#Elizabeth Kortright
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
You mention in a reblog that it would have been very easy for Hamilton's family-in-law and enemies to discover his real birthdate. Genuinely, though - how? Records, if they were accurate or even kept, were inaccessible to them. Hamilton's West Indies contacts were all clearly muddled about his birth year (given the many contradictory answers - and frankly, I wouldn't know off hand when many of my close friends were born either). Surely his lying about it would have been trivially easy?
I hadn't meant by records, seeing as how we struggle to this day to find any concrete records of Hamilton's true birthyear. But yeah, his contacts. A good, but small, handful of Hamilton's associates from the West Indies were also located at New York, or the Colonies in general—And others at least remained in contact with him or his family. To name a few, Hamilton's father and cousin, Anne Mitchell, remained in contact with him, and Anne even visited and wrote to Eliza after his death. We have scarce surviving correspondence between Hamilton and his father, but if he was planning to let him move to NYC to live with them; it can be speculated that Eliza may have written a few letters to him, or he sent his own to others in New York.
Or the can of worms Edward Stevens' offers, he was Hamilton's boyhood best friend from St. Croix, and attended King's College where they attended the same class club and had shared some of the same friends, Nichoals Fish, Robert Troup, etc. If there was one person who we had to trust to know Hamilton's birthyear out of the surviving relatives or friends he had at the time, it would have likely been Stevens. Stevens's brother-in-law, James Yard, knew a good amount about Hamilton and his childhood considering later he was able to provide information for Timothy Pickering, who was planning to write a biography about Hamilton. The same one that mentions the possibility of Thomas Stevens being Hamilton's real father. Additionally, there is the Kortright family; Monroe's wife, Elizabeth Kortright Monroe, was a cousin of Hester Kortright Amory, Stevens's wife. And Elizabeth K. Monroe's uncle was one of Hamilton's employers from the Island, Cornelius Kortright, who worked with Nicholas Cruger. He helped handle Hamilton's financial dealings when he first made it to the Colonies. With all this being said, I highly doubt everyone was just keeping this a secret. Especially with their close relations to James Monroe, one of Hamilton's rivals, who could have easily used it against him.
And going back to Cruger, he would have definitely known Hamilton's contrasting age considering he was his employer at the Cruger Counting house. He also moved back to New York and saw Hamilton again, even once there were rumors spreading by the press that Hamilton could become governor with him as lieutenant governor in 1795. Catharine Church, the eldest Church daughter, married Bertram Peter Cruger, Cruger's son.
And all of Hamilton's associates from the Colonies roughly followed the 1757 belief. But you are right saying; “and frankly, I wouldn't know off hand when many of my close friends were born either.” Because as @46ten as recently added on, we are putting way too much emphasis on a birth year than what those of that day would. We value birth dates more strongly than when even as recently as a century ago, we did not. Today birth dates are now widely used for identification, but back when containing written documents was more of a hassle (As finding documents from Nevis has proven), not many were inclined to do such. In a day in age, where many families didn't even celebrate birthdays often, it wasn't much more than a passing thought for most. There is even a humorous story of Eliza forgetting JCH's birthday when he was young;
John is as industrious as usual and this Evening has ascertained that he is not more than twelve last August. I had thought him to have been thirteen but he is not more than twelve.
Elizabeth Hamilton to Philip Schuyler, [1804]
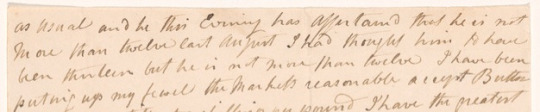
So, not only is it likely Hamilton wasn't even sure of his own birth year, but it wasn't a large deal back then. Does that mean it never would have been brought up? No, and I'm sure with all the previously mentioned close ties to Hamilton's in-laws and rivals, something would have noticeably not connected if so. And I doubt this many people were just in on Hamilton's whole facade. But it seems like a bunch of worthless mental gymnastics and risky lie for Hamilton to maintain for nearly 30+ years of his life, especially when many were out looking for anything to use against him.
#amrev#american history#historical alexander hamilton#edward stevens#james hamilton#anne mitchell#james yard#elizabeth kortright monroe#james monroe#cornelius kortright#nicholas cruger#history#birth year#queries#sincerely anonymous#cicero's history lessons#18th century#alexander hamilton
42 notes
·
View notes
Note
Wasn't Monore his uncle in law?
Yeah if that's what you call it. Alex Jr's wife was Eliza Knox. Her mother was Mary Kortright Knox. Mary's younger sister was Elizabeth Kortright. Elizabeth married James Monroe and boom. By marriage, Eliza Knox is James Monroe's niece.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Right in the centre of my mind: 06.1. In my head I did everything right
Thomas Jefferson X Black!O.C
Ch.6.1
Warnings:
Mentions of sex
Swearing/cursing
Mentions of alcohol use
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
5 years.
That's how long Iman doesn't speak to Thomas for. Her reasoning? She didn't need that kind of emotional scarring at such a young age. It's easy for her to distance herself because she stops taking the bus. Her mother is suprised by this decision but Iman seems sure about it. It doesn't take much effort to pretend he doesn't exist at school because after all, he's a year older. She changes her number and always makes sure she's never home on weekends.
After his senior year, she thinks she's made it out alive after she hears that he'll be moving to France. But he doesn't. Instead Lafayette does and Thomas goes to Yale. Coming around the neighborhood every second weekend. Even becoming friends with her friends and hanging out at the shack more often.
She can barely breathe anymore. His presence intoxicates her every time, so immediately when he shows up, she goes home. It doesn't stop her heart from falling though. Doesn't matter who she dates or goes to senior prom with. He's right in the centre of her mind.
So she goes to Oxford after high school. Doesn't tell anyone about it either.
She dates twice. Both girls.
The first one is Henrietta Fox-Strangeways. Otherwise known as Harriet. Comes from a Christian home which suprises Iman. Absolute rebel with a cause, activist for LGBTQ+ rights, social studies major, vegan and all around nice girl. They only last 3 months. They don't talk after the breakup.
The second one is Amelia Osborne. Skater girl, dance major, music minor, lives to break the rules, tattoo artist by night (they met when Iman was getting the words "Emotional sexual bender" in Japanese under her boob with Harriet), party animal, but generally also a nice girl. They last 1 year. They remain close friends (with benefits) after the breakup.
Harriet and Iman broke up because of her lack of commitment and sudden closeness with Amelia. While Amelia and Iman break up due conflicts of interest.
That's what both girls believed.
Iman knew they both somewhat ended because she couldn't stop thinking about Thomas.
So she doesn't return home after Freshman year. Instead she spends her summer in an apartment she's sharing with Angelica Schuyler, getting wasted with the British.
Sophomore year rolls around pretty quickly and she re-establishes communication with her friends in New York. She'd have to go back eventually so why not reconnect with them.
She explains herself and they accept her bullshit excuse with open arms. Which is why it's not awkward when she spends the next summer in New York. She thankfully never encounters Thomas at the shack. She does however encounter Lafayette. Who, if Iman was being honest looked far better than he did in high school.
They reconnect, but it's mostly physical. Coincidentally, they've both sworn off relationships for a while. But it doesn't stop them from having casual sex.
