US embassy in Tehran sent repeated warnings of the likely Iranian reaction if the terminally ill shah was allowed into the US, but they were ignored by the White House. Within three weeks of his arrival for medical treatment, the embassy had been seized and 53 of its staff held hostage. A bad situation was made far worse by an ill-conceived and ultimately disastrous attempt to mount a rescue operation. Its chances of success were always slight and were wholly nullified by the combination of equipment failures and excessive interference from above.
Had Carter been held in greater confidence by his countrymen, they might have had more sympathy for his dilemma. He had nothing to bargain with, and it became evident that for Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, the fundamentalist Shia cleric who had overthrown the shah, the crisis had become a personal contest. He released the American hostages only at the moment when Carter was succeeded by Reagan.
Carter’s political ambition far outreached his experience or capacity, but his brief sojourn in the Oval office at least gave him the international standing to carry out the humanitarian work for which he will probably be best remembered. With his wife, Rosalynn (nee Smith), whom he married in 1946, he visited more than 140 countries.
He wrote 30 books, including A Call to Action (2014), which addressed discrimination and violence against women, and A Full Life: Reflections at Ninety (2015). Having turned 100 last October, he fulfilled his aim of voting in the presidential election.
Rosalynn died in November 2023. He is survived by their four children, Amy, Jack, Chip and Jeff, 11 grandchildren and 14 great-grandchildren.
🔔 James Earl Carter, politician, born 1 October 1924; died 29 December 2024
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
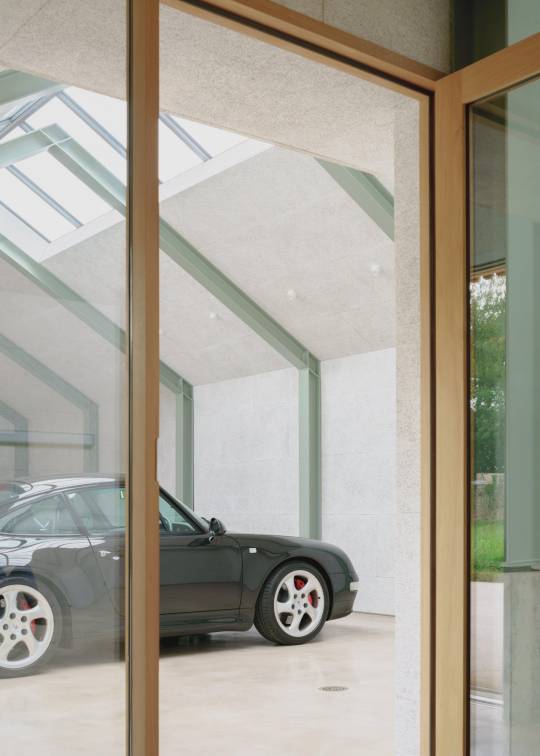
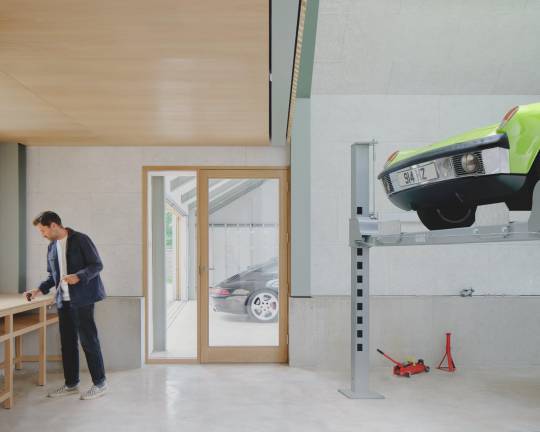
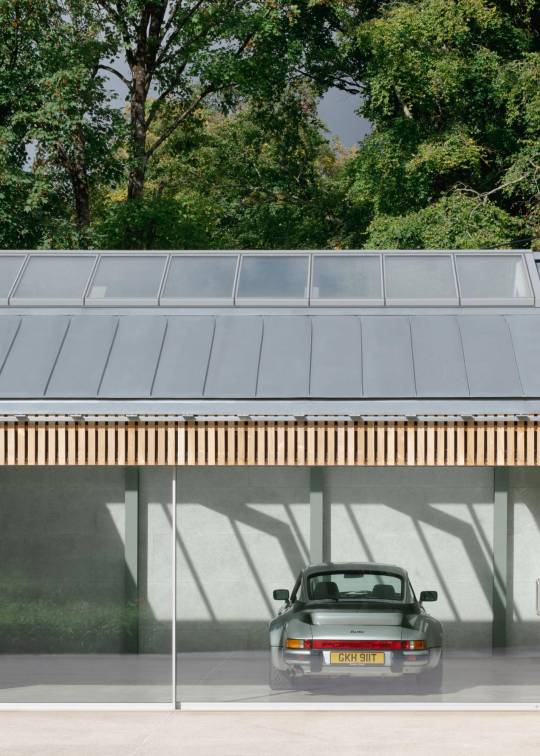
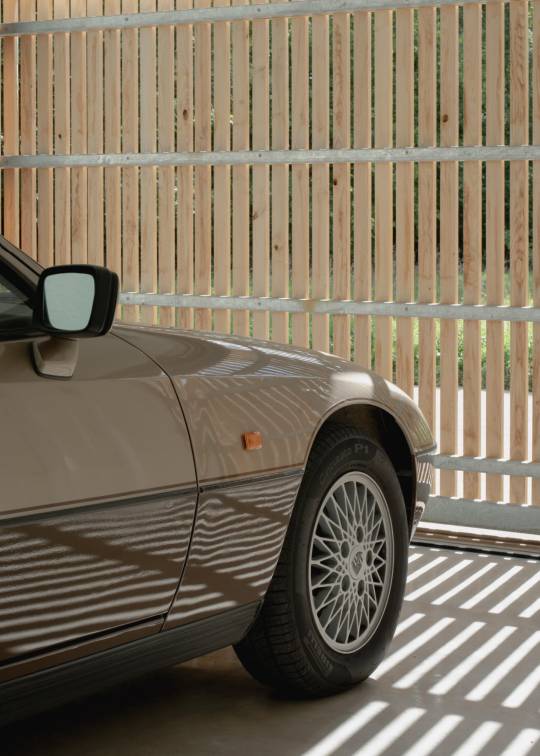
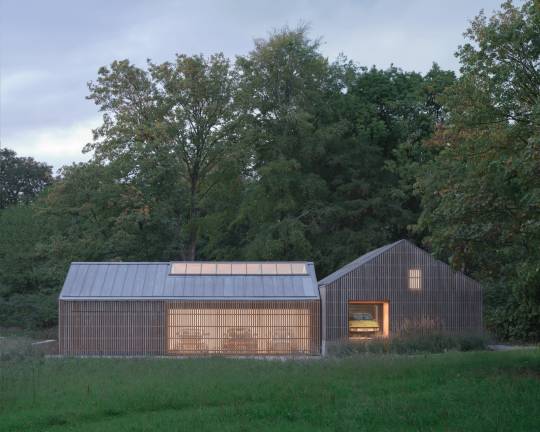

















Autobarn by Bindloss Dawes
The Autobarn is the realisation of our client's long-term dream to house his collection of classic German cars. The project is composed of two volumes: a clean, five-bay garage for everyday use and a taller workshop for repairs and future restoration projects.
