#Heibai
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HEIBAI AND WUKONG RAAAHHH



#oc#oc tag#art#lmk#lego monkie kid#lego monkie kid season 5#Sun Wukong#Heibai#digital art#hyperfixation is back baby#LMK WOOOOOOOOO
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
I can’t believe it took me this long to realize what Hei meant when by saying Bai was the worst thing to happen to him.
He knew she’d change him, that’d she’d be the ruin of him and he’d let her. That he would give up everything for her—revenge, his title, his life
Stroking in a broad brush; Hei was on a very self destructive path(he was in his emo phase lmao), his only motivator was spite and revenge but Bai showed—gave him a different one
And that makes the thread scene even more impactful, he’s acknowledging this, that she’ll be his ruin and and gladly accepting it. “Let it bind me forever.”
Anyway someday I promise I’ll write an actual analysis on who rules the world or at least the thread scene
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ghost Month Special: Heibai Wuchang
Today is the middle of Lunar Seventh Month, a.k.a. Zhongyuan Festival, and I feel like there can't be a more appropriate day to do a deep dive on my favorite ghost cops, a.k.a. the Black and White Impermanences, a.k.a. Seventh and Eighth Master, a.k.a. Tua Di Ya Pek, a.k.a. Xie Bi'an & Fan Wujiu.

Now, I've talked briefly about them in my Chinese Underworld post, and if you watch C-dramas or play certain Chinese games, you might have seen these two + learned a few things about them already. But for those who haven't, here's the five-minute summary:
-they are (one variant of ) Chinese psychopomps, who show up to take the souls of the deceased to the Underworld.
-they are also ghost cops, who go after troublesome ghosts that are disturbing the living.
-both wear tall hats with four characters on it (which also varied), as well as nearly identical black and white robes.
-for their Hokkien, Taiwanese and SEA versions, there's a significant height difference between the two; the white-robed one is tall and skinny, while the black-robed one is short and stout.

-the White Impermanence is often depicted with his tongue hanging out of his mouth (reminiscent of those who died by hanging) and a more cheerful expression, while the Black Impermanence is dark/blue-faced (reminiscent of death by drowning) and relatively more grim and fierce.
-the White Impermanence is also worshipped as a god of wealth by some.
However, outside of these bullet points, their tales and trajectory of development are a fascinating rabbit hole. I'd call them thorough folk gods, who evolved out of the greater existing character archetype of "ghost bureaucrats fetching people to the Underworld" and became their own unique characters almost entirely through folklore and oral legends.
So, without further ado, let's dive in.
Impermanence
The Great Spectre of Impermanence could arrive unexpectedly. (无常大鬼,不期而到) ——Sutra of Ksitigarbha's Fundamental Vows
To start talking about these two, we need to go into the general category of beings they separated out of later: Underworld officials.
Some conceptions of those petty ghost bureaucrats that mirrored living ones already existed in the Han dynasty; in burial goods and "grave scripts", there were paperwork dedicated to those officials, who were supposed to keep track of the Dead People Belongings List and maintain the segregation between the dead and the living.
Their characterization would get expanded a lot as time went on, in Northern-Southern dynasty and Tang legends, but this isn't an article about the ghost officials as a whole.
We are still tracing the origins of two specific ones, and to do that, we have to start with etymology——the "Wuchang" in their names.

It is the translation of the Buddhist concept of "Anitya", referring to the impermanence of everything, which is always changing and dying and being reborn, with no constant to be found.
Yeah, you can see why a word describing the fleeting nature of life might eventually become associated with death and native psychopomps at some point in the Northern-Southern dynasty.
In the 39 chapter translation of the Dhammapada (interlaced with additional parables) by Fa Ju and Fa Li, the "Killing Spectre of Impermanence" (无常杀鬼) was first mentioned in the "On Impermanence" (无常品) chapter.
Another name for this grim-reaper-esque figure was "The Great Spectre of Impermanence", which appears in the quote at the beginning.
It appeared earlier than Ksitigarbha's Sutra, though: in another Northern-Southern dynasty translation of the Sutra of Golden Light, a Great Spectre of Impermanence was mentioned as this scary being that swallowed a king's younger son up whole.
By the Tang dynasty, the Spectre of Impermanence had appeared in both poetry and Buddhist text collections, as a generic name for the ghost that came to get you when you die.
However, the name wasn't exactly common or widespread, as made evident by all the N & S. dynasty and Tang legends about ghost bureaucrats where they were just referred to as, well, ghost bureaucrats.
Similarly, the Scripture on the Ten Kings doesn't mention anything about a Spectre of Impermanence. Instead, the second variant of the sutra says there are 3 ghosts working under King Yama——the "Soul-seizing Ghost" (夺魂鬼), "Essence-seizing Ghost" (夺精鬼), and "Spirit-binding Ghost" (缚魄鬼), responsible for dragging souls away in chains to the tree near the Underworld entrance pass.
(Their names might have corresponded to the idea of the Three Souls, each grabbing one of them, or the alternate division of Hun-Po plus the "vital force/essence".)
Right after that, however, they mentioned two demonic-looking birds sitting on the tree, one of which was named the "Bird of Impermanence", who would angrily scold and torment the dead for their misdeeds.
In this text, whatever the birds were, they were seen as a separate thing from the 3 ghosts that brought the souls of the dead to the Underworld entrance.
(A brief tangent about the 2 variants of the Ten Kings Scripture: the first could be found in the Dunhuang manuscripts, its name was 佛说预修十王生七经, and, as Teiser's translation of the scripture at the end of his academic book has showned, didn't have the 3 ghosts or the birds.)
(The variant mentioned above is 地藏菩萨发心因缘十王经, which is likely a Song dynasty Japanese apocrypha based on the first variant.)
Buddy Ghost Cops
When the ghostly officials of the Tang legends showed up, they could be alone, in pairs or in groups.
It was only in the Song-Yuan era that the idea of ghost cops showing up in pairs began to populate, and the first mention of the "Two Spectres of Impermanence" appeared in Vol. 3 of the Song dynasty 随隐漫录.
However, even without the word "Impermanence" attached, in various Song texts, the idea of there being 2 ghosts coming to get you instead of a single one or a group had already showed up with more frequency than before.
Come Ming dynasty, the Two Spectres of Impermanence got even more notable mentions in vernacular novels: a descriptive poem in Chapter 115 of Water Margins brings them up alongside the "Generals of the Five Paths" (五道将军), another native Underworld deity that showed up in Tang novels.
Plum in the Golden Vase, a.k.a. "that one Ming classic novel that often got censored and un-classic-ed because of its graphic sexual content", also has a folk Precious Scroll singing session (a story within a story, basically) that mentioned them.
In this story, King Yama sent a pair of "Impermanence Spectres" after Lady Huang, the protagonist of the scroll, who were also referred to as "Divine Boys/Acolytes of Good and Evil".

