#East Africa Shipping Company
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Navigating Africa’s Trade Routes: Leading Shipping & Logistics Companies

African economies are strong because trade lines connect countries throughout the region and the world. As global product demand rises, Africa has become more significant in shipping and transit. Local Shipping Companies in Africa make transferring goods easier, boosting economic growth. These logistics titans transport commodities from East Africa to the rest of the continent securely and promptly. These enterprises are testing trade barriers on a continent rich with potential. Shipping innovation is also their focus.
A Thriving Hub for International Trade
The East African maritime and transportation business is vital to global trade. The region is a central import-export hub due to its proximity to the Suez Canal and the Indian Ocean. Many goods enter and leave Africa through Mombasa, Dar es Salaam, and Djibouti. These big ports are receiving more modern facilities to simplify shipping. As product demand rises, East Africa Shipping Company adapts to fulfill foreign trade demands.
Pioneering Logistics Innovation
Many African maritime businesses priorities innovation. Logistics businesses are embracing new tools to streamline work and hasten delivery. These companies seek to streamline operations with enhanced tracking and autonomous storage. AI-powered innovative transportation platforms are transforming continental cargo transit by forecasting delivery patterns and discovering the optimum routes. Companies and customers benefit from these new technologies as Africa's commerce network converts, making service faster and more dependable.
Overcoming Infrastructure Challenges
Despite the expansion, East Africa's logistics industry still has infrastructural issues. Logistics Companies in East Africa is improving highways, ports, and rail systems to function better. Working with private enterprises has allowed the government to invest heavily in infrastructure, such as boosting internal transit and port size. These measures help move goods across borders swiftly and safely and reduce gridlock.

Sustainability in Shipping and Logistics
African maritime company’s priorities sustainability as environmental concerns develops. Many transport companies are becoming green to reduce carbon emissions. Shipping energy-efficient ships and utilizing eco-friendly packaging are becoming increasingly common. Global trends in "green logistics," which provide African firms with an edge in international marketplaces, support sustainability.
Conclusion
African shipping and transportation firms are vital to economic growth and global commerce. They overcome challenges, try new things, and consider how to survive along Africa's commerce routes. Africa has a promising logistics industry. As infrastructure and technology improve, commerce will flow more smoothly, promptly, and sustainably. These enterprises will remain at the top as the region becomes increasingly crucial to the global supply chain. They will boost Africa's economy and international standing.
For more information, you can visit our website https://fgi-africa.com/ or call us at +971 6 88 11 467
0 notes
Text
Seeking a leading Shipping Agency Somalia? Look no further than FGi Solutions! We offer an array of services that include international shipping and logistics, supply chain and procurement, and project operation and support. For more information, you can visit our website https://fgi-africa.com/ or call us at +971 6 88 11 467
#Shipping Companies in Eastern Africa#Top Shipping Companies in Eastern Africa#East Africa Shipping Company
0 notes
Text
Handle your shipment efficiently with top Shipping Companies in Mogadishu! We, FGi Solutions, are one of the top companies that are known for delivering exceptional services to all clients. For more information, you can visit our website https://fgi-africa.com/ or call us at +971 6 88 11 467
0 notes
Text
Seeking top Shipping Companies in Somalia that deliver fast shipping services? Get in touch with FGi Solutions! By approaching us, you can make the move cost-effective and comfortable. For more information, you can visit our website https://fgi-africa.com/ or call us at +971 6 88 11 467
0 notes
Photo

Uganda: 'Inconsistency in Policies Will Derail Investment in E-Mobility' [Independent (Kampala)] Kampala, Uganda -- Uganda's manufacturers are ready to invest in the emerging E-Mobility sub-sector but the government's inconsistency in investment policies will derail progress, according to the Uganda Manufacturers Association Chairman, Deo Kayemba. https://allafrica.com/stories/202308030288.html
#Economy#Business and Finance#Company News#East Africa#Governance#Innovation#Investment#Manufacturing#Transport and Shipping#Uganda#AllAfrica News: Economy
0 notes
Text
One of the major legacies of the British control of India was the planting of peoples of Indian origin all over the British Empire, including Britain itself. India was considered to be a reservoir of cheap labour. After African slavery was legally ended in 1833, ‘indentured’ labourers were recruited from India to work on plantations in Mauritius, Guyana, Trinidad, and Jamaica. This was slavery in a new guise: many laboured under conditions no less degrading than slavery. Thereafter wherever need arose, Indian labour was employed. Indians worked in the plantations and mines in Ceylon, Malaya, Burma, South Africa and Fiji. Indian labour provided the manpower to build the East African Railway. Indian sailors worked the British merchant navy. Indian soldiers not only helped to maintain the British Raj in India, but were used as cannon fodder overseas in colonial wars of conquest to extend its frontiers.
Indians were brought to Britain too. They did not come as ‘indentured’ labourers, but the principle of cheap labour applied here as well. Many Indian servants and ayahs (nannies or ladies’ maids) were brought over by British families returning from India. Indian sailors were employed by the East India Company to work on its ships. Some of these servants and sailors settled permanently in Britain.
One of the results of the policy of introducing western education in India was that, from about the middle of the nineteenth century, many Indian students began arriving in Britain, some on scholarships, to study law or medicine or to prepare for other professions. Some came to take the examination for entry into the Indian civil service since this examination could only be taken in London. Some Indian students settled in Britain after qualifying, to practise as doctors, lawyers or in other professions. Some Indian business firms opened branches in England. Nationalist politicians came to London, the centre of power, to argue the cause of Indian freedom. Indian princes and maharajahs visited England, not only as guests of the Crown on formal occasions, like the coronations, but also to pay their ‘respects’ to the monarch or for pleasure. London, as the metropolitan capital, attracted many visitors from India. Exhibitions of Indian arts and crafts were displayed in England too. The Asian presence in Britain therefore goes a long way back and forms a prelude to the post-independence migration of Asians to Britain.