Beyond satisfying this initial use, the project ambition was to create a flexible, 'long-life, loose-fit' building that could be used for a range of different uses. Currently it doubles up as event space, however the ambition is that the Autobarn could one day become a low-energy house.
Located on the outskirts of a small Somerset village, the project is set within the grounds of an eighteenth-century Grade 2 listed house. It replaces several haphazard outbuildings and consolidates their amenity into an elegant architectural proposal, nestled within a glade of mature trees.
The project's design references the language of neighbouring agricultural barns. As a practice we are interested in reassessing the rural vernacular, both for its contextual appropriateness and its lessons in low-cost, pragmatic design. As such, the Autobarn re-interprets simple forms and methods of construction, adapting more temporary, rudimentary methods into a robust and elegant paradigm for low-cost, rural architecture. Composed of a concrete base and steel framed structure, intermittent timber cladding and zinc metal roof, the Autobarn adapts barn typologies with varying levels of refinement. Consideration was also given to its weathering, with the natural zinc roof dulling to complement the silver patination of the sweet chestnut cladding.
Like many barns, permeability to light and air is controlled through a series of movable layers. First experienced as a closed solid mass, the barn walls open up via a number of doors, including an heroic 7m sliding timber screen. The intermittent timber slats of the screens create internal dappled light during the day, which is reversed at night as interior lighting illuminates the surrounding landscape. Internally the steel structure is expressed in an array of simple portal frames, with sustainably-sourced wood-fibre acoustic board forming internal wall and ceiling. The garage space is calm and gallery-like, while the workshop space presents a tougher, taller workshop, surrounded with concrete wainscotting and designed to accommodate a car lift.
The building's 'long-life/loose-fit' ambitions have meant that the insulation and energy performance exceed residential standards. Although thermostats are currently turned down for its current use, the building includes underfloor heating powered by an Air Source Heat Pump, as well as additional first fix services hidden behind the internal wall paneling for future conversion.
Construction started in November 2020 and was completed at the end of 2021, with the project effected by the global pandemic and building material inflation. Despite these challenges, and the inclusion of some one-off expensive items (such as the electric garage doors), the Autobarn was built for under £2,300 / m2. In tandem with high energy performance and the use of natural materials, it combines our studio's goal to combine beauty, affordability, and sustainability.
Design: Bindloss Dawes Location: Frome, United Kingdom Area: 165 m² Year: 2022 Photography: Building Narratives
#architecture#gable roofs#garages#barns#british barns#british garages#united kingdom#bindloss dawes#building narratives#interiors
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Essential Auxiliary Machinery on Ship
1. Generators
Generators are the heartbeat of a ship’s electrical system. They provide electrical power for various onboard systems, such as lighting, navigation equipment, communication systems, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning). Depending on the ship’s size and power requirements, multiple generators may be installed to ensure redundancy and continuous power supply during extended voyages.
2. Boilers
Boilers are essential for producing steam, which is utilized for various purposes on board. Steam is used for heating fuel oil and other fluids, running steam turbines for power generation, and operating various machinery and auxiliary machinery equipment, such as steam-driven pumps and winches.
3. Air Compressors
Air compressors generate compressed air used to power pneumatic tools, such as wrenches and chipping hammers, and operate pneumatic control systems. They also provide compressed air for starting main engines and auxiliary engines.
4. Purifiers
Fuel and lube oil purifiers play a critical role in maintaining the quality of fuels and lubricants used onboard. These machines remove impurities, water, and solids from fuel and oil, ensuring smooth engine operation and prolonging the life of critical machinery.
5. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems
Refrigeration and air conditioning systems are vital for maintaining the temperature of provisions, perishable cargo, and living spaces. These systems use refrigerants and cooling coils to control temperature, humidity, and air quality throughout the ship.
6. Ballast Water Treatment Systems
To maintain stability and maneuverability, ships require ballast water to be pumped in or out as cargo is loaded or unloaded. Ballast water treatment systems are responsible for purifying and treating the ballast water to prevent the spread of invasive species and maintain marine ecosystem health.
7. Sewage Treatment Plants
Sewage treatment plants are responsible for processing and treating wastewater generated onboard. They help ensure that treated effluent meets international environmental standards before it is discharged into the sea.
8. Bilge Water Separators
Bilge water separators remove oil and other contaminants from the bilge water, a mix of seawater and oil that collects in the lower parts of the ship. The clean water is then discharged, while the separated oil is collected for proper disposal.
9. Incinerators
Incinerators are used to burn solid waste generated onboard, such as paper, cardboard, and non-recyclable plastics. Proper incineration reduces waste volume and ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
10. Water Makers
Water makers use reverse osmosis or distillation processes to convert seawater into potable water for drinking, cooking, and various onboard applications. They are especially vital for long voyages where access to freshwater sources may be limited.
Conclusion
The auxiliary machinery found on ships plays a crucial role in maintaining the vessel’s efficiency, safety, and comfort during journeys at sea. From power generation to waste management and water purification, each system contributes to the smooth operation and sustainability of modern ships. The continuous advancement of auxiliary machinery technology further enhances the capabilities and environmental performance of ships, making them safer, greener, and more reliable for maritime transportation across the globe.
#generator parts#ship machinery parts#navigation equipment#Auxiliary Machinery Equipment#Ship Machinery Parts#Auxiliary Machinery#Generator Parts#Automation#Navigation#pumps#automation systems
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Corporate Governance Consulting

Corporate governance consulting plays an essential role in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of companies operating in Turkey. The country hosts a wide range of domestic and international firms, all of which must navigate a dynamic legal and commercial landscape. Corporate governance consulting ensures that companies comply with international standards while optimizing their management, auditing, and operational structures. By implementing best practices in corporate governance, companies can not only improve their competitiveness but also ensure long-term growth.
What is Corporate Governance in Turkey?
Corporate governance refers to a framework of rules, practices, and processes that direct and control a company. The primary responsibility for corporate governance typically lies with the board of directors, who are accountable for managing senior leadership, conducting audits, and organizing key meetings, such as general assemblies and board meetings. These activities must be carried out according to both Turkish regulations and international standards to promote transparency and accountability within the company.
The Four Principles of Corporate Governance
Globally, corporate governance revolves around four key principles that all companies must follow:
Transparency – Ensuring openness in all business dealings and communication.
Fairness – Maintaining an impartial approach to stakeholders and employees.
Responsibility – Making decisions that prioritize long-term success while upholding ethical standards.
Accountability – Being answerable for decisions and the overall governance of the company.
Companies that adhere to these principles can build stronger relationships with investors, employees, and customers, ensuring sustainable growth.
What is Corporate Governance Advisory?
Corporate governance advisory involves offering professional advice and services to companies to help them establish and maintain sound governance structures. A comprehensive corporate governance advisory service includes:
Drafting policies for hiring and overseeing senior executives.
Ensuring regulatory compliance across all operational areas.
Developing strategies for investment and risk management.
Guiding structural changes within the company, such as mergers or capital alterations.
Corporate governance consulting services also play a vital role in establishing companies in Turkey by aligning their operations with international standards for accounting, auditing, and management. By enhancing transparency and accountability, these services help companies operate more efficiently and ethically.