Now, the Boy-Acolytes of Good and Evil (善恶童子) were a pair of existing Underworld deities that had appeared in Dunhuang manuscripts and Ksitigarbha-themed artworks, responsible for recording the good and bad deeds of people respectively.
Their first mention was in the Tang translation of Surangama Sutra, and according to the second variant of the Ten Kings Scripture, the one recording bad deeds was said to look like a Raksha, while the one responsible for good deeds just looked like a regular divine acolyte.
Plum in the Golden Vase might have briefly aluded to that quirk too, in the story-within-a-story, where it was said that "Good people are welcomed by the acolyte(s), while bad people get the Yaksha(s)".
In the earlier Song dynasty compendium, Yijian Zhi, there are also mentions of two kids leading a fortunate guy's soul out of the Underworld, as well as showing up to inform some guy's wife that her days were numbered.
The second story is kinda funny, because after she had pretty much rolled over and accepted her fate, the two kids suddenly returned and were like "Excuse me, was Zhao your maiden name, or your husband's?"
Upon being informed that it was the latter case, they were like "Dangit, almost got the wrong person." Immediately after they left, another woman in the neighborhood whose surname was actually Zhao died.
Both stories do not use the specific name of "Acolytes of Good & Evil" for them, though, nor are they described as recorders of good and evil deeds.
For all I know, these two kids could be just like the pair of "young boys in blue robes" (青衣童子) who led Taizong into the Ghost Gate and the Underworld proper in JTTW Chapter 11: generic ghost workers.
But in Plum in the Golden Vase at least, they seemed to have been absorbed into the larger category of the Impermanence Ghosts, even though the Impermanence Ghosts still weren't their own characters yet, or gained any iconic uniforms.
Rather, it's more that 1) the catch-all name of "Impermanence" has become somewhat widespread for the generic ghost cops, though not yet universal, and 2) the Underworld apparently has a buddy-cop system in place now, where there had to be two ghostly officials for every newly dead person.
Psychopomp Outsourcing
In the late Ming and Qing dynasty, we got another twist on the Wuchang thing: Zou Wuchang, literally "Walk as Impermanences".
I've talked before about the early version of Taizong's trip to the Underworld, where Cui Jue/Ziyu, instead of being posthumously made a ghost judge, was a living official working part-time for the Underworld.
Well, Zou Wuchang is similar, but less prestigious, and you don't get paid either. The Underworld is short of hands (somehow), so they just grab a random living person and be like "Go fetch dead people for us."
The earliest mention of such a tradition in the Ming dynasty 语怪 placed the custom in Fengdu, the famous "ghost city" of Sichuan.
According to the text, when someone's soul was yanked off its streets to work as part-time psychopomps, they just fainted on the spot, and would revive after a few hours or overnight. The phenomenon was so common, the locals weren't even shocked, nor bothered getting them any medical attention.
Yuewei Caotang Biji goes further into the rationales of why Underworld needed those living conscripts. Apparently, all the living people clustered around a sickbed created a blazing aura of Yang, which certain venerable/fierce/brutish individuals also possessed in abundance, and was anathema to the ghost cops.
They were beings of pure Yin, after all, while the conscripts, whose bodies were Yin but still had plenty of Yang-aligned Qi, didn't have to worry about that.
Zou Wuchang was also not gender-exclusive, and there were mentions of multiple female conscripts in Qing legend compendiums.
Also, though the recruitment was forceful, you could actually retire after serving for a number of years——in one tale from 庸闲斋笔记, a woman fought the conscript for her mother-in-law's soul, who took pity on her and reported back to the City God.
In response, the City God said he'd send a report to Yama to see if she could be spared, and also released the conscript from her duty on account of her kind heart.
The popularity of this tradition across multiple sources and a long stretch of time signalled that, to an even greater extent than before, the ghost cops weren't generic ghost cops no longer: they are The Impermanences, which is only a few step away from developing into their own characters with unique iconography.
Black and White
First: where did their signature robe colors come from?
According to the first variant of the Ten Kings Scripture, officials under the Ten Kings were supposed to be dressed in black robes, riding a black horse, and carrying a black banner.

But in Tang folklore compendiums, that dress code wasn't a thing at all. A Taiwanese paper actually goes through tales of ghost officials inside Taiping Guangji where their appearances were described, and counted 22 cases of them wearing yellow robes, 7 cases of red robes, and only 8 stories involving ghost officials in either black or white robes.
Though ghost officials in black as well as white robes never appeared in the same story, they did have two things in common: 1) they tended to be quite tall, and 2) almost half of them were carrying weapons of some sorts.
The very late Ming/early Qing novel, Cu Hulu, also has a character ask Bodhisattva Ksitigarbha a bunch of questions in Chapter 12.
One of them was about the discrepancy between the depiction of Underworld officials in temples and the ones he personally saw, and he mentioned that the statues of "Impermanences" were 1) dressed in mourning robes and 2) about a Zhang and two Chi (3+ meter) in height.