For a second, she forgets about Thomas.
For the first time in 5 years, her heart, mind and soul are at peace.
Tagging: @ramp-it-up @oh-so-coco @sebastianabucknettastan @daveedsfigs
Let me know if you wanna be on the taglist❤️
#Hamilton#Hamilton the musical#Thomas Jefferson#Thomas Jefferson x reader#Thomas Jefferson fanfiction#Alexander Hamilton#Eliza Schuyler#Angelica Schuyler#Peggy Schuyler#Maria Reynolds#Martha Jefferson#Elizabeth Kortright#James Madison#James Monroe#Aaron Burr#John Adams#John Laurens#Hercules Mulligan#Lafayette
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Letter by Virginie de La Fayette
I was really pleased to find this letter the other day. It is an undated letter by La Fayette’s youngest child, Marie Antointte Virginie de La Fayette Lasteyrie du Saillant (she was already married at that point) to a friend of hers, Madame Hay. Madame Hay was Elizabeth Kortright Monroe Hay, oldest daughter of President James Monroe. The matters discussed in this letter are primarily concerning Virginie’s father, the Marquis de La Fayette. I am so happy about this find because it is the first letter by Virginie that I have ever seen and while we have the book that she and her mother wrote together, I am not aware of any other handwritten document that has been published beside this letter.
Ideally, I would have transcribed and translated the document for everybody to read … but I am a bit short on time at the moment and transcribing letters, especially letters written in French, always takes a fair bit of time for me. I furthermore find Vriginie’s handwriting not entirely pleasant and therefor I thought I would share this letter with you all and maybe one of my amazing French (-speaking) friends has the time and is willing to provide a faster transcript than I would be able to do. :-)


Monroe-Hay Family Papers, Special Collections Research Center, Swem Library, College of William and Mary. (03/17/2022).
#virginie de lafayette#marquis de lafayette#la fayette#french history#american history#letter#handwriting#elizabeth kortright monroe hay#james monroe#french#resources#college of william and mary
22 notes
·
View notes
Photo










sophs-style:
Molly Sims (wearing Monique Lhuillier), Kelly Rowland (wearing Nicole + Felicia Couture), Cat Deeley, Rachel Zoe, Kelly Sawyer, Sarah Wright, Monique Lhuillier, Christen Harper, Elizabeth Turner, Anne Marie Kortright, Norah Weinstein and Nicole Williams-English at the 2019 Baby2Baby Gala on Saturday (9th November 2019) at 3LABS in Culver City, CA.
#Molly Sims#kelly rowland#Nicole + Felicia Couture#cat deeley#rachel zoe#kelly sawyer#sarah wright#sarah wright olsen#Monique Lhuillier#Christen Harper#elizabeth turner#anne marie kortright#norah weinstein#Nicole Williams-English#2019 Baby2Baby Gala#appearance#event#outfit#outfits#fashion#style#stylish#celebrity#celebrities#celebrity style#celeb style#celebrity event
24 notes
·
View notes
Photo
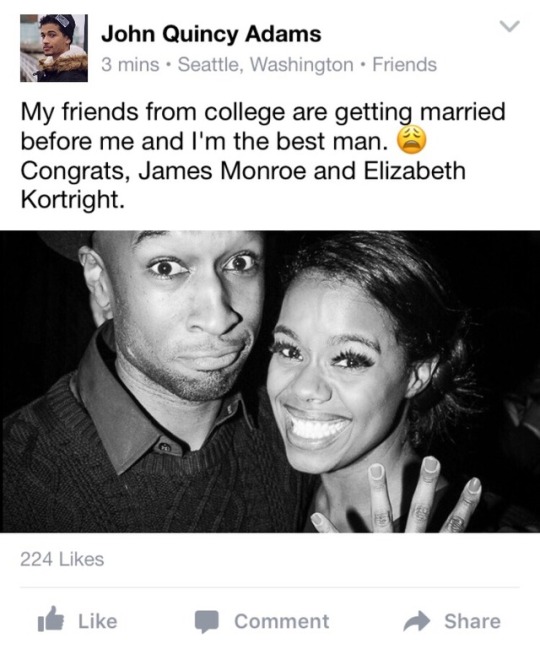
Someone better hold back Marsha’s girlfriend before she does something stupid.
#hamilton#something rotten#1776 musical#anne hathaway#jean paul marat#john quincy adams#james monroe#elizabeth kortright#abigail adams#laura benanti#jordan fisher#lexi lawson#syndee winters#rebecca covington#donald webber jr#usher raymond#charlotte corday#facebook
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Elizabeth Monroe, First Lady of the United States (30 June 1768 - 23 September 1830)
#elizabeth jane kortright#elizabeth monroe#daughter of lawrence kortright#wife of james monroe#first lady of the united states#hiistory#women in history#18th century#19th century#art
8 notes
·
View notes
Quote
...Genl Mifflin’s, McDougall’s, Heard’s, Wadworth’s, and Fellow’s Brigades, and the Brigades under the Command of Cols. Silliman & Douglass, are to have each a regiment in the Field this evening, by Mr Kortright’s house.
General Orders, 18 September 1776 [x]
General Joseph Spencer’s headquarters was at a house rented by Lawrence Kortright in the area east of present-day Amsterdam Avenue near 148th Street. The grand parade ground of the army was in an adjoining field. Elizabeth Monroe was only eight at this time when her father housed American soldiers in their family home that would burn to the ground in 1778. The home was near Harlem Heights, New York and it had served as a headquarters for American officers in the autumn of 1776.
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo

T H E F I R S T L A D I E S #5 // Elizabeth Monroe & Eliza Monroe Hay
One of six children, Elizabeth Jane Kortright was born into a wealthy New York merchant family in 1768. She was educated by her mother and paternal grandmother and was probably given lessons in French, dancing, music, and literature, subjects considered appropriate for a young lady of her class. Elizabeth was from an early age seen as elegant and gracious. Her mother died when she was just nine years old, and the family’s home partially burned down during the American Revolution the following year. After the war ended, Elizabeth caught the eye of a young Continental Army officer from Virginia named James Monroe. The two were married in February 1786; Elizabeth was just seventeen.
The Monroes’ first child, a daughter named after her mother but called “Eliza,” was born that December. The little family lived in Philadelphia and Virginia before moving to Paris in 1794 when Monroe was appointed Minister to France. Regarded as beautiful, fashionable, and well-mannered, Elizabeth was popular in France, where both she and her young daughter flourished. She famously intervened on behalf of Adrienne de Noailles, the wife of her husband’s friend and American hero Lafayette, who was imprisoned during the infamous Reign of Terror. Eliza meanwhile attended the school established by Henriette Campan, where she befriended Hortense de Beauharnais, Napoleon Bonaparte’s stepdaughter and the future queen of Holland. The Monroes returned to Virginia in 1796. Elizabeth then had two more children: a short-lived son and a second daughter, Maria.
