#Indigenous people in tech
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
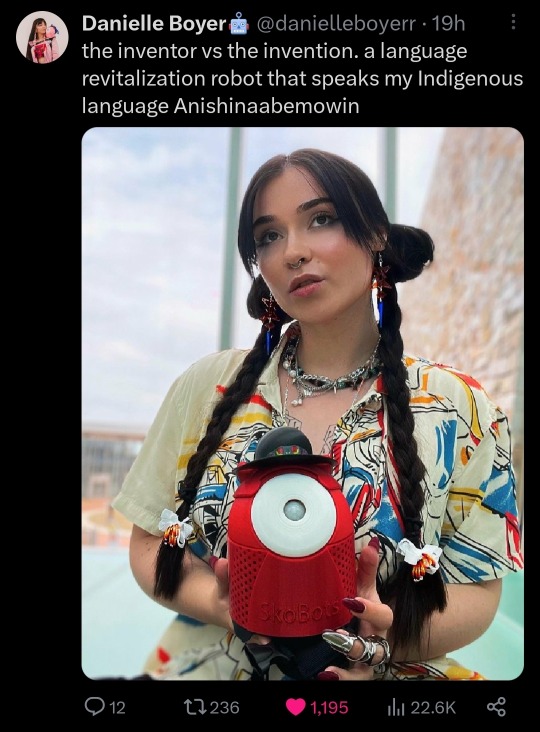

Alt: the inventor vs the invention. a language revitalization robot that speaks my Indigenous language Anishinaabemowin pic.twitter.com/ydo88kMzT9
Photo of inventor Daniel Boyer holding language bot. Hair in large buns with braids going down and wearing cream shirt with colorful abstract design on it.
— Danielle Boyer🤖 (@danielleboyerr) February 1, 2024
#Danielle Boyer#Inventors#Engineers#Language#Robots#Anishinaabemowin#Indigenous#Indigenous people in tech#Tech#Technology#Alt text in image#Image description in image
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
FIELD NOTES: FROM THE SHALLOW END

