#Fat Activism
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I really hate the extent to which any conversation about fatness and ending fat phobia and fat acceptance always turns into managing the emotions of thin people.
Like you have to manage the emotions of thin people in the comments who insist that they also experience discrimination against their bodies because somebody told them once they were too skinny. You have to manage the emotions of thin people who feel like they deserve to publicly air their own anxieties about ever looking like we do. You have to manage the emotions of thin people who don't know the difference between systemic oppression faced by fat people and their own self-image issues.
And then you have to manage the emotions of thin people who are existentially terrified that if we as a society acknowledge that it's okay to be fat, they will no longer be able to view being thin as an accomplishment instead of like a fucking luck of the draw, genetic accident and then they will have basically tormented themselves for nothing.
And then we have to manage the emotions of people who are convinced that somehow the actual goal of fat acceptance is to take their diet away from them. When, in fact, literally nobody within fat acceptance cares what you're doing with your body. The point is that we should be able to live in the bodies that we are existing in and be given the same dignity and healthcare and pay and opportunities as everyone else, and shouldn't be discriminated against because of what our bodies look like.
Like we have more important shit to do than manage your anxieties around whether or not somebody's gonna find your diet problematic. That is not fat acceptance's concern. That's something you need to journal about or talk to your therapist about. But that is not any fat activist's concern what you do with your body, what diet you're on, what exercise regimen. Nobody fucking cares.
And then we have to manage the emotions of the thin person who's offended that nobody fucking cares. Or the person who's mid-sized and gets mad that their voice isn't amplified enough within a space that's not really for them. And they feel shamed and left out because they're not being given the platform in a fat activist space because they're used to the hierarchy of the world that prioritizes thin people. So the fact that they are within the space, a thin person, but not being prioritized feels like an attack on them and then we have to manage those emotions too, and I'm just...
It's fucking exhausting. It's like I'm tired of managing the emotions of thin people when I'm trying to do fat activism. I have better shit to do I have more important shit to do!
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anti-Obesity Drugs in Sociopolitical Context
Abstract
This literature review critically examines the use of Body Mass Index (BMI) as a diagnostic tool for obesity, highlighting its historical and scientific flaws. The diagnosis and treatment of obesity is heavily stigmatized and reflects deeper socio-economic and racial biases. Fatphobia, or anti-fatness, is deeply rooted in white supremacy and colonial history. I argue that anti-fatness and weight-based discrimination significantly impact health outcomes, rather than body fat percentage alone. The way that the medical system focuses on body size rather than the overall health of patients perpetuates harm and yields even poorer health outcomes. To genuinely improve the lives of fat individuals, we must dismantle anti-fat systems and remove barriers to healthcare, job equity, and basic infrastructure by implementing legal protections, rather than simply promoting weight loss. This review emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to health that considers socio-economic factors and systemic discrimination.
Journal Summary
Recently, two anti-obesity medications, Ozempic and Wegovy, which are primarily prescribed for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), have shown promise in causing weight loss. The 2022 scientific journal “Ozempic and Wegovy for Weight Loss, Pharmacological Component and Effect” by Abdullah Mohammed, et al explores the pharmacological components and effects of these medications on weight reduction, summarizing findings from existing clinical studies.
Ozempic is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist primarily used to manage T2DM. Clinical studies indicate that semaglutide can also promote significant weight loss. Ozempic's mechanism involves binding to GLP-1 receptors in the brain, reducing food intake and increasing feelings of fullness. This leads to a decrease in body weight and improvement in glycemic control. Wegovy, also a GLP-1 receptor agonist, is the same drug as Ozempic but two times the dose, specifically approved for weight loss for fat people even without T2DM. Administered as a weekly injection, Wegovy has shown effectiveness in inducing sustained weight loss. The STEP trials demonstrated that participants using Wegovy experienced an average weight loss of 15.8% over 68 weeks. Wegovy's pharmacokinetics involve prolonged activation of GLP-1 receptors, enhancing satiety and reducing hunger. GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide mimic the action of the natural hormone GLP-1, which regulates appetite and blood sugar levels. By slowing gastric emptying and promoting a feeling of fullness, these medications reduce caloric intake. Clinical trials have shown that GLP-1RAs, including semaglutide, can result in weight loss from 5% or up to 10-15% of body weight. However, sustained weight loss requires ongoing lifestyle modifications, as discontinuation of the medication leads to weight regain. Common side effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Other potential side effects include increased heart rate, fatigue, headaches, and changes in thyroid function.