Around this time Elizabeth also began suffering from seizures and other health problems which severely limited her social activities. In 1808, Eliza Monroe married prominent Virginia lawyer George Hay. When her father was elected president in 1817, she, her husband, and their daughter moved to Washington. Eliza began stepping into the role usually performed by the president’s wife due to her mother’s ill health. Unlike her mother, however, she was thought to be haughty and even rude by much of Washington society. She refused to call on the wives of foreign diplomats, and the presidential social circle grew much more exclusive than before under her influence. Her self-important behavior, influenced by her time in Paris living with daughters of the French aristocracy, was at odds with the warmer and less formal conventions in place during previous administrations.
The extent of Elizabeth Monroe’s political influence–unlike that of Abigail Adams and Dolley Madison–is unknown: her husband burned their correspondence after her death. Her health continued to decline following the end of Monroe’s presidency, and she died in 1830 at the age of 62. James Monroe died less than a year later. After his death, the now-widowed Eliza left the United States. She returned to her beloved France and retired to a convent, where she lived until her death in 1840, aged 53.
#elizabeth monroe#james monroe#american history#first lady#historyedit#*firstlady#don't let the length of this text mislead you#the edit isn't great and that's partially b/c these are by far the least-interesting ladies in this series so far#and have the least available information about them too
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
…wait a moment. looking through the list of the family, I think Elizabeth Monroe may have been distantly related to Edward Stevens’ wife
#again another useless fact if this turns out right#elizabeth monroe#edward stevens#hester amory kortright
4 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you know anything about Eliza P. Knox and her relationship with Alexander Hamilton Junior?
Love your blog, thank you for everything<3
After serving as Aide-de-camp to his late father's friend, General Morgan Lewis, until June of 1815, Alexander resumed law practice and “paid his addresses to” Eliza P. Knox. [x] Eliza was the daughter of Thomas (Records sometimes name him William) Knox and Mary Hester “Kortright” Knox. Mary was the sister of Elizabeth Monroe, James Monroe's wife. And Knox was at that time a leading merchant in New York City. Her birthdate and location of birth are both unknown, unsubstantial sources vary between her birth year being around 1796 or 1801.
In 1817, Alexander married Eliza. According to John Pintard, Eliza and Alexander eloped and ran away from the Knoxs' initially, before matters were resolved;
The father wd not consent & a runaway match ensued. A reconciliation took place a year after, when Prest Monroe visited this city, Mrs Knox, deceased, & Mrs M. being sisters.
Barck, Dorothy C., and Pintard, John. Letters from John Pintard to His Daughter, Eliza Noel Pintard Davidson, 1816-1833. United States, New-York Historical Society, 1940.
It is possible Alexander, perhaps with his wife, went and saw his uncle-in-law - James Monroe - on his deathbed. As he writes devastatingly to James Madison, [30 June 1831];
The newspapers having announced the dangerous indisposition of your much respected friend Col James Monroe, I have the melancoly task of informing you that his death is inevitable, and will most probably take place before this reaches you. Mr Monroe retains entire possession of his mental faculties and with perfect firmness and integrity awaits his demise.
“Alexander Hamilton[, Jr.] to James Madison, 30 June 1831,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Madison/99-02-02-2379. [This is an Early Access document from The Papers of James Madison. It is not an authoritative final version.]
In 1833, Alexander bought from Thomas E. Davis a Federal style townhouse constructed two years prior for his mother and his family in New York City, located at 4 St. Mark's Place in the East Village section of Manhattan, for $15,500. At the same time, Davis purchased The Grange from Elizabeth - age 76 years old - for $25,000. For nine years, from 1833, to 1842, Alexander and his wife Eliza, lived there with his mother, his sister Eliza Hamilton Holly, and her husband Sidney Augustus Holly (Yes, that's three whole Elizas'). The house still survives to this day, and is known as the Hamilton-Holly house.
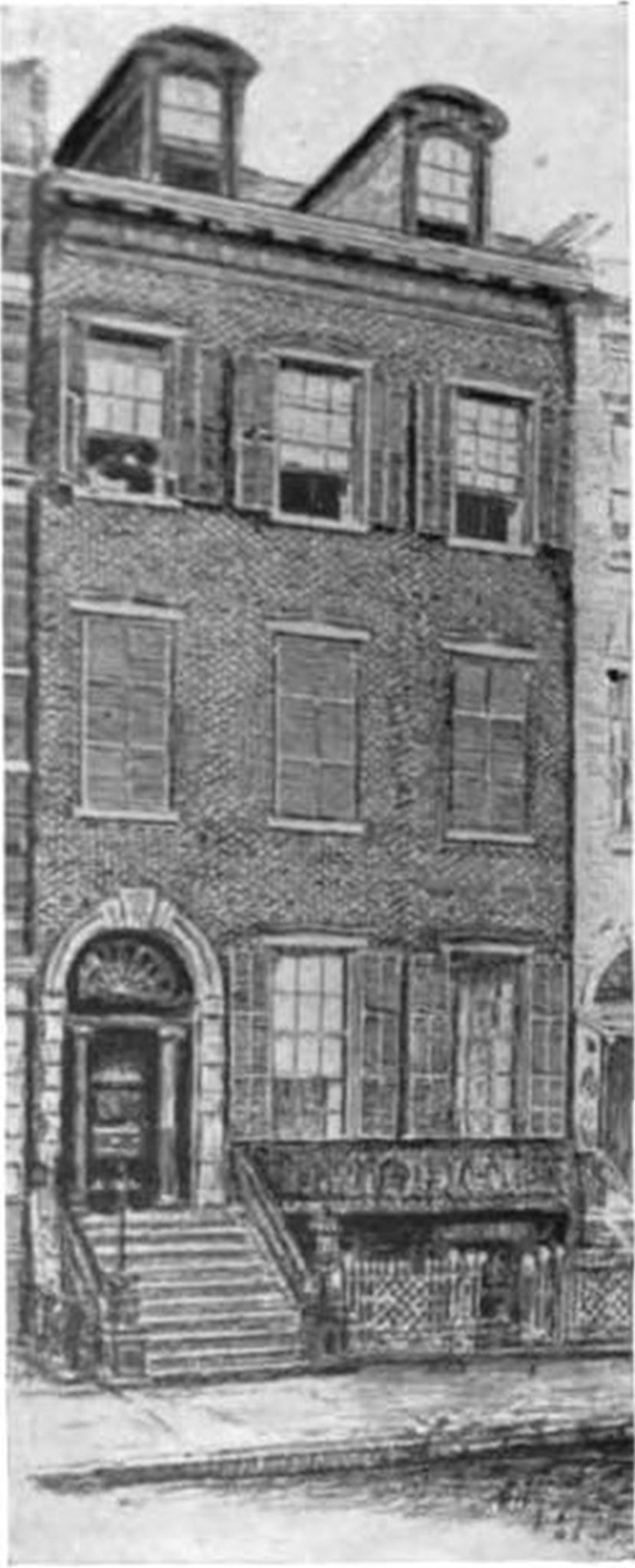
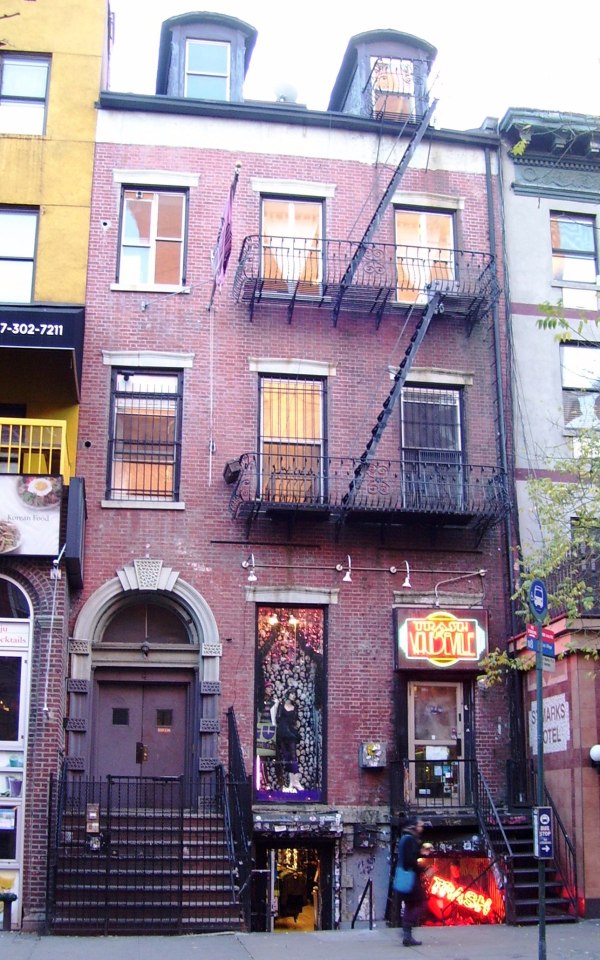


In 1835, Eliza and Alexander drove in a coach and four through the West travelling over four thousand miles. It was on this trip, in Illinois, where he met Abraham Lincoln in a grocery store. Lincoln was reportedly; “lying upon the counter in midday telling stories.” [x]
When Eliza Knox died July 21st of 1871, Alexander moved to New Brunswick, New Jersey. Before residing in New York City, where he lived his last few years before dying August 2nd, 1875, at his home, 83 Clinton Place, in Greenwich Village. The couple seemed to have been happily in love, and never had any children.