Legal Framework Governing Corporate Governance in Turkey
In Turkey, corporate governance is primarily governed by the Turkish Commercial Code (TCC) No. 6102 and the Capital Markets Law No. 6362. These legal frameworks have evolved in response to global economic changes and emerging commercial needs. The 2024 amendments to these laws reflect the ongoing transformation of corporate governance practices, offering companies clearer guidelines and more flexibility in managing their affairs.
Key revisions to the Turkish Commercial Code include changes to the roles of the board of directors, such as eliminating the annual election requirement for chairs and vice chairs and updating procedures for calling board meetings. Additionally, the minimum capital requirements for both limited liability and joint-stock companies have been increased significantly to encourage stability and growth in Turkey's corporate landscape.
Corporate Governance Services by Pi Legal Consultancy
Pi Legal Consultancy offers a wide range of corporate governance services designed to help companies comply with Turkish and international regulations. Our corporate governance consultants provide legal and strategic advice on various matters, such as:
Organizing board of directors and general assembly meetings.
Managing capital increases or decreases.
Ensuring good governance during structural changes, such as mergers and acquisitions.
Addressing legal liability issues for company founders, members, and managers.
Assisting with taxation and taking legal action when necessary.
Our firm also specializes in helping foreign companies establish and operate in Turkey, providing tailored solutions to improve their competitiveness and legal compliance. For more information about this topic https://www.pilc.law/practice-areas/corporate-governance-law/
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey, sorry to bother you! But last night's ep of Chicago PD was pretty poor by PD standards at least with my eye, which is ironic given how we were being begged to watch. But what does a 0.44 demo mean? How do they know the age demo of an audience?
Also does PD (or most One Chicago shows) ever actually have competition to challenge for viewings? Do you know of anything coming up? When I see TVline everything alongside it looks dull so I can see why One Chicago always comes up top still. I'm not from the US so a lot of the other shows don't mean much to me especially if reality TV/sport!
Ye olde ratings question!
Alright- to answer your demo question, the number 0.44 is an abstract measurement for how many people in the 18-49 year old age category (the target audience) watched the show. It is calculated through an extrapolation of viewers who report to a company called Nielsen. These Nielsen viewers complete surveys about their age, race, or other defining demographics, which is how they know the ages of people watching. THIS article explains how all the math is done, but the biggest thing to remember is that these numbers are an estimation of what the whole American population is watching based on a sampling of people.
The question of are these good ratings? is very loaded. I believe this is at or around a series low for PD so, no it's not good for them and it has been dropping. However, broadcast TV is dropping across the board and these ratings are higher than several other scripted programs on network TV right now. To answer your competition question, yes they will eventually have more scripted competition (all of One Chicago will), but several shows have not returned from their hiatus yet. We will likely get a clearer look at how the show is faring in the next couple months as networks bring their primetime programming back. It is worth remembering that PD has been a top-rated show for most of its run. While they are dropping, that ranking still may not change if everyone else is dropping too.
Then it becomes a money question. These ratings help set ad rates, so is the ad money coming in enough to sustain the show still? So far, it seems so- just with a lot of purse strap tightening.
Edit: forgot to mention that ad money is not the only source of income for these shows. Syndication, international markets, etc.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
It was only a matter of time before Russia’s fast-growing shadow fleet, a group of vessels whose owners do their utmost to conceal their identity while carrying oil to evade sanctions on Moscow, started becoming a serious maritime risk. Russian vessels are now regularly turning down pilotage in Danish waters, the Financial Times reports—a practice that not only breaches maritime etiquette but could also lead to a disastrous accident.
The collision involving a container ship and Baltimore’s Francis Scott Key Bridge in the United States on March 26 demonstrates the dangers involved when bulky ships vessels through difficult waters. Indeed, the Dali struck the bridge despite being steered by two pilots. Even if just a small share of vessels turn down pilotage, similar disasters risk becoming commonplace.
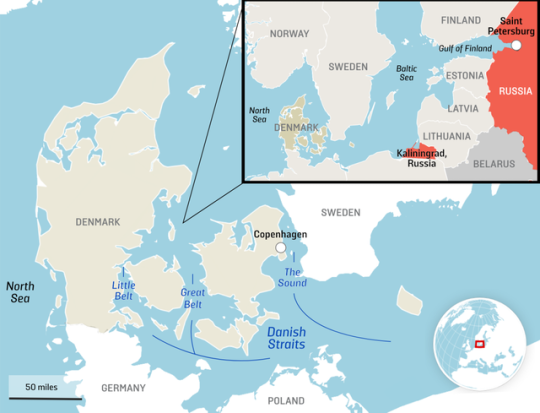
International maritime rules strongly recommend the use of pilots with specialized local knowledge for most vessels sailing through Denmark’s Great Belt, the narrow passage between the country’s largest islands. The Great Belt is not just narrow���it also has treacherous waters and is extremely busy: Every year, some 70,000 vessels pass through the Great Belt and the nearby Sound (Oresund), which sits between the shores of Denmark and Sweden. It’s standard practice to follow international maritime recommendations and take on an experienced local pilot when it comes to difficult navigation routes, whether that’s the Great Belt or the Suez Canal.
The Geography of the Danish Straits
For the sake of maritime order and safety, Copenhagen could block ships that refuse pilotage. That, though, might trigger a standoff with Russia—if Moscow admits its role as a patron of the shadow fleet. Indeed, blocking these rule-breaking vessels would itself violate international maritime rules. Before forcing such a choice, however, the open-source intelligence community could help by revealing the identities and whereabouts of shadow vessels’ owners.
Since the beginning of this year, at least 20 tankers that are suspected to be shadow vessels transporting Russian oil have refused to take Danish pilots on board, according to internal reports leaked to the Financial Times and the Danish research group Danwatch.
That’s at least 20 tankers that have sailed through the Baltic Sea—in most cases via the Gulf of Finland, passing through the exclusive economic zones of Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Sweden, and Germany—into Danish waters and the Great Belt, from which they have traveled on to Kattegat (comprising Danish and Swedish waters) and Skagerrak (Danish and Norwegian waters) and into the North Sea and the oceans that will bring them to their buyers in countries such as India and China.
Shadow vessels are clapped-out ships that spend their last remaining years providing transportation to and from sanctioned countries that official vessels and their owners won’t touch. The risk that these and other dark vessels pose to coastal states is further increased by the fact that they sail under the flags of countries unlikely to come to anyone’s aid if they cause accidents or incidents (Gabon is a particular favorite) and don’t undergo regular maintenance. Any accident—be it a collision or an oil leak—is likely to be doubly disastrous as a result.
Add to that the fact that their owners are hard to track down—and that they lack proper insurance. If a shadow vessel were to sustain a massive oil spill in, say, Finnish waters, Finnish authorities and taxpayers would end up on the hook. And shadow vessels are more likely than law-abiding ones to be involved in accidents since they frequently turn off their AIS (automatic identification system), a GPS-like navigation tool that allows vessels to see one another.
Since the start of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, Russia’s attempts—often successful—to avoid sanctions have caused the shadow fleet to balloon; it’s currently thought to encompass some 1,400 vessels, though like all illicit activities, it’s impossible to measure precisely. (My report about the shadow fleet from last December provides an in-depth examination of the ships and the threats posed by them.)