— Rozina Visram, Ayahs, Lascars and Princes: Indians in Britain, 1700-1947 (London: 1986), pp. 9-10.
158 notes
·
View notes
Note
Lieutenant! Can you tell us about Cape Horn and why it was so dangerous?
Of course I would,
So let's get to the location:
Cape Horn is located at 55° 59′ south latitude and 67° 17′ west longitude. The headland is located on the rocky island of Isla Hornos (Horn Island, not to be confused with the Horn Islands in Micronesia, also discovered by Schoutens), which belongs to Chile, and is the southernmost point in the Tierra del Fuego archipelago. Like the southernmost 2,000 kilometres of South America, it lies in the cold Antarctic circumpolar current. Unlike South Africa, which is twenty degrees further north with the warm Agulhas Current, Tierra del Fuego is never reached by a warm Atlantic current (Brazil Current). Instead, the cold polar current (Falkland Current) reaches as far as the Río de la Plata in the southern summer and as far as southern Brazil in the winter, meaning that Cape Horn is under the influence of a large-scale subpolar current all year round.
The air temperature at Cape Horn is almost identical to the water temperature all year round - day and night - which is 8 °C in January and 5 °C in July. During the day, it rarely gets warmer than 12-13 °C. There are only occasional frosts in winter and it almost never snows, although it rains over 280 days a year.

With few exceptions, the wind blows from the western half of the compass rose all year round; easterly winds are very rare. However, the wind force in the sea area around the Cape tends to be lower than in the neighbouring south-east Pacific and off the Chilean coast near the Strait of Magellan, for example, where there is always one wind force more and twice as much chance of storms. Nevertheless, the wind blows almost constantly in summer (January) with at least five Beaufort, but only once a month with more than seven Beaufort, and once a week to the west. In July, at least seven Beaufort and one storm per week are recorded every third day, while two storms per week can be expected to the west.
The Cape was rounded for the first time by an expedition of Dutch sailors Willem Cornelisz Schouten and Jakob Le Maire on 29 January 1616, sailing on behalf of the Australian Company, which was founded by Jakob Le Maire's father Isaac Le Maire together with other Hoorn businessmen after an internal dispute with the Dutch East India Company (VOC). As Dutch ships at the time were only allowed to use the Strait of Magellan if they belonged to the VOC, Isaac Le Maire was looking for a passage to the Pacific untouched by the rights of the VOC to trade with the East Indies Spice Islands.
The expedition's mission was to explore a new route to the ‘East Indies’.It was considered fulfilled when a passage opened up between Tierra del Fuego (in the language of the Spanish owner) and the hypothetical huge southern continent of Terra Australis.It was named Fretum le Maire (literally Le Maire Strait) in Latin in honour of the initiator and most important financier Isaac Le Maire, and the ‘peninsula’ to the east belonging to Terra Australis was given the name Staatenlandt in honour of the newly constituted Dutch parliament.The rededication in favour of the son Jakob Le Maire took place after his tragic death at the instigation of his father.The island character of Staatenlandt, which is only sixty kilometres long, could not be recognised, as even at sea you can rarely see further than about forty kilometres. Not being able to see the connection of the state island to the huge Terra Australis only proved that one could not see further than twenty nautical miles - and this was already known.
According to the published records of the ‘shipwrecked passenger’ Jacob le Maires (his expedition ship, the Hoorn, burnt up during cleaning work in Patagonia), he and Captain Schouten were of the opinion that Tierra del Fuego was a rugged, rocky but contiguous island, the supposed southern tip of which was named Capo Hoorn in Latin by Schouten, who was responsible for it, in honour of the second great financier, the council of the city of Hoorn.The Le Maire Strait, the short and easy passage between America and Terra Australis at Staateninsel or Staatenlandt, was the important discovery; Cape Horn was already a clear 180 kilometres into the Pacific. Isaac le Maire had the discovery of this passage, supported by a ‘silent’ Schouten, attributed to his son by court order, with the father as heir.However, the associated and desired exploitation rights of the strait were immediately expropriated and granted to the monopoly of the East India Company.The last lawsuits over this were lost in 1648.
With the realisation that even Staatenlandt was not connected to Terra Australis and that Cape Horn was the decisive landmark, neither the Strait of Magellan nor the Le Maire Strait could be permanently managed with customs duties. Due to the factually and historically incorrect, commercially motivated court judgement that Jacob le Maire found his way into the Pacific via the Le Maire Strait, the discovery of Cape Horn is attributed to him just as incorrectly and abbreviated. Usually, however, all discoveries made on such a voyage are attributed to the captain, as he decides which unknown waters his ship sails into, is responsible for them and also has to assess and interpret what he sees. However, Schouten did not insist on a public acknowledgement of his exploratory achievement, presumably due to an ‘agreement’ between him and Isaac le Maire. In addition, the published documentation of the voyage was undoubtedly written by the representative of the shipping company Jacob le Maire, so that the impression of a discovery by the travelling merchant was already being conveyed to contemporaries
But according to the German author Wolf-Ulrich Cropp, the Englishman Francis Drake was the first European to sail around the Cape 40 years earlier, in 1578, on his circumnavigation of the globe, after he had reached the Pacific through the Strait of Magellan and then travelled south-east for a few days in search of the missing escort ships. However, this discovery was declared a state secret by Queen Elizabeth I.