Which suggests that, by the novel's time, the ghost cops had already gained a set of uniforms, one associated with funerary affairs.
(Also: I love Ksitigarbha's answer to that particular question——"Yeah we used to have a really tall ghost cop like that, people just call him 'Wuchang' because they don't know what the heck he is. Also, Impermanence isn't actually a real name, it's a concept.")
However, as far as I know, the earliest mention of a pair of ghost cops, one in white and one in black, was in Vol. 19 of Yuewei Caotang Biji. And the story is quite funny.
Basically, this Sun guy was temporarily residing in someone else's house, and the host's mother was severely ill. One day, the family servant boy carried in some dinner for him, and because Sun was busy with something else, he told the boy to put it on a nearby table in another room.
Suddenly, a white robed guy just appeared out of nowhere and entered the house, followed by a short black robed guy.
Sun hurried into the room, saw the two guys stealing his dinner, and angrily yelled at them. The white robed guy noped out of there, leaving the black robed guy behind and hiding in a corner, unable to exit the room because Sun was blocking the door.
He kinda just sat outside and kept an eye on them for a while, before the host of the family suddenly showed up, telling him that his mother had just spoken.
Basically, the ghost officials had come for her, and one of them happened to be cornered in the room by Sun, so would he please move? She didn't want to be punished for showing up late.
The host didn't know if it was true either, and was just going out there and checking. But the moment Sun went and sat somewhere else, the ghost in black scampered out of the room. Soon afterwards, wailing began to come out of the mother's room, suggesting she had been taken away.
As hilariously pathetic as these two unnamed ghost cops are, the only thing connecting them to the Heibai Wuchang of much later times is their robe colors, and the black-robed one being short.
There are no tales featuring both 1) a pair of ghost cops in black and white, and 2) the pair being referred to as "Impermanences", though.
The middle-late Qing stories that do refer to the ghost cops as such tend to only feature a single Impermanence: unnaturally tall, dressed in white robes and hats, either holding a fan or carrying strings of paper money on his shoulders, sometimes bleeding from his eyes or nose/mouth.

(Yep, you know how the White Impermanence is often seen as the older of the two sworn brothers? As far as their historical existence goes, he really is the older guy.)
It was in the 19th century 醉茶志怪 that we saw the first signs of the two converging. In the three stories with "Impermanence" in their titles, two featured the "white-robed ghost cop in tall hat" alone, one of which described him as looking like a 10+ years old kid, standing at the side of the road like a temple clay statue.
The third story, however, featured a sighting of two giant ghosts, one in white and one in blue/green, near the City God's temple. Out of the four people involved in the encounter, three died after a few days, and the only survivor was the one who had his line of sight blocked by the palaquin.
How did 1 become 2?
How did the single unique Impermanence become the Black and White Impermanences?
Well…it's a complicated question with no definitive answers. We know that in the (probably Qing dynasty) Jade Records, there are already mentions of a pair of ghosts called Huo Wuchang ("Life-is-Impermanent" or "Living Impermanence") and Si Youfen ("Death-Has-a-Part").

The former wears a black official hat and formal robes, holds brushes and papers in his hands, with blades on his shoulders and torture tools on his belts. He has big bulging eyes and is often laughing.
The latter has dirty, bloodied face, wears a white robe, holds an abacus, carries a sack of rice on his shoulder and has paper money dangling in front of his chest like a necklace. He has a sad frown on his face and is always sighing.
As you can see, there are similarities, but also notable differences from the "iconic" Black & White Impermanences. Whereas the White Impermanence is usually depicted as the cheerful one in white robes, carrying an abacus and wearing strings of paper money, here, he is the sad and grim one.
Their jobs also differ: instead of fetching souls to the Underworld, in the Jade Records, these two are responsible for pushing the dead off the bridges after they have drunken Mengpo's amnesia soup, into the scarlet river so they can reincarnate.
Personally, I view them as a transistory stage between the "Generic Impermanence Ghosts" and "The Two Unique Psychopomps We Know and Love", one strand of the folk god evolutionary process that was captured in written sources.
A Japanese paper goes into another strand in the evolution: the addition of the Black Impermanence. Namely, he might have grown out of a ghost that commonly showed up in City God worship and parades, the so-called "Wall-touching Ghost" (摸壁鬼).
The claim was based on very late Qing newspaper illustrations, where the Black Impermanence was depicted as holding up his two arms like this:

Which was a gesture commonly used by the "Wall-touching Ghost" during parades in the Jiangsu area, who also wore black robes and tall hats.
The author of the paper then dug into sources about the Wall-touching Ghost, and not only found records of the parades, but also a Qianlong era Mulian opera script, 劝善金科, that paired him together with the Impermanence Ghost as fetchers of the dead.