Obesity as a Disease
How does one get an obesity diagnosis? There is one single criterion used for diagnosing someone with this disease: The Body Mass Index (BMI). A person’s BMI is their weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in meters, rounded to one decimal place. It does not account for muscle mass versus body fat. For these reasons, the BMI has been widely proven to be an ineffective health measure. The BMI was also never intended to be a measure of health in the first place.
The BMI was created in the 1800s by a statistician named Adolphe Quetelet, who did not study medicine, to gather statistics of the average height and weight of specifically white, European, upper-middle-class men to assist the government in allocating resources. It was never intended as a measure of individual body fat, build, or health (Karasu, 2016). Quetelet is also credited with founding the field of anthropometry, including the racist pseudoscience of phrenology. Quetelet’s L’homme Moyen would be used as a measurement of fitness to inspire, and as a scientific justification, for eugenics (Eugenics archive).
Studies have observed that about 30% of "normal” weight people are “unhealthy," whereas about 50% of "overweight" people are “healthy” (Rey-López, et al, 2014). Thus, using the BMI as an indicator of health misclassifies 75 million people in the United States alone. “Healthy*” lifestyle habits are associated with a significant decrease in mortality regardless of baseline body mass index (Matheson, et al, 2012).
*I put “healthy” in quotation marks here because the definition of an individual’s health is oversimplified and depends on many socioeconomic factors.
While epidemiologists use BMI to calculate national obesity rates, the distinctions between weight classes can be arbitrary. Ever notice that the weight classes on the BMI are nearly intervals of five? In 1998, the National Institutes of Health lowered the overweight threshold from 27.8 to 25—making roughly 29 million Americans "overweight" overnight—to match international guidelines (Butler, 2014). Critics have also noted that those guidelines were drafted in part by the International Obesity Task Force, whose two principal funders were companies making weight loss drugs.
Jackie Scully, Senior Research Fellow at the Unit for Ethics in the Biosciences, University of Basel, in her scientific journal titled “What is a Disease?” states the following: “As the business literature shows, new clinical diagnoses are often welcomed primarily as opportunities for market growth (Moynihan et al, 2002). One recent example of this is female sexual dysfunction (FSD). The huge commercial success of sildenafil (Viagra) for erectile dysfunction in men provides a strong motivation for drug companies to identify an equivalent market (that is, condition) in women. And some ethicists feel that drug companies were, to put it mildly, over-involved in the medical consensus meetings held between 1997 and 1999 that effectively drew up very inclusive clinical criteria for the definition of FSD (Moynihan, 2003)."
How can one diagnose a person with a disease and sell them medications solely based upon an outdated measure that was never meant to indicate health in the first place, especially when obesity has no proven causative role in the onset of any chronic condition? (Kahn, et. al., 2000), (Cofield, et al, 2010).
This is why the term “obese” is recognized as a slur by fat communities. It's a stigmatizing term that medicalizes fat bodies even in the absence of disease. The word directly translates to "having eaten oneself fat" in Latin. Obesity, as a medical diagnosis, doesn’t have much ground to stand on. Aside from being overtly incorrect as a medical tool, the BMI is used to deny certain medical treatments and gender-affirming care, as well as insurance coverage. Employers still often offer bonuses to workers who lower their BMI. Although science recognizes the BMI as deeply flawed, it's going to be tough to get rid of. It has been a long-standing and effective tool for the oppression of fat people and the profit of the weight loss industry.
To treat obesity, patients must eat less. Making someone smaller still means they will be healthier, right?
Fatness and Mortality
The idea that obesity is unhealthy and can cause or exacerbate illnesses is a biased misrepresentation of the scientific literature that is informed more by bigotry than credible science (Medvedyuk, et al, 2017). Fatphobia existed long before fatness became medicalized. Yes, obesity is correlated with conditions such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and diabetes, but some scientists are looking into possibilities that don't equate correlation with causation. Obesity has no proven causative role in the onset of any chronic condition (Kahn, et al, 2000), (Cofield, et al, 2010) and its appearance may be a protective response to the onset of numerous chronic conditions generated from currently unknown causes (Lavie, et al, 2009), (Uretsky et al, 2007), (Mullen, et al, 2013), (Tseng, 2013). A portion of these correlated conditions are likely brought on by the stress of being part of one or more marginalized groups with little to no support or basic access in society. Weight stigma itself is deadly. Research shows that weight-based discrimination increases risk of death by 60% (Sutin, et al, 2014).
