#IT City in India 2022
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
For the sleepover Saturday thing, have you ever need memorably disappointed by a place you've gone to?
alienmythologist asked: *been not need in that last ask
memorably disappointed?? ummm, let me think.
honestly? no, i don't think so. everywhere i've been i feel like there's always been SOMETHING rewarding and exciting about the experience. sure there have been trips where things weren't as fun as i wanted or i didn't get to do as much as i hoped, but whatever disappointments might have existed in the moment fade over time. all that remains is the good.
sleepover weekend
#ask#alienmythologist#kat travels#the closest i can get is on my first solo int'l work trip in oct 2022#(my first int'l work trip was a group trip to india in sept 2022)#i ended up spending a whole weekend by myself in milan and going out and about to do things on my own#and it was? a little lonely.#but i was so proud of myself for doing it! for not just hanging out in my hotel room alone. for spending the day walking around a new city#and just exploring#after milan i had to fly to ankara which took all day bc i had to go milan-istanbul-ankara#and there was a MOMENT in the istanbul airport while i was walking to my gate#where i was like#'fuck do i hate this??? is solo traveling not for me??? did i make a mistake???'#and then i got to ankara. i made a friend. we went to istanbul together. i had SO much fun and it is one of my most memorable trips#and i haven't looked back since
1 note
·
View note
Text
Top 10 Cleanest Cities in India of 2022
These are our top 10 Cleanest Cities in India in 2022. Read the full article to explore some of the cleanest Indian cities.
0 notes
Text
(de) Coding Mumbai Exhibition at IF.BE, Mumbai. June 2022
As part of SPARE, the research side of sP+a, Mumbai we put together a study of Mumbai’s building regulations and its impact on the production of housing. More information can be found in the links below: IF.BE Covered in The Hindu Worldarchitecture.org Question of Cities Camp

View On WordPress
#2022#architectural thought#architecture#architecture exhibition#Architecture in india#architecture models#architecture research#building regulations#city#form#ifbe#mumbai#sameep padora#sameep padora and associates#sp+a#urban studies#urbanism#urbanization in India
0 notes
Text
christmas is on the 25th mr grinch
why do only children's and fantasy books have illustrations. what crime did other readers commit that the industry decided we weren't worthy of lil drawings
#jeez#also this was absolutely meant for literary fiction in 'mundane' settings bcs thats my favourite genre and if you think the everyday doesnt#deserve the same amount of imagination and thought as the fantastical youre just. hopeless.#all art ever has been a response to the everyday. you dont need the lens of dragons to see the beauty and horror and heartbreak of a random#city street. it doesnt need a justification to be worthy of visual art#and!!!!! THE WORLD IS ABSOLUTELY DIVERSE AND BEAUTIFUL!#im from india and i would like illustrations from a novel set in rural ireland. people from 50 years from now or on a different continent#won't find 2022 delhi so obvious. what a limited worldview jfc.
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
When electronics manufacturing took off in China in the 1980s, rural women who had just begun moving to the cities made up the majority of the factory workforce. They didn’t have many other options. Managers at companies like Foxconn preferred to hire women because they believed them to be more obedient [...]
Hiring a young, female workforce in India comes with its own requirements — which include reassuring doting parents about the safety of their daughters. The company offers workers free food, lodging, and buses to ensure a safe commute at all hours of the day. On days off, women who live in Foxconn hostels have a 6 p.m. curfew; permission is required to spend the night elsewhere. “[If] they go out and not return by a specific time, their parents would be informed,” a former Foxconn HR manager told Rest of World. “[That’s how] they offer trust to their parents.”
[...] the Tamil Nadu government sent a strong signal welcoming Foxconn and other manufacturers: Authorities approved new regulations that would increase workdays from eight to 12 hours. This meant that Foxconn and other electronics factories would be able to reduce the number of shifts needed to keep their production line running from three to two, just like in China. [...] Political parties aligned with the government called the bill “anti-labor” and, during the vote, walked out of the legislative assembly. After the bill passed, trade unions in the state announced a series of actions including a demonstration on motorbikes, civil disobedience campaigns, and protests in front of the ruling party’s local headquarters. The government shelved its new rule within four days.
Indian Foxconn workers told Rest of World that eight hours under intense pressure is already hard to bear. “I’ll die if it’s 12 hours of work,” said Padmini, the assembly line worker.
For the expatriate workers, the slower pace of the factory floors in India is its own shock to the system. A Taiwanese manager at a different iPhone supplier in the Chennai area told Rest of World that India’s 8-hour shifts and industry-standard tea breaks were a drag on production. “You have barely settled in on your seat, and the next break comes,” the manager lamented.
In China, Foxconn relies on lax enforcement of the country’s labor law — which limits workdays to eight hours and caps overtime — as well as lucrative bonuses to get employees to work 11 hours a day during production peaks [...] five Chinese and Taiwanese workers said they were surprised to discover that their Indian colleagues refused to work overtime. Some attributed it to a weak sense of responsibility; others to what they perceived as Indian people’s low material desire. “They are easily content,” an engineer deployed from Zhengzhou said. “They can’t handle even a bit more pressure. But if we don’t give them pressure, then we won’t be able to get everything right and move production here in a short time.” [...] At the same time, the expat staff enjoy the Indian work culture of tea breaks, chatting with colleagues, and going home on time. They recognize they are helping the company spread a Chinese work culture that they know can be unhealthy. [...]
On the assembly line, Foxconn’s targets were tough to reach, workers said. Jaishree, 21, joined the iPhone shop floor in 2022 as a recent graduate with a degree in mathematics. (With India’s high level of unemployment, Foxconn’s assembly line has plenty of women with advanced degrees, including MBAs.) [...] “At the start, during my eight-hour shift, I did about 300 [screws]. Now, I do 750,” she said. “We have to finish within time, otherwise they will scold us.” [...]
Mealtimes are an issue, too. In December 2021, thousands of Indian Foxconn employees protested after some 250 colleagues contracted food poisoning. In response, the company changed food contractors, and increased its monthly base salary from 14,000 rupees to 18,000 rupees ($168 to $216) — double the minimum wage prescribed by the Tamil Nadu labor department for unskilled workers. [...]
Working conditions take a physical toll. Padmini has experienced hair loss because she has to wear a skull cap and work in air-conditioned spaces, she said. “Neck pain is the worst, since we are constantly bending down and working.” She has irregular periods, which she attributes to the air conditioning and the late shifts. “[Among] girls with me on the production line, some six girls have this problem,” Padmini said. Workers said they regularly see colleagues become unwell. “The day before yesterday, a girl fainted and they took her to the hospital,” [...] Padmini, at 26, believes she is close to the age where the company might consider her too old. “They used to hire women up to age 30, now they hire only up to 28,” she said.
998 notes
·
View notes
Text
here's how armand can still be bengali
why do i think so? no other good reason than i am bengali myself and i want armand to be. (also assad zaman's family is from bangladesh. bengali solidarity!!!)
bengal: the region in south asia comprising present-day bangladesh and the indian states of west bengal, odisha, assam and parts of bihar.
armand said in the season one finale, that takes place in 2022, he is a 514 year old vampire. is it 514 years including or excluding his human years? let's go with including. that means armand would have been born in 1508.


now what was going on in india and bengal in 1508? well, the mughals hadn't come to india yet; it's still about two decades before babur makes his way here. delhi was under the rule of the lodi dynasty, the delhi sultanate was in its dying days. most of north india, mainly uttar pradesh and bihar was under the jaunpur sultanate. bengal was still it's own independent kingdom, called the bengal sultanate. alauddin hussain shah had just seized power and become the sultan of bengal in 1494, beginning the hussain shahi dynasty (they ruled in bengal till 1538 when the mughals captured the region).
india as a country did not exist yet. even it's conception would be a few centuries away still. the subcontinent was a collection of big and small kingdoms and sultanates, constantly warring amongst themselves, some ruled by hindu rulers others by muslims, each with their own distinct histories and cultures. bengal was one of the most prosperous and thriving among them. the bangla language and bengali culture was just beginning to develop.