༄.° pairing: jeon wonwoo x f!reader | ༄.° wc: 7.7k ༄.° genre: nanny diary au | au pair!reader ༄.° warnings: definitely some angst + self-spiraling, bad/negligent rich people parenting, consumption of alcohol, mentions of vomit ༄.° a/n: for cam and em's carat bay collab! was so grateful to take part in another collab and experiment with my writing style a bit :)) please do check out all the other amazing authors in this collab, they are all so so so dear to me
Entry #1: On the Indigenous Habits of the Affluent Family on Summer Vacation June 13th, 3:04 PM
In the wilds of Carat Bay, the modern matriarch is most commonly spotted with an oat milk matcha and AirPods, muttering something about KPIs. The modern patriarch is nowhere to be seen, having mumbled something about a “board meeting” and “golf with the boys.” Their offspring, small but feral, roam through chlorinated terrain. Their natural prey? Au pairs in department store swimsuits.
Junseo had eaten four frozen lemonades and was now in the middle of what experts in the field might call “a sugar-induced sprint toward cardiac disaster.”
“Junseo, no running by the pool!” you shout, too late. He slips, recovers, and keeps going like a greased piglet on roller skates.
Across the concrete savannah of Carat Bay’s family pool zone, Junhee is in her usual position: crouched at the border between chlorinated civilization and murky wilderness, pool noodle in hand. She is attempting to commit amphibicide via repeated poking of a highly displeased frog.
“Junhee, love, leave the frog alone—he lives here!”
“His name is Boba!” she screams back.
The frog does not look like a Boba. He looks like he’s reconsidering all of his life choices, which, frankly, makes two of you.
Your sandals squeak—a mistake you didn’t realize you’d made until about an hour into your first shift. They’re cute, sure. But tractionless. Supportless. Flat as your social life ever since you moved back in with your parents and became, for lack of better options, an anthropologist in exile.
It wasn’t supposed to be like this.
Just a few months ago you were crossing the graduation stage in soft linen, clutching your master’s degree in anthropology like it meant something. You had been so certain academia would need someone like you—sharp-eyed, good at syntax, fluent in both fieldwork and feminist theory.
Turns out, the only people hiring anthropologists in this economy are tech companies doing ethics theater and pharmaceutical firms in need of plausible deniability.
You had been dying slowly on your parents’ couch for exactly three weeks when your friend Lexi sent the flyer:
Want to make $$$ babysitting rich kids all summer? Full access to country club, pool, catered lunches. No drowning allowed. :)
You had laughed. And then, somewhere between the fourth rejection email and your mother asking if you wanted to help organize her sock drawer, you’d sent in a resume. You even lied and said you liked children. Two days later, you were hired. The check had commas in it.
Now you’re standing in a wet Target swimsuit, sunburn blooming across your chest, wondering if the rash on your neck is from stress, sweat, or the “reef-safe, organic, mommy-formulated” sunscreen that smells like expired chamomile and four-day-old chlorine.
“Junseo,” you call again, “do not eat that bandaid!”
The bandaid goes into his mouth. The bandaid is chewed. You scream internally.
Your employer, Mrs. Cho, the mother of these twin terrors, has not moved from her perch in the family cabana for the last forty minutes. She’d tossed you a dismissive “just make sure they don’t drown” before retreating into her kaftan and a Zoom meeting. She’s been there ever since: AirPods in, matcha sweating on the teakwood side table, gesturing wildly as she mutters about influencers and packaging aesthetics.
You, meanwhile, are the last line of defense between civilization and frog-assisted chaos.
Later, after bribing the children into a nap with gummy worms and a story you mostly made up about a magical flamingo who goes to therapy, you collapse onto a sun-warmed lounger just outside the cabana. It's one of the only moments of quiet you’ve had since arriving. The kind of quiet that rings a little in your ears.
You close your eyes. Take a deep breath. Maybe consider what a plane ticket to literally anywhere else might cost.
That’s when you feel it—a shift in the light. A shadow cast across your body.
You blink up.
There’s a boy—no, not quite. A man. Mid-twenties, maybe. Dark hair falling slightly into his eyes, expression unreadable. His nametag says Wonwoo. He’s wearing the Carat Bay staff polo, a towel slung casually over his shoulder. His left hand holds a chilled bottle of water, condensation trailing lazy rivulets down his fingers.
He offers it wordlessly.
You take it, startled. “Thank you,” you say, your voice hoarse from yelling and sun.
He doesn’t speak. Just gives you a single, small nod, and walks away.
You watch his back retreat into the shimmer of pool heat, the bottle already cold against your lips.
You don’t know it yet, but this is the last peaceful moment you’ll have for a while.
Entry #2: On Power Hierarchies and Poolside Social Climbing June 20th, 11:35 AM
In most pack dynamics, the alpha asserts dominance through elaborate displays of confidence. At Carat Bay, this involves hosting themed pool parties and knowing the regional manager’s golf handicap. Among the matriarchs, alliances shift over whose offspring made swim team and who dared to bring store-bought cupcakes to the birthday cabana. It is important to master the subtle art of pretending one is not competing.
You lose your hearing somewhere around the fifth time Junhee screams, “I DON’T WANNA BE A ZEBRA.”
Junseo, face flushed with fury and injustice, echoes her like a demonic chorus: “WE’RE NOT ZEBRAS! I WANNA BE A T-REX!”
“Fine,” you hiss, crouched on the cabana floor with one knee in a puddle of apple juice, “be a godda–dang dinosaur in a zebra onesie, just get in the outfit.”
Today is not your day.
Today is Savannah Safari Birthday™, an event as horrifying as it is aggressively coordinated. The themed party, hosted by one of the more alpha Carat Bay mothers (you learn her name is Seoyeon, but she goes by Stacie, spelled with an ‘ie�� like a threat), has transformed her family cabana into an influencer’s fever dream. Giant cardboard giraffes. Balloon arches in beige and gold. Matching straw hats for all children. And a disturbingly lifelike stuffed zebra standing near the dessert table like it's waiting for a sacrifice.
You wrangle the twins into their assigned costumes—faux-animal-print rompers with little ears on the hoods—while they shriek like banshees at a frequency NASA might want to study.
By the time you emerge into the main cabana area, sweating and frayed, the pool moms are already circling each other like predators in designer plumage.
“Did you hear?” one says, adjusting her visor. “Eunkyung got waitlisted for pre-competitive swim. Waitlisted. And they just redid their pool.”
A blonde with glistening shoulders gasps theatrically. “Waitlisted? Oh no. Maybe she can take up something less... saturated. Pickleball, maybe.”
There’s laughter, brittle as pressed glass.
You hover near the fruit skewers, pretending to supervise the twins as they pelt each other with animal crackers. That’s when you hear it: the first volley fired in your direction.
“Aw, is your niece helping you today?” one of the moms trills, gesturing at you without looking. Her sunglasses are enormous and opaque.
“She’s adorable,” another adds, tone sweet and scalding. “That suit is so… real. You just don’t see people being brave about texture anymore.”
You blink, mouth parting slightly. You’re not sure whether to laugh or start quoting Margaret Mead in self-defense.
“Actually,” you say slowly, “I’m their au pair.”
They blink back, uncomprehending. One finally nods. “Oh! Like an assistant.”
Sure. Like that.
You eventually find yourself corralled in a shady corner with the other au pairs and nannies—two from Portugal, one from Toronto, and one with an indeterminate accent who looks like she’s seen war. Together, you trade horror stories like wartime nurses. One saw a child try to feed a wedding ring to a koi fish. Another was asked to prepare an all-raw vegan lunch for a toddler who eats crayons. You are both horrified and comforted. Trauma loves company.
It ends, as all things do, in carnage. A child screams because someone else got to sit on the fake zebra. Another sobs over the injustice of the animal-shaped cupcakes melting in the heat. You grab the twins, now sticky with fruit and full on far too much cake for their afternoon nap, and make a beeline for the cabana exit just as one of the moms begins berating a nanny for not predicting her daughter’s alleged strawberry allergy.
You’re almost free.
Almost.
And then you crash directly into someone solid.
You go down like a bowling pin.
“Oh my god!” Junseo howls. “YOU FELL!”
“Like, BOOM!” Junhee adds, collapsing into giggles.
You are on the hot concrete, stunned, clutching your elbow and your remaining dignity.
And there he is again.
Wonwoo.
He’s traded his polo for a linen button-up, slightly wrinkled and unfairly flattering. He looks down at you, impassive.
“Hey,” he says.
You blink up at him. “Hi.”
He offers a hand. You take it, and he pulls you up with barely any effort. His hand is warm. Callused. There’s a quiet strength to him, like a character in a Ghibli film who lives alone in the woods and speaks only in cryptic haikus.
Before you can say anything else, one of the moms descends like a hawk. Or a hyena that’s recently had fillers.
“Oh, Wonwoo,” she purrs, practically draping herself across his side. Her teeth gleam. “I didn’t know you were back from Singapore. Is your father joining us for the benefit this year?”
He gently disentangles himself.
“He’s expecting me for lunch,” he replies, tone polite and final.
Her lips purse. You watch her recalibrate in real time, already turning toward another potential social rung.
Wonwoo glances back at you. His expression doesn’t change, but there’s something faint in his eyes. Amusement, maybe. Or pity. Or just wind.
Then he’s gone.
Later, when the twins are face-first in naps (which took a significant amount of wrangling to achieve) and your phone finally has a signal, you search his name.
Jeon Wonwoo.
Son of the owner. Executive board. Dartmouth-educated. There’s a press photo of him at a ribbon-cutting ceremony for a sustainability initiative.
Of course.
You drop the phone onto the lounge chair beside you and cover your face with a towel.
Maybe he’s not so different from the moms after all.
Or maybe worse—maybe he’s just better at pretending he isn’t.
Entry #3: On The Nanny Condition (Also Known As: “Doormat Syndrome”) June 30th, 12:47 PM
Subservience in child-rearing roles is often mistaken for passivity. However, this is more accurately understood as the practiced stillness of someone who has weathered too many juice spills and tantrums. It is not a weakness, but a form of strategic surrender – resignation honed into an art.
It starts the way all days start now: with screaming.
You don’t even flinch anymore. Junseo has weaponized volume as a strategy. Junhee has started using phrases like “I’m telling Mommy!” even though Mommy, at this point, might as well be a cryptid. You text Mrs. Cho about the lunch situation and get no response. You text again. Then once more, with slightly more passive-aggression. Still nothing.
Mr. Cho is presumably in a meeting, on a plane, or golfing through time. His only presence this week has been the sound of an engine disappearing down the driveway at six-fifteen each morning. You’re beginning to suspect he has never actually seen the twins awake.
By 11:30, it’s full meltdown hour. Junhee has decided to sob violently about the wrong flavor of juice. Junseo is lying on the pool deck and pretending to die of hunger. You make the tragic mistake of attempting to fix this by visiting the snack bar—only to find it’s out of chicken nuggets.
Of course it is.
The cabana attendant (your supposed lifeline in this glittering suburban dystopia) is nowhere to be found. Probably hiding behind a towel cart and Googling how to fake appendicitis.
A mom walks by, sipping iced espresso in a wine glass. She clocks the situation—the spilled juice, your panicked rustling through bags, the tantrum echoing off the water—and gives you the kind of look normally reserved for videos of shelter dogs.
Then, like a scene change in a commercial for laundry detergent, he appears.
Wonwoo. The cabana attendant from three down, and apparently some sort of summer camp MacGyver.
Without a word, he crouches beside your mess of a pool chair, reaches into his tote, and withdraws two juice boxes like they’ve been summoned by divine intervention.
“Trade secret,” he says, handing them over. “I keep a stash for emergencies.”
The twins freeze mid-wail. Their heads swivel toward the juice. Junhee actually snatches it like a raccoon who’s just spotted an unattended churro.
You mouth thank you as chaos briefly, miraculously, subsides. Wonwoo gives a small shrug, like it's no big deal that he's just singlehandedly de-escalated a Code Red tantrum. Then he starts rummaging through his bag again.
“Here,” he says, offering you a slightly squished protein bar. “You look like you might pass out before 2. Not a great look in front of the junior elite.”
You stare at the bar, then at him. “Are you always this prepared?”
He squints at the twins, now peacefully arguing over whether dinosaurs could swim. “Experience.”
He rises, but pauses. “Oh, and: sing to them,” he adds, like it’s obvious. “The nap goes easier if you sing. Something simple. Doesn’t matter what.”
You blink. “You know a lot about naps.”
He smirks. Whisper-soft, barely there. “Only the essential ones.”
And then he’s walking away. You’re about to call after him, maybe say something actually coherent, when you spot it. Just barely poking out of his overstuffed bag, next to sunscreen and a spare shirt:
A Secret History, cover creased, dog-eared, loved.
The twins fall asleep in your lap thirty minutes later, sticky fingers curled around juice boxes, heads tilted together like cherubs.
You hum a lullaby under your breath. It works.
Maybe this doormat thing isn’t about surrender, you think, watching the sun cut soft lines through their hair. Maybe it’s about endurance. Outlasting the storm. Knowing when to bend, and when to hum.
And maybe—just maybe—you’re not the only one pretending.
Entry #4: A Brief Field Guide to Cabana Boys (Genus: Mysteriousus Hotus) July 12th, 7:30 PM
Often underestimated, the Cabana Boy is a curious species: quiet, observant, and frequently found next to industrial-sized coolers. Contrary to popular belief, he is not just decorative. He may, in fact, be reading Donna Tartt during fireworks displays and composing short fiction between towel runs.
You're not sure when you started paying attention. Not in the obvious way—wrangling two five-year-olds who are constantly on the verge of a sugar-induced existential crisis leaves little room for distractions. But somewhere between juice box negotiations and sunscreen reapplications, you noticed the pattern.
Wonwoo clocks in for his 1:00 PM shift at 12:53 on the dot, every day. Rain or shine.
He always brings a slightly crumbly granola bar at exactly 12:45 and hands it over without ceremony. He’s also taken to giving unsolicited (but disturbingly effective) child-wrangling tips.
“If you let them watch an episode of Clifford in the shade, they mellow out.” “Junhee will eat steamed broccoli if Junseo is watching.” “They nap better if you hum the Indiana Jones theme.”
When you ask how he knows this, he just shrugs.
“I’ve watched them grow up here.”
He folds towels into perfect thirds—perfect enough to undo the entire previous shift’s work, muttering about symmetry.
And he always—always—has a book in his bag. You’ve clocked A Secret History, Beloved, Middlesex, and now—somehow—Antigone. You, being a civilized person, use sticky notes. He dog-ears. He highlights. You try not to hold it against him.
Then one night, the miracle. A fireworks show lures both Mr. and Mrs. Cho into spending quality time with their children—together—and for the first time in thirty-one days, you are given a few hours off.
You wander the resort grounds in what you tell yourself is idle exploration. You're not looking for him, not exactly. You're just…curious.
You find him perched in the shade outside the Cabana Attendants' Shack, book open, fingers curled at the spine. The sunset drapes him in gold.
“Greek tragedy?” you ask, nodding at the cover.
He startles slightly. Then sees it’s you and offers that small, lopsided smile that always feels like a secret.
“Loyalty to family and all that.” He snaps the book shut. “Why, do you have a favorite?”
The conversation unfolds in sideways glances and thoughtful pauses. He’s more well-read than you expected—not that you ever assumed he was dumb, but you didn’t quite picture him as the kind of guy who casually references Antigone while sipping Gatorade.
You want to bring up the fact that he’s the rumored heir to the waterpark conglomerate whose name is literally embroidered on your staff polo, but you don’t. He doesn’t bring it up, either.
Instead, you trail him as he clocks back in and begins his closing duties. You talk as he refolds towels, delivers last-call lemonades, and waves kids off the splash pad.
He’s soft-spoken but sharp, a bit of a walking contradiction. He debates philosophy with the same tone he uses to explain popsicle storage procedures.
He quotes The Odyssey unprompted. You’re unsure if you’re gagging or swooning. Possibly both. He laughs. The good kind—the kind that makes you want to say something clever, just to earn it again.
And then:
A string of texts from Mrs. Cho.
Where are you? Can you be back in ten? Junseo is trying to drink the pool water again.
Three hours gone in a blink.
You sigh, brushing off your shorts. “Duty calls.”
He doesn’t protest. Just reaches into his bag and hands you a worn paperback with a faded spine.
“You’d like this,” he says. “Don’t worry. I only highlighted a little.”
As you jog back to the family villa, the book clutched under your arm, you catch yourself smiling. You don’t know what exactly just happened—but you know you’re already looking forward to tomorrow.
The Cabana Boy: mysterious, mythological, mildly infuriating.
You’re definitely going to need another field guide.
Entry #5: On Emotional Labor (And How to Pretend You’re Fine) July 18th, 3:56 PM
Among caretakers, the phrase “I’m fine” functions less as a truth and more as a survival mechanism – an autopilot response honed through repetition, like muscle memory or disassociation. It’s not an admission of wellness so much as a polite way of saying: I have exactly six fruit snacks and half a juice box keeping me together right now, please do not ask follow-up questions.
Today is the worst day on record. Not just this summer—ever.
Junhee is feverish and glassy-eyed. Junseo hasn’t stopped crying since 9:07 AM. The phrase “I want mommy” has been used with increasing volume and ferocity for six straight hours.
And still, Mrs. Cho floats in after breakfast, clacking away in her designer heels like you’re just another inconvenience in a long string of logistics. She deposits them into your arms with the same care one might give a bag of dry cleaning. She clacks off in Valentino heels without a glance back. She says “they’ve been so moody lately,” as if their tear-streaked faces and refusal to be peeled off your torso aren’t a screaming counterargument.
Even Wonwoo, usually the child-whisperer, strikes out. He tries Clifford. He tries juice box diplomacy. He even pulls out the secret popsicle stash. Nothing works.
The grand finale: Junhee vomits bright blue Slushie all over your shirt just as Mrs. Cho reappears.
She gasps, horrified—not at her child, no. At you. “This is completely inappropriate. What did you even feed him?”
You’re too shocked to speak.
Wonwoo watches from across the cabana, eyes wide, towel frozen mid-fold. And then—just like that—you snap.
Your eyes are already stinging, breath hitching. You mutter something about needing a minute, and walk fast. Not away from the cabana—out.
You don’t know where you're going, just that it needs to be anywhere else. You barrel through pool chairs, past shrieking toddlers, past lifeguards gossiping about hot guests, and you barely notice the quiet footsteps trailing behind you.
A hand catches your upper arm. Not rough, just... certain.
Wonwoo pulls you into the cool, echoey silence of the staff locker room and sits you down like it’s the most normal thing in the world. You don’t resist.
You sit, shoulders trembling. He turns to his locker, rifling through it. A few seconds later, he tosses a shirt into your lap.
“Here. It’s clean. Smells weird, though. You might smell like sunscreen and... me.”
You pick it up with shaking hands. Chlorine, citrus deodorant, rain. Wonwoo. It hits like a trigger.
And then— You lose it.
Not the gentle, single-tear kind of cinematic breakdown. No. This is a crash out. Full-body. Unfiltered.
You're pacing now, the shirt clutched in your hand like a lifeline, voice cracking with every word.
“I hate this family.” “I swear to God, if that woman says one more thing about how hard parenting is—while dumping her kids on me like they’re furniture—I’m gonna lose my actual goddamn mind.” “I’m twenty-three! I should be backpacking in Spain or studying abroad or—I don’t know—eating a yogurt in peace without someone screaming about their sock being too tight.”
You kick a locker.
“And I’m trying so hard. I’m doing everything right. I’ve read so many blogs, Wonwoo.”
You turn toward him, eyes red-rimmed and wild.
“And you know what I get? Vomited on. In public.”
He hasn’t moved. Just sits on the bench, legs spread, arms on his knees, staring up at you like he’s watching a fire he’s not sure how to put out. Like he knows he’ll burn if he gets too close—but also that maybe it’s worth it.
“Are you… done?” he asks, finally. Gently.
You stop. Blink. And then let out a small, wet laugh that sounds more like a sob. You sit down hard next to him, the adrenaline draining from your limbs all at once.
“I think so.”
He leans back slightly. Not touching you, but close enough that you can feel the calm radiating off him.
“Better?”
You don’t answer immediately. You don’t know. But you nod anyway. And he accepts it, like that’s enough.
You sit there, the two of you, in chlorine-scented silence. His shirt still bunched in your lap. Your breathing slows. You count your heartbeats.
And for the first time all summer, someone lets you be tired. Not “still smiling” tired. Not “push through it” tired. Just... human.