At the time, it was believed that the Pacific could only be reached from the Atlantic via the Spanish-controlled Strait of Magellan further north, and the British did not want other nations to know about the second route.Drake's first discovery was only claimed after 1618 for political and economic reasons and was quickly disproved by examining the records and voyage reports and by interviewing the surviving travellers.The English naming of the sea area Drake Passage was only given in 1769 by James Cook when he surveyed the coast and is presumably only an expression of general reverence for the greatest English naval hero to date.
In fact, Drake no longer had any escort ships in the Pacific that he could miss; he had already lost them in the Atlantic or in the Strait of Magellan.In the event of a separation, a rendezvous point 2500 kilometres to the north had been agreed with the remaining Elisabeth; a search for missing persons in the south was therefore not very promising. Instead, Drake sought shelter between the islands west of the Strait of Magellan in a supposed ‘50-day storm’ and had no interest in drifting further and further south-east, where he would inevitably be wrecked on the expected Terra Australis in the storm.In any case, he took his time to ‘conquer’ the inhospitable islands of the archipelago one by one.Furthermore, the navigational documents show that he never travelled further south than 55° south, which, in view of his otherwise perfect latitude measurements throughout the voyage, rules out the possibility that he came closer than about 300 km to Cape Horn.Under no circumstances was he south of the Cape, travelling through the Drake Strait and the Le Maire Strait or Falkland Strait to the Atlantic entrance of the Strait of Magellan, in order to make a statement about its passability.The ambitious Drake would have seized even the slightest opportunity to make and verify such a glorious discovery, as he was well aware of the economic, personal, political and military benefits.Similar legends were subsequently spread about the Spanish captains Francisco de Hoces (1526) and Gabriel de Castilla (1603). However, the sources and evidence for both are so sparse and uncertain that the best that can be surmised is that they both sailed past the entrances to the Strait of Magellan for different reasons and then wandered south of it for a short time. In the case of de Hoces, the legend led to the same conclusion as with Drake: the sea area south of Tierra del Fuego, the Drake Strait, is called Mar de Hoces in Spanish.
The rounding of the Cape was one of the most feared passages for ships, as evidenced by the founding of the Cape Horn Community. Commanding captains who conquered Cape Horn on a cargo ship without an auxiliary engine became honorary members of this international community.
Until the completion of the Panama Canal in 1914, sailing around the Cape was the slightly more favourable way to reach the west coast of South America from the Atlantic. The Strait of Magellan and the Beagle Channel, which had already been sailed through centuries earlier by ships of the Dutch East India Company and British exploration ships, also offered difficult weather and current conditions for sailing ships.
At Cape Horn, the passage from the Atlantic to the Pacific against the westerly wind drift was particularly dangerous and difficult. It required ships sailing in this direction to constantly cross in high seas, rain, cold, poor visibility and icebergs. The False Cape Horn caused additional navigational difficulties due to the risk of confusion. However, to this day there are still ships that round the cape, albeit with the help of engines and modern navigation. But that does not mean that it is any less dangerous.
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily update post:
Two independent terrorist attacks against Israelis took place over the last 24 hours. Yesterday, a Hamas terrorist stabbed in the back a 49 years old Israeli reserves soldier, who stopped to buy something at a shop in a gas station, on his way home. The soldier turned around and, despite being injured, pursued the terrorist, shot and wounded him. The terrorist was later arrested, he had a permit to work in Israel. In the second one, a terrorist started shooting at civilian vehicles passing by, and ended up injuring a 27 years old woman. Thankfully, a baby who is 1.5 months old, who was in the car with her, was not injured, despite at least 10 bullets being retrieved from her vehicle. The IDF is searching for the terrorist.
Israeli soldiers have found and confiscated suitcases with 5 million shekels in cash from the home of a senior Hamas terrorist in Gaza. I want everyone to understand that this sum is currently 1,369,507 $ (yes, I checked with professor Google), and that most Israelis will never see that kind of money. I imagine a majority of "privileged" westerners never will, either. And this kind of money was just lying around in this terrorist's home...

The IDF has exposed and is now in control of what is likely the biggest Hamas terror tunnel. It is about 4 kilometers long (roughly 2.5 miles), and it is wide enough for vehicles to comfortably drive through it. Israeli soldiers have also found footage showing Muhammad Sinwar, the brother of Hamas leader in Gaza Yahya Sinwar, doing exactly that, in addition to footage showing the construction of this terror tunnel...
youtube
I don't post every single day about the Israeli soldiers injured and killed in Gaza, because the truth is that it has become technically difficult and emotionally painful to keep track. Yesterday, five more soldiers were confirmed as killed, one of them having been injured last week, and he has now succumbed to his wounds. So far, 128 soldiers were killed in Gaza.
Last month, there was a cyber attack on Israeli hospital Ziv, trying to derail its medical activity. Israel has confirmed today that it has traced Iran and Hezbollah as responsible for the attack. If we count the cyber war (and in terms of requiring manpower and resources, as well as in terms of the potential loss in human life, there is no reason not to count it), then Israel has been defending its citizens on no less than six fronts.
The Iran-funded terrorist Houthis in Yemen have been attacking ships unconnected to Israel, for simply passing through territory close to Yemen. A lot of shipment companies from around the world have announced they will not be sailing through this area for at least a time, which means they would have to sail all around Africa, to pass goods between the far east and the western world. This will hurt the entire world's economy, as shipment prices are expected to rise (think of the Evergreen ship blockade of the Suez Canal... these ships will not be trying to get anywhere near the canal. Symbolically, Evergreen is one of the companies announcing they will no longer sail through the Red Sea due to the threat of the Houthis). This will financially hurt so many countries, including Egypt (which operates the Suez Canal), the US and China (this means Iran's move has created a rare moment when American and Chinese financial interests align). The biggest question is, when will the world fully take in the fact that the biggest threat to world peace is the Islamist regime in Iran, and start acting accordingly?