Dieting also poses serious health risks. The reason that these weight loss drugs are so successful by comparison is that dieting is unsustainable and does not lead to prolonged weight loss. Over 50 years of research conclusively demonstrates that virtually everyone who intentionally loses weight by manipulating their eating and exercise habits will regain the weight they lost within 3-5 years, and 75% will regain more weight than they lost (Mann, et al, 2007). Evidence suggests that repeatedly losing and gaining weight is linked to cardiovascular disease, stroke, diabetes, and altered immune function (Tomiyama, et al, 2017). If most fat people have historically tried to lose weight their whole lives through dieting, this has major implications on overall health. Prescribed weight loss is also the leading predictor of eating disorders (Patton, et al, 1999).
Another factor that may be impacting fat people’s rate of mortality is that they are being mistreated at the doctor’s office. I have personally heard dozens of stories about doctors refusing to treat or investigate a problem that a fat person came in for until they lost a certain amount of weight, only to discover years later that the problem was unrelated to their weight and has progressed severely because it went untreated. Fat people are often mistreated and looked at with disgust and disdain in medical settings, leading them to avoid going to the doctor in shame or fear of abuse. This can seriously worsen health issues. Fat stigma in the medical establishment (Puhl, et al, 2012) and society at large arguably (Engber, 2009) kills more fat people than fat does (Teachman, et al, 2003), (Chastain, et al, 2009), (Sutin, et al, 2015). This impact is too significant not to be taken under consideration.
Anti-Fatness as Anti-Blackness
The issue of anti-fat bias is directly rooted in white supremacy. The ideal thin body was constructed as a marker of whiteness and “purity” before any of this was ever made to be about health. Dr. Sabrina Strings has spent her career studying this history. In her book, Fearing the Black Body: The Racial Origins of Fat Phobia, Dr. Strings discusses how constructions of race led to the thin ideal. “Over the decades, the rise in biracial children would break down the way that slave owners saw Blackness and whiteness. To combat the hypocrisy they created, owners invented new ways to dehumanize the enslaved population. They made a calculated decision to start putting more value on white physiques versus Black ones. In her research, Strings found that Black women’s bodies were otherized even more than Black males. For colonizers who hadn’t seen diverse body types before, they quickly categorized the Black female figure as ‘deviant,’ ‘greedy,’ and ‘overtly sexual.’ The fact that we still use these terms to describe fat bodies today is all the evidence we need to understand that fatphobia is directly linked to racism, not health. This mindset was also strengthened by Protestantism. Slave owners looked for any way to prove their power over the enslaved people, and they frequently used religion as ‘proof’ of their racist superiority. Additionally, Protestant belief encouraged various ways to become closer to God, which included eating as little as possible. This would resonate the most with white women. They had as much to do with perpetuating fatphobia as their husbands. White women were desperate to show their own power against Black women on the plantation, and the difference between their bodies was the perfect rift. And so began the centuries-old belief that thinness is beautiful, and fatness is ugly” (Sassenrath, 2023).
Revisiting the Journal with Context
Thinness has been an important value throughout history in the United States. Our positive associations with thinness and negative associations with fatness have led to a collective schema that is black and white, good versus bad, beautiful versus ugly, healthy versus unhealthy, and life versus death. This has led the FDA to approve Wegovy as a weight loss drug with haste, after just sixteen months of testing. It is known that going off the drug will result in rapid weight regain, so patients are expected to be on it for the rest of their lives when there have been no long-term studies. We do not yet know if the drug will have long-term effects, yet it has been approved for kids as young as twelve (FDA, 2021). As of July 2024, Novo Nordisk has a market cap of $633.01 billion (Marketcap).