vasco da gama had arrived in india in 1498, landing at kozhikode on the malabar coast. this began the arrival of the portugese in india, and soon other european colonialists followed. they soon set up their capital in goa, built forts all along the western coast and established trade through obtaining licenses and exclusive permits from local rulers. they first made their way to the bay of bengal region around 1516, with the first portugese representative- a guy called joao coelho- coming to chittagong (present day bangladesh). the first factory was set up in chittagong the next year.
the portugese traded in spices and cotton and fruits and muslin and also slaves. the european indian ocean slave trade began with the coming of the portugese in the early 16th century. slavery in south asian societies had obviously existed long before, and it was a deeply complex and diverse system of dependency and regimes of slavery. slavery of youth and children was also pretty prevalent: it would not be uncommon for poor, farming families to sell away themselves or their children to zamindars (landlords) and colonial overlords in desperation. there were many, many cases of young children being forced to get onboard ships where they'd be held agains their will and taken to europe, the americas or south-east asia. goa and lisbon were the two cities that linked the movement of goods and people between the indian and atlantic oceans, but goa wasn't the only place where enslaved children were traded in portugese india nor lisbon the only european they were taken to.
one of those kids might as well have been arun.


i know the brief glimpse at the talamasca files showed armand's origin to be in delhi but in this particular scene he clearly says that he was sent *to* delhi, thinking he was going to work on a merchant boat.
this is just a theory i have btw. armand could've been from maharastra or the deccan as well idk. anyway.
armand is a monster, a vicious, villanious creature of unfathomable powers and ferocity. but he is also so deeply tragic. he had been forcibly torn away from his people and his land. he has no memory of his family or his humanity. he has lived for over half a millenium. the india he might've known hasn't existed for centuries, and he never got to know the one that exists today. the bangla he might've spoken no one remembers anymore. he has nothing left of the human he was except that name.
further readings (STRONGLY SUGGESTED!!!):
262 notes
·
View notes
Text
"India’s announcement that it aims to reach net zero emissions by 2070 and to meet fifty percent of its electricity requirements from renewable energy sources by 2030 is a hugely significant moment for the global fight against climate change. India is pioneering a new model of economic development that could avoid the carbon-intensive approaches that many countries have pursued in the past – and provide a blueprint for other developing economies.
The scale of transformation in India is stunning. Its economic growth has been among the highest in the world over the past two decades, lifting of millions of people out of poverty. Every year, India adds a city the size of London to its urban population, involving vast construction of new buildings, factories and transportation networks. Coal and oil have so far served as bedrocks of India’s industrial growth and modernisation, giving a rising number of Indian people access to modern energy services. This includes adding new electricity connections for 50 million citizens each year over the past decade.
The rapid growth in fossil energy consumption has also meant India’s annual CO2 emissions have risen to become the third highest in the world. However, India’s CO2 emissions per person put it near the bottom of the world’s emitters, and they are lower still if you consider historical emissions per person. The same is true of energy consumption: the average household in India consumes a tenth as much electricity as the average household in the United States.
India’s sheer size and its huge scope for growth means that its energy demand is set to grow by more than that of any other country in the coming decades. In a pathway to net zero emissions by 2070, we estimate that most of the growth in energy demand this decade would already have to be met with low-carbon energy sources. It therefore makes sense that Prime Minister Narendra Modi has announced more ambitious targets for 2030, including installing 500 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity, reducing the emissions intensity of its economy by 45%, and reducing a billion tonnes of CO2.
These targets are formidable, but the good news is that the clean energy transition in India is already well underway. It has overachieved its commitment made at COP 21- Paris Summit [a.k.a. 2015, at the same conference that produced the Paris Agreement] by already meeting 40% of its power capacity from non-fossil fuels- almost nine years ahead of its commitment, and the share of solar and wind in India’s energy mix have grown phenomenally. Owing to technological developments, steady policy support, and a vibrant private sector, solar power plants are cheaper to build than coal ones. Renewable electricity is growing at a faster rate in India than any other major economy, with new capacity additions on track to double by 2026...
Subsidies for petrol and diesel were removed in the early 2010s, and subsidies for electric vehicles were introduced in 2019. India’s robust energy efficiency programme has been successful in reducing energy use and emissions from buildings, transport and major industries. Government efforts to provide millions of households with fuel gas for cooking and heating are enabling a steady transition away from the use of traditional biomass such as burning wood. India is also laying the groundwork to scale up important emerging technologies such as hydrogen, battery storage, and low-carbon steel, cement and fertilisers..."
-via IEA (International Energy Agency), January 10, 2022
Note: And since that's a little old, here's an update to show that progress is still going strong:
-via Economic Times: EnergyWorld, March 10, 2023
#india#solar power#renewable energy#green energy#sustainability#wind power#population grown#economic growth#developing economies#renewable electricity#carbon emissions#good news#hope#hope posting
860 notes
·
View notes
Text
Climate change-driven heatwaves threaten millions

Extreme record-breaking heat leads to severe crises across the world.
Already in 2024, from Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria in the West; to Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam, China, and the Philippines in the East; large regions of Asia are experiencing temperatures well above 40°C (104°F) for days on end.
The heatwave has been particularly difficult for people living in refugee camps and informal housing, as well as for unhoused people and outdoor workers.
Using the Heat Index Calculator, at that temperature and a relative humidity of 50%, residents see a heat index of 55°C (131°F) - a temperature level humans cannot long survive:
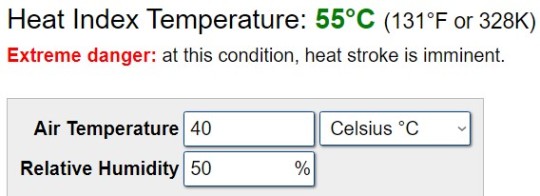
In February, the southern coastal zone of West Africa also experienced abnormal early-season heat. A combination of high temperatures and humid air resulted in average heat index values of about 50°C (122°F) - the danger level, associated with a high risk of heat cramps and heat exhaustion.
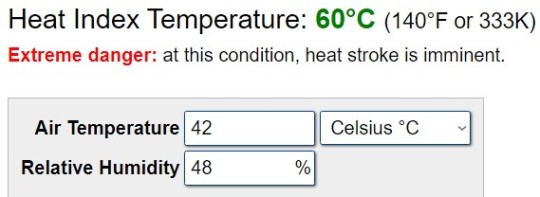
Locally, temperatures entered the extreme danger level associated with high risk of heat stroke, with values up to 60°C (140°F):
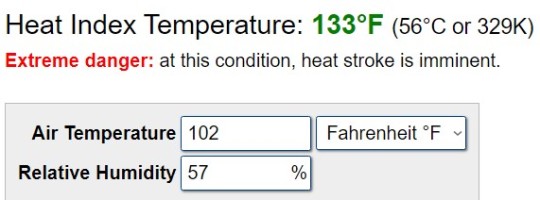
Even here at Ad Astra's HQ in Kansas, last summer we saw several days with high temperatures of 102°F (39°C) at 57% humidity, resulting in a heat index of 133°F (56°C):
Of course, the major difference in survivability in Kansas versus some of the places suffering extreme heat right now is that air-conditioning abounds here. Those who live somewhere that faces extreme heat but can escape it indoors are a lot more likely to survive, but a person who lives somewhere without such life-saving gear faces not just discomfort, but heat stroke and even death.