(The two were also given names in this opera: the Impermanence Ghost is named Ba Yang, and the Wall-touching Ghost, Wu Qi.)
Earlier mentions of the Wall-touching Ghost in Qing folklore compendiums, however, didn't depict him as a ghost cop. The story in 夜航船 just described it as a ghost thing that hid between walls and used its chill breath to suck up people's souls.
Another story in the 1878 浇愁集, even though it described the ghost more——dark-faced, holding its arms up like in the drawing, could turn into a cloud of black smoke and disappear into walls——still had it as your typical "ghost shows up, people die" ill omen.
So the paper's proposition is that, after the White Impermanence has separated out of the "Generic Ghost Cop Impermanences" and become his own thing, people in southern Jiangsu built on their existing Wall-touching Ghost and made him into the former's partner, absorbing most of his iconography in the process.
Similarly, the "tall and short" pair-up that was popular in Fujian and spread across Taiwan and SEA might also be a result of parallel local evolution, together with the name Xie Bi'an and Fan Wujiu.
Xie and Fan
Yes! At last, at last, we are getting to the most well-known and popular origin story, a.k.a. the Nantai Bridge Tale.
A summary: Xie Bi'an and Fan Wujiu were a pair of best friends/sworn brothers from Fujian, working as constables for the local magistrate. One day, while they were out on a mission, they saw a storm brewing. Xie went back to grab umbrellas while Fan waited for him under the bridge.
Unfortunately, the downpour soon began, causing the river to flood. Fan, unwilling to break his promise, continued waiting for Xie under the bridge and drowned. When Xie returned and saw his sworn brother's corpse, he hang himself out of guilt and grief too.
(…As a casual reader, I, always wondered why "waiting ON the bridge instead of under it" never crossed his mind as an option. Okay, sure, it was raining. But that's all the more reason to not stand under the darn bridge.)
Touched by their loyalty to each other, the City God/King Yama/Jade Emperor appoints them as ghostly constables, responsible for fetching the dead to the Underworld.
This story bears a lot of similarity to the fable of Wei Sheng in Zhuangzi. Basically, the guy made a promise to meet a girl under a bridge, the girl didn't show up, there was a flood, and, unwilling to leave, he drowned while still clinging to the bridge pillar.
Zhuangzi's opinion of the guy wasn't too high, because honestly, what a stupid way to die.
However, Sima Qian held him up as an exemplar of loyalty and keeping one's word, and the reading stuck. For later folktales about Wei Sheng as well as others that adopted the basic premise, like one tale in the 七世夫妻 story cycle, it also tended to get turned into a straight-up love story.
Though the Nantai Bridge Tale is the most popular version of their backstory, it's far from the only version. One version has them as Tang dynasty officials, working under the historical figure Zhang Xun, who died during the Anshi Rebellion.
While they were trying to get reinforcements, Xie was caught and hung on the city gate by the rebels, while Fan accidentally drowned.
When Zhang Xun was made a City God after the city fell and the rebels killed him, these two also became deified as his attendants.
In another version, Xie was a filial son with an aging mother, who had been wrongly imprisoned because of a friend's crime. During the Lunar New Year, Fan found him crying in the cell, and, upon learning about his sad backstory, released him secretly to visit his mother, on the condition that he returns after seven days.
However, his mother died soon after his return. Busy with her funeral, Xie did not return in time, and Fan, unable to answer to his superiors, committed suicide via drinking poison. When Xie returned and learned of the terrible news, he, too, hang himself.
And these three are far from the only known versions! Like, seriously, there are probably as many variations of the story as there are variations of the objects they held in their hands.
Though some elements stay more constant——using their deaths to explain their iconography, Xie being more commonly associated with the fan, umbrella, and abacus and Fan, chains, everything is subjected to changes and regional differences.
(For example, SEA oral legends tend to associate them with opium. Most of the time, they are constables or mercenaries employed to track down opium smugglers and other criminals, but some have them as Robin Hood-esque opium smugglers.)
Anyways, I hope this long post has offered some insight into the two iconic, yet also somewhat obscure ghost cops. I might add an "Appendix of Fun Facts and Tales" that doesn't fit into the main body of the post, but for now? That will be all.
May the readers who celebrate it have a nice Zhongyuan Festival.
Bibliography:
蔺坤:《无常鬼考源》
大谷亨:《黑无常的诞生与演变—— 以江苏南部的摸壁鬼传说为中心》
陈威伯、施静宜:《七爷八爷成神故事研究》
江義雄:《臺灣「黑白無常」與「范謝將軍」研究》
吳彥鋒:《臺灣七爺八爺傳說及其與信仰關係研究》
中国国家博物馆藏《十一面观音变相》的阐释
劉榕峻:狂放不羈、怪異獨特:談香港藝術館展出的「揚州八怪」
Stephen F. Teiser, The Scripture on the Ten Kings and the Making of Purgatory in Medieval Chinese Buddhism
Fabian Graham, Voices from the Underworld: Chinese Hell Deity Worship in Contemporary Singapore and Malaysia
CBETA: 《地藏王菩萨本愿经》
CBETA:《佛说地藏王菩萨发心因缘十王经》
夷坚���/支癸07,“赵彥珍妻”
《金瓶梅词话》,Chapter 74
《醋葫芦》,Chapter 12
《劝善金科》Vol.5, Part 2
The Jade Guidebook: Appendices, translated by David K. Jordan
Journey to the West Vol.1, Chapter 11, translated by Anthony C. Yu
#chinese folklore#heibai wuchang#fan wujiu#xie bi'an#chinese folk religion#chinese underworld#cw: death#cw: suicide#hell#ghosts#ghost month#hungry ghost festival
139 notes
·
View notes
Text














Yan Yan and Seven (part 1)
#shes his mom your honor#scissor seven#killer seven#伍六七#刺客伍六七#killer 7#cike wu liuqi#donghua#wu liuqi#scissor seven spoilers#seven#yan yan#manhua#black and white twin dragons#Heibai Shuanglong
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