You think, maybe, that matters more than anything.
Entry #6: On the Sociocultural Function of Shared Snacks (And Other Low-Stakes Intimacies) July 25th, 6:23 PM
Anthropological theory suggests that the exchange of Goldfish and Capri Suns constitutes a primitive yet potent form of courtship. Especially when accompanied by verbal rituals such as, “You look like you need a break,” and, “Do you want the last one?” While not as elaborate as other mating rituals, these offerings appear to hold significant emotional currency. Further study is required, but initial findings suggest: this may be how modern love begins.
There’s a rhythm now. He always saves the last piña colada juice box for you. You always act like you don’t care and then accept it anyway, muttering something about “fake cocktails for fake lifeguards.” He always laughs. You always drink it.
You make fun of the way he organizes the towel bins—by saturation level, apparently. “This one’s damp-damp, and that one’s wet-wet? You okay, Marie Kondo?”
Wonwoo shrugs like he’s heard worse, like maybe he’s even proud of it. “It brings me peace.”
It’s easy with him. He always finds his way to your cabana when things are quiet. No one sends him. He just appears. He drops into the lounge chair beside you like he belongs there, legs stretched out, sunglasses slipping down his nose. Sometimes he brings snacks—peanut butter pretzels, Goldfish, gummy worms he claims are “for the kids.” You both know better.
You talk books. Somehow he’s never read Magic Treehouse, which you find personally offensive. “It’s basically required reading for emotionally unstable gifted kids.”
He grins. “Sounds like I dodged a bullet.”
“You’d love it,” you tell him, tossing a pretzel at his face. “You’re such a Virgo.”
“I’m not a Virgo.”
“Spiritually, though.”
He makes you laugh at least once a day. Not a polite laugh. An ugly, tired, full-body snort—the kind that feels like exhaling something heavy.
One afternoon, your fingers brush when he hands you a juice box. The contact is brief, but it lingers. Just enough to make you glance up, and he’s already looking back. Not with some dramatic, swoon-worthy gaze—just steady. Familiar. Like he knows you. Like he sees you.
And then, inevitably, the twins start screaming about a grasshopper. One of them insists it’s going to bite their nose off. The moment cracks clean in half. Wonwoo groans, gets up, and trudges off to play bug bouncer. You watch him go, vaguely amused. A little disappointed.
Later, when the cabana is blissfully quiet again, you ask him something you’ve been holding onto for a while.
“Why do you work here when you don’t need to?”
He doesn’t answer immediately. Just stares at the pool, unreadable. For a second, you think he’s going to deflect with a joke—but instead, he says, quietly, “It’s easier to know people when they’re not pretending.”
He says it like it’s obvious. Like it’s been sitting in the air this whole time, waiting for you to notice.
You don’t quite know what to do with that. But you don’t push.
Instead, you hand him the last peanut butter pretzel without a word. He takes it. And for now, that feels like enough.
Entry #7: On Burnout, Bus Rides, and the Quiet in Between July 31st, 8:39 PM
The much-awaited night off is often viewed as an unproductive lull in the performance of domestic labor. But for the emotionally fried caretaker figure, it is the only sanctioned absence where no one cries, no one spills, and no one demands apple slices cut the “right” way. It is the lone moment in which the help is not expected to perform servitude with a smile. In anthropological terms: a brief return to personhood.
You end up at a bus stop just outside the waterpark. The sun’s long gone, and so are your responsibilities, at least for the next few hours. You’re not even sure where you’re headed. You just wanted to leave. To move. To breathe. You might be a little tipsy—courtesy of the fully stocked cabana bar—but that’s between you and whatever god watches over tired girls with aching feet and full hearts.
Wonwoo finds you under the weak, flickering light of the stop like it’s the most natural thing in the world.
“What are you doing here?”
“I have the night off,” you say, nudging a pebble with the toe of your sandal. “Didn’t know where to go. I’m not from here.”
He looks at you for a moment, then smiles. “You’ve got the whole night off?”
You nod just as the bus pulls up. He doesn’t hesitate, just holds out his arm and asks, “Wanna do something fun?”
You giggle, loop your arm through his, and climb aboard.
The bus ride is a quiet kind of lovely. The kind that lets your bones settle after a day of noise and chlorine and children threatening to stage a coup over who gets the blue floatie. You’re too tired to flirt, and he doesn’t seem to mind. He offers his shoulder, opens a book, and lets you lean.
“I didn’t know you took the bus,” you mumble, sleep thick in your voice.
He chuckles. “Why? Thought I had a Porsche?”
You smile into the fabric of his shirt. “What kind of chaebol son doesn’t have a sports car?”
“I do,” he says, tapping his fingers as he leans in close enough for you to get a whiff of his cologne. It’s earthy. Warm. “It’s just hard to park.”
Eventually, the bus rolls into a small downtown area lit with fairy lights, where families drift between ice cream shops and late-night cafés. Wonwoo takes your hand and tugs you down a side street, stopping in front of what looks like an abandoned bookstore. The sign is faded. The windows are dark.
You squint. “On my one night off this summer, you brought me to a murder scene?”
He scoffs, already pulling keys from his pocket. “I clerked here in high school. The owner never asked for them back.”
Inside, the air smells like dust and old stories. He flips on a few lamps and the space flickers to life—messy and charming in a way that feels sacred.
What follows is, undeniably, a reading date. But you both pretend it’s not. It can’t be. Not when summer is almost over. Not when you’ve seen what happens to girls who let themselves want too much.
Still, you talk. You read. He shows you where he used to stash beanbags as a teenager and the corner of a shelf where he carved his name when he was seventeen. He pulls down a hollowed-out book that still contains an unopened bag of gummy bears. When he throws one toward you, you catch it in your mouth without breaking eye contact, and he laughs so hard he nearly drops the whole bag.
At some point, you sigh about how much you miss Cherry Garcia ice cream. He disappears, and a few minutes later, returns with a milkshake.
“It’s not ice cream,” he says, offering it to you, “but it is Cherry Garcia.”
You take one sip and groan. “You’re dangerous.”
“We can split it,” he offers, clearly pleased with himself.
You settle back into the beanbags with the milkshake between you. His shoulder brushes yours. Your pinkies touch. You’re pretty sure this is what love feels like—soft and slow and unbearably sweet.
You’re just about to lean in when your phone rings.
Mrs. Cho.
You answer, and before you can even say hello, her voice cuts through, sharp and desperate. “I need you back. They won’t sleep until you sing to them. Come back now.”
The twins are screaming in the background.
You shoot up, already apologizing, already stuffing your phone in your pocket and looking for your bag.
Wonwoo follows you to the door. Just as you reach for the handle, his hand wraps gently around your wrist.
“You’re the only person from the waterpark I’ve shown this store to,” he says, voice low, almost unsure, and it takes all the willpower in the world not to push him up against the stacks and kiss him stupid. “We should– we should do this again. If you want.”
You should go. You have to go. But instead, you rise on your tiptoes and press a feather-light kiss to his cheek.
“I would love that,” you whisper.
Then you're gone, milkshake in hand, racing back to the chaos. But the softness of that night stays with you.
Entry #8: On the Perfect Family (And Other Bedtime Stories) August 12th, 1:56 PM
Anthropologists agree that the family unit, built on generations of blood and loyalty, is sacred. This theory begins to unravel around 1:07 PM, when the matriarch of the Cho family – Balenciaga-clad and Bluetooth’d – screams at her offspring for dripping popsicle juice on her Hermès towel. The offspring seek emotional refuge in the arms of the hired help. This only infuriates the matriarch further. Field notes suggest that the sacred family unit may, in fact, be a PR stunt.
The cabana smells like sun-warmed linen and something floral—maybe Mrs. Cho’s perfume. You sit cross-legged on the floor, the twins clambering onto your lap, sticky popsicle juice glistening on their chins. Junseo hiccups, eyes wide, while Junhee presses her damp cheek against your arm, seeking shelter.
Then it happens.
A sharp, slicing voice cuts through the quiet: “Why is there juice dripping on my Hermès towel?” Mrs. Cho storms in, Balenciaga heels clicking like thunder on pavement. The Bluetooth earpiece flashes a faint blue as she glares at you, voice rising like a storm.
The twins flinch. Junhee blinks up at her mother like she’s seeing a stranger. Junseo presses closer to you, face buried in your shirt. You feel the warmth of their small bodies, the tremble in their chests. You are not their mother. You know that. But in moments like this, someone has to be.
Mrs. Cho snaps, “Do not coddle them. This is why they don’t respect me.”
You stand slowly, steadying the children behind you.
“I’m just trying to calm them down,” you say, carefully.
“Oh, please.” Her tone sharpens. “You don’t think I see what you’re doing? What everyone sees? The other mothers laugh behind your back — the little nanny girl and the owner’s son playing house.”
Your breath catches.
“I’m not—”
“I’m not finished.” She steps closer. “You are not their mother. Stop pretending to be. Stop making them believe you are.”
You blink once, twice. And then you break.
“No,” you snap. “You stop. You stop making them believe I’m their mother. You leave them with me for ten hours a day, five days a week. You miss their birthdays. You forget their allergies. You don't even know Junhee likes frogs or that Junseo has nightmares when it rains. You don’t see them. But I do.”
She stiffens. You press the twins behind you gently.
“For fuck’s sake, Mrs. Cho,” you whisper, too tired to yell anymore. “Do you really think this is how good mothers act?”
The silence that follows is jagged. Sharp.
You don't wait for her to respond. You turn. You walk — briskly, almost blindly — past the frozen faces in the walkway, past Wonwoo standing by the corner, unreadable.
You don’t stop until you’re outside.
Night comes like a soft blanket. You’re at the twins’ bedside again, tracing their damp hair, humming lullabies until their breathing evens out. Mrs. Cho sits stiffly across the room, staring at her phone. Her husband lounges on the couch, like nothing happened. As if nothing ever happens.
You're walking beside the lazy river, hands stuffed into the pockets of your hoodie, when you hear the familiar tread of footsteps behind you.
Wonwoo.
You don’t look at him.
“I heard everything,” he says.
You don’t say anything. You keep walking.
“She was way out of line.”
You stop. “You don’t need to defend me.”
“I’m not,” he says quietly. “I’m angry.”
You turn to him. “Why? Why do you even care?”
He falters. “Because I—”
You laugh bitterly. “You what, Wonwoo? You care about me? You want to play the hero now? Where were you earlier? When she humiliated me in front of everyone? You just stood there.”
“I didn’t know what to do—”
“You never know what to do,” you snap, voice cracking. “You always wait until I’m falling apart and then you show up when it’s safe again. When I’ve already picked up my pieces.”
His jaw clenches.
“I’m sorry,” he says, but it sounds like sandpaper. “I should’ve said something. I wanted to.”
“And now what? You want me to pat you on the back because you chased me down after sunset?” Your voice breaks. “This isn’t a fucking romance movie, Wonwoo. You don’t get points for showing up late.”
He stares at you — really stares — and then he says, low and quiet, “I didn’t chase you down for points.”
You shake your head and look away.
“I came because I couldn't let you walk away thinking I didn’t care.” He takes a step closer. “You’re not just someone I flirt with by the pool. You’re not just the girl who helps with the twins. You’re...”
His voice falters.
“You’re the only person who makes this place feel real.”
You feel the ache of it — like something soft tearing.
“I didn’t ask for this,” you whisper.
“Neither did I,” he says. “But I’m here.”
And then he kisses you.
It starts hesitant — a question, a breath — but when you don't pull away, he deepens it, slow and hungry. One hand slides to your jaw, the other finds your waist. You kiss him back like you’ve been holding your breath for two whole months. Because you have.
He pulls back just enough to whisper, “Come with me.”
You nod, breathless.
You stumble through the grass, past the empty lounge chairs, half-laughing, half-shaking. He kisses you again by the maintenance shed. Again near the outdoor shower. You lose track of where you’re going. You only know his hands, his mouth, the way he looks at you like you’re something he’s been dying to touch.
By the time you reach the locker room, he’s pushing you gently against the door, lips trailing fire down your neck.
“Fucking finally,” he groans, like it’s been killing him not to say it. His voice in your ear makes your knees buckle.
You grip his shirt, feel the muscles of his back flex under your fingers. He smells like chlorine and sunscreen and gummy bears and sweat and you want, want, want.
He kisses you again, deeper this time — all tongue and teeth and desperation. The kind of kiss that says I missed you, I wanted you, I want you still.
And then, suddenly — mid-kiss, mid-moment — the world crashes back in.
He’s the son of the owner. He drives a Porsche that probably never sees the road and reads Bukowski like it’s gospel.
You? You read bedtime stories and wipe juice off a Hermès towel. You’re an au pair with a paper degree and an expiring visa. Your chest tightens with a thousand what-ifs.
The summer is bleeding out.
And you're kissing a boy who might not be yours when it ends.
Shit. Shit. Shit.
Entry #9: On the Danger of Wanting More August 19th, 4:21 PM
In most societal structures, the help is expected to exist quietly on the periphery – present but visible, useful but never central. And falling for someone above one’s pay grade? Historically ill-advised, frequently humiliating, and almost always doomed. But anthropologists agree that humans are predictable irrational – no amount of emotional detachment can fully protect you from a boy that kisses you stupid and casually quotes Euripedes.
You pulled away after the kiss, gasping. Dizzy. Brain short-circuiting.
The class divide. The logistics. The impossible futures.
He’s the son of the owner. He could never work another day and still live comfortably into infinity. You’re scraping together tips and spare change, trying to stretch your contract into a real life. He’s got gilded options. You’ve got a ticking clock.
So you avoid him.
When you see him walking toward the cabana for his daily granola bar pilgrimage, you redirect the twins toward the kiddie pool. When he shows up with your favorite pina colada — extra pineapple, no cherry — you pretend it’s nap time. You dodge, deflect, disappear. You rehearse polite excuses until they become muscle memory.
It takes a week for him to finally corner you.
You’re headed to the bathroom, sunglasses on, hoodie up despite the August heat. He intercepts you by the towel stand.
“What are you doing?” he asks, voice low, not angry but confused.
You blink. “Nothing. Peeing?”
“You’re avoiding me.”
“No…”
“You are,” he says, stepping closer. “Don’t lie. You won’t even look at me.”
You focus intently on a damp footprint on the pavement. “I’ve just been… busy.”
“What did I do wrong?”
He says your name like it matters. Like he means it. A question and a plea and a prayer all at once.
“I thought this was going somewhere,” he says. “Where did I go wrong?”
You open your mouth. Close it. Swallow. Then:
“You didn’t.”
His shoulders drop in relief. He starts to move closer, arms lifting — but you stop him with a hand on his chest.
“You didn’t do anything wrong,” you repeat. “I did.”
Now he looks confused. “What are you talking about?”
“Wonwoo,” you sigh. “One day, you’re going to take over. You’re going to be CEO of a global resort empire. And me? I’m going to be here. Covered in five-year-olds’ snot and banana crumbs, probably chasing a preschooler into a fountain.”
“So?” he scoffs. “I don’t want this.” He gestures broadly at the lazy river, the snack bar, the sunburned luxury. “I’m not staying. I got into an MFA program. I’m leaving at the end of the month.”
That throws you. “Wait—what? Really?”
He nods. “I want to write. Always have.”
You blink. “Okay… and?”
He reaches out and takes your hand, threading your fingers together like it’s the most obvious thing in the world.
“You don’t have it all figured out,” he says softly. “That’s okay. Neither do I. But what are you gaining from babysitting your own life?”
You want to laugh. Or cry. Or kiss him again. Maybe all three.
But you don’t answer. Not yet.
That night, you get a text.
[Attachment: IMG_0142.jpeg]
A photo of an email. Congratulations! You’ve been accepted to the Creative Writing MFA program at—
[Attachment: PDF Lease Agreement]
Two bedrooms. Hardwood floors. Half a mile from the university. Your hometown.
Then a message from him:
You could write too, you know. I’d read every word.
Entry #10: On Exit Strategies (And the Beginnings We Don’t See Coming) August 23rd, 7:54 AM
In the study of human nature, we often assume that endings are marked, observable events – clean breaks punctuated by ritual. But fieldwork reveals a more complex truth: endings, like goodbyes, are rarely so precise. Sometimes the dissolve quietly, like mist off the surface of a morning pool. Sometimes they masquerade as beginnings. And sometimes, they don’t happen at all – not really.
It’s your last day at Carat Bay.
The twins start kindergarten on Monday. Their regular au pair — a disheveled girl who looks like she once studied French literature and now only speaks in juice box negotiations — has returned.
You say goodbye to the kids, crouched low to meet their eyes. Junhee hugs you, sticky-fingered and sad. Junseo asks, “Who’ll sing to us now?” in a voice so small it nearly breaks you.
You press teary kisses to their damp little heads. Promise they’ll be okay. They’re good kids. You tell yourself that means something.
You say goodbye to Mr. and Mrs. Cho.
Mrs. Cho barely glances up from her phone. She waves vaguely. Her acrylics glint in the sun.
Mr. Cho squints at you from over his tablet. “We had a new nanny this summer?”
You roll your eyes as you walk away, his confusion trailing behind you like bad perfume.
You drag your suitcase down the cobbled path toward the villa’s front gate, sunscreen and chlorine still clinging to your skin. The early morning air smells like pool chemicals and hotel pastries.
And then you see it — the Porsche, parked crooked in the drive like it doesn’t know it’s expensive.
Wonwoo is leaned against the side, arms crossed, sunglasses perched low on his nose like he’s auditioning for a commercial titled Regret Nothing.
He straightens when he sees you, already moving to grab your suitcase.
“So,” he says, like it’s casual. Like it’s not everything. “You comin’ with me?”
You pretend to think. Just for show. Just for the story.
Then you’re moving — fast, reckless — throwing your arms around him like you never learned how to say goodbye. His mouth finds yours in a kiss that feels like a collision — breathless, greedy, impossible. He laughs against your lips as you stumble back against the car, the heat of the hood warming your spine.
“You ever driven a Porsche?” he asks, his grin crooked, summer-sick and daring.
You break the kiss just long enough to smile. “Not yet.”
He presses the keys into your hand like a promise. Like a dare. Like the start of something you didn’t plan for — and maybe that’s the point.
You take the keys. Open the door.
And you drive — not toward an ending.
But into something new.
Epilogue: On Retrospective Analysis and the Unscientific Nature of Love Not Dated (yet)
Anthropologists caution against emotional entanglement with their subjects, citing compromised objectivity, blurred boundaries, and the potential erosion of professional distance. This author would like to report that such boundaries are far more porous when your subject brings you coffee and quotes Aeschylus. In the interest of full disclosure: This author ignored the rule. Repeatedly. And with alarming enthusiasm.
Three years later, you live together in a house with creaky floors and a crooked porch light. Wonwoo brings you coffee before you've asked for it, sets it beside your laptop with the reverence usually reserved for sacred texts. He reads your pages in silence, a red pen tucked behind one ear, and presses soft kisses to the back of your neck when you write too late into the night.
The work is fiction. Technically. But when he gets to the part about juice boxes and Clifford the Big Red Dog, his fingers find yours. He doesn’t say anything, just smiles that slow, knowing smile he saves for when he catches you pretending not to be sentimental.
He's finished his MFA now. Teaches English at the local high school, spends his afternoons grading essays about Of Mice and Men and trying not to laugh when his students call The Iliad “a chore to read.” He comes home smelling like school lunches and adolescent chaos, drops his bag by the door and finds you, always.
The Porsche sits untouched under your window—an inheritance he never asked for, gathering dust and sun-bleached leaves. He takes the train instead. Says he likes the time to read.
Sometimes, you still wake up waiting for someone to call your name and hand you someone else’s kids. Sometimes, you still flinch when your phone rings. But mostly, you write. And mostly, you’re okay.
There is no neat conclusion. Only this: You’re allowed to want things. You’re allowed to keep them, too.
#seventeen fics#seventeen fluff#seventeen drabbles#caratbaycollab#svthub#wonwoo x reader#jeon wonwoo#jeon wonwoo x reader#seventeen wonwoo#keopihausnet#wonwoo fluff#seventeen imagines#seventeen x you#svt x reader#seventeen#tara writes#svt: jww#mansaenetwork#kvanity#thediamondlifenetwork
297 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - January 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Landmark debt swap to protect Indonesia’s coral reefs

