#Forever Chemicals
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
From the article:
One of the most promising aspects of this new photocatalytic system is its simplicity. The setup is essentially a small vial illuminated by two LEDs, with two small fans added to keep it cool during the process. It operates under mild conditions and does not use any metals, which are often hazardous to handle and can sometimes be explosive. The system’s reliance on light – a readily available and renewable energy source – could make it economically viable and sustainable. As we refine it, we hope that it could one day operate with minimal energy input, outside of the energy powering the light. This platform can also transform other organic molecules that contain carbon-fluorine bonds into valuable chemicals. For instance, thousands of fluoroarenes are commonly available as industrial chemicals and laboratory reagents. These can be transformed into building blocks for making a variety of other materials, including medicines and everyday products.
#PFAS#forever chemicals#chemicals#pollution#chemical pollution#environment#hope#good news#science#technology
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #13
April 5-12 2024
President Biden announced the cancellation of a student loan debt for a further 277,000 Americans. This brings the number of a Americans who had their debt canceled by the Biden administration through different means since the Supreme Court struck down Biden's first place in 2023 to 4.3 million and a total of $153 billion of debt canceled so far. Most of these borrowers were a part of the President's SAVE Plan, a debt repayment program with 8 million enrollees, over 4 million of whom don't have to make monthly repayments and are still on the path to debt forgiveness.
President Biden announced a plan that would cancel student loan debt for 4 million borrowers and bring debt relief to 30 million Americans The plan takes steps like making automatic debt forgiveness through the public service forgiveness so qualified borrowers who don't know to apply will have their debts forgiven. The plan will wipe out the interest on the debt of 23 million Americans. President Biden touted how the plan will help black and Latino borrowers the most who carry the heavily debt burdens. The plan is expected to go into effect this fall ahead of the election.
President Biden and Vice-President Harris announced the closing of the so-called gun show loophole. For years people selling guns outside of traditional stores, such as at gun shows and in the 21st century over the internet have not been required to preform a background check to see if buyers are legally allowed to own a fire arm. Now all sellers of guns, even over the internet, are required to be licensed and preform a background check. This is the largest single expansion of the background check system since its creation.
The EPA published the first ever regulations on PFAS, known as forever chemicals, in drinking water. The new rules would reduce PFAS exposure for 100 million people according to the EPA. The Biden Administration announced along side the EPA regulations it would make available $1 billion dollars for state and local water treatment to help test for and filter out PFAS in line with the new rule. This marks the first time since 1996 that the EPA has passed a drinking water rule for new contaminants.
The Department of Commerce announced a deal with microchip giant TSMC to bring billions in investment and manufacturing to Arizona. The US makes only about 10% of the world's microchips and none of the most advanced chips. Under the CHIPS and Science Act the Biden Administration hopes to expand America's high-tech manufacturing so that 20% of advanced chips are made in America. TSMC makes about 90% of the world's advanced chips. The deal which sees a $6.6 billion dollar grant from the US government in exchange for $65 billion worth of investment by TSMC in 3 high tech manufacturing facilities in Arizona, the first of which will open next year. This represents the single largest foreign investment in Arizona's history and will bring thousands of new jobs to the state and boost America's microchip manufacturing.
The EPA finalized rules strengthening clean air standards around chemical plants. The new rule will lower the risk of cancer in communities near chemical plants by 96% and eliminate 6,200 tons of toxic air pollution each year. The rules target two dangerous cancer causing chemicals, ethylene oxide and chloroprene, the rule will reduce emissions of these chemicals by 80%.
the Department of the Interior announced it had beaten the Biden Administration goals when it comes to new clean energy projects. The Department has now permitted more than 25 gigawatts of clean energy projects on public lands, surpass the Administrations goal for 2025 already. These solar, wind, and hydro projects will power 12 million American homes with totally green power. Currently 10 gigawatts of clean energy are currently being generated on public lands, powering more than 5 million homes across the West.
The Department of Transportation announced $830 million to support local communities in becoming more climate resilient. The money will go to 80 projects across 37 states, DC, and the US Virgin Islands The projects will help local Infrastructure better stand up to extreme weather causes by climate change.
The Senate confirmed Susan Bazis, Robert White, and Ann Marie McIff Allen to lifetime federal judgeships in Nebraska, Michigan, and Utah respectively. This brings the total number of judges appointed by President Biden to 193
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#student loans#student loan debt#debt forgiveness#gun control#forever chemicals#PFAS#climate change#green energy
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Maryland is suing the company that produces the waterproof material Gore-Tex often used for raincoats and other outdoor gear, alleging its leaders kept using "forever chemicals" long after learning about serious health risks associated with them. The complaint, which was filed last week in federal court, focuses on a cluster of 13 facilities in northeastern Maryland operated by Delaware-based W.L. Gore & Associates. It alleges the company polluted the air and water around its facilities with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, jeopardizing the health of surrounding communities while raking in profits.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Health#Environment#Chemistry#Forever Chemicals#PFAS#Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances#Maryland#USA
349 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Alexis Dominguez
Published: Jan. 23, 2025 at 3:26 PM MST|Updated: 13 hours ago
PHOENIX (AZFamily) — Just days into President Donald Trump’s second term, the federal government has made major changes to environmental regulations.
A significant change is the regulation of toxins in drinking water or so-called “forever chemicals” that can build up in the environment and our bodies.
These chemicals are found in the drinking water consumed by most people in Arizona. This week, the Trump administration withdrew a pending plan to limit the amount of PFAS chemicals the industry can release into the environment.
“If you’re wondering right now, have I picked those PFAS? The answer is yes, definitely,” explained Dr. Rhett Larson, a water law professor at Arizona State University.
While there is still very little known about the chemicals, he says there’s strong evidence that exposure to PFAS can cause cancer.
“They’re everywhere. If you use nonstick appliances, if you have Scotchgard on your couches, it’s often used in making more flame retardant materials, so frequently in your clothing,” he said.
Since the chemicals don’t break down, they pollute the environment, earning them the name “forever chemicals.”
#donald trump#second term#environmental protection agency#drinking water#regulations#forever chemicals#pfas
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dandelion News - January 22-28
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735 or check out my Dandelion Doodles!
1. Sunfish that got sick after aquarium closed has recovered — thanks to human cutouts