Xiyuan as Heibai Wuchang
Day 3: mythology @qiyeweek
Literal old man yaoi
#qi ye week#qi ye week 2024#xiyuan#wu xi#jing beiyuan#七爷#qi ye#qiye#jing qi#wuxi#乌溪#景北渊#黑白无常#qi ye fanart#priest novels#my art#fanart#digital art#Heibai Wuchang#lord seventh#lord seventh fanart#I took old man yaoi too seriously for this one
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Last week we talked about the 10 Kings of the Underworld, so how about we look at some of the lower-ranking spirits and deities that populate the afterlife, shall we?
First up, the Chinese grim reaper, or rather reapers as there are two of them. Collectively called the Heibai Wuchang and individually Hei Wuchang and Wei Wuchang, these guys are responsible for what's essentially clean up duty. They go and find wandering souls that haven't passed on and bring them to the Diyu. I guess that means if you see a ghost they've been slacking off, huh? Hei, literally meaning black, wears all black robes and carries handcuffs with a nasty scowl on his face. Bai, which means white, naturally wears white clothes and had an umbrella and a smile. Seeing them is bad luck, as they have exactly one job to do: take you to the underworld.
Next are the pair that you'll see guarding the gates, Niutou (ox head) and Mamian (horse face). Well don't they sound handsome? Originally independent deities in their own right, they got reincarnated into human form (reluctantly, in Niutou's case). They end up as friends that take the official exam in the capital, but while Niutou is a hard worker Mamian is a hard schmoozer and passes by sucking up. Niutou is so pissed he full on beats Mamian to death.... and then drops dead himself from exhaustion from all the way too much studying he'd done. When they get to the Diyu and face King Yama, Niutou furiously argues what a lazy kiss ass Mamian is for a whole day. Yama is convinced.... until Mamian speaks up in his own defense and charms the king of the underworld into not punishing him. 110% DONE with this, Niutou breaks out of hell and goes straight to the Jade Emperor. The song and dance repeats, and the Jade Emperor commands them to become guardians of the gates of the underworld. Yama is reasonably worried they might duke it out again, though, so he has them drink this special forget-things soup. They made nice, and are still standing guard to this day.
Lastly we're gonna talk about this magic soup, or rather the nice old lady who makes it. Her name is Mengpo and she has a very important role to play in the cycle of reincarnation. Before crossing the river out of the underworld every soul has to drink a bowl of her special soup that makes you forget everything before you get reborn. However, as I said she's a nice old lady who will sometimes cut people (specifically lovers) a break and give them watered down soup so they can find each other in the next life. She can also sometimes make a bad batch of soup that doesn't work as well (she's old, give her a break).
Honestly I think it's really cute how thoe last person you see on your way out of the diyu is this cute old grandma who gives you a warm bowl of soup and a pat on the back. Isn't that just the most wholesome thing you've ever heard about the underworld?
#mythology sh*tposting#chinese mythology#diyu#king yama#king enma#king yan#heibai wuchang#mengpo#niutou and mamian#niutou#mamian#the underworld#chinese underworld#lmk#lego monkie kid
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
World no. 1 Wuchang
by 少爷丶 @ 41407527391
#douyin#tiktok#identity v#idv#wuchang#idv wuchang#wu chang#heibai wuchang#susan#well#少爷丶#41407527391#xie bian#fan wujiu
6 notes
·
View notes
Text


Got the plague. Got better. Got my missing creative motivation back from Santa and drew this on Christmas! :D
I’ve recently been watching Who Rules the World (just finished ep 19) and was struck with the urge to draw Hei-Bai Fengxi.
The greyscale version turned out pretty well, kinda prefer it even. I find it fitting for the 黑 (hēi, black) 白 (bái, white) couple!
Drawn Dec. 25, 2022 | Posted Jan. 22 2023
#heibai fengxi#bai fengxi#hei fengxi#who rules the world#且试天下#fanart#my art#also been learning Mandarin and it’s so fun to actually catch some of what they’re saying!#I don’t know a lot but there ARE a few words and phrases I recognize and it’s always exciting when I do!
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
i dont think aang can do that......
0 notes
Text
'The Heibai Wuchang, or Hak Bak Mo Seong, literally "Black and White Impermanence", are two Deities in Chinese folk religion in charge of escorting the spirits of the dead to the underworld. As their names suggest, they are dressed in black and white respectively.' (Wikipedia)
Looking at laughter
English added by me :)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