“The government of Indonesia announced this week a deal to redirect more than US$ 35 million it owes to the United States into the conservation of coral reefs in the most biodiverse ocean area on Earth.”
2. [FWS] Provides Over $1.3 Billion to Support Fish and Wildlife Conservation and Outdoor Access

“Through these combined funds, agencies have supported monitoring and management of over 500 species of wild mammals and birds, annual stocking of over 1 billion fish, operations of fish and wildlife disease laboratories around the country, and provided hunter and aquatic education to millions of students.”
3. Philippine Indigenous communities restore a mountain forest to prevent urban flooding

“Indigenous knowledge systems and practices are considered in the project design, and its leaders and members have been involved throughout the process, from agreeing to participate to identifying suitable land and selecting plant species that naturally grow in the area.”
4. Responsible Offshore Wind Development is a Clear Win for Birds, the U.S. Economy, and our Climate

“[T]he total feasible offshore wind capacity along U.S. coasts is more than three times the total electricity generated nationwide in 2023. […] Proven strategies, such as reducing visible lights on turbines and using perching deterrents on turbines, have been effective in addressing bird impacts.”
5. Illinois awards $100M for electric truck charging corridor, Tesla to get $40M

“The project will facilitate the construction of 345 electric truck charging ports and pull-through truck charging stalls across 14 sites throughout Illinois[…. E]lectrifying [the 30,000 daily long-haul] trucks would make a huge impact in the public health and quality of life along the heavily populated roadways.”
6. Reinventing the South Florida seawall to help marine life, buffer rising seas

“[The new seawall] features raised areas inspired by mangrove roots that are intended to both provide nooks and crannies for fish and crabs and other marine creatures and also better absorb some of the impact from waves and storm surges.”
7. Long Beach Commits to 100% All-Electric Garbage Trucks
“[Diesel garbage trucks] produce around a quarter of all diesel pollution in California and contribute to 1,400 premature deaths every year. Electric options, on the other hand, are quieter than their diesel counterparts and produce zero tailpipe emissions.”
8. ‘This Is a Victory': Biden Affirms ERA Has Been 'Ratified' and Law of the Land

“President Joe Biden on Friday announced his administration's official opinion that the amendment is ratified and its protections against sex-based discrimination are enshrined in the U.S. Constitution.”
9. A Little-Known Clean Energy Solution Could Soon Reach ‘Liftoff’

“Ground source heat pumps could heat and cool the equivalent of 7 million homes by 2035—up from just over 1 million today[…. G]eothermal energy is generally considered to be more popular among Republicans than other forms of clean energy, such as wind and solar.”
10. Researchers combine citizens' help and cutting-edge tech to track biodiversity

“Researchers in the project, which runs from 2022 to 2026, are experimenting with tools like drones, cameras and sensors to collect detailed data on different species, [… and] Observation.org, a global biodiversity platform where people submit pictures of animals and plants, helping to identify and monitor them.”
January 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#good news#hopepunk#nature#national debt#coral reef#conservation#funding#fish and wildlife#philippines#indigenous#agroforestry#green infrastructure#offshore wind#wind energy#electric vehicles#illinois#florida#sea wall#habitat#california#equal rights#human rights#us politics#geothermal#biodiversity#citizen science#climate change#invasive species#endangered species#clean energy
280 notes
·
View notes
Text
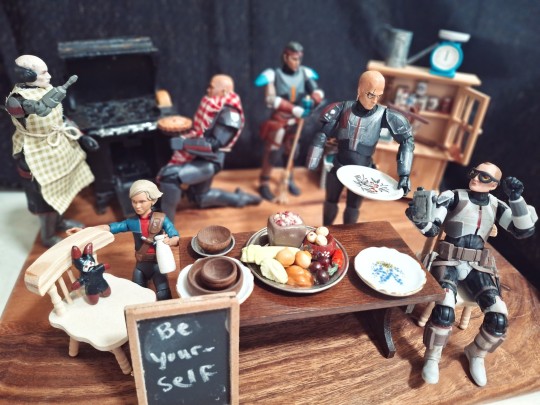