Hope this helps, and you're welcome!
#amrev#american history#19th century#alexander hamilton jr#eliza p knox#history#hamilchildren#hamilton children#hamilkids#hamilton kids#hamilton family#queries#cicero's history lessons#lolacatemary
39 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello! I love your blog and find it very informative! Could you write something about AH relationship with James Monroe?
A lovely early friendship torn apart by political rivalry and misunderstandings that descended into harsh accusations, duel invitations, and never-ending Hamilton family hatred for the man? You can read the letters between them that Founders has here. I am unaware of AH ever discussing his opinion on Monroe in greater depth than what I’ve quoted below, and I’m completely unaware if Monroe ever offered a lengthy opinion on AH personally. There’s a new Monroe biography out (James Monroe: A Life by Tim McGrath) that may be more interesting than anything I write about.
But I’ll try. Things must have started out okay between them. They were both at the Battle of Trenton (Monroe was wounded). Monroe then served as aide-de-camp to William Alexander, Lord Stirling, whose brother-in-law was AH supporter William Livingston and daughter was Catherine Alexander, who would marry AH Treasury right-hand-man William Duer. They spent time at Valley Forge together, they both became good friends with Lafayette, etc. AH wrote positively of Monroe in 1779 to John Laurens:
Monroe is just setting out from Head Quarters and proposes to go in quest of adventures to the Southward. He seems to be as much of a night errant as your worship; but as he is an honest fellow, I shall be glad he may find some employment, that will enable him to get knocked in the head in an honorable way. He will relish your black scheme if any thing handsome can be done for him in that line. You know him to be a man of honor a sensible man and a soldier. This makes it unnecessary to me to say any thing to interest your friendship for him. You love your country too and he has zeal and capacity to serve it. 22May1779
With notes of recommendation from Hamilton, Lord Stirling, and Washington, Monroe became a lt. col, but with no field command available (AH certainly sympathized), he decided to resume his studies instead of continuing with the Army. He went on to become a member of the Continental Congress, etc.
In Feb 1786, Monroe (age 27) married Elizabeth Kortright at Trinity Church NY, with Rev. Benjamin Moore presiding (see here for my notes about the Hamiltons’ church affiliation). The Hamiltons may have attended; EH gave birth to Alex Jr. three months later. Elizabeth was the niece of Cornelius Kortright, who was a frequent business partner of Nicolas Cruger, AH’s old boss on St. Croix (AH worked for Kortright & Cruger 1769-1771). So Monroe - as did many others - likely had knowledge of AH’s personal background (and despite the current narrative surrounding AH, at the time almost no one seemed to care or consider AH’s background especially noteworthy; AH also freely introduced his cousins to friends, so it’s not at all clear that he ever thought he had something to hide and offered up the “blemish” of his parents’ relationship/his illegitimacy to several people).
But Monroe was a friend of Jefferson and Madison and ended up on their side politically (Monroe preceded Madison as an anti-federalist). His position in the Senate, and his authorship of articles in response to AH’s articles (written under several pseudonyms) all certainly aggravated AH.
And then there was the matter of Gouverneur Morris. In 1792, Monroe was one of the people trying to block the appointment of G. Morris as U.S. Minister Plenipotentiary to France. (Read an account of Morris’ actions in France/England here and enjoy the pettiness of his leaving Thomas Paine in jail.) In 1794, Monroe replaced Morris as Minister to France (1794 to 1796). He opposed AH as Minister to Great Britain (x) and his reasons are pretty sound and fair-minded (John Jay famously got the position and a treaty named after himself). Monroe was replaced in June 1796, both for anonymously publishing letters criticizing Washington and just not doing as the Federalists wanted, and replaced by Pinckney. Of course, AH played a part behind the scenes in encouraging his replacement and choosing Pinckney.
So by the 1790s they are political rivals, with Monroe writing in defense of Jefferson and Monroe blocking the appointment of AH’s friends/allies and AH interfering with Monroe’s business and encouraging his removal.
But in 1797, things got really personal. Rewinding to Dec 1792, Monroe was contacted by a jailed James Reynolds, who offered information about acting as AH’s agent/partner for speculation on gov’t securities. (Why Reynolds was in jail is a great deal more complicated than this, but I’m skipping all that.) Monroe investigated, got others involved, got the disclosure from AH himself that the money was actually because of blackmail over an affair with Maria Reynolds and produced letters showing this and gave letters and asked for copies of theirs, etc. (I think this part has been written about a lot, so I’m not going to go into further details). Five years later, the following was AH’s recollection of the matter (written to Muhlenberg and Monroe, 17July1797):
It is very true, that after the full and unqualified expressions which came from you together with Mr Venable, differing in terms but agreeing in substance, of your entire satisfaction with the explanation I had given, and that there was nothing in the affair of the nature suggested; accompanied with expressions of regret at the trouble and anxiety occasioned to me—and when (as I recollect it) some one of the Gentlemen expressed a hope that the manner of conducting the enquiry had appeared to me fair & liberal—I replied in substance, that though I had been displeased wtih the mode of introducing the subject to me (which you will remember I manifested at the time in very lively terms) yet that in other respects I was satisfied with and sensible to the candour with which I had been treated. And this was the sincere impression of my mind.