This includes unhoused and poor people here in the wealthier parts of the world, who often do not have access to indoor refuge from the heat.
About 15% of US residents live below the poverty line. Many low-wage earners work outside in construction or landscaping, exposed to the ravages of heat. Many do not own an air conditioner, and those who do might need to budget their body's recovery from heat against cost to purchase and run cooling equipment. Because heat stress is cumulative, when they go to work the next day, they’re more likely to suffer from heat illness.
Bad as that is, for those living on the street, heatwaves are merciless killers. Around the country, heat contributes to some 1,500 deaths annually, and advocates estimate about half of those people are homeless. In general, unhoused people are 200 times more likely to die from heat-related causes than sheltered individuals.
For example, in 2022, a record 425 people died from heat in the greater Phoenix metro area. Of the 320 deaths for which the victim’s living situation is known, more than half (178) were homeless. In 2023, Texans experienced the hottest summer since 2011, with an average temperature of 85.3°F (30°C) degrees between June and the end of August. Some cities in Texas experienced more than 40 days of 100°F (38°C) or higher weather. This extreme heat led to 334 heat-related deaths, the highest number in Texas history and twice as many as in 2011.
The Pacific Northwest of Canada and the USA suffered an extreme heat event in June, 2021, during which 619 people died. Many locations broke all-time temperature records by more than 5°C, with a new record-high temperature of 49.6°C (121°F). This is a region ill-suited to such weather, and despite having relatively high wealth compared to much of the world, many homes and businesses there do not have air-conditioning due to a history of much lower temperatures.
Heatwaves are arguably the deadliest type of extreme weather event because of their wide impact. While heatwave death tolls are often underreported, hundreds of deaths from the February heatwave were reported in the affected countries, including Bangladesh, India, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, and the Philippines.
Extreme heat also has a powerful impact on agriculture, causing crop damage and reduced yields. It also impacts education, with holidays having to be extended and schools closing, affecting millions of students - in Delhi, India, schools shut early this week for summer when temperatures soared to 47°C (117°F) at dangerous humidity levels:
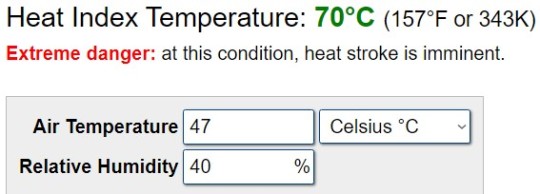
At 70°C (157°F !), humans simply cannot function and face imminent death, especially when humidity is high. This is the notion of "heat index," a derivative of "wet-bulb temperature."
Though now mostly calculated using heat and humidity readings, wet-bulb temperature was originally measured by putting a wet cloth over a thermometer and exposing it to the air.
This allowed it to measure how quickly the water evaporated off the cloth, representing sweat evaporating off skin.
The theorized human survival limit has long been 35°C (95°F) wet-bulb temperature, based on 35°C dry heat at 100% humidity - or 46°C (115°F) at 50% humidity. To test this limit, researchers at Pennsylvania State University measured the core temperatures of young, healthy people inside a heat chamber.
They found that participants reached their "critical environmental limit" - when their body could not stop the core temperature from continuing to rise – at 30.6°C wet bulb temperature, well below what was previously theorized. That web-bulb temperature parallels a 47°C (117°F) heat index.
The team estimates that it takes between 5-7 hours before such conditions reach "really, really dangerous core temperatures."
youtube
On March 5, 2024, Hong Kong saw temperatures of 27°C (80°F) with 100% humidity, which results in a heat index of 32.2°C (90°F) - seemingly not so bad until considering it's higher than the critical wet-bulb temperature. Also, if you watch the video, imagine the long-term effects of water accumulating in residences, such as dangerous mold.
We are witnessing the effects of climate change right now, all around the world, and rising temperatures are just the most-obvious (what we used to call "global warming"). Many, many other side-effects of climate change are beginning to plague us or headed our way soon, and will affect us all.
Unfortunately, those most affected - and those being hit the hardest right now - are people most vulnerable to heatwaves. With climate crises increasing in both intensity and frequency, and poverty at dangerous levels, we face a rapidly rising, worldwide crisis.
We must recognize the climate crisis as an international emergency and treat it as such. So much time, creative energy, resources, and life is wasted in war and the pursuit of profit or power - consider how much good could come from re-allocating those resources to ensuring a future for Earthlings, instead.
(Expect to see a "Science into Fiction" workshop on climate change coming soon - SF writers have a particular responsibility to address such important topics of change and global consequence.)
#climate crisis#climate change#global warming#heatwaves#poverty and homelessness#climate emergency#in response to asks for a post on this topic#stay tuned for posts on other crises arising from climate change
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anansi Boys by Neil Gaiman (2005)
When Fat Charlie's dad named something, it stuck. Like calling Fat Charlie "Fat Charlie." Even now, 20 years later, Charlie Nancy can't shake that name, one of the many embarrassing "gifts" his father bestowed-before he dropped dead on a karaoke stage and ruined Fat Charlie's life. Because Mr. Nancy left Fat Charlie things. Things like the tall, good-look-ing stranger who appears on Charlie's doorstep, who appears to be the brother he never knew. A brother as different from Charlie as night is from day, a brother who's going to show Charlie how to lighten up and have a lit-the fun. And all of a sudden, things start getting very interesting for Fat Charlie. Exciting, scary, and deeply funny, Anansi Boys is a kaleidoscopic journey deep into myth, a wild adventure, as Neil Gaiman shows us where gods come from, and how to survive your family.
Gemma Doyle by Libba Bray (2003-2007)
It's 1895, and after the suicide of her mother, 16-year-old Gemma Doyle is shipped off from the life she knows in India to Spence, a proper boarding school in England. Lonely, guilt-ridden, and prone to visions of the future that have an uncomfortable habit of coming true, Gemma's reception there is a chilly one. To make things worse, she's been followed by a mysterious young Indian man, a man sent to watch her. But why? What is her destiny? And what will her entanglement with Spence's most powerful girls—and their foray into the spiritual world—lead to?
Babel: An Arcane History by R. F. Kuang (2022)
Traduttore, traditore: An act of translation is always an act of betrayal.
1828. Robin Swift, orphaned by cholera in Canton, is brought to London by the mysterious Professor Lovell. There, he trains for years in Latin, Ancient Greek, and Chinese, all in preparation for the day he'll enroll in Oxford University's prestigious Royal Institute of Translation — also known as Babel. Babel is the world's center of translation and, more importantly, of silver-working: the art of manifesting the meaning lost in translation through enchanted silver bars, to magical effect. Silver-working has made the British Empire unparalleled in power, and Babel's research in foreign languages serves the Empire's quest to colonize everything it encounters.
Oxford, the city of dreaming spires, is a fairytale for Robin; a utopia dedicated to the pursuit of knowledge. But knowledge serves power, and for Robin, a Chinese boy raised in Britain, serving Babel inevitably means betraying his motherland. As his studies progress Robin finds himself caught between Babel and the shadowy Hermes Society, an organization dedicated to sabotaging the silver-working that supports imperial expansion. When Britain pursues an unjust war with China over silver and opium, Robin must decide: Can powerful institutions be changed from within, or does revolution always require violence? What is he willing to sacrifice to bring Babel down?
Magnus Chase and the Gods of Asgard by Rick Riordan (2015-2017)
Magnus Chase has seen his share of trouble. Ever since that terrible night two years ago when his mother told him to run, he has lived alone on the streets of Boston, surviving by his wits, staying one step ahead of the police and the truant officers.
One day, Magnus learns that someone else is trying to track him down—his uncle Randolph, a man his mother had always warned him about. When Magnus tries to outmaneuver his uncle, he falls right into his clutches. Randolph starts rambling about Norse history and Magnus's birthright: a weapon that has been lost for thousands of years.