Wrecker baked a berry pie and a fresh loaf of bread.
Echo helped by hovering over him, making sure he didn't leave anything out.
Hunter cleaned up the kitchen.
Omega played "Lula is my baby".
Crosshair set the table, and Tech found a most interesting article on the origins of indigenous peoples that he shared with everyone.
Happy Thanksgiving!
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
LANGUAGE HEADCANONS
including the vegimals, also some pirate culture lore for kwazii ig
@calamaroo
BARNACLES
Barnacles learned basic English as an extracurricular when he was younger, but he only really learned it (and gained the accent) when he went to university in Manitoba (polar bear capital of the world and the university works by, with, and for indigenous people with a lot of foreign people coming to study). he's got a similar thing with the speaking Russian and I'm gonna steal the specific language of inuktuk from you.
Also because the Arctic has so many different countries in it (although everyone in the Arctic considers themselves as just "the Arctic because wtf are u gonna do about borders? come through the snow storm and take me to another snowy white spot that looks exactly the same (to you) as the other snowy white spot I was in? FCK borders in the Arctic no one there gives a sht)
Anyways they do have a common sign language because I LOVE SIGN LANGUAGE AND WILL INSERT IT EVERYWHERE I CAN
------------------------------------------------------------
KWAZII:
Kwazii did grow up with a very mixed pirate crew, although A LOT of members were either English speaking or Japanese speaking predominantly , he also watched a lot of old kids anime as a kid in Japanese as well lol. not to mention the native island cultures they often interacted with including my very fictional "meowri" (they're sphinx cats with ttattoes and very loosely inspired by Polynesian cultures)...
Because of the general culture of the pirate crew being diverse (esp cuz of interactions on ports/other crews) there was also a lot slang and terms that was known shared and sort of used as a basic communication system for everyone.
so there'd be random Spanish and Arabic terms from the most niche origin points just being used commonly, and that includes a lot of outdated ones, cultural sayings, or words that just don't exist in a lot of other languages, and etc
not to mention that because of how old the pirate clan he was a part of was (founded in 1920s) and because of the different crews there's genuinely like hundreds and hundreds of them being in these isolated communities and even being born and raised in them. so there's a lot of words that cant even be found anywhere else, so kwazii does get frustrated when he cant express what he wants to say but he just... cant even translate the word
OR the words everyone else uses for it doesn't make any sense! it... it kinda makes him feel stupid sometimes
also because his clan did work with a lot of wild animals as non tech sources of information (you feed them and then they get u good info!! for strategy, spying, whatever! and no one even blinks an eye cuz its just a crow (an extremely intelligent bird)!) but uh... the problem with that is that well alot of animals uhhhh misunderstand stuff
so that means that all the names of locations, descriptions of wild animals, ways of naming ships, and all the information would've have to have been animal comprehension friendly. not to mention be more coded cuz of non-friend pirate clans and G O V E R N M E N T S- so I'd get some wacky name replacements for all sorts of things.... its really a mess XD, a beautiful mess but still
also explained why so many of the pirate tales about *insert scientific name of the episode's animal* was often over exaggerated with strange details... including ones pirates shouldn't even known. Like how could they know about sword fish making the water around them warm?
its because a lot of that info CAME from the animals... animals who... don't understand numbers and say things like "and it was 20 feet tall!" even if it was only 5.... because it FEELS that tall to the small animal yk? also not understanding science on a deeper level so its all explained in a strange way. Ofc the pirates DONT help the issue because they be exaggerating the hell out of their own stories-
yeah sure the snake was "long as the river itself" Cj and SURE it was 20 sharks or whatever and not THREE that chased you kwazii
lying in story telling is just a form of pirate love actually, so is pranks and pickpocketing but kwazii refrains lol... this turned into me yapping about the blorbo
-----------------------------------------------------------
BASIC COMMUNICATION SKILLS:
Speaking of the basic communication thing, the octonauts crew was trained on the main words for rescue related communication in more common languages like Arabic, Chinese, Spanish, etc and will take time to learn (or just refresh) before heading to a new location.
Because in my own au the communication abilities of the wildlife is a lot more limited based on their level of intelligence. so an orca would technically be bi lingual in their own orca language and be able to speak nearly identical to a humanoid person
also like I said before about sign language, BASIC PIRATE SIGNS THAT ONLY OTHER PIRATES KNOW AYYYYYYYYY
-------------------------------------------------------------
DASHI:
Australian Dashie my beloved<3 honestly she WOULD have learned several languages and learned more for/from her friends shes so capable and incredible fr. also FCK it MORE sign language! I headcanon shes CODA, which means you're the child of one or two parents who are both either hard of hearing or Deaf! so she actually was learning sign very VERY young from her mom <3 and well the rest of her family cuz they all knew it lol
--------------------------------------------------------
PESO:
peso is obviously bilingual and he's the BEST at the basic communications skills thing and most well versed cuz he deals with the most animals one on one, so he actually can communicate with pretty much all the animal creatures, even taking the time to learn some slang terms the animals might have learned so that they'll feel safer and more comfortable around him!
he also picks up on a lot of dialects especially since his cousins are so diverse
-----------------------------------------------
TWEAK:
as for tweak she knows a lot of Spanish actually because hey! Miami has A LOT Spanish speakers, so much that's its actually made an entirely new developing dialect unique to the area!
tweak actually understands a decent amount of Japanese and Russian but.... not for normal conversations, more like because of all the engineering studying she did! research papers, studies, articles, lectures, books etc etc... so she could probably have a full conversation about the physics and math of submarines in those languages but if you wanted to talk about like... how you're feeling today or what you want for dinner she can not answer that LMSO
INKLING:
inkling would absolutely know like SO many languages, I have the headcanon that the reason he actually met barnacles in that university was actually because he studied LAND SPECIES for years (and continues to enjoy observing his crew and doing behavioural experiments on them without anyone noticing, esp since they're so diverse and they're in such a unique social environment on the octopod! but shhhh don't tell the others it would ruin the natural response they have! he does this with love btw)
hes also literally mega brained so I'd be surprised if he didn't at least understand the basics of any language the octonauts knew purely based on his own curiosity....
SHELLINGTON:
hehe Gaelic go brrrrrr
also because I headcanon Shellie as being a a mix of Eurasian otters and small clawed Asian otters, I think he does have some Philippine heritage and knows some Tagalog but not that much and he's a bit sad about that in all honesty. his *ss would also know latin
VEGIMALS:
IVE BEEN PLANNING TO MAKE A VEGIMALESE LANGUAGE POST:
ok so basically their language is entirely unique and not just because of them being the only known vegimals:
the thing is that their vocal cords (or vegetable/fish equivalent) isn't really made for the languages they hear on the octopod... or English.
the thing is they are their own little pod, and during their earliest developmental years they spent the MAJORITY of their time only with eachother or with shellington, what this means is that while some of the verbal and auditorial cues they have is just innate to vegimal understanding- (and also had difficult time replicating sounds shellington made, while it being easier to replicate a word one of the other vegimals made)
they quite literally made their own words for a lot of things while talking with eachother, before shellington had even realized! a lot of their language development did formulate very similarly to english (and Gaelic) because that's what they were hearing from shellington!
as they continue to grow and get older (they're really only about like 11 to me) their English has actually improved a lot, because they've learned how to mimic the others better, that's how they learned that the vegimals still used a lot of the literal baby talk words that shellington used with them while they were growing up, but just in their own original language
not to mention a lot of their language does have a lot of the meaning derived from the enunciation, tone, rhythm, and etc... so that means its a bit harder for those who just.. don't have the built in brain biology to distinguish those sounds to understand them
ofc shellington did literally raise them so its much much easier for him to understand because (whether he realizes it or not) he was actually learning the language AS they developed it! ofc over the years the other octonauts have actually started to subconsciously pick up on the meanings of those more subtle language features of vegimalese, and combined with knowing the vegimals slang/phrases, and the vegimals learning how to replicate more and more English ones, their understanding of the vegimals only keeps increasing
but to anyone else who isn't an octonaut its.... kinda like hearing a lil guy yip yip a bunch of gibberish and then everyone else in the room going "oh yes of course! that's a great idea Tototofrit! and don't worry, well make sure our fish friends aren't scared as we perform your very clever and crafty plan!"
also my friend said I can pull off a decent vegimal accent so if anyone wants any tips lmk (I would stim in vegimalese in middle school btw LMSO but I did learn a decent amount on how they pronounce things and their speech patterns... still working on perfecting it but I got some starter tips LOL)
also the reasons halibeet and pikato don't show up as much as the other vegimals is because they're just genuinely more introverted, halibeet and pikato do enjoy each other's quiet company tho (as well as the other vegimals, but they're really more homebodies who just aren't as into the whole adventure stuff)
#octonauts#octonauts headcanons#octo headcanons#yap post#lore post#octonauts kwazii#octonauts captain barnacles#octonauts peso#captain barnacles#octonauts barnacles#octonauts shellington#octonauts dashi#octonauts tweak#octonauts professor inkling#tweak bunny#kwazii cat#dashi dog#shellington sea otter#peso penguin#professor inkling#octonauts vegimals#vegimals
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
worldbuilding in spiritkeep
okay howdy again :) the second place winner of the spiritkeep poll was to talk about worldbuilding!!
for new folks, spiritkeep is a multiplayer campaign ttrpg designed around inducing therapeutic emotional growth
if you want to learn more about the playbook options you can find the write up here and the deep dive into the lonesome playbooks and the minder playbooks here
so … worldbuilding!!