Wegovy is prescribed along with diet and exercise, which has been proven to lead to weight regain and eating disorders. Patients are being prescribed Wegovy and Ozempic when they are fat, but otherwise metabolically healthy. If this drug is truly a game changer for public health, we should be measuring how patients' health improves over the long-term rather than how much weight they lose. For example, if these drugs improve heart health, they should be prescribed as a heart health medication for patients with heart disease, rather than prescribed as a weight loss fix based on body size alone. With the evidence we have, we know it is possible to be fat and healthy, so these drugs may be solely cosmetic in many cases.
Future
If we want to improve the lives of fat people, we will remove barriers to care, not try as hard as we can to make all fat people disappear. That will never happen. If we truly cared about the well-being of fat people and not their disappearance, we would work to dismantle the systems that oppress them and abolish anti-fatness.
Currently, fat people have next to no legal protections for being discriminated against (NAAFA, 2023). Fat people are denied housing, (Kariss, 1977) jobs, and receive less pay and promotions legally because of their size (The Economist). They are denied access to clothing, seating, transportation, and other human rights because infrastructure has been designed to exclude them. Fat people have less likelihood of receiving a fair trial (Beely, 2013), and are denied necessary surgeries (Barrett, 2022) ––but not weight loss surgery that amputates the digestive tract. Fat people are denied gender-affirming care (Conley, 2023), in vitro fertilization and reproductive healthcare (Muir, 2024), even adopting children (Carter, 2009). Fat children have been removed from their loving parents because when their diets failed, it was seen as neglect (Badshah, 2021). Fat people have disproportionately high suicide rates (Wagner, et al, 2013), and are facing medical malpractice and mistreatment (Kolata, 2016).
Can a drug fix that?
References
Karasu, Sylvia. Adolphe Quetelet and the Evolution of Body Mass Index (BMI). Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/blog/the-gravity-of-weight/201603/adolphe-quetelet-and-the-evolution-of-body-mass-index-bmi 2016, March 8.
“Quetelet, Adolphe.” Eugenics Archive, www.eugenicsarchive.ca/connections? id=5233cb0f5c2ec5000000009c. Accessed 5 July 2024.
Rey-López JP, de Rezende LF, Pastor-Valero M, Tess BH. The prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity: a systematic review and critical evaluation of the definitions used. ObesRev.2014 Oct;15(10):781-90. doi: 10.1111/obr.12198. Epub 2014 Jul 16. PMID: 25040597.
Matheson EM, King DE, Everett CJ. Healthy lifestyle habits and mortality in overweight and obese individuals. J Am Board Fam Med. 2012 Jan-Feb;25(1):9-15. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2012.01.110164. PMID: 22218619.
Butler, Kiera. “Why BMI Is a Big Fat Scam.” Mother Jones, 25 Aug. 2014, www.motherjones.com/politics/2014/08/why-bmi-big-fat-scam/.
Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000 Aug;106(4):473-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI10842. PMID: 10953022; PMCID: PMC380258.
Cofield SS, Corona RV, Allison DB. Use of causal language in observational studies of obesity and nutrition. Obes Facts. 2010 Dec;3(6):353-6. doi: 10.1159/000322940. Epub 2010 Dec 10. PMID: 21196788; PMCID: PMC3280017.
Medvedyuk, S., Ali, A., & Raphael, D. (2017). Ideology, obesity and the social determinants of health: a critical analysis of the obesity and health relationship. Critical Public Health, 28(5), 573–585. https://doi.org/10.1080/09581596.2017.1356910
Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2000 Aug;106(4):473-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI10842. PMID: 10953022; PMCID: PMC380258.
Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009 May 26;53(21):1925-32. doi: 10.1016/ j.jacc.2008.12.068. PMID: 19460605.
Uretsky S, Messerli FH, Bangalore S, Champion A, Cooper-Dehoff RM, Zhou Q, Pepine CJ. Obesity paradox in patients with hypertension and coronary artery disease. Am J Med. 2007 Oct;120(10):863-70. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.05.011. PMID: 17904457.
Mullen JT, Moorman DW, Davenport DL. The obesity paradox: body mass index and outcomes in patients undergoing nonbariatric general surgery. Ann Surg. 2009 Jul;250(1):166-72. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181ad8935. PMID: 19561456.
Tseng CH. Obesity paradox: differential effects on cancer and noncancer mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis. 2013 Jan;226(1):186-92. doi: 10.1016/ j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Sep 21. PMID: 23040832.