The more Randolph talks, the more puzzle pieces fall into place. Stories about the gods of Asgard, wolves, and Doomsday bubble up from Magnus's memory. But he doesn't have time to consider it all before a fire giant attacks the city, forcing him to choose between his own safety and the lives of hundreds of innocents. . . .
Sometimes, the only way to start a new life is to die.
Abhorsen by Garth Nix (1995-2016)
Sent to a boarding school in Ancelstierre as a young child, Sabriel has had little experience with the random power of Free Magic or the Dead who refuse to stay dead in the Old Kingdom. But during her final semester, her father, the Abhorsen, goes missing, and Sabriel knows she must enter the Old Kingdom to find him. She soon finds companions in Mogget, a cat whose aloof manner barely conceals its malevolent spirit, and Touchstone, a young Charter Mage long imprisoned by magic, now free in body but still trapped by painful memories.
As the three travel deep into the Old Kingdom, threats mount on all sides. And every step brings them closer to a battle that will pit them against the true forces of life and death--and bring Sabriel face-to-face with her own destiny.
The Starless Sea by Erin Morgenstern (2019)
Zachary Ezra Rawlins is a graduate student in Vermont when he discovers a mysterious book hidden in the stacks. As he turns the pages, entranced by tales of lovelorn prisoners, key collectors, and nameless acolytes, he reads something strange: a story from his own childhood. Bewildered by this inexplicable book and desperate to make sense of how his own life came to be recorded, Zachary uncovers a series of clues--a bee, a key, and a sword--that lead him to a masquerade party in New York, to a secret club, and through a doorway to an ancient library, hidden far below the surface of the earth.
What Zachary finds in this curious place is more than just a buried home for books and their guardians--it is a place of lost cities and seas, lovers who pass notes under doors and across time, and of stories whispered by the dead. Zachary learns of those who have sacrificed much to protect this realm, relinquishing their sight and their tongues to preserve this archive, and also those who are intent on its destruction.
Together with Mirabel, a fierce, pink-haired protector of the place, and Dorian, a handsome, barefoot man with shifting alliances, Zachary travels the twisting tunnels, darkened stairwells, crowded ballrooms, and sweetly-soaked shores of this magical world, discovering his purpose--in both the mysterious book and in his own life.
The Roots of Chaos by Samantha Shannon (2019-2023) The House of Berethnet has ruled Inys for a thousand years. Still unwed, Queen Sabran the Ninth must conceive a daughter to protect her realm from destruction--but assassins are getting closer to her door.
Ead Duryan is an outsider at court. Though she has risen to the position of lady-in-waiting, she is loyal to a hidden society of mages. Ead keeps a watchful eye on Sabran, secretly protecting her with forbidden magic.
Across the dark sea, Tané has trained all her life to be a dragonrider, but is forced to make a choice that could see her life unravel.
Meanwhile, the divided East and West refuse to parley, and forces of chaos are rising from their sleep.
The Winternight Trilogy by Katherine Arden (2017-2019)
Winter lasts most of the year at the edge of the Russian wilderness, and in the long nights, Vasilisa and her siblings love to gather by the fire to listen to their nurse’s fairy tales. Above all, Vasya loves the story of Frost, the blue-eyed winter demon. Wise Russians fear him, for he claims unwary souls, and they honor the spirits that protect their homes from evil.
Then Vasya’s widowed father brings home a new wife from Moscow. Fiercely devout, Vasya’s stepmother forbids her family from honoring their household spirits, but Vasya fears what this may bring. And indeed, misfortune begins to stalk the village.
But Vasya’s stepmother only grows harsher, determined to remake the village to her liking and to groom her rebellious stepdaughter for marriage or a convent. As the village’s defenses weaken and evil from the forest creeps nearer, Vasilisa must call upon dangerous gifts she has long concealed—to protect her family from a threat sprung to life from her nurse’s most frightening tales.
The Tale of Despereaux by Kate DiCamillo (2003)
As the only surviving mouse of the litter, Despereaux was always considered the loser, the runt, so naturally, he falls in love with a princess named Pea. The story also tells of a mouse called Roscuro, who lives in the darkness but wishes for light, and Miggery Sow, a serving girl who wants one wish. They set off on a journey that will end them up in a terrible dungeon, a wonderful castle, and of course, with each other.
Legends & Lattes by Travis Baldree (2022-2024)
Worn out after decades of packing steel and raising hell, Viv the orc barbarian cashes out of the warrior’s life with one final score. A forgotten legend, a fabled artifact, and an unreasonable amount of hope lead her to the streets of Thune, where she plans to open the first coffee shop the city has ever seen.
However, her dreams of a fresh start pulling shots instead of swinging swords are hardly a sure bet. Old frenemies and Thune’s shady underbelly may just upset her plans. To finally build something that will last, Viv will need some new partners and a different kind of resolve.
#best fantasy book#poll#anansi boys#gemma doyle#babel an arcane history#magnus chase#abhorsen#the starless sea#the roots of chaos#the winternight trilogy#the tale of despereaux#legends and lattes
91 notes
·
View notes
Text
List of russian lies in the UN or during diplomatic speeches:
1. In January-February of 2022 russia claimed in the UN that they will not invade Ukraine, that they have no plans to invade Ukraine, and evidence of upcoming invasion are lies made by the US or others.
End of the same month russia launched a full-scale invasion.
2. Russia claimed in the UN that the reason they attacked Ukraine was to fight some "local nazis" and that they are indeed good guys fighting Ukrainian hatred. That, however, does not explain why: a) russia opposed the grain deal until Turkey threatened to make it work one way or the other, showing their intention to starve hundreds of millions of people in neutral countries for no reason whatsoever, b) russia refused to allow UN or Red Cross etc to observe the conditions of POWs or to open humanitarian corridors for people to escape from Mariupol or other conflict zones, with thousands of witnesses reporting abductions, filtration camps, and shelling of retreating civilians, c) russia claimed to only want to protect local russian population, yet completely destroyed whole cities in majorly-russian-speaking Eastern Ukraine, like Mariupol (satellites showing mass graves), and bombing mainly civilian targets - schools, hospitals, theatres, a shopping mall during peak hours, a train station where people waited for evacuation, apartment buildings, etc. Currently we can see that there is no effort on the russian-controlled side of Dnipro river to help people in flooded areas, with videos and citizen testimonies reporting shelling of all disaster aid attempts, d) russia claimed that they only hate the "nazi" Ukrainian government, yet they openly shelled Ukrainian power grids during winter, for no other reason than to leave innocent civilians with no gas or electricity.
3. Russian state TV, public figures like Solovyov, former President and Prime Minister as well as head of security council of russia Medvedev openly stated either on national TV or in their social media pages that they want to "exterminate" Ukrainians. That the whole country should not exist, that Ukrainian language is fake, etc etc. This is genocidal speech and it is not limited to Ukraine either. The Baltic States, Poland, etc also received such claims - that they "do not exist" that they "belong to russia" or that they "should be invaded". Makes it very obvious who the imperialistic, colonist aggressor actually is. Medvedev also repeatedly threatened Western European countries with missile or even nuclear attack, yet they claim to only be "defending themselves".
4. Lavrov got laughed at during a summit in India for claiming that "russia was invaded by Ukraine". Do I even need to explain why this is a lie? If I do, check 1st point again. Or just turn on your brain.
5. Then there's more sci-fi nutjobby official russian claims (or lies) about - bioweapons in Ukraine, pidgeons carrying disease or weapons to russia, Ukraine having some super-soldiers, or even dark magic, as indicated by russian Ministry of Defense changing the goal of their "special military operation" from "denazification" to "desatanization".