But actually, Monroe didn’t entirely believe AH’s account (”I hate you” point number 1) and conducted his own further interviews with Clingman and Maria Reynolds, which AH would only learn about in 1797 with the publication of pamphlet V of the History, but then Monroe pretty much left it alone, by his own account. He stated he sent all papers about this to a friend in Va (more on this below), and this is where the matter rested publicly for nearly five years.
But it’s not a real secret. By spring 1793, everyone in major political circles knows about it (and EH knew about it, it’s impossible for me to believe she didn’t). In under a week back in Dec 1792, Monroe, Wadsworth, Wolcott, Venable, Muhlenberg, Randolph, Webb, Beckley, and Jefferson all know, and Clingman talks freely. AH had permitted copies of letters to be made (and according to Monroe’s account, knew Beckley’s clerk had copied them), and on and on. BUT, no one is going to publish stuff about it - the confession of an extramarital affair would have been seen as a private family matter that would only serve to disturb “the peace of the family” - indeed, for AH naysayers then and historians since, claiming adultery was a convenient excuse if there was financial impropriety, because the matter wouldn’t be vigorously pursued further. (Philadelphia was a huge city for prostitution, and no one wanted the private sexual escapades of famous men broadcast to the world.) AH, I’m sure, knew everyone knew too, but worked from an understanding that no one was going to try to score political points on something that would expose his wife to public ridicule. But even though it was private, it was still Great Gossip! If AH was willing to taunt TJ publicly about Sally Hemings and, according to TJ, privately about his sexual pursuit/harassment 30 years ago of Elizabeth Moore Walker (wife of one of TJ’s best friend), and J. Adams is still repeating crazy gossip about AH 30 years later, you better believe there were references made to this affair at parties, gatherings, etc. EH dealt with it however she dealt with it, and I hope that AH’s “I have paid pretty severely for the folly” confession refers to some harsh treatment by EH.
And then in June 1797 Callendar began publishing pamphlets (lost to history except where AH quotes them in the Reynolds Pamphlet), some of which were gathered in some unknown order in his The History of the United States for 1796. Remember that Monroe was recalled from France in July 1796. It seemed to be a persistent belief of the Hamilton family that Monroe authorized and perhaps himself gave copies of the letters to Callendar for publication (”I hate you” point number 2).
And to be clear, because this gets muddled in some historian’s accounts - Callendar publishes AH’s account of his “particular connection” to Maria Reynolds and continues to goad him about it in published pamphlets and letters throughout June and July 1797 (the “harassment” of AH on this point in vague terms in pamphlets and newspaper letters actually started at least as early as 1795). AH’s confession in his own pamphlet was not an out-of-the-blue revelation of an affair that hadn’t already been publicly revealed.
Why would Monroe do this, in the Hamilton mind? Because he was pissed about no longer being French minister and blamed AH - he took a political dispute and decided to drag the Hamilton family into it. His delay in responding to AH, however, was likely seen as some kind of admission of guilt. On 5July1797, AH wrote to Monroe:
[Quoting from pamphlet V of the History] “When some of the Papers which are now to be laid before the world were submitted to the Secretary; when he was informed that they were to be communicated to President Washington, he entreated in the most anxious tone of deprecation, that the measure might be suspended. Mr Monroe was one of the three Gentlemen who agreed to this delay. They gave their consent to it on his express promise of a guarded behaviour in future, and because he attached to the suppression of these papers a mysterious degree of solicitude which they feeling no personal resentment against the Individual, were unwilling to augment” (Page 204 & 205). It is also suggested (Page 206) that I made “a volunteer acknowledgement of Seduction” and it must be understood from the context that this acknowlegement was made to the same three Gentlemen.
The peculiar nature of this transaction renders it impossible that you should not recollect it in all its parts and that your own declarations to me at the time contradicts absolutely the construction which the Editor of the Pamphlet puts upon the affair.
I think myself entitled to ask from your candour and justice a declaration equivalent to that which was made me at the time in the presence of Mr Wolcott by yourself and the two other Gentlemen, accompanied by a contradiction of the Representations in the comments cited above. And I shall rely upon your delicacy that the manner of doing it will be such as one Gentleman has a right to expect from another—especially as you must be sensible that the present appearance of the Papers is contrary to the course which was understood between us to be proper and includes a dishonourable infidelity somewhere.
And AH went ahead and wrote the following to editor John Fenno defending himself (6July1797):
For this purpose recourse was had to Messrs James Monroe, Senator, Frederick A. Muhlenbergh, Speaker, and Abraham Venable, a Member of the House of Representatives, two of these gentlemen my known political opponents. A full explanation took place between them and myself in the presence of Oliver Wolcott, jun. Esq. the present Secretary of the Treasury, in which by written documents I convinced them of the falshood of the accusation. They declared themselves perfectly satisfied with the explanation, and expressed their regret at the necessity which had been occasioned to me of making it.
But Monroe had just returned from France in June 1797, and he denied any prior knowledge of Callendar’s publication, and in general seemed to have had a “WTF!” reaction to AH’s sudden accusations. According to David Gelston’s account of the meeting between AH and Monroe on 11July1797:
Colo. M then began with declaring it was merely accidental his knowing any thing about the business at first he had been informed that one Reynolds from Virginia was in Gaol, he called merely to aid a man that might be in distress, but found it was a Reynolds from NYork and observed that after the meeting alluded to at Philada he sealed up his copy of the papers mentioned and sent or delivered them to his Friend in Virginia—he had no intention of publishing them & declared upon his honor that he knew nothing of their publication until he arrived in Philada from Europe and was sorry to find they were published. (my emphasis)
AH was so agitated that this conversation went downhill from there, seeing that “[AH] expected an immediate answer to so important a subject in which his character the peace & reputation of his Family were so deeply interested.” And then (”I hate you” point number 3):
Colo. M then proceeded upon a history of the business printed in the pamphlets and said that the packet of papers before alluded to he yet believed remained sealed with his friend in Virginia and after getting through Colo. H. said this as your representation is totally false (as nearly as I recollect the expression) upon which the Gentlemen both instantly rose Colo. M. rising first and saying do you say I represented falsely, you are a Scoundrel. Colo. H. said I will meet you like a Gentleman Colo. M Said I am ready get your pistols, both said we shall not or it will not be settled any other way. Mr C [John Church] & my self rising at the same moment put our selves between them Mr. C. repeating Gentlemen Gentlemen be moderate or some such word to appease them, we all sat down & the two Gentn, Colo. M. & Colo. H. soon got moderate, I observed however very clearly to my mind that Colo. H. appeared extremely agitated & Colo. M. appeared soon to get quite cool and repeated his intire ignorance of the publication & his surprize to find it published, observing to Colo. H. if he would not be so warm & intemperate he would explain everything he Knew of the business & how it appeared to him.
Monroe called him a scoundrel to his face! (After having been called a liar.)
And THEN, Monroe refused to sign a document absolving AH of any accusations of financial speculation with Reynolds (”I hate you” point number 4).
If I cod. give a stronger certificate I wod. (tho’ indeed it seems unnecessary for this with that given jointly by Muhg. & myself seems sufficient) but in truth I have doubts upon the main point & wh. he rather increased than diminishd by his conversation when here & therefore can give no other.