The queen returns
(ITS ABOUT TIME YAAAA
#oc#art#oc tag#digital art#lmk#lego monkie kid season 4#lego monkie kid#jttw#lmk oc#lmk oc art#Heibai#HEIBAI OUR PAN QUEEN
0 notes
Text
Something something about how Hei could let all of his worry strands except for Bai’s and how when Hei was dying Bai knew speeding up the healing process could kill her and did it anyway and how when he wakes up and his qi flow has deviated and he’s attacking her but before Bai hits his last pressure point to bring him back she begins to faint the light literally returns to his eyes and he pulls her to his chest
They make me ill(affectionate)
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Guide to the Chinese Underworld (and what it isn't)
As many FSYY and fox posts as there were on my blog, I am actually a huge fan of the Chinese Underworld mythos. Mostly because I was once a morbid little kid that loved reading about the excavations of ancient tombs, and found the statues depicting hellish torture in the Haw Par Villa "super cool".
Apart from the aesthetics, the history of its evolution is also fascinating. Most of us, Chinese or not, only know the most popular version of the Underworld——the "Ten Kings" system, yet that isn't always the case. So today, I'll start off with a short summary of that.
In pre-Qin era, there was already this generic idea of a "Realm of the Dead" called the Yellow Spring, Youdu, or Youming, but we know very little about it.
Then, in the Han dynasty, two ideas start to emerge: 1) the Underworld is a bureaucracy, 2) the God of Mt. Tai ruled over the dead.
This early bureaucracy might not function as an agent of punishment; the main focus was on keeping the dead segregated from the living so they wouldn't bring diseases and misfortune to the latter, as well as using those ghosts to enforce collective punishments upon people for their lineage's wrongdoings while they were still alive.
Post-Han, after Buddhism entered China and took root, its idea of karmic punishments and reincarnation and the figure of King Yama was merged with folk and Daoist ideas of the Underworld bureaucracy, and, came Tang dynasty, resulted in the "Ten Kings" system that first appeared in Dunhuang manuscripts.
It was very rudimentary and far from well-established, as seen in Tang legends, with some adopting the Ten Kings system, some sticking to the Lord of Mt. Tai and some favoring King Yama, and overall little agreements on who's in charge of the Underworld.
But the "Ten Kings" system would become the mainstream version from then onwards, used in Ming vernacular novels and made even more popular by folk religion scrolls like the Jade Records (Yuli Baochao).
As such, most points in the following sections will be based on the fully matured "Ten Kings" system of the Underworld, as seen in the Jade Records and JTTW.
What happens when you die?
(This is a fictionalized walkthrough of the posthumous fate of souls under the "Ten Kings" system. I try to stick to the very broad progression outlined in the Jade Records, but many creative liberties are taken on the details.)
Let's say there's a guy named Xiao Ming, and he had just died of a heart attack. Bummers. What now?
Well, the first thing he saw would be the ghost cops.
There isn't really an unanimous agreement on who these ghost cops are: they may be a pair of ghosts in white and black robes, wearing tall hats (Heibai Wuchang), they may have the heads of farm animals (Ox-Head and Horse-Face), or they can just be generic ghost bureaucrats. For convenience's sake, let's say it was the first scenario.
"Who are you guys and where are you taking me?"
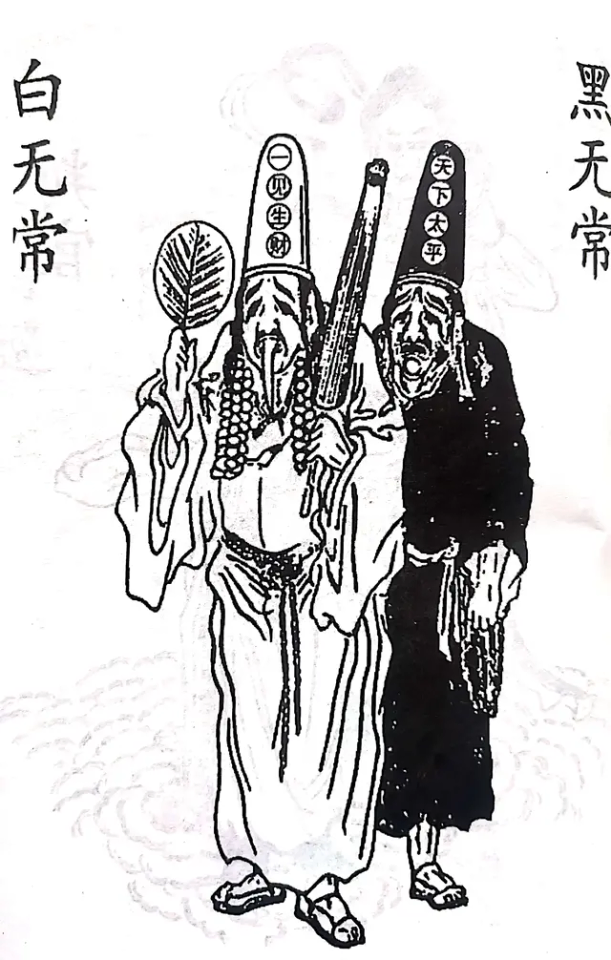

"Glad you asked!" The taller ghost cop, being the cheerful one of the pair, replied. It wasn't very reassuring, considering that his tongue was dangling out of his mouth way further than it should. "I'm the White Impermanence, my sour-looking colleague here is the Black Impermanence, and we are taking you to the City God's office."
This City God, a.k.a. Chenghuang, is just like how it sounds: the divine guardian of a city, who also pulls double duty as the head of the local Dead People Customs Office. They are usually virtuous officials deified posthumously, and in JTTW, they fall under the category of "Ghostly immortals", together with the Earth Gods a.k.a. Tudi.

So Xiao Ming went with the two ghost cops——not like he had much of a choice, made his way through the long queue at the City God's office, and was now standing in front of a gruff old magistrate in traditional robes.
"Name?"
"Wang Xiao Ming."
"Age and birth dates?"
"21, April 16 2003…"
After he was done asking questions, the City God flipped through his ledger, then picked up a brush, ticked off Xiao Ming's name, and told him to go get his pass in the next room. More waiting in a queue. Wonderful.
"I never heard anything about needing a pass to get to the Underworld," the girl in front of Xiao Ming asked the ghost cops, who were standing guard nearby. "Is this a new policy or something?"
"Yeah. In the old days, we'd just drag y'all straight to the Ghost Gate." The ghost cop in black said, then muttered to himself, "Fuckin' paperworks and overpopulation, man…"
(This "Dead People Passport" thing was popularized in the middle-to-late Ming dynasty, as shown by the discovery of such documents inside tombs in southern China. )
(It might have evolved from similar passes to the Western Pure Land in lay Buddhism that recorded their acts of merits. Which, in turn, might be traced back to the "Dead People Belongings List" of Han dynasty, to be shown to Underworld bureaucrats so that no one would take away the dead's private property down there or something.)
Anyways, after he received his pass, Xiao Ming departed together with the rest of the bunch, to be led to the Ghost Gate. It was like the world's most depressing tourist group, where instead of tour guides, you got two ghost cops in funny hats, and the only scenery in sight was the desolation of the Yellow Spring Road.
They weren't the only travellers on the road, though. Xiao Ming noticed other groups moving in the far distance, behind the fog and the flickering ghostfire, led by similar figures in black and white.
It made a lot of sense; realistically, there was no way two ghost cops could fetch hundreds of thousands of dead people all by themselves.
(SEA Tang-ki mediums believed there were multiple Tua Di Ya Peks——Hokkien name for the Black and White Impermanences, working for different Underworld Courts.)