This is Haj Amin al-Husseini.
Out of all of the people who helped shape the Israeli-Arab conflict, he's probably the most influential one, an antisemite, a Nazi collaborator, and a believer in pan-Arab nationalism (he didn't want to fight Jews to establish a Palestinian state, he wanted to exterminate the Jews and establish a greater Arab Islamic state, a new chaliphate, if you will. There is a FASCINATING docu series in Israel, dedicated to the Arab and Muslim leaders who have fought Jews and Israel, interviewing intelligence agents from many countries. The ep dedicated to al-Husseini is unbelievable, and I wish everyone could watch it. It's available online, but sadly, only in Hebrew. The truth is, I don't think anyone can understand the Israeli-Arab conflict without understanding the role of al-Husseini in it, and how different things could have been, if only the more moderate Arab leaders in the Land of Israel at the time had managed to squash his influence, or if the British hadn't tried to "tame" him by appointing him to the position of Jerusalem's grand mufti.
This is the Belchassan family, 31 years old Yuval and Ofir, and their two years old son Tai.
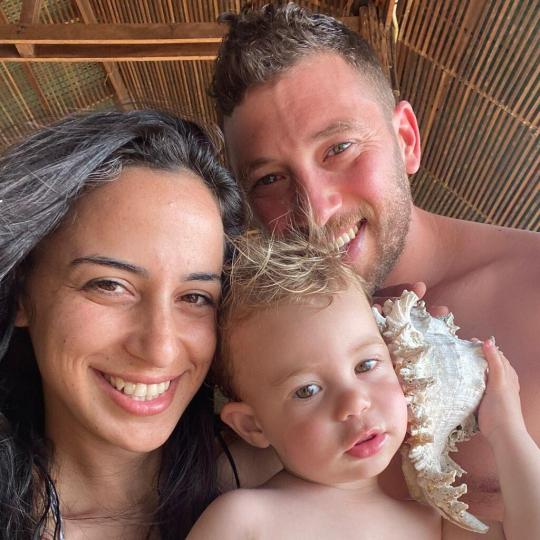

On Oct 7, Yuval left Ofir and Tai to hide in the bomb shelter, and went out to fight off the Hamas terrorists. He and his friends saved their kibbutz, but now, as Ofir is due to give birth to a daughter, they have no home to bring her back to.
(for all of my updates and ask replies regarding Israel, click here)
#israel#antisemitism#israeli#israel news#israel under attack#israel under fire#israelunderattack#terrorism#anti terrorism#hamas#antisemitic#antisemites#jews#jew#judaism#jumblr#frumblr#jewish#Youtube
106 notes
·
View notes
Text



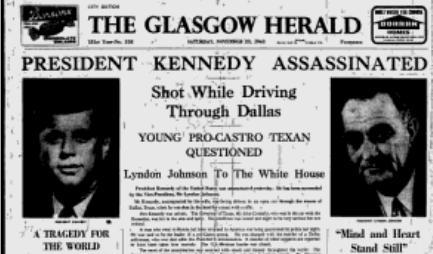



On January 27th 1784 the newspaper the Glasgow Herald was published for the first time.
As the birth of America brought the decline of the city’s lucrative tobacco trade and an end to its first phase of imperial expansion, the first issue of a newspaper called The Glasgow Advertiser was published.
When John Mennons - writer, editor, printer and publisher of The Glasgow Advertiser - sold the few hundred copies of his first issue around the coffee houses of Glasgow in 1783, he was already dealing with international businessmen, the tobacco lords and the other members of the Merchants’ House who traded with the Americas and Caribbean, who owned plantations and mansions across the Atlantic and whose fortunes would provide the basis for Glasgow’s early and hugely successful participation in the Industrial Revolution. The American colonies were lost, but the city continued to trade across the Atlantic, and soon added businesses in Africa, Australia and the Far East.
That first issue of The Herald showed the international interests of the Glasgow business community. On the front page alone there was intelligence from London, Dresden, Hispaniola (now Haiti and the Dominican Republic), Jamaica, New York, Gibraltar and Madrid, and reports of ships belonging to the East India Company sailing for Africa and the South Sea (the South China Sea). In addition, a disapproving account of the princes and princesses of Europe changing their religion “as if it were part of their dress” when marrying for family or national advantage was enlivened by the news that the Sultan of the Ottomans (Turkey) and the Sophia of Persia (Iran) had sent ambassadors to south Germany to ask for the hands in marriage of two princesses of the House of Wurttemberg.
The Glasgow Herald is the longest running national newspaper in the world and is the eighth oldest daily paper in the world. The paper was originally named the Glasgow Advertiser, and after a short spell as The Herald and Advertiser and Commercial Chronicle, became The Glasgow Herald in 1804.
The paper’s first editor John Mennons worked from offices at Duncan’s Land on Gibson’s Wynd, with the company moving to ‘The Lighthouse’ in Mitchell Street in 1895,the building is creditted cto architect John Keppie, but he apprenticed the young Charles Rennie Mackintosh.
On the 19th of July, 1980, the paper moved to offices in Albion Street. It is currently printed at Carmyle just south east of Glasgow.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Dutch King apologizes for Netherlands’ role in slavery.”
The Dutch/Netherlands abducted slaves from West Africa; hosted the Dutch West India Company; operated an extensive profitable sugar plantation industry built on slave labor; and established colonies in the greater Caribbean region including sites at Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, Bonaire, and the adjacent “Wild Coast” (land between the Orinoco and Amazon rivers, including Guyana and Suriname). Many of these places remained official colonies until between the 1950s and 1990s.