“A solitary sunfish […] appeared unwell days after the facility closed last month for renovations. As a last-ditch measure to save the popular fish, its keepers hung their uniforms and set up human cutouts outside the tank. The next morning, the sunfish ate for the first time in about a week and has been steadily recovering[….]”
2. Costco stands by DEI policies, accuses conservative lobbyists of 'broader agenda'

“[Each of the board of directors and 98% of shareholders voted to reject a measure against DEI.] Costco's board wrote that “our commitment to an enterprise rooted in respect and inclusion is appropriate and necessary[….]””
3. Nearly $37 Million Will Support Habitat Restoration in Coastal Louisiana

“The project will restore nearly 380 acres of marsh and construct more than 7,000 feet of terraces in St. Bernard Parish. […] Coastal wetlands help protect communities [… from] wind, waves, and flooding[… and] support a statewide seafood industry valued at nearly $1 billion per year.”
4. Cooling green roofs seemed like an impossible dream for Brazil's favelas. Not true!

“[… A Brazilian nonprofit] teaches favela residents how to build their own green roofs as a way to beat the heat without overloading electrical grids[…,] dampen noise pollution, improve building energy efficiency, prevent flooding by reducing storm water runoff and ease anxiety.”
5. Bacteria found to eat forever chemicals -- and even some of their toxic byproducts
“"Many previous studies have only reported the degradation of PFAS, but not the formation of metabolites. We not only accounted for PFAS byproducts but found some of them continued to be further degraded by the bacteria," says the study's first author[….]”
6. A father and daughter’s to turn oil data into life-saving water

“The aquifer [discovered through oil-owned seismic data], it turned out, was vast enough to provide water for 2 million people for more than a century.”
7. Trump’s funding pause won’t impact federal student loans, Pell Grants
“[… T]he temporary pause will not impact “assistance received directly by individuals,” including federal direct student loans and Pell Grants, which are government subsidies that help low-income students pay for college.”
8. In Uganda, a women-led reforestation initiative fights flooding, erosion