The above was sent to Burr on 16Aug 1797. AH had already pled his case to Monroe:
“...there appears a design at all events to drive me to the necessity of a formal defence—while you know that the extreme delicacy of its nature might be very disagreeable to me. It is my opinion that as you have been the cause, no matter how, of the business appearing in a shape which gives it an adventitious importance, and this against the intent of a confidence reposed in you by me, as contrary to what was delicate and proper, you recorded Clingman’s testimony without my privity and thereby gave it countenance, as I had given you an explanation with which you was satisfied and which could leave no doubt upon a candid mind—it was incumbent upon you as a man of honor and sensibility to have come forward in a manner that would have shielded me completely from the unpleasant effects brought upon me by your agency. This you have not done.
On the contrary by the affected reference of the matter to a defence which I am to make, and by which you profess your opinion is to be decided—you imply that your suspicions are still alive. And as nothing appears to have shaken your original conviction but the wretched tale of Clingman, which you have thought fit to record, it follows that you are pleased to attach a degree of weight to that communication which cannot be accounted for on any fair principle. The result in my mind is that you have been and are actuated by motives towards me malignant and dishonorable; nor can I doubt that this will be the universal opinion when the publication of the whole affair which I am about to make shall be seen.” 22July1797
In his mind, AH then believed he had to make a full accounting of the whole Reynolds debacle, since this jackass Monroe wasn’t going to sign-off on a denial of the whole matter of financial speculation on government securities. And back to the Hamilton family ire - it seemed that Monroe was not going to stop them from being slandered and dragged by doing what they felt he had already done - agreed that AH did not engage in financial speculation with Reynolds. Because Monroe would not acquiesce on that one matter, the Reynolds Pamphlet with all its detailed glory/humiliation where AH had to lay out his whole case was published, at least in the spin that occurred in the Hamilton family mind. (I’ve already written about the Reynolds Pamphlet here and here and briefly here and addressed a question about AH and infidelity here.)
Who was this “friend in Va?” Some historians have written this was TJ, but there are letters from decades later that Madison was the person who received the original letters and copies that Monroe had re Reynolds investigation, and they remained unopened until Monroe returned to the U.S. in 1797:
I have always understood from Mr. Monroe, that when he left this country he deposited with you, his packet of papers, relating to the investigation into the conduct &c of Genl. Hamilton—which was never opened, until it was returned by you to him, after his mission had terminated, and after the developement of its contents had been made from an other quarter. It would be very gratifying to me, if you have any facts, within your immediate reach, respecting the matter,if you would cause them at a leisure moment, to be communicated to me—The subject to which I refer, was, as you no doubt know, one of great feeling & excitement subsequently between Genl. H. & Mr. M., arising from causes of which I am aware, & particularly from the impression made on Genl. H. or the declaration by him of the belief, that the contents of the papers referred to, were made public by Mr. M—The children of Genl. H. have always indulged a feeling on this subject towards Mr. M. which renders it desirable that all the evidence in the case should be procured by his family. It has occasionally been hinted to me, that in a proposed publication of the Life of Genl. H., the subject might be touched, and it is equally my duty, as it would be my inclination, under such circumstances to have it in my power to do full justice to the character & memory of Mr. M. on this, as on all other occasions, where either might even by implication be assailed—I feel great reluctance in troubling you on the subject, but a conviction that you will appreciate my motives, impels me to do so. Samuel L. Gouverneur to James Madison, 1Feb1833
S.L. Gouverneur was the son-in-law of James Monroe (married their daughter) and nephew of Elizabeth Kortright Monroe. (Yes, he married his first cousin.) From the draft of Madison’s response (Feb 1833, Founders does not have a copy of the letter sent, if it’s still in existence):
I can only therefore express my entire confidence that the part Mr. Monroe had in the investigation alluded to, was dictated by what he deemed a public duty; and that after the investigation he was incapable of any thing that wd. justify resentful feelings on the part of the family of General Hamilton.
Of the public disclosure of the matter of the investigation, other than that from the avowed source, I know nothing; except that it could not proceed from the packet of papers deposited with me by Mr. M., which was never opened until it was returned to him, after his Mission had terminated.
Back to the main topic: the Hamiltons clearly saw Monroe playing a decisive role in the whole thing. But who was actually responsible for passing copies of letters to Callendar? Monroe was sure it was Beckley, former House clerk:
You know I presume that Beckley published the papers in question. By his clerk they were copied for us. It was his clerk who carried a copy to H. who asked (as B. says) whether others were privy to the affr. The clerk replied that B. was, upon wh. H. desired him to tell B. he considered him bound not to disclose it. B. replied by the same clerk that he considered himself under no injunction whatever—that if H. had any thing to say to him it must be in writing. This from B.—most certain however it is that after our interviews with H. I requested B. to say nothing abt. it & keep it secret—& most certain it is that I never heard of it afterwards till my arrival when it was published. Monroe to A.Burr, 2Dec 1797, in a letter that may have never gotten to him (entrusted to TJ)
Others at the time also believed it to be Beckley, though one historian suspected Tench Coxe too. Why was this ever published? Well, Callendar wrote in the History that it was because of the treatment of Monroe:
Attacks on Mr. Monroe have been frequently repeated from the stock-holding presses. They are cowardly, because he is absent. They are unjust, because his conduct will bear the strictest enquiry. They are ungrateful, because he displayed, on an occasion that will be mentioned immediately, the greatest lenity to Mr. Alexander Hamilton, the prime mover of the federal party.
Theodore Sedgewick told Rufus King it was Beckley, too and provides another motivation:
The House of Representatives did not re-elect Mr. Beckley as their Clerk. This was resented not only by himself but the whole party, and they were rendered furious by it. To revenge, Beckley has been writing a pamphlet mentioned in the enclosed advertisement. The ‘authentic papers’ there mentioned are those of which you perfectly know the history [46ten interjects: haha, some secret. So if Sedgewick and King know, Troup knows, Ames knows, G. Morris knows, etc. AH’s affair with Reynolds and the investigation was never a secret with this crowd], formerly in the possession of Messrs. Monroe, Muhlenberg & Venable. The conduct is mean, base and infamous. It may destroy the peace of a respectable family, and so gratify the diabolical malice of a detestable faction, but I trust it cannot produce the intended effect of injuring the cause of government.
So William Jackson is the second for AH, Aaron Burr the second for Monroe, and this Monroe-AH duel possibility stretched into the Winter of 1798 (x, x), having picked up again in December 1797 (Monroe replaces Burr with Dawson). TJ was still writing to Monroe about it in February 1798.
What had Monroe been doing that late summer/fall instead or figuring out how to conduct his affair of honor with AH? After an illness in August, oh, writing his own book (or having TJ ghostwrite it, depending on your views of Monroe’s intelligence) entitled A View of the Conduct of the Executive, in the Foreign Affairs of the United States, Connected with the Mission to the French Republic, During the Years 1794, 5, & 6, criticizing G. Washington and the administration every which way (published in Phila. 21Dec1797). GW, as he liked to do, made responses in the margins of Monroe’s little book; this editorial comment is hilarious: “GW’s remarks on Monroe and his book, taken together, comprise the most extended, unremitting, and pointed use of taunts and jibes, sarcasm, and scathing criticism in all of his writings.” Read that here.