---
Scholarship on resistance to Dutch practices of slavery, colonialism, and imperialism in the Caribbean:
“Decolonization, Otherness, and the Neglect of the Dutch Caribbean in Caribbean Studies.” Margo Groenewoud. Small Axe. 2021.
“Women’s mobilizations in the Dutch Antilles (Curaçao and Aruba, 1946-1993).” Margo Groenewoud. Clio. Women, Gender, History No. 50. 2019.
“Black Power, Popular Revolt, and Decolonization in the Dutch Caribbean.” Gert Oostindie. In: Black Power in the Caribbean. Edited by Kate Quinn. 2014.
“History Brought Home: Postcolonial Migrations and the Dutch Rediscovery of Slavery.” Gert Oostindie. In: Post-Colonial Immigrants and Identity Formations in the Netherlands. Edited by Ulbe Bosma. 2012.
“Other Radicals: Anton de Kom and the Caribbean Intellectual Tradition.” Wayne Modest and Susan Legene. Small Axe. 2023.
Di ki manera? A Social History of Afro-Curaçaoans, 1863-1917. Rosemary Allen. 2007.
Creolization and Contraband: Curaçao in the Early Modern Atlantic World. Linda Rupert. 2012.
“The Empire Writes Back: David Nassy and Jewish Creole Historiography in Colonial Suriname.” Sina Rauschenbach. The Sephardic Atlantic: Colonial Histories and Postcolonial Perspectives. 2018.
“The Scholarly Atlantic: Circuits of Knowledge Between Britain, the Dutch Republic and the Americas in the Eighteenth Century.” Karel Davids. 2014. And: “Paramaribo as Dutch and Atlantic Nodal Point, 1640-1795.” Karwan Fatah-Black. 2014. And: Dutch Atlantic Connections, 1680-1800: Linking Empires, Bridging Borders. Edited by Gert Oostindie and Jessica V. Roitman. 2014.
Decolonising the Caribbean: Dutch Policies in a Comparative Perspective. Gert Oostindie and Inge Klinkers. 2003. And: “Head versus heart: The ambiguities of non-sovereignties in the Dutch Caribbean.” Wouter Veenendaal and Gert Oostindie. Regional & Federal Studies 28(4). August 2017.
Tambú: Curaçao’s African-Caribbean Ritual and the Politics of Memory. Nanette de Jong. 2012.
“More Relevant Than Ever: We Slaves of Suriname Today.” Mitchell Esajas. Small Axe. 2023.
“The Forgotten Colonies of Essequibo and Demerara, 1700-1814.” Eric Willem van der Oest. In: Riches from Atlantic Commerce: Dutch Transatlantic Trade and Shipping, 1585-1817. 2003.
“Conjuring Futures: Culture and Decolonization in the Dutch Caribbean, 1948-1975.” Chelsea Shields. Historical Reflections / Reflexions Historiques Vol. 45 No. 2. Summer 2019.
“’A Mass of Mestiezen, Castiezen, and Mulatten’: Fear, Freedom, and People of Color in the Dutch Antilles, 1750-1850.” Jessica Vance Roitman. Atlantic Studies 14, no. 3. 2017.
---
This list only covers the Caribbean.
But outside of the region, there is also the legacy of the Dutch East India Company; over 250 years of Dutch slavers and merchants in Gold Coast and wider West Africa; about 200 years of Dutch control in Bengal (the same region which would later become an engine of the British Empire’s colonial wealth extraction); over a century of Dutch control in Sri Lanka/Ceylon; Dutch operation of the so-called “Cultivation System” (”Cultuurstelsei”) in the nineteenth century; Dutch enforcement of brutal forced labor regimes at sugar plantations in Java, which relied on de facto indentured laborers who were forced to sign contracts or obligated to pay off debt and were “shipped in” from other islands and elsewhere in Southeast Asia (a system existing into the twentieth century); the “Coolie Ordinance” (”Koelieordonnanties”) laws of 1880 which allowed plantation owners to administer punishments against disobedient workers, resulting in whippings, electrocutions, and other cruel tortures (and this penal code was in effect until 1931); and colonization of Indonesian islands including Sumatra and Borneo, which remained official colonies of the Netherlands until the 1940s.
162 notes
·
View notes
Text

The threat to Israeli-linked commercial ships in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean from Yemen's Ansarallah-led government is now extending to Israel's commercial shipping in the Mediterranean, Israeli business newspaper Globes reported on 31 May.
Globes reports that Israeli car importers received a message from Alaloff shipping company, which represents the Grimaldi shipping company in Israel, stating that on 15 June, transport prices for cars and mobile equipment in dedicated ships traveling from Europe to Israel will sharply increase.
The increased shipping costs for ships in the Mediterranean are due to a sharp 200 percent increase in the War Risk Surcharge. The increase aligns with similar increases in insurance rates for commercial ships coming from East Asia to Israel after Yemen began its attacks in the Red Sea in November.
At that time, Yemeni forces began to target Israeli-linked ships traveling from Asia through the Red Sea and Suez Canal in response to Israel's genocide in Gaza. In response, many shipping companies rerouted their ships around the southern coast of Africa instead, extending the journey to Europe by two weeks and significantly raising shipping costs.
The increase in shipping costs for cars transported through the Mediterranean is expected to be about NIS 800 (USD 215) per vehicle.
#palestine#gaza#free palestine#ceasefire#free gaza#adropofhumanity#israel#usa is a terrorist state#israel is a terrorist state#rafah#all eyes on rafah#yemen under attack#hands off yemen#free yemen#stand with yemen#yemen
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
(...)
"What is the Houthi movement?