“[… T]he Kasese municipality has established nurseries to provide free tree seedlings, particularly to women, to support reforestation efforts. [… They] plant Ficus trees near their homesteads to provide shade and help control erosion, and Dracaena trees on their fields to retain soil moisture.”
9. [A Texas school board] votes yes to provide low-cost housing to staff at no cost to the district

“The program will include 300 homes[…] only a short commute to campuses. […] Rent will be determined on a sliding scale based on their salaries, with those making less receiving a larger discount. The proposed community would include amenities, like childcare facilities[….]”
10. Heat pumps keep widening their lead on gas furnaces

“Americans bought 37% more air-source heat pumps than the next-most-popular heating appliance, gas furnaces, during the first 11 months of the year. That smashes 2023’s record-setting lead of 21%.”
January 15-21 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#fish#sunfish#mola mola#aquarium#us politics#costco#dei#diversity equity and inclusion#louisiana#habitat restoration#green infrastructure#brazil#global warming#science#forever chemicals#recycling#water#water scarcity#big oil#student loans#federal aid#reforestation#gardening#low income#affordable housing#housing#school#heat pump installation
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Despite a huge amount of political opposition from the chemical industry, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced its first regulations aimed at limiting quantities of PFAs, or ‘forever chemicals,’ in American drinking water.
For decades, Polyfluoroalkyl substances or PFAs have been used for coatings that resist fire, oil, stains, and water and are now found in a wide variety of products like waterproof clothing, stain-resistant furniture, food packaging, adhesives, firefighting spray foams, and non-stick cooking surfaces.
There are thousands of PFAS compounds with varying effects and toxicity levels, and the new EPA regulations will require water utilities to test for 6 different classes of them.
The new standards will reduce PFAS exposure—and thereby decrease the health risk—for 100 million people in the U.S.
A fund worth $1 billion for treatment and testing will be made available to water utilities nationwide—part of a $9 billion investment made possible by the 2021 Bipartisan Infrastructure Law to assist communities impacted by PFAS contamination.
“Drinking water contaminated with PFAS has plagued communities across this country for too long,” said EPA Administrator Michael S. Regan in a statement Wednesday.
Under Regan’s leadership, the EPA began in 2021 to establish a roadmap for dealing with widespread PFAS contamination, and so far they’ve gathered much data, including monitoring drinking water, and begun requiring more reports from businesses about use of the unregulated substances.
The agency reported that current peer-reviewed scientific studies have shown that exposure to certain levels of PFAS may lead to a myriad of health issues that are difficult to specify because of the variety of compounds coming from different places.
Regardless, the 66,000 water utility operators will have five years to test for the PFAS pollution and install necessary technology to treat the contamination, which the EPA estimates that 6%–10% of facilities will need. [Note: Deeply curious where they got a number that low, but anyway.]
Records show that some of the manufacturers knew these chemicals posed health hazards. A few major lawsuits in recent years have been settled that sought to hold chemical companies, like 3M, accountable for the environment damage.""
-via Good News Network, April 13, 2024
#united states#pfas#forever chemicals#epa#environmental protection agency#water quality#water pollution#clean water#good news#hope
478 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anything with the F in it 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#reeducate yourselves#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do your own research#do some research#ask yourself questions#question everything#teflon#dupont#pfoa#pfos#forever chemicals#cookware
302 notes
·
View notes
Text


This regulation was long overdue.
#VotingMatters #VoteBlue
368 notes
·
View notes
Text




Whether you call it climate change or pollution, it’s still a series of policy decisions (deregulation). Deregulation that is disproportionately upheld by greedy corporations, red state Democrats, and is enforced overwhelmingly by Republican and Libertarian controlled legislatures.
(sources and other relevant links beneath the cut)
👉🏿 https://heatmap.news/climate/wildfire-smoke-east-air-quality
👉🏿 https://www.volts.wtf/p/volts-podcast-david-wallace-wells
👉🏿 https://threadreaderapp.com/thread/1666541345069219840.html
👉🏿 https://threadreaderapp.com/thread/1648986424098652160.html
#politics#republicans#pollution#climate change#environment#climate change deniers#deregulation#libertarians#smog#forest fires#nyc#climate catastrophe#climate crisis#forever chemicals#pfps
744 notes
·
View notes
Text