So in the Hamilton mind, not only was Monroe trying to score points against Hamilton (and dragging private family matters into it), but he was criticizing GW too (and thereby AH, since even in retirement he continued to run the GW and Adams administrations, practically)! (”I hate you” point number 5.) In the first half of 1798, Monroe’s work got a lot of attention, earning the ire (and vocal and written condemnations) of Pres. Adams, of Timothy Pickering, and of many other Federalists. Monroe went back to Va. and appeared to lick his wounds and feel sorry for himself, based on his letters to TJ. I think it’s reasonable to speculate that Monroe is the “dirty fellow” alluded to in Angelica S. Church’s June 1798 letter to EH when the latter traveled to Albany - it was most likely seen that Monroe was the cause, or at least could have stopped, all the pain/attention of the public disclosure of the Reynolds affair. I don’t know if AH and Monroe ever really interacted after this. Monroe became Gov of Va, and then replaced Rufus King in 1803 as Minister to G.B.
EH and the Hamilton kids never forgot, see recollection here re. EH. Or watch a dramatization here. That Monroe remained a political rival of the Federalists and AH’s friends/allies also certainly didn’t help (Monroe & Madison and G. Morris continue at each other for many years.) On basic facts, it doesn’t quite make sense to me - I don’t think Monroe was culpable in the sharing of information, and I think he was being as fair-minded as he felt he could be - but there may have been additional encounters/statements/whatevers known to these parties that are now lost to history. There may also be fun details in JCH’s volumes on his father.
(For giggles, see this attached clipping: "the passage [in the Reynolds Pamphlet] in which Hamilton owns and laments his fault is admirably written.”
https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/imgsrv/image?id=uc2.ark:/13960/t90864f94;seq=231;size=125;rotation=0
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Right in the centre of my mind: o3. First breath, in the wrong direction.
Thomas Jefferson X Black!O.C
Ch.3
Warnings:
Swearing/cursing
Slight violence
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
9th grade. The first time Iman and Thomas exchange words. They see more of each other. Be it at the shack, or at school. Sometimes even on the basketball courts near the shack where he and his friends would play against Alex and their other friends.
They never speak.
They don't even exchange greetings.
Fresh out of toxicity, Iman's a freshman. At Claredon high. Eliza, Alex, John, Herc, Laf, Pegs. All in different schools. So Iman has to make new friends. She befriends a couple kids in her class. Including a french girl named Adrienne de Noailles. And Elizabeth Kortright.
From Buxton Middle school, there's Maria Reynolds. They were never really the best of friends. Never even saw eye to eye. An intellectual rivalry was what they called it.
Eventually though, after realising that they have a lot in common (they just happened to have a crush on the same guy but on separate occasions) they become friends.
Maria even begins to take the bus with Iman.
They get to sit upstairs.
They sit in the row second to last on the right with Peggy and Eliza. Joining the Hamilsquad who sat on the left side of the aisle.
The large group engages in a playful argument about whose school is better. It becomes physical when a pencil is sent flying in the girls' direction.
Many mundane items are used as ammunition, but none as significant as Iman's deodorant spray can. It flies in the wrong direction.
The bus is silent.
"Alexander who did I-"
The can flies right into Iman's face. "Fuck!" A chorus of boisterous laughter can be heard from behind the girls seats. Against all the warning looks sent her way, Iman gets up and makes her way to the culprits, spray can in hand. There's three of them. Iman recognizes all but only knows the name of one.
Thomas Jefferson.
"You, Big bird. Who threw this?" she demands.
He smirks. "That would be me." His friends are still laughing. They're making her nervous, but also simultaneously pissing her off. "Are you gonna apologize?" He starts laughing.
It is at this point when everyone expects her to knock him out with the can.
"Well, I'm sorry for accidentally throwing you with this," she says raising it up. Her apology is sincere, it stops the laughter and softens their features.
"Apology accepted," he says with a nod. His returned sincerity gives her hope. "Is this the part where you apologize?" His features harden. "No."
He and his friends laugh. Her friends know that she's just about done with their shit. But before she can do anything, he gets up and brushes past her, heading to the bottom of the bus. He has to get off. That meant she does to.
She scrambles to grab her stuff and rushes down the stairs, pushing Jefferson into the rail in the process. "Fuck!" She flips him off.
The bus stops and she gets off. Jefferson unfortunately, doesn't. Meaning he has to get off 3 miles away from his house.
His demeanor is calm, but the fury in his eyes is terrifying. He nods slowly at her as the bus keeps going with him inside it.
Maybe she should just stay off the bus for a week.
Tagging: @ramp-it-up @ohsoverykeri @sebastianabucknettastan @daveedsfigs
#Hamilton#Hamilton the musical#Thomas Jefferson#Thomas Jefferson x reader#Maria Reynolds#Peggy Schuyler#Eliza Schuyler#Alexander Hamilton#John Laurens#Hercules Mulligan#Lafayette#Adrienne de Noailles#Elizabeth Kortright Monroe#The chronicles of Tee and Kat#Right in the centre of my mind#RITCOMM
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Edward Stevens: facts
After the suicide of his uncle and guardian Peter Lytton, James Hamilton went off to train with an elderly carpenter and his younger brother, Alexander Hamilton, was whisked off to the King Street home of Thomas Stevens, a well-respected merchant and his wife, Ann. Of the five children born to the married couple, Edward born a year before Alexander became his closest friend, "an intimate acquaintance begun in early youth," as Hamilton described their relationship. As they both matured, the often seemed to display parallel personalities: both were quick and clever, disciplined and persevering, fluent in French, versed in classical history, held the same morals and were interested in medicine. In later years, Edward reminded Alexander of "those vows of eternal friendship, which we have so often mutually exchanged," he often fretted about his friend's delicate health.
Their physical appearance was close. Thirty years later, when Timothy Pickering, then secretary of state, first set eyes on Edward Stevens, he was torn by their resemblance. "At first glance, I was struck with the extraordinary similitude of his and General Hamilton's faces–I thought they must be brothers." Pickering confided with shock to Edward's brother-in-law, James Yard of St. Croix only to be told that this remark was said many times before. Pickering even concluded to himself that they were in fact brothers and Hamilton was an illegitimate child of "Stevens".
Edward Stevens also went to Kings College and years before Hamilton. November 11th, 1769 is Hamilton's oldest letter surviving in his pen–the recipient was Stevens. Arriving in New York 1773, the only person he knew was Stevens. In his first months at King's, he and a friend, Robert Troup, formed a club that gathered weekly to hone debating, writing and speaking skills. Stevens was one of the members.
While married to Elizabeth Schuyler, Edward Stevens became "the guardian angel" of the household and he appeared at providential moments and tended to Eliza reassuring her she was in no danger at times of illness. During the yellow fever epidemic in 1793, Edward Seven turned up Philadelphia and attended to both Alexander and Eliza when they both contracted the disease. He treated with bark, wine, and cold baths, a regimen that stirred some controversy since Stevens scorned the bloodletting treatment advocated by most doctors including Rush. Upon his recovery, Hamilton became an advocate for Stevens's method.