If oil spills do occur, the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) International Oil Pollution Compensation Funds assist the countries affected. But if oil and other toxic spills increase substantially, as they’re likely to do as a result of the shadow fleet, the fund won’t have enough money to compensate everyone.
So should Denmark simply block shadow vessels refusing pilotage, or all shadow vessels for that matter?
Not so fast. Yes, shadow vessels violate international maritime rules and conventions—but the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) gives all vessels the right of so-called innocent passage, meaning the right to sail through other countries’ territorial waters and exclusive economic zones. The fact that shadow vessels violate maritime rules doesn’t give coastal states the right to violate the rules in turn.
And, noted retired Rear Adm. Nils Wang—a former chief of the Danish Navy, which also covers a range of coast guard tasks—“according to international law, the Danish Straits are international straits and are not under Danish jurisdiction. For this reason, too, Denmark doesn’t have the legal right to force ships to use pilots.”
Though most ships follow the IMO’s recommendations and use pilotage, for which they pay a fee, over the years there have been some cheapskates that turned down pilotage. In some cases, those ships caused oil spills. “Every time there’s a leak from a vessel that didn’t use pilotage, there’s an outcry to ban offenders, but we can’t,” Wang said.
Then, in the mid-2010s, the number of cheapskates traveling without pilotage grew.
Danish authorities got creative and announced that if ships with drafts (the amount that the extends beneath the waterline) of more than 11 meters (about 36 feet) didn’t request pilotage, then the Danish authorities would call them on VHF, the radio used by sailors, and remind them that they weren’t following international recommendations, and that Denmark would report them to their flag state and the IMO.
What’s more, a call on VHF allows every vessel in the vicinity to hear the conversation. “And then we started doing it,” Wang said. “And it changed behavior, because it was embarrassing for the ships and the captains to be called out like this. But if you’re part of the dark fleet, you don’t give a damn. Calling these vessels out won’t make a difference.”
Coastal states do have the right to block access in their territorial waters in certain cases—such as if transiting vessels are in poor repair or lack proper insurance. But when nations agreed and signed UNCLOS in 1982, a situation in which a country systematically evades globalization-based economic sanctions by using a fleet of dark vessels was inconceivable.
In response to the emergency of the shadow fleet, the world’s UNCLOS signatories could convene to make pilotage in sensitive waters mandatory. But such negotiations would take a long time, and under the current geopolitical conditions may never reach a conclusion. And because the Danish Straits are international waters, Denmark can’t impose new rules on its own.
This is globalization in a fiercely geopolitical era: Russia can invade Ukraine and evade the resulting sanctions by means of a fleet that sails through law-abiding countries’ waters—and their governments can’t stop it. On the contrary, with Russia now having joined Iran, Venezuela, and North Korea in using a shadow fleet, more countries will conclude that misbehaving and incurring economic sanctions is no big deal. And trade using dark vessels is cheaper than using legally operating ones.
An even larger shadow fleet would, of course, increase the risks both for marine wildlife and regular shipping. If a Russian shadow vessel collides in the Danish Straits with a legal merchant vessel, or even a Danish Navy vessel, what would Denmark do? What would NATO do?
But for now, there’s one group of dark-fleet operators that can be targeted completely legally and without risk of geopolitical escalation: the shadow vessels’ owners. They are plentiful and hide behind post office box addresses in countries such as the United Arab Emirates—because they don’t want to emerge from the shadows.
On the good side in this standoff, though, we have a large and growing community of open-source investigators, both professionals and amateurs. These investigators should take on a good deed for the global maritime order and investigate shadow-vessel owners, then share their identity and activities. Some may be hardened criminals immune to the embarrassment of public scrutiny, but many others may simply be ordinary businesspeople who have spotted an opportunity.
Just as with the ships once called out on Danish radio, public shame may be one way to force people to act for the better.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
CASH FLOW: The Bloodline of Business
See Into Your Financial Future
In the dynamic world of entrepreneurship, success hinges not only on brilliant ideas and strategic planning but also on mastering the art of cash flow management. Cash flow, often referred to as the lifeblood of a business, is the movement of money in and out of your business, and understanding its importance is paramount for new entrepreneurs.
The Importance of Cash Flow
Cash flow is the heartbeat of your business, fueling its daily operations, growth initiatives, and long-term sustainability. Here's why it's crucial for new entrepreneurs:
Survival and Stability: Positive cash flow ensures your business can cover its day-to-day expenses, such as rent, utilities, payroll, and inventory. Without sufficient cash flow, even the most promising ventures can falter and fail.
Opportunity and Growth: Healthy cash flow provides the flexibility to seize opportunities for expansion, innovation, and investment. Whether it's launching new products, entering new markets, or scaling operations, a robust cash flow empowers entrepreneurs to pursue growth with confidence.
Identify potential cash flow problems early on.
Make better business decisions.
Attract investors and lenders.
Debt Management: Effective cash flow management helps entrepreneurs avoid excessive reliance on debt to finance their operations. By maintaining positive cash flow, businesses can reduce interest expenses, improve creditworthiness, and mitigate financial risk.
Risk Mitigation: Anticipating and managing cash flow fluctuations allows entrepreneurs to identify and address potential risks before they escalate into crises. By maintaining a buffer of cash reserves, businesses can weather unexpected challenges and maintain financial stability.
The History and Complexity of Cash Flow Statements
In 1987, the Financial Accounting Standards Board mandated that firms provide cash flow statements. Following this, in 1992, the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued International Accounting Standard 7 (IAS 7), titled Cash Flow Statement, which took effect in 1994, requiring firms to provide cash flow statements.
Two primary methods exist for calculating cash flow: the direct method and the indirect method. The Direct Cash Flow Method involves totaling all cash payments and receipts, including payments to suppliers, receipts from customers, and salary disbursements. This method is simpler, particularly suited for very small businesses operating on a cash basis accounting method.
However, most companies utilize the accrual basis accounting method, where revenue is recognized upon earning rather than upon receipt. This distinction leads to a disparity between net income and actual cash flow. Consequently, certain items, such as accounts receivable (AR), inventory, taxes payable, salaries, and prepaid insurance, necessitate reevaluation when calculating cash flow from operations. For many new entrepreneurs, navigating these intricacies can be challenging.
New entrepreneurs may find that traditional Cash Flow Statements are not immediately beneficial to their business endeavors, and are better left for their accounting software to generate and for an Accountant to review. Instead, their efforts are best directed towards the daily activities of the business: documenting transactions, monitoring cash flow, and making informed decisions in real-time. By prioritizing day-to-day cash flow management, entrepreneurs can sustain financial stability and swiftly respond to changes in their business environment. It's more valuable for them to gain a thorough understanding of the inflows and outflows of cash within their business operations.
What affects cash flow the most?
Typically, sales and revenue affect cash flow the most, though this can vary from business to business. An increase in sales generally contributes positively to cash flow, while a decline can hinder cash flow.
Additionally, expense management can make a huge difference in a company’s cash flow as it directly impacts the amount of cash retained. The timing of payments also plays a crucial role — even profitable businesses can face cash flow issues if it doesn’t manage the timing of receiving payments and settling financial obligations like debts and payroll.