Sutin, A. R., Stephan, Y., & Terracciano, A. (2015). Weight Discrimination and Risk of Mortality. Psychological Science, 26(11), 1803-1811. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797615601103
Tomiyama, A Janet, et al. “Long‐term Effects of Dieting: Is Weight Loss Related to Health. Socialand Personality Psychology Compass, 6 July 2017, escholarship.org/uc/item/0tv27311.
Mann T, Tomiyama AJ, Westling E, Lew AM, Samuels B, Chatman J. Medicare's search for effective obesity treatments: diets are not the answer. Am Psychol. 2007 Apr;62(3):220-33. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.62.3.220. PMID: 17469900.
Patton GC, Selzer R, Coffey C, Carlin JB, Wolfe R. Onset of adolescent eating disorders: population based cohort study over 3 years. BMJ. 1999 Mar 20;318(7186):765-8. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7186.765. PMID: 10082698; PMCID: PMC27789.
Puhl, Rebecca, and Kelly D. Bronwell. “Bias, Discrimination, and Obesity.” Obesity Research, 6 Sept. 2012. doi.org/10.1038/oby.2001.108
Engber, Daniel. “Glutton Intolerance: What If a War on Obesity Only Makes the Problem Worse?” Slate, https://slate.com/technology/2009/10/the-health-effects-of-discrimination-against-fat-people.html 5 Oct. 2009.
Teachman, B. A., Gapinski, K. D., Brownell, K. D., Rawlins, M., & Jeyaram, S. (2003). Demonstrations of implicit anti-fat bias: The impact of providing causal information and evoking empathy. Health Psychology, 22(1), 68–78.
Chastain, Ragen. “So My Doctor Tried to Kill Me.” Dances With Fat, https://danceswithfat.org/2009/12/15/so-my-doctor-tried-to-kill-me/ 15 Dec. 2009.
Sutin AR, Stephan Y, Terracciano A. Weight Discrimination and Risk of Mortality. Psychol Sci. 2015 Nov;26(11):1803-11. doi: 10.1177/0956797615601103. Epub 2015 Sep 29. PMID: 26420442; PMCID: PMC4636946.
Sassenrath, Jenna. “Anti-Blackness Is Anti-Fatness in ‘Fearing the Black Body.’” Bookstr, bookstr.com/article/anti-blackness-is-anti-fatness-in-fearing-the-black-body/ 26 July 2023.
“Novo Nordisk (NVO) - Market Capitalization.” CompaniesMarketCap.Com - Companies Ranked by Market Capitalization, companiesmarketcap.com/novo-nordisk/marketcap/ 2024.
Commissioner, Office of the. “FDA Approves New Drug Treatment for Chronic Weight Management, First since 2014.” U.S. Food and Drug Administration, FDA, www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management-first-2014. 5 July 2024.
Karris, L. (1977). Prejudice against Obese Renters. The Journal of Social Psychology, 101(1), 159–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224545.1977.9924002
“Campaign for Size Freedom.” NAAFA, 2023,
naafa.org/sizefreedom. 5 July 2024.
“The Obesity Pay Gap Is Worse than Previously Thought.” The Economist, The Economist Newspaper, www.economist.com/finance-and-economics/2023/11/23/the-obesity-pay-gap-is-worse-than-previously-thought. 5 July 2024.
Elizabeth Beety, Valena (2013) "Criminality and Corpulence: Weight Bias in the Courtroom," Seattle Journal for Social Justice: Vol. 11: Iss. 2, Article 4. https:// digitalcommons.law.seattleu.edu/sjsj/vol11/iss2/4
Berrett, Martyn. “More Obesity Discrimination: The NHS Will Deny Non-Urgent Surgery to Obese Patients.” Healthier Weight, 24 Nov. 2022, www.healthierweight.co.uk/blog/more-obesity-discrimination-the-nhs-will-deny-non-urgent-surgery-to-obese-patients/.
LaRosa, John. “U.S. Weight Loss Industry Grows to $90 Billion, Fueled by Obesity Drugs Demand.” Market Research Blog, The Freedonia Group, Inc., 2 May 2024, blog.marketresearch.com/u.s.-weight-loss-industry-grows-to-90-billion-fueled-by-obesity-drugs-demand.