collaborative worldbuilding is actually the first stage of play, even before you make your characters. i took inspiration from yarnspinner by edda mendes and spool by jade ravens especially, as well as the community building aspect of songs for the dusk by kavita poduri
there are a few things about the world of spiritkeep that always stay the same:
1) this is a fantasy world with low/no tech, and medium-high magic (i think some people would call it low magic because the pcs aren't terribly powerful, there isn't a spellcasting system, and also because they're used to thinking of high magic as looking specifically like medieval european fantasy. but there is actually a lot of magic in this world even if a typical human isn't particularly high powered)
2) there are various lineages of human, but all the pcs are human. (a notable exception is the othered archetype, which includes paragons for werecreatures, changelings, and ghosts. these characters are still humanoid though!) the lineages include what we would think of as regular humans and then various kinds of people, diverse in appearance and beliefs, who are descended from humans blessed or cursed by spirits. we'll get more into that next time!!
3) the world is inhabited by humans, animals, and spirits. the worlds of spiritkeep are animist and inspired by nature religions. in particular, i took a lot of inspiration from slavic paganism, shintoism, and various indigenous american religions but most specifically diné religion. in spiritkeep, many aspects of nature and daily life have spirits, from homes to rivers to trees. many spirits have minor magical abilities, and most will stay fairly hidden or out of the way, but there are rarer spirits who are quite powerful. parties will have to interact with spirits sometimes, such as doing favors for or solving problems for them to get boons
4) humans also have their own spirits. there are times when these spirits become independent & tangible enough to interact with. this is how pcs get advancements, boons, and can change playbooks. your spirit can also be harmed, though, so watch out!
5) the game always takes place in a community that is struggling and in need of repair
the rest of the world is up to the players to flesh out during the session zero!!
the session zero includes worldbuilding and community building. players will decide on details about the major cities, cultures, and geographic features in the area. they'll also work together to decide on more thematic elements like conflicts between groups of people, spiritual traditions, or the presence of bigotry within the world (yes, there can definitely be explorations of bigotry in spiritkeep. i am not an ascriber to cozy game escapist fantasy culture and i dont think those work well for the purpose of this game)
after a broad sketch of the world is laid out, the group turns to building the community. here, they'll focus on a few aesthetic features of the community, community values, and a few major features (does the community have a doctor or no? do they have a post office? is this a farming community or do they trade textiles? what are people's houses made of? etc)
i have a general idea on how to make the collaborative worldbuilding process approachable, cooperative, and safe, but it definitely needs playtesting before i explain :) im approaching this with the mindset of 1) players hard no's will have already been discussed in a separate process 2) players might be strangers to each other and might have never played a ttrpg before. i also want it to be feasible both in person and on a vtt. so i'm still working that out :)
so that's the basics! a baseline that all games follow, while the cultures and settings within the world are still pretty flexible
next up i'll be talking about the lineages, or the different kinds of human you can be!!
i also have a bunch of stuff on sale right now to fund spiritkeep in its early stages!!
you can support this sale to fund more promo material like art, and this sale to help me pay to become a certified therapeutic gm!!
thanks for reading :)
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Read this one. Read it carefully. Read it thoroughly. Yes, it's long. Take the time.
Heather Cox Richardson
March 9, 2025 (Sunday)
Lately, political writers have called attention to the tendency of billionaire Elon Musk to refer to his political opponents as “NPCs.” This term comes from the gaming world and refers to a nonplayer character that follows a scripted path and cannot think or act on its own, and is there only to populate the world of the game for the actual players. Amanda Marcotte of Salon notes that Musk calls anyone with whom he disagrees an NPC, but that construction comes from the larger environment of the online right wing, whose members refer to anyone who opposes Donald Trump’s agenda as an NPC.
In The Cross Section, Paul Waldman notes that the point of the right wing’s dehumanization of political opponents is to dismiss the pain they are inflicting. If the majority of Americans are not really human, toying with their lives isn’t important—maybe it’s even LOL funny to pretend to take a chainsaw to the programs on which people depend. “We are ants, or even less,” Waldman writes, “bits of programming to be moved around at Elon’s whim. Only he and the people who aspire to be like him are actors, decision-makers, molding the world to conform to their bold interplanetary vision.”
Waldman correctly ties this division of the world into the actors and the supporting cast to the modern-day Republican Party’s longstanding attack on government programs. After World War II, large majorities of both parties believed that the government must work for ordinary Americans by regulating business, providing a basic social safety net like Social Security, promoting infrastructure projects like the interstate highway system, and protecting civil rights that guaranteed all Americans would be treated equally before the law. But a radical faction worked to undermine this “liberal consensus” by claiming that such a system was a form of socialism that would ultimately make the United States a communist state.
By 2012, Republicans were saying, as Representative Paul Ryan did in 2010, that “60 Percent of Americans are ‘takers,’ not ‘makers.’” In 2012, Ryan had been tapped as the Republican vice presidential candidate. As Waldman recalls, in that year, Republican presidential candidate Mitt Romney told a group of rich donors that 47% of Americans would vote for a Democrat “no matter what.” They were moochers who “are dependent upon government, who believe that they are victims, who believe the government has a responsibility to care for them, who believe that they are entitled to health care, to food, to housing, to you-name-it.”
As Waldman notes, Musk and his team of tech bros at the Department of Government Efficiency are not actually promoting efficiency: if they were, they would have brought auditors and would be working with the inspectors general that Trump fired and the Government Accountability Office that is already in place to streamline government. Rather than looking for efficiency, they are simply working to zero out the government that works for ordinary people, turning it instead to enabling them to consolidate wealth and power.
Today’s attempt to destroy a federal government that promotes stability, equality, and opportunity for all Americans is just the latest iteration of that impulse in the United States.
The men who wrote the Declaration of Independence took a revolutionary stand against monarchy, the idea that some people were better than others and had a right to rule. They asserted as “self-evident” that all people are created equal and that God and the laws of nature have given them certain fundamental rights. Those include—but are not limited to—life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. The role of government was to make sure people enjoyed these rights, they said, and thus a government is legitimate only if people consent to that government. For all that the founders excluded Indigenous Americans, Black colonists, and all women from their vision of government, the idea that the government should work for ordinary people rather than nobles and kings was revolutionary.
From the beginning, though, there were plenty of Americans who clung to the idea of human hierarchies in which a few superior men should rule the rest. They argued that the Constitution was designed simply to protect property and that as a few men accumulated wealth, they should run things. Permitting those without property to have a say in their government would allow them to demand that the government provide things that might infringe on the rights of property owners.
By the 1850s, elite southerners, whose fortunes rested on the production of raw materials by enslaved Black Americans, worked to take over the government and to get rid of the principles in the Declaration of Independence. As Senator James Henry Hammond of South Carolina put it: “I repudiate, as ridiculously absurd, that much lauded but nowhere accredited dogma of Mr. Jefferson that ‘all men are born equal.’”
“We do not agree with the authors of the Declaration of Independence, that governments ‘derive their just powers from the consent of the governed,’” enslaver George Fitzhugh of Virginia wrote in 1857. “All governments must originate in force, and be continued by force.” There were 18,000 people in his county and only 1,200 could vote, he said, “[b]ut we twelve hundred…never asked and never intend to ask the consent of the sixteen thousand eight hundred whom we govern.”
Northerners, who had a mixed economy that needed educated workers and thus widely shared economic and political power, opposed the spread of the South’s hierarchical system. When Congress, under extraordinary pressure from the pro-southern administration, passed the 1854 Kansas-Nebraska Act that would permit enslavement to spread into the West and from there, working in concert with southern slave states, make enslavement national, northerners of all parties woke up to the looming loss of their democratic government.
A railroad lawyer from Illinois, Abraham Lincoln, remembered how northerners were “thunderstruck and stunned; and we reeled and fell in utter confusion. But we rose each fighting, grasping whatever he could first reach—a scythe—a pitchfork—a chopping axe, or a butcher’s cleaver” to push back against the rising oligarchy. And while they came from different parties, he said, they were “still Americans; no less devoted to the continued Union and prosperity of the country than heretofore.” Across the North, people came together in meetings to protest the Slave Power’s takeover of the government, and marched in parades to support political candidates who would stand against the elite enslavers.
Apologists for enslavement denigrated Black Americans and urged white voters not to see them as human. Lincoln, in contrast, urged Americans to come together to protect the Declaration of Independence. “I should like to know if taking this old Declaration of Independence, which declares that all men are equal upon principle and making exceptions to it where will it stop?... If that declaration is not the truth, let us get the Statute book, in which we find it and tear it out!”
Northerners put Lincoln into the White House, and once in office, he reached back to the Declaration—written “four score and seven years ago”—and charged Americans to “resolve that…this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.”
The victory of the United States in the Civil War ended the power of enslavers in the government, but new crises in the future would revive the conflict between the idea of equality and a nation in which a few should rule.
In the 1890s the rise of industry led to the concentration of wealth at the top of the economy, and once again, wealthy leaders began to abandon equality for the idea that some people were better than others. Steel baron Andrew Carnegie celebrated the “contrast between the palace of the millionaire and the cottage of the laborer,” for although industrialization created “castes,” it created “wonderful material development,” and “while the law may be sometimes hard for the individual, it is best for the race, because it insures the survival of the fittest in every department.”
Those at the top were there because of their ��special ability,” Carnegie wrote, and anyone seeking a fairer distribution of wealth was a “Socialist or Anarchist…attacking the foundation upon which civilization rests.” Instead, he said, society worked best when a few wealthy men ran the world, for “wealth, passing through the hands of the few, can be made a much more potent force for the elevation of our race than if it had been distributed in small sums to the people themselves.”
As industrialists gathered the power of the government into their own hands, people of all political parties once again came together to reclaim American democracy. Although Democrat Grover Cleveland was the first to complain that “[c]orporations, which should be the carefully restrained creatures of the law and the servants of the people, are fast becoming the people's masters,” it was Republican Theodore Roosevelt who is now popularly associated with the development of a government that took power back for the people.
Roosevelt complained that the “absence of effective…restraint upon unfair money-getting has tended to create a small class of enormously wealthy and economically powerful men, whose chief object is to hold and increase their power. The prime need is to change the conditions which enable these men to accumulate power which it is not for the general welfare that they should hold or exercise.” Roosevelt ushered in the Progressive Era with government regulation of business to protect the ability of individuals to participate in American society as equals.
The rise of a global economy in the twentieth century repeated this pattern. After socialists took control of Russia in 1917, American men of property insisted that any restrictions on their control of resources or the government were a form of “Bolshevism.” But a worldwide depression in the 1930s brought voters of all parties in the U.S. behind President Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s “New Deal for the American people.”
He and the Democrats created a government that regulated business, provided a basic social safety net, and promoted infrastructure in the 1930s. Then, after Black and Brown veterans coming home from World War II demanded equality, that New Deal government, under Democratic president Harry Truman and then under Republican president Dwight D. Eisenhower, worked to end racial and, later, gender hierarchies in American society.
That is the world that Elon Musk and Donald Trump are dismantling. They are destroying the government that works for all Americans in favor of using the government to concentrate their own wealth and power.
And, once again, Americans are protesting the idea that the role of government is not to protect equality and democracy, but rather to concentrate wealth and power at the top of society. Americans are turning out to demand Republican representatives stop the cuts to the government and, when those representatives refuse to hold town halls, are turning out by the thousands to talk to Democratic representatives.
Thousands of researchers and their supporters turned out across the country in more than 150 Stand Up for Science protests on Friday. On Saturday, International Women’s Day, 300 demonstrations were organized around the country to protest different administration policies. Senator Bernie Sanders (I-VT) is drawing crowds across the country with the "Fighting Oligarchy: Where We Go From Here” tour, on which he has been joined by Shawn Fain, president of the United Auto Workers.
“Nobody voted for Elon Musk,” protestors chanted at a Tesla dealership in Manhattan yesterday in one of the many protests at the dealerships associated with Musk’s cars. “Oligarchs out, democracy in.”
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Celto-Nahuan Empire
For a stroll down memory lane, I've been playing some Civilization III lately. I started as the Celts on an archipelago map, hoping to be left alone as a I re-learn the game.
I discovered that I shared my starting continent with the Aztecs, whom I conquered over the course of three grueling wars that left us both in a tech deficit relative to several other larger powers on other continents. It's currently 1600 AD and I'm halfway through the Medieval Era. Persia is already in the Industrial Era and has a massive culture lead, too.
During one of my wars with the Aztecs, the Dutch hopped over and tried to plant a colony where I had just razed an Aztec city, but I stomped that out right quick. They never sent retribution, and accepted a peace treaty a few decades later.
Anyhow, I have role-played as a magnanimous conqueror who embraces the multicultural nature of his new empire. While I did have to raze a lot of Aztec cities in sub-optimal locations, I repopulated the new cities I founded with captured Aztec workers & settlers. Now that Montezuma is defeated, I don't have to worry about their disloyalty.
This all has me wondering what a cultural fusion of Celts and the indigenous peoples of Central Mexico would look like...
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heritage News of the Week
Discoveries!
The ship was part of a Spanish colonizing expedition led by the conquistador Tristán de Luna y Arellano, who was voyaging from Mexico under the Spanish crown. In September 1559, a hurricane in Pensacola Bay wrecked several of the 11 ships, which had been anchored near the new Spanish settlement of Santa María de Ochuse. Researchers found one of these wrecks, known as Emanuel Point II, in 2006. This shipwreck holds the remains of an adult and a juvenile domestic cat (Felis catus), according to the new study.

'Overkill' injuries on Bronze Age skeletons reveal fierce feuding in ancient China
A unique Bronze Age cemetery in China has revealed a high frequency of injuries suggestive of intense, violent interactions.
Hikers make stunning discovery of $340,000 gold hoard in Czech mountains
The Museum of Eastern Bohemia in the Czech Republic city of Hradec Králové has announced the discovery of a 20th-century gold trove worth more than $340,000.
2,300-year-old sword unearthed at necropolis in France
Two 2,300-year-old swords discovered in a Celtic Iron Age necropolis in France "have few equivalents in Europe," and one is decorated with tiny swastikas, the French National Institute of Preventive Archaeological Research reports.
Mummy mystery solved: ‘air-dried’ priest was embalmed via rectum
Intrigue had long swirled around the mummified body stored in the church crypt of St Thomas am Blasenstein. The remains were rumoured to be the naturally preserved corpse of an aristocratic vicar, Franz Xaver Sidler von Rosenegg, who died in 1746 at the aged of 37, gaining the mummy the moniker of the “air-dried chaplain”. Now experts say they have discovered the body was embalmed with the abdominal and pelvic cavities packed with wood chips, fragmented twigs, fabrics such as hemp and silk, and zinc chloride – materials that would have absorbed fluids inside the body.
Tw: Image of human remains at link
This facility once produced the ancient world’s rarest dye at a grand scale
Archaeologists in Israel have turned up the remains of a massive operation that once produced Tyrian purple.
'Groundbreaking' ancient DNA research confirms Pueblo peoples' ties to famous Chaco Canyon site
New genetic research confirms what the oral traditions of the Picuris Pueblo people of New Mexico have long described — that they're related to the Indigenous people of Chaco Canyon.
Ancient tomb of nomadic horse lord yields untouched treasures and weapons
A archaeological discovery near Grozny has unearthed an undisturbed Alanian tomb dating back over two millennia, revealing a wealth of exquisite artifacts including unique triple-edged weapons and elaborate horse adornments.
Egyptologist uncovers hidden messages on Paris’s iconic obelisk
Olette-Pelletier found seven crypto-hieroglyphs on the monument that could only be read by elites.
Unique lion-headed handles unveiled from a Roman-period cist tomb near Khirbat Ibreika
Beneath the ancient dust of Khirbat Ibreika in southern Israel, archaeologists have unearthed an unexpected enigma: four bronze discs, each adorned with powerful lion head reliefs and accompanied by functional rings, carefully extracted from a tomb dating back to the first and second centuries CE of the Roman Empire.
Neanderthals made the oldest bone spear tip found in Europe
The 3.5-inch object was made between 80,000 and 70,000 years ago and was likely fashioned out of a bison bone.
Mass grave of Black Union soldiers slaughtered during the Civil War may lie under a Kentucky soybean field, high-tech scans reveal
Archaeologists have identified two potential mass graves of Black Union soldiers who were targeted by Confederate guerrillas in the Civil War.
2,000-year-old garlanded sarcophagus unearthed in "City of Gladiators"
A remarkably well-preserved, 2,000-year-old sarcophagus adorned with intricate garlands has been discovered during ongoing excavations in the ancient city of Stratonikeia, in southwestern Türkiye.
New evidence suggests Scots may have invented the game of soccer
In what may cause major ramifications for the history of sports, The Times reports that a team of researchers may have identified the world’s oldest known soccer field—not in England, where the “beautiful game” was purportedly invented in the mid-nineteenth century, but in Kirkcudbrightshire, Scotland.
Numerous statue fragments unearthed at lost Apollo sanctuary in Cyprus
The Sanctuary of Apollo at Frangissa, located near ancient Tamassos and lost for approximately 140 years, has been rediscovered through recent excavations.
Archaeological project maps historic boat sheds on Isles of Scilly
An archaeological project has highlighted just how crucial the agile, tough “pilot gigs” were for islanders by mapping 90 sites of sheds that housed the boats, the earliest believed to date back to the 17th century.
Unique column capital depicting a menorah unveiled in Jerusalem
The carved limestone block was originally discovered in 2020 in a 6th- or 7th-century CE. Byzantine house during excavations in Motza, outside Jerusalem. Yet archaeologists believe that the capital is centuries older, likely dating to the second or third century, and had been subsequently moved to this location.
Museums
A temporary restraining order was issued by the U.S. District Court to block the Trump Administration‘s dismantling of the Institute of Museum and Library Services.
Smithsonian Institution says it won’t remove anti-segregation exhibits
The Smithsonian Institution denied reports this morning, April 28, that its National Museum of American History and the National Museum of African American History and Culture intended to remove object displays documenting anti-segregation demonstrations during the Civil Rights Movement.
Vatican museums, including Sistine Chapel, closed indefinitely for conclave to elect the next pope
The Vatican Museums, which includes the Sistine Chapel, has been closed to the public as Vatican City prepares for the gathering of cardinals who will vote to elect a new pope following the death of Pope Francis on April 28.