At last, the Ghost Gate stood in front of Xiao Ming, guarded by two towering figures. Normally, they'd be Ox-Head and Horse-Face, like what you see at Haw Par Villa's Underworld entrance.
However, older Han dynasty works like Wang Chong's 论衡·订鬼 also mentioned two gods, Shenshu and Yulei, as guardians of the Ghost Gate, who would use reed ropes to capture malicious ghosts and feed them to tigers, making them possibly the earliest incarnation of "Gate Gods".
So here, they were what Xiao Ming sees, standing side by side like proper doormen, silently watching herds of ghosts being funneled through the entrance.
The place was more crowded than a train station during the CNY Spring Rush; the ghost cops had already said their quick goodbye and left to fetch the next group of dead people, leaving the resident officials of the Underworld proper to maintain order and quell any would-be riots.
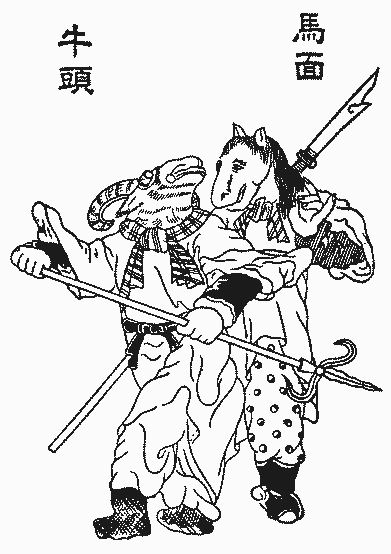
Now you started seeing the Ox-Head and Horse-Face guys, poking at unruly ghosts with their pitchforks and dragging away the violent ones in chains. Among their ranks were other monstrous beings, blue-faced yakshas and imps, but also regular dead humans who look 100% done with their jobs, like the lady who stamped Xiao Ming's pass when it was finally his turn.
After this point, Xiao Ming had entered the Underworld proper, and his next destination would be the First Court, led by King Qin'guang. Here, his fate should be decided by what is revealed in the King's magical mirror.
If Xiao Ming was a good guy, or someone who had done an equal amount of good and bad things in life, he'd be sent straight to the Tenth Court for reincarnation. However, if the mirror, while replaying his life events, had displayed more evil deeds than good ones, he'd be sent to one of the 2nd-9th Courts for judgment and then punished inside the Eighteen Hells.

Each of the Ten Kings was also assisted by ghostly judges. Many of them were righteous and just officials in life who had been recruited into the Ten Courts posthumously——Cui Jue from JTTW is one such example, while others were living people working part-time for the Underworld, like how Wei Zheng, Taizong's minister, works part-time for the Celestial Bureaucracy in JTTW.
We decide to be nice to Xiao Ming, so, after reliving some embarrassing childhood incidents and cringy teenage phases in front of a bunch of dead bureaucrats, he was found innocent and sent to the Tenth Court.
The queue here was almost as long as the First Court's, stretching on and on alongside of the banks of the Nai River. King of the Turning Wheel made his judgment without even lifting his head when it was Xiao Ming's turn:
"Path of Humans, male, healthy in body and mind, ordinary family. Next!"
Exiting the Tenth Court building, Xiao Ming saw the Terrace of Forgetfulness, standing tall before six bridges, made of gold, silver, jade, stone, wood, and…some unidentified material. Before he could get a good look at them and the little dots moving across those bridges, he was hurried into the Terrace by the ghostly officials.
Now, both JTTW and the Jade Records mention multiple bridges across the Nai River. In the former, there is 3, and the latter, 6. The bridges made of precious materials are for people who will reincarnate into better lives, as the wealthy, the fortunate, and the divine, while the Naihe Bridge is either the common option or the terribad shitty option.
However, the Naihe Bridge proved to be so iconic, it became THE bridge you walk across to reincarnate in popular legends.
Anyways, back to Xiao Ming. He found himself standing in a giant soup kitchen of sorts, with an old lady at the counter, scooping soup out of her steaming pot and into one cup after another.