Conley, H. “Studies Show Top Surgery Is Safe for FAT Patients, but Some Surgeons Still Mandate Weight Loss.” STAT, 25 July 2023, www.statnews.com/2023/06/02/top-surgery-safe-fat-patients/.
Muir, Becca. “Opinion: Women with Obesity Are Often Restricted from IVF. That’s Discriminatory.” NPR, 14 Jan. 2024, www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2024/01/14/1224546666/opinion-women-with-obesity-are-often-restricted-from-ivf-thats-discriminatory.
Carter, Helen. “Too Fat to Adopt - the Married, Teetotal Couple Rejected by Council Because of Man’s Weight.” The Guardian, Guardian News and Media, 13 Jan. 2009, www.theguardian.com/society/2009/jan/13/adoption-rejected-couple.
Badshah, Nadeem. “Two Teenagers Placed in Foster Care after Weight Loss Plan Fails.” The Guardian, Guardian News and Media, 11 Mar. 2021, amp.theguardian.com/society/2021/mar/10/two-teenagers-placed-in-foster-care-after-weight-loss-plan-fails.
Wagner B, Klinitzke G, Brähler E, Kersting A. Extreme obesity is associated with suicidal behavior and suicide attempts in adults: results of a population-based representativesample. Depress Anxiety. 2013 Oct;30(10):975-81. doi: 10.1002/da.22105. Epub 2013 Apr 10. PMID:23576272.
Kolata, Gina. “Why Do Obese Patients Get Worse Care? Many Doctors Don’t See Past the Fat.” The New York Times, The New York Times, 26 Sept. 2016, www.nytimes.com/2016/09/26/health/obese-patients-health-care.html.
#fat liberation#systemic anti fatness#systemic fatphobia#medical fatphobia#medicalized fatphobia#fat activism#fat acceptance#anti fat bias#fatphobia#essay
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fat Liberation Mini Zine
You've always wanted to spread the word about Fat Liberation, but didn't know how? Well, you and me both. And then a few months ago I had the idea to use the results of my research to create a mini zine, intended to inform people about some of the basics of Fat Liberation. And now it's finally done!

While I did my research on Fat Liberation in the US, I don't actually live there and wanted to make a zine that fits more accurately for Germany. Most parts are still identical, but especially when it comes to literature or modern day organisations, there are some differences.


(It comes in an English and a German version.)
Guessing that the picture quality might not be very sufficiant for printing these out, you can get a PDF version here. The folder also includes a Word document version, in case anyone wants to translate it or use it as a basis to create a version specific to their own country.
Here you can see how to properly fold it into a mini zine:
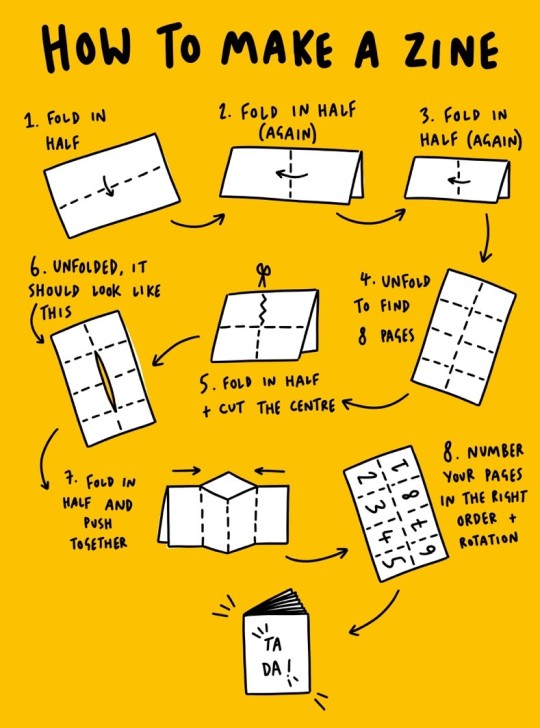
You can print as many of them as you want and spread them whenever you want - hand them out at events, ask your local businesses to display them, sneak them into books in your local library or bookshop, ...
A big thank you to @fatliberation for offering advise and a ton of research of their own to help me out in creating this. (The flag on the front page is also their design 💙🐋)
134 notes
·
View notes
Photo
Same, even me an asian id reject a fatass reall quick!

Id take a thi dude in a heartbeat.