The Houthi insurgency is a Zaydi Shiite Islamist political movement established in 1992 to challenge Yemen’s longtime, and increasingly corrupt, leader Ali Abdullah Saleh. Following massive street protests, Saleh resigned his post in 2011. After the resignation, a national unity dialogue was held in Yemen’s capital Sana’a to try to resolve a host of Yemeni political conflicts. However, those talks eventually broke down, prompting the Houthis to advance on Sana’a with the goal of taking power. This sparked Saudi Arabia’s deadly US-backed air, ground, and naval invasion of Yemen, which lasted for seven years and killed an estimated 9,000 civilians, as well as significant numbers of Houthi forces, in repeated airstrikes. Despite the overwhelming force used by Saudi Arabia, however, the Houthis gained control over roughly a third of Yemen’s land—and two-thirds of its population—over the course of the war.
In April 2022, Saudi Arabia and the Houthis negotiated a truce that has nearly eliminated the fighting in Yemen. The truce halted offensive military operations, allowed fuel ships to enter Yemeni ports, and restarted commercial flights from Sana’a airport. However, it did not offer a comprehensive political settlement, leaving open the threat of renewed hostilities.
How have the Houthis become involved in the war?
After Israel began bombing Gaza on October 7th, the Houthi movement—which has long held what Yemen expert Helen Lackner called a “fundamentalist foreign policy position against the US and Israel”—announced that it was ready to intervene in solidarity with Palestinians. “There are red lines in the situation related to Gaza, and we are coordinating with our brothers in the jihad axis and are ready to intervene with all we can,” the Houthis’ leader said. As part of this effort, the movement has carried out 27 attacks in the Red Sea between November 19th and January 11th, most of them on commercial ships linked to Israel (although some of the attacks have targeted ships without a clear connection to Israel). The movement has also tried to fire on American warships and on Israel itself.
In the attacks on commercial ships, the Houthis have mostly fired missiles at them, though on November 20th, the group’s fighters seized a cargo ship and detained the crew members onboard. These attacks have discouraged shipping companies from traversing the Red Sea, the fastest route from Asia to Europe; many are instead sailing around the Horn of Africa, which adds $1 million to the typical cost of a roundtrip. On January 11th, the White House cited this trade disruption as a key motivating factor for the US’s bombings in Yemen, noting that “more than 2,000 ships have been forced to divert thousands of miles to avoid the Red Sea—which can cause weeks of delays in product shipping times.”
The Houthi movement’s attacks in the Red Sea, as well as the retaliation the attacks have generated, have revitalized the group’s power within Yemen. Prior to October 7th, the Houthis were facing discontent due to their authoritarian rule, their failure to pay salaries, and their control of aid in the face of spiraling poverty. Their confrontation with Israel, however, has seen “their popularity suddenly skyrocket, including in areas in Yemen where they don’t rule and in stark contrast to other Arab [states] who are at best being silent, or at worse, helping the enemy,” Yemen expert Helen Lackner told Jewish Currents. After incurring significant losses in their conflict with Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, the Houthis’ firm opposition to Israel has also helped them to recruit more young men to their military who believe they will have the opportunity to fight in Palestine, according to Lackner.
In this context, experts say it is unlikely the spate of Western bombings will end the Houthi attacks in the Red Sea—and such attacks could even contribute to the group’s bolstered popularity. “They’re willing to live with some level of retaliation because they can then position themselves as having been targeted by this Western alliance that is serving the interests of Israel,” said Mohamad Bazzi, director of New York University’s Kevorkian Center for Near Eastern Studies. Other experts have also warned that the US strikes risk provoking further escalations: For instance, the Houthis could decide to attack Saudi Arabia in a bid to up the pressure on American allies.
(...)
What is Iran’s role in the regional escalation?
While the groups responding to Israel’s bombing of Gaza—Hamas, Hezbollah, the Houthis, and the Iraqi and Syrian paramilitaries—are spread out across the region, they are all supported by Iran, which has armed and financed them as part of an overall strategy to contest US and Israeli hegemony in the Middle East. This Iran-supported network is often called the “axis of resistance,” and the alliance’s close collaboration reflects an approach developed by Qassem Soleimani, who was a key Iranian military leader until he was assassinated by the US in January 2020. “A big part of his strategy in the region was for the groups to get to know each other, and to share training and expertise—and that continued after the assassination in Baghdad,” said Bazzi.
Experts emphasize that Iran does not have full control over the groups it funds and arms, which often pursue their own agendas. For example, the relationship between the Houthis and Iran, according to Lackner, “is a bit like Netanyahu’s relationship to Biden. If they agree, and they want to do the same thing, then they do it. But they are not afraid to diverge either,” said Lackner. For instance, the Houthis ignored Iran’s orders to halt their advance on Sana’a in 2014, which sparked the years-long civil war and the conflict with Saudi Arabia. In the current conflagration, Bazzi said, Iran is unlikely to be directing the various forces to pursue “specific attacks,” but Iranian military leadership is “probably involved in larger-scale conversations about the division of responsibilities of different parts of the axis of resistance.”
According to Bazzi, at this moment Iran is carefully calculating how to maintain regional credibility by showing support for Hamas, while not going far enough to provoke a war with powerful foes like the US and Israel. “The primary Iranian calculation is about regime survival, and they don’t want to do anything that seriously jeopardizes their survival,” said Bazzi. Parsi said that so far, Iran has benefited from avoiding risky moves—in contrast to Israel, which has diminished its own “global standing” with its operations in Gaza. “Israel’s pariah status globally—at least outside of the West—is something that the Iranians are drawing benefits from. But that only works to the point that this doesn’t escalate into a larger conflict,” he said.
How is the US responding to the regional conflict?