And that's just a few of the main ones. More is discussed in the latest UN meeting, you can watch the video on their official website.
So, knowing all of this, why the fuck would you believe ANYTHING they say? Especially about the destruction of dam?
Russia has repeatedly shown aggressive attitude towards neighbouring countries, claimed their wish to occupy them, russian officials called for extermination of whole nationalities, and both President putin and Belova have enough evidence against them for ICC to issue a warrant for them for GENOCIDE AND WAR CRIMES.
If you still believe in russia, despite anything they themselves say, you're either a genocide-supporter or unbelievably stupid.
377 notes
·
View notes
Text
you must have this many dead friends to ride
it's TDOR (well, it was). unable to sleep, i read through all the deaths reported in the 2022-23 trans murder report (a year out of date, I don't think they've released this year's one yet.)
I'm not quite sure why i felt i should do this. if it's a gesture for the victims... well, if someone murders me one day, i don't think it will mean much one way or another if someone in faraway country reads a brief two sentence report that a 30-35 year old trans woman with 'other' occupation was found tied up with burn marks or something. nevertheless, it is the time of year for this ritual.
most of the deaths are reported in central and south american countries, largely due to reporting bias, though there's more reporting now from countries like India and Pakistan - almost nothing from east asia though, probably due to language barriers. it's hard to draw much of a conclusion about anything since many of the reports don't say much, the stats are subject to extreme sampling bias, etc etc. but the general types of story are: "her partner murdered her", "she was killed by gunmen on the street/in her house", "there was an argument and the other person decided to kill her over it", "the mob killed her for extortion reasons", 'her body was found in some awful condition", "the cops killed her" (including Tortugita, who they shot 57 times at the 'cop city' protest), and of course good old "explicitly anti trans hate crime" (which covers Brianna Ghey, the one death from my country, and several from the US).
my murdered sisters are in most cases very young. younger than me.
the statistician in my brain wants me to acknowledge that i don't know the degree that trans women are specifically subject to murder for being trans women or by abusive partners etc, and how much it's "just" about being poor and racialised and living in a place where paramilitaries, gangs etc routinely murder people. sex work is a dangerous line of work for many reasons, but it's also going to be the case that a lot of us are sex workers so even if we were all equally likely to be murdered, a huge number of the dead would be sex workers, just as many of them were beauticians.
but honestly, even bearing that in mind, a whole lot of sex workers were killed.
there is something particularly ghoulish in talking so drily about death statistics; the website uses the painful phrase 'concerning trend' in regards to the demographics of people killed (overwhelmingly trans women, sex workers and not white), as if a perfectly proportional series of murders would be less 'concerning' somehow, but what exactly are you supposed to say? it is of course a window into who a society is comfortable getting rid of, but we already knew that. there's a reason that a sex worker is the go-to plot-inciting murder victim in fiction.
collating death reports like this... in part it is done as a matter of political advocacy, saying 'look, we are being murdered by the hundreds [multiplied by some nebulous but significant underreporting factor]'. but of course, if that's our goal, we are holding our deaths up against, for example, the tens of, likely hundreds of thousands of people killed by violence in Gaza, Sudan and Ukraine in the last year - events which have already divided the world into people who can't stop it, and people who can but don't care to. and what do we want done about it? to beg the state to come down and apply its monopoly on violence more stringently? often the police are the ones killing trans women.
so what remains is ritual. we light candles, and read out the names of strangers who nevertheless have this one important thing in common with us, the ~global community~ of trannies and such - this was a person who refused to take the awful role they were given, asserted their own will to change their body, managed to live a life at least partly on their own terms, and then got killed over it.
but we don't have time to tell the life story, no time to describe the mess of relationships and aspirations that drive a life; there is no time to imagine what feelings we shared, what they enjoyed, what stories we might have laughed about if we'd known each other...
we have time for 'found dead in a car'.
if that.
in my country, we face a very different threat distribution - i don't really expect anyone i know to get murdered (though it's not impossible, there are people I'm close to who have been viciously attacked and there was little to do to stop the attacker coming back), but I'm sure Fall won't be the last of my friends to die by suicide. if we are 'fighting like hell for the living', our project here is more about trying to build lives that are worth living for, and weathering whatever fashy deluge is coming down the political pipes. what does fighting like hell even mean here? i think i used to think i knew.
but this night at least, I'm remembering my friend Fall, who we lost back in 2022. I made this page about her, and the feelings that came up from her death, with writing from friends who knew her better than me. I'd be grateful if you read it and helped some part of her memory live on. (apparently they wrote a little memorial for her in the recent translation of Shōnen Note: Boy Soprano which she worked on.)
I never got to ask what Fall thought of all these TDoR rituals - it's one of many things I didn't get to talk to her about and I bet she'd give me something unexpected to think about, formed some ingenious connection. or maybe she didn't think much of it! but it's as good a reason to think of her as any. she was awesome, she should have been given a much better hand by this world, and it is more shit for not having her in it.
I bet the friends of any of the 321 people on that list, and everyone on this year's list, would be able to say something pretty similar.
entropy always gets its way. but I'll hold onto what I can of her, my fragment of her ghost, for as long as we can. i guess that's the point of the ritual. hold onto our ghosts. tell each other that, one day, they'll stop accumulating so fast.
35 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi! SUPER interesting excerpt on ants and empire; adding it to my reading list. have you ever read "mosquito empires," by john mcneill?
Yea, I've read it. (Mosquito Empires: Ecology and War in the Greater Caribbean, 1620-1914, basically about influence of environment and specifically insect-borne disease on colonial/imperial projects. Kinda brings to mind Centering Animals in Latin American History [Few and Tortorici, 2013] and the exploration of the centrality of ecology/plants to colonialism in Plants and Empire: Colonial Bioprospecting in the Atlantic World [Schiebinger, 2007].)
If you're interested: So, in the article we're discussing, Rohan Deb Roy shows how Victorian/Edwardian British scientists, naturalists, academics, administrators, etc., used language/rhetoric to reinforce colonialism while characterizing insects, especially termites in India and elsewhere in the tropics, as "Goths"; "arch scourge of humanity"; "blight of learning"; "destroying hordes"; and "the foe of civilization". [Rohan Deb Roy. “White ants, empire, and entomo-politics in South Asia.” The Historical Journal. October 2019.] He explores how academic and pop-sci literature in the US and Britain participated in racist dehumanization of non-European people by characterizing them as "uncivilized", as insects/animals. (This sort of stuff is summarized by Neel Ahuja, describing interplay of race, gender, class, imperialism, disease/health, anthropomorphism. See Ahuja's “Postcolonial Critique in a Multispecies World.”)
In a different 2018 article on "decolonizing science," Deb Roy also moves closer to the issue of mosquitoes, disease, hygiene, etc. explored in Mosquito Empires. Deb Roy writes: 'Sir Ronald Ross had just returned from an expedition to Sierra Leone. The British doctor had been leading efforts to tackle the malaria that so often killed English colonists in the country, and in December 1899 he gave a lecture to the Liverpool Chamber of Commerce [...]. [H]e argued that "in the coming century, the success of imperialism will depend largely upon success with the microscope."''
Deb Roy also writes elsewhere about "nonhuman empire" and how Empire/colonialism brutalizes, conscripts, employs, narrates other-than-human creatures. See his book Malarial Subjects: Empire, Medicine and Nonhumans in British India, 1820-1909 (published 2017).