This is Mengpo, the amnesia soup granny; according to the Jade Records, she was born in the Western Han era, and a pious cultivator who thought of neither the past nor the future, only knowing that her surname was Meng.
Made into an Underworld god by the Jade Emperor, she cooks a soup of five flavors that will wipe the memory of the dead, making sure they do not remember any of their past lives once they reincarnate.
It tastes awful. Like what you get after pouring corn syrup, coffee, chilli sauce, lemon juice and seawater into the same cup.
Such was Xiao Ming's last thought, as he gulped down the soup, and then he knew no more.
Things you should know about the Chinese Underworld:
1. It's not the Christian Hell.
Rather, the Chinese Underworld functions somewhat like the Purgatory, in that there are a lot of torment, but the torment's not eternal, however long the duration may be. Once you finish your sentence, you get reincarnated as something else, though that "something else" is not a guaranteed good birth.
Other people can also speed up the process via transferring of merits: hiring a priest/monk to chant sutras and perform rituals, for example, or performing good deeds in life in dedication to the dead, or they can pray to a Daoist/Buddhist deity to save their loved ones from a dreadful fate.
Interestingly enough, a thesis paper I read mentions that, whereas Buddhist salvation from the Hells was based on transference of merits——you give monks offerings and pay them to chant sutras, so they can cancel out the sinners' bad karma with good ones, Daoist ideas of salvation tend to involve the priest going down there, sorting it out with the Underworld officials, and taking the dead out of the Hells themselves.
(The paper also stops at the Northern-Southern and Tang dynasties, so the above is likely period-specific.)
2. Nor is it run by evil demons.
Underworld officials are not nice guys and look pretty monstrous and torture the sinful dead, but they are not the embodiment of evil. Rather, the faction as a whole is what I'd call Lawful Neutral, who function on this "An Eye for An Eye" logic, where every harm the sinner caused in life must be returned to them, in order for their karmic debts to be cleansed and move on to their next life.
They can absolutely be corrupt and incompetent and take bribes——Tang dynasty Zhiguai tales and Qing folklore compendiums featured plenty of such cases, but that's a very mundane and human kind of evil, not a cosmic/innate one.
This is just my personal opinion, but if you want to do an "evil" Chinese Underworld? It should be a very bureaucratic evil, whose leaders are bootlickers to the higher-ups, slavedrivers to their rank-and-file workers, and bullies who abuse their power over regular dead people.
Not, y'know, Satan and his infernal legions or conspiring Cthulu cultists.
3. The Ten Kings are not Hades.
Make no mistake, they still have a lot of power over your average dead mortal. But in the grand scheme of things? They are the backwater department of the pantheon, who only show up in JTTW to get pushed around and revive the occasional dead people.
When Taizong made his trip to the Underworld, the Ten Kings greeted him as equals——kings of ghosts to the king of the living. If they see themselves as equal in status to a mortal emperor, then, like any mortal emperors, they are subordinate to the Celestial Host, and the balance of power is not even remotely equal or in their favor.
Also, it isn't said outright, but under the Zhong-Lv classification of immortals JTTW is using, Underworld officials will likely be considered Ghostly immortals, the lowest and weakest of the five types, much like Tudis and Chenghuangs.
Essentially: they are ghosts that are powerful enough to not reincarnate and linger on and on, spirits of pure Yin as opposed to true immortals, who are beings of pure Yang.
It's pretty much the shittiest form of immortality, the result you get when you try to speedrun cultivation (the Zhong-Lv text also made a dig at Buddhist meditation here), and if they don't reincarnate or regain a physical body, there is no chance of progressing any further.
Oh, and fun fact? In the Song dynasty, commoners and literati elites alike believed that virtuous officials in life would get appointed as ghostly officials in death.
However, the latter viewed it as a punishment. Which was strange, considering how they still held the same position and the same amount of authority, just over dead people instead of living ones, so there should be no big losses, right?
Well...it was precisely the "dead people" part that made it a punishment. See, a lot of the power and prestige they had as officials came from the benefits they could bring to their families and kins and native places, as well as the potential wealth and reputation bonuses for themselves.
A job in the Dead People Supreme Court would give them the same workload, but with none of those benefits. Since all the dead people had to reincarnate eventually, they couldn't have a fixed group as their power base, or keep their old familial ties and connections. At most, they could help out an occasional dead relative or two.
Like, working for the Underworld Courts was the kind of deadend (no pun intended) job not even living officials wanted for themselves in the afterlife. That's how hilariously sad and pathetic they are.
4. In JTTW at least, they aren't even the highest authorities of the Underworld.
That would be Bodhisattva Ksitigarbha, who is technically their boss, though he seems to be more of a spiritual leader than someone who is actually involved in running the bureaucracy.
Which makes sense, since he has sworn an oath to not attain Buddhahood until all Hells are empty, and his role is to offer relief and salvation to the suffering souls, not judging and punishing them.
Now, historically...even though Ksitigarbha in early Tang legends was still the savior of the dead, he seemed to be unable to interfere with the judicial process of the Underworld, merely showing up to take people away before they were judged by King Yama.
However, in the mid-Tang apocryphal "Sutra of Bodhisattva Ksitigarbha" (地藏菩萨经), he had evolved into the equal of King Yama, with the power of supervision over his judgements. By the time the Scripture on the Ten Kings came out, in artistic depictions, the Ten Kings had become fully subservient to him.
5. Diyu usually refers to the prison-torture chamber part, not the courthouse, nor is it the entirety of the Underworld.
And for the majority of souls that haven't committed crimes, they'll only see the courthouse part before they are sent to reincarnation. That's why I personally don't like, or use the name Diyu for the Chinese Underworld: I prefer the term Difu ("Earth Mansions"), which encompasses the whole realm better.
Also: even though historical sources like the Scripture on the Ten Kings and Jade Records seem to suggest that the dead were just funneled through this Courthouse-Prison-Reincarnation pipeline with no breaks in between, in practice, that isn't the case.
According to popular folk beliefs, after the dead were done with their trials/sentences, they stayed in the Underworld for a period of time and led regular lives, while functioning as ancestor spirits and receiving offerings.
Which would imply that the Underworld had a civilian district of sorts, populated by regular ghosts, making the whole realm even less of a direct Hell/Purgatory equivalent.
6. It is located in a different realm, but still part of the Six Paths and doesn't exist outside of reality.
In Buddhist cosmology, like the Celestial Realm, the Underworld is part of the Realm of Desires and thus subject to all the woes of samsara.
The pain and misery of the Path of Hell may be the worst and most obvious, but becoming a celestial being isn't the goal of serious Buddhists either: despite all the pleasures and near-infinite lifespan they enjoy, they are not free from samsara and will eventually have to reincarnate.
So if, say, the world is being destroyed at the end of a kalpa, all beings of the Six Paths will perish alongside it, leaving behind a clean slate for the cycle to start anew. The dead won't all end up in the Underworld and face eternal damnation.
7. The Black and White Impermanences would not appear in the Underworld pantheon formally until the Qing dynasty.
The concept that when you die, you get fetched to the Underworld by petty ghost bureaucrats is already well-established in Tang legends, but these were just generic ghost bureaucrats in all sorts of colorful official robes, with yellow being the most common color.
The idea of there being two specific psychopomps in black and white would only become popular in the Qing dynasty. Mengpo is kinda similar: although she existed before the Ming-Qing era as a goddess of wind, venerated by boatmen, her "amnesia soup granny" incarnation came from the Jade Records.
#chinese mythology#chinese folklore#chinese underworld#diyu#chinese religion#cw: death#hell#underworld#journey to the west#I'm lazy so if you want a “work cited” list#just dm me
1K notes
·
View notes
Text



Interesting...
#scissor seven#killer seven#伍六七#刺客伍六七#killer 7#cike wu liuqi#donghua#wu liuqi#scissor seven spoilers#seven#yan yan#manhua#black and white twin dragons#Heibai Shuanglong
38 notes
·
View notes
Photo
Lord Seventh series when 😬😭

“Why were Wuxi and Beiyuan even at the wedding?” I see people ask. Well.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

Heibai Wuchang
Bai Wuchang / Hei Wuchang 白无常 黑无常
Since lmk4 was left with the underworld guys, I decided to draw these two from among the 10 Shady Commanders of the underworld.
Twitter

#lmk season 4#lego monkie kid#lego monkey kid fanart#hei bai#hei wuchang lmk#bai wuchang lmk#my artwork#desing character#Shady Commanders#Monkie kid#Monkie Kid
94 notes
·
View notes