‘The eighth wonder of the world’: China’s terracotta warriors to march on Australia for blockbuster show
Perth will host huge exhibition of ancient treasures from first emperor’s tomb in June, with 40% of the artefacts leaving China for the first time ever
Trump fires Doug Emhoff and others from US Holocaust Memorial Council
Husband of Kamala Harris calls move political and decries turning historical atrocity into ‘a wedge issue’
Trump names eight new appointees to US Holocaust Memorial Museum board
Eight new appointees for the US Holocaust Memorial Museum board were announced by President Donald Trump in a social media post on Thursday night. These trustees will replace the board members appointed by former President Joe Biden that Trump removed just a few days ago.
Edward II’s coronation roll goes on display alongside King Charles’s
The two rolls, part of a tradition dating back at least seven centuries, are on public display for the first time in an exhibition at the National Archives that also includes works of art commissioned by the government to mark the coronation.
The Getty’s Provenance Index makes more than 12 million records publicly available
The Getty Provenance Index (GPI) initially launched in the 1980s to keep track of the ownership history of each artwork in the museum’s collection. Since then, it has become an integral part of the Getty’s research on provenance, collecting, and art markets. Today, the records included in the GPI extend well beyond the Getty itself.
Repatriation
Ancestral human remains taken by a "grave robber" and brought to Belfast almost 200 years ago have begun their journey back to Hawaii. The human remains were repatriated in an emotional ceremony held at the Ulster Museum in Belfast, attended by representatives from Hawaii.
A looted Greco-Roman statue goes on display before its return
After a months-long legal battle, the sculpture is on view at the Cleveland Museum of Art ahead of its repatriation to Turkey, with newly added context about its provenance.
Heritage at risk
Ignorance appears to be no barrier as Trump seeks to grasp control of the US’s historical narrative in the run-up to next year’s landmark celebration of the 250th anniversary of the declaration of independence, also known as the semiquincentennial. Under an executive order issued in January, the president has started to churn out his own approved version of US history that professional historians fear will resort to the tried and tested authoritarian playbook of airbrushing out inconvenient and inglorious chapters that do not align with his vision of American greatness.
Famed Memphis church associated with Martin Luther King damaged by fire
A fire has severely damaged the historic Clayborn Temple in downtown Memphis, which is closely associated with the US civil rights movement and Dr Martin Luther King.
Odds and ends
Modern-day conclaves are steeped in mystery: cardinal electors swear an oath of secrecy – and so do the cooks, drivers, medics and others who support their deliberations. Before the conclave begins next week, the Sistine Chapel will be swept for electronic bugs, jamming devices will be installed, and special coatings will be placed on windows to stop laser scanners picking up anything audible. It wasn’t always this way: in the past, letters, diaries and other writings by cardinals and their attendants gave revealing accounts of what happened in the meetings convened in order to choose a pope.
How African popes changed Christianity - and gave us Valentine's Day
Now predominantly Muslim, North Africa was once a Christian heartland, producing Catholic popes who left their mark on the Church to this day.
The buried hoard: a story of treachery and greed
This is a story of treachery, secrecy and greed which led to two friends ending up in jail and a mystery about buried coins.
Pompeii aerial tour helicopters seized in safety investigation
Italian police have seized eight helicopters and are investigating four pilots associated with a company offering aerial tours of Pompeii’s archaeological ruins last week, alleging a laundry list of safety and operations violations.
Two men filmed felling of Sycamore Gap tree during ‘mindless’ act, court hears
Two men filmed themselves using a chainsaw to fell the famous Sycamore Gap tree on Hadrian’s Wall in an act of “mindless criminal damage”, a court has heard.
Titanic survivor's letter sold for £300,000 at auction
Colonel Archibald Gracie's letter was purchased by an anonymous buyer at Henry Aldridge and Son auction house in Wiltshire on Sunday, at a price five times higher than the £60,000 it was expected to fetch.Colonel Archibald Gracie's letter was purchased by an anonymous buyer at Henry Aldridge and Son auction house in Wiltshire on Sunday, at a price five times higher than the £60,000 it was expected to fetch.
How did Hitler’s film-maker hide her complicity from the world?
A new documentary delves into controversial German film-maker Leni Riefenstahl’s private archive to uncover a director who spent a lifetime covering up her central role in the Nazi propaganda machine
#big week for the conclave fandom#heritage news of the week#archaeology#history#museums#gifs#post-posting update about Trump's attempts to rewrite history!#sorry for putting his horrible face on your timeline
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
So... I could be totally wrong, but based on the new promo pictures for Avatar 3, I think the Ash People are going to be less of a tribe and more of a cult.

I mean, just look at this image for starters. The ones one surrounding Varang are wearing some freaky looking masks, and Varang seems to be wearing an outfit made entirely of Na'vi braids. That is insane and defiantly makes me afraid of this woman. So no wonder she and Quaritch team up at some point.
You can actually see glimpses of Lyle and Quaritch in the back here as Varang introduces a new kind of creature, which is also pretty dope.

In fact, you can see a LOT of Na'vi here weilding guns, like WHAT?!?!

Which brings me to another image that I think really proves that not only are these people a cult, but they're a cult that worships the Sky People.

Yep. They have air balloon ships. We literally have Na'vi Sky Pirates.
All jokes aside though, what I think is going on is that the Ash People are a Cargo Cult, a group of indigenous people who see bizarre looking strangers coming from a foreign land (or in this case, planet) and basically liken them to Gods (for better details, I recommend watching Game Theory's Minecraft Cult video.)
Anyway, what I'm getting at here is that Na'vi like Varang probably were inspired by the Sky People and their giant metal ikran that could fit more then one person, and their weapons and tried to recreate them, disregarding the way of Eywa, which likely didn't go over well with the other Na'vi. Especially after Grace's School; they were probably banished when those particular Na'vi still supported them after the fact.
But when the RDA was first defeated and sent away, Varang and those Na'vi, like the Cargo Cults of Earth, tried anything to get them to return. They wear masks over their faces, they recreated their ships, they teach themselves how to use their weapons and basically making menaces of themselves to other Na'vi.
And so, Varang become the Olo'eykte of a new clan. A clan that worships the innovations and technologies of the Sky People.
And I bet they would be very excited if they were ever to come across Miles and Lyle, humans that have been reborn into Na'vi, hence why they start working together, which would be a scary thought to think about.
But it would make sense too, because, before, when I still thought of the Ash People as a legitimate clan, I never understood why a clan would be supportive of what they're doing if they worshipped Eywa and help them attack other Na'vi. Like why side with Quaritch when he wants to help the RDA perform a hostile takeover and not Jake, who wants to preserve the Na'vi home and way of life. But it does make sense to me, if they were ostracized by their people for their continued adoration of their techniques.
In fact, if I was to really dig into this, this might explain Teylan and his fascination with human tech too. If others are just as intrigued by their tech, then so would he.
So yeah, that is my reasoning for why I think the Ash People are a cult and why they would align themselves with the RDA. Please let me know what you think and I can't wait to see this movie!!!💙
EDIT!!
So these airships...

What I may have misinterpreted as a Ash People replication of ships may actually belong to another tribe that's to feature in the film. The Windtraders.

And that makes sense with this image of Neytiri and her Ikran flying beside them. The Ikran's calm, Neytiri has no weapon ready, so I can only assume that the Windtraders are a tribe of nomadic merchants, who travel from place to place and, as the name implies, trade with other clans.
Maybe one such clan they trade with is the Metkayina, and that's how we'll get introduced to this clan and their way of living.
I still %100 believe that the Ash People are a cult, but I just wanted to clarify my mishap.
And who knows? Maybe the Ash People are scheming to steal their ships so that they can really imitate the Sky People and that's how the Sully's confront them.
Be a good way to kick start the plot is all I'm thinking.
#avatar james cameron#avatar 3#avatar fire and ash#avatar ash people#cult vibes#i am genuinely scared of varang now#if Quaritch and Varang does happen then its a match made in Eywa#also makes me scared for spider and the other sully kids#and literally everyone#atwow#avatar the way of water#afop teylan#avatar windtraders
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
I understand why people love railways and all but I just can't buy into the sunny fantasy of a heavily infrastructured high speed rail covered socialist utopia or whatever given how much the development of national railways was central to the genocide of Indigenous people and theft of their lands. alongside the declaration of land grant universities and other supposed public works. i'm not anti civilization but im not exactly not either, and i dont think the high tech, still colonialist, yimby socialism a lot of white people dream of is it dog
170 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - April 1-7
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles! Last month’s Doodles are free to the public, so go take a look :D
1. Galapagos tortoises at Philadelphia Zoo become first-time parents at nearly 100

“Mommy, the female tortoise, is considered one of the most genetically valuable Galapagos tortoises in the Association of Zoos and Aquariums’ species survival plan. [… T]he zoo said it is “overjoyed” at the arrivals of the four hatchlings, a first in its more than 150-year history.”
2. Massachusetts home-electrification pilot could offer a national model

“In total, the program is providing free or heavily subsidized solar panels and heat pumps to 55 participating households, 12 of which also received batteries at no cost. […] It’s a strategy that program planners hope can help address the disproportionate energy burden felt by lower-income residents of the region[….]”
3. National Park Rangers rebel against queer erasure on Trans Day of Visibility

“[… A] group of over 1,000 off-duty, fired, and retired National Park Service employees launched Rangers Uncensored, an online archive that restores and amplifies LGBTQ+ stories quietly scrubbed from government websites since President Donald Trump’s second inauguration.”
4. World's largest wildlife crossing reaches critical milestone

“Over the next few days they'll be adding 6,000 cubic yards of specially manufactured soil to cover the crossing, a mix of sand, silt and clay inoculated with a bit of compost and hyperlocal mycorrhizal fungi, carefully designed and tested to mimic the biological makeup of native soils around the site.“
5. Bipartisan bill to boost green building materials glides through House

“[B]ipartisan legislation the House of Representatives passed in a 350-73 vote last week would give the Department of Energy a clear mandate to develop a full program to research, develop, and deploy clean versions of the building materials.”
6. Tribal Wildlife Grants Funding Announced
“Tribal Wildlife Grants are intended to help Tribes develop programs for the conservation of habitat and species of traditional or cultural importance[….] Typically funded projects include: conservation planning, fish and wildlife management and research, habitat mapping and restoration, inventory and monitoring, and habitat preservation. […] A total of $6.1 million is available for this round of funding[….]”
7. Germany adds another one million PV arrays to take solar total to 104 gigawatts

“Following a rapid rise in household solar panel installations, Germany’s total number of PV arrays has passed the five million “milestone[.…]” Solar systems already cover almost 15 percent of Germany’s electricity demand, BSW-Solar said. […] The total capacity of all PV systems installed in Germany surpassed 100 GW at the start of the year.”
8. Stronger together: Bilby conservation efforts enhanced by Indigenous knowledge

“Ms. Geyle said the results showed combining [conventional science and traditional tracking methods] more accurately estimated bilby abundance than using either technique individually[….] "[… ensuring] that Indigenous people remain central to decision-making about their lands and species that inhabit them," Ms. Geyle said.”
9. Lennar will build 1,500new Colorado homes with geothermal heat pumps