What causes a lack of cash flow?
Declines in sales or revenue, high expenses, and slow-paying customers can cause a lack of cash flow. Ineffective financial management or a lack of planning can also contribute to cash flow shortages, which is why adopting technology to help you track expenses is crucial for business.
A Groundbreaking Tool for Tracking Cash Flow:
Because cash flow management is imperative for business success, NOBOSS has a more practical and efficient approach to handling finances on a day-to-day basis: the Cash Requirements report.
This innovative tool provides entrepreneurs with real-time insights into their cash needs, allowing them to anticipate, plan, and manage financial resources with precision and agility.
By leveraging the Cash Requirements report, entrepreneurs can stay ahead of cash flow challenges, make informed decisions, and optimize their business operations for sustained growth and profitability.
Managing Cash Flow with the Cash Requirement Report
With Cash Requirements report, managing cash flow becomes not just a necessity, but a strategic advantage in navigating the complexities of entrepreneurship.
For new entrepreneurs, mastering cash flow management requires a proactive approach and a solid understanding of key principles.
Here's how the Cash Requirements Report identify and manage cash flow effectively:
Track Cash Flow: Update and diligently tracking your cash inflows and outflows on a regular basis.
Forecast Cash Flow: The beauty of this report is that you can see into your financial future! Develop cash flow projections to anticipate future income and expenses based on historical data, market trends, and business objectives. This forward-looking approach allows you to plan ahead and make informed decisions.
Manage Accounts Receivable: Accelerate your cash flow by invoicing promptly and following up on overdue payments. Implement clear payment terms, offer incentives for early payment, and consider using online payment platforms to streamline the billing process.
Control Expenses: Evaluate your business expenses regularly and identify areas where costs can be reduced or optimized. Negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, scrutinize discretionary spending, and prioritize investments that yield the highest return on investment.
Build Cash Reserves: Establish a buffer of cash reserves to cushion against unexpected expenses, seasonal fluctuations, and economic downturns. Aim to maintain a healthy cash balance that covers at least three to six months' worth of operating expenses.
Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor your cash flow performance and adjust your strategies as needed. Stay proactive in addressing cash flow challenges, seizing opportunities for improvement, and adapting to changes in the business environment.
These six essential steps to identifying and managing cash flow are seamlessly integrated into the functionality of the Cash Requirements report. This powerful tool empowers new entrepreneurs with the same level of financial insight and leverage enjoyed by big businesses.
THE BOTTOM LINE
Cash flow management is a fundamental skill that every entrepreneur must master to build a resilient and thriving business. By recognizing the importance of cash flow, implementing proactive strategies, and staying vigilant in monitoring and managing cash flow, new entrepreneurs can navigate the challenges of entrepreneurship with confidence and unlock the full potential of their ventures. Remember, cash flow isn't just about survival—it's about laying the foundation for long-term success and prosperity.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
USPS Proposes Raising The Prices of First Class Stamps To 73 Cents
"I don’t know how I’m going to afford 73 cents for one stamp," a customer said.
— By Bill Hutchinson | April 10, 2024

If the U.S. Postal Service gets its way, the price of a first-class stamp will go up for the fourth time in less than two years.
The USPS is proposing hiking the cost of a first-class stamp to 73 cents, or roughly 7% on all forms of postage.
If approved, the plan, which was announced on Tuesday, will raise the price of metered 1-ounce letters to 69 cents, international ounce-size letters and postcards to $1.65 and domestic postcards to 56 cents.
The proposal has been sent to the independent Postal Regulatory Commission for final approval. If the commission signs off, the new prices will take effect in July.

Proposed Increases in Stamps! ABC News
The price-hike proposal comes after the USPS raised the cost of a first-class stamp to 68 cents from 66 cents on Jan. 21. Stamp prices rose twice in 2023.
In the past 20 years, the price of a first-class stamp has climbed about 84%.
"It's ridiculous, absolutely ridiculous," New Yorker Jacqueline Pollen told ABC News as she exited a post office on the upper West Side of Manhattan. "I’m a senior on a fixed income. I cannot really afford stamps that much. I do have a lot of Forever stamps that I bought years ago and I’m using them up, but I don’t know how I’m going to afford 73 cents for one stamp."
Like millions of Americans, Pollen said she has cut back on mailing letters, even Christmas cards, saying, "I use E-cards and email. That's what I use now to save money."
But Manhattan resident Albert Quiles, who was going into the post office to purchase stamps, said he's resigned to paying the higher postal prices.
"I've got to deal with it. What else can you do? You've got to go with the flow, man. Times change," Quiles told ABC News. "There's nothing you can do. The government says this is what you've got to do. It's not like it's just me -- it's everybody. I don't feel bad about that."

Price of postage stamps may go up by 5 cents! If the plan is approved, the price hike would be the highest stamp increase ever. A USPS mail delivery vehicle is seen outside a post office, July 3, 2022, in Louisville, Ky. Luke Sharrett/Bloomberg via Getty Images
The postage price jump is part of a 10-year "Delivering for America" plan launched in March 2021 to transform the USPS from a money-strapped organization to one that is self-sustaining and high-performing.
The USPS reported a $6.5 billion net loss in 2023 as revenue fell 0.4% to $78.2 billion and the use of first-class mail dropped to its lowest level since 1968, postal officials said.
In 2022, Postmaster General Louis DeJoy issued a warning for customers to expect "uncomfortable" increases in postage until the USPS gets on track to be self-sustaining.
"While our pricing decisions are ultimately made under the authority of the Board of Governors, in the near term, I will most likely be advocating for these increases," DeJoy said during a meeting with the USPS Board of Governors in 2022. "I believe we have been severely damaged by at least 10 years of a defective pricing model, which cannot be satisfied by one or two annual price increases, especially in this inflationary environment."
Despite the price hike in postage, a USPS survey done in 2023 showed the prices of stamps in the United States are still lower compared to 31 other countries it analyzed.
"The 2023 price of a standard domestic letter in the U.S. was nearly half the average price in our 31 sampled countries," according to the USPS Office of Inspector General report released in March.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Football is Not Famous in India

India is a country known for its diverse culture, traditions, and a deep-rooted passion for sports. However, when it comes to football, a sport that enjoys immense global popularity, it hasn’t reached the same level of fame and recognition in India. Several factors contribute to the limited popularity of football in the country.
Cricket Dominance: Cricket has long been the dominant sport in India. The country’s obsession with cricket, driven by historical successes and an unending stream of cricketing idols, has left little room for other sports to flourish. The Indian Premier League (IPL) and the Indian national cricket team’s successes have only cemented cricket’s dominance in the sports landscape.
Lack of Infrastructure: Football requires significant investment in infrastructure, including stadiums, training facilities, and coaching academies. While cricket enjoys a well-developed infrastructure, football in India has struggled with inadequate facilities and poorly-maintained pitches, making it challenging for talent to thrive.
Limited Funding: In comparison to cricket, football in India receives limited funding. The Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) is one of the wealthiest sports bodies globally, while the All India Football Federation (AIFF) faces financial constraints, which affects the development and promotion of the sport.
Scarcity of Role Models: Cricket in India boasts a plethora of iconic figures who serve as role models for aspiring athletes. Football, on the other hand, lacks such figures, which makes it harder for young talent to envision a successful career in the sport.