---
Like Rohan Deb Roy, Jonathan Saha is another scholar with a similar focus (relationship of other-than-human creatures with British Empire's projects in Asia). Among his articles: "Accumulations and Cascades: Burmese Elephants and the Ecological Impact of British Imperialism." Transactions of the Royal Historical Society. 2022. /// “Colonizing elephants: animal agency, undead capital and imperial science in British Burma.” BJHS Themes. British Society for the History of Science. 2017. /// "Among the Beasts of Burma: Animals and the Politics of Colonial Sensibilities, c. 1840-1940." Journal of Social History. 2015. /// And his book Colonizing Animals: Interspecies Empire in Myanmar (published 2021).
---
Related spirit/focus. If you liked the termite/India excerpt, you might enjoy checking out this similar exploration of political/imperial imagery of bugs a bit later in the twentieth century: Fahim Amir. “Cloudy Swords” e-flux Journal Issue #115. February 2021.
Amir explores not only insect imagery, specifically caricatures of termites in discourse about civilization (like the Deb Roy article about termites in India), but Amir also explores the mosquito/disease aspect invoked by your message (Mosquito Empires) by discussing racially segregated city planning and anti-mosquito architecture in British West Africa and Belgian Congo, as well as anti-mosquito campaigns of fascist Italy and the ascendant US empire. German cities began experiencing a non-native termite infestation problem shortly after German forces participated in violent suppression of resistance in colonial Africa. Meanwhile, during anti-mosquito campaigns in the Panama Canal zone, US authorities imposed forced medical testing of women suspected of carrying disease. Article features interesting statements like: 'The history of the struggle against the [...] mosquito reads like the history of capitalism in the twentieth century: after imperial, colonial, and nationalistic periods of combatting mosquitoes, we are now in the NGO phase, characterized by shrinking [...] health care budgets, privatization [...].' I've shared/posted excerpts before, which I introduce with my added summary of some of the insect-related imagery: “Thousands of tiny Bakunins”. Insects "colonize the colonizers". The German Empire fights bugs. Fascist ants, communist termites, and the “collectivism of shit-eating”. Insects speak, scream, and “go on rampage”.
---
In that Deb Roy article, there is a section where we see that some Victorian writers pontificated on how "ants have colonies and they're quite hard workers, just like us!" or "bugs have their own imperium/domain, like us!" So that bugs can be both reviled and also admired. On a similar note, in the popular imagination, about anthropomorphism of Victorian bugs, and the "celebrated" "industriousness" and "cleverness" of spiders, there is: Claire Charlotte McKechnie. “Spiders, Horror, and Animal Others in Late Victorian Empire Fiction.” Journal of Victorian Culture. December 2012. She also addresses how Victorian literature uses natural science and science fiction to process anxiety about imperialism. This British/Victorian excitement at encountering "exotic" creatures of Empire, and popular discourse which engaged in anthropormorphism, is explored by Eileen Crist's Images of Animals: Anthropomorphism and Animal Mind and O'Connor's The Earth on Show: Fossils and the Poetics of Popular Science, 1802-1856.
Related anthologies include a look at other-than-humans in literature and popular discourse: Gothic Animals: Uncanny Otherness and the Animal With-Out (Heholt and Edmunson, 2020). There are a few studies/scholars which look specifically at "monstrous plants" in the Victorian imagination. Anxiety about gender and imperialism produced caricatures of woman as exotic anthropomorphic plants, as in: “Murderous plants: Victorian Gothic, Darwin and modern insights into vegetable carnivory" (Chase et al., Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 2009). Special mention for the work of Anna Boswell, which explores the British anxiety about imperialism reflected in their relationships with and perceptions of "strange" creatures and "alien" ecosystems, especially in Aotearoa. (Check out her “Anamorphic Ecology, or the Return of the Possum.” Transformations. 2018.)
And then bridging the Victorian anthropomorphism of bugs with twentieth-century hygiene campaigns, exploring "domestic sanitation" there is: David Hollingshead. “Women, insects, modernity: American domestic ecologies in the late nineteenth century.” Feminist Modernist Studies. August 2020. (About the cultural/social pressure to protect "the home" from bugs, disease, and "invasion".)
---
In fields like geography, history of science, etc., much has been said/written about how botany was the key imperial science/field, and there is the classic quintessential tale of the British pursuit of cinchona from Latin America, to treat mosquito-borne disease among its colonial administrators in Africa, India, and Southeast Asia. In other words: Colonialism, insects, plants in the West Indies shaped and influenced Empire and ecosystems in the East Indies, and vice versa. One overview of this issue from Early Modern era through the Edwardian era, focused on Britain and cinchona: Zaheer Baber. "The Plants of Empire: Botanic Gardens, Colonial Power and Botanical Knowledge." May 2016. Elizabeth DeLoughrey and other scholars of the Caribbean, "the postcolonial," revolutionary Black Atlantic, etc. have written about how plantation slavery in the Caribbean provided a sort of bounded laboratory space. (See Britt Rusert's "Plantation Ecologies: The Experiential Plantation [...].") The argument is that plantations were already of course a sort of botanical laboratory for naturalizing and cultivating valuable commodity plants, but they were also laboratories to observe disease spread and to practice containment/surveillance of slaves and laborers. See also Chakrabarti's Bacteriology in British India: laboratory medicine and the tropics (2012). Sharae Deckard looks at natural history in imperial/colonial imagination and discourse (especially involving the Caribbean, plantations, the sea, and the tropics) looking at "the ecogothic/eco-Gothic", Edenic "nature", monstrous creatures, exoticism, etc. Kinda like Grove's discussion of "tropical Edens" in the colonial imagination of Green Imperialism.
Dante Furioso's article "Sanitary Imperialism" (from e-flux's Sick Architecture series) provides a summary of US entomology and anti-mosquito campaigns in the Caribbean, and how "US imperial concepts about the tropics" and racist pathologization helped influence anti-mosquito campaigns that imposed racial segregation in the midst of hard labor, gendered violence, and surveillance in the Panama Canal zone. A similar look at manipulation of mosquito-borne disease in building empire: Gregg Mitman. “Forgotten Paths of Empire: Ecology, Disease, and Commerce in the Making of Liberia’s Plantation Economy.” Environmental History. 2017. (Basically, some prominent medical schools/departments evolved directly out of US military occupation and industrial plantations of fruit/rubber/sugar corporations; faculty were employed sometimes simultaneously by fruit companies, the military, and academic institutions.) This issue is also addressed by Pratik Chakrabarti in Medicine and Empire, 1600-1960 (2014).
---
Meanwhile, there are some other studies that use non-human creatures (like a mosquito) to frame imperialism. Some other stuff that comes to mind about multispecies relationships to empire:
Lawrence H. Kessler. “Entomology and Empire: Settler Colonial Science and the Campaign for Hawaiian Annexation.” Arcadia (Spring 2017)
No Wood, No Kingdom: Political Ecology in the English Atlantic (Keith Pluymers)
Archie Davies. "The racial division of nature: Making land in Recife". Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers Volume 46, Issue 2, pp. 270-283. November 2020.
Yellow Fever, Race, and Ecology in Nineteenth-Century New Orleans (Urmi Engineer Willoughby, 2017)
Pasteur’s Empire: Bacteriology and Politics in France, Its Colonies, and the World (Aro Velmet, 2022)
Tom Brooking and Eric Pawson. “Silences of Grass: Retrieving the Role of Pasture Plants in the Development of New Zealand and the British Empire.” The Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History. August 2007.