202 notes
·
View notes
Text
Socialists, get into fat liberation theory right the fuck now. I am speaking as a fellow dirty commie, DO IT.
You all like to lump fatness into either the category of "product of bourgeoisie decadence" or "side effect of capitalism forcing us to eat bad food" when neither is the actual case.
Fat people exist in all social classes and all walks of life, often regardless of individual choices.
Fat people are victims of capitalist exploitation at the hands of the multi billion dollar diet and weight loss industry that pushes eating disorder behavior and unnecessary surgeries on to us all in the name of profits.
Fatphobia ties into beauty standards that capitalists use to manipulate people into hating their bodies so they can be sold beauty. Think about how many of the ads you get every day are for weight loss.
#socialism#leftism#leftist#communism#anti capitalism#capitalism#late stage capitalism#beauty standards#anti fatness#anti fatphobia#fatphobia#fat positive#fat activism#fat liberation#anti diet#anti diet culture
6K notes
·
View notes
Text

From the zine “Fat Is Beautiful” by Crystal Hartman
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
the fact that fat people are made to feel bad about everything down to how loud or hard they are breathing says a lot about this society
#plus size blogger#softestjilly#fat acceptance#fat activism#fat liberation#fat libreration#cw fatphobia
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
The number of times I've earnestly seen the take "but it's good for fat people to be mean to them! It motivates them to lose weight!"
Also whenever you provide even light pushback that maybe bullying people does not magically make them skinny but instead makes them depressed, they immediately demand scientific sources as if "bullying fat people is good for them" is scientific concensus and you therefore owe them a peer reviewed paper.
No babe I'm so sorry you're not actually doing people a service by being an asshole to them you just want an acceptable target and have decided that fat people are one. You don't get to be a bad person until you've produced 3 peer reviewed meta analyses that being a dick to random fat people improves their health, OK? I'm sure people will thank you for your invaluable service of being an asshole.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
anti-fatness is not just body shaming.
anti-fatness is discrimination. anti-fatness is having next to no legal protections for being discriminated against. anti-fatness is being denied housing, jobs, receiving less pay and promotions (legally) because of your size. anti-fatness is being denied access to clothing, seating, transportation, and other human rights because infrastructure has been designed to exclude you. anti-fatness is less likelihood of receiving a fair trial. anti-fatness is dehumanization. anti-fatness is being denied necessary surgeries, but not surgery that amputates the digestive tract with the intent to starve and shrink you (it doesn’t work either). anti-fatness is mutilation. anti-fatness is being subject to torture devices that bolt your mouth shut. anti-fatness is being told by close friends, family, and professionals that you are better off living with an eating disorder or other life-threatening illness. anti-fatness sells you starvation as a guaranteed opt-out of oppression, but doesn’t tell you that bodies will always regain weight to survive. anti-fatness blames and punishes you for failing at an achievement that is quite literally impossible. anti-fatness is a $90 billion dollar industry. anti-fatness is being denied gender-affirming care. anti-fatness is being barred from in vitro fertilization and reproductive healthcare. anti-fatness is being barred from adopting children. anti-fatness is being removed from your loving parents because they couldn’t make you thin. anti-fatness is intentionally starving your own baby so they won’t get fat. anti-fatness is disproportionately high suicide rates. anti-fatness is being killed at the hands of medical neglect and mistreatment. anti-fatness is the world preferring a dead body over a fat one.
#i’m sorry that my fellow fat followers have to see this. you all already know it. you’ve lived it.#spread this like wildfire so that thin people can wake up.#resources#tw anti fatness#tw fatphobia#tw medical fatphobia#tw anti fat bias#tw anti fat violence#fat liberation#fat acceptance#fatphobia#fat activism
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey You reading this!
check yourself and see if your sucking in your tummy
if you are let it go, release that tension! LET THAT TUMMY OUT💕
unlearn hiding yourself!
if your already letting it go, carry on, continue scrolling you’re good to go!