International Performance: The Indian national football team has struggled on the international stage, which has had a dampening effect on the sport’s popularity. Unlike cricket, where India has excelled in both the One Day and Test formats, football hasn’t experienced similar success, leading to a lack of public interest and investment.
Regional Differences: India’s vast regional diversity plays a role in the varying levels of popularity of football. While some regions, like West Bengal, Kerala, and Goa, have a strong football culture, other parts of the country remain relatively indifferent to the sport.
Lack of Grassroots Development: Grassroots development is crucial for nurturing young talent. Unfortunately, football in India has struggled to establish an effective grassroots system that can identify and develop promising players from a young age.
Lack of Marketing and Promotion: While the Indian Premier League (IPL) has set the gold standard for marketing and promotion, football leagues in India have not been as successful in this regard. A lack of effective promotion has hindered the growth of football as a spectator sport.
Competition from Other Sports: In addition to cricket, India has a thriving kabaddi league and a burgeoning interest in badminton and wrestling, which further reduces football’s share of the sporting audience.
Despite these challenges, there has been some growth in football’s popularity in India in recent years. The Indian Super League (ISL) has brought attention to the sport, and with continued investment, grassroots development, and a growing interest in European leagues, football may eventually see a rise in fame in India. However, it will likely take time and sustained effort to overcome the formidable dominance of cricket and other sporting interests in the country.
Find out a detailed case study on why football is not popular in India by clicking on the link.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Internal audit in India- PK Chopra and Co.
Internal Audit in India is one of the major areas which aid the organization in enhancing business performance by identifying the growth areas with greater scope for improvement and We provides best Internal audit in India, Process Audit Services in India. contact us: +91 98101 58561.
Internal audit in India is a crucial component of corporate governance and risk management within organizations. It involves the systematic review, assessment, and improvement of an organization's operations, controls, and processes to ensure they align with the organization's objectives, policies, and regulatory requirements. Here are some key points to consider about internal audit in India:
Regulatory Framework: Internal audits in India are conducted as per the guidelines set by various regulatory bodies, including the Companies Act, 2013. The Act mandates that certain classes of companies need to establish an internal audit process.
Independence and Objectivity: Internal auditors maintain an independent and objective stance to ensure unbiased evaluation of the organization's operations. They report directly to the Audit Committee or the Board of Directors to ensure their autonomy.
Scope: The scope of internal audit covers a wide range of areas, including financial controls, operational processes, risk management, compliance with laws and regulations, and overall effectiveness of governance structures.
Risk Assessment: Internal auditors assess risks associated with various processes and functions within the organization. This helps in identifying potential areas of vulnerability and designing effective risk mitigation strategies.
Controls Evaluation: Evaluating internal controls is a central aspect of internal audit. Auditors assess the adequacy and effectiveness of internal controls to prevent errors, fraud, and inefficiencies.
Operational Efficiency: Internal audits also focus on enhancing operational efficiency and effectiveness. By identifying process bottlenecks and recommending improvements, they contribute to streamlined operations.
Reporting: Internal auditors prepare comprehensive reports outlining their findings, recommendations, and suggestions for improvements. These reports are presented to management and the Audit Committee for review and action.
Continuous Improvement: Internal audits are not just about identifying problems; they are also about fostering continuous improvement. Auditors work closely with management to implement suggested changes and monitor their impact.
Technology Integration: With the rise of digital transformation, internal auditors in India are increasingly incorporating data analytics and technology tools to improve audit accuracy and efficiency.
Professional Standards: Internal auditors in India follow internationally recognized professional standards, often guided by the Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) framework. These standards ensure consistency and quality across internal audit practices.
Outsourcing: Some organizations opt to outsource their internal audit functions to specialized firms that provide expertise and objectivity. This practice is gaining popularity in India.
Value Addition: Effective internal audits not only help in compliance but also add value to the organization by identifying opportunities for cost savings, process improvements, and strategic insights.
In conclusion, internal audit in India plays a pivotal role in ensuring organizational integrity, compliance, and performance. It provides a systematic approach to evaluate and enhance various aspects of an organization's operations, contributing to its overall success and sustainability.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Knitted Fabric Testing in NABL Accredited Laboratories
Introduction:
Knitted fabrics have become integral components of our daily lives, finding applications in a wide range of industries, including fashion, sports, and home textiles. To ensure the quality, performance, and compliance of these fabrics, rigorous testing procedures are conducted in NABL accredited laboratories. This blog explores the significance of knitted fabric testing in NABL accredited laboratories and highlights the key tests and standards employed to evaluate various properties and characteristics of knitted fabrics.
The Importance of Knitted Fabric Testing:
Understanding knitted fabrics: Provide an overview of knitted fabrics, including their construction, characteristics, and applications. Explain how testing plays a crucial role in determining the quality, durability, and performance of these fabrics.
Ensuring compliance and safety: Discuss the importance of knitted fabric testing in ensuring compliance with industry standards, regulations, and safety requirements. Highlight how NABL accredited laboratories adhere to stringent guidelines and protocols to maintain the highest levels of quality and reliability in their testing processes.
Key Tests for Knitted Fabrics:
Physical and dimensional properties: Explore the tests conducted to evaluate physical properties such as fabric weight, thickness, density, and dimensional stability. Explain how these tests provide insights into the fabric's structure, handle, and performance characteristics.
Mechanical properties: Discuss the tests performed to assess the fabric's strength, elongation, tear resistance, and bursting strength. Highlight the significance of these tests in determining the fabric's durability and ability to withstand various stresses and strains.
Colorfastness and dyeing properties: Explain the tests carried out to evaluate colorfastness to various factors such as washing, rubbing, light, and perspiration. Discuss the importance of assessing dyeing properties, including color uniformity and colorfastness, to ensure consistent and long-lasting colors in knitted fabrics.
Standards and Certifications for Knitted Fabric Testing:
Overview of relevant standards: Introduce internationally recognized standards for knitted fabric testing, such as ISO, ASTM, AATCC, and EN standards. Explain how these standards provide guidelines and specifications for conducting tests related to different fabric properties.
NABL accreditation: Highlight the significance of NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories) accreditation for knitted fabric testing laboratories. Discuss how NABL accreditation ensures adherence to international standards, competence in testing methodologies, and accurate and reliable test results.
Innovations and Challenges in Knitted Fabric Testing:
Advancements in testing techniques: Explore innovative testing techniques and technologies that have enhanced the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of knitted fabric testing. Discuss the benefits of automated testing systems, digital imaging, and computerized data analysis in improving testing processes.
Addressing emerging challenges: Shed light on the evolving challenges faced in knitted fabric testing, such as the testing of eco-friendly and sustainable materials or the characterization of advanced functional textiles. Highlight how NABL accredited laboratories adapt to these challenges by updating their testing capabilities and incorporating new methodologies.
Conclusion:
Knitted fabric testing conducted in NABL accredited laboratories ensures the quality, performance, and compliance of these versatile fabrics. By subjecting knitted fabrics to a battery of tests encompassing physical, mechanical, and colorfastness properties, NABL accredited laboratories contribute to the production of reliable, safe, and high-quality knitted fabrics for diverse industries. Through their commitment to excellence, adherence to standards, and continuous innovation, these laboratories play a vital role in promoting consumer confidence and driving the advancement of knitted fabric technologies.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lithium Ion Battery Products of Eco Power
Eco Power Group is more than a lithium battery company. We design, manufactures, and sell advanced lithium-ion energy storage electrification solutions for different types of lithium ion battery.