Under Osman's Tree: The Ottoman Empire, Egypt, and Environmental History (Alan Mikhail)
The Herds Shot Round the World: Native Breeds and the British Empire, 1800-1900 (Rebecca J.H. Woods, 2017)
Imperial Bodies in London: Empire, Mobility, and the Making of British Medicine, 1880-1914 (Kristen Hussey, 2021)
Red Coats and Wild Birds: How Military Ornithologists and Migrant Birds Shaped Empire (Kirsten Greer, 2020)
Animality and Colonial Subjecthood in Africa: The Human and Nonhuman Creatures of Nigeria (Saheed Aderinto, 2022)
Imperial Creatures: Humans and Other Animals in Colonial Singapore, 1819-1942 (Timothy P. Barnard, 2019)
Biotic Borders: Transpacific Plant and Insect Migration and the Rise of Anti-Asian Racism in America, 1890-1950 (Jeannie N. Shinozuka)
#ecology#bugs#multispecies#landscape#indigenous#haunted#temporal#colonial#imperial#british entomology in india#mosquitoes#carceral#tidalectics#intimacies of four continents#carceral geography#pathologization
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
definitely a longer piece so these excerpts are far from showcasing everything this piece has to offer! read the whole thing on your own time, and in general, just check out jewish currents, an educational, leftist, anti-zionist jewish magazine!
Every August, the township of Edison, New Jersey—where one in five residents is of Indian origin—holds a parade to celebrate India’s Independence Day. In 2022, a long line of floats rolled through the streets, decked out in images of Hindu deities and colorful advertisements for local businesses. People cheered from the sidelines or joined the cavalcade, dancing to pulsing Bollywood music. In the middle of the procession came another kind of vehicle: A wheel loader, which looks like a small bulldozer, rumbled along the route bearing an image of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi aloft in its bucket. For South Asian Muslims, the meaning of the addition was hard to miss. A few months earlier, during the month of Ramadan, Indian government officials had sent bulldozers into Delhi’s Muslim neighborhoods, where they damaged a mosque and leveled homes and storefronts. The Washington Post called the bulldozer “a polarizing symbol of state power under Narendra Modi,” whose ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) is increasingly enacting a program of Hindu supremacy and Muslim subjugation. In the weeks after the parade, one Muslim resident of Edison, who is of Indian origin, told The New York Times that he understood the bulldozer much as Jews would a swastika or Black Americans would a Klansman’s hood. Its inclusion underscored the parade’s other nods to the ideology known as Hindutva, which seeks to transform India into an ethnonationalist Hindu state. The event’s grand marshal was the BJP’s national spokesperson, Sambit Patra, who flew in from India. Other invitees were affiliated with the Hindu Swayamsevak Sangh (HSS), the international arm of the Hindu nationalist paramilitary force Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), of which Modi is a longtime member.
...
On December 6th, 1992, a mob of 150,000 Hindus, many of whom were affiliated with the paramilitary group the RSS, gathered at the Babri Masjid, a centuries-old mosque that is one of the most contested sacred sites in the world. Over the preceding century, far-right Hindus had claimed that the mosque, located in the North Indian city of Ayodhya, was built not only upon the site where the Hindu deity Ram was born but atop the foundations of a demolished Hindu temple. The RSS and its affiliates had been campaigning to, in the words of a BJP minister, correct the “historical mistake” of the mosque’s existence, a task the mob completed that December afternoon. “They climbed on top of the domes and tombs,” one witness told NPR. “They were carrying hammers and these three-pronged spears from Hindu scripture. They started hacking at the mosque. By night, it was destroyed.” The demolition sparked riots that lasted months and killed an estimated 2,000 people across the country.
The destruction of the Babri Masjid was arguably Hindu nationalism’s greatest triumph to date. Since its establishment in 1925, the RSS—whose founders sought what one of them called a “military regeneration of the Hindus,” inspired by Mussolini’s Black Shirts and Nazi “race pride”—had been a marginal presence in India: Its members held no elected office, and it was temporarily designated a terrorist organization after one of its affiliates shot and killed Mohandas Gandhi in 1948. But the leveling of the Babri Masjid activated a virulently ethnonationalist base and paved the way for three decades of Hindutva ascendance. In 1998, the BJP formed a government for the first time; in 2014, it returned to power, winning a staggering 282 out of 543 seats in parliament and propelling Modi into India’s highest office. Since then, journalist Samanth Subramanian notes, all of the country’s governmental and civil society institutions “have been pressured to fall in line” with a Hindutva agenda—a phenomenon on full display in 2019, when the Supreme Court of India awarded the land where the Babri Masjid once stood to a government run by the very Hindu nationalists who illegally destroyed it. (Modi has since laid a foundation stone for a new Ram temple in Ayodhya, an event that a prominent RSS activist celebrated with a billboard in Times Square.) The Ayodhya verdict came in the same year that Modi stripped constitutional protections from residents of the Muslim-majority region of Kashmir and passed a law that creates a fast track to citizenship for non-Muslim immigrants, laying the groundwork for a religious test for Indian nationality. Under Modi, “the Hinduization of India is almost complete,” as journalist Yasmeen Serhan has written in The Atlantic.
To achieve its goals, the RSS has worked via a dense network of organizations that call themselves the “Sangh Parivar” (“joint family”) of Hindu nationalism. The BJP, which holds more seats in the Indian parliament than every other party combined, is the Sangh’s electoral face. The Vishwa Hindu Parishad (VHP) is the movement’s cultural wing, responsible for “Hinduizing” Indian society at the grassroots level. The Bajrang Dal is the project’s militant arm, which enforces Hindu supremacy through violence. Dozens of other organizations contribute money and platforms to the Sangh. The sheer number of groups affords the Sangh what human rights activist Pranay Somayajula has referred to as a “tactical politics of plausible deniability,” in which the many degrees of separation between the governing elements and their vigilante partners shields the former from backlash. This explains how, until 2018, the CIA could describe the VHP and Bajrang Dal as “militant religious organizations”—a designation that applies to non-electoral groups exerting political pressure—even as successive US governments have maintained a warm relationship with their parliamentary counterpart, the BJP.
...
The most extreme figures in the Hindu nationalist and Zionist movements were especially frank about the nature of their partnership: “Whether you call them Palestinians, Afghans, or Pakistanis, the root of the problem for Hindus and Jews is Islam,” Bajrang Dal affiliate Rohit Vyasmaan told The New York Times of his friendly relationship with Mike Guzofsky, a member of a violent militant group connected to the infamous Jewish supremacist Meir Kahane’s Kach Party.
...
In 2003, Gary Ackerman—a Jewish former congressman who was awarded India’s third-highest civilian honor for helping to found the Congressional Caucus on India—told a gathering of AJC and AIPAC representatives and their Indian counterparts that “Israel [is] surrounded by 120 million Muslims,” while “India has 120 million [within].” Tom Lantos, another Jewish member of the caucus, likewise enjoined the two communities to collaborate: “We are drawn together by mindless, vicious, fanatic, Islamic terrorism.”
#reaux speaks#hindutva#nationalism#islam#religion#india#narendra modi#south asia#muslim#new jersey#Bharatiya Janata Party#history#resources#jewish currents#anti zionism#palestine#islamophobia#afghanistan#hindu#jewish#free palestine#israel
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
No one would call an artist from India “British” or an artist from Peru “Spanish,” so why do museums continue to label Ukrainian artists as “Russian”?
The misnomer issue is nothing new. Researchers and curators from Ukraine have been contacting institutions like the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) and Centre Pompidou for years to ask them to acknowledge the Ukrainian descent of some of the artists in their Russian collection. These requests were mostly ignored before the full-scale Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
Ukrainian culture (and any other post-Soviet/post-Russian Empire oppressed culture, for that matter) is successfully erased from global art history. And virtually every museum collection is an example of this erasure. Ukrainian art historian Oksana Semenik, who is now studying at Rutgers University, provides more proof of that. As an assistant curator at the Zimmerli, the biggest collection of Soviet non-conformist art in the US, Semenik examined the museum archive to find out that out of 900 artists labeled “Russian,” 71 were Ukrainians, and 80 were artists of other nationalities like Belarusian, Latvian, Lithuanian, etc. “About 15% of the ‘Russian’ collection is misidentified. But when I asked if this could be changed, the response was: The identity question is not relevant these days,” Semenik said.