Since October 7th, the US has repeatedly said that it wants to prevent more fighting in the region. Early on, the US dispatched warships and fighter jets to the Mediterranean to deter Hezbollah from entering the fray. Biden administration officials have also ramped up diplomatic efforts to halt a regional conflagration: The president sent envoy Amos Hochstein to Lebanon to try to negotiate a solution to the fighting around the blue line, and reportedly warned Israel against escalation with Hezbollah in private conversations. In October, when Israel had made plans to pre-emptively strike Lebanon, President Biden called Netanyahu to tell him to “stand down” on the attack plans, and ultimately, Israel did not launch a wide scale attack, according to a December Wall Street Journal report. “The priority for the Biden administration is to limit or prevent the broadening of the conflict,” said Schenker.
At the same time, the US has carried out repeated bombings in Iraq, Syria, and now Yemen, even as officials continue to talk about de-escalation. “We’re not looking for conflict with Iran. We’re not looking to escalate and there’s no reason for it to escalate beyond what happened over the last few days,” National Security Council spokesman John Kirby said last Friday, after the first US bombings of Yemen. But yesterday, the US military again bombed Houthi targets for the third time in a week, and then designated the Houthis as a terror organization, blocking the group’s access to the global financial system. By targeting Yemen, experts say the US is significantly expanding the regional war—“escalating regional tensions and adding fuel to a conflict,” as Bazzi wrote in a recent column published in The Guardian. “The conflagration could spiral out of control, perhaps more by accident than design,” he noted.
Many Middle East analysts say the Biden administration’s attempt to avert regional war is failing for one main reason: its refusal to couple a plea for de-escalation with advocacy for a ceasefire in Gaza. “Seeing the wider regional conflict as something that can be managed separately from Gaza is the source of the dissonance [in the administration’s strategy],” Bazzi told Jewish Currents. “You can’t prevent the wider regional war effectively without addressing the core immediate issue, which is the Israeli assault on Gaza. It’s just wishful thinking in the Biden administration that somehow it can separate the two.”
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
FGi Solutions Africa is a leading company that provider of Armored Vehicle Rentals across various African countries. FGi Solutions Africa offers a variety of services, including supply chain and procurement, project operation and support, international shipping and logistics, crane rental, security services, and auto rental. For more information, you can visit our https://fgi-africa.com/ and call us at +971 6 88 11 467
0 notes
Text
You know, it's interesting to me that I saw an article as I was scrolling through my dash this morning that (supposedly) blames the U.S. for being deeply involved in a genocide in Sudan. You might think from such a description that we'd be talking about U.S. military aid or boots on the ground or the CIA or something like that, and not just the Trump administration tanking our diplomatic efforts and Biden's administration not making the best decisions to right the ship. You might also think that such an article would not include a section like this:
David Satterfield, who replaced Feltman as US special envoy to the Horn of Africa and who has since resigned, said that Washington did not have anything but bad choices in Sudan, and therefore had to strike deals with the Sudanese military. According to Satterfield, “If there is ever an opportunity to return to a path towards restoration of a civilian-led government, you’re going to have to talk to the military then as well.
You also might not think that such an article would outright reference Russian involvement in Sudan, which it does.
Russia believes that its strong presence in Sudan will augment its status in Africa and the Middle East, which is considered an American redoubt. Since 2014, and with Moscow’s aspirations to exploit African mineral riches, the Kremlin has strengthened its ties to Sudan in order to ameliorate western sanctions following its invasion of Crimea, sanctions that became even harsher after its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.16 In 2017, former Sudanese President al-Bashir visited Russia and met with Russian President Vladimir Putin. The two countries agreed to establish a holding company run by the paramilitary Wagner Group to mine gold ore. Russia also signed a 25-year lease in December 2020 to build a military base at Port Sudan on the Red Sea that can receive nuclear-powered ships. It was also interesting that Hemedti headed an official delegation to Moscow on the eve of the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
And while we're talking about Russian involvement in Sudan, which is why I'm here in the first place, it's really really really interesting to me that this article was phrased as proof that the U.S. was heavily involved in genocide in Sudan, despite the fact that the Russian Wagner group (accused of war crimes in Ukraine) has been providing missiles and military training to the Sudanese paramilitary group RSF while smuggling gold out of Sudan to fund their own activities in Ukraine. Fun fact about the Wagner group: They're also heavily involved in social media misinformation campaigns.
Wasn't there a Russian misinformation campaign on tumblr leading up to the Presidential elections in 2016?
And despite the "mysterious" death of Yevgeny Prigozhin in a plane crash (a short time after his aborted march on Moscow), Russia is still working on bringing the Wagner organization back under their control. Because, you know, they still have that whole invasion of Ukraine they're working on. An invasion of Ukraine that would sure be a whole lot easier for them if they could convince Americans to stop providing military support to Ukraine. They're already doing pretty nicely with the Republican party, but the Democrats (and the American left in general) have been harder to get on-side.
It does kind of feel like tying American military involvement in other countries to active genocide would be a great way to discourage people on the American left from supporting continued involvement in Ukraine, wouldn't it?
We're slightly less than a year away from the next American presidential election. There is no reason to believe that the Russian propaganda machine, which has already been operating at full blast since Russia's full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February of 2022, is going to slow down. This quote from the linked article is particularly chilling:
A particular challenge is that people tend to spread falsehoods “farther, faster, deeper, and more broadly than the truth”; this is particularly the case for false political news (Vosoughi, Roy and and Aral, 2018[7]). For example, one study found that tweets containing false information were 70% more likely to be retweeted than accurate tweets (Brown, 2020[8]). Another study found that false information on Facebook attracts six times more engagement than factual posts (Edelson, 2021[9]). In addition, feedback loops between the platforms and traditional media can serve to further amplify disinformation, magnifying the risk that disinformation can be used to deliberately influence public conversations, as well as confuse and discourage the public.