66 notes
·
View notes
Text
#hey why are they in makeup???????#to make them water proof?? oh fuck#good news#science#environmentalism#nature#environment#new zealand#pfas#forever chemicals
207 notes
·
View notes
Text
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
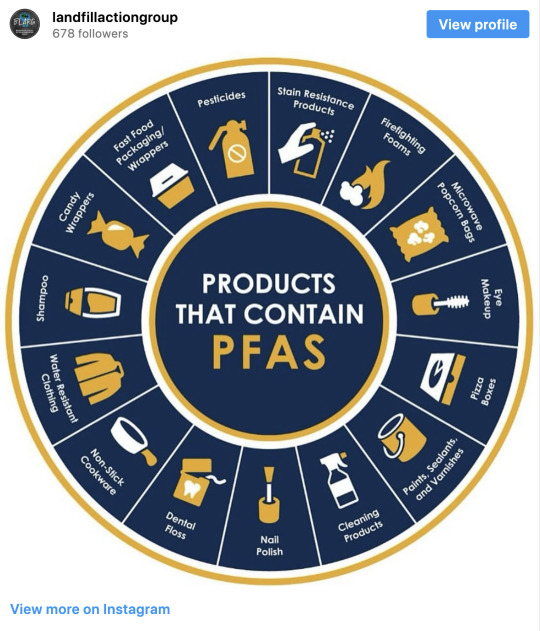
Excerpt from this story from The Revelator:
The water flowing from taps in Wilmington, North Carolina, looked clean, tasted normal, and gave no indication that it carried an invisible threat. For decades the Cape Fear River had provided drinking water to hundreds of thousands of residents in the region. But in 2017 tests revealed what many had feared: high levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), chemicals linked to cancer, immune dysfunction, and reproductive issues, coursing through their water supply.
The contamination had been traced to Chemours, a spinoff of DuPont, which had been releasing PFAS chemicals from its Fayetteville Works plant for years.
The discovery sent shockwaves through the community, triggering lawsuits, emergency water-treatment plans, and a reckoning over how corporations and government regulators had failed to protect public health. But even as residents fought to hold polluters accountable, the company responsible for much of the contamination was tightening its grip on the agencies meant to regulate it.
A former DuPont and American Chemistry Council lobbyist, Nancy Beck, now holds a key position at the Environmental Protection Agency, shaping chemical safety policies that will determine how — or if — PFAS pollution is addressed. In the first days of the second Trump administration, the agency withdrew a proposed rule that would have imposed limits on PFAS discharges, a move that watchdog groups say amounts to giving polluters free rein to continue contaminating water supplies.
The crisis in Cape Fear and Bentham reveals the creeping, silent danger of PFAS, which has infiltrated groundwater, rivers, and drinking-water supplies across the world.
And yet, as the Trump administration accelerates its environmental rollbacks, the ability to regulate and mitigate this growing threat in the United States is being systematically dismantled.
“North Carolina is one area that I’m most familiar with where there’s an entire river system that serves hundreds of thousands of people [and] is very badly contaminated with PFAS,” Erik D. Olson, senior strategic director for health at the Natural Resources Defense Council, told The Revelator. “A lot of people are drinking that water every day.”
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
Forever chemicals are falling in the rain, running through our waterways, and swimming in our bloodstreams, and now, initial research suggests these potentially harmful pollutants are 'clogging up' a crucial drainage system in our bodies. The new study indicates forever chemicals are impacting kidney health, with changes to the gut microbiome explaining at least some of the effects. Kidneys filter excess water and toxins out of the bloodstream, and forever chemicals are now circling these two 'drains' in a worrisome way. While evidence is currently limited, there is a chance that pollutants gathering in the kidneys are driving chronic disease, as well as cancer. In rodents, when some forever chemicals accumulate in the kidneys, the high concentrations lead to injury via oxidative stress.
Continue Reading.
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
A group of bacteria has proved adept at destroying the ultratough carbon-fluorine bonds that give “forever chemicals” their name. This finding boosts hopes that microbes might someday help remove these notoriously pervasive pollutants from the environment.
Nearly 15,000 chemicals commonly found in everyday consumer products such as pizza boxes, rain jackets and sunscreens are recognized as perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFASs. These chemicals can enter the body via drinking water or sludge-fertilized crops, and they have already infiltrated the blood of almost every person in the U.S. Scientists have linked even low levels of chronic PFAS exposure to myriad health effects such as kidney cancer, thyroid disease and ulcerative colitis.