(Text above is credited to sonofhistory)
- He cured Eliza and Alexander of the fever within five days
- Stevens graduated from King's College in 1774 and then sailed to Britain to study Medicine at the University of Edinburgh
- He gained his doctorate (M.D.) on September 12, 1777
- Stevens' dissertation on gastric digestion was entitled "De alimentorum concoction"
- Based on this work, he was the first researcher to isolate human gastric juices
- His work confirmed that of René Antoine Ferchault de Réaumur, who showed the digestive power of gastric juices, and helped dispel earlier theories of digestion
- Stevens's work on digestion would influence Lazzaro Spallanzani
- On January 20, 1776, Stevens was admitted to the university's Royal Medical Society
- He served as the Society's president for the academic year 1779/1780. Stevens remained in Edinburgh until 1783 and was one of the joint founders of the Royal Society of Edinburgh in that year
- Stevens returned to St. Croix in 1783. He worked there as a physician for ten years
- He maintained his friendship with Hamilton through correspondence
- In adulthood, Hamilton tended to shun his turbulent adolescence, and Stevens was the only person from his childhood, including even his closest living family members, with whom he kept in regular contact
- Following the death of his wife, Eleanora, in 1792, Stevens decided to move to North America
- Stevens had considered a move to Guyana, but William Thornton urged him to choose the United States
- Also in 1792, Stevens married Hester Kortright Amory. Stevens ended his ten years of practicing medicine in the Caribbean and moved to Philadelphia in 1793
- (A/N" so he was widowed one year and married that same year, good job Ned)
- While in Philadelphia, he engaged in a controversy with Benjamin Rush on methods for treating an outbreak of yellow fever
- Stevens was admitted to the American Philosophical Society on April 18, 1794. Stevens's work in digestion may have influenced other researchers in Philadelphia, notably John Richardson Young
- In 1795, Stevens was appointed as a professor at King's College
- Stevens served as the United States consul-general in Saint-Domingue (later Haiti) from 1799 to 1800
- Stevens's title, "consul", suggested a diplomat attached to a country not a colony, reflecting the administrations view of the Haitian situation
- Following his arrival in Haiti in April 1799, Stevens succeeded in accomplishing several of his objectives, including: the suppression of privateers operating out of the colony, protections for American lives and property, and right of entry for American vessels
- Stevens pushed for similar privileges for the British, who, like the United States, were engaged in war with France
- Negotiations between Haiti and Britain were difficult given Haiti's fears of Britain's desire to take control of the colony, and Britain's fears of the Haitian slave revolt spreading to its own Caribbean colonies. In fact, Stevens had to serve as the British agent for a time since Haitian troops feared having a British official in the colony
- Little is known of Stevens's last years. For two and a half months in 1809-10, during the British occupation of the Danish West Indies, Stevens served as President of St. Croix. He corresponded with David Hosack, including a letter introducing his son in 1823
- He outlived Hamilton by thirty years
- He also referred to Hamilton as "My Dr. Ham"
- Meanwhile, Hamilton called Edward "Ned" and "Neddy" and often reffered to him as his "particular friend"
- "Throughout the remainder of 1803 Stevens attended the American Philosophical Society regularly. He is recorded as being present on October 7, October 21, November 4, November 18. In 1804 he attended on February 17 and February 24. A minute on August 17 of that year is confusing. Apparently he donated two volumes of books, but the precise readings of the Minutes is unclear. The description is "Steven's Wars. 2 Vols". Thereafter Stevens never attended again. It will be recalled that in 1804 Alexander Hamilton died in a duel with Burr, and possible then, or later Stevens retired to St Croix. David Hossack wrote to him in St. Croix in a letter dated September 20th, 1809, from New York, so by that year, certainly, Stevens had left the United States."
— Edward Stevens: Gastric physiologist, physician and American statesman
(Ned must have been significantly distressed by Hamilton's death and perhaps even moved back to St Croix because of this)
Some letters between Ned and Alexander:
"I have written you so repeatedly since my Arrival in Scotland, without having ever received an Answer... I am perfectly at a Loss I assure you, my Dr: Hamilton, to account for your Silence. I have written you frequently, and, as I know that you was at a Distance from New York, enclosed your Letters to some of our common Friends in that City, and requested them to transmit them to you. But I have not been able to collect the least Intelligence concerning you from any Quarter..."
—To Alexander Hamilton from Edward Stevens, 23 December 1777
"Who could have imagined my friend that a man of your greatness, of your delicacy of constitution, and of your tranquility, would have shone so much, and in a short space of time, in the Champ de Mars, that you did it? I assure you, my Colonel, that I have tormented myself a great deal about your health, which has always been very dear to me since the beginning of our acquaintance. I do not know how you can sustain the hardships and fatigues of a winter campaign in America. Surely your constitution would never have sustained such severity without the assistance of something very extraordinary."
— To Alexander Hamilton from Edward Stevens, 1778
"Dear Edward
This just serves to acknowledge receipt of yoursper Cap Lowndeswhich was delivered me Yesterday. The truth of Cap Lightbourn & Lowndes information is now verifyd by the Presence of your Father and Sister for whose safe arrival I Pray, and that they may convey that Satisfaction to your Soul that must naturally flow from the sight of Absent Friends in health, and shall for news this way refer you to them. As to what you say respecting your having soon the happiness of seeing us all, I wish, for an accomplishment of your hopes provided they are Concomitant with your welfare, otherwise not, tho doubt whether I shall be Present or not for to confess my weakness, Ned, my Ambition is prevalent that I contemn the grov'ling and condition of a Clerk or the like, to which my Fortune &c. condemns me and would willingly risk my life tho' not my Character to exalt my Station. Im confident, Ned that my Youth excludes me from any hopes of immediate Preferment nor do I desire it, but I mean to prepare the way for futurity. Im no Philosopher you see and may be jusly said to Build Castles in the Air. My Folly makes me ashamd and beg youll Conceal it, yet Neddy we have seen such Schemes successfull when the Projector is Constant I shall Conclude saying I wish there was a War.
. . .
PS I this moment receivd yoursby William Smith and am pleasd to see you Give such Close Application to Study."
- Alexander Hamilton to Edward Stevens, St Croix, November 11th, 1769
(Alex, hon, GET YOUR GRAMMAR TOGETHER MY BOY)
#Edward Stevens#Alexander Hamilton#Historical#Facts#Founding father facts#Historical facts#NEDDY#YEET#historical Hamilton facts#my stuff
20 notes
·
View notes
Photo



Welcome to Monticello Middle School!
Here you’ll meet our wonderful variety of teachers who are all masters at their respective crafts (more or less).
So please, enjoy your stay and feel free to ask any of our outstanding staff any questions about their lives in and out of the school!
A list of important names (some people are not mentioned here but will arrive sooner or later):
Thomas Jefferson: 7th grade science
James Madison: 7th grade social studies
Martha Wayles: 8th grade French
Dolley Payne: 7th grade math
James Monroe: full-time substitute (all grade levels)
Elizabeth Kortright: Art (all grade levels)
John Marshall: counselor (all grade levels)
Patrick Henry: 8th grade drama
George Wythe: Principal
#thomas jefferson#james madison#james monroe#dolley madison#martha jefferson#elizabeth monroe#john marshall#patrick henry#george wythe#jeffmads
32 notes
·
View notes