“The homebuilder is partnering with Dandelion Energy to install the tech, which is efficient but expensive — unless it’s built into new homes from the start. […] And by eliminating the need for new gas pipelines and reducing the peak electricity demands on the power grid, subdivisions built on this model could save a bundle on utilities as well[….]”
10. New strategy launched to protect Tanzanian biodiversity hotspot

“Conservationists have launched a 20-year-long project to protect what is arguably Tanzania’s most biologically rich landscape: the Udzungwa Mountains. The strategy places notable emphasis on communities living here, with more than half of its budget allocated to social and economic projects and managing human-wildlife conflict.”
March 22-28 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#nature#philadelphia#zoo#galapagos#tortoise#solar panels#clean energy#national park service#lgbt+#lgbt#lgbtq#park ranger#wildlife#us politics#ecology#green infrastructure#indigenous#habitat restoration#germany#solar energy#solar power#australia#geothermal#heat pump#energy efficiency#biodiversity#tanzania#animals
269 notes
·
View notes
Note
hello fatehbaz dot tumblr dot com, I seem to recall that years ago you posted an article or articles about the construction of canals in Arizona & the threat it posed to desert cienegas. I tried finding it on your archive to no avail. I did find research about similar circumstances in chihuahua, but not specifically what you posted. i seem to recall that the specific canal was the CAP. does this ring any bells?
Thank you for sticking around and tolerating me for such a long time. Glad you're here. And thank you for remembering the posts (from August 2020) about Cuatro Cienegas in the Chihuahuan Desert.
---
Thinking of Arizona specifically, what you described sounds similar to an August 2022 post about ephemeral intermittent streams of the Agua Fria and canals to service Prescott/Phoenix? (Briefly describes progression from early water diversion to grow alfalfa for cattle; then the damming of Agua Fria to make reservoir in 1930s; then the construction of 16 copper mines. Cites an article from Rachel Howard at Edge Effects: "The history of the Agua Fria can be read not so much as a warning but rather a symbol of what happens to small bodies of water in Arizona. This is the state of the five Cs: cotton, copper, cattle, citrus, and climate.")
---
From August 2020, might be thinking of this post about the unique endemic Yaqui catfish, an icon of the desert; post described the drying of cienegas (and how the fish is functionally extinct in the US) due to progression of cattle rangeland, farms, and canal diversion? (About how despite popular conception of the desert as dry, "prior to European colonization, the region supported rich waterways and aquatic communities." Post described how, by the 1880s, to service agriculture, "meandering cienegas" were strongly channelized and became deep-etched arroyos. And by 1960s, the pumping of water had meant most cienegas were gone. And by 2016 it was estimated that maybe only 30 of the fish remained in Arizona, a fish sometimes described as the "only catfish native to US west of the Rockies." Which also brings to mind, for me, the 2016 edition of Inland Fishes of the Greater Southwest: Chronicles of a Vanishing Biota from University of Arizona Press.)
---
Also sounds similar to this one from July 2020? That one was about cienegas in Arizona, specifically the corridor of riparian habitat (cottonwood, mesquite, etc.) along the San Pedro. Post made criticism of Arizona agencies which managed surface water and groundwater separately despite their physical/ecological interconnectivity. Post made mention of Arizona eryngo (Eryngium sparganophyllum), which only survives at three-ish sites specifically at cienegas within borders of Arizona and one site in New Mexico; couple of years after that post, the US federal government formally recognized it as endangered.
---
But in 2020, I also made a series of several posts about Quitobaquito Springs (at Arizona-Mexico border, in the Sonoran Desert) and Indigenous efforts to protect it? (The springs are a rare freshwater ecosystem at Organ Pipe Cactus area. US border wall construction was extracting and pumping vast amounts of water every day. In 2020, major demonstrations were held by Akimel O'odha, Tohono O'odham, and Hia-Ced O'odham. Brings to mind how, in the same area in 2019, Indigenous people brought more widespread attention to how a major global surveillance tech company collaborated with US border security agencies to field-test new a surveillance "command and control center" on Tohono O'odham communities, like a laboratory; the "virtual wall" functions with multiple towers which continuously surveil personal devices, sound, physical movement, etc. In those posts, I also mentioned that the springs at Quitobaquito are also pretty much the only home within US borders to the endangered Sonoyta mud turtle and endangered Sonoyta pupfish. The entire subspecies/lineage of the turtle only lives in maybe 5 sites total.)
---
Somewhat related, also made many posts from 2019 to 2023 about Indigenous protection of Oak Flat Chi-chil Bildagoteel in Arizona?
Regarding more recent irrigation and water loss in Arizona, I've posted about Natalie Koch's work in Arid Empire on the impact of diverting water for alfalfa farms and how current Arizona agencies facilitate the "colonial technologies" and market "the desert as a narrative resource"; she also describes how, in 1940s/1950s, the US State Department had a hand in encouraging international petroleum investors to invest in hundreds of thousands of cattle for dairy farms, a network which still influences much water diversion today. Aside from the Sonoyta mud turtle, also brings to mind threatened amphibians in Arizona related to cienegas, like Sonoran tiger salamander (likes permanent or standing water, estimated to survive in about 50 ponds in Cochise and Santa Cruz counties) and Chiricahua leopard frog (also likes the standing water, which is often diverted for agriculture or overtaken by non-native bullfrogs, estimated to survive in maybe 80 to 100 ponds). (Vaguely related but fun: There were a couple of long effort-posts I did about historical distribution range of American crocodiles in mangroves and coastal marshes on far southern edge of the Sonoran Desert general ecoregion before lower Yaqui river was depleted by agriculture.)
---
Shout-out to Cuatro Cienegas in the Chihuahuan Desert.
An oasis. A "bacterial lost world." About 300 pools. More than 90% dried-up in historic record; agricultural canals drain tens of millions of gallons of water a year. Home to 38-ish endemic animal species. Not one, not two, but three endemic species of turtles: A slider, a softshell (I love softshells), and the planet's only "aquatic" species of box turtle (I also love box turtles). Home to some of planet's only terrestrial or freshwater populations of stromatolites (bacterial mats composing structures reminiscent of Precambrian era; usually found in deep-sea hydrothermal vents, but here have been isolated from the sea for millions of years). Also home to some of planet's highest diversity of Archaea (taxonomic order of lifeforms potentially "older than bacteria"?).
52 notes
·
View notes
Text

The underground shelter, which was revealed last year, prompted conspiracy theories on social media about wealthy tech moguls building doomsday bunkers.
Mark Zuckerberg is downplaying the massive 5,000-square-foot bunker beneath his Hawaiian compound that was revealed in WIRED last year and prompted conspiracy theories on social media about wealthy tech moguls building doomsday bunkers.
The billionaire Facebook co-founder pushed back when Bloomberg reporter Emily Chang, in a video published Tuesday that chronicled her visit to Zuckerberg’s Lake Tahoe property, asked him what he’s “worried about” — and if there’s something he knows “that we don’t” in regard to the bunker.
“No, I think that’s just, like, a little shelter,” he told Chang. “It’s a basement! It’s a basement.”
Zuckerberg said the “basic house” on Kauai is largely used for storage space and that he frequently works from there but admitted to the underground bunker there, referring to it as a “hurricane shelter or whatever.”
“I think it got, like, blown out of proportion, as if the whole ranch was some kind of doomsday bunker, which is just not true,” he added.
Back in February, Ron Hubbard, the CEO of Atlas Survival Shelters, and Robert Vicino, founder of underground survival shelter company Vivos, spoke to The Hollywood Reporter about how news of Zuckerberg’s bunker increased business for them.
Hubbard said that it had “caused a buying frenzy,” while Vicino said, “Now that Zuckerberg has let the cat out of the bag, that’s got other people who share his status or are near his status starting to think, ‘Oh God, if he’s doing that, maybe he knows something that I don’t, maybe I should seek this out myself.’”
Zuckerberg purchased the 1,400-acre estate, which is known as Koolau Ranch, in a series of deals beginning in 2014, WIRED reported in 2023. According to planning documents for the property reviewed by the outlet, the compound will have its own energy and food supplies.
Construction of the compound and purchase of the land was estimated to cost around $270 million. Zuckerberg told Chang that he and his wife, Priscilla Chan, use the property for ranching and that he wants to “create the highest quality beef in the world.”
Along with Zuckerberg, other bunker-having tech moguls allegedly include Bill Gates, with Vicino telling THR in 2016 that Gates “has huge shelters under every one of his homes.”
PayPal CEO Peter Thiel had similar plans for a bunker-like compound in New Zealand, but those were thwarted in 2022 after backlash from local conservationists, according to The Guardian.
Zuckerberg’s property spawned similar criticism from locals and Indigenous groups in Kauai, with one former laborer on the compound telling WIRED, “It’s crazy that a man not from Hawaii comes here and purchases a bunch of land that limits the locals [from potentially buying] land. But it’s already happening.”
(continue reading)
42 notes
·
View notes
Note
I recall plenty of complaints about Jewish erasure on Wikipedia, and I was reading their Manual of Style (MOS) which stated this:

Ethnicity, religion, or sexuality should generally not be in the lead unless relevant to the subject's notability. Similarly, neither previous nationalities nor the country of birth should be mentioned in the opening paragraph unless relevant to the subject's notability.
URL: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Manual_of_Style/Biography#Nationality_examples
That said, they also noted how details of their ethnicity "can be introduced in the second sentence if they are of defining importance".

Isaac Asimov (c. January 2, 1920 – April 6, 1992) was an American writer Per the above guidance, we do not add ethnicity ("Jewish-American") or country of birth ("Russian-born American"). These details can be introduced in the second sentence if they are of defining importance.
It kinda explains why mentions of ethnicity are being removed, and it's not just Jews but other indigenous people as nationality takes precedence.
Dear Kang,
this is so NOT why
the reason why is because "Techs for "palestine'" vandalized and then locked all the pages and this one guy hell bent on Jewish erasure. the style guide is part of the problem but you can't blame malice on the style guide, that's like saying Kristallnacht happened because the way the Weimar republic was set up
yours,
Cecil
#dear cecil#antisemitism#leftist antisemitism#leftist brainrot#leftist hypocrisy#wikipedia vandalism
25 notes
·
View notes
Note
okay so i’ve never really grasped this, might as well ask now — how exactly does the cyberspace & nft stuff mine resources? i’ve heard the basics (i.e. crypto mining uses energy and what not) but i’ve never been able to understand how internet connects to real resources. could you sort of explain that (along the lines with the spam email post) in a simpler way?
ok, put very simply: it's easy for people who only interact with the internet as users to treat 'cyberspace' or 'the virtual world' as immaterial. i type something out on my phone, it lives in the screen. intuitively, it feels less real and physical than writing the same words down on a piece of paper with a pencil. this is an illusion. the internet is real and physical; digital technology is not an escape from the use of natural resources to create products. my phone, its charger, the data storage facility, a laptop: all of these things are physical objects. the internet does not exist without computers; it is a network of networks that requires real, physical devices and cables in order to store, transmit, and access all of the data we use every time we load a webpage or save a text document.

this is one of google's data centres—part of the physical network of servers and cables that google operates. these are real objects made of real materials that need to be obtained through labour and then manufactured into these products through labour. the more data we use, the more capacity the physical network must have. google operates dozens of these data centres and potentially millions of servers (there is no official number). running these facilities takes electricity, cooling technologies (servers get hot), and more human labour. now think about how many other companies exist that store or transmit data. this entire network exists physically.
when you look at a server, or a phone, or a laptop, you might be glossing over a very simple truth that many of us train ourselves not to see: these objects themselves are made of materials that have supply chains! for example, cobalt, used in (among other things) lithium-ion batteries, has a notoriously brutal supply chain relying on horrific mining practices (including child labour), particularly in the congo. lithium mining, too, is known to have a massive environmental toll; the list goes on. dangerous and exploitative working conditions, as well as the environmental costs of resource extraction, are primarily and immediately borne by those who are already most brutally oppressed under capitalism: poor workers in the global south, indigenous people, &c. this is imperialism in action. digital technologies cannot exist without resources, and tech companies (like all capitalist firms!) are profitable because they exploit labour.
all commodities require resources and labour to make and distribute. digital technology is no different. these are material objects with material histories and contexts. nothing about the internet is immaterial, from the electromagnetic waves of wi-fi communication to the devices we use to scroll tumblr. it is, in fact, only by a fantastical sleight-of-hand that we can look at and interact with these objects and still consider the internet to be anything but real resources.
393 notes
·
View notes