If this question is irrelevant, then why does “Russian” remain? “Some curators told me that using Ukraine in the caption is incorrect since there was no such country at that time,” Semenik continued. She also checked the online archive of the Smithsonian Institution and found 42 Ukrainian artists labeled “born Kharkov, Russia” or “born Odessa, Russia,” among other examples. In fact, a country called “Russia” did not exist before 1991, either. But the problem is bigger here — attributing Ukrainian cities to Russia, especially in the current context, rings like blatant Kremlin propaganda.
To be unable to recognize the difference between the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union, and the Russian Federation or Russia is a shameful mistake for institutions whose archives are used as credible academic sources. “It’s tough to acknowledge that the history Western art historians were learning for years, all those tons of books about Malevych and the Russian avant-garde, were part of the Russian propaganda,” Semenik added.
#ukraine#russia#art#russian culture#russian art#ukrainian culture#ukrainian art#cultural appropriation#decolonisation#colonialism
462 notes
·
View notes
Text
"We want justice,” doctors chanted in Kolkata, waving handwritten signs that read, “No safety, no service!”
16 Aug 2024
Indian doctors have called for a nationwide shutdown of hospital services as public fury over the rape and murder of a trainee medic in the eastern city of Kolkata last week mounts.
The Indian Medical Association (IMA), the country’s largest grouping of medics with 400,000 members, said the 24-hour shutdown would be implemented on Saturday, affecting most hospital departments except for essential services.
The shutdown comes after thousands of people took to the streets in several cities to express their outrage at the rape and murder of a 31-year-old trainee doctor, whose brutalised body was found on August 9 at Kolkata’s state-run RG Kar Medical College and Hospital.
On Friday, large protests were held in various cities – including Kolkata, the capital of West Bengal state, Mumbai in the west and Hyderabad in southern India – demanding justice and better security at medical campuses and hospitals.
“We want justice,” doctors chanted in Kolkata, waving handwritten signs that read, “No safety, no service!”
Demonstrators held banners calling for accountability as they gathered near parliament in New Delhi.
“Doctors, especially women are vulnerable to violence because of the nature of the profession. It is for the authorities to provide for the safety of doctors inside hospitals and campuses,” the IMA said in a statement issued on Thursday on X.

Doctors hold posters and shout slogans during a protest condemning the rape and murder of the trainee doctor, at a medical college in Ahmedabad, western India, on August 16 [Amit Dave/Reuters]
Multiple medical unions in both government and private systems have backed the strike.
Doctors in government hospitals across several states on Monday had halted elective services “indefinitely” in protest.
Indian media have reported that the murdered doctor was found in the teaching hospital’s seminar hall, suggesting she had gone there for a brief rest during a long shift.
An autopsy confirmed sexual assault. Doctors say the circumstances of the rape point to the vulnerability of medics left without proper protection and facilities.
Though police have detained a man who worked at the hospital helping people navigate busy queues, state government officers have been accused of mishandling the case.
On Wednesday night, the hospital where the trainee doctor was killed was attacked. Police did not identify who was behind the rampage, but said they have arrested 19 people so far.
Little has changed
There were more than 31,000 reported rapes in India in 2022, the latest year for which data is available, according to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB).
The gang rape and murder in 2012 of a young woman on a bus in Delhi, northern India, led to nationwide protests and outrage over the country’s failure to tackle sexual violence against women.

Since 2012, the government has brought in sweeping changes to the criminal justice system, including tougher sentences and the death penalty for repeat offenders.
Conviction rates for rape ranged between 27-28 percent from 2018-2022, according to NCRB data.
The definition of rape has also been widened to include non-penetrative acts and the age threshold for rape trials lowered so 16-year-olds can be tried as adults.
But campaigners say little has changed despite the tougher laws.
Criminal lawyer Rebecca M John, who has represented many rape victims, said some rapists still believe they can get away with their crimes.
“One of the factors would be the absence of fear of the law,” she said.
Many cases of crimes against women also go unreported because of the stigma surrounding sexual violence and a lack of faith in the police.
#India#Kolkata#The Indian Medical Association (IMA)#RG Kar Medical College and Hospital#Male violence#Violence against women#There were more than 31000 reported rapes in India in 2022#May she Rest In Peace
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Historical and Modern Perspectives on Same-Sex Unions
Same-Sex Unions in Antiquity Even in antiquity, there were cultures that recognized same-sex relationships in various forms. Although formal marriages between same-sex partners are rarely documented, numerous examples of love unions and symbolic partnerships exist.
Ancient Greece: In Greek culture, same-sex relationships, particularly between men, were widespread and often socially accepted. These relationships, known as pederasty, had an educational character, where an older man (the Erastes) took a younger man (the Eromenos) under his wing. These connections were often marked by love and affection and played an important role in the education and social life of Greek cities.
Rome: Hadrian, who ruled from 117 to 138 AD, is an example of a same-sex relationship in Rome. Hadrian had a famous relationship with Antinous, a young Greek man. This relationship was so significant that Hadrian honored Antinous's memory in an extraordinary way after his death in 130 AD.
Mesopotamia: In ancient Mesopotamian cultures, such as the Sumerians and Assyrians, there is evidence of the acceptance of same-sex relationships. Texts and inscriptions suggest that such relationships were part of the social fabric, although formal marriages are not documented.
India: In ancient India, there are also indications of the acceptance of same-sex relationships. In Hindu mythology, there are stories of gods and heroes in same-sex relationships. This spiritual and cultural acceptance shows that such unions were recognized in certain contexts.
Indigenous Cultures of North America: Many indigenous cultures in North America had the concept of "Two-Spirit" individuals, who possessed both male and female qualities. Such individuals could assume ceremonial roles and enter into same-sex partnerships that were considered spiritually and socially acceptable.
Modern Developments: Marriage for All In modern times, the social and legal recognition of same-sex partnerships has significantly improved. Many countries have enacted laws granting same-sex couples the right to marry and the associated rights and obligations.
Switzerland: On July 1, 2022, Switzerland's "Marriage for All" law came into effect, granting same-sex couples the same rights as heterosexual couples. This was the result of a referendum in September 2021, where the Swiss population overwhelmingly voted in favor of legalization.
Worldwide: In addition to Switzerland, many other countries have previously legalized marriage for same-sex couples, including:
Netherlands (2001): The Netherlands was the first country in the world to introduce same-sex marriage. Belgium (2003): Belgium followed shortly after the Netherlands and legalized same-sex marriage. Spain (2005): Spain was one of the first major European countries to allow same-sex marriage. Canada (2005): Canada legalized same-sex marriage nationwide. South Africa (2006): South Africa became the first country in Africa to permit same-sex marriage. Norway (2009), Sweden (2009), Portugal (2010), Iceland (2010), Argentina (2010), Denmark (2012), Uruguay (2013), New Zealand (2013), France (2013), Brazil (2013), England and Wales (2014), Luxembourg (2015), Ireland (2015), USA (2015), Colombia (2016), Finland (2017), Germany (2017), Australia (2017), Austria (2019), Taiwan (2019), Costa Rica (2020). The legalization of same-sex marriage in these countries was often the result of decades of activism and social change, leading to greater acceptance and legal equality.
From antiquity to the present, same-sex unions and partnerships have a long and often complex history. While symbolic marriages and stable partnerships existed in antiquity, the legal and social recognition of same-sex marriages is an achievement of modern times. Today, many countries, including Switzerland, have introduced "Marriage for All," taking a significant step toward equality and acceptance.
Text supported by GBT-4o Image generated with SD1.5, overworked with manual inpainting and composing
22 notes
·
View notes