Our expertise of custom lithium ion battery is based on its know-how in electrochemistry and battery management system to provide safe, efficient and sustainable solutions to various industries such as automotive, commercial transportation, off-highway vehicles/equipment, rail, air, marine, energy storage, solar energy systems, communication equipement, and more.
We are your experienced partner of lithium ion battery wholesale, from the feasibility study to the conception and the final installation with our complete product portfolio.
If you are considering to buy lithium ion battery, we are highly welcome you to consult and cooperate with us.
Different Types of Lithium Ion Battery Products
On-board energy solution at Eco Power Group with complete reference from cell to system to be the best fitting solution for your lithium ion battery types.
Battery Cell
This type of custom lithium ion battery cell is the very basic energy storage unit. Based on many years experience from cell design, battery materials and simulation, we are always at the cutting edge of technology. Our li ion batteries for sale comply with the strict safety standards UN 38.3, which guarantees our customers high quality and safety even after years of operation of charging lithium ion batteries.
Battery Module
In terms of battery modules for different types of lithium ion battery, there we offer standard modules with metal sheet plate for electric vehicle applications, Custom lithium ion battery module with binding tape for energy storage, and VDA size modules for passenger vehicles.
Battery Pack
Standard battery packs for commercial vehicles. Standard battery packs of charging lithium ion batteries in series with DNV certification for marine propulsion. Customized power li ion charging voltage systems for forklift applications ,etc.
Battery Energy Storage System
With a team of experienced engineers, we provide end to end custom lithium ion battery services starting from customer requirement analysis going through battery pack design, testing, prototype production and serial production. During the design phase we focus on the application area requirements as much as the li ion charging voltage battery design itself.
Why Choose The Lithium Ion Battery From Eco Power?
Quality
Our established quality management system of lithium ion battery wholesale, certified according to the international standard DIN EN ISO 9001: 2008, guarantees compliance with our high quality standards.
01
Customised Solution
Customised solutions for lithium ion battery replacement energy storage or mobile applications of electromobility.
02
Experience
As one of the leading lithium ion battery companies, we have more than 10years experience in lithium li ion voltage battery industry with hundreds of different application scenario. With our high quality lithium ion batteries for sale, you can trust us with your project .
03
Technical Support
From customer request input all the way to delivery final different types of lithium ion battery product, we will assign project technical consultant to accompany our customer to solve all of li ion charging voltage questions or problems during the whole process.
04
What Does A Lithium Ion Battery Module Do?
Battery module of li ion batteries for sale contains the energy storing battery cells by laser-welded technology, the mechanically stable against shock demonstrates high productivity and flexibility to make sure the long term performance of li ion charging voltage battery system.
How A Lithium Ion Battery System Works?
A battery system of li ion charging voltage consists of lithium battery cell connected in series to reach the system voltage and parallel to achieve greater capacity.
The li ion battery voltage and capacity can be verified by different combination of packs. The pack contains a fuse and a slave BMS. High security and provide lithium ion cell voltage and temperature to master BMS.
The Lithium-Ion battery system with charging lithium ion batteries in parallel is a composite set of battery electronics, high voltage circuits, overcurrent protection devices, battery boxes and interfaces with other external systems such as cooling, high voltage, auxiliary low voltage and communications.
What Is The Difference Between Lithium Ion Battery Pack And Power Bank?
This kind of battery pack of lithium ion battery types cannot be a power bank, but a power bank can be a li ion battery charging voltage pack with added electronic circuitry to prevent over charging, over discharge, etc to protect the batteries.
A lithium ion battery pack in series is merely a bunch of batteries connected in Series/Parallel configuration with one positive and one negative terminal.
A power bank contains one or more batteries in mostly parallel but could also be a Series/Parallel configuration. These types of li ion batteries for sale are connected to a battery management circuit (module) which controls the charging of the batteries. All this is housed in a compact enclosure.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why Custom Designed Distribution Boards Are Essential for Efficient Power Management
In today's industrial and commercial sectors, power management is a critical aspect of ensuring smooth operations. One of the key components in an efficient electrical system is a custom designed distribution board. Unlike standard boards, these tailored solutions optimize power distribution, enhance safety, and improve energy efficiency. This blog explores why custom electrical distribution boards are essential for modern infrastructure and how they contribute to effective energy management.
What is a Custom Designed Distribution Board?
A custom distribution board is an electrical panel specifically designed to meet the unique needs of a building, industry, or commercial setup. Unlike off-the-shelf solutions, these boards are engineered to handle specific load capacities, circuit requirements, and safety standards.
Key Features of Custom Designed Distribution Boards:
Optimized Power Distribution: Ensures equal and efficient power allocation to different circuits.
Enhanced Safety Mechanisms: Equipped with circuit breakers, surge protection, and overload control.
Scalability and Flexibility: Can be upgraded or modified based on future requirements.
Energy Efficiency: Helps in reducing power wastage and improving overall performance.

Why Custom Designed Distribution Boards Are Essential
1. Improved Electrical Safety
One of the most significant advantages of using a custom electrical distribution board is enhanced safety. Poorly designed or generic distribution boards can lead to electrical failures, short circuits, and even fires. With a customized power distribution board, you can ensure:
Proper load management to prevent overloads.
Installation of high-quality circuit breakers and fuses.
Compliance with local electrical safety standards.
2. Enhanced Energy Efficiency
A custom power distribution board helps reduce energy wastage by:
Balancing the electrical load efficiently.
Preventing unnecessary power fluctuations.
Integrating smart energy monitoring systems for real-time tracking.
By optimizing power usage, businesses can significantly cut down on energy costs and improve sustainability.
3. Tailored to Specific Needs
Different industries and buildings have unique power requirements. A custom designed power distribution board ensures that:
The right number of circuits are installed.
Voltage and current requirements are accurately met.
Special provisions for backup power systems like UPS or generators are included.
4. Future-Proof Electrical Infrastructure
With the growing demand for automation, smart distribution boards are becoming the norm. A custom-built electrical panel can integrate with IoT-based monitoring systems, allowing real-time power analysis and remote operation.
5. Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run
While custom designed distribution boards may have a higher initial cost than standard ones, they offer long-term savings by:
Reducing maintenance and repair costs.
Preventing equipment failures due to electrical issues.
Improving overall energy utilization.
Industries That Benefit from Custom Distribution Boards
Custom electrical distribution solutions are crucial for several industries, including:
Manufacturing plants – Require high-load capacity and reliable power distribution.
Data centers – Need stable and continuous power supply.
Commercial buildings – Demand flexible and scalable electrical systems.
Hospitals – Require fail-proof electrical setups to support life-saving equipment.
Renewable energy installations – Need specialized boards to integrate with solar and wind energy systems.
How to Choose the Right Custom Distribution Board
When selecting a customized power distribution board, consider the following factors:
Load Capacity: Determine the total power consumption of your facility.
Safety Standards: Ensure compliance with national and international electrical safety regulations.