I think it's important to remember, especially now, that we are capable of spreading misinformation. The article about U.S. involvement in Sudan wasn't placed on there by an algorithm. This is fucking tumblr. That was one of my mutuals. Because they're concerned about American military intervention and they're against genocide and it sounded bad and they were upset and they didn't think to read the article. Because they didn't spend the time of Prigozhin's march on Moscow mainlining information on the Wagner group the way that I did, so they didn't go "Hey, Sudan? Wait a minute --" the way I did. Because misinformation that isn't targeted at your group is designed to be easy to spot, so you'll think that the misinformation that is targeted to your group will also be easy to spot, and it fucking isn't.
Because this culture of "If you care, you'll share" has gotten people to click that reblog button without thinking twice about it.
Don't keep falling for it. You don't have to spend an hour digging up sources and pulling out quotes for a ten-note post the way that I did. I'm like this as a human. It's fine if you're not. But if you're not even going to click the link to read the article and actually read it critically (or if there's no sources at all except a twitter screenshot, which I've also seen quite a bit of), then don't reblog it. Save it as a draft for when you have time to do the research, or just don't do anything with it at all. You're not obligated.
And if you have the relevant background to spot the disinfo, I mean -- again, look, you're not obligated to take that hour and search those sources. Even I don't do this all the time. It's hard, it's frustrating, and it will not spread the way the disinfo does. I'm gonna see that genocide post like five times at least on my dash, and I'm probably going to see it at least once from someone who has at least liked this post (if not reblogged it as well). But if you can. If you have the energy and the time. Try to put a little info out there. It might help someone.
That's all. Be good. Be skeptical.
#disinformation#misinformation#russia#wagner group#sudan#ukraine#like i don't have mad love for the us military industrial complex either#but that doesn't mean i'm going to blindly support russian misinfo campaigns designed at distracting from their own atrocities#we can suck and they can suck we are both capable of sucking#but the us military is under the control of biden and russia's is under the control of putin and they're honestly not comparable right now#like it's not even close#so try not to fall for it#we all fail at that sometimes but try
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why outsource your logistics to a professional logistics company?

Having your own logistics department increases the cost of goods because you pay for the work of staff, regardless of the load. An outsourcing contract saves you from these costs. You do not need to spend money on staffing and training employees, paying for warehouses' rent, creating supply chains, and maintaining your own fleet of vehicles.
Logistics outsourcing is a multi-level business process that includes several types of services. Logistics outsourcing is a long-term contract with transport and Shipping Companies in Eastern Africa for the transportation of goods, goods, and their delivery to the client.
What is included in the logistics outsourcing service?
Package
Warehouse processing
Stock control
Insurance
Information support
Expedition
Delivery of goods to the client
Why is it beneficial?
You will appreciate the benefits of outsourcing not earlier than a few months to get statistics comparing shipping costs before and after outsourcing the logistics function of your company. Professional Logistics Companies in East Africa take all control over the transportation of goods. You simply hand over the goods to the shipping company, and they deliver them to the right address. This allows you to focus on developing your core business, increasing production, increasing sales, and improving the quality of your products. Also, long-term cooperation gives an advantage in the cost of transport services and allows you to respond to changes in work.
Summarizing
If your company does not have its own courier service, storage facilities, and a fleet of vehicles, and you put the development of your core business in the first place, then the logistics outsourcing service is for you.
For more information please visit:- https://fgi-africa.com/
0 notes
Text
I haven't rly seen a lot of ppl on here talk about the Ben Gurion Canal project + its relevance to what's going on in Palestine/Israel rn so I wrote something up abt it
The Ben Gurion Canal project is a proposed canal through occupied Palestine, named after Israel's first Prime Minister. It would connect the Red Sea (the Gulf of Aqaba, more specifically) to the Mediterranean Sea. Currently, the only canal connecting the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea is the Suez Canal.
Without the Suez Canal, trade ships would have to circle around the entirety of Africa, which is expensive and inefficient. The proposed Ben Gurion Canal would rival the Suez Canal that runs through Egypt. As of the financial year June 30, 2023, Egypt grossed over 9 billion dollars USD annually from the Suez Canal alone.
Historically, the canal was supposed to be accessible to all nations however after the Nakba (mass displacement and massacre of Palestinians in 1948) the Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser shut down the canal and shortly thereafter strategically nationalized the canal so the UK, US, France, etc. no longer held shares and profited off the commissary companies that were running Suez Canal operations. Although the canal is currently accessible due to a Peace Treaty (Camp David 1978), the Suez Canal has long been a source of tension.
The proposed Ben Gurion Canal project currently runs north of Gaza, however the current proposal requires a detour that could be made significantly more efficient if Israel gains control over the Gaza Strip, specifically the northern portion. Do you think it's a coincidence that the Israeli regime is bombing the northern Gaza strip more heavily than the south? I don't, and it's precisely why I think talking about this proposed canal is important - it puts into context the strategic measures Israel is implementing to carry out this genocide.
The Ben Gurion Canal project has many advantages over the Suez Canal - because of its rocky terrain, it can be built larger and deeper than the Suez Canal and would require significantly less maintenance. The larger size of the Ben Gurion canal would also mean that the US could deploy larger modern warships, which is currently impossible as the Suez Canal is too narrow. The Ben Gurion Canal would be projected to gross around 6 billion USD annually, which is significant from both a financial + regional control standpoint.
So ya, while the canal is not the only reason for the current war, thousands of Palestinian lives are being martyred so the West can gain military and financial control in the Middle East + build this canal as efficiently as possible.
37 notes
·
View notes