Current methods to destroy PFASs require extreme heat or pressure, and they work safely only on filtered-out waste. Researchers have long wondered whether bacteria could break down the chemicals in natural environments, providing a cheaper and more scalable approach. But carbon-fluorine bonds occur mainly in humanmade materials, and PFASs have not existed long enough for bacteria to have specifically evolved the ability to digest them. The new study—though not the first to identify a microbe that destroys carbon-fluorine bonds—provides a step forward, says William Dichtel, a chemist at Northwestern University who studies energy-efficient ways to chemically degrade PFASs.
To identify a promising set of bacteria, the study’s authors screened several microbe communities living in wastewater. Four strains from the Acetobacterium genus stood out, the team reported in Science Advances. Each strain produced an enzyme that can digest caffeate—a naturally occurring plant compound that roughly resembles some PFASs. This enzyme replaced certain fluorine atoms in the PFASs with hydrogen atoms; then a “transporter protein” ferried the fluoride ion by-products out of the single-celled microbes, protecting them from damage. Over three weeks most of the strains split the targeted PFAS molecules into smaller fragments that could be degraded more easily via traditional chemical means.
By directly targeting carbon-fluorine bonds, the Acetobacterium bacteria partially digested perfluoroalkyls, a type of PFAS that very few microbes can break down. Even so, these Acetobacterium strains could work only on perfluoroalkyl molecules that contain carbon-carbon double bonds adjacent to the carbon-fluorine ones. These “unsaturated” perfluoroalkyl compounds serve as building blocks for most larger PFASs; they are produced by chemical manufacturers and also emerge when PFASs are destroyed via incineration.
Scientists had previously demonstrated that a microbe called Acidimicrobium sp. strain A6 could break down carbon-fluorine bonds and completely degrade two of the most ubiquitous perfluoroalkyls. This microbe grows slowly, however, and requires finicky environmental conditions to function. And researchers do not yet fully understand how this bacterial strain does the job.
The Acetobacterium lines target a separate group of PFASs, and the team hopes to engineer the microbes to either improve their efficiency or expand their reach—potentially to more perfluoroalkyls. Lead study author Yujie Men of the University of California, Riverside, imagines the microbes would perform best in combination with other approaches to degrade PFASs. The range of chemical structures in these compounds means “a single lab cannot solve this problem.”
Any future commercial use of the microbes would face numerous hurdles, including breakdown speed and replicability outside of the lab, but Men looks forward to seeing how far her team can push the technique. “We’re paving the road as we go,” she says with a laugh.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text
When plastic straws were banned, new alternative straws of paper, bamboo, and glass were advertised as more sustainable, eco-friendly, and healthy. Groffen’s team wanted to know if they hold up to the hype, but they found that the majority of them do not. With the exception of the stainless steel straws they tested, all of the brands they examined—which are commercially available in Belgium—contained chemicals that are harmful not only for the environment, but also for people. Known as PFAS, which stands for poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances, and dubbed forever chemicals, these compounds don’t break down under heat or sunlight and dissolve in neither water nor oil. For a few decades these PFAS were the darlings of the chemical industry, used in everything from fire-resistant cushions to water-repellant clothing and from nonstick pan coating to disposable plates. Unfortunately, what makes PFAS so durable in kitchenware and other products is also what makes it last so long in the environment. More importantly, in recent years, scientists have linked them to a gamut of damaging health effects, including thyroid disease, high cholesterol, pregnancy problems, liver damage, and several cancers. They have also been linked to adverse reproductive, developmental and immunological effects in animals. The team found PFAS to be present in 90 percent of the paper straws, 80 percent of bamboo, 75 percent of plastic, and 40 percent of glass ones.
133 notes
·
View notes