Material Quality: Use high-quality components to enhance durability.
Smart Features: Opt for digital monitoring and automation capabilities.
Future Expansion: Choose a design that allows easy scalability.
Conclusion
Investing in a custom designed distribution board is essential for efficient power management and long-term cost savings. These boards ensure optimal energy distribution, enhanced safety, and scalability for future needs. Whether you are running an industrial facility, a commercial complex, or a renewable energy setup, a tailor-made electrical panel can significantly enhance your power management efficiency.
Need a Custom Distribution Board for Your Business?
If you're looking for custom electrical distribution solutions, get in touch with our experts today. We specialize in designing high-performance distribution boards tailored to your specific power requirements. Contact us now to optimize your power management system!
0 notes
Text
Queen Rania’s Interview with Times of India
February 10, 2025
Queen Rania Al Abdullah of Jordan emphasises the importance of women's leadership in business and governance, and calls for inclusive education systems. She also highlights the dire humanitarian situation in Gaza and urges a sustainable solution to the Palestinian-Israeli conflict.
In an exclusive interview to TOI, Queen Rania Al Abdullah of Jordan spoke on a range of issues. Excerpts: What are the biggest barriers to women's leadership in business and governance, and how can they be reimagined?
Women's rise into leadership roles has been slow, but significant. In 1960, there was only one female head of state - in 2023, 60 countries were headed by female leaders, as were just over 10% of Fortune 500 companies. Every success story provides more proof of women's unique leadership qualities, such as the tendency to listen before leaping into action, and to choose cooperation over competition. Ensuring women's pathways to leadership positions is smart business. As multiple studies have shown, companies with more women on their boards outperform those without. If economies want to attract and foster talented women, they need to provide stable, flexible, family-friendly workplaces.
How can education systems be reshaped to create a more inclusive future?
An inclusive future begins with inclusive education. Unfortunately, millions of children worldwide are robbed of their right to education due to conflicts, instability, and governments failing to make it a priority. All children deserve better. Education must also be constantly adapted to keep up with our fast-paced world. It's not just about improving standardized test scores; it is about fostering creative, driven youth. Through emerging technologies, including AI, and highly-skilled educators, we must continue to reinvent education from the ground up to prepare upcoming generations for any curveballs life throws their way.
What are your thoughts on the ceasefire currently taking effect in Gaza? Do you believe it is a hopeful sign of future peace?
The ceasefire has brought some relief. The bombs have stopped, and aid is coming in. However, the humanitarian situation in Gaza is catastrophic: 90% of homes, 90% of schools, and nearly every hospital is in ruins. Recovery and reconstruction will be a long, arduous process, requiring enormous levels of global support. My country Jordan has been active on this front, coordinating aid via airbridge and truck convoys.
A ceasefire is just the beginning. The ongoing targeting and displacement of Palestinians in the Occupied West Bank is proof that we need a lasting solution to the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. We cannot go back to the days before this war. That status quo has been broken forever, and the future needs to include respect for international law, self-determination for the Palestinian people, and mutual security for all.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How Travel Bags Got Lighter and Smarter — What’s Next for Luggage?

The way we move has always shaped the bags we carry. Once, trunks — massive, heavy, impossible to maneuver without porters — defined travel. They signified status, built for the elite crossing oceans on grand steamships. Remember the scene in Titanic where passengers scramble to board the RMS Titanic on that fateful April morning in 1912? Porters heave elaborate trunks onto the ship, a testament to a world where travel demanded excess. These trunks weren’t just luggage; they embodied wealth and preparedness for long, luxurious voyages.
Then, in 1958, the Boeing 707 took flight, the first successful commercial jetliner that slashed travel time across continents and ushered in a new era of mobility. But the Boeing 747, introduced in 1970, truly revolutionized air travel. Dubbed the “Jumbo Jet,” it carried more than twice the passengers of its predecessors and made long-haul international flights accessible to the masses. A year later, in 1971, Southwest Airlines pioneered the low-cost carrier model, making air travel an everyday convenience.
Suddenly, luggage design wasn’t just about elegance; it had to be efficient, lightweight, and easy to maneuver through rapidly expanding airports.
Airports adapted, airlines expanded, and travel became a mainstream experience. As more travelers took to the skies, luggage shed bulk and gained portability.
In the golden age of travel, steamships and long-haul rail dominated journeys. Bags, too, echoed this slower, more deliberate pace. Made from leather and reinforced with brass, early luggage emphasized durability over portability. Louis Vuitton’s stackable, flat-topped trunks changed how travelers packed. These pieces, as much a status symbol as a necessity, defined an era of measured, luxurious transit.
With the rise of commercial aviation in the mid-20th century, travelers struggled with cumbersome cases, dodging uniformed porters. Then, in 1970, Bernard Sadow had an idea: put wheels on a suitcase. Initially met with skepticism, his invention ushered in an era of hands-free travel. In 1987, Robert Plath, a Northwest Airlines pilot, refined the design with an upright carry-on and a telescopic handle. Mobility had a new benchmark.
Every aspect of today’s luggage focuses on performance. Materials have become lighter and stronger, resilient yet flexible. Polycarbonate, now the gold standard, absorbs impact better than aluminum while weighing significantly less.
Research from the American Society for Testing and Materials confirms that polycarbonate is durable, making it an ideal choice for frequent travelers.
Compression systems, once an afterthought, now shape premium luggage interiors. Expandable compartments, vacuum-sealed sections, and structured packing cubes maximize space while keeping items organized. These innovations helped clothes arrive as pristine as when they were packed.
Connectivity dominates today’s world, and luggage has evolved beyond a simple container. GPS tracking, biometric locks, and built-in charging ports have become standard in high-end suitcases. A 2022 Statista report notes that 60% of business travelers consider smart luggage essential. The shift isn’t just about convenience — it’s about security.
With the U.S. Department of Transportation reporting a 35% spike in lost baggage claims in 2022, location-enabled suitcases have never been more relevant. Security concerns have also fueled the rise of fingerprint-activated locks, restricting access to their rightful owners.
Travelers expect more from their luggage — not just in function but in environmental responsibility. A Travel Goods Association study indicates that 68% of consumers now value sustainability in their travel gear. Brands have responded with luggage made from recycled polycarbonate, biodegradable fabrics, and carbon-neutral production. These innovations aren’t passing trends — they define the new benchmark in premium luggage design.
Luggage stands at the edge of another transformation. The events of 9/11 permanently altered airport baggage security. Screening intensified, carry-on restrictions tightened, and security solutions advanced. Checked luggage now undergoes extensive scanning, and TSA-approved locks are an industry standard. These changes, driven by necessity, have reshaped how manufacturers design luggage — security is no longer an afterthought but a core feature.
Apart from security, self-propelling suitcases introduce a future where bags glide effortlessly beside their owners. Artificial intelligence could soon optimize packing layouts, predicting what travelers need based on trip length, destination, and climate.
At its core, luggage remains what it has always been — a fundamental piece of travel that has changed with the traveler. It reflects how travel has changed — the way we move, the places we go, and the experiences that depict our journeys.
#rareklub#fashionbags#travelbags#designer bags#bags for women#bagstyle#bags & purses#fashion#bags#america#usa#luggage#bag#blog#trending#viral#trend
0 notes