#anti fatphobia#fat acceptance#fat liberation#fat positive#fat positvity#fat pride#wg text#feederist#fat#fat is not a bad word#feedists for fat liberation#fat is beautiful#fat activism#fat belly#fat girls#fatboy#feedee encouragement#feedee belly#feeding kink#ethical feedism#feedist thoughts#queer feedee#queer feedism#trans feedee#trans feedism#feedee girl#stuffed feedee
591 notes
·
View notes
Video
Legit it scared me how they get so reckless like this paired up with an enabler family/friend/,s/o then the one making sence is another friend or the doctor of all people yet these fatasses stay ....Fat ....Trapped in your own body everyday functions is hard to move then the only "Joy" is a shit load of heavy foods or Big portion ...now thats hell ;-;
youtube
If this show cant scare you out of your bad diet and non existent exercise- I dont know what will shy of a near death experience.
127 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*for decades, fat people in media are constantly shown as bullies even tho fat people are more likely to be bullied and harassed in real life*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*fat people in communities and fandoms are pushed out of them due to constant fatphobic harassment*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*fat people not being able to show their talents or interests online without people constantly bringing up their weight*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*fat people struggling to find clothes in their size especially online and when they do find clothes in their size their either overpriced or look ugly*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*people actually debating whether or not fat people should exist and even saying that fat people are a disease*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*fat people getting called cows, pigs, literal animals*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*skinny people being put in fat body suits for movies, tv shows, etc instead of just getting a fat actress*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*the ongoing dangerous stereotype about fat people being gr00mers/p€d0philes that just gets reduced to a joke*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*fat characters in books will be made skinny for movies, tv shows, etc*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
*fat people die every day due doctors not actually helping them until they lose weight*
“Fat people aren’t oppressed 🙄”
Do you guys not see a pattern here? Cause I see it and it's clear as day
#dont even get me started on fat poc#fat liberation#fat activism#fat acceptance#fatphobia#medical fatphobia#anti fatphobia#anti fat bias#anti fatspo
300 notes
·
View notes
Text

f2u, no credit needed!
#tw eyestrain#tw blinkies#tw blinking#tw flashing#blinkie#blinkies#resources#resouce#page deco#page decor#web graphics#gif#pixel#fat positivity#fat positive#fat pride#fat liberation#fat acceptance#fat activism#fat is not a bad word
173 notes
·
View notes
Text


our love story. 💍🩷🌈✨
fat people get engaged.
fat people get married.
fat people are loved, desired, needed, and wanted.
#softestjilly#plus size blogger#fat positvity#fat posi blog#fat acceptance#fat liberation#body positive#body neutrality#fat activism#queer couple#plus size couple#pride month#proposal
951 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finding art of fat people is so hard that even though I’ve promised myself that the moment I see a local artist with a print of a fat person I’ll buy the piece, I still haven’t managed to find a single artist locally (and I struggle to find artists who do so even internationally) who makes art of fat people.
Like I will purposfully go around in a market looking out for art of fat people, and I see no art of anyone who isn’t thin. I’ve also tried looking up art of fat bodies from local artists on the internet, and I still haven’t found anything.
And while I don’t personally blame any specific artist for doing this, it gets a bit more annoying when a small business that’s centered around feminist or leftist art, still has no art of fat people.
(Love you artists but kindly do better guys!)
#fat liberation#anti fatphobia#fat acceptance#fat is not a bad word#anti fat bias#fat positive#fat positivity#being fat#fat is beautiful#fatphobia#artwork#art#artists on tumblr#fat pride#fat activism#fat people
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
Important reminder that malnourishment, while often can be visible on the outside, is a STATE, not a LOOK. Fat people can be malnourished. Malnourishment ≠ skinny. Malnourishment means a person isn't getting all the necessary nutrients their body needs to keep itself healthy and energized. Already fat people will not automatically become skinny if they become malnourished, for the exact same reasons that many fat people can't/wont/have difficulty becoming skinny in the first place. Which is normal. It varies by person.
We need to abolish the idea that you can tell a person's health by whether they're fat or not.
Speaking for myself, I've actually become fatter even though I'm malnourished (due to parental control, disability and mental illness). This is because 1. the foods easily available to me in my current condition are often high calorie and fatty - partly because I crave more calories and fats due to my imbalanced diet and exhaustion. And 2. Because my ability crashed heavily within the last two years and I don't have enough energy to exercise regularly, or do so without pain and exhaustion.
Malnourishment is so much more than weight. It's lack of fibres, vitamins, essential nutrients, iron, and much more. It's Eating just enough to not feel hungry, instead of eating so you feel satisfied and full.
130 notes
·
View notes